Interaction of Mycotoxins with α1-Acid Glycoprotein (AGP) and Bovine Milk Proteins: Zearalenone, Zearalenols, and Sterigmatocystin Form Highly Stable Complexes with AGP
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
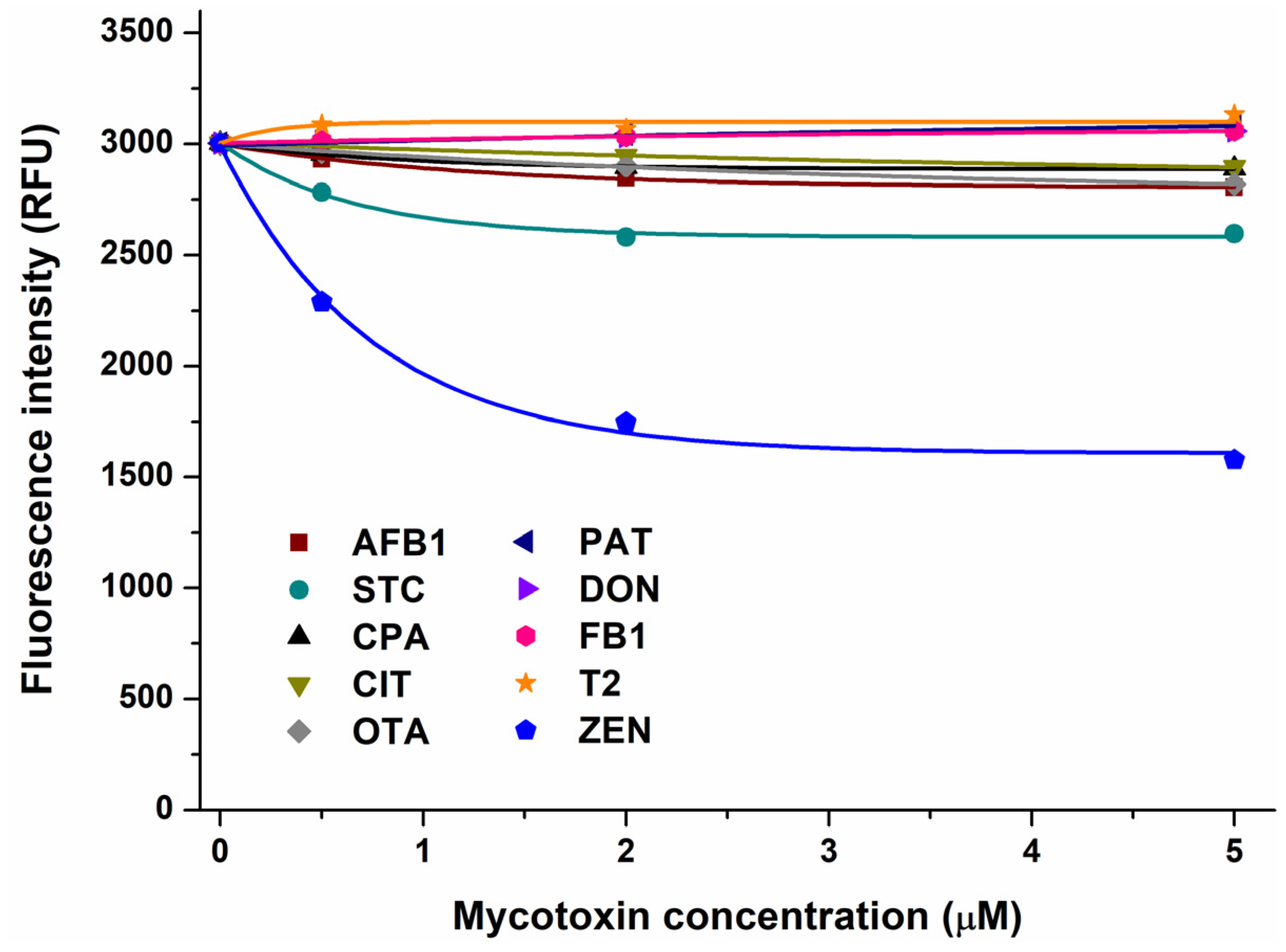
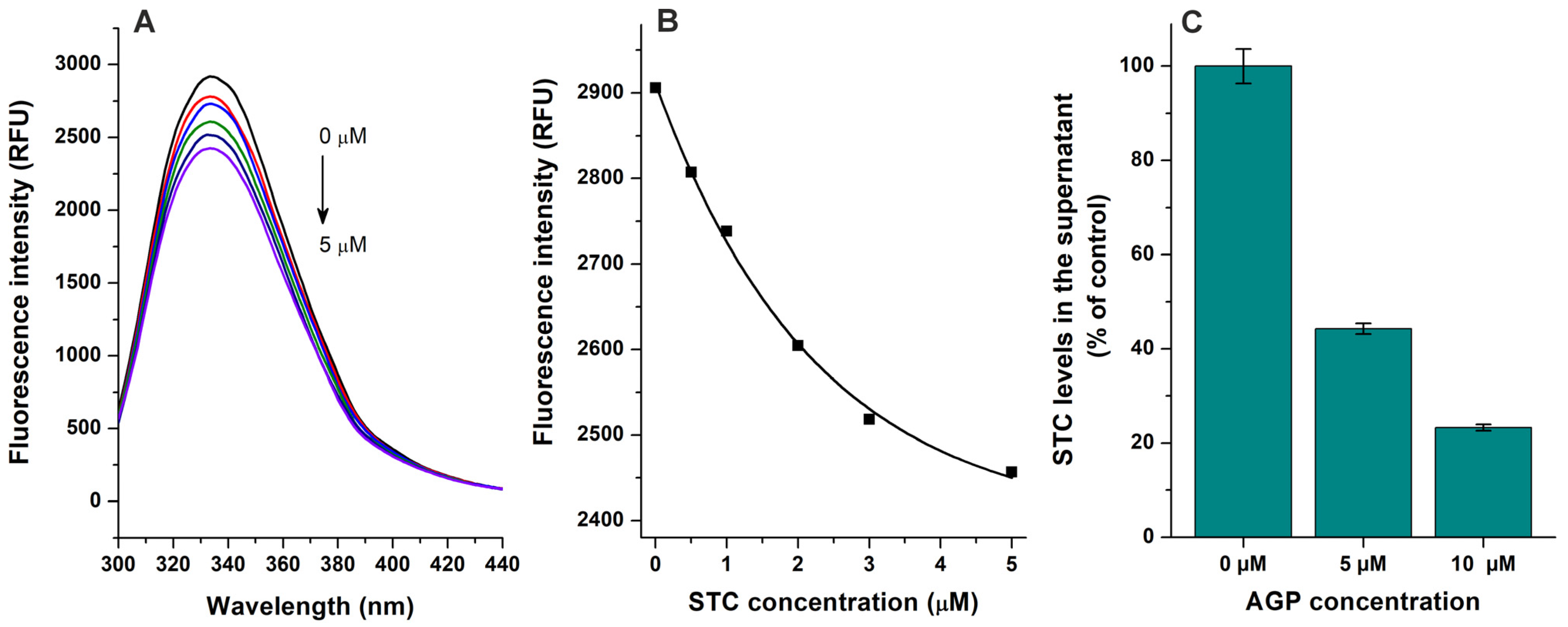
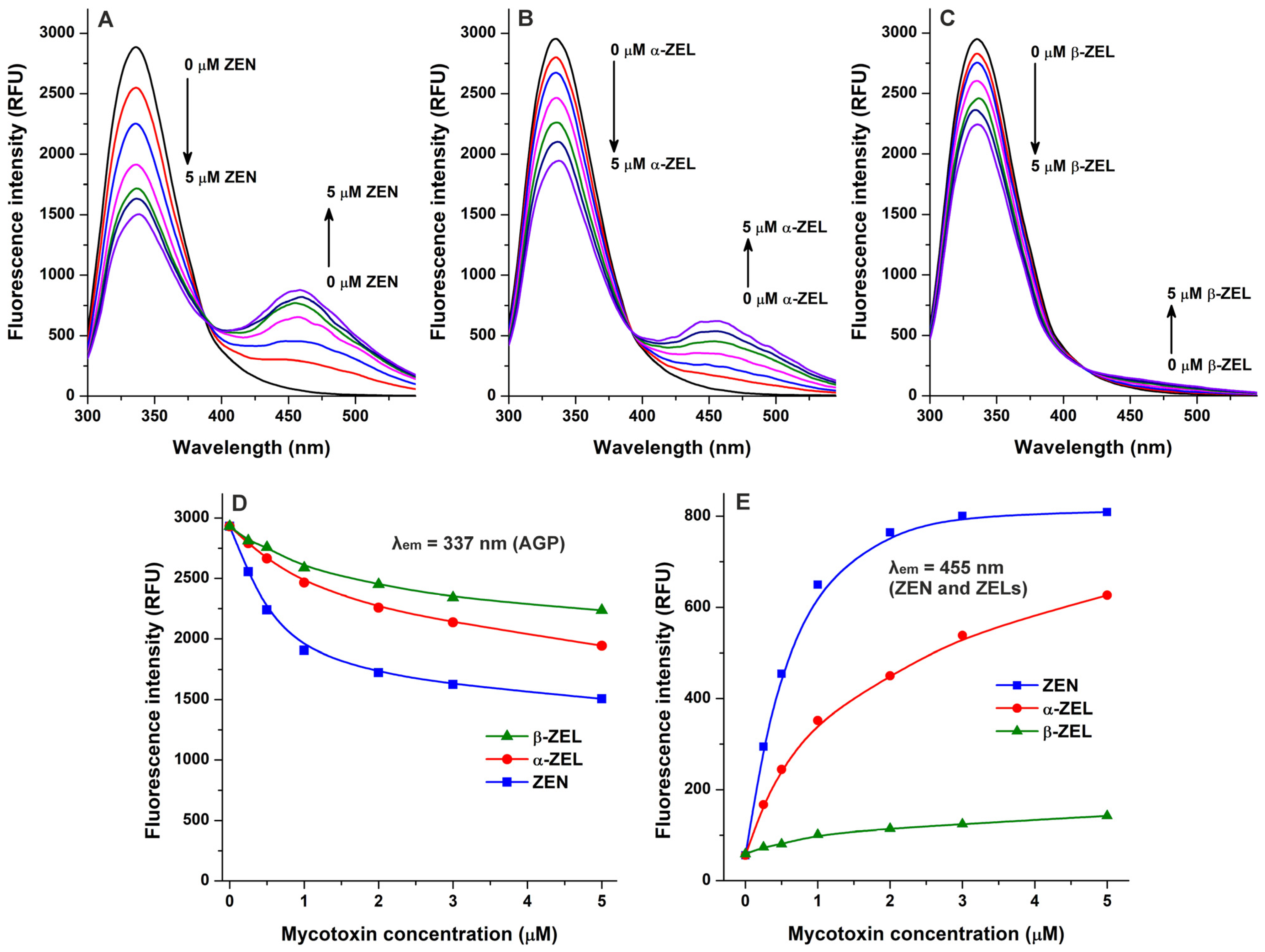
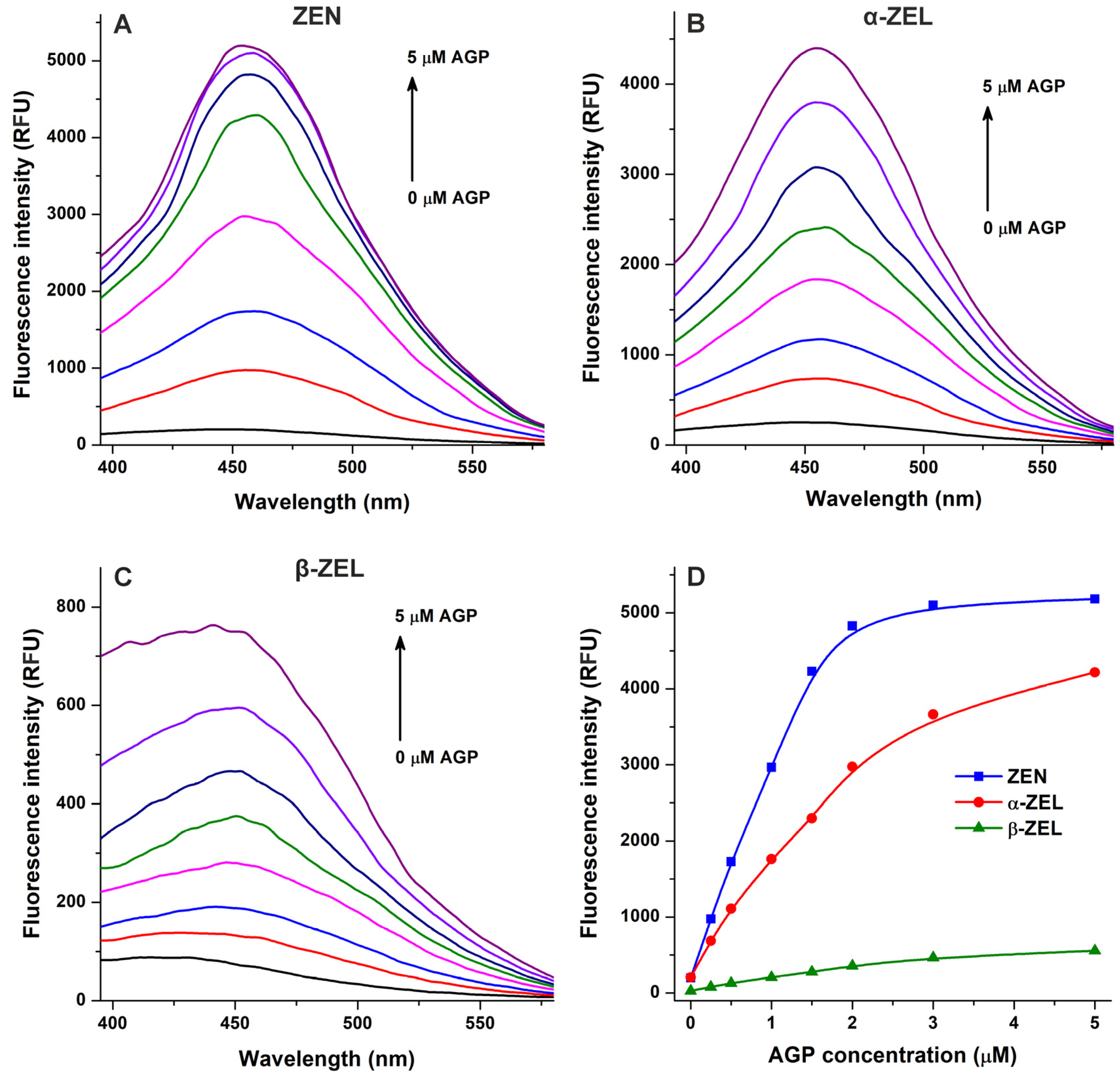
2.1. Interaction of Mycotoxins with α1-Acid Glycoprotein
2.2. Interaction of Mycotoxins with Milk Proteins
2.3. Limitations
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Fluorescence Spectroscopic Studies
4.3. Ultracentrifugation Studies
4.4. LC–MS Analyses of ZEN, α-ZEL, and β-ZEL
4.5. HPLC–UV Analyses
4.6. Molecular Modeling Studies
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFB1 | aflatoxin B1 |
| AFM1 | aflatoxin M1 |
| AGP | α1-acid glycoprotein |
| BSA | bovine serum albumin |
| CAS | casein |
| CIT | citrinin |
| CPA | cyclopiazonic acid |
| DON | deoxynivalenol |
| FB1 | fumonisin B1 |
| HSA | human serum albumin |
| LA | α-lactalbumin |
| LG | β-lactoglobulin |
| OTA | ochratoxin A |
| PAT | patulin |
| RFU | relative fluorescence unit |
| STC | sterigmatocystin |
| T2 | T-2 toxin |
| ZEN | zearalenone |
| α-ZEL | α-zearalenol |
| β-ZEL | β-zearalenol |
References
