Algicidal Activity and Microcystin-LR Destruction by a Novel Strain Penicillium sp. GF3 Isolated from the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Identification of the GF3 Strain
2.2. The Spectrum of the Algicidal Activity of Strain GF3
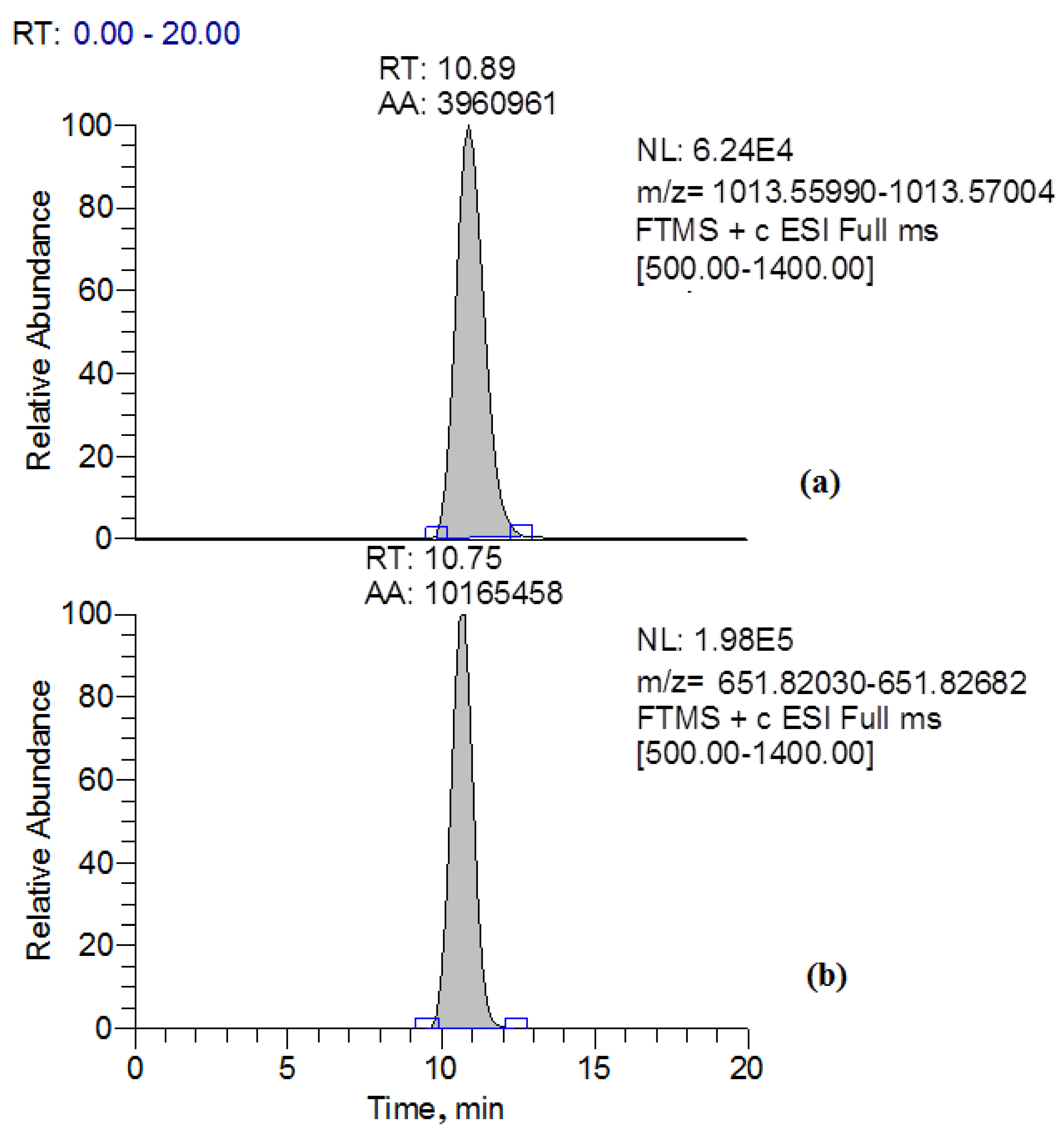
2.3. MC-LR Removal by the Strain Penicillium sp. GF3
2.4. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation and Antioxidant
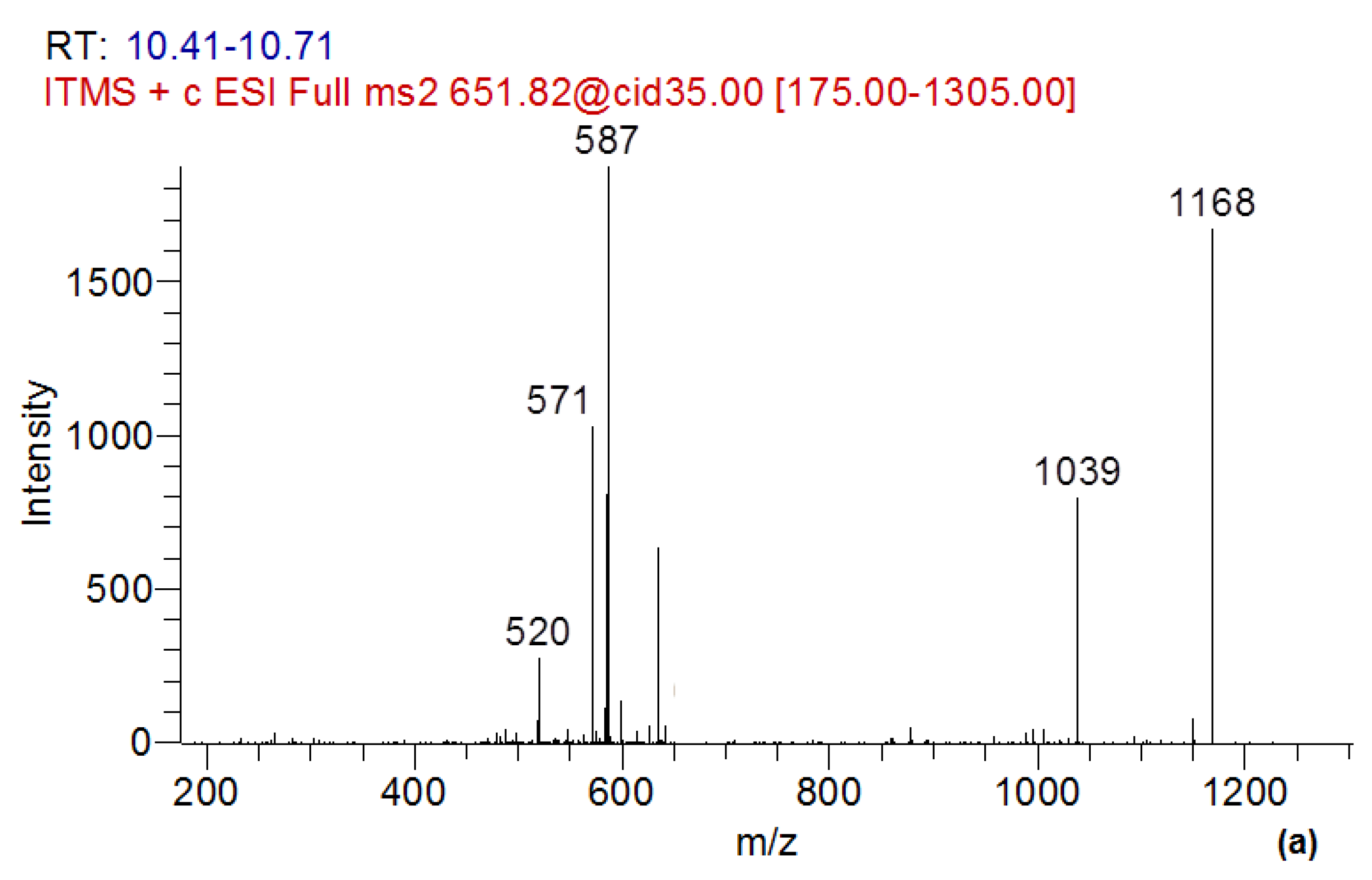
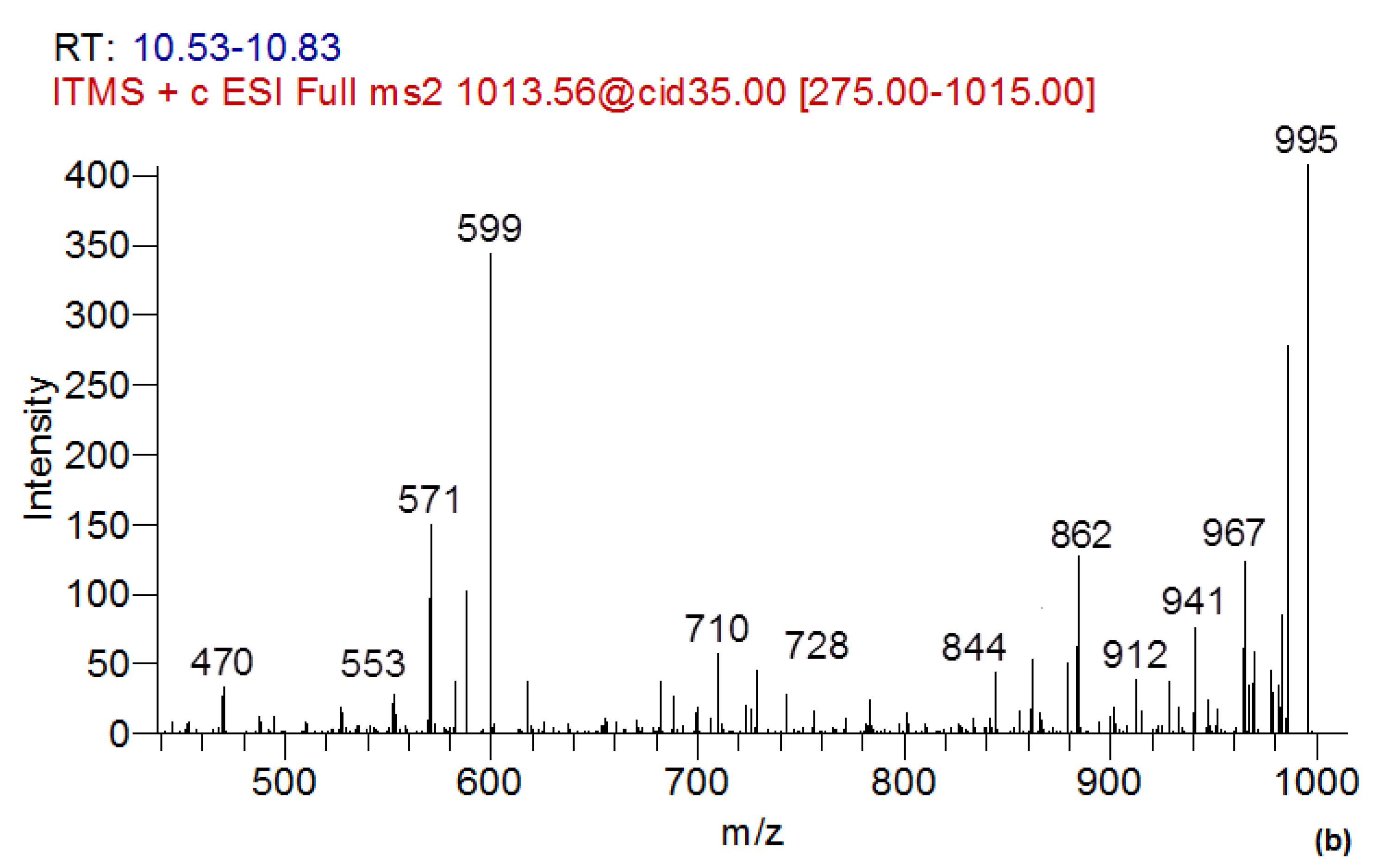
2.5. Determination of MC-LR Biotransformation Products
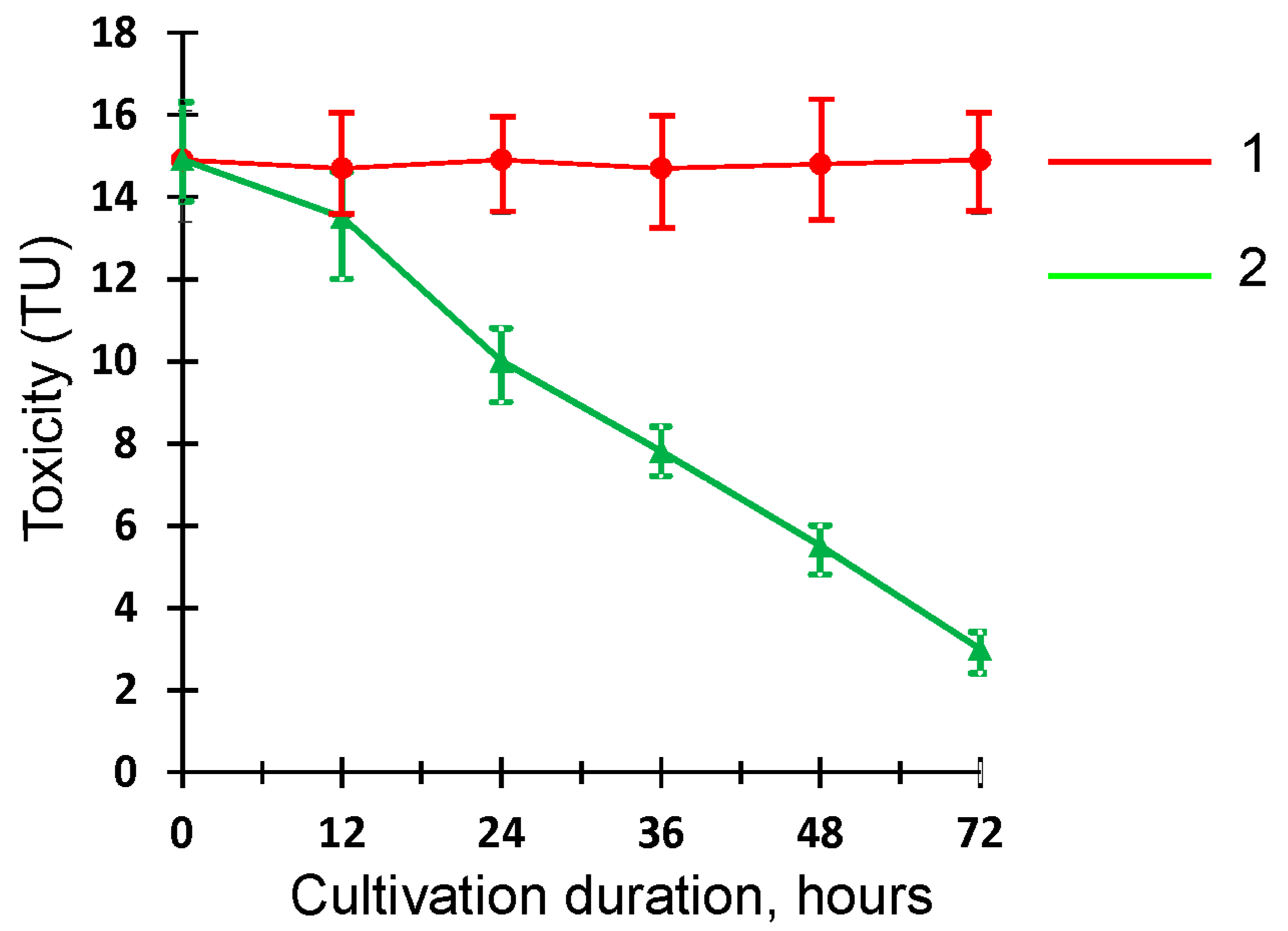
2.6. Evaluation of GF3 Filtrate Toxicity
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Water Sampling
4.2. Isolation and Identification of the GF3 Strain
4.3. Cultivation of the Strain GF3
4.4. Determination of the Algicidal Activity Spectrum of the Strain GF3
4.5. Preparation of Microcystin-LR Crude Extract
4.6. Quantification of MC-LR and Identification of Its Transformation Products by LC–MS/MS Analysis
4.7. Assay of Antioxidants and Lipid Peroxidation
4.8. Toxicity Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, Y.; Yin, F.; Xie, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ashraf, T. Inversion and monitoring of the TP concentration in Taihu Lake using the landsat-8 and sentinel-2 images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buratti, F.M.; Manganelli, M.; Vichi, S.; Stefanelli, M.; Scardala, S.; Testai, E.; Funari, E. Cyanotoxins: Producing organisms, occurrence, toxicity, mechanism of action and human health toxicological risk evaluation. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1049–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suikkanen, S.; Fistarol, G.O.; Graneli, E. Effects of cyanobacterial allelochemicals on a natural plankton community. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 287, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, B. Microcystin-LR in primary liver cancers: An overview. Toxins 2022, 14, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Molecular mechanisms of microcystin toxicity in animal cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, C.; Valerio, E.; Dias, E. The kidney Vero-E6 cell line: A suitable model to study the toxicity of microcystins. In New Insights into Toxicity and Drug Testing; Sivakumar, G., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-0946-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, Z.; Ding, J.; Han, X. Learning