The Anthelmintic Activity of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Ichthyocrinotoxins and Their Potential as Novel Therapeutics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
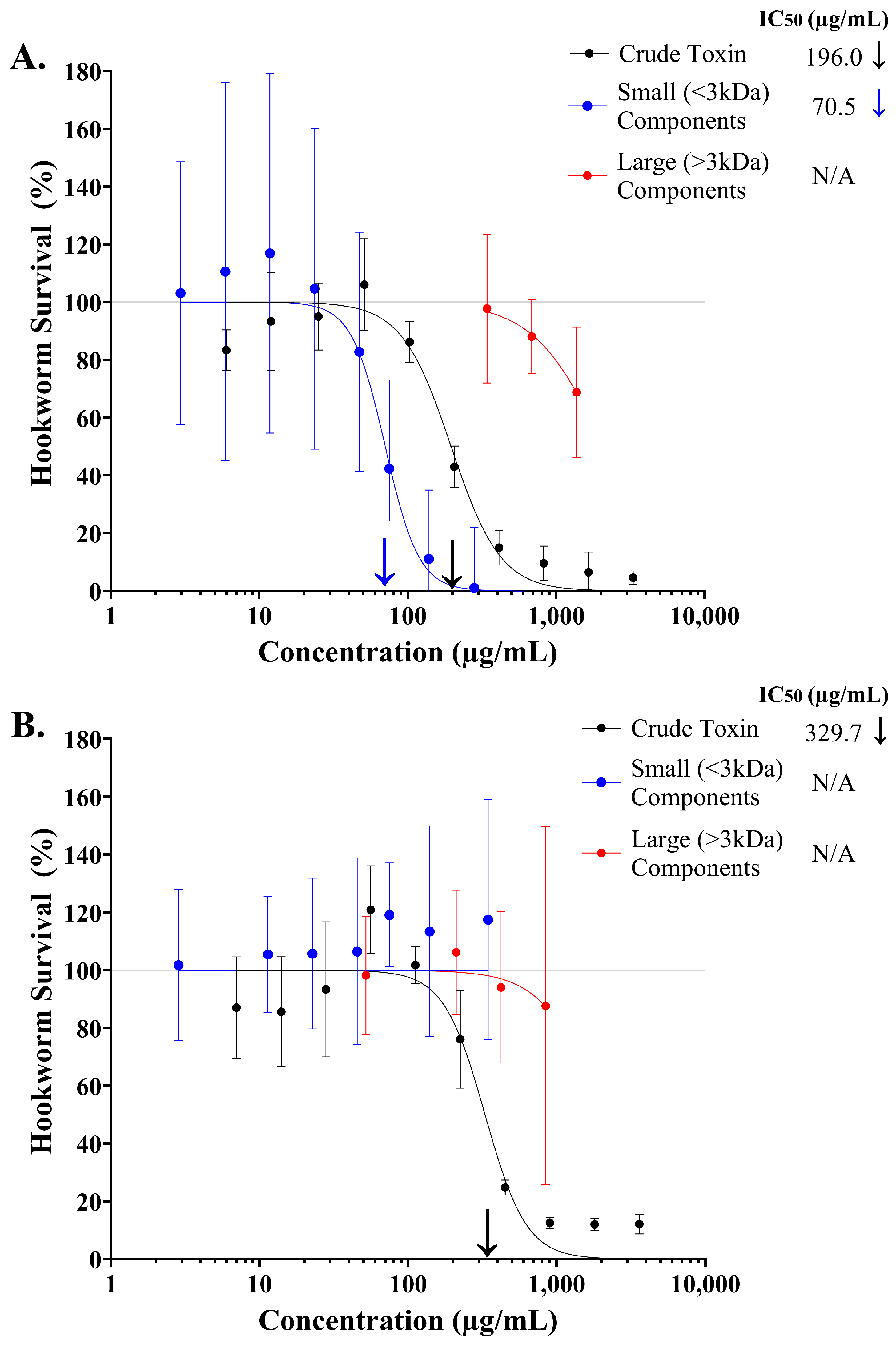
2.1. Assessing the Toxicity of Crude Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins to Infective Rodent Hookworm Larvae
2.2. Identifying Components in Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins with Anthelmintic Activity
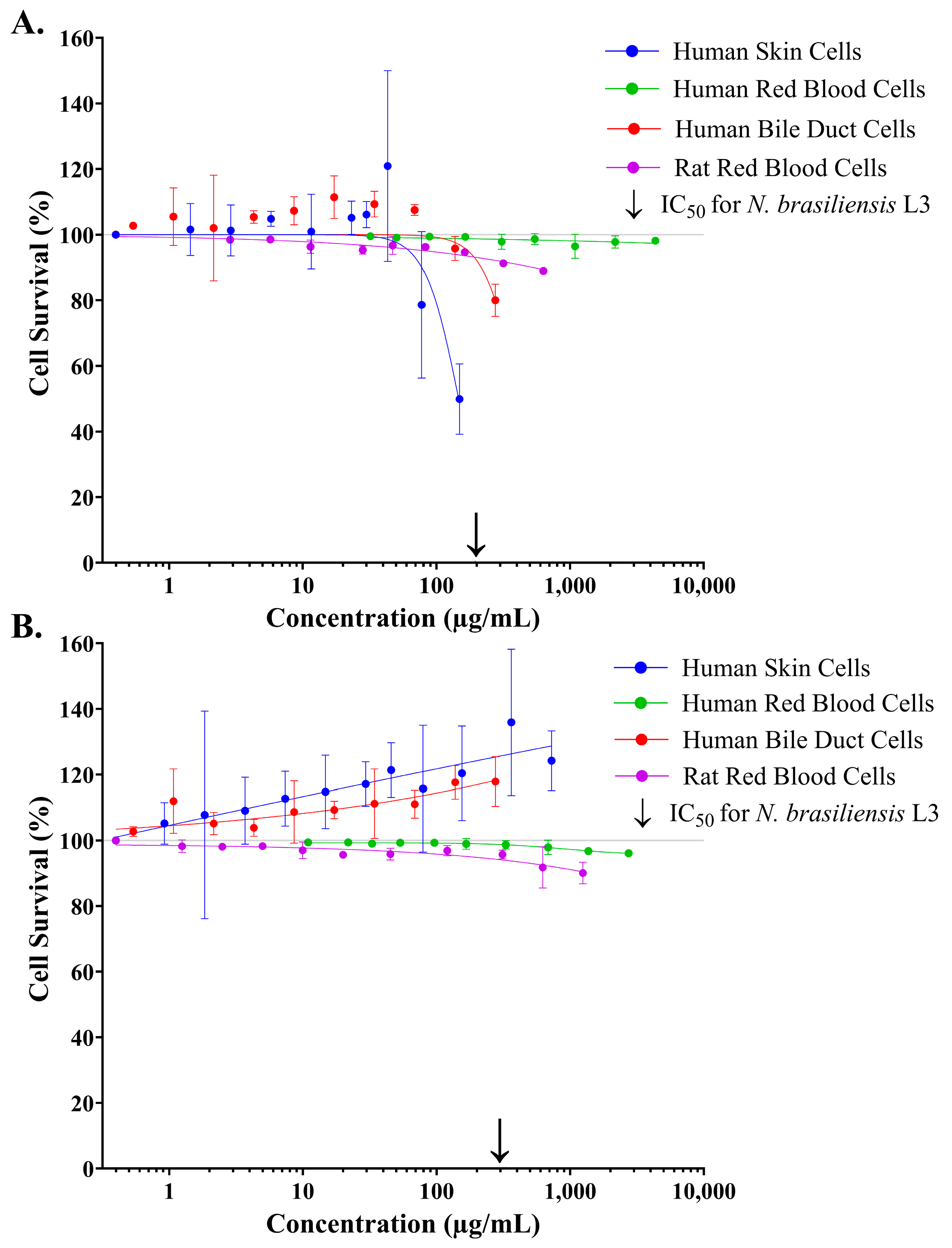
2.3. Assessing the Cytotoxicity of Crude Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins to Mammalian Cell Lines In Vitro
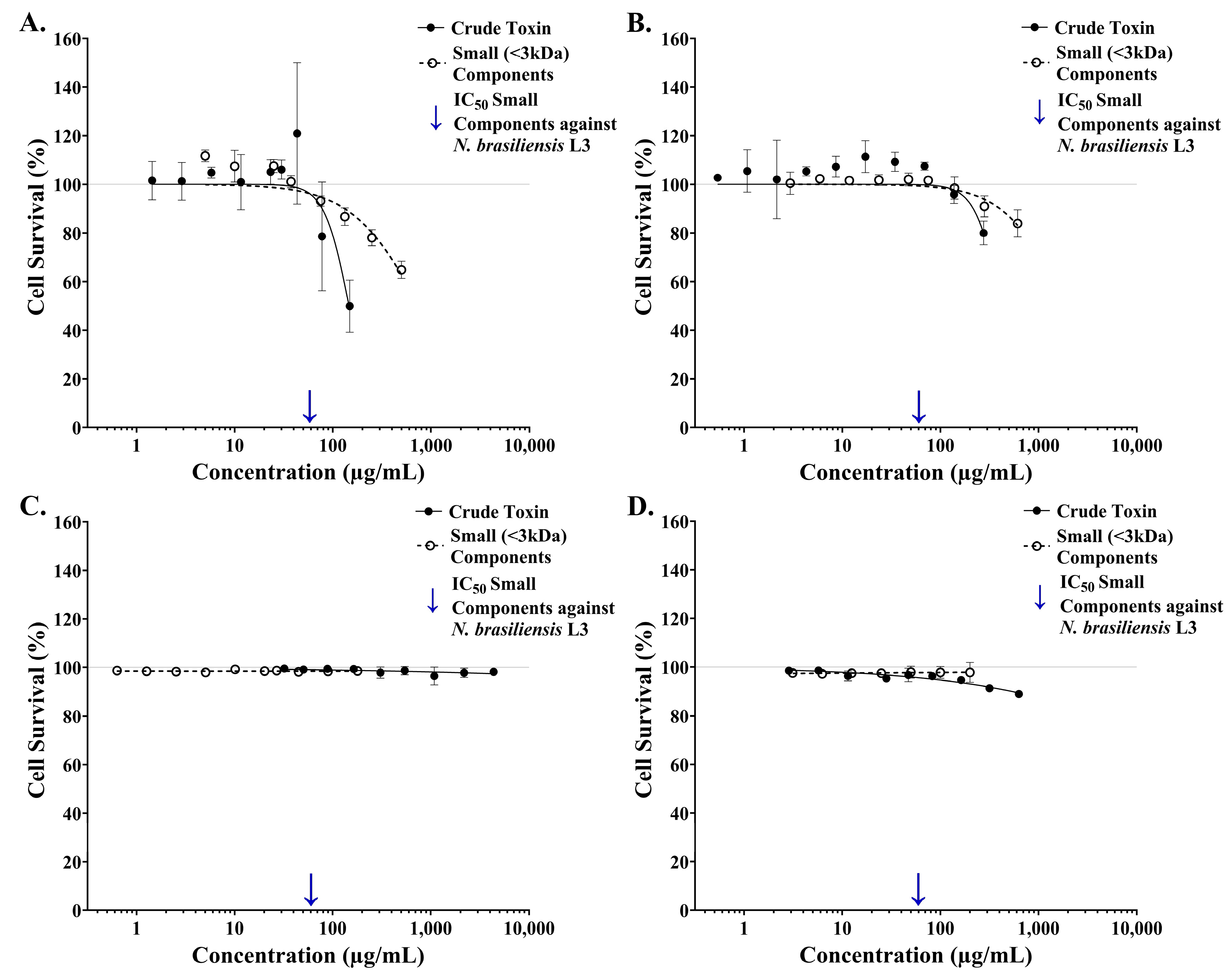
2.4. Assessing the Cytotoxicity of Isolated Small Components from Estuarine Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins to Mammalian Cell Lines In Vitro
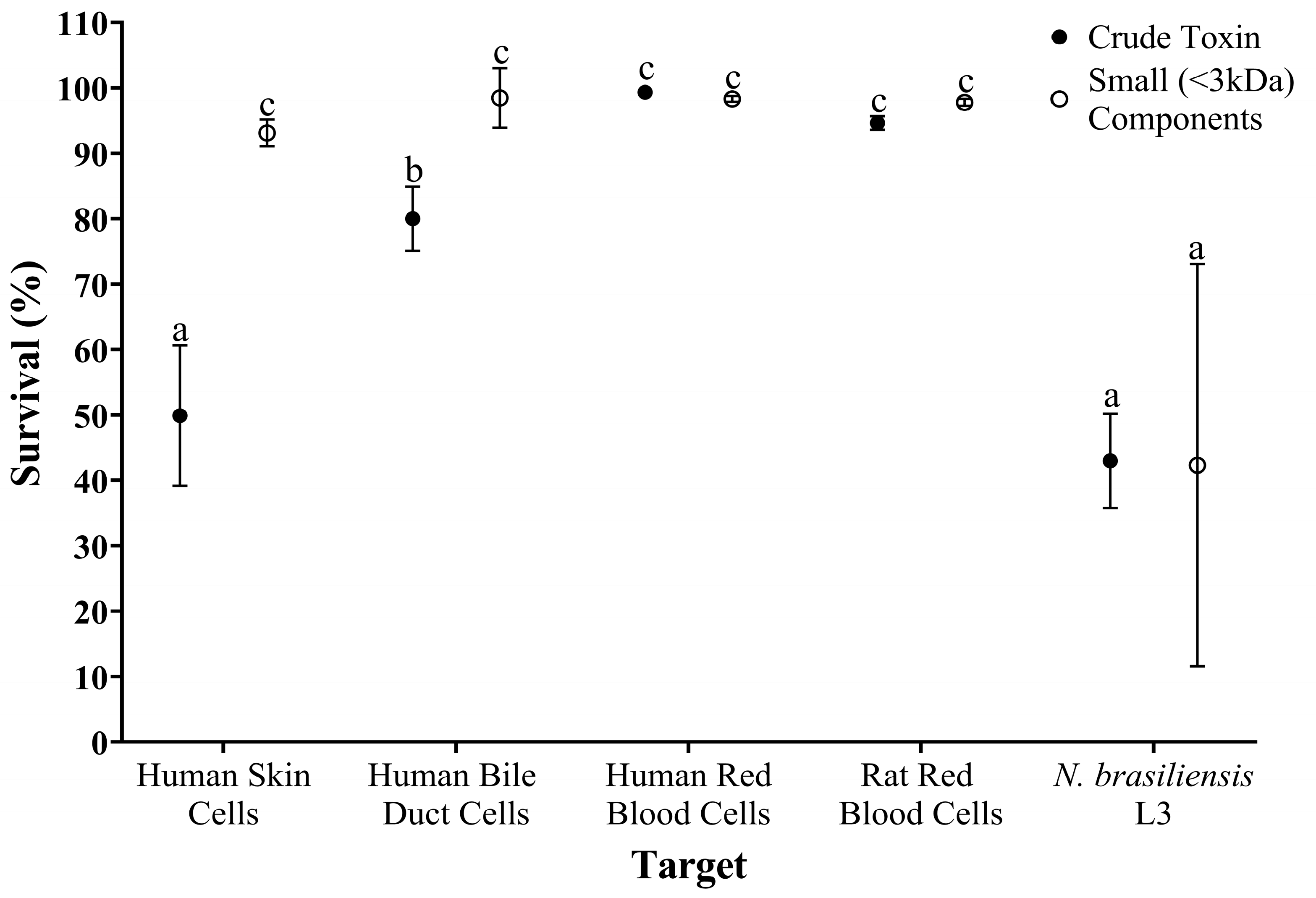
2.5. Comparing the Toxicity of Crude and Isolated Small-Component Samples from Estuarine Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins Between Parasite and Cellular Targets
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Ichthyocrinotoxin Collection and Parasite Cultivation
5.1.1. Ichthyocrinotoxin Collection
5.1.2. Parasite Cultivation
5.2. Measuring Hookworm Larvae Motility with xWORM
5.2.1. Measuring Hookworm Larvae Motility
5.2.2. Data Transformation to Motility Index/Percent Parasite Survival
5.3. Assessing the Anthelmintic Activity of Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins and Identifying Hookworm-Toxic Components
5.3.1. Determining the Effect of Crude Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins on Hookworm Larvae Survival
5.3.2. Isolating the Large (>3 kDa) and Small (<3 kDa) Components from Crude Toxin
5.3.3. Measuring the Dose-Dependent Effect of Isolated Toxin Components and Comparing Their Activity Against Crude Toxin
5.4. Determining the Cytotoxicity of Stonefish Ichthyocrinotoxins to Mammalian Cell Lines In Vitro
