Persistence of Microcystin in Three Agricultural Ponds in Georgia, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Data Summary
2.1.1. Weather Data
2.1.2. Microcystin Concentrations
2.1.3. Water Quality Measurements
2.2. Spatial and Temporal Stability of Microcystin and Wind Data
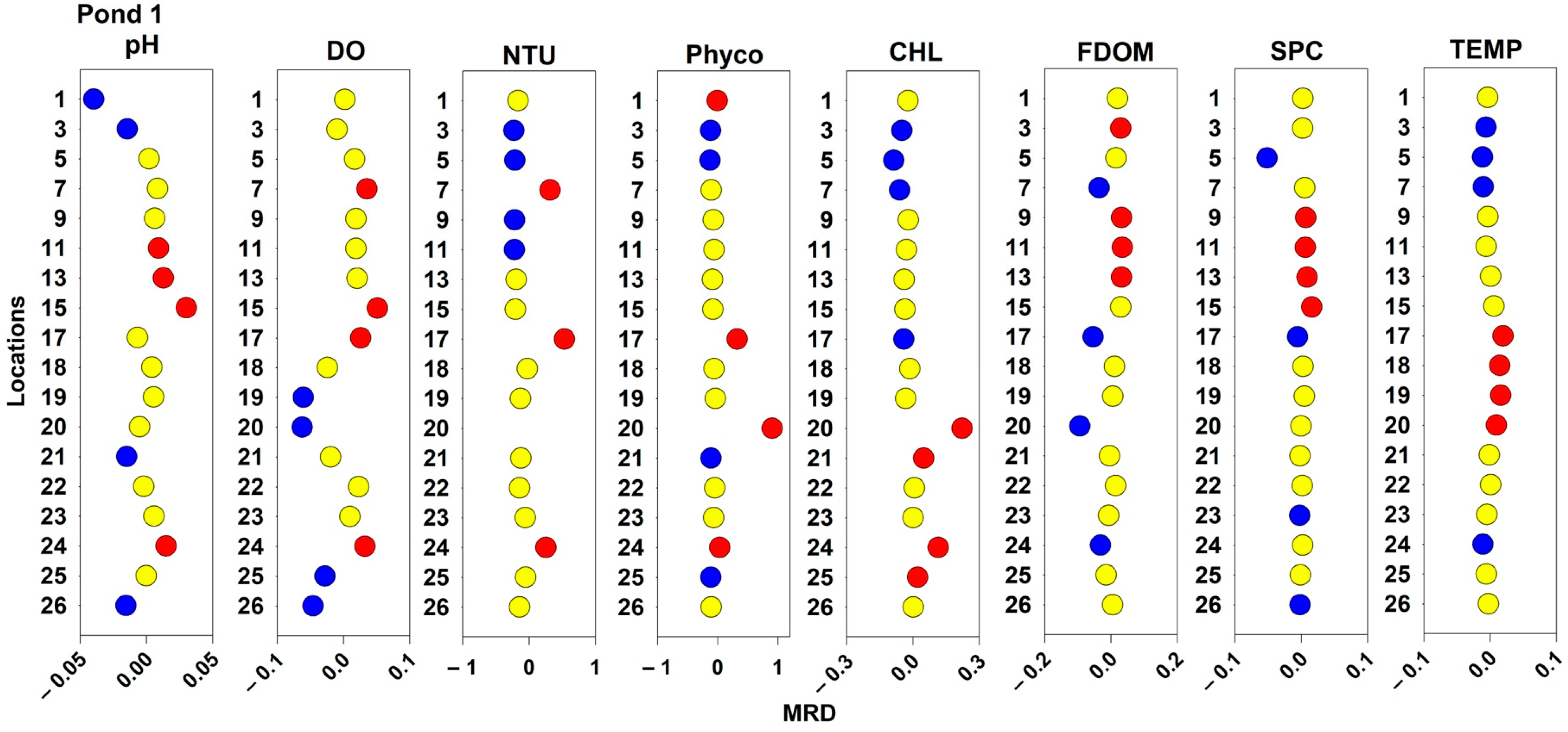
2.2.1. Pond 1 Mean Relative Differences and Wind Data
2.2.2. Pond 2 Mean Relative Differences and Wind Data
2.2.3. Pond 3 Mean Relative Differences and Wind Data
2.3. Spatial and Temporal Stability of Water Quality Parameters
2.4. Microcystin and Water Quality Mean Relative Difference Correlations
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sites; Field and Laboratory Analyses
4.2. Weather Conditions
4.3. Software and Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms Like It Hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrone, B.L.; Banerjee, S.; Talapatra, A.; Gonzalez-Esquer, C.R.; Pilania, G. Toward a Predictive Understanding of Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms through AI Integration of Physical, Chemical, and Biological Data. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Madamwar, D.; Incharoensakdi, A. Bloom Dynamics of Cyanobacteria and Their Toxins: Environmental Health Impacts and Mitigation Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaas, H.E.; Paerl, H.W. Toxic Cyanobacteria: A Growing Threat to Water and Air Quality. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haida, M.; El Khalloufi, F.; Mugani, R.; Essadki, Y.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Oudra, B. Microcystin Contamination in Irrigation Water and Health Risk. Toxins 2024, 16, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaram, R.; Newton, A.R.; Chafin, J. Microcystin Contamination and Toxicity: Implications for Agriculture and Public Health. Toxins 2022, 14, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.; Seawright, A.A.; Shaw, G.R. Cyanobacterial Poisoning in Livestock, Wild Mammals and Birds—An Overview. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2008, 619, 613–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, M.; Batool, F.; Khan, S.S.; Khokhar, I.; Qamar, M.K.; Yasir, C. Effects of Microcystins Toxins Contaminated Drinking Water on Hepatic Problems in Animals (Cows and Buffalos) and Toxins Removal Chemical Method. Buffalo Bull. 2017, 36, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Dreher, T.W.; Collart, L.P.; Mueller, R.S.; Halsey, K.H.; Bildfell, R.J.; Schreder, P.; Sobhakumari, A.; Ferry, R. Anabaena/Dolichospermum as the Source of Lethal Microcystin Levels Responsible for a Large Cattle Toxicosis Event. Toxicon X 2019, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwimmer, M.; Schwimmer, D. Algae, Man and Environment. In Medical Aspects of Phycology; Syracuse University Press: Syracuse, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 279–358. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, R. Acute Animal and Human Poisonings from Cyanotoxin Exposure—A Review of the Literature. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esterhuizen-Londt, M.; Pflugmacher, S. Chapter 37—Microcystins as Environmental and Human Health Hazards. In Handbook of Algal Science, Technology and Medicine; Konur, O., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 591–604. ISBN 978-0-12-818305-2. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Wang, W.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Teng, J.; Yan, H.; Liu, X. Microcystins in Water: Detection, Microbial Degradation Strategies, and Mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Introduction: Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management, 2nd ed.; Chorus, I., Welker, M., Eds.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–11. ISBN 978-1-00-308144-9. [Google Scholar]
