Application of Aspergillus niger Fumonisin Amine Oxidase (AnFAO) to Detoxify Fumonisin-Contaminated Maize
Abstract
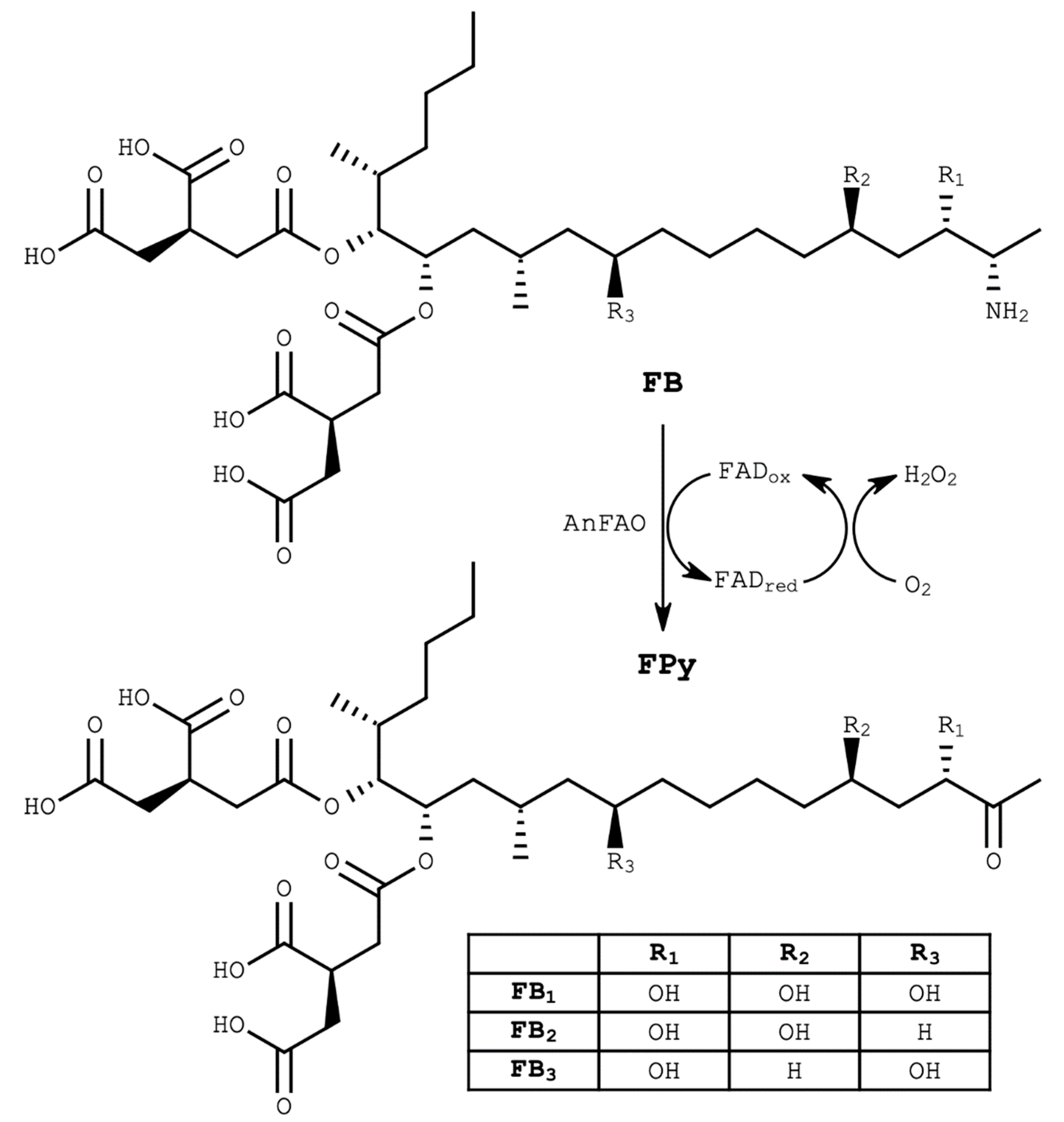
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Recombinant AnFAO Deaminates Intact Fumonisins in QCM Milled Maize Flour
2.2. AnFAO Deaminates Intact Fumonisins in F. verticillioides-Contaminated Whole Kernel Maize
2.3. AnFAO Deaminates Fumonisins within DDGS
2.4. Pichia Pastoris Produces Active AnFAO in Both Secreted and Intracellular Forms
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Expression Vectors, and Reagents
4.2. LC-MS Analysis of Fumonisins
4.3. AnFAO Expression and Purification
4.4. Deamination of Fumonisins in QCM Milled Maize Flour
4.5. Deamination of Fumonisins on Whole Kernel Maize Infected with F. verticillioides
4.6. Deamination of Fumonisins in Dried Distillers’ Grains with Solubles (DDGS)
4.7. Recombinant Production of AnFAO in the Methylotrophic Yeast Pichia pastoris
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, J.D. Mycotoxins in food and feed: A challenge for the 21st century. In Biology of Microfungi; Li, D.-W., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 469–493. [Google Scholar]
- Munkvold, G.P.; Arias, S.; Taschl, I.; Gruber-Dorninger, C. Mycotoxins in corn: Occurrence, impacts, and management. In Corn; Press, A.I., Ed.; AACC International Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 235–287. [Google Scholar]
- Shephard, G.S.; Burger, H.-M.; Rheeder, J.P.; Alberts, J.F.; Gelderblom, W.C.A. The effectiveness of regulatory maximum levels for fumonisin mycotoxins in commercial and subsistence maize crops in south africa. Food Control 2019, 97, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.P.; Miller, J.D.; Groopman, J.D. Mycotoxin Control in Low and Middle Income Countries; IARC Working Group Report #9; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2015; p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, R.T.; Edwards, S.G.; Aidoo, K.; Alexander, J.; Bolger, M.; Boon, P.E.; Cressey, P.E.; Doerge, D.R.; Edler, L.; Miller, J.D.; et al. Fumonisins. In Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food; WHO Food Additives Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 74, pp. 415–571. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, O.A.; Palencia, E.; Lopez de Pratdesaba, L.; Grajeda, R.; Fuentes, M.; Speer, M.C.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; O’Donnell, K.; Bacon, C.W.; Glenn, A.E.; et al. Estimated fumonisin exposure in guatemala is greatest in consumers of lowland maize. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2723–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Riley, R.T.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Ceramide synthase inhibition by fumonisins: A perfect storm of perturbed sphingolipid metabolism, signaling, and disease. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Sullards, M.C.; Wang, E.; Voss, K.A.; Riley, R.T. Sphingolipid metabolism: Roles in signal transduction and disruption by fumonisins. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. 2), 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Renaud, J.B.; DesRochers, N.; Hoogstra, S.; Garnham, C.P.; Sumarah, M.W. Structure activity relationship for fumonisin phytotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Iarc monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans: Some naturally occurring substances, food items and constituents, heterocyclic aromatic amines and mycotoxins. IARC Monogr. 1993, 56, 391–392. [Google Scholar]
- Missmer, S.A.; Suarez, L.; Felkner, M.; Wang, E.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Rothman, K.J.; Hendricks, K.A. Exposure to fumonisins and the occurrence of neural tube defects along the texas-mexico border. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, P.G.; Shephard, G.S.; Sydenham, E.W.; Marasas, W.F.O.; Nelson, P.E.; Wilson, T.M. Levels of fumonisins b1 and b2 in feeds associated with confirmed cases of equine leukoencephalomalacia. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1991, 39, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haschek, W.M.; Gumprecht, L.A.; Smith, G.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Constable, P.D. Fumonisin toxicosis in swine: An overview of porcine pulmonary edema and current perspectives. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109 (Suppl. 2), 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Riley, R.T.; Wu, F. Dietary fumonisin and growth impairment in children and animals: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1448–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food: Eighty-Third Report of the Joint Fao/Who Expert Committee on Food Additives; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; p. 182. [Google Scholar]
- United States Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Fumonisin Levels in Human Foods and Animal Feeds. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-industry-fumonisin-levels-human-foods-and-animal-feeds (accessed on 15 June 2022).
