An Extended Investigation of Unexpected Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) Survival and Ear Injury on a Transgenic Maize Hybrid Expressing Cry1A/Cry2A/Vip3A Toxins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Unexpected H. zea Larval Survival and Ear Injury in 2021 in Two Sentinel Plots in Louisiana
2.2. Field-Derived Populations of H. zea Collected from SNT-I and SNT-II Were Resistant to Cry1A.105 and Cry2Ab2, but Still Susceptible to Vip3Aa
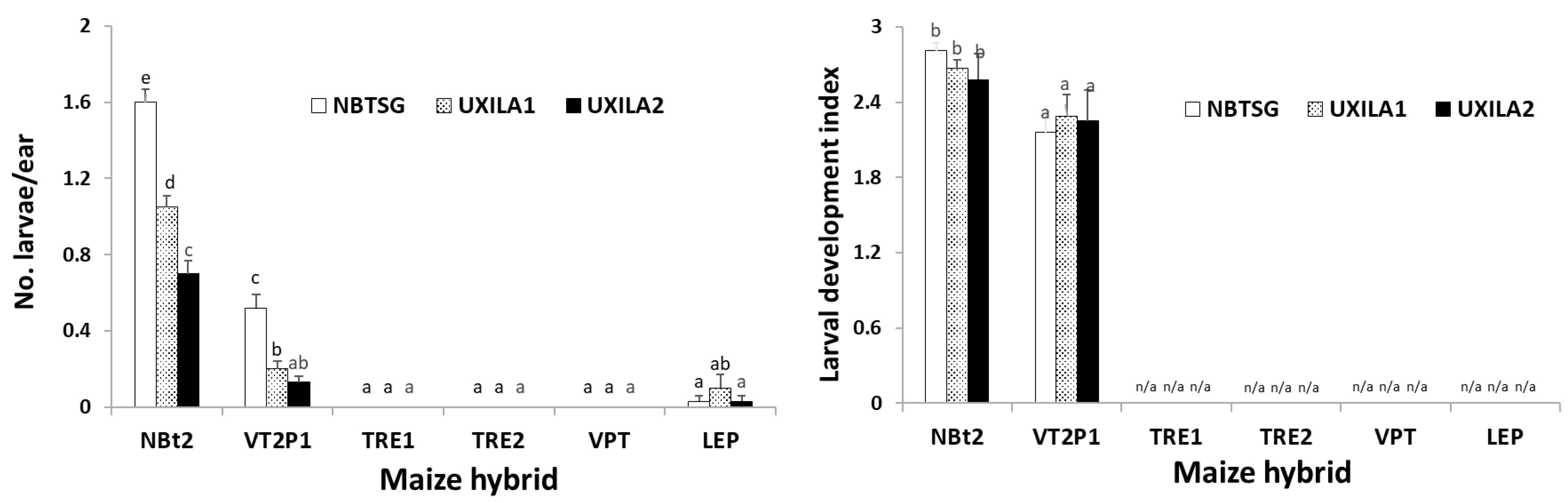
2.3. Maize Expressing Cry1A/Cry2A Was Partially Active against UXILA1 and UXILA2, While Larval Mortality on Ears Containing Cry and vip3A Transgenes Was Nearly 100%
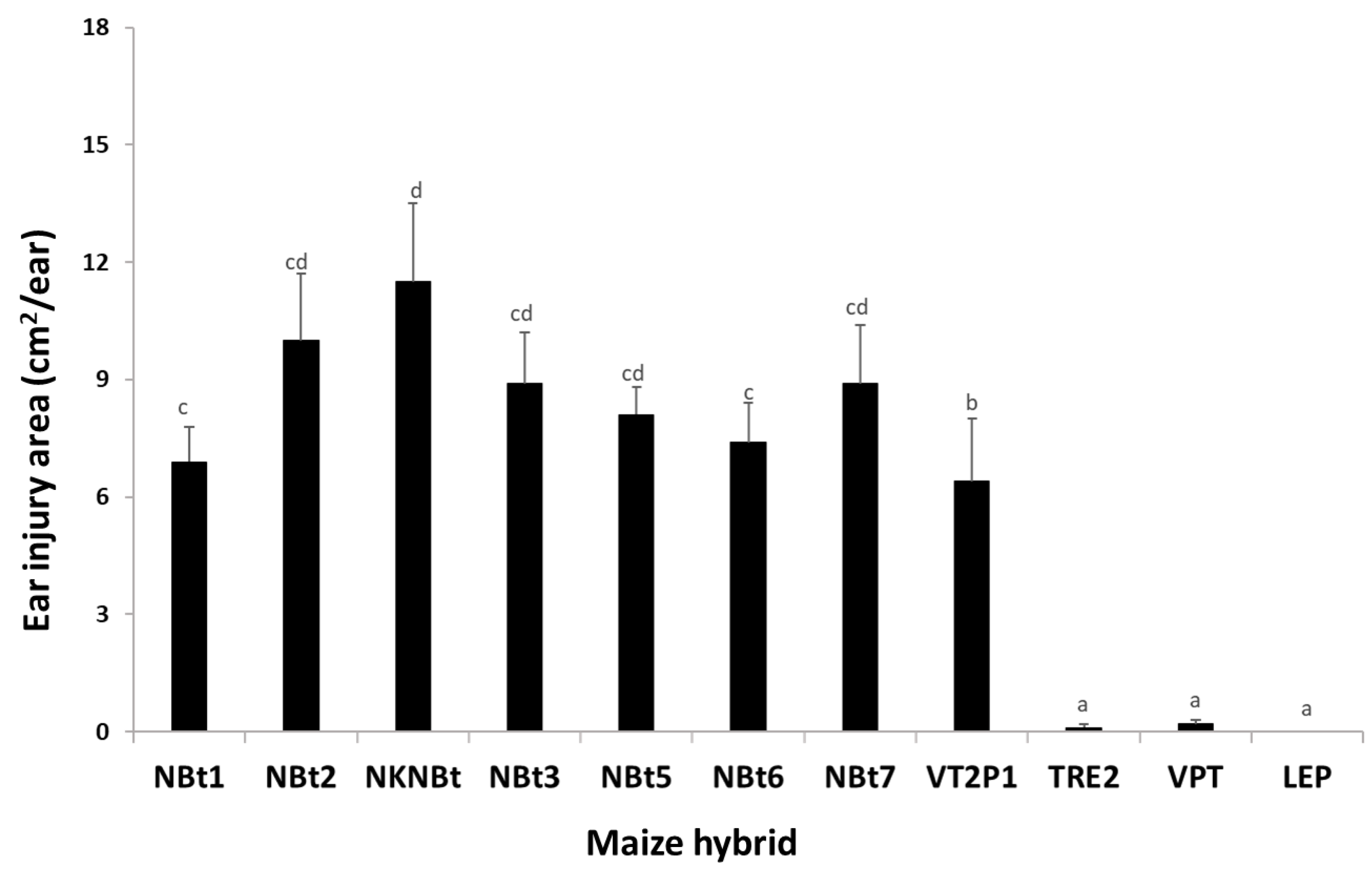
2.4. Maize Expressing Only Cry Toxins Failed to Control H. zea in Multiple Field Trials, While Hybrids Expressing Cry and Vip3Aa Toxins Were Still Highly Effective, including in the Area Where the UXIs Were Observed
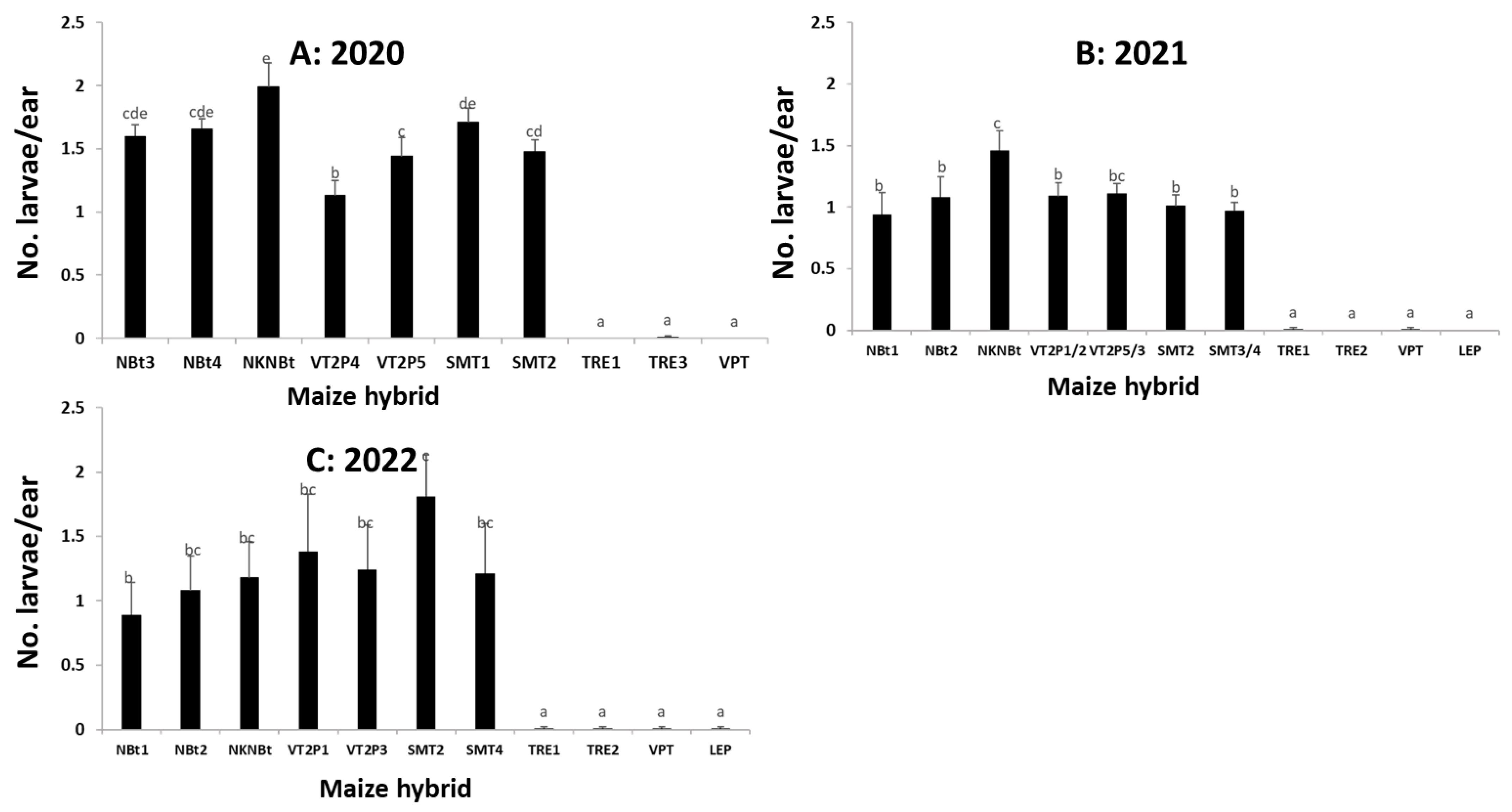
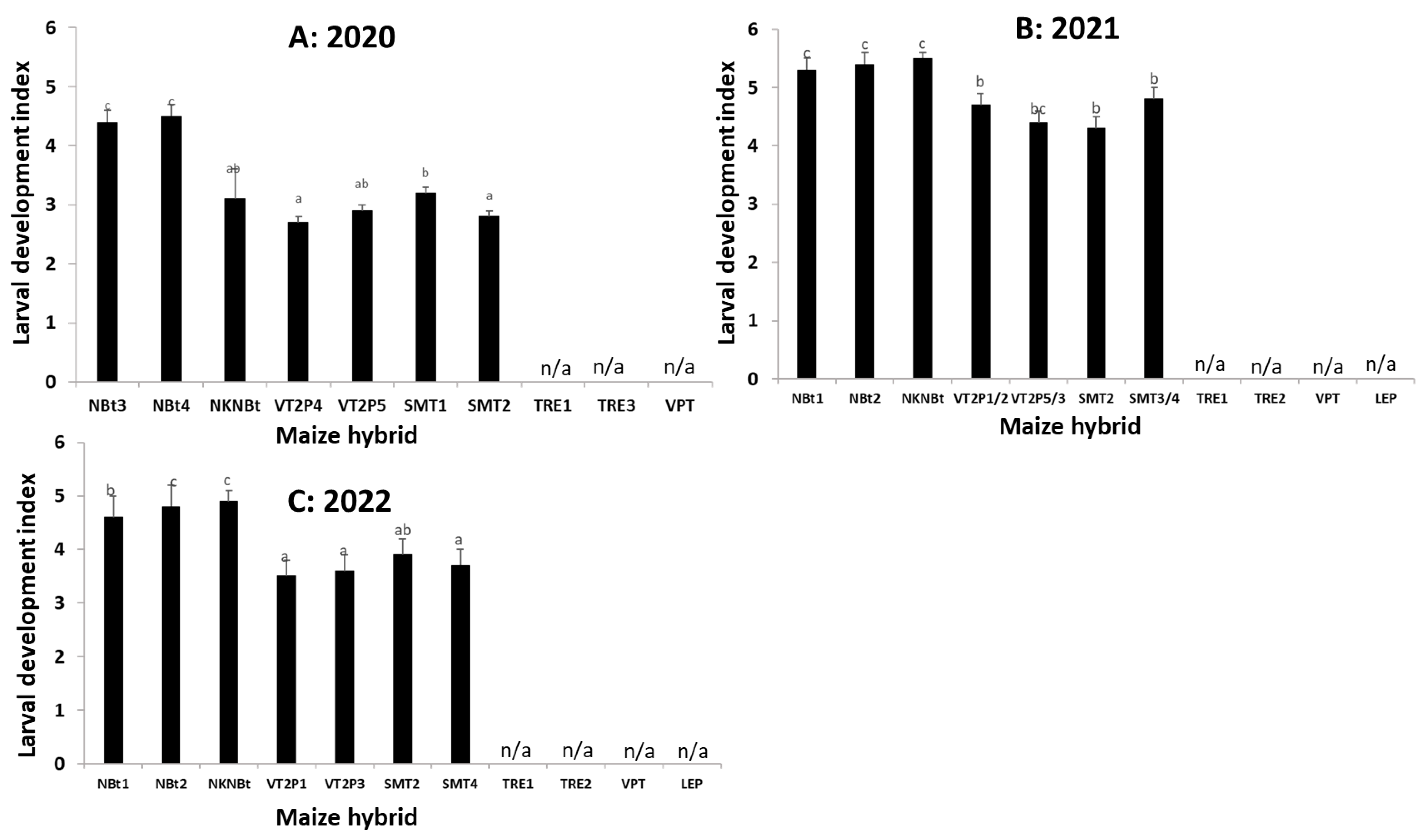
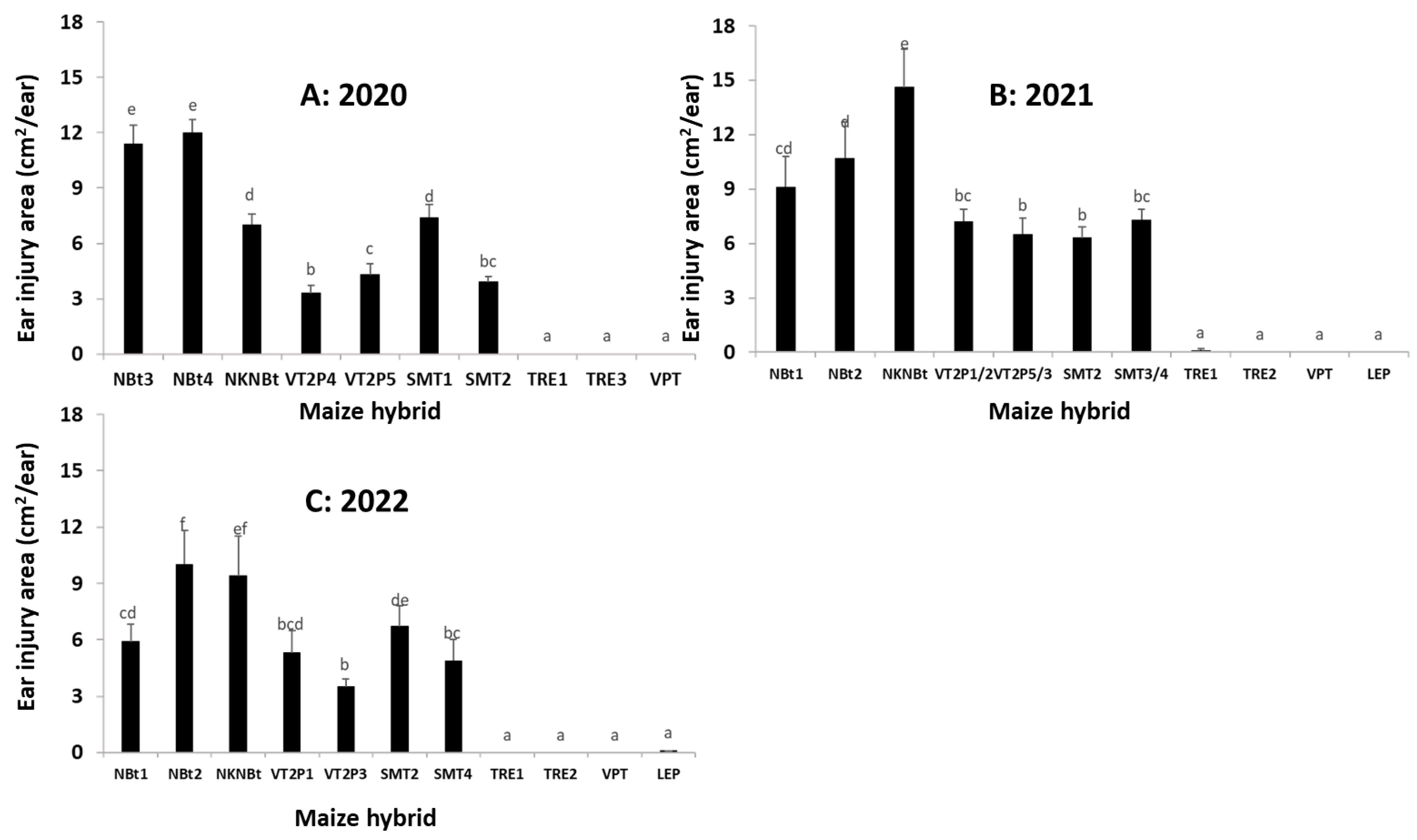
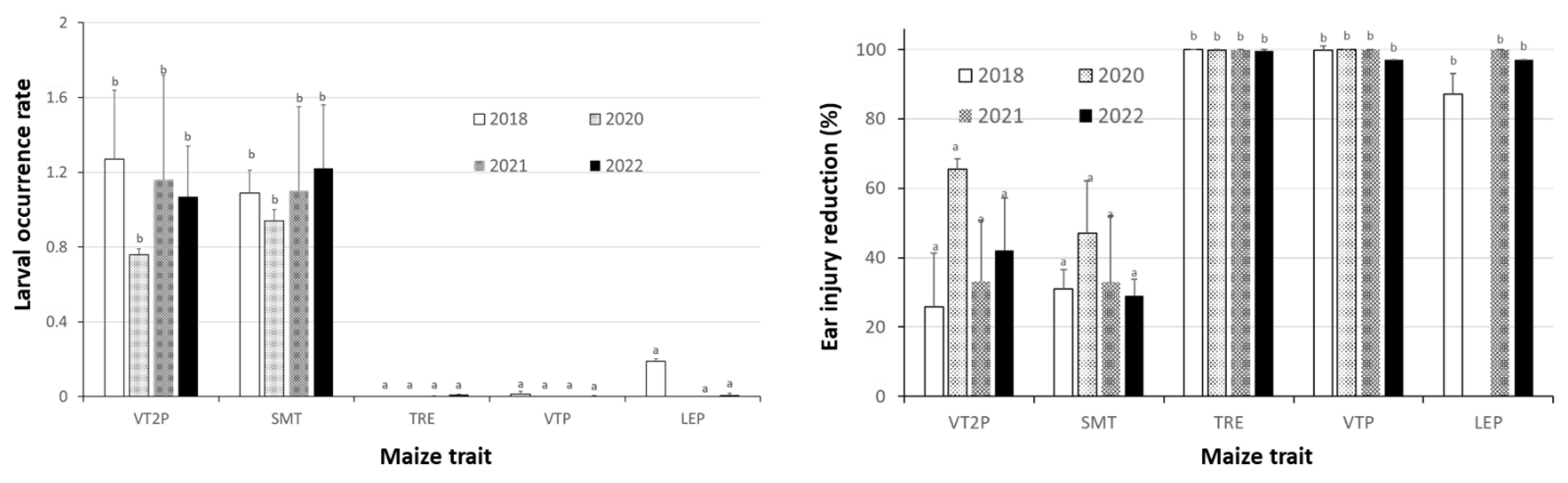
2.5. Relative to Non-Bt Maize, H. zea Occurrence Rate and Reduction on Ear Injury in Field Trials Were Similar from 2018 to 2022 for Each Bt Maize Trait
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Field Surveys of H. zea Occurrence and Ear Injury in Sentinel Plots for Bt Resistance Monitoring in LOUISIANA
5.2. Insect Collections and Establishment of Field-Derived H. zea Populations in the Laboratory
