Abstract
Oxaliplatin, a chemotherapeutic drug for colorectal cancer, induces severe peripheral neuropathy. Bee venom acupuncture (BVA) has been used to attenuate pain, and its effect is known to be mediated by spinal noradrenergic and serotonergic receptors. Morphine is a well-known opioid used to treat different types of pain. Here, we investigated whether treatment with a combination of these two agents has an additive effect on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain in mice. To assess cold and mechanical allodynia, acetone and von Frey filament tests were used, respectively. Significant allodynia signs were observed three days after an oxaliplatin injection (6 mg/kg, i.p.). BVA (0.25, 1, and 2.5 mg/kg, s.c., ST36) or morphine (0.5, 2, and 5 mg/kg, i.p.) alone showed dose-dependent anti-allodynic effects. The combination of BVA and morphine at intermediate doses showed a greater and longer effect than either BVA or morphine alone at the highest dose. Intrathecal pretreatment with the opioidergic (naloxone, 20 μg) or 5-HT3 (MDL-72222, 15 μg) receptor antagonist, but not with α2-adrenergic (idazoxan, 10 μg) receptor antagonist, blocked this additive effect. Therefore, we suggest that the combination effect of BVA and morphine is mediated by spinal opioidergic and 5-HT3 receptors and this combination has a robust and enduring analgesic action against oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain.
1. Introduction
Oxaliplatin is a third-generation platinum-based chemotherapy drug commonly used for colorectal cancer [1], which is the third most common cancer in men and the second most common cancer in women worldwide [2]. It is widely used as there are no nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity symptoms, unlike after the use of other platinum based drugs, such as cisplatin and carboplatin [3,4]. However, it causes peripheral neuropathy characterized by dysesthesias of the hands and feet, which is a major dose-limiting side effect. Even a single administration of oxaliplatin can evoke this abnormal sensation [5,6]. About 90% of oxaliplatin-treated patients rapidly develop significant pain without motor dysfunction during or shortly after a single infusion, peaking at the first 24–48 h [7]. Efforts are underway to determine an efficacious treatment, but currently, an optimal treatment without major side effects is not available [8,9]. Therefore, an effort to determine novel therapeutic options is urgently needed.
Bee venom acupuncture (BVA) is a treatment method that involves injecting diluted bee venom into acupoints, and it has been used in Korean medicine to treat various diseases, such as cervical disc protrusion [10], progressive muscle atrophy [11], idiopathic Parkinson’s disease [12], and cancer [13] in humans and animals. In addition, it has been traditionally used to alleviate pain, like arthritis pain [14] and musculoskeletal pain [15], and the results of a clinical trial have suggested that BVA can be effective in chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) [16]. Recent experimental studies performed in our laboratory have demonstrated that it effectively attenuates peripheral neuropathic pain induced by a single injection of oxaliplatin [17,18]. Unlike electroacupuncture, in which the analgesic effect is mediated via opioids as well as other various receptors [19,20], the analgesic actions of BVA have been reported to be mediated by the descending pain inhibitory system, involving spinal noradrenergic and serotonergic receptors, but not opioidergic receptors [17,21,22].
Morphine is a well-known analgesic drug and its effect is most likely mediated via opioid receptors [23]. However, whether it can efficaciously attenuate neuropathic pain is still a controversial issue. Previous studies have reported that neuropathic pain might be resistant or less responsive to opioids than nociceptive pain and higher dosages of opioidergic agents are required to evoke the same pain-relieving effects [24,25,26]. However, the American Society of Clinical Oncology still does not provide recommendations regarding the use of opioids for the treatment of CIPN [27]. Nonetheless, some articles have reported that morphine effectively attenuates neuropathic pain [28], and furthermore, that morphine can significantly suppress the neuropathic pain induced by a single injection of oxaliplatin in rats [29], suggesting that morphine might be effective in CIPN. These results let us speculate that the combination treatment of BVA and morphine might have an additive effect, as the analgesic effect of BVA is mediated by spinal noradrenergic and/or serotonergic receptors, and the effect of morphine is mediated by opioidergic receptors.
