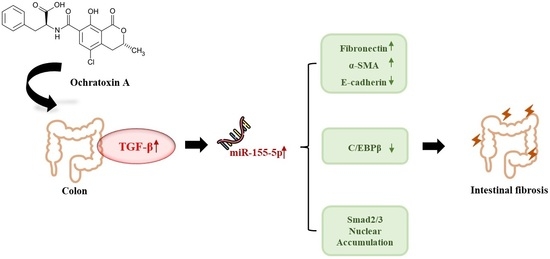
MiR-155-5p Elevated by Ochratoxin A Induces Intestinal Fibrosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition through TGF-β Regulated Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Histopathological Changes in Mice Colon Tissues after OTA Exposure
2.2. OTA Induced EMT and Fibrosis in Colon In Vivo and In Vitro
2.3. Differently Expressed miRNAs in Mice Colon Tissues after OTA Exposure
2.4. miR-155-5p Targets C/EBPβ under OTA Treatment
2.5. Regulation of EMT and Fibrosis by miR-155-5p under OTA Treatment
2.6. miR-155-5p Induces Fibrosis under OTA Treatment by Regulating TGF-β/Smad/2/3 Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animal Study
4.3. Histopathological Analysis
4.4. microRNA-Sequencing (miR-seq)
4.5. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.6. Cell Transfection
4.7. Isolation of Nuclear and Cytosolic Extracts
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabanes, F.J.; Bragulat, M.R.; Castella, G. Ochratoxin A producing species in the genus Penicillium. Toxins 2010, 2, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Liao, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Advances in Biodetoxification of Ochratoxin A-A Review of the Past Five Decades. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Han, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, S.; Wang, H.; Shen, X.L. Excessive ER-phagy contributes to ochratoxin A-induced apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 176, 113793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, X.; Shen, X.L. Central role of TRAP1 in the ameliorative effect of oleanolic acid on the mitochondrial-mediated and endoplasmic reticulum stress-excitated apoptosis induced by ochratoxin A. Toxicology 2021, 450, 152681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.A.; Snedeker, S.M. Ochratoxin a: Its cancer risk and potential for exposure. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2006, 9, 265–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, M.C.; Chae, S.A.; Yoo, H.J.; Lee, K.W. Ochratoxin A induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis through TGF-beta/Smad2/3 and Wnt1/beta-catenin signaling pathways in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 3329–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.A.; Pyo, M.C.; Yoo, H.J.; Lee, K.W. Ochratoxin a induces hepatic fibrosis through TGF-beta receptor I/Smad2/3 signaling pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 2084–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Pyo, M.C.; Ryu, D.; Lee, K.W. Ochratoxin A-Induced Hepatotoxicity through Phase I and Phase II Reactions Regulated by AhR in Liver Cells. Toxins 2019, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speca, S.; Giusti, I.; Rieder, F.; Latella, G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of intestinal fibrosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 3635–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zhou, H.; Guan, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.J. IL-17A Promotes Initiation and Development of Intestinal Fibrosis Through EMT. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2898–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, G.; Li, N. MicroRNAs, intestinal inflammatory and tumor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.Y.; Chang, D.C.; Lin, S.L. The microRNA (miRNA): Overview of the RNA genes that modulate gene function. Mol. Biotechnol. 2008, 38, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan, S. Posttranscriptional upregulation by microRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2012, 3, 311–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.Q.; Maulud, S.Q.; Dhawan, M.; Priyanka; Choudhary, O.P.; Jalal, P.J.; Ali, R.K.; Tayib, G.A.; Hasan, D.A. MicroRNAs in the development of potential therapeutic targets against COVID-19: A narrative review. J. Infect. Public Health 2022, 15, 788–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Komers, R.; Carew, R.; Winbanks, C.E.; Xu, B.; Herman-Edelstein, M.; Koh, P.; Thomas, M.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.; Gregorevic, P.; et al. Suppression of microRNA-29 expression by TGF-beta1 promotes collagen expression and renal fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Nijhuis, A.; Mehta, S.; Kumagai, T.; Feakins, R.; Lindsay, J.O.; Silver, A. Intestinal fibrosis in Crohn’s disease: Role of microRNAs as fibrogenic modulators, serum biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2015, 21, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, S. MicroRNAs in fibrosis: Opportunities and challenges. Arthritis. Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.; Berg, T.; Kurzejamska, E.; Pang, M.F.; Tabor, V.; Jansson, M.; Roswall, P.; Pietras, K.; Sund, M.; Religa, P.; et al. MiR-155-mediated loss of C/EBPbeta shifts the TGF-beta response from growth inhibition to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5614–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Tang, Y.; Chen, C.; Jing, R.; Liu, T. miR-155-5p Implicates in the Pathogenesis of Renal Fibrosis via Targeting SOCS1 and SOCS6. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 6263921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.A.; Rhee, K.H.; Yoo, H.J.; Pyo, M.C.; Lee, K.W. Ochratoxin A induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and fibrosis in the kidney via the HIF-1alpha/miR-155-5p link. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Chen, Y.; He, T.L.; Wang, C.; Guo, S.W.; Hu, H.; Ni, C.M.; Jin, G.; Zhang, Y.J. Menin Coordinates C/EBPbeta-Mediated TGF-beta Signaling for Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Growth Inhibition in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, M.; Mahfoud, R.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Fantini, J. The mycotoxin ochratoxin A alters intestinal barrier and absorption functions but has no effect on chloride secretion. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 176, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaaf, G.J.; Nijmeijer, S.M.; Maas, R.F.; Roestenberg, P.; de Groene, E.M.; Fink-Gremmels, J. The role of oxidative stress in the ochratoxin A-mediated toxicity in proximal tubular cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1588, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.Z.