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escrivá, L.; Font, G.; Manyes, L. In vivo toxicity studies of fusarium mycotoxins in the last decade: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 78, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Flores, M.E.; Lizarraga, E.; López de Cerain, A.; González-Peñas, E. Presence of mycotoxins in animal milk: A review. Food Control 2015, 53, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker-Algeri, T.A.; Castagnaro, D.; de Bortoli, K.; de Souza, C.; Drunkler, D.A.; Badiale-Furlong, E. Mycotoxins in Bovine Milk and Dairy Products: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, R544–R552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidenbörner, M. Mycotoxins and Their Metabolites in Humans and Animals; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa, J.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ruiz, M.J.; Vila-Donat, P. Multi-mycotoxin occurrence in feed, metabolism and carry-over to animal-derived food products: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 158, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelberg, S.; Hult, K.; Fuchs, R. Toxicokinetics of ochratoxin A in several species and its plasma-binding properties. J. Appl. Toxicol. 1989, 9, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poor, M.; Li, Y.; Matisz, G.; Kiss, L.; Kunsagi-Mate, S.; Koszegi, T. Quantitation of species differences in albumin-ligand interactions for bovine, human and rat serum albumins using fluorescence spectroscopy: A test case with some Sudlow’s site I ligands. J. Lumin. 