In this article, firstly, we investigated whether and to what extent BVA or morphine administered alone at different doses can attenuate oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia in mice, and secondly, we assessed whether the combination treatment of these two mechanistically distinct analgesic treatment strategies can improve analgesic efficacy compared to the use of one agent alone. Finally, we determined which spinal receptors were involved in mediating the effects of the combined BVA and morphine treatment.
2. Results
2.1. Induction of Cold and Mechanical Allodynia by a Single Intraperitoneal Administration of Oxaliplatin in Mice
Single administration of oxaliplatin (6 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly increased the frequencies of licking and shaking of the hind paw in response to cold acetone stimuli (10 μL), from 3 to 5 days after the injection, compared to the vehicle injected group (Figure 1a). Also, single administration of oxaliplatin significantly increased the withdrawal responses of the hind paw to von Frey filament (0.4 g bending force) application (expressed as percentage of paw withdrawals) at day 3, and they were maintained up to day 7 (Figure 1b). We interpreted these results as a sign of cold and mechanical allodynia as they indicate that mice in the experimental group developed significant hypersensitivity to cold and mechanical stimuli. Treatment with 5% glucose as control, had no effect on cold and mechanical sensitivity (Figure 1). These results are in accordance with other articles, where a single injection of oxaliplatin induced allodynia in rodents [29,30].
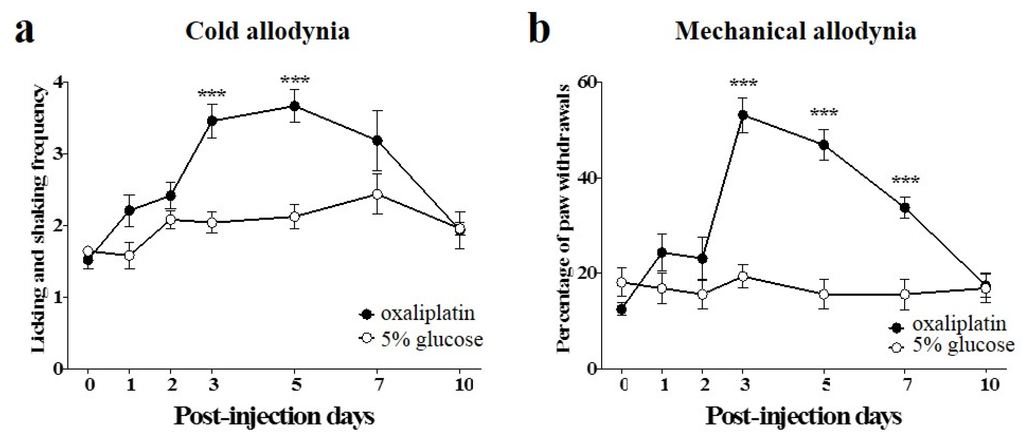
Figure 1.
Time courses of cold and mechanical allodynia induced by a single injection of oxaliplatin in mice. (a,b) Behavioral tests for cold and mechanical allodynia were performed before (day point zero) and after the administration of oxaliplatin (6 mg/kg, i.p.). 5% glucose was used as control and was injected intraperitoneally. Cold and mechanical allodynia were assessed by the acetone and von Frey filament tests, respectively. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. for 8 mice; *** p < 0.001 vs. 5% glucose, by unpaired t-test.
Figure 1.
Time courses of cold and mechanical allodynia induced by a single injection of oxaliplatin in mice. (a,b) Behavioral tests for cold and mechanical allodynia were performed before (day point zero) and after the administration of oxaliplatin (6 mg/kg, i.p.). 5% glucose was used as control and was injected intraperitoneally. Cold and mechanical allodynia were assessed by the acetone and von Frey filament tests, respectively. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M. for 8 mice; *** p < 0.001 vs. 5% glucose, by unpaired t-test.