5.4.1. Culturing Mammalian Cell Lines In Vitro
5.4.2. xCELLigence Cell Viability Assay
5.4.3. Haemotoxicity Assay
5.4.4. Dose–Response Analysis—Mammalian Cell Lines
5.5. Comparing the Activity of Crude- and Small-Component Samples from S. horrida Ichthyocrinotoxin Across Targets
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlson, C.J.; Dallas, T.A.; Alexander, L.W.; Phelan, A.L.; Phillips, A.J. What Would It Take to Describe the Global Diversity of Parasites? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.; Aslam, N.; Zainab, R.; Aziz-Ur, R.; Rasool, G.; Ullah, M.I.; Daniyal, M.; Akram, M. Prevalence, Risk Factors, Challenges, and the Currently Available Diagnostic Tools for the Determination of Helminths Infections in Human. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2020, 18, 2058739220959915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Soil-Transmitted Helminth Infections; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Piazzesi, A.; Putignani, L. Impact of Helminth-Microbiome Interactions on Childhood Health and Development: A Clinical Perspective. Parasite Immunol. 2023, 45, e12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segoviano-Lorenzo, M.D.C.; Trigo-Esteban, E.; Gyorkos, T.W.; St-Denis, K.; Guzman, F.M.; Casapia-Morales, M. Prevalence of Malnutrition, Anemia, and Soil-Transmitted Helminthiasis in Preschool-Age Children Living in Peri-Urban Populations in the Peruvian Amazon. Cad. Saúde Pública 2022, 38, e00248221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldo, D.; Perez-Saez, J.; Vounatsou, P.; Utzinger, J.; Arcand, J.L. The Economic Impact of Schistosomiasis. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2021, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlier, J.; Rinaldi, L.; Musella, V.; Ploeger, H.W.; Chartier, C.; Vineer, H.R.; Hinney, B.