Variability in Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Profiles and Dinoflagellate Diversity in Mussels and Seawater Collected during Spring in Korean Coastal Seawater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
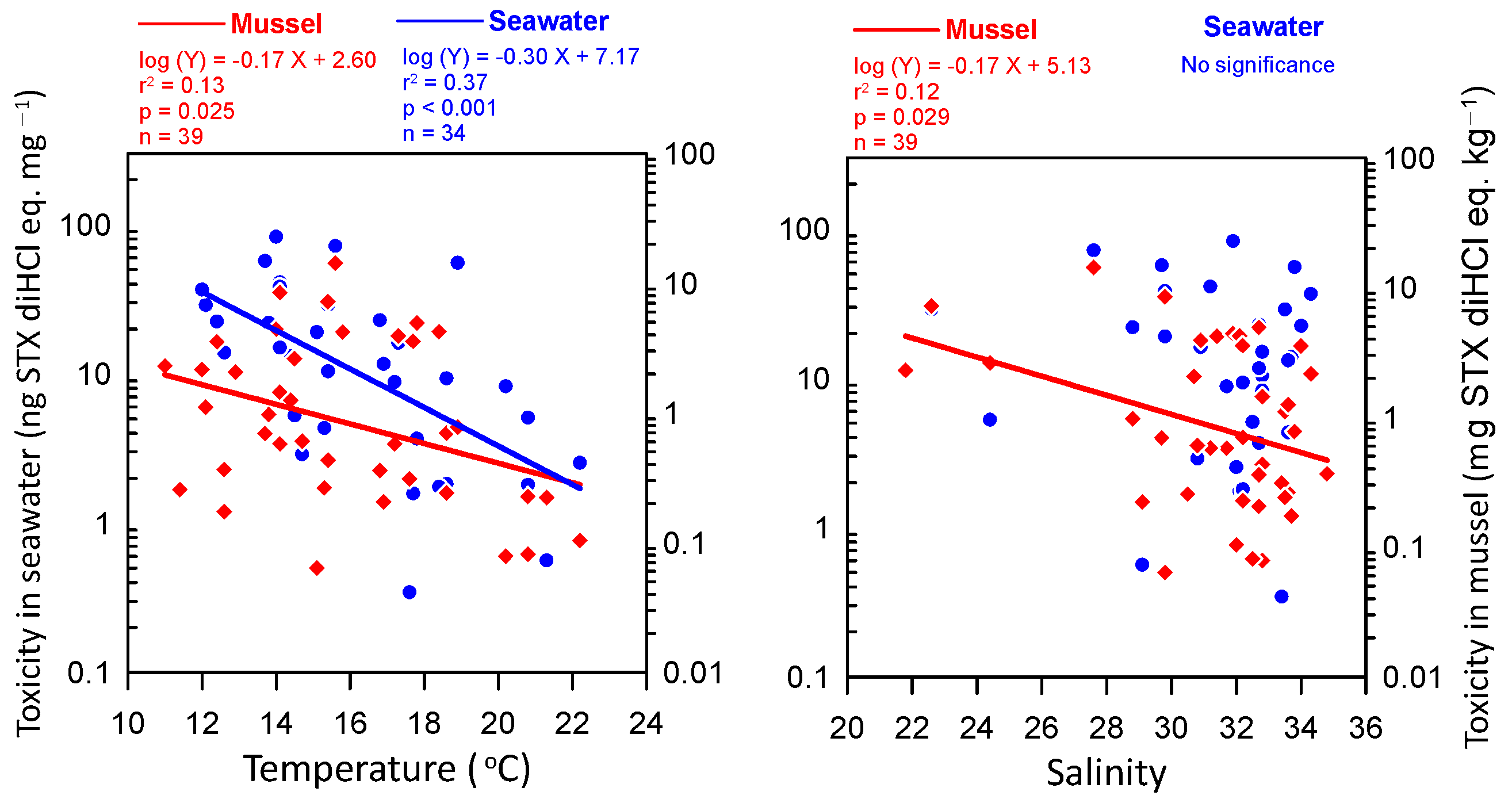
2.1. Seawater Temperature and Salinity Variations
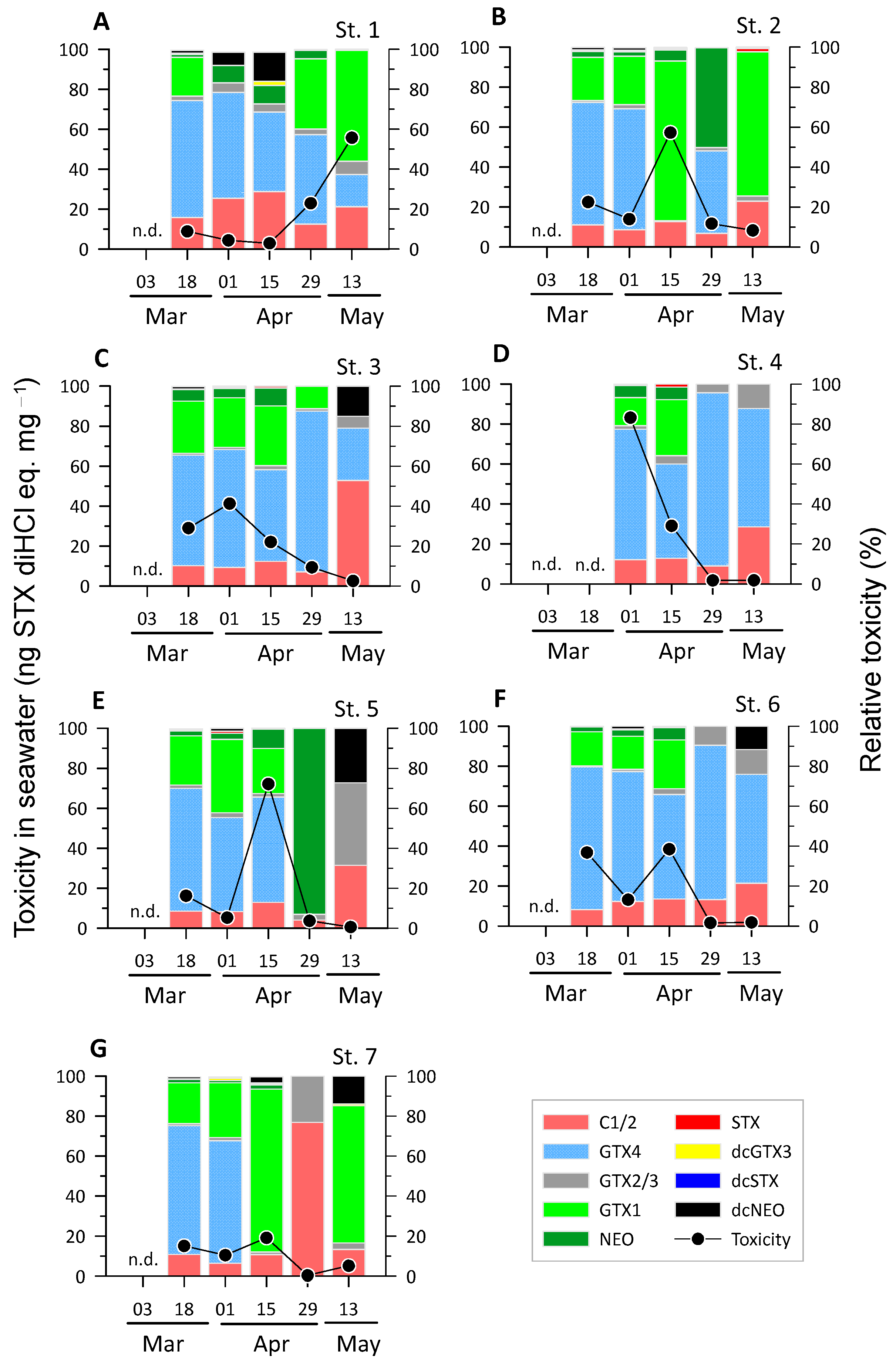
2.2. Concentration of PSTs in Seawater
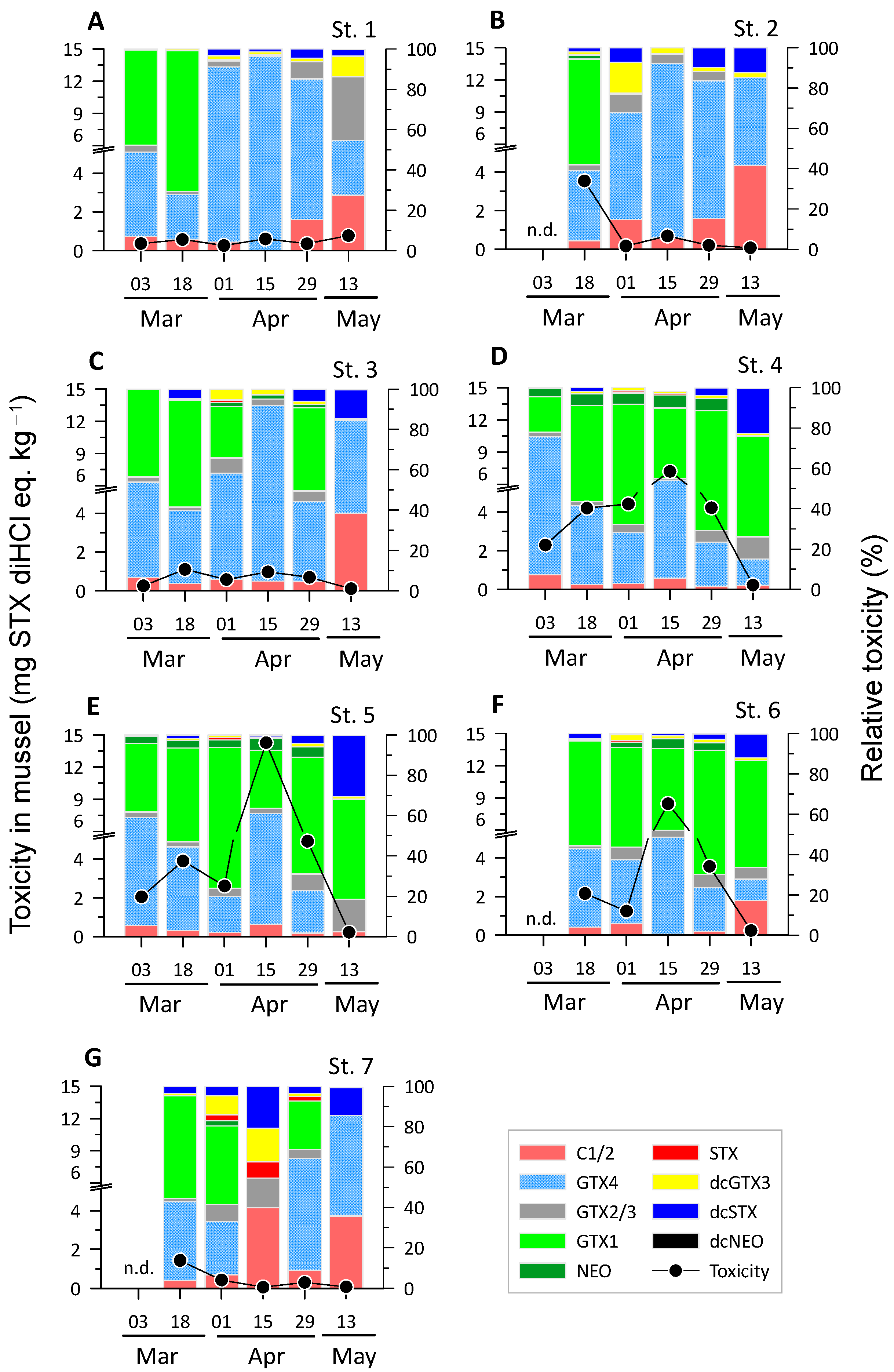
2.3. Concentration of PSTs in Mussels
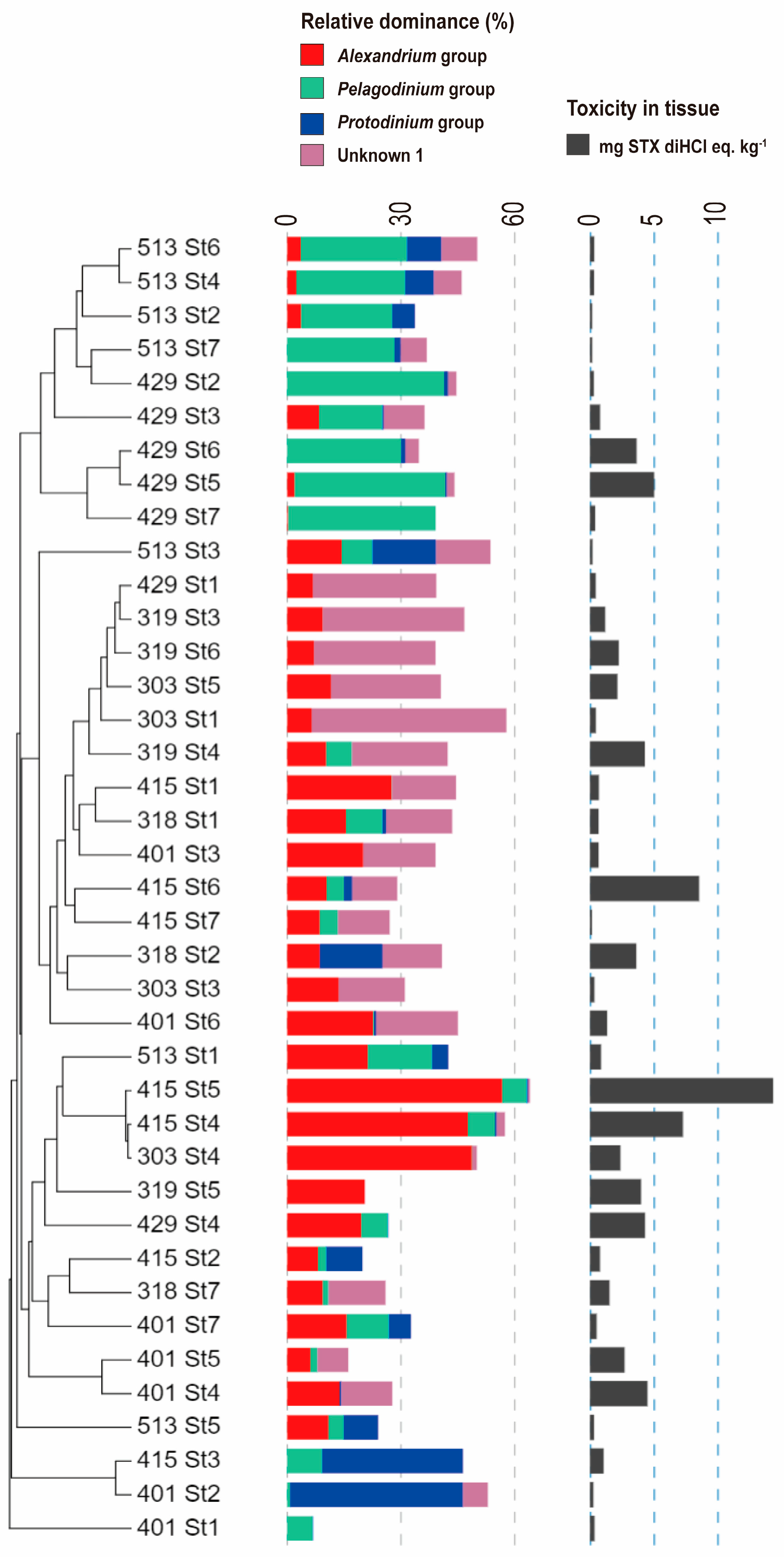
2.4. Dinoflagellate Composition in Seawater and Mussel Samples
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
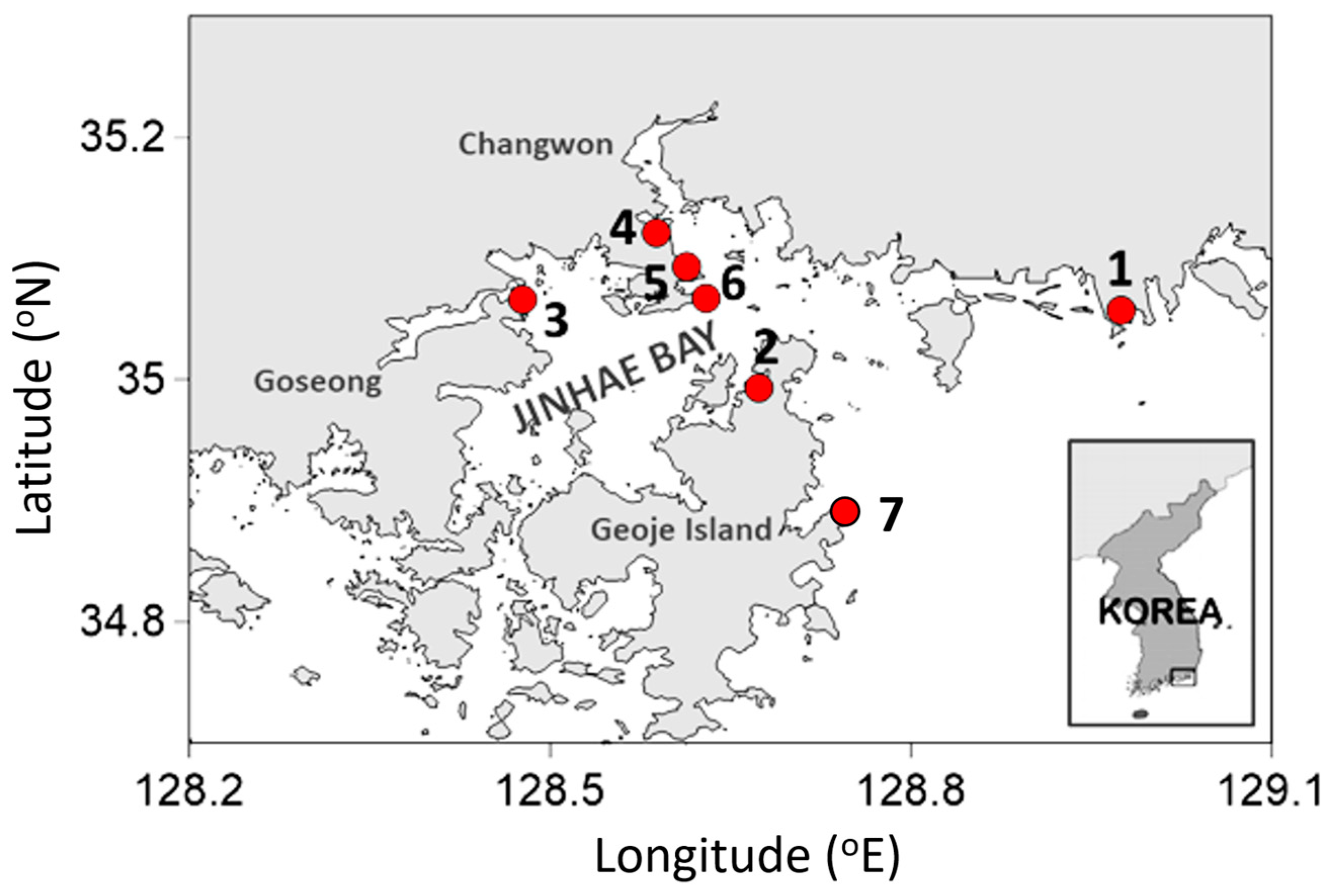
5.1. Study Areas and Sampling
5.2. PST Concentration in Microalgae and Mussel Tissues
5.3. DNA Extraction and Amplicon Library Construction and Sequencing
5.4. Sequence Data Analyses
5.5. Other Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bricelj, V.M.; Shumway, S.E. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs: Occurrence, Transfer Kinetics, and Biotransformation. Rev. Fish. Sci. 1998, 6, 315–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; McNabb, P.S.; Harwood, D.T.; Selwood, A.I.; Boundy, M.J. Single-Laboratory Validation of a Multitoxin Ultra-Performance LC-Hydrophilic Interaction LC-MS/MS Method for Quantitation of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Shellfish. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 98, 609–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnich, N.; Thébault, A. Dose-Response Modelling of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP) in Humans. Toxins 2018, 10, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Marine biotoxins in shellfish—Saxitoxin group. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selander, E.; Thor, P.; Toth, G.; Pavia, H. Copepods induce paralytic shellfish toxin production in marine dinoflagellates. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 273, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergkvist, J.; Selander, E.; Pavia, H. Induction of toxin production in dinoflagellates: The grazer makes a difference. Oecologia 2008, 156, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, R.; Nojima, K.; Tsuruda, S.; Gomez-Delan, G.; Barte-Quilantang, M.; Taniyama, S.; Sagara, T.; Nishio, S.; Takayama, H.; Miyazawa, K.; et al. Occurrence of PSP-producing dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamiyavanichii in Bingo-Nada, the central coastal water of the Seto Inland Sea, Hiroshima Prefecture, Japan. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.H.; Yoon, Y.H.; Kawami, H.; Iwataki, M.; Kazumi, M. The First Appearance of Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae) Responsible for the PSP Contaminations in Gamak Bay, Korea. Algae 2008, 23, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Ye, R.-M.; Zheng, J.-W.; Luo, Z.-H.; Gu, H.-F.; Yang, W.-D.; Li, H.-Y.; Liu, J.-S. Molecular phylogeny and PSP toxin profile of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex along the coast of China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 89, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdenadher, M.; Hamza, A.; Fekih, W.; Hannachi, I.; Zouari Bellaaj, A.; Bradai, M.N.; Aleya, L. Factors determining the dynamics of toxic blooms of Alexandrium minutum during a 10-year study along the shallow southwestern Mediterranean coasts. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 106, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D.M.; Keafer, B.A.; Kleindinst, J.L.; McGillicuddy, D.J.; Martin, J.L.; Norton, K.; Pilskaln, C.H.; Smith, J.L.; Sherwood, C.R.; Butman, B. Alexandrium fundyense cysts in the Gulf of Maine: Long-term time series of abundance and distribution, and linkages to past and future blooms. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 103, 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya, O.; Quintanilla, R.; Stacy, B.A.