5.3. Sources of Bt Toxins for Diet-Overlay Bioassays
5.4. Diet-Overlay Bioassays to Determine the Susceptibility of H. zea Populations to Cry1A.105, Cry2Ab2, and Vip3Aa Toxins
5.5. Detached Ear Assays to Determine the Survival and Development of H. zea Populations on Non-Bt and Bt Maize Expressing Only Cry and/or Vip3Aa Toxins
5.6. Field Trials to Monitor the Occurrence of H. zea and Ear Injury on Common Bt Maize Traits
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dively, G.P.; Venugopal, P.D.; Finkenbinder, C. Field-evolved resistance in corn earworm to Cry proteins expressed by transgenic sweet corn. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisig, D.D.; Huseth, A.S.; Bacheler, J.S.; Aghaee, M.A.; Braswell, L.; Burrack, H.J.; Flanders, K.; Greene, J.K.; Herbert, D.A.; Jacobson, A. Long-term empirical and observational evidence of practical Helicoverpa zea resistance to cotton with pyramided Bt toxins. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbo, T.R.; Reay-Jones, F.P.F.; Reisig, D.D.; Greene, J.K. Susceptibility of corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Cry1A.105 and Cry2Ab2 in North and South Carolina. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1845–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Guo, J.; Brown, S.; Head, G.P.; Price, P.A.; Paula-Moraes, S.; Ni, X.; Dimase, M.; Huang, F. Field-evolved resistance of Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) to transgenic maize expressing pyramided Cry1A. 105/Cry2Ab2 proteins in northeast Louisiana, the United States. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 163, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dively, G.; Kuhar, T.; Taylor, S.; Doughty, H.; Holmstrom, K.; Gilrein, D.; Nault, B.; Ingerson-Mahar, J.; Whalen, J.; Reisig, D.; et al. Sweet corn sentinel monitoring for lepidopteran field-evolved resistance to Bt toxins. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Lin, S.; Dimase, M.; Niu, Y.; Brown, S.; Head, G.P.; Price, P.A.; Reay-Jones, F.P.F.; Cook, D.; Reisig, D.; et al. Extended investigation of the field-evolved resistance of the corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A.105 and Cry2Ab2 proteins in the southeastern United States. J. Invertebr. Path. 2021, 183, 107560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-González, J.C.; Kerns, D.L.; Yang, F. Resistance Allele Frequency of Helicoverpa zea to Vip3Aa Bacillus thuringiensis Protein in the Southeastern US. Insects 2023, 14, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiFonzo, C.; Porter, P. The Handy Bt Trait Table for U.S. Corn Production. 2023. Available online: https://www.texasinsects.org/uploads/4/9/3/0/49304017/bttraittable_feb_2023.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Estruch, J.J.; Warren, G.W.; Mullins, M.A.; Nye, G.J.; Craig, J.A.; Koziel, M.G. Vip3A, a novel Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein with a wide spectrum of activities against lepidopteran insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5389–5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Walters, F.S.; Hart, H.; Palekar, N.; Chen, J.S. The mode of action of the Bacillus thuringiensis vegetative insecticidal protein Vip3A differs from that of Cry1Ab δ-endotoxin. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 4648–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, R.W. A review of Vip3A mode of action and effects on Bt Cry protein-resistant colonies of Lepidopteran larvae. Southwest Entomol. 2010, 35, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasupramaniam, S.; Moar, W.J.; Ruschke, L.G.; Osborn, J.A.; Jiang, C.; Sebaugh, J.L.; Brown, G.R.; Shappley, Z.W.; Oppenhuizen, M.E.; Mullins, J.W.; et al. Toxicity and characterization of cotton expressing Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab2 proteins for control of lepidopteran pests. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vélez, A.M.; Spencer, T.A.; Alves, A.P.; Moellenbeck, D.; Meagher, R.L.; Chirakkal, H.; Siegfried, B.D. Inheritance of Cry1F resistance, cross-resistance and frequency of resistant alleles in Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2013, 103, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, D.; Salmeron, E.; Horikoshi, R.J.; Bernardi, O.; Dourado, P.M.; Carvalho, R.A.; Martinelli, S.; Head, G.P.; Omoto, C. Cross-resistance between Cry1 proteins in fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda) may affect the durability of current pyramided Bt maize hybrids in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Amaya, O.F.; Rodrigues, J.V.; Souza, T.C.; Tavares, C.S.; Campos, S.O.; Guedes, R.N.; Pereira, E.J. Resistance to dual-gene Bt maize in Spodoptera frugiperda: Selection, inheritance, and cross-resistance to other transgenic events. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Oyediran, I.; Yu, W.; Lin, S.; Dimase, M.; Brown, S.; Reay-Jones, F.P.F.; Cook, D.; Reisig, D.; Thrash, B.; et al. Populations of Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) in the southeastern United States are commonly resistant to Cry1Ab, but still susceptible to Vip3Aa20 expressed in MIR 162 corn. Toxins 2021, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; González, J.C.; Williams, J.; Cook, D.C.; Gilreath, R.T.; Kerns, D.L. Occurrence and ear damage of Helicoverpa zea on transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis maize in the field in Texas, US and its susceptibility to Vip3A protein. Toxins 2019, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dively, G.P.; Kuhar, T.P.; Taylor, S.V.; Doughty, H.; Holmstrom, K.; Gilrein, D.O.; Nault, B.A.; Ingerson-Mahar, J.; Huseth, A.; Reisig, D.; et al. Extended sentinel monitoring of Helicoverpa zea resistance to Cry and Vip3Aa toxins in Bt sweet corn: Assessing changes in phenotypic and allele frequencies of resistance. Insect 2023, 14, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay-Jones, F.P.F. Pest status and management of corn earworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in field corn in the United States. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2019, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US-EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). White Paper on Resistance in Lepidopteran Pests of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Plant Incorporated Protectants in the United States. 2018. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2018-07/documents/position_paper_07132018.pdf (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Yang, F.; González, J.C.S.; Little, N.; Reisig, D.; Payne, G.; Dos Santos, R.F.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Kurtz, R.; Kerns, D.L. First documentation of major Vip3Aa resistance alleles in field populations of Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Texas, USA. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US-EPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). EPA’s Response to Comments Received on the 9 September 2020 Draft Proposal to Address Resistance Risks to Lepidopteran Pests of Corn and Cotton Containing the Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) Plant-Incorporated Protectant (PIP) and Revised Framework for Industry Negotiations. 2021. Available online: https://www.regulations.gov/document/EPA-HQ-OPP-2019-0682-0052 (accessed on 19 May 2023).
