Effects of Dietary Ferulic Acid Supplementation on Hepatic Injuries in Tianfu Broilers Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
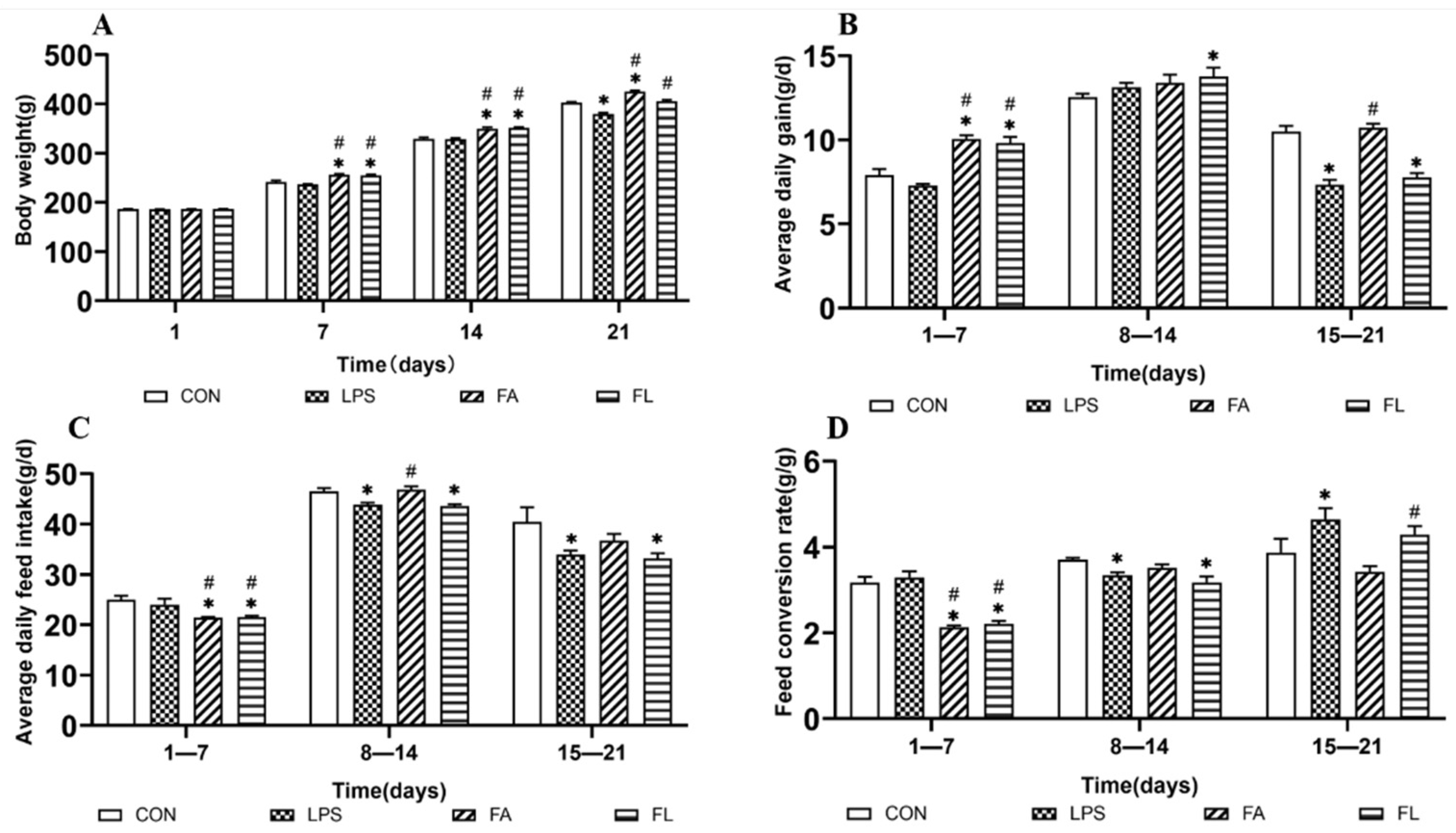
2.1. Growth Performance among Treatment Groups
2.2. LPS-Induced Histopathological Changes of Hepatocytes
2.3. Liver Antioxidant Status
2.4. LPS-Induced Apoptosis and Changes of Mitochondrial Depolarization Ratio
2.5. Expressions of Antioxidant and Apoptosis Associated Genes
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Reagents
5.2. Experimental Animals and Management
5.3. Study Design
5.4. Growth Performance Parameters
5.5. Sample Collection and Measurements
5.6. Histopathological Observation
5.7. Activities of Antioxidants Parameters
5.8. Detection of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Apoptosis
5.9. Real-Time Quantification PCR (RT-qPCR)
5.10. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, X.J.; Li, W.L.; Feng, Y.; Yao, J.H. Effects of immune stress on growth performance, immunity, and cecal microflora in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2011, 90, 2740–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Berndt, C.; Jones, D.P. Oxidative Stress. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 715–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Protective Role of 4-Octyl Itaconate in Murine LPS/D-GalN-Induced Acute Liver Failure via Inhibiting Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9932099. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Wali, A.F.; Rehman, M.U.; Khan, A.; Raish, M.; Kazi, M.; Alnemer, O.; Rao, P.G.M. Therapeutic Potential of Rhododendron arboreum Polysaccharides in an Animal Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Inflicted Oxidative Stress and Systemic Inflammation. Molecules 2020, 25, 6045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, G.; Dong, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, L.; Lu, W. Quercetin Protects Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Intestinal Oxidative Stress in Broiler Chickens through Activation of Nrf2 Pathway. Molecules 2020, 25, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Son, G.; Kremer, M.; Hines, I.N.; Seki, E. Contribution of Gut Bacteria to Liver Pathobiology. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 453563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Schwabe, R.F. The gut microbiome and liver cancer: Mechanisms and clinical translation. Nature reviews. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Li, S.; Li, S. The role of the liver in sepsis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 33, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katsuoka, F.; Motohashi, H.; Ishii, T.; Aburatani, H.; Engel, J.D.; Yamamoto, M. Genetic Evidence that Small Maf Proteins Are Essential for the Activation of Antioxidant Response Element-Dependent Genes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 8044–8051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuadrado, A.; Rojo, A.I.; Wells, G.; Hayes, J.D.; Cousin, S.P.; Rumsey, W.L.; Attucks, O.C.; Franklin, S.; Levonen, A.L.; Kensler, T.W.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of the NRF2 and KEAP1 partnership in chronic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, Z. The Nrf2 Pathway in Liver Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 826204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghvami, M.; Ebrahimi, F.; Zarei, M.H.; Salimi, A.; Jaktaji, R.P.; Pourahmad, J. Matrine Induction of ROS Mediated Apoptosis in Human ALL B-lymphocytes Via Mitochondrial Targeting. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2018, 19, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Wong, Y.S.; Xu, G.; Chan, J.C. Selenium-enriched Spirulina protects INS-1E pancreatic beta cells from human islet amyloid polypeptide-induced apoptosis through suppression of ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and PI3/AKT pathway. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini, M.J.; Shaki, F.; Ghazi-Khansari, M.; Pourahmad, J. Toxicity of copper on isolated liver mitochondria: Impairment at complexes I, II, and IV leads to increased ROS production. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Luo, Q.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. The mitochondrial pathway is involved in sodium fluoride (NaF)-induced renal apoptosis in mice. Toxicol. Res. 2018, 7, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cecconi, F.; Alvarez-Bolado, G.; Meyer, B.I.; Roth, K.A.; Gruss, P. Apaf1 (CED-4 Homolog) Regulates Programmed Cell Death in Mammalian Development. Cell 1998, 94, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volkmann, N.; Marassi, F.M.; Newmeyer, D.D.; Hanein, D. The rheostat in the membrane: BCL-2 family proteins and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.D.; Birdi, T.J. Development of botanicals to combat antibiotic resistance. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2017, 8, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Park, J.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, S. In vitro and in vivo antithrombotic and cytotoxicity effects of ferulic acid. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxic. 2018, 32, e22004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, H.; Summah, B.S.; Liu, H.; An, D.; Zhan, Q.; Lai, W.; Zeng, Q.; Ren, H.; et al. Ferulic acid increases intestinal Lactobacillus and improves cardiac function in TAC mice. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 120, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Maldonado, A.F.; Schieber, A.; Ganzle, M.G. Structure-function relationships of the antibacterial activity of phenolic acids and their metabolism by lactic acid bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yang, H. Ferulic acid exerts neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mir, S.M.; Ravuri, H.G.; Pradhan, R.K.; Narra, S.; Kumar, J.M.; Kuncha, M.; Kanjilal, S.; Sistla, R. Ferulic acid protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing inflammatory events and upregulating antioxidant defenses in Balb/c mice. Biomed. Pharm. 2018, 100, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumrungpert, A.; Lilitchan, S.; Tuntipopipat, S.; Tirawanchai, N.; Komindr, S. Ferulic Acid Supplementation Improves Lipid Profiles, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory Status in Hyperlipidemic Subjects: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, Q.; Ma, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tan, H.; Xiao, C.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y. Antithrombotic activities of ferulic acid via intracellular cyclic nucleotide signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 777, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Ghosh, S.; Das, A.K.; Sil, P.C. Ferulic Acid Protects Hyperglycemia-Induced Kidney Damage by Regulating Oxidative Insult, Inflammation and Autophagy. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogiwara, T.; Satoh, K.; Kadoma, Y.; Murakami, Y.; Unten, S.; Atsumi, T.; Sakagami, H.; Fujisawa, S. Radical scavenging activity and cytotoxicity of ferulic acid. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 2711. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.; Guo, J.; Majeed, H.; Zhu, K.; Guo, X.; Peng, W.; Zhou, H. Ferulic acid renders protection to HEK293 cells against oxidative damage and apoptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2015, 51, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetoni, A.R.; Mancuso, C.; Eramo, S.L.M.; Ralli, M.; Piacentini, R.; Barone, E.; Paludetti, G.; Troiani, D. In vivo protective effect of ferulic acid against noise-induced hearing loss in the guinea-pig. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Kao, S.T.; Hsieh, C.L. Ferulic Acid Administered at Various Time Points Protects against Cerebral Infarction by Activating p38 MAPK/p90RSK/CREB/Bcl-2 Anti-Apoptotic Signaling in the Subacute Phase of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e155748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Song, Q.; Zhou, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, X.; Qian, Q.; Chai, H.; Han, Q.; Pan, H.; Dou, X.; et al. Ferulic acid alleviates lipotoxicity-induced hepatocellular death through the SIRT1-regulated autophagy pathway and independently of AMPK and Akt in AML-12 hepatocytes. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.C.; Wu, Q.J.; Song, Z.H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, T.Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, T. Effects of Oridonin on growth performance and oxidative stress in broilers challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Y. Bacillus subtilis–fermented products ameliorate the growth performance and alter cecal microbiota community in broilers under lipopolysaccharide challenge. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhong, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, G.; Du, H.; Wang, T. Dietary RRR-alpha-tocopherol succinate attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokines secretion in broiler chicks. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peña Torres, E.F.; Dávila Ramírez, J.L.; Peña Ramos, E.A.; Valenzuela Melendres, M.; Pinelli Saavedra, A.; Avendaño Reyes, L.; González Ríos, H. Effects of dietary ferulic acid on growth performance, carcass traits and meat quality of heifers. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wu, F.; Tian, J.; Lu, X.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W. Effects of ferulic acid on growth performance, immunity and antioxidant status in genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fed oxidized fish oil. Aquacult. Nutr. 2020, 26, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ansari, A.R.; Huang, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Sun, Z.; Peng, K.; Zhong, J.; Liu, H. Lipopolysaccharide mediates immuno-pathological alterations in young chicken liver through TLR4 signaling. BMC Immunol. 2017, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roghani, M.; Kalantari, H.; Khodayar, M.J.; Khorsandi, L.; Kalantar, M.; Goudarzi, M.; Kalantar, H. Alleviation of Liver Dysfunction, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Underlies the Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid in Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, L.; Song, M.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Coffie, J.W.