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y.; Flewelling, L.; Hardy, R.; Dueñas, C.; Ruiz, G. Large-Scale Sea Turtle Mortality Events in El Salvador Attributed to Paralytic Shellfish Toxin-Producing Algae Blooms. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morquecho, L.; Alonso-Rodríguez, R.; Arreola-Lizárraga, J.A.; Reyes-Salinas, A. Factors associated with moderate blooms of Pyrodinium bahamense in shallow and restricted subtropical lagoons in the Gulf of California. Bot. Mar. 2012, 55, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.R.; Botelho, M.J.; Lefebvre, K.A. Characterization of paralytic shellfish toxins in seawater and sardines (Sardina pilchardus) during blooms of Gymnodinium catenatum. Hydrobiologia 2010, 655, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gu, H.; Krock, B.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Toxic dinoflagellate blooms of Gymnodinium catenatum and their cysts in Taiwan Strait and their relationship to global populations. Harmful Algae 2020, 97, 101868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeds, J.R.; Landsberg, J.H.; Etheridge, S.M.; Pitcher, G.C.; Longan, S.W. Non-traditional vectors for paralytic shellfish poisoning. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 308–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condie, S.A.; Oliver, E.C.J.; Hallegraeff, G.M. Environmental drivers of unprecedented Alexandrium catenella dinoflagellate blooms off eastern Tasmania, 2012–2018. Harmful Algae 2019, 87, 101628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collos, Y.; Vaquer, A.; Laabir, M.; Abadie, E.; Laugier, T.; Pastoureaud, A.; Souchu, P. Contribution of several nitrogen sources to growth of Alexandrium catenella during blooms in Thau lagoon, southern France. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numano, S.; Kudo, Y.; Cho, Y.; Konoki, K.; Yotsu-Yamashita, M. Temporal Variation of the Profile and Concentrations of Paralytic Shellfish Toxins and Tetrodotoxin in the Scallop, Patinopecten yessoensis, Cultured in a Bay of East Japan. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos, L.G.; Santinelli, N.H.; Sastre, A.V.; Marino, G.; Almandoz, G.O. Spatiotemporal distribution of paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxins in shellfish from Argentine Patagonian coast. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, S.; Levasseur, M.; Doucette, G.; Cantin, G. Particle size fractionation of paralytic shellfish toxins (PSTs): Seasonal distribution and bacterial production in the St Lawrence estuary, Canada. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Choi, J.M.; Lee, M.; Park, B.S.; Zhang, Y.; Arakawa, O.; Takatani, T.; Jeon, J.-K.; Kim, Y.O. Change in Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Depending on Dynamics of Harmful Alexandrium catenella (Group I) in the Geoje Coast (South Korea) during Bloom Season. Toxins 2020, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.-S.; Song, K.-C.; Lee, K.-J.; Kim, J.-H. Variation and Profile of Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning Toxins in Jinhae Bay, Korea. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 16, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, C.J.; Kim, C.H.; Sako, Y. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin analysis of the genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) occurring in Korean coastal waters. Fish. Sci. 2005, 71, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Lee, H.; Anderson, D.M.; Kim, B. Paralytic shellfish toxin production by the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum (Chinhae Bay, Korea) in axenic, nutrient-limited chemostat cultures and nutrient-enriched batch cultures. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 104, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, S.; Ogata, T.; Sato, S.; Kodama, M.; Takeuchi, T. Causative organism of paralytic shellfish toxins other than toxic dinoflagellates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Oldendorf 1992, 89, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbart, B.; Pitcher, G.C.