and memory deficits and alzheimer′s disease-like changes in mice after chronic exposure to microcystin-LR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 504–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Huang, F.; Massey, I.Y.; Wen, C.; Zheng, S.; Xu, S.; Yang, F. Effects of microcystin-LR on the microstructure and inflammation-related factors of jejunum in mice. Toxins 2019, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, L.; Hou, J.; Ma, T.; Pan, C.; Zhou, Y.; Han, R.; Ding, Y.; Peng, H.; Xiang, Z.; et al. The mechanisms in the altered ontogenetic development and lung-related pathology in microcystin-leucine arginine (MC-LR)-paternal-exposed offspring mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Zhang, L.; Meng, X.; Qin, H.; Xiang, Z.; Gong, W.; Luo, W.; Li, D.; Han, X. Chronic exposure to microcystin-LR increases the risk of prostate cancer and induces malignant transformation of human prostate epithelial cells. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Ingested nitrate and nitrite, and cyanobacterial peptide toxins. IARC Monogr. Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum. 2010, 94, 450. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchett, G.; Oliveira-Filho, E.C. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins: From impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human health to anticarcinogenic effects. Toxins 2013, 5, 1896–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máthé, C.; M-Hamvas, M.; Vasas, G.; Garda, T.; Freytag, C. Subcellular alterations induced by cyanotoxins in vascular plants—A review. Plants 2021, 10, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, E.; Sidelev, S.; Russkikh, I.; Voyakina, E.; Zhakovskaya, Z. First observation of microcystin- and anatoxin-a-producing cyanobacteria in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Finland (the Baltic Sea). Toxicon 2019, 157, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lürling, M.; Meng, D.; Faassen, E.J. Effects of hydrogen peroxide and ultrasound on biomass reduction and toxin release in the cyanobacterium, Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins 2014, 6, 3260–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.-C.; Lee, C.