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Băcescu, B.; Mickiewicz, M. Initial Assessment of the Economic Burden of Major Parasitic Helminth Infections to the Ruminant Livestock Industry in Europe. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 182, 105103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menconi, V.; Lazzaro, E.; Bertola, M.; Guardone, L.; Mazzucato, M.; Prearo, M.; Bilska-Zajac, E.; Cortinovis, L.; Manfrin, A.; Arcangeli, G.; et al. The Occurrence of Freshwater Fish-Borne Zoonotic Helminths in Italy and Neighbouring Countries: A Systematic Review. Animals 2023, 13, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, C.; Green, A.; Lowenthal, J.; Melland, R.; Younus, F. Megatrends, Opportunities and Challenges Facing Australian Livestock Industries; Australian Animal Health Council: Braddon, ACT, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fissiha, W.; Kinde, M.Z. Anthelmintic Resistance and Its Mechanism: A Review. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 5403–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourguinat, C.; Lee, A.C.; Lizundia, R.; Blagburn, B.L.; Liotta, J.L.; Kraus, M.S.; Keller, K.; Epe, C.; Letourneau, L.; Kleinman, C.L.; et al. Macrocyclic Lactone Resistance in Dirofilaria immitis: Failure of Heartworm Preventives and Investigation of Genetic Markers for Resistance. Vet. Parasitol. 2015, 210, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prichard, R.K. Macrocyclic Lactone Resistance in Dirofilaria immitis: Risks for Prevention of Heartworm Disease. Int. J. Parasitol. 2021, 51, 1121–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crellen, T.; Walker, M.; Lamberton, P.H.; Kabatereine, N.B.; Tukahebwa, E.M.; Cotton, J.A.; Webster, J.P. Reduced Efficacy of Praziquantel Against Schistosoma mansoni Is Associated With Multiple Rounds of Mass Drug Administration. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, A.R.; Quagraine, J.E.; Suwondo, P.; George, S.; Harrison, L.M.; Dornas, F.P.; Evans, B.; Caccone, A.; Humphries, D.; Wilson, M.D.; et al. Genetic Markers of Benzimidazole Resistance among Human Hookworms (Necator americanus) in Kintampo North Municipality, Ghana. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2019, 100, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardene, K.L.T.D.; Palombo, E.A.; Boag, P.R. Natural Products Are a Promising Source for Anthelmintic Drug Discovery. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, S.A.; Welz, C.; Woods, D.J.; Costa-Junior, L.; Zamanian, M.; Martin, R.J. Where Are All the Anthelmintics? Challenges and Opportunities on the Path to New Anthelmintics. Int. J. Parasitol. —Drugs Drug Resist. 2020, 14, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajickova, M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Skalova, L.; Raisova Stuchlikova, L.; Matouskova, P. Anthelmintics in the Future: Current Trends in the Discovery and Development of New Drugs Against Gastrointestinal Nematodes. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurdy, C.R.; Scully, S.S. Analgesic Substances Derived from Natural Products (Natureceuticals). Life Sci. 2005, 78, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luddecke, T.; Blank, S. Animal Toxins: Biodiscovery, Mechanistic Insights and Translational Potential. Toxins 2024, 16, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.M.; Surridge, J.; Stablum, W.; Lewis, R.J. A Crinotoxin from the Skin Tubercle Glands of a Stonefish (Synanceia trachynis). Toxicon 1981, 19, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, B.W. Poisonous and Venomous Marine Animals of the World, 2nd rev. ed.; Halstead, L., Ed.; Darwin Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Endean, R. A Study of Distribution, Habitat, Behaviour, Venom Apparatus, and Venom of the Stone-Fish. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1961, 12, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox-Bulow, D.; Courtney, R.; Ebner, B.; Seymour, J. Diel activity patterns and habitat preferences of stonefish (Synanceia spp.) in captivity. Mem. Qld. Mus. 2024, 65, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, J.; Shamsi, S. The occurrence and abundance of infective stages of zoonotic nematodes in selected edible fish sold in Australian fish markets. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 154, 104833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timi, J.T.; Buchmann, K. A century of parasitology in fisheries and aquaculture. J. Helminthol. 2023, 97, e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.L.; Barnett, S.K.; Seymour, J.E.; Jenkins, T.P.; McNamara, M.; Adlard, R.D. Biliary Tract-Infecting Myxosporeans from Estuarine and Reef Stonefish (Scorpaeniformes: Synanceiidae) Off Eastern Australia, with Descriptions of Sphaeromyxa horrida n. sp. and Myxidium lapipiscis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida). J. Parasitol. 2018, 104, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, A.M.; Endean, R. Epidermal Secretions and the Evolution of Venom Glands in Fishes. Toxicon 1973, 11, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox-Bulow, D.; Smout, M.; Loukas, A.; Seymour, J. Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Ichthyocrinotoxins: An Ecological Review and Prospectus for Future Research and Biodiscovery. Toxicon 2023, 236, 107329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.L.; Schubert, M.; Baggio, J.A.; Jones, G.P.; Caley, M.J.; Grutter, A.S. Skin Toxins and External Parasitism of Coral-Dwelling Gobies. J. Fish. Biol. 2003, 62, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, A.W.; Cameron, A.M. Effect of a Smooth Muscle Relaxant from the Stonefish, Synanceia trachynis, on KCl-Induced Responses in the Guinea-Pig Vas Deferens. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 129, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox-Bulow, D.; Smout, M.; Wilson, D.; Seymour, J. Inter-Species Variation in Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Ichthyocrinotoxins; An Ecological Perspective. Toxicon 2023, 221, 106977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Sun, S.; You, Q.; Wang, L. Forward or Backward: Lessons Learned from Small Molecule Drugs Approved by FDA from 2012 to 2022. Molecules 2023, 28, 7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.X.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S. What are the Drugs of the Future? Med. Chem. Commun. 2018, 9, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahjoub, H.A.; Bedenice, D.; Stryhn, H.; Yu, J.; Greenwood, S.J.; Conboy, G.A. An In Vitro Larval Motility Assay Characterizes Anthelmintic Efficacy against Crenosoma vulpis, Angiostrongylus vasorum, and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2024, 85, e885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smout, M.J.; Kotze, A.C.; McCarthy, J.S.; Loukas, A. A Novel High Throughput Assay for Anthelmintic Drug Screening and Resistance Diagnosis by Real-Time Monitoring of Parasite Motility. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2010, 4, e885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberis, M.; Le Gros, G.; Urban, J., Jr. Animal model of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis and Heligmosomoides polygyrus. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2003, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, G.; Loukas, A.; Brindley, P.J.; Irelan, J.T.; Smout, M.J. Viability of Developmental Stages of Schistosoma mansoni Quantified with xCELLigence Worm Real-Time Motility Assay (xWORM). Int. J. Parasitol. —Drugs Drug Resist. 2015, 5, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennox-Bulow, D.; Becker, L.; Loukas, A.; Seymour, J.; Smout, M. Optimizing the xWORM assay for Monitoring Hookworm Larvae Motility. Front. Parasitol. 