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A.D. Toxigenic phytoplankton and concomitant toxicity in the mussel Choromytilus meridionalis off the west coast of South Africa. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Belmonte, A.; Inostroza, I.; Carrillo, K.S.; Franco, J.M.; Riobo, P.; Gomez, P.I. The combined effect of salinity and temperature on the growth and toxin content of four Chilean strains of Alexandrium catenella (Whedon and Kofoid) Balech 1985 (Dinophyceae) isolated from an outbreak occurring in southern Chile in 2009. Harmful Algae 2013, 23, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Nagashima, Y.; Taguchi, S. N:P ratios controlling the growth of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense: Content and composition of paralytic shellfish poison. Harmful Algae 2012, 20, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.S.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, J.H.; Pyun, J.H.; Choe, W.K. Detoxification of PSP and relationship between PSP toxicity and Protogonyaulax sp. Bull. Korean Fish. Soc. 1989, 22, 177–188. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.J.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, T.S.; Son, K.T.; Byun, H.S.; Park, J.H.; Jang, D.S. Comparison of paralytic shellfish poison contents and components in the different bivalve species. J. Food Hyg. Saf. 2000, 15, 293–296. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Shon, M.B.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, C.R. Paralytic shellfish poisoning of Mediterranean mussels from Jinhae Bay in Korea. Korean J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2009, 42, 366–372. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Z.; Chen, F.; Li, H.S.; Xiang, W.Z.; Li, Y.J.; Jiang, Y. Effect of iron on growth, biochemical composition and paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins production of Alexandrium tamarense. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C.Q.; Shen, X.S. Combined Effects of Temperature and Toxic Algal Abundance on Paralytic Shellfish Toxic Accumulation, Tissue Distribution and Elimination Dynamics in Mussels Mytilus coruscus. Toxins 2021, 13, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsur, M.; Takatani, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Sagara, T.; Noguchi, T.; Arakawa, O. Accumulation and elimination profiles of paralytic shellfish poison in the short-necked clam Tapes japonica fed with the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 48, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-Z.; Jiang, T.-J.; Hsieh, D.P.H. Toxin composition variations in cultures of Alexandrium species isolated from the coastal waters of southern China. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimi, K.; Suzuki, T.; Ito, A. Variety of PSP toxin profiles in various culture strains of Alexandrium tamarense and change of toxin profile in natural A. tamarense population. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 273, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.F.; Cristiano, M.L.S. Marine paralytic shellfish toxins: Chemical properties, mode of action, newer analogues, and structure–toxicity relationship. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botelho, M.J.; Vale, C.; Grilo, R.V.; Ferreira, J.G. Uptake and release of paralytic shellfish toxins by the clam Ruditapes decussatus exposed to Gymnodinium catenatum and subsequent depuration. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 77, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krock, B.; Seguel, C.G.; Cembella, A.D. Toxin profile of Alexandrium catenella from the Chilean coast as determined by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection and liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Lee, K.-J.; Yu, H.