2014, 145, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, Z.; Lemli, B.; Szerencsés, D.; Kunsági-Máté, S.; Bálint, M.; Hetényi, C.; Kuzma, M.; Mayer, M.; Poór, M. Interactions of zearalenone and its reduced metabolites α-zearalenol and β-zearalenol with serum albumins: Species differences, binding sites, and thermodynamics. Mycotoxin Res. 2018, 34, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliszár-Nyúl, E.; Lemli, B.; Kunsági-Máté, S.; Dellafiora, L.; Dall’Asta, C.; Cruciani, G.; Pethő, G.; Poór, M. Interaction of mycotoxin alternariol with serum albumin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, Z.; Jan, K.; Vendula, S.; Jana, K.Z.; Kamil, M.; Kamil, K. Albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein: Old acquaintances. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Waters, N.J. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations for Drugs Binding to Alpha-1-Acid Glycoprotein. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Meletharayil, G.; Kapoor, R.; Abbaspourrad, A. Bioactives in bovine milk: Chemistry, technology, and applications. Nutr. Rev. 2021, 79, 48–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.F.; Uniacke-Lowe, T.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; O’Mahony, J.A. Milk Proteins. In Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 145–239. [Google Scholar]
- Indyk, H.E.; Gill, B.D.; Woollard, D.C. An optical biosensor-based immunoassay for the determination of bovine serum albumin in milk and milk products. Int. Dairy J. 2015, 47, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackett, R.E.; Marth, E.H. Association of aflatoxin M1 with casein. Z. Lebensm.-Unters. Und-Forsch. 1982, 174, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Pérez, C.; Tello-Solís, S.R.; Gómez-Castro, C.Z.; Alatorre-Santamaría, S.; Gómez-Ruiz, L.; Rodríguez-Serrano, G.; Cruz-Borbolla, J.; García-Garibay, M.; Cruz-Guerrero, A. Spectroscopic studies and molecular modelling of the aflatoxin M1-bovine α-lactalbumin complex formation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 209, 111957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, J.P.; Carlos, G.C.; Sergio, A.S.; Lorena, G.R.; Gabriela, R.S.; Mariano, G.G.; Alma, C.G. Evaluation of the pH effect on complex formation between bovine β-lactoglobulin and aflatoxin M1: A molecular dynamic simulation and molecular docking study. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 12133–12143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamkar, A.; Karim, G.; Aliabadi, F.S.; Khaksar, R. Fate of aflatoxin M1 in Iranian white cheese processing. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2236–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavarría, G.; Molina, A.; Leiva, A.; Méndez, G.; Wong-González, E.; Cortés-Muñoz, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Granados-Chinchilla, F. Distribution, stability, and protein interactions of Aflatoxin M1 in fresh cheese. Food Control 2017, 73, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliszár-Nyúl, E.; Faisal, Z.; Skaper, R.; Lemli, B.; Bayartsetseg, B.; Hetényi, C.; Gömbös, P.; Szabó, A.; Poór, M. Interaction of the Emerging Mycotoxins Beauvericin, Cyclopiazonic Acid, and Sterigmatocystin with Human Serum Albumin. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, D.W.; Walle, U.K.; Walle, T. Extensive binding of the bioflavonoid quercetin to human plasma proteins. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1998, 50, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poor, M.; Kunsagi-Mate, S.; Balint, M.; Hetenyi, C.; Gerner, Z.; Lemli, B. Interaction of mycotoxin zearalenone with human serum albumin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 2017, 170, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poor, M.; Zand, A.; Szente, L.; Lemli, B.; Kunsagi-Mate, S. Interaction of alpha- and beta-zearalenols with beta-cyclodextrins. Molecules 2017, 22, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, T.; Abrunhosa, L.; Domingues, L.; Venâncio, A.; Oliveira, C. BSA-based sample clean-up columns for ochratoxin A determination in wine: Method development and validation. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fliszár-Nyúl, E.; Szabó, Á.; Szente, L.; Poór, M. Extraction of mycotoxin alternariol from red wine and from tomato juice with beta-cyclodextrin bead polymer. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poor, M.; Balint, M.; Hetenyi, C.; Goder, B.; Kunsagi-Mate, S.; Koszegi, T.; Lemli, B. Investigation of Non-Covalent Interactions of Aflatoxins (B1, B2, G1, G2, and M1) with Serum Albumin. Toxins 2017, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Javed, S. Aflatoxin B1Induced Structural and Conformational Changes in Bovine Serum Albumin: A Multispectroscopic and Circular Dichroism-Based Study. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 18054–18064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kandeel, S.A.; Megahed, A.A.; Ebeid, M.H.; Constable, P.D. Ability of milk pH to predict subclinical mastitis and intramammary infection in quarters from lactating dairy cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landin, E.J.B.; Williams, C.; Ryan, S.A.; Bochel, A.; Akter, N.; Redfield, C.; Sessions, R.B.; Dedi, N.; Taylor, R.J.; Crump, M.P. The structural basis for high affinity binding of α1-acid glycoprotein to the potent antitumor compound UCN-01. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Ruth, H.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Software news and updates AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsidó, B.Z.; Börzsei, R.; Pintér, E.; Hetényi, C. Prerequisite binding modes determine the dynamics of action of covalent agonists of ion channel trpa1. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
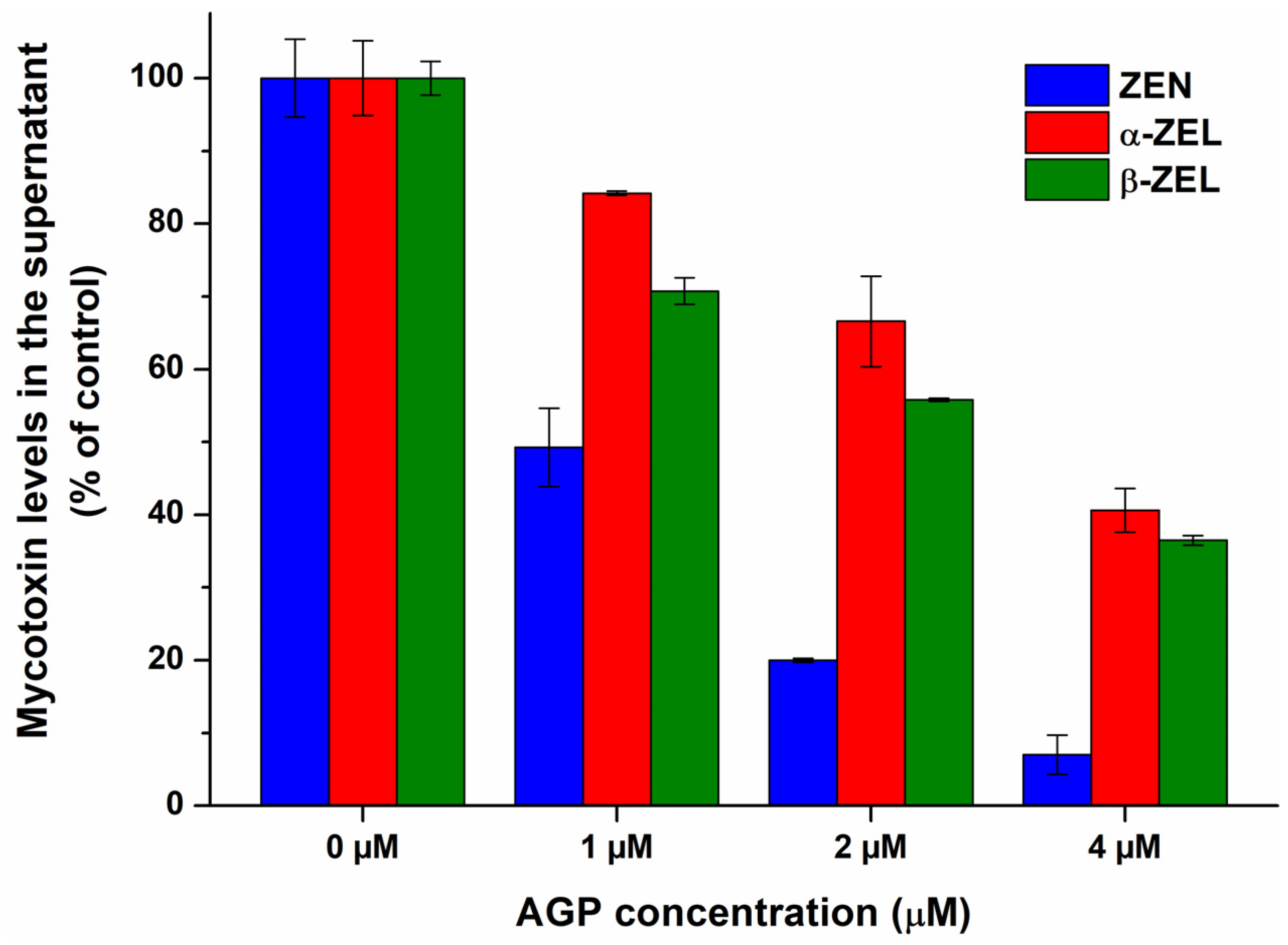

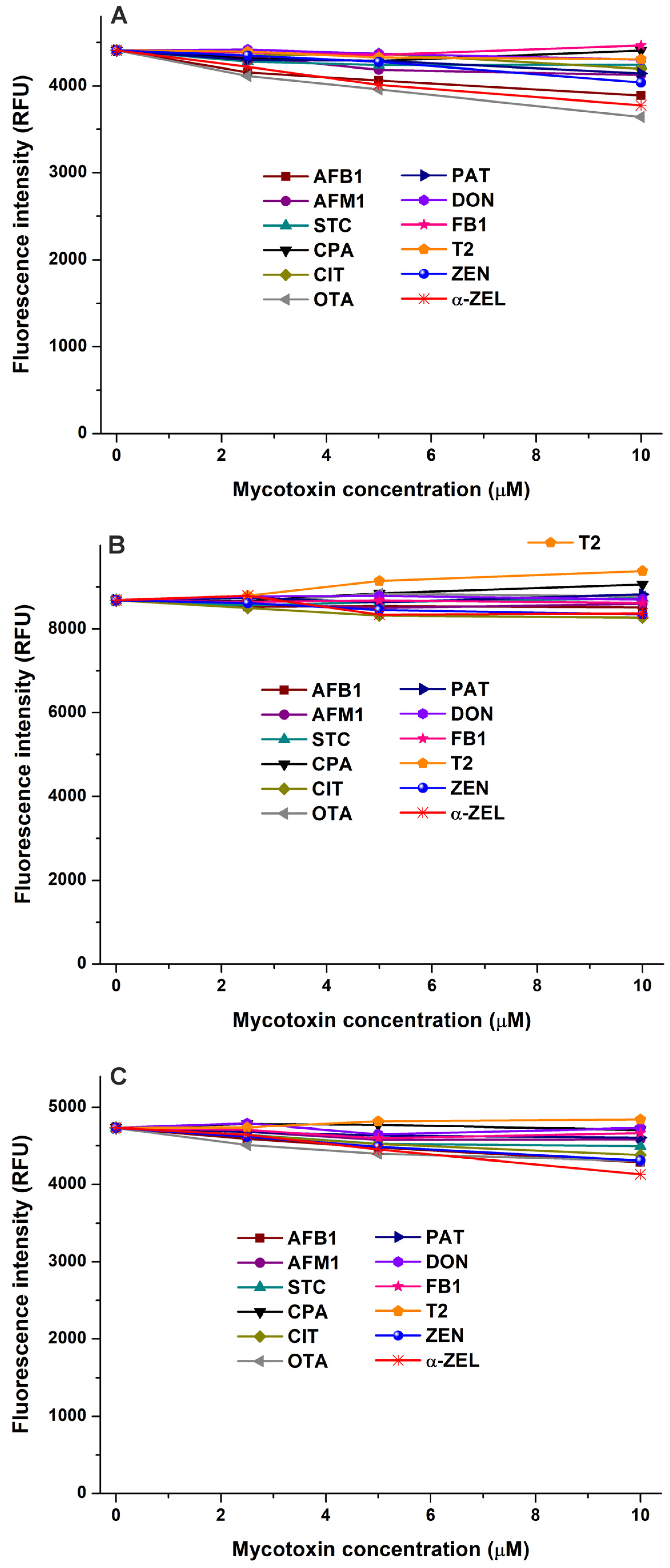
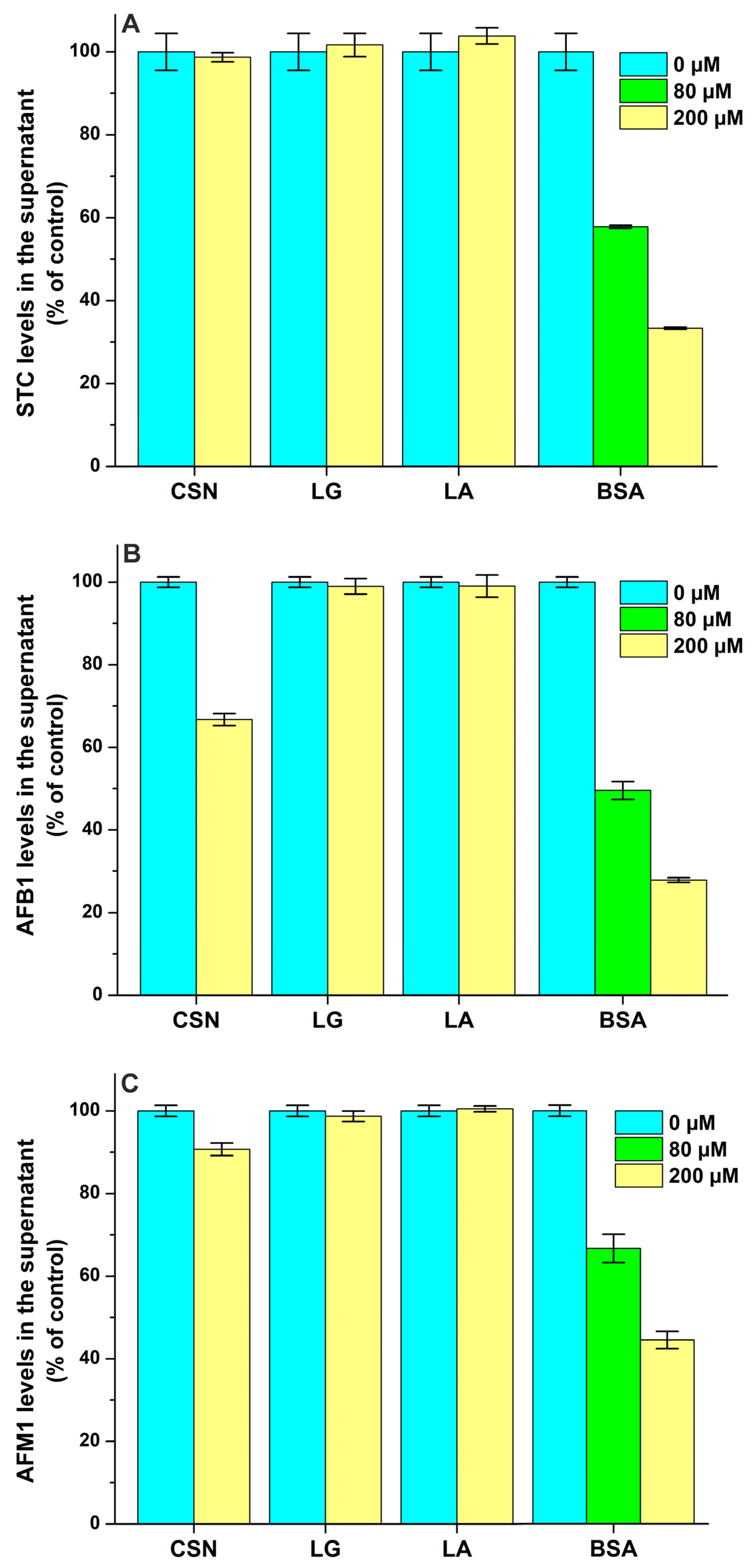
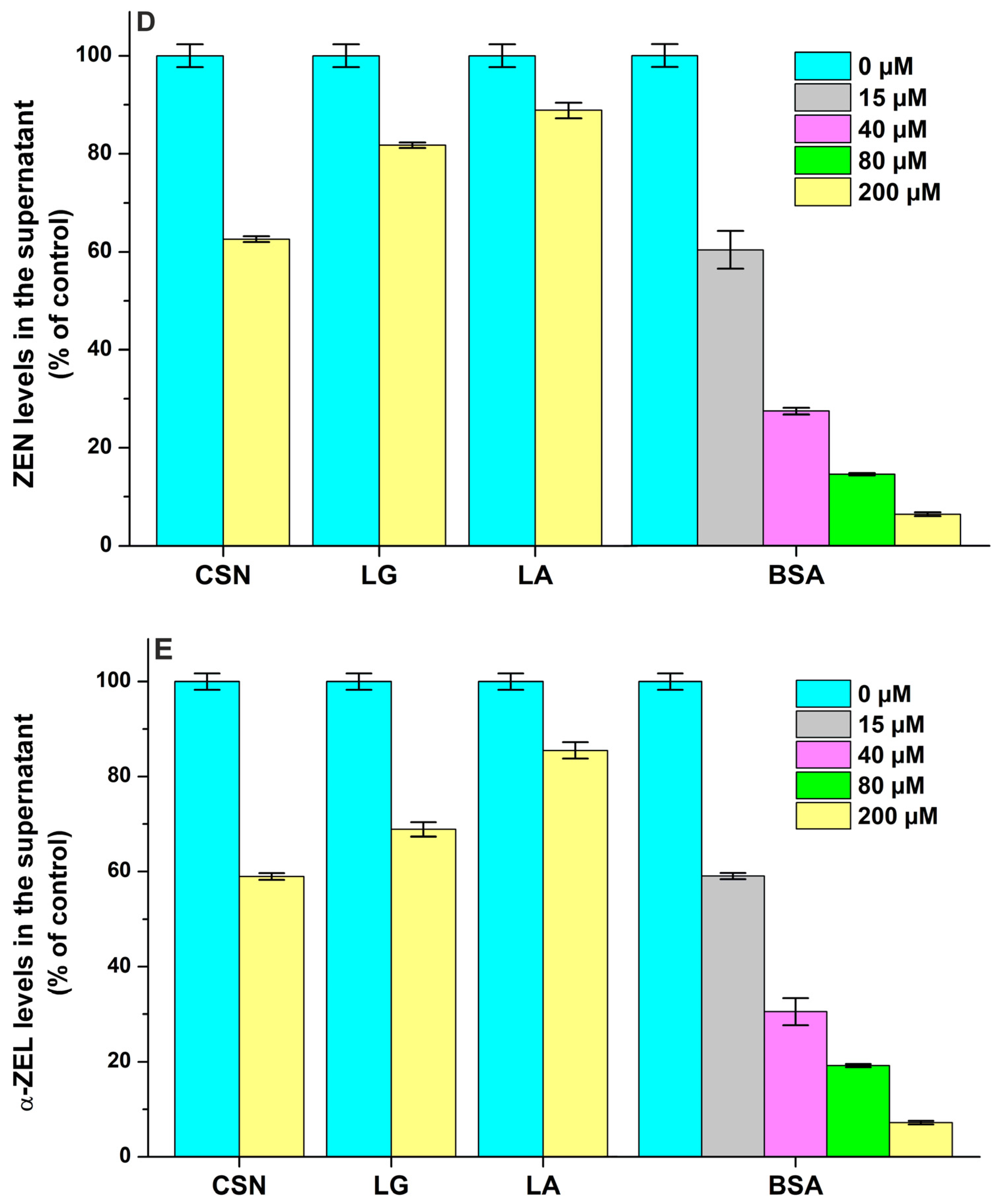
| Mycotoxin–Protein Complex | logK FL Quenching | logK FL Enhancement | logK Ultracentrifugation |
|---|---|---|---|
| STC–AGP | 5.85 ± 0.01 | – | 5.55 ± 0.02 |
| ZEN–AGP | 5.90 ± 0.05 | 6.28 ± 0.06 | 6.43 ± 0.06 |
| α-ZEL–AGP | 5.65 ± 0.04 | 5.51 ± 0.05 | 5.48 ± 0.07 |
| β-ZEL–AGP | 5.78 ± 0.02 | 5.94 ± 0.06 | 5.73 ± 0.02 |
| CSN | LG | LA | BSA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STC | – | – | – | 3.98 ± 0.01 |
| AFB1 | 3.34 ± 0.03 | – | – | 4.11 ± 0.02 |
| AFM1 | 2.70 ± 0.08 | – | – | 3.80 ± 0.03 |
| ZEN | 3.48 ± 0.01 | 3.05 ± 0.02 | 2.79 ± 0.08 | 4.79 ± 0.05 |