- Huang, F. Resistance of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (J. E. Smith), to transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1F corn in the Americas: Lessons and implications for Bt corn IRM in China. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 574–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabashnik, B.E.; Fabrick, J.A.; Carrière, Y. Global patterns of insect resistance to transgenic Bt crops: The first 25 years. J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 116, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Ghimire, M.N.; Leonard, B.R.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Head, G. Susceptibility of field populations of sugarcane borer from non-Bt and Bt maize plants to five individual Cry toxins. Ins. Sci. 2012, 19, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay-Jones, F.P.F.; Bessin, R.T.; Brewer, M.J.; Buntin, D.G.; Catchot, A.L.; Cook, D.R.; Flanders, K.L.; Kerns, D.L.; Porter, R.P.; Reisig, D.D.; et al. Impact of Lepidoptera (Crambidae, Noctuidae, and Pyralidae) pests on corn containing pyramided Bt traits and a blended refuge in the Southern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1859–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkness, E.C.; Dively, G.; Patton, T.; Morey, A.C.; Hutchison, W.D. Novel Vip3A Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) maize approaches high-dose efficacy against Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under field conditions. GM Crop. 2010, 1, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilcutt, C.F.; Tabashnik, B.E. Contamination of refuges by Bacillus thuringiensis toxin genes from transgenic maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 7526–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón-Calva, P.S.; Twyman, R.M.; Albajes, R.; Gatehouse, A.M.; Christou, P. The Impact of Environmental Stress on Bt Crop Performance. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trtikova, M.; Wikmark, O.G.; Zemp, N.; Widmer, A.; Hilbeck, A. Transgene Expression and Bt Protein Content in Transgenic Bt Maize (MON810) under Optimal and Stressful Environmental Conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, R.; Qin, Q.; Fu, J.; Liu, B. Expression of Bt Protein in Transgenic Bt Cotton Plants and Ecological Fitness of These Plants in Different Habitats. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacterial Pesticidal Protein Resource Center. 2023. Available online: https://camtech-bpp.ifas.ufl.edu/bestmatchfinder_database_sequence_run/ (accessed on 24 May 2023).
- Finney, D.J. Probit Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- SAS Institute. SAS/STAT User’s, 3rd ed.; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
| Maize Trait | Hybrid | Abb. in Figure | Bt Toxins for Lepidopteran Pest Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| NBt: Non-Bt maize | DKC 65-93 | NBt1 | Non-Bt maize hybrids genetically closely related to one or more Bt hybrids used in the study |
| DKC 67-70 | NBt2 | ||
| DKC 62-05 | NBt3 | ||
| DKC 68-24 | NBt4 | ||
| DKC 63-56 | NBt5 | ||
| DKC 66-94 | NBt6 | ||
| DKC 67-25 | NBt7 | ||
| DKC 67-25 | NBt8 | ||
| NK 1694-GT | NKNBt | ||
| VT2P: Genuity VT Double PRO® | DKC 67-72 | VT2P1 | Cry1A.105, Cry2Ab2 |
| DKC-67-44 | VT2P2 | ||
| DKC 65-95 | VT2P3 | ||
| DKC 70-27 | VT2P4 | ||
| DKC 66-18 | VT2P5 | ||