2023, 2, 1189872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motulsky, H. The GraphPad Guide to Comparing Dose-Response or Kinetic Curves; GraphPad Software: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Smout, M.J.; Sotillo, J.; Laha, T.; Papatpremsiri, A.; Rinaldi, G.; Pimenta, R.N.; Chan, L.Y.; Johnson, M.S.; Turnbull, L.; Whitchurch, C.B.; et al. Carcinogenic Parasite Secretes Growth Factor That Accelerates Wound Healing and Potentially Promotes Neoplasia. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; McInerney, B.V.; Mulvenna, J.; Seymour, J.E.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Chironex fleckeri (box jellyfish) venom proteins: Expansion of a cnidarian toxin family that elicits variable cytolytic and cardiovascular effects. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4798–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lennox-Bulow, D.; Seymour, J.; Loukas, A.; Smout, M. The Anthelmintic Activity of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Ichthyocrinotoxins and Their Potential as Novel Therapeutics. Toxins 2025, 17, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020066
Lennox-Bulow D, Seymour J, Loukas A, Smout M. The Anthelmintic Activity of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Ichthyocrinotoxins and Their Potential as Novel Therapeutics. Toxins. 2025; 17(2):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020066
Chicago/Turabian StyleLennox-Bulow, Danica, Jamie Seymour, Alex Loukas, and Michael Smout. 2025. "The Anthelmintic Activity of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Ichthyocrinotoxins and Their Potential as Novel Therapeutics" Toxins 17, no. 2: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020066
APA StyleLennox-Bulow, D., Seymour, J., Loukas, A., & Smout, M. (2025). The Anthelmintic Activity of Stonefish (Synanceia spp.) Ichthyocrinotoxins and Their Potential as Novel Therapeutics. Toxins, 17(2), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17020066





