Age and Sex as Determinants of Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity in a Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
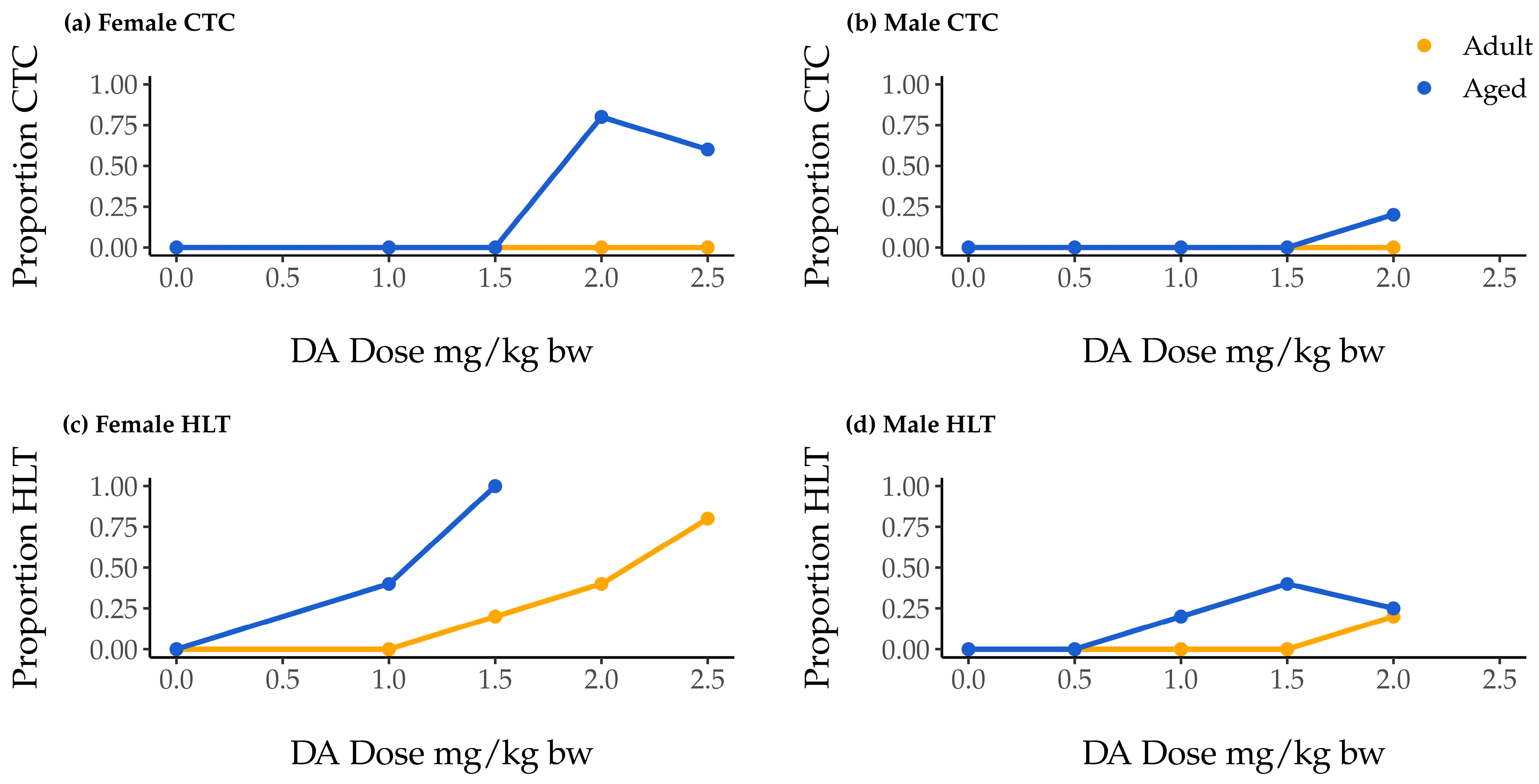
2.1. Associations of Dose, Age, and Sex with Clonic–Tonic Convulsion Risk
2.2. Association of Dose, Age, and Sex with Hindlimb Tremor Risk
2.3. Association of Dose and Age with Mean and Maximum Seizure Scores
2.4. Association of Dose and Age with Concentrations of DA in Tissues
2.4.1. Concentrations of DA in Female Mouse Tissues 90 Min Post Exposure
2.4.2. Concentrations of DA in Male Mouse Tissues 90 Min Post Exposure
2.4.3. Concentrations of DA in the Cortices of Mice Euthanized Early for CTCs
3. Discussion
3.1. Dose-Dependent Acute Domoic Acid Neurotoxicity
3.2. Age-Associated Susceptibility to Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity
3.3. Sex-Associated Susceptibility to Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity
3.4. Conclusions and Implications for Human Health
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Test Animal Care
4.3. Domoic Acid Dosing
4.4. Real-Time Observations and Video Recording
4.5. Tissue Collection and Quantification of Domoic Acid
4.6. Video Recordings Post Exposure
4.7. Statistical Analysis of Behavioral Endpoints
4.7.1. Statistical Analysis of Binary Behavioral Endpoints: Clonic–Tonic Convulsion and Hindlimb Tremor Occurrence
4.7.2. Statistical Analysis of Continuous Behavioral Endpoints: Mean and Maximum Seizure Score
4.8. Statistical Analysis of Tissue Domoic Acid Concentrations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zabaglo, K.; Chrapusta, E.; Bober, B.; Kaminski, A.; Adamski, M.; Bialczyk, J. Environmental Roles and Biological Activity of Domoic Acid: A Review. Algal Res. 2016, 13, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, O.M. Domoic Acid Toxicologic Pathology: A Review. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 180–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.S.; Hubbard, K.A.; Lundholm, N.; Montresor, M.; Leaw, C.P. Pseudo-Nitzschia, Nitzschia, and Domoic Acid: New Research since 2011. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.R.; Garrido, S. Domoic Acid Accumulation in the Sardine Sardina Pilchardus and Its Relationship to Pseudo-Nitzschia Diatom Ingestion. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 284, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, P.R.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Botelho, M.J.; de M Sampayo, M.A. A Potential Vector of Domoic Acid: The Swimming Crab Polybius Henslowii Leach (Decapoda-Brachyura). Toxicon 2003, 42, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; Powell, C.L.; Coale, S.L.; Busman, M.; Doucette, G.J.; Silver, M.W. Krill: A Potential Vector for Domoic Acid in Marine Food Webs. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 237, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perl, T.M.; Bédard, L.; Kosatsky, T.; Hockin, J.C.; Todd, E.C.D.; Remis, R.S. An Outbreak of Toxic Encephalopathy Caused by Eating Mussels Contaminated with Domoic Acid. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 1775–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroff, R.; Hendrix, A.; Shum, S.; Grant, K.S.