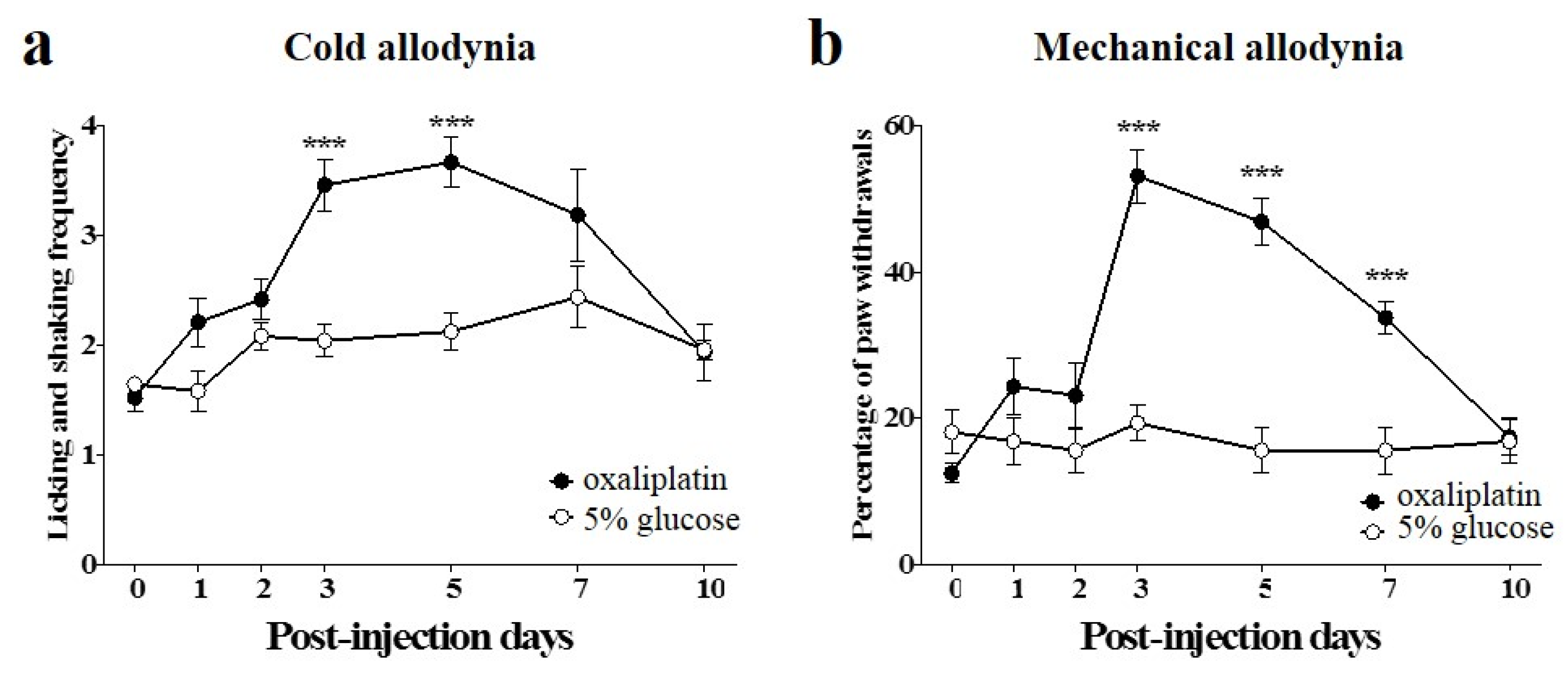
2.2. Time Course of Dose-Dependent Effects of BVA or Morphine on Oxaliplatin-Induced Cold and Mechanical Allodynia in Mice
The anti-allodynic effects of different doses of BVA (s.c., ST36 acupoint) or morphine (i.p.) are shown in Figure 2. All assessments were conducted three days after the injection of oxaliplatin, when cold and mechanical allodynia were significantly induced. To observe the time course of the effects, evaluations were conducted at time point zero (before the administration of BVA or morphine), and at 30, 60, 90, and 180 min after the initiation of the treatments. The effects of BVA on cold and mechanical allodynia are shown in Figure 2a,b. The medium and highest doses of BVA (1 and 2.5 mg/kg) exhibited similar relieving effects, lasting until 90 min after the injection, for both cold and mechanical allodynia, although the highest dose of BVA appeared to have a slightly greater suppressive effect. The effect of a lower dose (0.25 mg/kg) of BVA was less significant compared to that in the 1 or 2.5 mg/kg treated groups. Among the mice treated with three different doses of BVA, some of the mice in the 2.5 mg/kg treated group only showed swelling at the injected area.