-L.; Chang, C.M. Adsorption of pesticides, antibiotics and microcystin-LR by graphene and hexagonal boron nitride nano-systems: A semiempirical PM7 and theoretical HSAB study. Crystals 2022, 12, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struewing, I.; Sienkiewicz, N.; Zhang, C.; Dugan, N.; Lu, J. Effective early treatment of microcystis exponential growth and microcystin production with hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyapatite. Toxins 2023, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Hashem, M.; Alamri, S.A. Growth inhibition of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa and degradation of its microcystin toxins by the fungus Trichoderma citrinoviride. Toxicon 2014, 86, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chang, Y.; Sun, L.; Du, F.; Cui, J.; Liu, X.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Yao, D. Abundant allelochemicals and the inhibitory mechanism of the phenolic acids in water dropwort for the control of Microcystis aeruginosa blooms. Plants 2021, 10, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Xie, W.; He, W.; Xie, J.; Liu, W. Identifying algicides of Enterobacter hormaechei F2 for control of the harmful alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; He, X.; Cao, L.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, B. An WA Novel wide-range freshwater cyanophage minS1 infecting the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Viruses 2022, 14, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Teng, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, X. Microcystins in water: Detection, microbial degradation strategies, and mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F. A mini review on microcystins and bacterial degradation. Toxins 2020, 12, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Hashem, M.; Alamri, S.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Fungal biodegradation and removal of cyanobacteria and microcystins: Potential applications and research needs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 37041–37050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Gao, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, D. Algicidal molecular mechanism and toxicological degradation of Microcystis aeruginosa by white-rot fungi. Toxins 2020, 12, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Zhou, Q.; Lilje, O.; Xu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ogtrop, F. Inhibition mechanism of Penicillium chrysogenum on Microcystis aeruginosa in aquaculture water. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 299, 126829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Feng, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C.; He, X.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, X. Isolation and evaluation of terrestrial fungi with algicidal ability from Zijin Mountain, Nanjing, China. J. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, K.; Wright, S.J. Isolation and properties of fungi that lyse blue-green algae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1978, 35, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Alamri, S.; Hashem, M.; Mostafa, Y. Growth inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa and adsorption of microcystin toxin by the yeast Aureobasidium pullulans, with no effect on microalgae. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2020, 27, 38038–38046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Han, G.; Wang, C.; Guo, P.; Jiang, W.; LiX, T.X. The efficacy and mechanisms of fungal suppression of freshwater harmful algal bloom species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 183, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.M.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y. Algicidal efficiency and mechanism of Phanerochaete chrysosporium against harmful algal bloom species. Algal Res. 2015, 12, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Hertel, S.; Pflugmacher, S. Uptake and biotransformation of pure commercial microcystin-LR versus microcystin-LR from a natural cyanobacterial bloom extract in the aquatic fungus Mucor hiemalis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valério, E.; Vilares, A.; Campos, A.; Pereira, P.; Vasconcelos, V. Effects of microcystin-LR on Saccharomyces cerevisiae growth, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicon 2014, 90, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsano, E.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Hoque, E.; Pflugmacher, S. Toxin resistance in aquatic fungi poses environmentally friendly remediation possibilities: A study on the growth responses and biosorption potential of Mucor hiemalis EH5 against cyanobacterial toxins. Int. J. Water Wastewater Treat 2015, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.; Huang, J.; Huang, W.; Li, D.