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Burbacher, T.M. Public Health Risks Associated with Chronic, Low-Level Domoic Acid Exposure: A Review of the Evidence. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriss, B.E.; Marcinek, D.J.; Ayres, D.; Borchert, J.; Lefebvre, K.A. Acute and Chronic Dietary Exposure to Domoic Acid in Recreational Harvesters: A Survey of Shellfish Consumption Behavior. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Wu, H.; Che, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, J.; Guo, M.; Tan, Z. Residue Analysis and Assessment of the Risk of Dietary Exposure to Domoic Acid in Shellfish from the Coastal Areas of China. Toxins 2022, 14, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargu, S.; Goldstein, T.; Roberts, K.; Li, C.; Gulland, F. Pseudo-Nitzschia Blooms, Domoic Acid, and Related California Sea Lion Strandings in Monterey Bay, California. Mar. Mamm. Sci. 2012, 28, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellner, K.G.; Doucette, G.J.; Kirkpatrick, G.J. Harmful Algal Blooms: Causes, Impacts and Detection. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 383–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaignard, P.; Savouroux, S.; Liere, P.; Pianos, A.; Thérond, P.; Schumacher, M.; Slama, A.; Guennoun, R. Effect of Sex Differences on Brain Mitochondrial Function and Its Suppression by Ovariectomy and in Aged Mice. Endocrinology. 2015, 156, 2893–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, N.; Sharpe, R.A.; Barciela, R.; Nichols, G.; Davidson, K.; Berdalet, E.; Fleming, L.E. Marine Harmful Algal Blooms and Human Health: A Systematic Scoping Review. Harmful Algae 2020, 98, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, D.S.; Razak, A.; Crawford, N. Age-Related Changes in Tolerance to the Marine Algal Excitotoxin Domoic Acid. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, B.R.; Clarkson, A.N.; Sawant, P.M.; Kerr, D.S. Domoic Acid Preconditioning and Seizure Induction in Young and Aged Rats. Epilepsy Res. 2007, 76, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetmore, L.; Nance, D.M. Differential and Sex-Specific Effects of Kainic Acid and Domoic Acid Lesions in the Lateral Septal Area of Rats on Immune Function and Body Weight Regulation. Exp. Neurol. 1991, 113, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, A.W.; Rushton, S.P.; Rens, N.; Morris, C.M.; Blain, P.G.; Judge, S.J. Sex Differences in Effects of Low Level Domoic Acid Exposure. Neurotoxicology 2013, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcoitia, I.; Fernandez-Galaz, C.; Sierra, A.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Gonadal Hormones Affect Neuronal Vulnerability to Excitotoxin-Induced Degeneration. J. Neurocytol. 1999, 28, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, R.M.; Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Adams, N.G.; Bill, B.D.; Gulland, F.; Thomson, R.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Trainer, V.L. An Unprecedented Coastwide Toxic Algal Bloom Linked to Anomalous Ocean Conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10366–10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tryphonas, L.; Truelove, J.; Nera, E.; Iverson, F. Acute Neurotoxicity of Domoic Acid in the Rat. Toxicol. Pathol. 