- Oudra, B.; Loudiki, M.; Vasconcelos, V.; Sabour, B.; Sbiyyaa, B.; Oufdou, K.; Mezrioui, N. Detection and Quantification of Microcystins from Cyanobacteria Strains Isolated from Reservoirs and Ponds in Morocco. Environ. Toxicol. 2002, 17, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collart, L.; Jiang, D.; Halsey, K.H. The Volatilome Reveals Microcystin Concentration, Microbial Composition, and Oxidative Stress in a Critical Oregon Freshwater Lake. mSystems 2023, 8, e00379-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Luo, L.; Liao, Q.; Yuan, L.; Wu, N. Seasonal and Spatial Variations of Microcystins in Poyang Lake, the Largest Freshwater Lake in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 6300–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkilen, H.; Fastner, J.; Bartram, J. Fieldwork: Site inspection and sampling. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management; Chorus, I., Bartram, J., Eds.; E & FN Spon: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 317–333. ISBN 978-0-419-23930-7. [Google Scholar]
- Bertani, I.; Steger, C.E.; Obenour, D.R.; Fahnenstiel, G.L.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Johengen, T.H.; Sayers, M.J.; Shuchman, R.A.; Scavia, D. Tracking Cyanobacteria Blooms: Do Different Monitoring Approaches Tell the Same Story? Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wynne, T.T.; Stumpf, R.P. Spatial and Temporal Patterns in the Seasonal Distribution of Toxic Cyanobacteria in Western Lake Erie from 2002–2014. Toxins 2015, 7, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozumi, A.; Ostrovsky, I.; Sukenik, A.; Gildor, H. Turbulence Regulation of Microcystis Surface Scum Formation and Dispersion during a Cyanobacteria Bloom Event. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, J.D.; Westrick, J.A.; Reitz, L.A.; Bridgeman, T.B. Microcystin Congeners in Lake Erie Follow the Seasonal Pattern of Nitrogen Availability. Harmful Algae 2023, 127, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Xie, L.; Yao, L.; Su, X.; Cao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, Y. Seasonal Variation and Potential Risk Assessment of Microcystins in the Sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastepa, A.; Taranu, Z.E.; Kimpe, L.E.; Blais, J.M.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Zurawell, R.W.; Pick, F.R. Reconstructing a Long-Term Record of Microcystins from the Analysis of Lake Sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Shan, K.; Gao, H.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, X. Spatio-Temporal Distribution Patterns in Environmental Factors, Chlorophyll-a and Microcystins in a Large Shallow Lake, Lake Taihu, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5155–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA—National Agricultural Statistics Service—Statistics by State. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/statistics_by_state/index.php (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Mullen, J.D.; Yu, Y.; Hoogenboom, G. Estimating the Demand for Irrigation Water in a Humid Climate: A Case Study from the Southeastern United States. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Sommer, U.; Katsiapi, M.; Vardaka, E. Monitoring of Cyanobacteria for Water Quality: Doing the Necessary Right or Wrong? Mar. Freshw. Res. 2020, 71, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; da Silva, A.L.B.R.; Dunn, L.L. Factors Impacting the Prevalence of Foodborne Pathogens in Agricultural Water Sources in the Southeastern United States. Water 2020, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, J.B.; Fernandez, M.; Johnson, T.E.; Shabani, A.; Lee, S.S. Geographic Analysis of the Vulnerability of U.S. Lakes to Cyanobacterial Blooms under Future Climate. Earth Interact. 2023, 27, e230004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.J.; Mishra, D.R.; Wilde, S.B.; Kramer, E. Risks for Cyanobacterial Harmful Algal Blooms Due to Land Management and Climate Interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, J.A. Estimated Use of Water in Georgia for 2015 and Water-Use Trends, 1985–2015; U.S. Geological Survey: Liston, VA, USA, 2019.
- Haynie, R.; Morgan, J.; Bartelme, B.; Willis, B.; Rodgers, J.H.; Jones, L.; Wilde, S. Harmful Algal Blooms and Toxin Production in Georgia Ponds. In Proceedings of the 2013 Georgia Water Resources Conference, Athens, GA, USA, 10–11 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Z.A.; Mostafa, Y.; Alamri, S.; Hashem, M. Accumulation of Microcystin Toxin in Irrigation Water and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa) Forage Plant, and Assessing the Potential Risk to Animal Health. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palagama, D.S.W.; Baliu-Rodriguez, D.; Snyder, B.K.; Thornburg, J.A.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Isailovic, D. Identification and Quantification of Microcystins in Western Lake Erie during 2016 and 2017 Harmful Algal Blooms. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, S.L.; Brunner, S.L.; Klump, J.V.; Houghton, E.M.; Miller, T.R. Spatial Analysis of Toxic or Otherwise Bioactive Cyanobacterial Peptides in Green Bay, Lake Michigan. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.R.; Beversdorf, L.J.; Weirich, C.A.; Bartlett, S.L. Cyanobacterial Toxins of the Laurentian Great Lakes, Their Toxicological Effects, and Numerical Limits in Drinking Water. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.B.; Ridal, J.; Boyer, G.L. Taste and Odour and Cyanobacterial Toxins: Impairment, Prediction, and Management in the Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 65, 1779–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, K.; Fujioka, H.; Muranaka, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Katagami, Y.; Homma, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Tsujimura, S.; Kumagai, M.; Watanabe, M.F.; et al. Spatial Distribution and Temporal Variation of Microcystis Species Composition and Microcystin Concentration in Lake Biwa. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, D.G.F.; Dodds, W.K.; Loiselle, S.A. Factors Related to Water Quality and Thresholds for Microcystin Concentrations in Subtropical Brazilian Reservoirs. Inland Waters 2018, 8, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. National Lakes Assessment: A Collaborative Survey of the Nation’s Lakes; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; 118p.
