Development of an Immunofluorescent Capillary Sensor for the Detection of Zearalenone Mycotoxin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
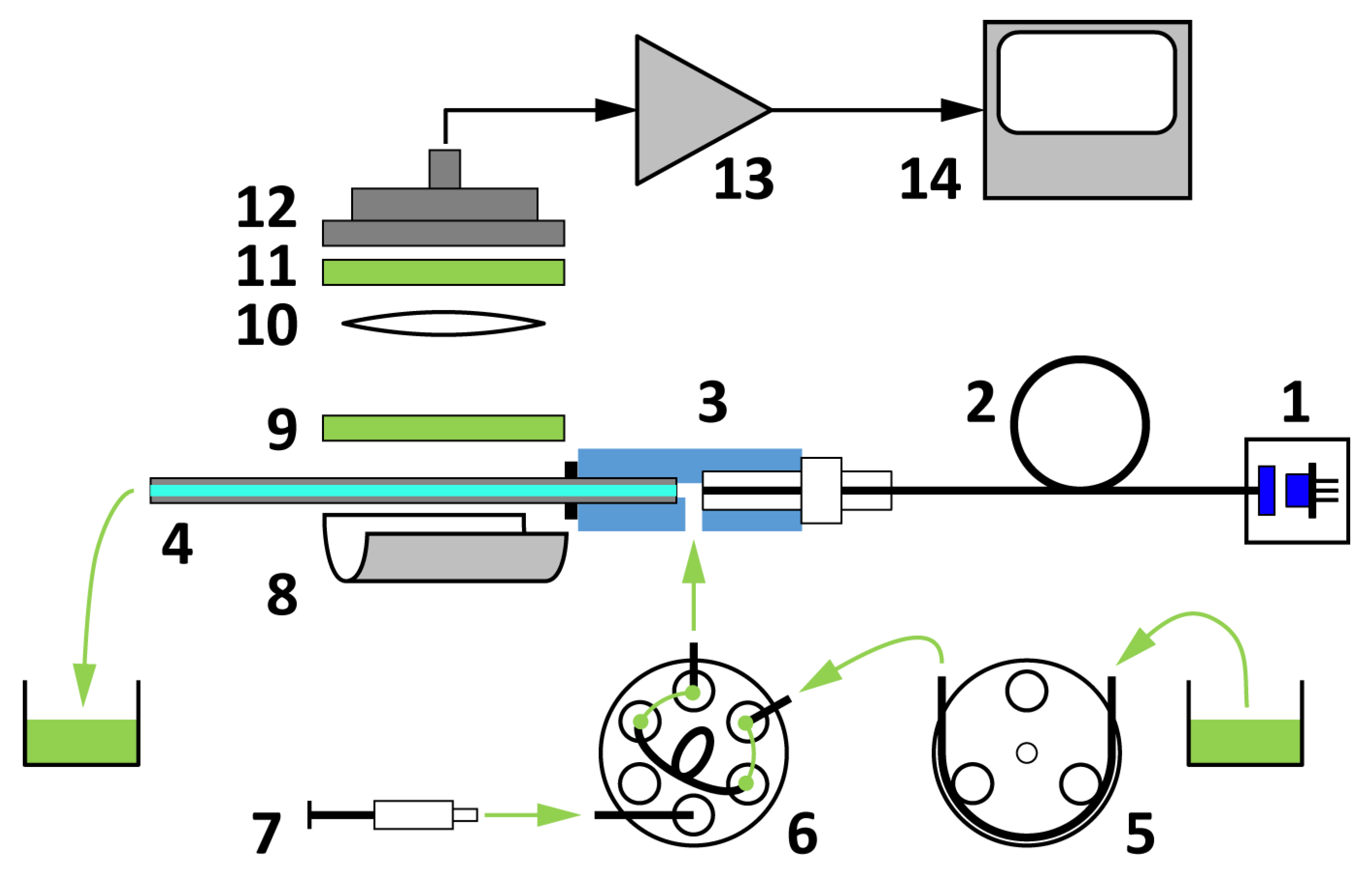
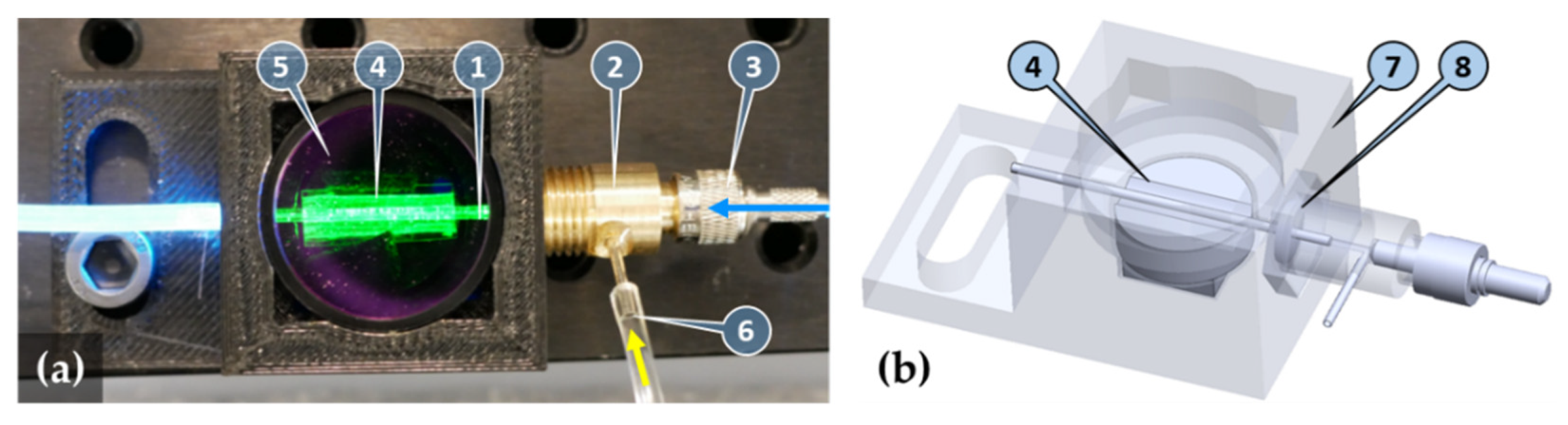
2.1. Capillary Waveguide-Based Biosensor Design
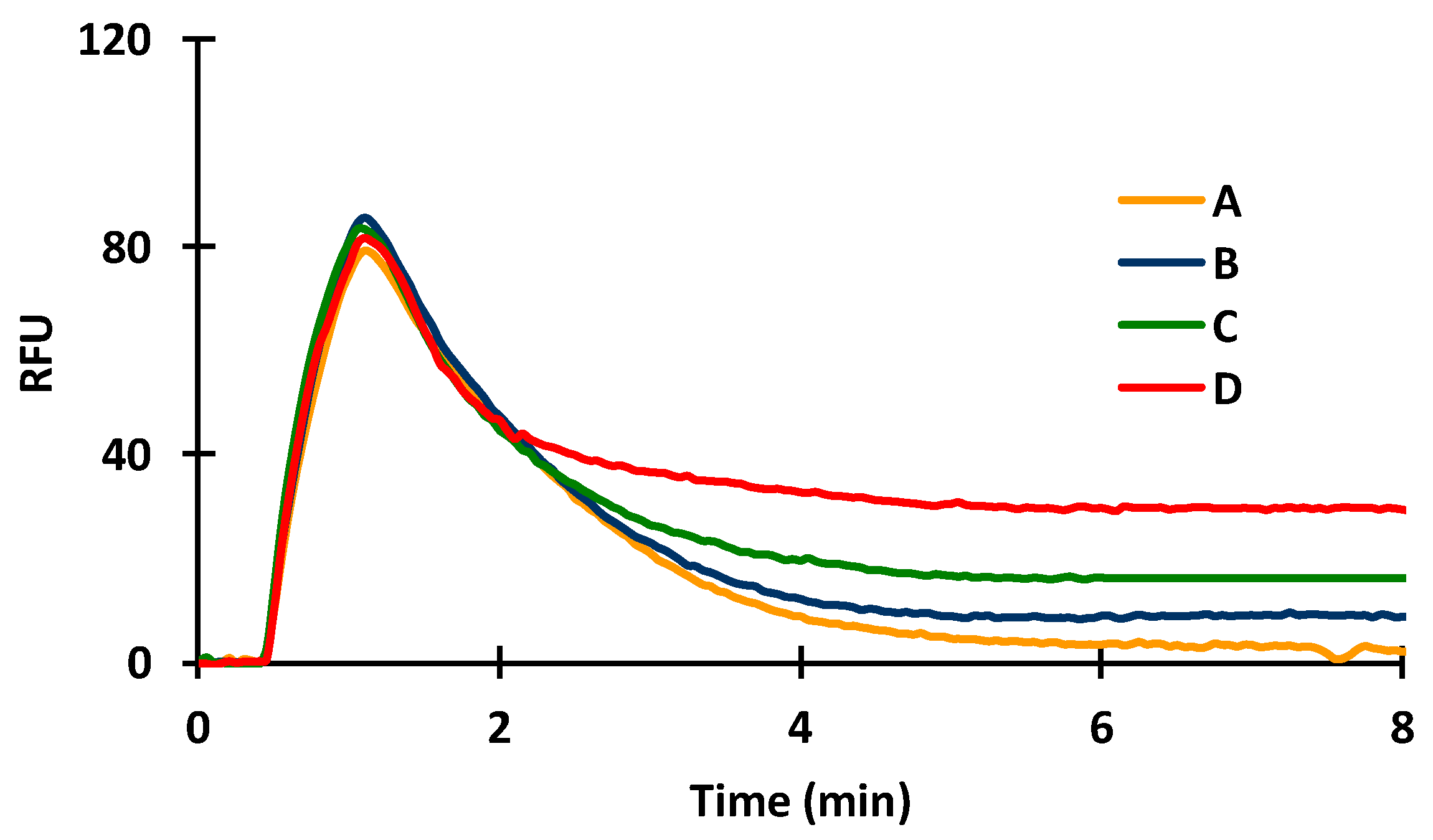
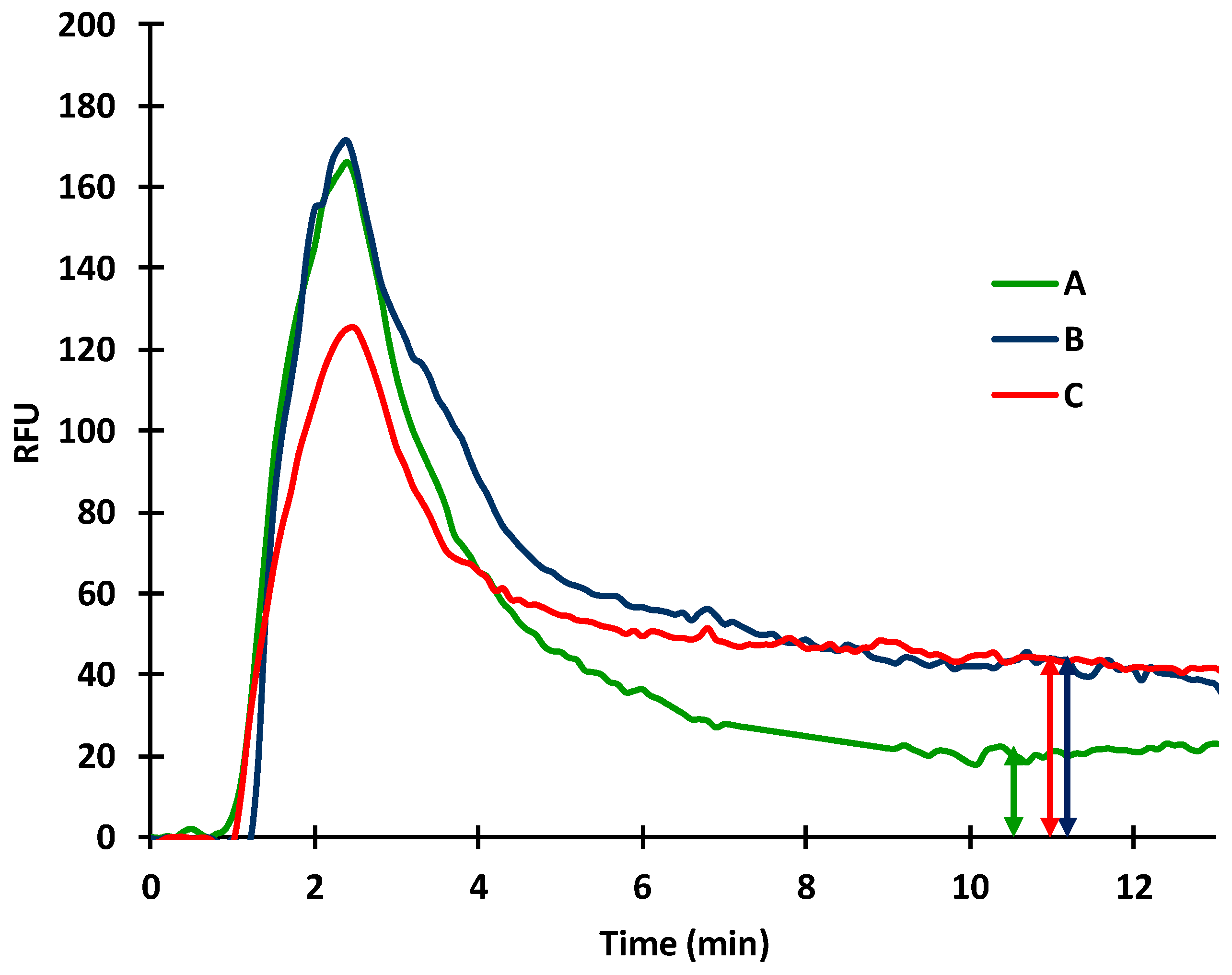
2.2. Protein Adsorption on the Inner Surface of the Silanized Capillary
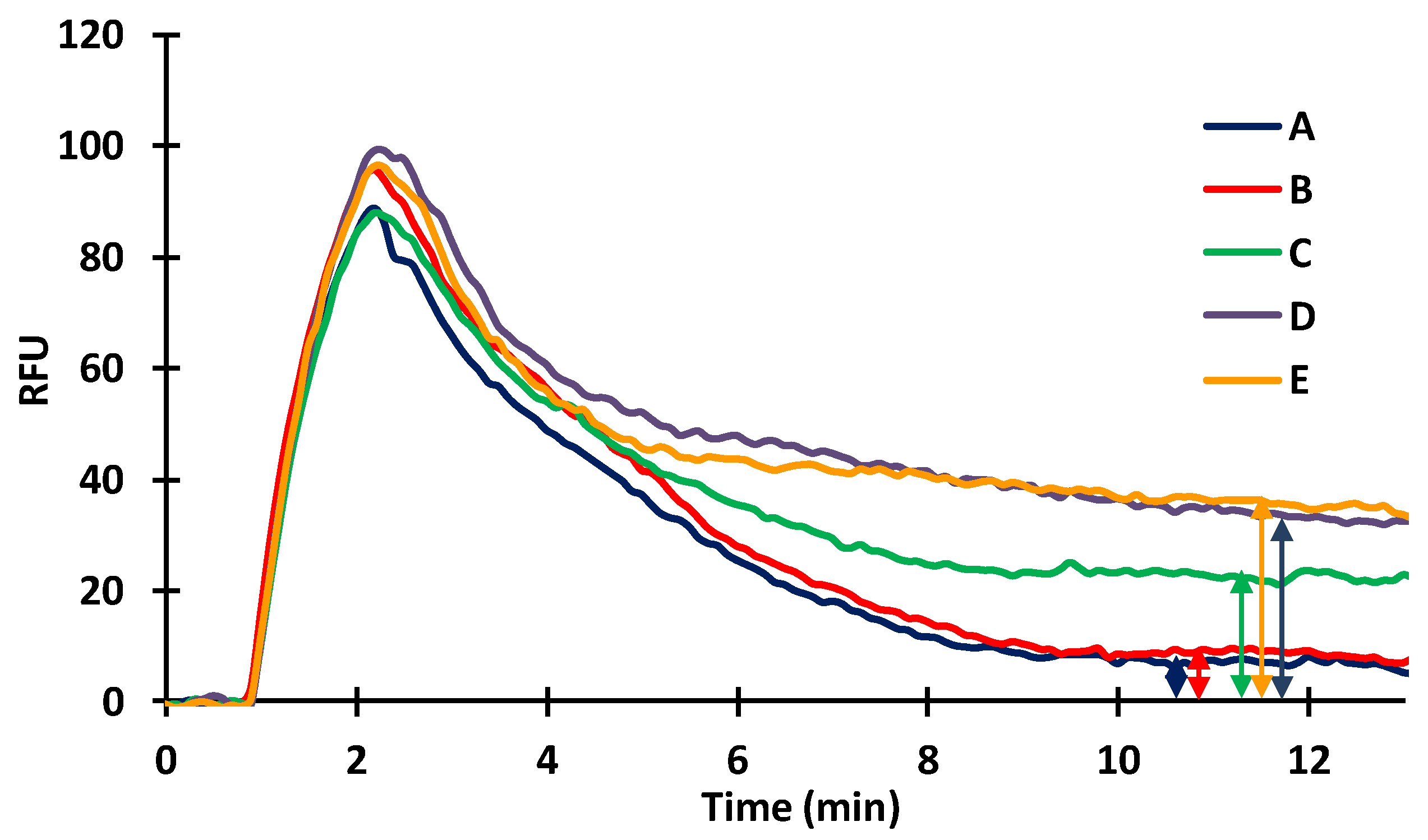
2.3. Coupling Potential of Protein Molecules onto the Inner Surface of the Silanized Capillary
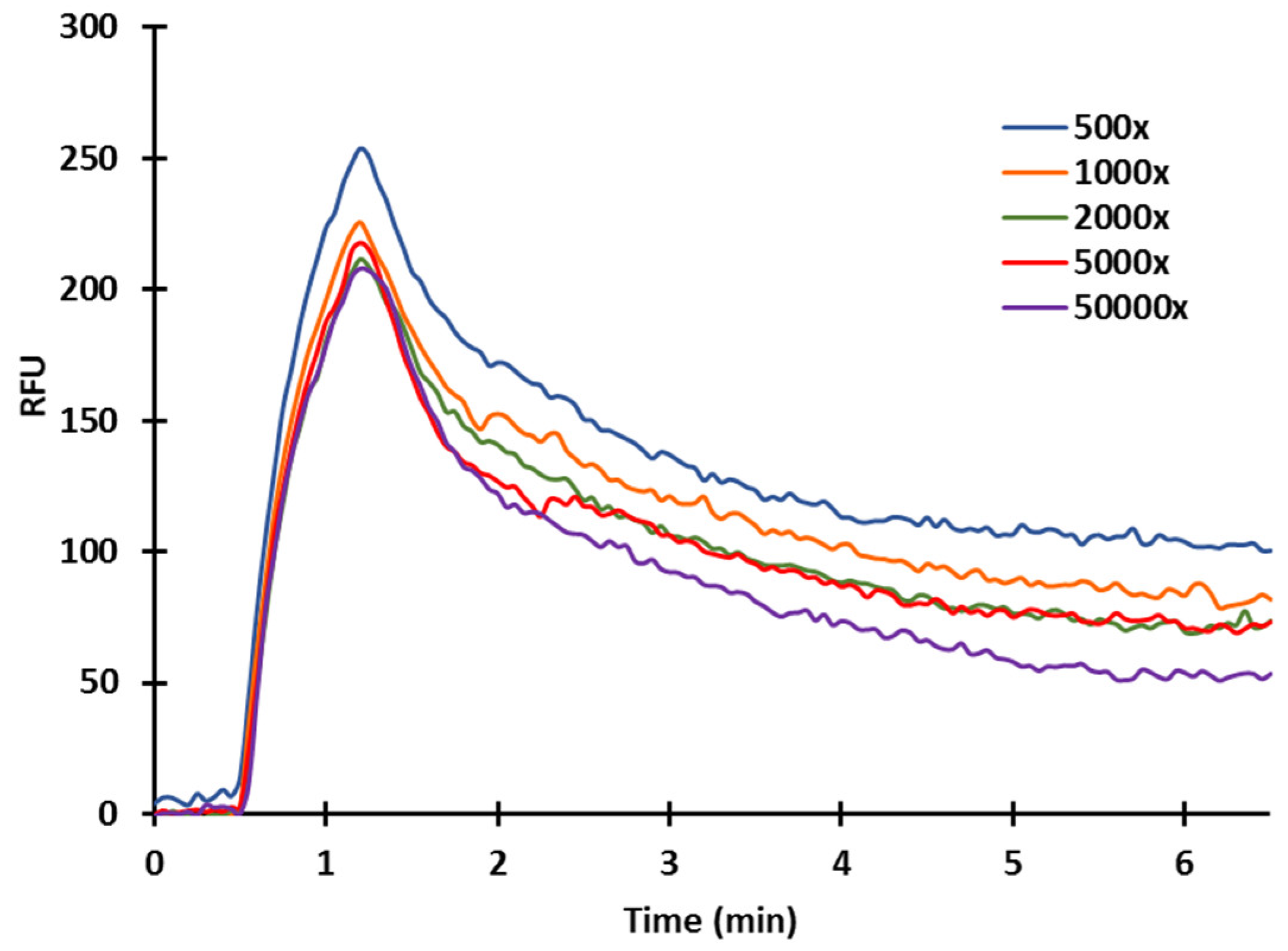
2.4. Effect of Acetonitrile
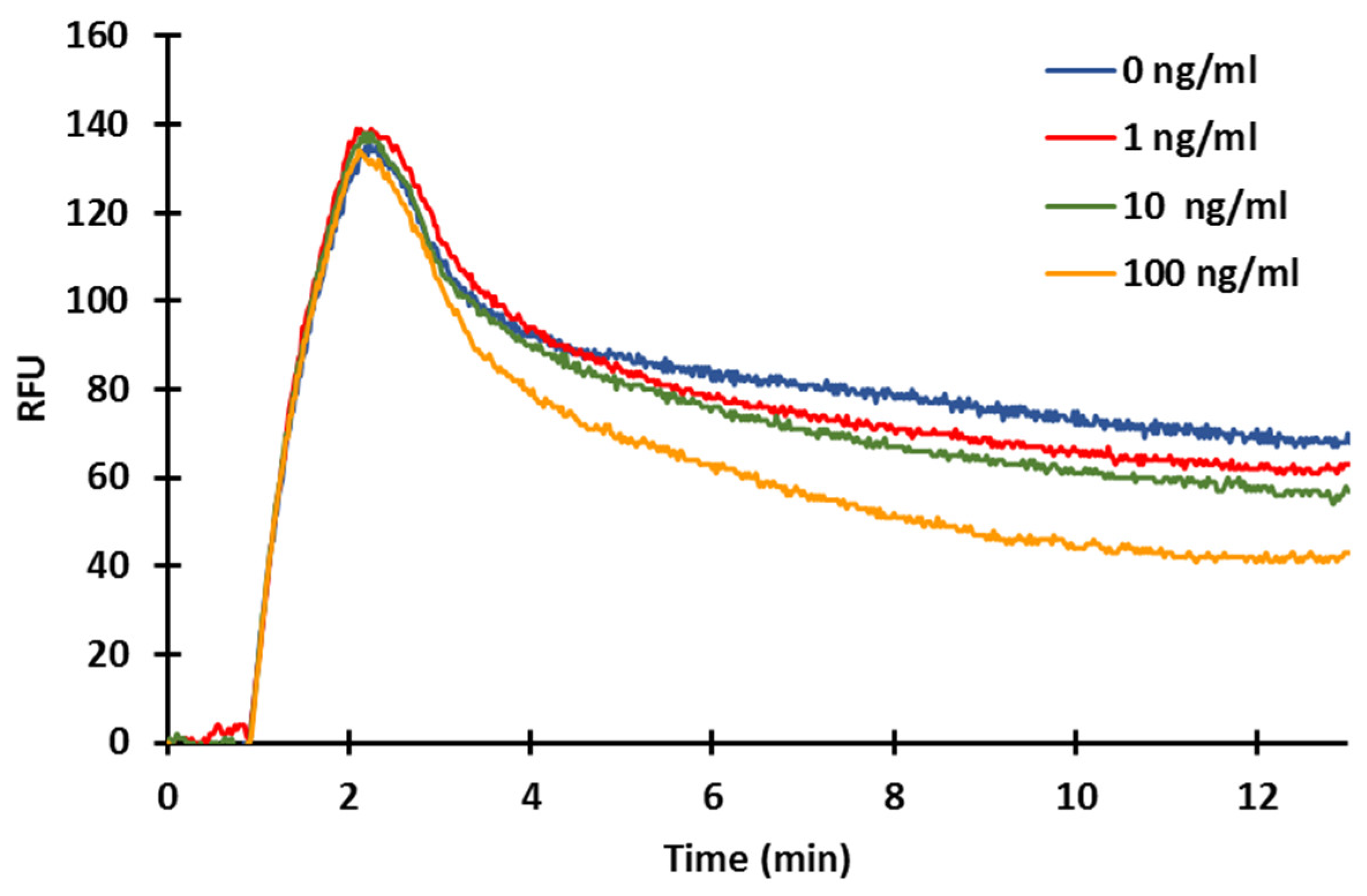
2.5. Fluorescence-Based Competitive Immunosensor for Measuring ZON
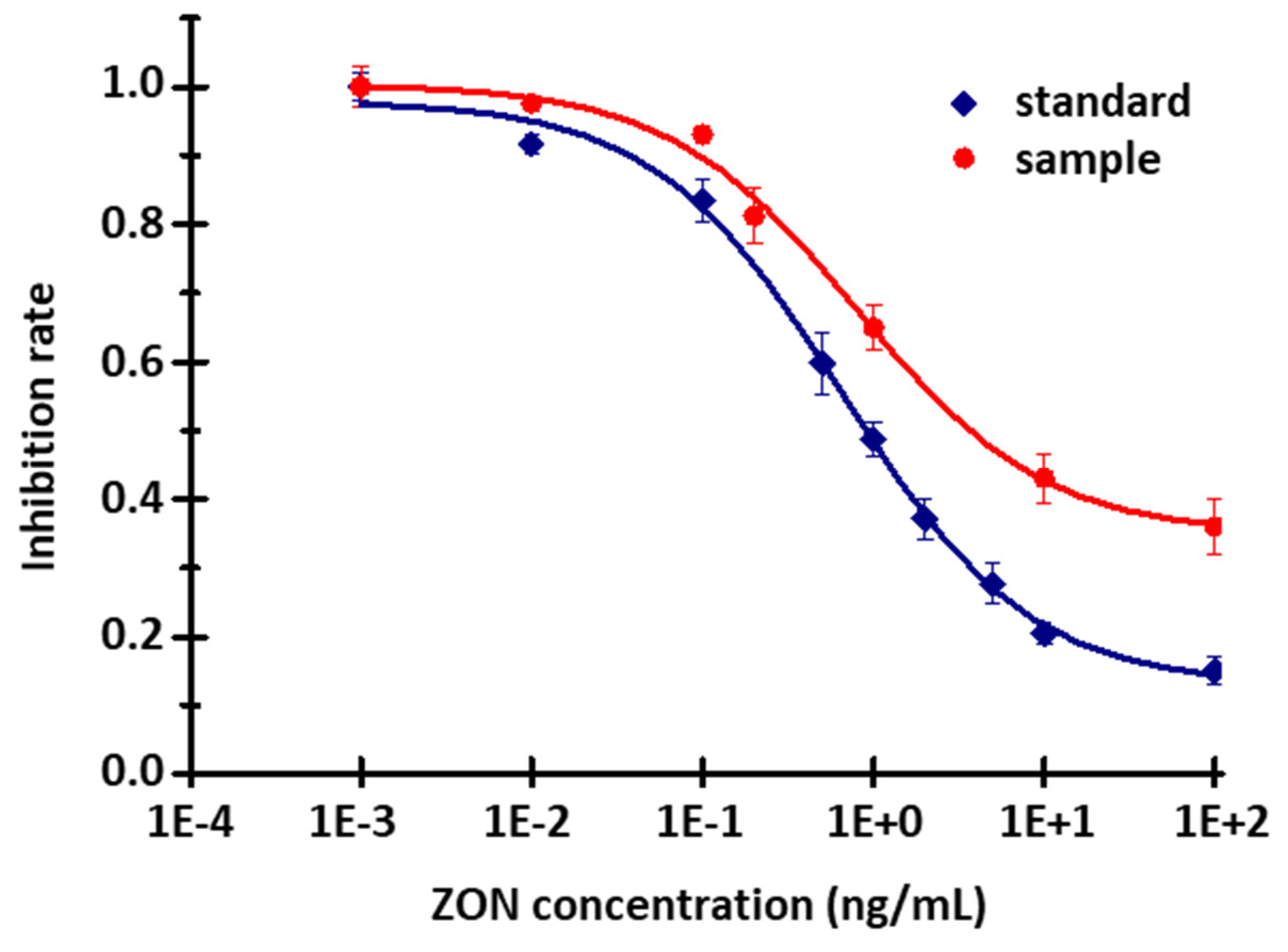
2.6. Investigation of the Selectivity of a ZON-Specific Sensor
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Instrumentation
4.3. Immunogen and Antibody Production
4.4. Functionalization of the Inner Surface of the Capillary
4.5. Sample Preparation and Measurement Conditions
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Zeareleone Determination
4.7. Statistical Evaluation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haque, M.A.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Li, X.; Saleemi, M.K.; He, C. Mycotoxin contamination and control strategy in human, domestic animal and poultry: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, F.; He, D.; Olaniran, A.O.; Mokoena, M.P.; Xu, J.; Shi, J. Occurrence, toxicity, production and detection of Fusarium mycotoxin: A review. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2019, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caglayan, M.O.; Şahin, S.; Üstündağ, Z. Detection strategies of zearalenone for food safety: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 52, 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahle, S.; El Khoury, A.; Atoui, A. Current status on the molecular biology of zearalenone: Its biosynthesis and molecular detection of zearalenone producing Fusarium species. Eur. J. Plant. Pathol. 2021, 159, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cela, E.; Kiaitsi, E.; Sulyok, M.; Medina, A.; Magan, N. Fusarium graminearum in Stored Wheat: Use of CO2 Production to Quantify Dry Matter Losses and Relate This to Relative Risks of Zearalenone Contamination under Interacting Environmental Conditions. Toxins 2018, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pleadin, J.; Sokolović, M.; Perši, N.; Zadravec, M.; Jaki, V.; Vulić, A. Contamination of maize with deoxynivalenol and zearalenone in Croatia. Food Control 2012, 28, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székács, A. (Ed.) Rapid Detection of Mycotoxin Contamination; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2021; ISBN 978-3-0365-1694-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, K.E.; Song, J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.W.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, B.; Lee, Y.; Yu, D.; Kim, D.W.; et al. Effects of High Levels of Deoxynivalenol and Zearalenone on Growth Performance, and Hematological and Immunological Parameters in Pigs. Toxins 2018, 10, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, B.K.; Cho, J.