-S.; Mok, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, K.-S.; Lee, M.-A.; Kim, M.-H. Intra-laboratory Validation of an HPLC Post-column Oxidation Method for the Analysis of PSP Toxins in Oysters and Mussels. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 45, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Hatfield, R.G.; Rapkova, M.; Higman, W.; Algoet, M.; Suarez-Isla, B.A.; Cordova, M.; Caceres, C.; van de Riet, J.; Gibbs, R.; et al. Comparison of AOAC 2005.06 LC official method with other methodologies for the quantitation of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in UK shellfish species. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 399, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambrook, J.; Fritsch, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, H.; Hou, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Miranda, L. High-level diversity of dinoflagellates in the natural environment, revealed by assessment of mitochondrial cox1 and cob genes for dinoflagellate DNA barcoding. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illumina. 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation. 2013. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/downloads/16s_metagenomic_sequencing_library_preparation.html (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Kozich, J.J.; Westcott, S.L.; Baxter, N.T.; Highlander, S.K.; Schloss, P.D. Development of a dual-index sequencing strategy and curation pipeline for analyzing amplicon sequence data on the MiSeq Illumina sequencing platform. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5112–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D36–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.H.; An, S.M.; Chun, S.; Yang, E.C.; Selph, K.E.; Lee, C.M.; Noh, J.H. Dynamic changes in the composition of photosynthetic picoeukaryotes in the northwestern Pacific Ocean revealed by high-throughput tag sequencing of plastid 16S rRNA