- Jenkins, M.B.; Adams, M.P.; Endale, D.M.; Fisher, D.S.; Lowrance, R.; Newton, G.L.; Vellidis, G. Storm Flow Dynamics and Loads of Fecal Bacteria Associated with Ponds in Southern Piedmont and Coastal Plain Watersheds with Animal Agriculture. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 148, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Census of Agriculture. United States Summary and State Data; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; 758p.
- Loftin, K.A.; Clark, J.M.; Journey, C.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Van Metre, P.C.; Carlisle, D.; Bradley, P.M. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Microcystin Occurrence in Wadeable Streams in the Southeastern United States. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 2281–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Felices, B.; Aznar-Sánchez, J.A.; Velasco-Muñoz, J.F.; Piquer-Rodríguez, M. Contribution of Irrigation Ponds to the Sustainability of Agriculture. A Review of Worldwide Research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.E.; Stocker, M.D.; Wolny, J.L.; Hill, R.L.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Intraseasonal Variation of Phycocyanin Concentrations and Environmental Covariates in Two Agricultural Irrigation Ponds in Maryland, USA. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.E.; Wolny, J.L.; Stocker, M.D.; Hill, R.L.; Pachepsky, Y.A. Temporal Stability of Phytoplankton Functional Groups within Two Agricultural Irrigation Ponds in Maryland, USA. Front. Water 2021, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarewicz, J.C.; Boyer, G.L.; Lewis, T.W.; Guenther, W.; Atkinson, J.; Arnold, M. Spatial and Temporal Distribution of the Cyanotoxin Microcystin-LR in the Lake Ontario Ecosystem: Coastal Embayments, Rivers, Nearshore and Offshore, and Upland Lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 2009, 35, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Zheng, M.; Su, J.; Xi, B.; Wei, D.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Threshold of Chlorophyll-a in Lake Taihu Based on Microcystins. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 49327–49338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, V.; Kiker, G.A.; Campbell, K.L.; Williams, M.J.; Coleman, S.W. GPS Monitoring of Cattle Location Near Water Features in South Florida. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2009, 25, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero, M.J.; Grau-Campanario, P.; Mullan, S.; Held, S.D.E.; Stokes, J.E.; Lee, M.R.F.; Cardenas, L.M. Factors Affecting Site Use Preference of Grazing Cattle Studied from 2000 to 2020 through GPS Tracking: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crush, J.R.; Briggs, L.R.; Sprosen, J.M.; Nichols, S.N. Effect of Irrigation with Lake Water Containing Microcystins on Microcystin Content and Growth of Ryegrass, Clover, Rape, and Lettuce. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, S.D.; Poppenga, R.H. Toxicosis Due to Microcystin Hepatotoxins in Three Holstein Heifers. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1993, 5, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschner, B.; Galey, F.D.; Johnson, B.; Dickie, C.W.; Vondy, M.; Francis, T.; Holstege, D.M. Blue-Green Algae Toxicosis in Cattle. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1998, 213, 1605–1607, 1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbis, C.R.; Simons, J.A.; Mitchell, G.F.; Anderson, J.W.; McCauley, I. A Biochemical Profile for Predicting the Chronic Exposure of Sheep to Microscystis Aeruginosa, an Hepatotoxic Species of Blue-Green Alga. Res. Vet. Sci. 1994, 57, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengappa, M.M.; Pace, L.W.; McLaughlin, B.G. Blue-Green Algae (Anabaena spiroides) Toxicosis in Pigs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1989, 194, 1724–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.E.; Chislock, M.F.; Yang, Z.; Barros, M.U.G.; Roberts, J.F. Pond Bank Access as an Approach for Managing Toxic Cyanobacteria in Beef Cattle Pasture Drinking Water Ponds. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.E. The spatiotemporal variability of microcystin concentrations and cyanobacteria in two agricultural ponds in Georgia, USA. In Proceedings of the 12th Symposium on Harmful Algae, Portland, Maine, 27 October–1 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin, J.D.; Westrick, J.A.; Furr, E.; Birbeck, J.A.; Reitz, L.A.; Stanislawczyk, K.; Li, W.; Weber, P.K.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Davis, T.W.; et al. Quantification of Microcystin Production and Biodegradation Rates in the Western Basin of Lake Erie. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2022, 67, 1470–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, R.; Feng, G.; Xue, Z. Rapid Horizontal Accumulation and Bloom Formation of the Cyanobacterium Microcystis under Wind Stress. Hydrobiologia 2023, 850, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kong, F.; Chen, Y.; Qian, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xing, P. Horizontal Distribution and Transport Processes of Bloom-Forming Microcystis in a Large Shallow Lake (Taihu, China). Limnologica 2010, 40, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Rai, P.K.; Chau, R.; Ravi, A.K.; Neilan, B.A.; Asthana, R.K. Temporal Variations in Microcystin-Producing Cells and Microcystin Concentrations in Two Fresh Water Ponds. Water Res. 2015, 69, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, T.T.; Le, T.P.Q.; Dao, T.-S.; Pflugmacher, S.; Rochelle-Newall, E.; Hoang, T.K.; Vu, T.N.; Ho, C.T.; Dang, D.K. Seasonal Variation of Cyanobacteria and Microcystins in the Nui Coc Reservoir, Northern Vietnam. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koreivienė, J.; Anne, O.; Kasperovičienė, J.; Burškytė, V. Cyanotoxin Management and Human Health Risk Mitigation in Recreational Waters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4443–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francy, D.S.; Brady, A.M.G.; Ecker, C.D.; Graham, J.L.; Stelzer, E.A.; Struffolino, P.; Dwyer, D.F.; Loftin, K.A. Estimating Microcystin Levels at Recreational Sites in Western Lake Erie and Ohio. Harmful Algae 2016, 58, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Hao, A.; Iseri, Y.; Wang, S.; Kuba, T.; Zhang, Z.; Katayama, H. Occurrence and Distribution of Microcystins in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 838176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Kong, F.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z.; Shi, X.; Du, M. The Dynamics of Microcystis Genotypes and Microcystin Production and Associations with Environmental Factors during Blooms in Lake Chaohu, China. Toxins 2014, 6, 3238–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinang, S.C.; Reichwaldt, E.S.; Ghadouani, A. Spatial and Temporal Variability in the Relationship between Cyanobacterial Biomass and Microcystins. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 6379–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, S.H.; Gin, K.Y.-H. The Dynamics of Cyanobacteria and Microcystin Production in a Tropical Reservoir of Singapore. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, T.; Stevenson, R.J.; Zhu, Y. Environmental Factors Regulating Cyanobacteria Dominance and Microcystin Production in a Subtropical Lake within the Taihu Watershed, China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2012, 13, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Xue, Q.; Steinman, A.D.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, L. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Microcystin Variants and Relationships with Environmental Parameters in Lake Taihu, China. Toxins 2015, 7, 3224–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaver, J.R.; Manis, E.E.; Loftin, K.A.; Graham, J.L.; Pollard, A.I.; Mitchell, R.M. Land Use Patterns, Ecoregion, and Microcystin Relationships in U.S. Lakes and Reservoirs: A Preliminary Evaluation. Harmful Algae 2014, 36, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.A.; Borges, H.; Puddick, J.; Biessy, L.; Atalah, J.; Hawes, I.; Dietrich, D.R.; Hamilton, D.P. Contrasting Cyanobacterial Communities and Microcystin Concentrations in Summers with Extreme Weather Events: Insights into Potential Effects of Climate Change. Hydrobiologia 2017, 785, 71–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.A.