1990, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truelove, J.; Iverson, F. Serum Domoic Acid Clearance and Clinical Observations in the Cynomolgus Monkey and Sprague-Dawley Rat Following a Single IV Dose. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1994, 52, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, A.C.; Martinez, J.M.C.; Pose, R.B.; Queijo, A.A.; Posadas, N.A.; Lopez, L.M.B. Dose-Response and Histopathological Study, With Special Attention to the Hypophysis, of the Differential Effects of Domoic Acid on Rats and Mice. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2015, 78, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, C.A.M.; Hierlihy, S.L. Renal Clearance of Domoic Acid in the Rat. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frame, E.; Lefebvre, K.A. ELISA Methods for Domoic Acid Quantification in Multiple Marine Mammal Species and Sample Matrices (NMFS-NWFSC-122); US Department of Commerce, NOAA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Tasker, R.A.R.; Connell, B.J.; Strain, S.M. Pharmacology of Systemically Administered Domoic Acid in Mice. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1991, 69, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, A.; Pandey, M.; Murthy, N.S. Survival Analysis: Caveats and Pitfalls. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 1999, 25, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group | CTC LOAEL | HLT LOAEL |
|---|---|---|
| Adult females | N/A | 1.5 mg/kg DA |
| Aged females | 2.0 mg/kg DA | 1.0 mg/kg DA |
| Adult males | N/A | 2.0 mg/kg DA |
| Aged males | 2.0 mg/kg DA | 1.0 mg/kg DA |
| Score | State or Symptoms |
|---|---|
| 0 | No apparent effect |
| 1 | Pressed flat, little movement or stumbling walk |
| 2 | Hunched, head bobbing |
| 3 | Hindlimb tremors |
| 4 | Forelimb tremors and/or wet dog shakes |
| 5 | Clonic–tonic convulsions, rearing and falling, full-body shaking |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hendrix, A.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Bowers, E.K.; Stuppard, R.; Burbacher, T.; Marcinek, D.J. Age and Sex as Determinants of Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity in a Mouse Model. Toxins 2023, 15, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040259
Hendrix AM, Lefebvre KA, Bowers EK, Stuppard R, Burbacher T, Marcinek DJ. Age and Sex as Determinants of Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity in a Mouse Model. Toxins. 2023; 15(4):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040259
Chicago/Turabian StyleHendrix, Alicia M., Kathi A. Lefebvre, Emily K. Bowers, Rudolph Stuppard, Thomas Burbacher, and David J. Marcinek. 2023. "Age and Sex as Determinants of Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity in a Mouse Model" Toxins 15, no. 4: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040259
APA StyleHendrix, A. M., Lefebvre, K. A., Bowers, E. K., Stuppard, R., Burbacher, T., & Marcinek, D. J. (2023). Age and Sex as Determinants of Acute Domoic Acid Toxicity in a Mouse Model. Toxins, 15(4), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15040259