genes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 92, fiv170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, W.; Strunk, O.; Westram, R.; Richter, L.; Meier, H.; Yadhukumar; Buchner, A.; Lai, T.; Steppi, S.; Jobb, G.; et al. ARB: A software environment for sequence data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.R.; Gorley, R.N. PRIMER V7: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2015; Volume 7, p. 296. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, D.H.; Yang, W.; Kim, Y.-E.; Park, B.S.; Sung, J.; Choi, J.; Rho, J.-R.; Han, Y.S.; Lee, Y. Variability in Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Profiles and Dinoflagellate Diversity in Mussels and Seawater Collected during Spring in Korean Coastal Seawater. Toxins 2024, 16, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16080338
Choi DH, Yang W, Kim Y-E, Park BS, Sung J, Choi J, Rho J-R, Han YS, Lee Y. Variability in Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Profiles and Dinoflagellate Diversity in Mussels and Seawater Collected during Spring in Korean Coastal Seawater. Toxins. 2024; 16(8):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16080338
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Dong Han, Wonseok Yang, Young-Eun Kim, Bum Soo Park, Jiyeon Sung, Jaeho Choi, Jung-Rae Rho, Young Seok Han, and Yeonjung Lee. 2024. "Variability in Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Profiles and Dinoflagellate Diversity in Mussels and Seawater Collected during Spring in Korean Coastal Seawater" Toxins 16, no. 8: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16080338
APA StyleChoi, D. H., Yang, W., Kim, Y.-E., Park, B. S., Sung, J., Choi, J., Rho, J.-R., Han, Y. S., & Lee, Y. (2024). Variability in Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Profiles and Dinoflagellate Diversity in Mussels and Seawater Collected during Spring in Korean Coastal Seawater. Toxins, 16(8), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins16080338






