Gut Microbiota of Freshwater Gastropod (Bellamya aeruginosa) Assist the Adaptation of Host to Toxic Cyanobacterial Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MC Concentration in Hepatopancreas Tissue
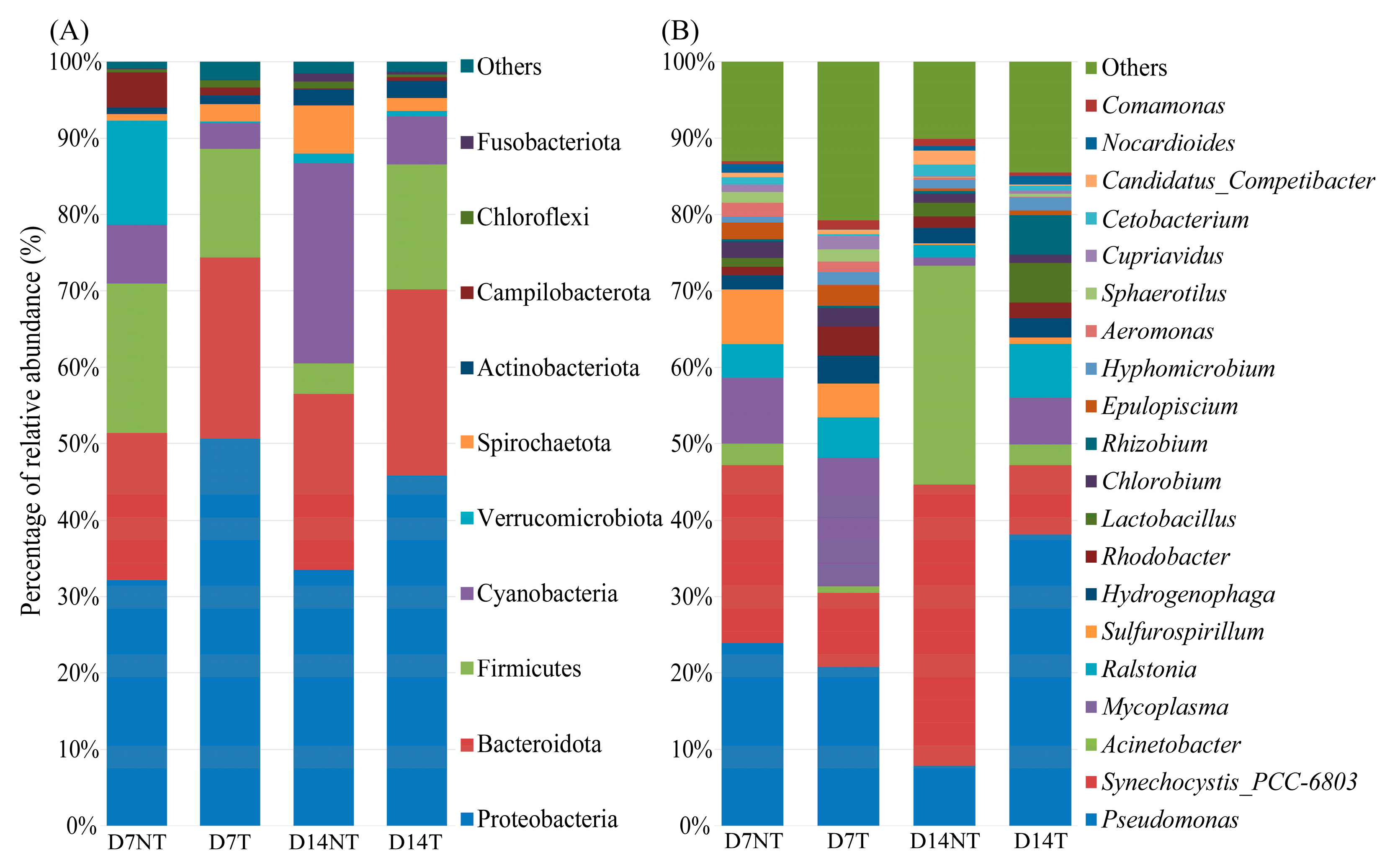
2.2. Changes in Intestinal Microbiota Composition
2.3. Diversity Analysis of Intestinal Microbiota
2.4. Biomarker Analysis
2.5. Gut Microbiota Assembly Process Analysis
2.6. Co-Occurrence Patterns of Intestinal Flora
3. Discussion
3.1. Toxic-Producing Cyanobacteria Alter the Intestinal Flora of B. aeruginosa
3.2. Gut Microbiota Assist B. aeruginosa to Adapt to Toxic Cyanobacterial Stress
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Biological Materials
5.2. Experimental Design
5.3. Determination of MC Concentration
5.4. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
5.5. Processing of Sequencing Data
5.6. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paerl, H.W. Mitigating Toxic Planktonic Cyanobacterial Blooms in Aquatic Ecosystems Facing Increasing Anthropogenic and Climatic Pressures. Toxins 2018, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Massey, I.Y.; Yang, F.; Ding, Z.; Yang, S.; Guo, J.; Tezi, C.; Al-Osman, M.; Kamegni, R.B.; Zeng, W. Exposure routes and health effects of microcystins on animals and humans: A mini-review. Toxicon 2018, 151, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bownik, A. Harmful algae: Effects of cyanobacterial cyclic peptides on aquatic invertebrates-a short review. Toxicon 2016, 124, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lance, E.; Brient, L.; Carpentier, A.; Acou, A.; Marion, L.; Bormans, M.; Gerard, C. Impact of toxic cyanobacteria on gastropods and microcystin accumulation in a eutrophic lake (Grand-Lieu, France) with special reference to Physa (= Physella) acuta. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 3560–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.C.; Vasconcelos, V.M. Microcystin dynamics in aquatic organisms. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2009, 12, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Lei, K.; Han, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, X.; An, L.; LeBlanc, G.A. No impacts of microcystins on wild freshwater snail Bellamya Aeruginosa fecundity from a eutrophic lake. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 60, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerard, C.; Poullain, V.; Lance, E.; Acou, A.; Brient, L.; Carpentier, A. Influence of toxic cyanobacteria on community structure and microcystin accumulation of freshwater molluscs. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Lu, K.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J. Blooms of toxic cyanobacteria cause the gastropod Bellamya aeruginosa to shift its diet from planktic to benthic material. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2017, 102, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liang, J.; Hu, Z. Biochemical and ultrastructural changes in the hepatopancreas of Bellamya aeruginosa (Gastropoda) fed with toxic cyanobacteria. ScientificWorldJournal 2011, 11, 2091–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, K.; Qiao, F.; Liu, Q.; Wei, Z.; An, L.; Qi, H.; Cui, S.; LeBlanc, G.A. Preliminary evidence for snail deformation from a Eutrophic lake. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 53, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Lei, K.; Li, Z.; Wei, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; He, J.; An, L.; Qi, H.; Cui, S. Transcriptomic responses of the freshwater snail (Parafossarulus striatulus) following dietary exposure to cyanobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.J.; Song, H.; Feng, J.; Yu, Z.L.; Shi, P.; Liang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, T. Symbiotic microbiome and metabolism profiles reveal the effects of induction by oysters on the metamorphosis of the carnivorous gastropod Rapana venosa. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evariste, L.; Barret, M.; Mottier, A.; Mouchet, F.; Gauthier, L.; Pinelli, E. Gut microbiota of aquatic organisms: A key endpoint for ecotoxicological studies. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Tong, Q.; Li, S.; Niu, H. Compositional and predicted functional analysis of the gut microbiota of Radix auricularia (Linnaeus) via high-throughput Illumina sequencing. PeerJ 2018, 6, e5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Guan, W.; Wu, H.; Li, L.; Abe, E.M.; Xue, J.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lv, S.; Xu, J.; et al. Intestinal microbiome profiles in Oncomelania hupensis in mainland China. Acta Trop. 2020, 201, 105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.-H.; Lv, S.; Lu, Y.; Bi, D.-Q.; Guo, Y.-H.; Wu, J.-T.; Yue, Z.-Y.; Mao, G.-Y.; Guo, Z.-X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Spatial structure of the microbiome in the gut of Pomacea canaliculata. Bmc Microbiol. 2019, 19, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Li, S.; Xiao, Q.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Qu, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, H. Composition and diversity of gut microbiota in Pomacea canaliculata in sexes and between developmental stages. Bmc Microbiol. 2021, 21, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, A.D.; Arp, A.; Cerbie, G.M.; Trujillo, D.A.; Kiss, A.J.; Berg, D.J. Phylogenetic relationship and habitat both impact the gut microbiome in two microendemic gastropods. J. Molluscan Stud. 2022, 88, eyac002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, W.; Zheng, Z. Responses of Gut Microbial Community Composition and Function of the Freshwater Gastropod Bellamya aeruginosa to Cyanobacterial Bloom. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 906278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankers, L.; Dahan, D.; Neiman, M.; Adrian-Tucci, C.; Frost, C.; Hurst, G.D.D.; King, K.C. Invasive freshwater snails form novel microbial relationships. Evol. Appl. 2021, 14, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, D.; Zeng, W.; Huang, J.; Wu, Z. Comparison of gut microbiome in the Chinese mud snail (Cipangopaludina chinensis) and the invasive golden apple snail (Pomacea canaliculata). PeerJ 2022, 10, e13245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Tong, Q.; Chang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, S.; Niu, H.; Ma, D. Gut bacterial communities in the freshwater snail Planorbella trivolvis and their modification by a non-herbivorous diet. Peerj 2021, 9, e10716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macke, E.; Callens, M.; De Meester, L.; Decaestecker, E. Host-genotype dependent gut microbiota drives zooplankton tolerance to toxic cyanobacteria. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, J.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Qu, Y.; Qiu, B. Effects of waterborne exposure to cadmium on biochemical responses in the freshwater gastropod, Bellamya aeruginosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-J.; Liao, M.-L.; Ding, M.-W.; Wang, Z.-K.; Dong, Y.-W. Compositional and functional features of the gut microbiota of the intertidal snail Nerita yoldii along China’s coast. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2022, 101, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Carmichael, W.W.; Miller, I. Immuno-gold localization of hepatotoxins in cyanobacterial cells. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 163, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, C.; Lok-Shun Lai, N.; Zhang, W.; Hua, J.; Lam, P.K.S.; Lam, J.C.W.; Zhou, B. Acute exposure to PBDEs at an environmentally realistic concentration causes abrupt changes in the gut microbiota and host health of zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 240, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriello, M.C.; Hoffman, J.B.; Vsevolozhskaya, O.; Morris, A.J.; Hennig, B. Dioxin-like PCB 126 increases intestinal inflammation and disrupts gut microbiota and metabolic