| α-ZEL | 3.54 ± 0.01 | 3.35 ± 0.03 | 2.92 ± 0.06 | 4.73 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poór, M.; Gömbös, P.; Szabó, A.; Zsidó, B.Z.; Hetényi, C.; Huber, T.; Lukács, A.; Kunsági-Máté, S. Interaction of Mycotoxins with α1-Acid Glycoprotein (AGP) and Bovine Milk Proteins: Zearalenone, Zearalenols, and Sterigmatocystin Form Highly Stable Complexes with AGP. Toxins 2025, 17, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040151
Poór M, Gömbös P, Szabó A, Zsidó BZ, Hetényi C, Huber T, Lukács A, Kunsági-Máté S. Interaction of Mycotoxins with α1-Acid Glycoprotein (AGP) and Bovine Milk Proteins: Zearalenone, Zearalenols, and Sterigmatocystin Form Highly Stable Complexes with AGP. Toxins. 2025; 17(4):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040151
Chicago/Turabian StylePoór, Miklós, Patrik Gömbös, András Szabó, Balázs Zoltán Zsidó, Csaba Hetényi, Tamás Huber, András Lukács, and Sándor Kunsági-Máté. 2025. "Interaction of Mycotoxins with α1-Acid Glycoprotein (AGP) and Bovine Milk Proteins: Zearalenone, Zearalenols, and Sterigmatocystin Form Highly Stable Complexes with AGP" Toxins 17, no. 4: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040151
APA StylePoór, M., Gömbös, P., Szabó, A., Zsidó, B. Z., Hetényi, C., Huber, T., Lukács, A., & Kunsági-Máté, S. (2025). Interaction of Mycotoxins with α1-Acid Glycoprotein (AGP) and Bovine Milk Proteins: Zearalenone, Zearalenols, and Sterigmatocystin Form Highly Stable Complexes with AGP. Toxins, 17(4), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17040151