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.Y.; He, X.Y.; Dweep, H.; Guo, M.Z.; Cheng, W.H.; Xu, W.T.; Luo, Y.B.; Gretz, N.; et al. Ochratoxin A induced early hepatotoxicity: New mechanistic insights from microRNA, mRNA and proteomic profiling studies. Sci. Rep. UK 2014, 4, 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhai, S.; Jiang, X.; Meca, G.; Wang, S.; et al. Melatonin alleviates Ochratoxin A-induced liver inflammation involved intestinal microbiota homeostasis and microbiota-independent manner. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Pyo, M.C.; Lee, K.W. Combined effects of cadmium and ochratoxin A on intestinal barrier dysfunction in human Caco-2 cells and pig small intestinal epithelial cells. Mycotoxin. Res. 2022, 38, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, D.; Yao, B.; Yang, S.; Li, P.; Long, M. Astaxanthin Alleviates Ochratoxin A-Induced Cecum Injury and Inflammation in Mice by Regulating the Diversity of Cecal Microbiota and TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 8894491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibi, D.; Kijima, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Jin, M.; Sugita-Konishi, Y.; Yanai, T.; Nishikawa, A.; Umemura, T. Effects of p53 knockout on ochratoxin A-induced genotoxicity in p53-deficient gpt delta mice. Toxicology 2013, 304, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, D.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nebbia, C.S.; Nielsen, E.; et al. Risk assessment of ochratoxin A in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, M.C.; Choi, I.G.; Lee, K.W. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the AhR, Smad2/3, and HIF-1alpha Pathways as the Mechanism of Ochratoxin A Toxicity in Kidney Cells. Toxins 2021, 13, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N. Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively. Toxins 2017, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warensjo Lemming, E.; Montano Montes, A.; Schmidt, J.; Cramer, B.; Humpf, H.U.; Moraeus, L.; Olsen, M. Mycotoxins in blood and urine of Swedish adolescents-possible associations to food intake and other background characteristics. Mycotoxin. Res. 2020, 36, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.H.; Chen, D.Q.; Wang, Y.N.; Feng, Y.L.; Cao, G.; Vaziri, N.D.; Zhao, Y.Y. New insights into TGF-beta/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 292, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Yuan, H.; Xu, Z.G.; Lanting, L.; Li, S.L.; Wang, M.; Hu, M.C.; Reddy, M.A.; Natarajan, R. Role of the Akt/FoxO3a pathway in TGF-beta1-mediated mesangial cell dysfunction: A novel mechanism related to diabetic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 3325–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Pu, L.; Zhuang, Z. miR-155-5p/FOXO3a promotes pulmonary fibrosis in rats by mediating NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2022, 45, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Chen, J.; Qin, J.; Chen, R.; Yi, Z. TGF-beta-induced alpha-SMA expression is mediated by C/EBPbeta acetylation in human alveolar epithelial cells. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, J.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wei, Q.; Ye, D.; Rong, X.; Guo, J. CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Proteins in Fibrosis: Complex Roles Beyond Conventional Understanding. Research 2022, 2022, 9891689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.Y.; Chan, M.K.; Li, J.S.; Chan, A.S.; Tang, P.C.; Leung, K.T.; To, K.F.; Lan, H.Y.; Tang, P.M. TGF-beta Signaling: From Tissue Fibrosis to Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, E.H. The Molecular Mechanism of Transforming Growth Factor-beta Signaling for Intestinal Fibrosis: A Mini-Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beres, N.J.; Kiss, Z.; Sztupinszki, Z.; Lendvai, G.; Arato, A.; Sziksz, E.; Vannay, A.; Szabo, A.J.; Muller, K.E.; Cseh, A.; et al. Altered mucosal expression of microRNAs in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassirpour, R.; Mathur, S.; Gosink, M.M.; Li, Y.; Shoieb, A.M.; Wood, J.; O’Neil, S.P.; Homer, B.L.; Whiteley, L.O. Identification of tubular injury microRNA biomarkers in urine: Comparison of next-generation sequencing and qPCR-based profiling platforms. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Pyo, M.C.; Jeon, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.W. Improved physicochemical properties and hepatic protection of Maillard reaction products derived from fish protein hydrolysates and ribose. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghirova, S.; Hughes, B.G.; Hendzel, M.J.; Schulz, R. Sequential fractionation and isolation of subcellular proteins from tissue or cultured cells. MethodsX 2015, 2, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rhee, K.H.; Yang, S.A.; Pyo, M.C.; Lim, J.-M.; Lee, K.-W. MiR-155-5p Elevated by Ochratoxin A Induces Intestinal Fibrosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition through TGF-β Regulated Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins 2023, 15, 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070473
Rhee KH, Yang SA, Pyo MC, Lim J-M, Lee K-W. MiR-155-5p Elevated by Ochratoxin A Induces Intestinal Fibrosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition through TGF-β Regulated Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins. 2023; 15(7):473. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070473
Chicago/Turabian StyleRhee, Kyu Hyun, Seon Ah Yang, Min Cheol Pyo, Jae-Min Lim, and Kwang-Won Lee. 2023. "MiR-155-5p Elevated by Ochratoxin A Induces Intestinal Fibrosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition through TGF-β Regulated Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo" Toxins 15, no. 7: 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070473
APA StyleRhee, K. H., Yang, S. A., Pyo, M. C., Lim, J.-M., & Lee, K.-W. (2023). MiR-155-5p Elevated by Ochratoxin A Induces Intestinal Fibrosis and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition through TGF-β Regulated Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins, 15(7), 473. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15070473