- Hartinger, D.; Schwartz, H.; Hametner, C.; Schatzmayr, G.; Haltrich, D.; Moll, W.D. Enzyme characteristics of aminotransferase fumi of sphingopyxis sp. Mta144 for deamination of hydrolyzed fumonisin B1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinl, S.; Hartinger, D.; Thamhesl, M.; Vekiru, E.; Krska, R.; Schatzmayr, G.; Moll, W.D.; Grabherr, R. Degradation of fumonisin b1 by the consecutive action of two bacterial enzymes. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 145, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvick, J.; Rood, T.; Maddox, J.; Gilliam, J. Detoxification of mycotoxins in planta as a strategy for improving grain quality and disease resistance: Identification of fumonisin-degrading microbes from maize. In Molecular Genetics of Host-Specific Toxins in Plant Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 369–381. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, B.A.; Gilliam, J.T.; Savard, M.E.; David Miller, J.; Duvick, J.P. Oxidative deamination of hydrolyzed fumonisin b(1) (ap(1)) by cultures of exophiala spinifera. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.; Schatzmayr, G.; Moll, W.D.; Davids, I.; Rheeder, J.; Burger, H.M.; Shephard, G.; Gelderblom, W. Detoxification of the fumonisin mycotoxins in maize: An enzymatic approach. Toxins 2019, 11, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.F.; Davids, I.; Moll, W.-D.; Schatzmayr, G.; Burger, H.-M.; Shephard, G.S.; Gelderblom, W.C.A. Enzymatic detoxification of the fumonisin mycotoxins during dry milling of maize. Food Control 2021, 123, 107726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, J.F.; Burger, H.-M.; Rheeder, J.; Shephard, G.; Gelderblom, W. Enzymatic Decontamination as an Approach for Reduction of Human Exposure to Mycotoxins in Rural Subsistence Farming Communities in Africa; World Nutrition Forum: Salzburg, Austria, 2019; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Lemke, S.L.; Ottinger, S.E.; Ake, C.L.; Mayura, K.; Phillips, T.D. Deamination of fumonisin b1 and biological assessment of reaction product toxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2001, 14, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnham, C.P.; Butler, S.G.; Telmer, P.G.; Black, F.E.; Renaud, J.B.; Sumarah, M.W. Identification and characterization of an aspergillus niger amine oxidase that detoxifies intact fumonisins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13779–13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, K.M.; Renaud, J.B.; McDowell, T.; Sumarah, M.W. Mechanistic insight into the biosynthesis and detoxification of fumonisin mycotoxins. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 2618–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Caupert, J. Survey of mycotoxins in U.S. Distiller’s dried grains with solubles from 2009 to 2011. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, A.W.; Limay-Rios, V.; Paul, D.E.; Miller, J.D. Mycotoxins in fuel ethanol co-products derived from maize: A mass balance for deoxynivalenol. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothast, R.J.; Bennett, G.A.; Vancauwenberge, J.E.; Richard, J.L. Fate of fumonisin b(1) in naturally contaminated corn during ethanol fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1992, 58, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Westhuizen, L.; Shephard, G.S.; Rheeder, J.P.; Burger, H.M.; Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Wild, C.P.; Gong, Y.Y. Optimising sorting and washing of home-grown maize to reduce fumonisin contamination under laboratory-controlled conditions. Food Control 2011, 22, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Westhuizen, L.; Shephard, G.S.; Rheeder, J.P.; Burger, H.M.; Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Wild, C.P.; Gong, Y.Y. Simple intervention method to reduce fumonisin exposure in a subsistence maize-farming community in south africa. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2010, 27, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, M.; Coker, R.D.; DiNovi, M.; Gaylor, D.; Gelderblom, W.; Olsen, M.; Paster, N.; Riley, R.T.; Shephard, G.; Speijers, G.J.A. Fumonisins. In Prepared by the 56th Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA), Safety Evaluation of Certain Mycotoxins in Food; WHO Food Additives Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; Volume 47, pp. 103–279. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa, M.A.; Chovau, S.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Espinosa, J. Ethanol production from corn contaminated with fumonisins: A preliminary economic analysis including novel processing alternatives. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 7504–7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, E.; Dunn-Coleman, N.; Frisvad, J.C.; Van Dijck, P.W. On the safety of aspergillus niger—A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Telmer, P.G.; Kelman, M.J.; Renaud, J.B.; Sumarah, M.W.; Garnham, C.P. Application of Aspergillus niger Fumonisin Amine Oxidase (AnFAO) to Detoxify Fumonisin-Contaminated Maize. Toxins 2022, 14, 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080544
Telmer PG, Kelman MJ, Renaud JB, Sumarah MW, Garnham CP. Application of Aspergillus niger Fumonisin Amine Oxidase (AnFAO) to Detoxify Fumonisin-Contaminated Maize. Toxins. 2022; 14(8):544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080544
Chicago/Turabian StyleTelmer, Patrick G., Megan J. Kelman, Justin B. Renaud, Mark W. Sumarah, and Christopher P. Garnham. 2022. "Application of Aspergillus niger Fumonisin Amine Oxidase (AnFAO) to Detoxify Fumonisin-Contaminated Maize" Toxins 14, no. 8: 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080544
APA StyleTelmer, P. G., Kelman, M. J., Renaud, J. B., Sumarah, M. W., & Garnham, C. P. (2022). Application of Aspergillus niger Fumonisin Amine Oxidase (AnFAO) to Detoxify Fumonisin-Contaminated Maize. Toxins, 14(8), 544. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14080544