A single injection of morphine also produced dose-dependent inhibitory effects on oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia (Figure 2c,d). In the acetone test, only the high dose (5 mg/kg) of morphine had a significant anti-allodynic effect at 30 min after the treatment, and the 0.5 and 2 mg/kg doses had no significant effect compared to that in the control group. In the von Frey filament test, the analgesic effect of the medium dose of morphine (2 mg/kg) was observable only at 60 min after the treatment, and the effect of the 5 mg/kg dose lasted longer (90 min) than the effect of the 2 mg/kg dose. Neither of the effects of these remained until 180 min. The lowest dose (0.5 mg/kg) of morphine had no significant effect on both cold and mechanical allodynia.
2.3. Time Course of Combined Effects of BVA and Morphine on Oxaliplatin-Induced Cold and Mechanical Allodynia in Mice
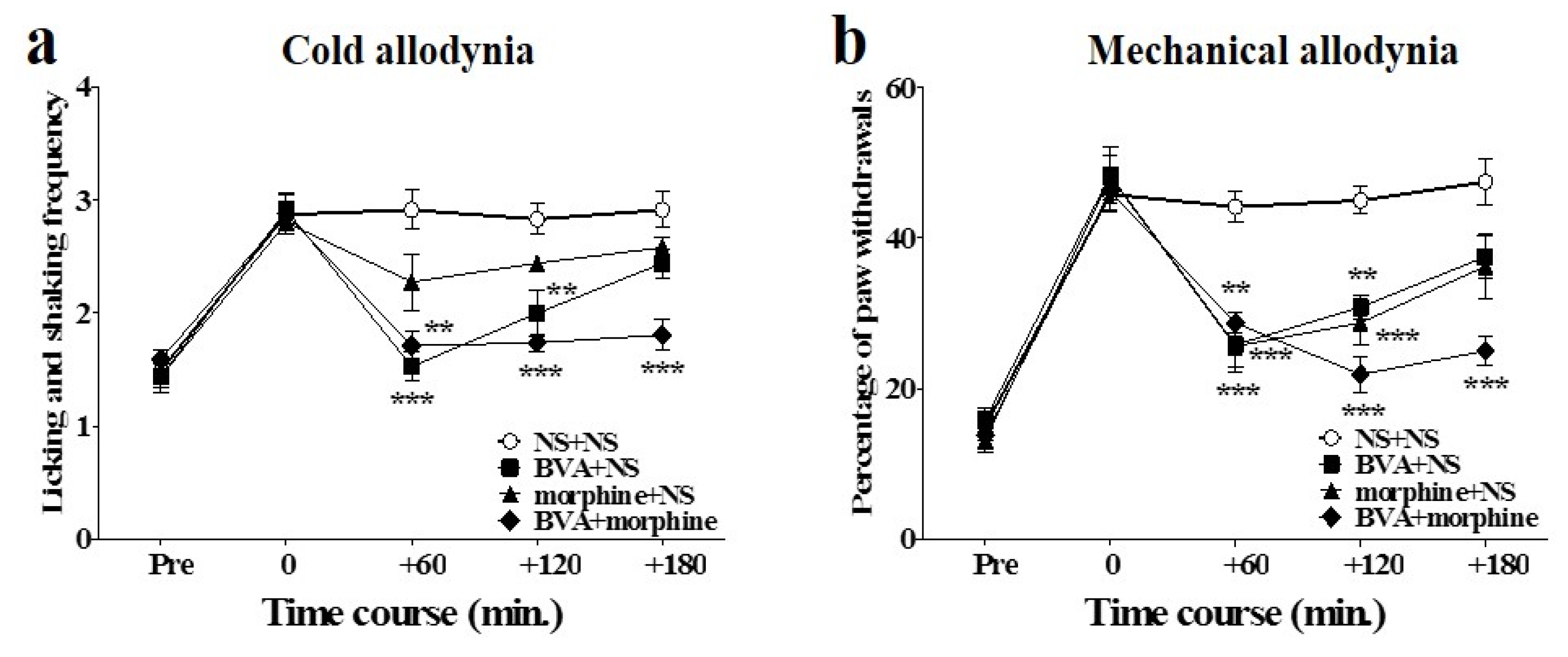
The combined effects of BVA and morphine on oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia in mice are shown in Figure 3. Intermediate doses of BVA (1 mg/kg, s.c., ST36) and morphine (2 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered simultaneously. The anti-allodynic effect of the combined administration of BVA and morphine was stronger and lasted longer than the effect of the combination of BVA or morphine with NS (i.e., NS + NS, BVA + NS, and morphine + NS) on both cold and mechanical allodynia. In the acetone test, BVA with NS had a strong effect at the beginning (60 min), but its analgesic effect disappeared at 180 min after administration. Morphine with NS did not have any significant analgesic effect. Combination of BVA and morphine had a longer lasting effect than that in the other groups (Figure 3a). In the von Frey filament test, both morphine with NS and BVA with NS had significant effects that lasted until 120 min after the treatment. However, these effects were less significant than the effect of the combination treatment, which lasted until 180 min (Figure 3b).