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Yang, W.; et al. Ferulic acid protects cardiomyocytes from TNF-α/cycloheximide-induced apoptosis by regulating autophagy. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, T.; Hou, J.; Li, M. Ferulic acid alleviates atopic dermatitis-like symptoms in mice via its potent anti-inflammatory effect. Immunopharm Immunot. 2020, 42, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suliman, H.B.; Welty-Wolf, K.E.; Carraway, M.S.; Tatro, L.; Piantadosi, C.A. Lipopolysaccharide induces oxidative cardiac mitochondrial damage and biogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 64, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.J.; Zhou, Y.M.; Wu, Y.N.; Zhang, L.L.; Wang, T. The effects of natural and modified clinoptilolite on intestinal barrier function and immune response to LPS in broiler chickens. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 153, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefipour, Z.; Ranganna, K.; Newaz, M.A.; Milton, S.G. Mechanism of acrolein-induced vascular toxicity. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2005, 56, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matés, J.M.; Pérez-Gómez, C.; Blanca, M. Chemical and biological activity of free radical ‘scavengers’ in allergic diseases. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2000, 296, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelainy, E.G.; Ibrahim Laila, I.M.; Ibrahim, S.R. The effect of ferulic acid against lead-induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in kidney and testes of rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 31675–31684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.W.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhou, H.B.; Guo, Y.P.; Ma, Q.G.; Ji, C.; Zhao, L.H. Effects of dietary pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium supplementation on inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and intestinal morphology in broiler chickens challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 5389–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Nioi, P.; Pickett, C.B. The Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Element Signaling Pathway and Its Activation by Oxidative Stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13291–13295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hafez, H.M.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Zedan, M.Z.; Hassan, M.; Hassanein, H. Nephroprotective effect of cilostazol and verapamil against thioacetamide-induced toxicity in rats may involve Nrf2/HO-1/NQO-1 signaling pathway. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2019, 29, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ding, M.; Gao, X.R.; Ding, F. Pyrroloquinoline quinone rescues hippocampal neurons from glutamate-induced cell death through activation of Nrf2 and up-regulation of antioxidant genes. Genet. Mol. Res. 2012, 11, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, V.; Calafato, S.; Puleo, E.; Cornelius, C.; Sapienza, M.; Morganti, P.; Mancuso, C. Redox regulation of cellular stress response by ferulic acid ethyl ester in human dermal fibroblasts: Role of vitagenes. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, V. Multiple pathways to apoptosis. Cell Biol. Int. 1993, 17, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. The Bcl2 family: Regulators of the cellular life-or-death switch. Nature reviews. Cancer 2002, 2, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, L.A.; Metcalf, D.; Adams, J.M.; Cecconi, F.; Huang, D.C.S.; Kuida, K.; Bouillet, P.; Nicholson, D.W.; Vaux, D.L.; O’Connor, L.; et al. Apoptosis initiated by Bcl-2-regulated caspase activation independently of the cytochrome c/Apaf-1/caspase-9 apoptosome. Nature 2002, 419, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsonage, G.; Scheel-Toellner, D.; Akbar, A.N.; Henriquez, N.V.; Lord, J.M.; Simmons, D.L.; Pilling, D.; Salmon, M.; Threlfall, K.; Buckley, C.D. RGD peptides induce apoptosis by direct caspase-3 activation. Nature 1999, 397, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, G.; Liang, X.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.; Luo, Y.; Shang, Y.; Yang, J.Q.; Zhou, P.; Gu, X.L. Effects of berberine on the growth performance, antioxidative capacity and immune response to lipopolysaccharide challenge in broilers. Anim. Sci. J. 2019, 90, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Item | Content (%) |
|---|---|
| Corn | 59.50 |
| Soybean meal | 32.90 |
| Vegetable oil | 4.65 |
| CaCO3 | 0.50 |
| CaHPO4 | 1.60 |
| NaCl | 0.30 |
| Choline | 0.10 |
| DL-Methionine | 0.12 |
| Premix 1 | 0.33 |
| Calculation of nutrients | |
| Metabolizable energy (MJ kg−1) | 12.80 |
| Crude protein | 19.70 |
| Lysine | 1.08 |
| Methionime | 0.40 |
| Methionime + Cystine | 0.74 |
| Calcium | 0.77 |
| Nonphytate P | 0.40 |
| Gene | Accession Number | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nrf2 | XM_015289381.3 | F: ACATCTTTTCTCATGATGGGTA R: TCACGAGCCCTGAAACCAA | 82 |
| NQO1 | NM_001277621.1 | F: TCTCTGACCTCTACGCCAT R: TCTCGTAGACAAAGCACTCGG | 93 |
| SOD | NM_205064 | F: AGGGGGTCATCCACTTCC R: CCCATTTGTGTTGTCTCCAA | 122 |
| GSH-Px | NM001277853 | F: TTGTAAACATCAGGGGCAAA R: ATGGGCCAAGATCTTTCTGTAA | 164 |
| CAT | NM_001031215.1 | F: GGTTCGGTGGGGTTGTCTTT R: CACCAGTGGTCAAGGCATCT | 211 |
| Bax | XM_422067 | F: TCCTCATCGCCATGCTCAT R: CCTTGGTCTGGAAGCAGAAGA | 195 |
| Bcl-2 | NM_205339 | F: TCCTCATCGCCATGCTCAT R: CCTTGGTCTGGAAGCAGAAGA | 205 |
| Caspase-3 | XM_015276122.3 | F: TGCTCCAGGCTACTACTCC R: CCACTCTGCGATTTACACGA | 134 |
| β-actin | NM_205518.1 | F: AAGGATCTGTATGCCAACACA R: AGACAGAGTACTTGCGCTCA | 148 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shu, G.; Tang, Z.; Du, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, L.; Li, H.; Xu, F.; Fu, H.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J. Effects of Dietary Ferulic Acid Supplementation on Hepatic Injuries in Tianfu Broilers Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide. Toxins 2022, 14, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030227
Shu G, Tang Z, Du H, Zheng Y, Chang L, Li H, Xu F, Fu H, Zhang W, Lin J. Effects of Dietary Ferulic Acid Supplementation on Hepatic Injuries in Tianfu Broilers Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide. Toxins. 2022; 14(3):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030227
Chicago/Turabian StyleShu, Gang, Ziting Tang, Hong Du, Yilei Zheng, Lijen Chang, Haohuan Li, Funeng Xu, Hualin Fu, Wei Zhang, and Juchun Lin. 2022. "Effects of Dietary Ferulic Acid Supplementation on Hepatic Injuries in Tianfu Broilers Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide" Toxins 14, no. 3: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030227
APA StyleShu, G., Tang, Z., Du, H., Zheng, Y., Chang, L., Li, H., Xu, F., Fu, H., Zhang, W., & Lin, J. (2022). Effects of Dietary Ferulic Acid Supplementation on Hepatic Injuries in Tianfu Broilers Challenged with Lipopolysaccharide. Toxins, 14(3), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14030227