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Microcystin-RR induced accumulation of reactive oxygen species and alteration of antioxidant systems in tobacco BY-2 cells. Toxicon 2005, 46, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greer, B.; Maul, R.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.T. Detection of freshwater cyanotoxins and measurement of masked microcystins in tilapia from Southeast Asian aquaculture farms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 2017, 409, 4057–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.B.; de Silva, H.A. Cellular oxidative stress stimulated by microcystin: Review. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e422101119765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, E. Lipid peroxidation products as oxidative stress biomarkers. BioFactors 2008, 34, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del, R.D.; Stewart, A.J.; Pellegrini, N. A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2005, 15, 316–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessler, N.N.; Aver’yanov, A.A.; Belozerskaya, T.A. Reactive oxygen species in regulation of fungal development. Biochemistry 2007, 72, 1091–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsano, E.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Hoque, E.; Lima, S.P. Responses of the antioxidative and biotransformation enzymes in the aquatic fungus Mucor hiemalis exposed to cyanotoxins. Biotechnol. Lett 2017, 39, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, L.P.; Suhovskaya, I.V. The role of glutathione in the functioning of antioxidant defense systems and biotransformation (review). Uch. Zap. Petrozavodsk. Gos. Univ. 2014, 6, 34–40. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Chi, Y.; Wu, D.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Igarashi, Y.; Luo, F. Algicidal characterization and mechanism of Bacillus licheniformis Sp34 against Microcystis aeruginosa in Dianchi Lake. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, J.R.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Boyer, G.L. The fate of microcystins in the environment and challenges for monitoring. Toxins 2014, 6, 3354–3387. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, D.G. Enzymatic pathway for the bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin LR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1996, 62, 4086–4094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chernova, E.N.; Russkikh, I.V.; Podol'skaya, E.P.