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Shin, H.S.; Son, S.W.; Yeo, Y.K.; Kang, H.G. Zearalenone affects immune-related parameters in lymphoid organs and serum of rats vaccinated with porcine parvovirus vaccine. Toxicol. Res. 2012, 28, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modrá, H.; Svobodová, Z. Incidence of animal poisoning cases in the Czech Republic current situation. Interdisc. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, D.K.; Devi, S.; Pandhi, S.; Sharma, B.; Maurya, K.K.; Mishra, S.; Dhawan, K.; Selvakumar, R.; Kamle, M.; Mishra, A.K.; et al. Occurrence, Impact on Agriculture, Human Health, and Management Strategies of Zearalenone in Food and Feed: A Review. Toxins 2021, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 1126/2007 of 28 September 2007 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards Fusarium toxins in maize and maize products. OJ 2007, L 255, 14.
- Soleimany, F.; Jinap, S.; Rahmani, A.; Khatib, A. Simultaneous detection of 12 mycotoxins in cereals using RP-HPLC-PDA-FLD with PHRED and a post-column derivatization system. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irakli, M.N.; Skendi, A.; Papageorgiou, M.D. HPLC-DAD-FLD Method for Simultaneous Determination of Mycotoxins in Wheat Bran. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, H.E.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, M.; Chun, H.S. HPLC and UPLC methods for the determination of zearalenone in noodles, cereal snacks and infant formula. Food Chem. 2014, 163, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drzymala, S.S.; Weiz, S.; Heinze, J.; Marten, S.; Prinz, C.; Zimathies, A.; Garbe, L.-A.; Koch, M. Automated solid-phase extraction coupled online with HPLC-FLD for the quantification of zearalenone in edible oil. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3489–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lijalem, Y.G.; Gab-Allah, M.A.; Choi, K.; Kim, B. Development of isotope dilution-liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for the accurate determination of zearalenone and its metabolites in corn. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Moltó, J.C.; Berrada, H.; Mañes, J. A survey of trichothecenes, zearalenone and patulin in milled grain-based products using GC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, P.; Auer, S.; Spehar, A.; Elliott, C.T.; Campbell, K. Current trends in rapid tests for mycotoxins. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2019, 36, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, A.; Khan, R.; Catanante, G.; Sherazi, T.A.; Bhand, S.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Designed Strategies for Fluorescence-Based Biosensors for the Detection of Mycotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro, R.C.; Saraiva, M.L.M.F.S.; Santos, J.L.M.; Ribeiro, D.S.M. Multiplexed detection using quantum dots as photoluminescent sensing elements or optical labels. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 448, 214181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goryacheva, O.A.; Beloglazova, N.V.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; De Saeger, S. Homogenous FRET-based fluorescent immunoassay for deoxynivalenol detection by controlling the distance of donoracceptor couple. Talanta 2021, 225, 121973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Wu, T.; Li, J.; Jin, Q.; Xiao, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, C. Difunctional immunochromatographic assay based on magnetic quantum dot for ultrasensitive and simultaneous detection of multiple mycotoxins in foods. Sens. Actuator. B Chem. 2022, 359, 131528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, J.; Ji, S.; Chen, G.; Lu, J. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor between nanoceria and graphene quantum dots for the determination of ochratoxin A. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1000, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Cui, M.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Chang, J.; Hao, J.; Wamg, H. Background-free upconversion-encoded microspheres for mycotoxin detection based on a rapid visualization method. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, M.H.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, S.F.; Peng, K.; Xu, H.S.; Liao, Z.Y.; Wang, H.J.; Chang, J. A smartphone-based quantitative detection platform of mycotoxins based on multiple-color upconversion nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 15865–15874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltomaa, R.; Benito-Peña, E.; Gorris, H.H.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Biosensing based on upconversion nanoparticles for food quality and safety applications. Analyst 2021, 146, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niazi, S.; Khan, I.M.; Yan, L.; Khan, M.I.; Mohsin, A.; Duan, N.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z. Simultaneous detection of fumonisin B1 and ochratoxin a using dual-color, time-resolved luminescent nanoparticles (NaYF4: Ce, Tb and NH2-Eu/DPA@SiO2) as labels. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Majdinasab, M.; Khan, R.; Li, Z.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Nanomaterials in fluorescence-based biosensors: Defining key roles. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2021, 27, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, H.; Du, G.; Guo, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Recent trends in fluorescent aptasensors for mycotoxin detection in food: Principles, constituted elements, types, and applications. Food Front. 2022, 3, 428–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Liao, X.; Fang, L.; Jia, B.; Liu, M.; Li, D.; Zhou, L.; Kong, W. Recent advances on immunosensors for mycotoxins in foods and other commodities. Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, P.R.; Messina, G.A.; Bertolino, F.A.; Pereira, S.V.; Baldo, M.A.F.; Raba, J. Nanomaterials in fluorescent laser-based immunosensors: Review and applications. Microchem. J. 2018, 141, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székács, I.; Adányi, N.; Szendrő, I.; Székács, A. Direct and competitive optical grating immunosensors for determination of Fusarium mycotoxin zearalenone. Toxins 2021, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabok, A.; Al-Jawdah, A.M.; Gémes, B.; Takács, E.; Székács, A. An Optical Planar Waveguide-Based Immunosensors for Determination of Fusarium Mycotoxin Zearalenone. Toxins 2021, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gémes, B.; Takács, E.; Gádoros, P.; Barócsi, A.; Kocsányi, L.; Lenk, S.; Csákányi, A.; Kautny, S.; Domján, L.; Szarvas, G.; et al. Development of an immunofluorescence assay module for determination of the mycotoxin zearalenone in water. Toxins 2021, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Székács, A. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for monitoring the Fusarium toxin zearalenone. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 1998, 36, 105–110. Available online: https://www.ftb.com.hr/images/pdfarticles/1998/April-June/36-2-3.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- Thouvenot, D.; Morfin, R.F. Radioimmunoassay for zearalenone and zearalanol in human serum: Production, properties, and use of porcine antibodies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 45, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harboe, N.; Inglid, A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulin, estimation of antibody titer. Scand. J. Immunol. 1973, 2 (Suppl. 1), 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidič, J.; Podgornik, A.; Štrancar, A. Effect of the glass surface modification on the strength of methacrylate monolith attachment. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1065, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trummer, N.; Adányi, N.; Váradi, M.; Szendrő, I. Modification of the surface of integrated optical wave-guide sensors for immunosensor applications. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 2001, 371, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Majer-Baranyi, K.; Barócsi, A.; Gádoros, P.; Kocsányi, L.; Székács, A.; Adányi, N. Development of an Immunofluorescent Capillary Sensor for the Detection of Zearalenone Mycotoxin. Toxins 2022, 14, 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120866
Majer-Baranyi K, Barócsi A, Gádoros P, Kocsányi L, Székács A, Adányi N. Development of an Immunofluorescent Capillary Sensor for the Detection of Zearalenone Mycotoxin. Toxins. 2022; 14(12):866. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120866
Chicago/Turabian StyleMajer-Baranyi, Krisztina, Attila Barócsi, Patrik Gádoros, László Kocsányi, András Székács, and Nóra Adányi. 2022. "Development of an Immunofluorescent Capillary Sensor for the Detection of Zearalenone Mycotoxin" Toxins 14, no. 12: 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120866
APA StyleMajer-Baranyi, K., Barócsi, A., Gádoros, P., Kocsányi, L., Székács, A., & Adányi, N. (2022). Development of an Immunofluorescent Capillary Sensor for the Detection of Zearalenone Mycotoxin. Toxins, 14(12), 866. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120866