homeostasis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBofsky, A.; Xie, Y.; Grimard, C.; Alcaraz, A.J.; Brinkmann, M.; Hecker, M.; Giesy, J.P. Differential responses of gut microbiota of male and female fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) to a short-term environmentally-relevant, aqueous exposure to benzo[a]pyrene. Chemosphere 2020, 252, 126461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Lin, J.; He, J.; Zeng, C.; Chen, J. Effects of microcystin-LR on gut microflora in different gut regions of mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 40, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Giesy, J.P.; Adamovsky, O.; Svircev, Z.; Meriluoto, J.; Codd, G.A.; Mijovic, B.; Shi, T.; Tuo, X.; Li, S.C.; et al. Challenges of using blooms of Microcystis spp. in animal feeds: A comprehensive review of nutritional, toxicological and microbial health evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 142319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, M. The Feeding Mechanism of the Freshwater Gastropod (Bellamya Aeruginosa)—Realizing its Potential in Controlling Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms. Ph.D Thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ping, X. Gut contents of silver carp, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix, and the disruption of a centric diatom, Cyclotella, on passage through the esophagus and intestine. Aquaculture 1999, 180, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P. Tertiary structural categories of leiurotoxin and some other scorpion venom toxins. Curr. Sci. 1994, 66, 680–682. [Google Scholar]
- Brendelberger, H. Bacteria and Digestive Enzymes in the Alimentary Tract of Radix peregra (Gastropoda, Lymnaeidae). Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, M.; Watanabe, K.; Maruyama, T.; Mori, T.; Niwa, K.; Chow, S.; Takeyama, H. Enrichment of bacteria and alginate lyase genes potentially involved in brown alga degradation in the gut of marine gastropods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Min, F.; Huang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; He, F. Factors affecting palatability of four submerged macrophytes for grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idella. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 28046–28054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, X.; Lu, X.; Jacob, J.; Sun, S.; Heath, R. Metagenomic identification of bacterioplankton taxa and pathways involved in microcystin degradation in lake erie. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manheim, D.; Cheung, Y.-M.; Jiang, S. The Effect of Organic Carbon Addition on the Community Structure and Kinetics of Microcystin-Degrading Bacterial Consortia. Water 2018, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.; Rzymski, P. Programmed Cell Death-Like and Accompanying Release of Microcystin in Freshwater Bloom-Forming Cyanobacterium Microcystis: From Identification to Ecological Relevance. Toxins 2019, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omidi, A.; Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Still challenging: The ecological function of the cyanobacterial toxin microcystin—What we know so far. Toxin Rev. 2018, 37, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Y.; Ng, T.H.; Wu, J.H.; Chen, J.W.; Wang, H.C. Microbiome Dynamics in a Shrimp Grow-out Pond with Possible Outbreak of Acute Hepatopancreatic Necrosis Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riera, J.L.; Baldo, L. Microbial co-occurrence networks of gut microbiota reveal community conservation and diet-associated shifts in cichlid fishes. Anim. Microbiome 2020, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Xu, G.; Han, M.; Xie, L. Effect of dietary histamine on intestinal morphology, inflammatory status, and gut microbiota in yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Fish Shellf. Immunol. 