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S.M.; Faber-Hammond, J.J. Environmental Influence on Cyanobacteria Abundance and Microcystin Toxin Production in a Shallow Temperate Lake. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zheng, H.; Pan, J.; Zhang, T.; Tang, S.; Lu, J.; Zhong, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Seasonal Dynamics of Photosynthetic Activity, Microcystis Genotypes and Microcystin Production in Lake Taihu, China. J. Great Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qin, J.; Zheng, L.; Liang, G. Factors Shaping the Pattern of Seasonal Variations of Microcystins in Lake Xingyun, a Subtropical Plateau Lake in China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 78, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; He, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. Spatial Distribution of Chlorophyll a and Its Relationship with the Environment during Summer in Lake Poyang: A Yangtze-Connected Lake. Hydrobiologia 2014, 732, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, Y.; Xie, P.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z.; Tao, M.; Qi, M.; Wu, L.; Guo, L. Factors Affecting Temporal and Spatial Variations of Microcystins in Gonghu Bay of Lake Taihu, with Potential Risk of Microcystin Contamination to Human Health. Sci. World J. 2010, 10, 348387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmful Algal Blooms Plan. Version 2.0. Available online: https://secoora.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/SECOORA-Harmful-Algal-Bloom-Plan-Version-2.0.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Ma, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Brookes, J.D.; Hall, N.S.; Shi, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. The Persistence of Cyanobacterial (Icrocystis Spp.) Blooms throughout Winter in Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Cai, Q.; He, F.; Huang, Y.; Tian, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, C.; Xiao, B. Flexibility of Microcystis Overwintering Strategy in Response to Winter Temperatures. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, O.; Nürnberg, G.; Horppila, J.; Haldna, M.; Niemistö, J. Redox-Related Release of Phosphorus from Sediments in Large and Shallow Lake Peipsi: Evidence from Sediment Studies and Long-Term Monitoring Data. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wu, X.; Rovelli, L.; Lorke, A. Dynamics of Microcystis Surface Scum Formation under Different Wind Conditions: The Role of Hydrodynamic Processes at the Air-Water Interface. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1370874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliland, J.M.; Black, A.W.; Durkee, J.D.; Murley, V.A. A Climatology of High-Wind Events for the Eastern United States. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shimizu, K.; Maseda, H.; Lu, Z.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Sugiura, N. Investigations into the Biodegradation of Microcystin-LR Mediated by the Biofilm in Wintertime from a Biological Treatment Facility in a Drinking-Water Treatment Plant. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 106, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezcano, M.Á.; Morón-López, J.; Agha, R.; López-Heras, I.; Nozal, L.; Quesada, A.; El-Shehawy, R. Presence or Absence of Mlr Genes and Nutrient Concentrations Co-Determine the Microcystin Biodegradation Efficiency of a Natural Bacterial Community. Toxins 2016, 8, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xie, W.; Lin, X.; Zhou, H.; Teng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Yao, L.; Xu, H. Controlling Toxic Microcystis Blooms: The Power of a Novel Microalgal Predator Poteriospumella lacustris in Water Safety Improvement. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 441, 141011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, L.; Wei, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. High Temperature Favors Elimination of Toxin-Producing Microcystis and Degradation of Microcystins by Mixotrophic Ochromonas. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowska, A.; Kaliński, T.; Koper, M.; Kostrzewska-Szlakowska, I.; Kwiatowski, J.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Jasser, I. Predicting Blooms of Toxic Cyanobacteria in Eutrophic Lakes with Diverse Cyanobacterial Communities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wejnerowski, Ł.; Dulić, T.; Akter, S.; Font-Nájera, A.; Rybak, M.; Kamiński, O.; Czerepska, A.; Dziuba, M.K.; Jurczak, T.; Meriluoto, J.; et al. Community Structure and Toxicity Potential of Cyanobacteria during Summer and Winter in a Temperate-Zone Lake Susceptible to Phytoplankton Blooms. Toxins 2024, 16, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinl, K.L.; Harris, T.D.; North, R.L.; Almela, P.; Berger, S.A.; Bizic, M.; Burnet, S.H.; Grossart, H.-P.; Ibelings, B.W.; Jakobsson, E.; et al. Blooms Also like It Cold. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 546–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, D.D.; Potter, T.L.; Truman, C.C.; Bednarz, C.W.; Strickland, T.C. Surface Runoff and Lateral Subsurface Flow as A Response to Conservation Tillage and Soil-Water Conditions. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 2137–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Master Health and Safety Plan: Beltsville Agricultural Research Center; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; 120p.
- UGA. Comprehensive Environmental Health and Safety Management System Manual; UGA: Athens, GA, USA, 2022; 51p. [Google Scholar]
- Pachepsky, Y.; Kierzewski, R.; Stocker, M.; Sellner, K.; Mulbry, W.; Lee, H.; Kim, M. Temporal Stability of Escherichia coli Concentrations in Waters of Two Irrigation Ponds in Maryland. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 84, e01876-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, M.D.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Smith, J.; Morgan, B.; Hill, R.L.; Kim, M.S. Persistent Patterns of E. coli Concentrations in Two Irrigation Ponds from 3 Years of Monitoring. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P.D. PAST: Paleontological Statistics Software Package for Education and Data Analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 9. [Google Scholar]









| Microcystin | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Quality Parameters | Pond 1 R Crit = 0.400 | Pond 2 R Crit = 0.426 | Pond 3 R Crit = 0.729 |
| CHL | 0.412 | 0.903 | 0.657 |
| FDOM | −0.699 | 0.001 | 0.486 |
| DO | −0.296 | −0.115 | −0.143 |
| SPC | −0.575 | 0.182 | 0.143 |
| Phyco | 0.478 | 0.926 | −0.257 |
| NTU | 0.697 | 0.750 | −0.429 |
| pH | −0.044 | −0.265 | 0.314 |
| TEMP | 0.344 | 0.400 | −0.429 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smith, J.E.; Widmer, J.A.; Wolny, J.L.; Dunn, L.L.; Stocker, M.D.; Hill, R.L.; Pisani, O.; Coffin, A.W.; Pachepsky, Y. Persistence of Microcystin in Three Agricultural Ponds in Georgia, USA. Toxins 2024, 16, 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16110482
Smith JE, Widmer JA, Wolny JL, Dunn LL, Stocker MD, Hill RL, Pisani O, Coffin AW, Pachepsky Y. Persistence of Microcystin in Three Agricultural Ponds in Georgia, USA. Toxins. 2024; 16(11):482. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16110482
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmith, Jaclyn E., James A. Widmer, Jennifer L. Wolny, Laurel L. Dunn, Matthew D. Stocker, Robert L. Hill, Oliva Pisani, Alisa W. Coffin, and Yakov Pachepsky. 2024. "Persistence of Microcystin in Three Agricultural Ponds in Georgia, USA" Toxins 16, no. 11: 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16110482
APA StyleSmith, J. E., Widmer, J. A., Wolny, J. L., Dunn, L. L., Stocker, M. D., Hill, R. L., Pisani, O., Coffin, A. W., & Pachepsky, Y. (2024). Persistence of Microcystin in Three Agricultural Ponds in Georgia, USA. Toxins, 16(11), 482. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16110482