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A. Determination of microcystins and anatoxin-a by low-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nauchnoe Priborostr. 2016, 26, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Riddles, P.; Jones, G.J.; Smith, W.; Blakeley, R.L. Characterisation of a gene cluster involved in bacterial degradation of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin LR. Environ. Toxicol. 2001, 16, 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Guida, M.; Inglese, M.; Meriç, S. A multi-battery toxicity investigation on fungicides. Desalination 2008, 226, 262–270. [Google Scholar]
- Samson, R.A.; Hoekstra, E.S.; Frisvad, J.C.; Filtenborg, O. (Eds.) Introduction to Food- and Airborne Fungi, revised 6th ed.; Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; c389p. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzikova, I.; Safronova, V.; Zaytseva, T.; Medvedeva, N.; Medvedeva, N. Fate and effects of nonylphenol in the filamentous fungus Penicillium expansum isolated from the bottom sediments of the Gulf of Finland. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 171, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Genetic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1974, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Humprhråy, G.E. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, N.; Zaytseva, T.; Kuzikova, I.; Chernova, E. The microcystin–LR biodestruction by autochthonous microbiota of 552 diverse water bodies in the northwest of Russia. Biol. Bull. 2023; in print. [Google Scholar]
- Chernova, E.; Russkikh, I.; Voyakina, E.; Zhakovskaya, Z. Occurrence of microcystins and anatoxin-a in eutrophic lakes of Saint 485 Petersburg, Northwestern Russia. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2016, 45, 466–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, W.F.; Fridovich, I. Assaying for superoxide dismutase activity: Some large consequences of minor changes in conditions. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 161, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.T.; Tam, N.F.Y. Growth, photosynthesis and antioxidant responses of two microalgal species, Chlorella vulgaris and Selenastrum capricornutum, to nonylphenol stress. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhindsa, R.S.; Plumb-Dhindsa, P.; Thorpe, T.A. Leaf senescence: Correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J. Exp. Bot. 1981, 32, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzikova, I.; Rybalchenko, O.; Kurashov, E.; Krylova, Y.; Safronova, V.; Medvedeva, N. Defense responses of the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus tubingensis to alkylphenols stress. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6341; Water Quality. Determination of the Inhibition of the Mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea)—Acute Toxicity Test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996.
- OECD. Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals; Daphnia sp. Acute Immobilization Test and Reproduction Test, Protocol no. 202; OECD: Paris, France, 1996; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]




| Microcystin Congeners | [M + H]+ | MC Content, ng/L |
|---|---|---|
| [D-Asp3]MC-LR | 981.541 | 36.3 |
| MC-LR | 995.5565 | 306.4 |
| [D-Glu-OCH36]MC-LR | 1009.572 | 3.4 |
| [Dha7]MC-HphR | 1029.541 | 29.9 |
| MC-YR | 1045.536 | 66.7 |
| Total MC content | 442.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuzikova, I.; Zaytseva, T.; Chernova, E.; Sazanova, A.; Sharov, A.; Medvedeva, N. Algicidal Activity and Microcystin-LR Destruction by a Novel Strain Penicillium sp. GF3 Isolated from the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea). Toxins 2023, 15, 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100607
Kuzikova I, Zaytseva T, Chernova E, Sazanova A, Sharov A, Medvedeva N. Algicidal Activity and Microcystin-LR Destruction by a Novel Strain Penicillium sp. GF3 Isolated from the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea). Toxins. 2023; 15(10):607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100607
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuzikova, Irina, Tatyana Zaytseva, Ekaterina Chernova, Anna Sazanova, Andrey Sharov, and Nadezda Medvedeva. 2023. "Algicidal Activity and Microcystin-LR Destruction by a Novel Strain Penicillium sp. GF3 Isolated from the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea)" Toxins 15, no. 10: 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100607
APA StyleKuzikova, I., Zaytseva, T., Chernova, E., Sazanova, A., Sharov, A., & Medvedeva, N. (2023). Algicidal Activity and Microcystin-LR Destruction by a Novel Strain Penicillium sp. GF3 Isolated from the Gulf of Finland (Baltic Sea). Toxins, 15(10), 607. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15100607