2021, 117, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science 2015, 350, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, T.; Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Hu, B.; Hu, J.; Penuelas, J.; Zhu, L.; Qian, H. Residual chlorine disrupts the microbial communities and spreads antibiotic resistance in freshwater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, J.; Chen, L.; Shan, K.; Hu, L.; Song, L.; Gan, N. Assessment of different mcy genes for detecting the toxic to non-toxic Microcystis ratio in the field by multiplex qPCR. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1132–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Pei, H.Y.; Hu, W.R.; Song, M.M. A multi-technique approach for the quantification of Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-905 biomass during high algae-laden periods. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ye, Y.; Lu, K.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, J. NMR-based metabolomic responses of freshwater gastropod Bellamya aeruginosa to MC-producing and non MC-producing Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2022, 40, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edgar, R.C. UNOISE2: Improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. bioRxiv 2016, 081257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginestet, C. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. J. R. Stat. Soc. 2011, 174, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gever, D. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolde, R.; Kolde, M.R. Package ‘pheatmap’. R Package 2018, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Harrell, M.F.E., Jr. Package ‘hmisc’. CRAN2018 2019, 2019, 235–236. [Google Scholar]
- Csardi, G.; Nepusz, T. The Igraph Software Package for Complex Network Research. Int. J. Complex Syst. 2005, 1695, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guimera, R.; Nunes Amaral, L.A. Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Deng, Y.; Luo, F.; He, Z.; Tu, Q.; Zhi, X. Functional molecular ecological networks. MBio 2010, 1, e00169-00110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Groups | MCs Concentration (μg · g−1 DW) | Unpaired t-Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 d | 7 d | 14 d | R2 | p | |
| NT | - | - | - | - | - |
| T | - | 2.41 ± 0.12 | 1.43 ± 0.10 | 0.961 | <0.0001 **** |
| Times | PERMANOVA | ANOSIM | MRPP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | p | R | p | A | p | |
| 7 d | 0.091 | 0.784 | −0.080 | 0.698 | −0.013 | 0.802 |
| 14 d | 0.254 | 0.035 * | 0.496 | 0.022 * | 0.095 | 0.029 * |
| Groups | Nodes | Edges | Average Degree | ACC | Density | Modularity | Diameter | APL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D7NT | 29 | 65 | 4.483 | 0.665 | 0.160 | 0.535 | 8 | 3.345 |
| D7T | 47 | 383 | 16.298 | 0.800 | 0.354 | 0.305 | 6 | 2.156 |
| D14NT | 55 | 280 | 10.182 | 0.759 | 0.189 | 0.621 | 8 | 3.452 |
| D14T | 65 | 579 | 21.055 | 0.766 | 0.390 | 0.247 | 4 | 1.834 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Yang, W.; Zheng, Z.; Zhu, J. Gut Microbiota of Freshwater Gastropod (Bellamya aeruginosa) Assist the Adaptation of Host to Toxic Cyanobacterial Stress. Toxins 2023, 15, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040252
Liu H, Yang X, Yang W, Zheng Z, Zhu J. Gut Microbiota of Freshwater Gastropod (Bellamya aeruginosa) Assist the Adaptation of Host to Toxic Cyanobacterial Stress. Toxins. 2023; 15(4):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040252
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongfang, Xianming Yang, Wen Yang, Zhongming Zheng, and Jinyong Zhu. 2023. "Gut Microbiota of Freshwater Gastropod (Bellamya aeruginosa) Assist the Adaptation of Host to Toxic Cyanobacterial Stress" Toxins 15, no. 4: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040252
APA StyleLiu, H., Yang, X., Yang, W., Zheng, Z., & Zhu, J. (2023). Gut Microbiota of Freshwater Gastropod (Bellamya aeruginosa) Assist the Adaptation of Host to Toxic Cyanobacterial Stress. Toxins, 15(4), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040252