| SMT: Genuity SmartStax® | DKC 63-08 | SMT1 | Cry1A.105, Cry2Ab2, Cry1F |
| DKC 67-42 | SMT2 | ||
| DKC 62-08 | SMT3 | ||
| DKC 65-94 | SMT4 | ||
| TRE: Trecepta® | DKC 65-99 | TRE1 | Cry1A.105, Cry2Ab2, Cry1F, Vip3Aa20 |
| DKC 67-94 | TRE2 | ||
| DKC 67-99 | TRE3 | ||
| LEP: Optimum® AcreMax® Leptra™ | PI 1622 VYHR | LEP | Cry1Ab, Cry1F, Vip3Aa20 |
| VPT: Agrisure VipteraTM | NK 1694-3111 | VPT | Cry1Ab, Vip3Aa20 |
| Insect Population | No. Larvae Assayed | Slope ± SE | LC50 (95%CI) (µg/cm2) | χ2 | p-Value | Resistance/Susceptibility Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cry1A.105 | ||||||
| BZ | 1152 | 2.06 ± 0.20 | 0.014 (0.011, 0.016) | 20.7 | 0.1104 | - |
| NBTDL | 590 | n/a | >>10 (mortality: 12.5%) | n/a | n/a | 741 |
| NBTSG | 1134 | 0.98 ± 0.12 | 2.55 (1.80, 4.20) | 14.5 | 0.4131 | 232 |
| UXILA1 | 638 | 1.28 ± 0.30 | 3.82 (2.27, 7.36) | 16.2 | 0.0927 | 234 |
| UXILA2 | 1140 | 1.02 ± 0.24 | 1.87 (0.92, 3.78) | 64.0 | <0.0001 | 134 |
| Cry2Ab2 | ||||||
| BZ | 1148 | 2.31 ± 0.31 | 0.126 (0.091, 0.169) | 67.5 | <0.0001 | - |
| NBTDL | 589 | 2.67 ± 0.70 | 1.56 (0.71, 2.52) | 43.3 | <0.0001 | 12 |
| NBTSG | 1130 | 1.69 ± 0.20 | 0.990 (0.752, 1.35) | 28.5 | 0.0121 | 8 |
| UXILA1 | 631 | 1.65 ± 0.34 | 0.571 (0.267, 0.927) | 38.5 | 0.0004 | 5 |
| UXILA2 | 1139 | 0.94 ± 0.16 | 0.672 (0.359, 1.16) | 66.9 | <0.0001 | 5 |
| Vip3A | ||||||
| BZ-SS | 557 | 2.23 ± 0.22 | 0.451 (0.364, 0.559) | 11.5 | 0.8294 | - |
| NBTDL | 1084 | 2.72 ± 0.35 | 0.083 (0.065,0.105) | 46.4 | 0.0003 | −5.4 |
| NBTSG | 1067 | 1.42 ± 0.09 | 0.160 (0.133, 0.193) | 22.9 | 0.4066 | −2.8 |
| UXILA1 | 1072 | 1.26 ± 0.12 | 0.265 (0.189, 0.364) | 49.9 | 0.0006 | −1.7 |
| UXILA2 | 1139 | 1.65 ± 0.23 | 0.016 (0.011, 0.023) | 30.7 | 0.0062 | −28.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, F.; Niu, Y.; Silva, T.; Brown, S.; Towles, T.; Kerns, D.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L.; Head, G.P.; Carroll, M.; Walker, W.; et al. An Extended Investigation of Unexpected Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) Survival and Ear Injury on a Transgenic Maize Hybrid Expressing Cry1A/Cry2A/Vip3A Toxins. Toxins 2023, 15, 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070474
Huang F, Niu Y, Silva T, Brown S, Towles T, Kerns D, Jurat-Fuentes JL, Head GP, Carroll M, Walker W, et al. An Extended Investigation of Unexpected Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) Survival and Ear Injury on a Transgenic Maize Hybrid Expressing Cry1A/Cry2A/Vip3A Toxins. Toxins. 2023; 15(7):474. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070474
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Fangneng, Ying Niu, Tiago Silva, Sebe Brown, Tyler Towles, Dawson Kerns, Juan Luis Jurat-Fuentes, Graham P. Head, Matthew Carroll, Wade Walker, and et al. 2023. "An Extended Investigation of Unexpected Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) Survival and Ear Injury on a Transgenic Maize Hybrid Expressing Cry1A/Cry2A/Vip3A Toxins" Toxins 15, no. 7: 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070474
APA StyleHuang, F., Niu, Y., Silva, T., Brown, S., Towles, T., Kerns, D., Jurat-Fuentes, J. L., Head, G. P., Carroll, M., Walker, W., & Lin, S. (2023). An Extended Investigation of Unexpected Helicoverpa zea (Boddie) Survival and Ear Injury on a Transgenic Maize Hybrid Expressing Cry1A/Cry2A/Vip3A Toxins. Toxins, 15(7), 474. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070474