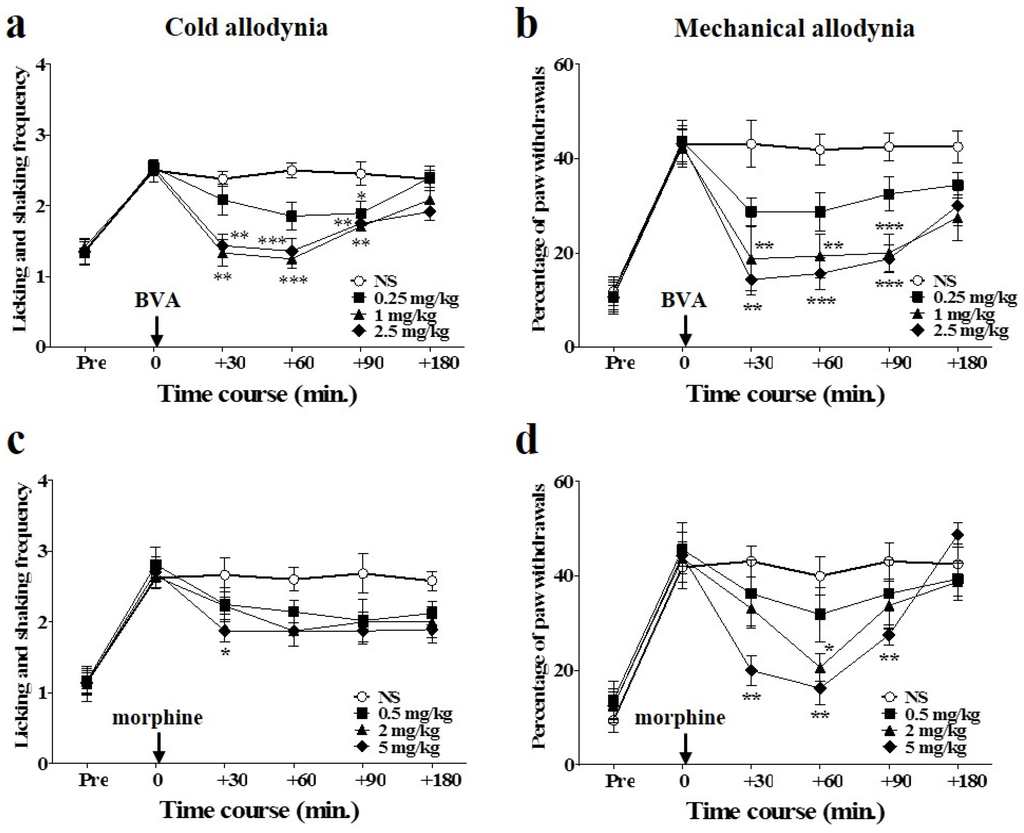
Figure 2.
Time course of dose-dependent effects of BVA or morphine on oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia in mice. (a,b) Time course and dose response of BVA for cold and mechanical allodynia. Normal saline (NS, control) and three different doses of BVA (0.25, 1, and 2.5 mg/kg) were subcutaneously administered at ST36 acupoint (n = 8/group). (c,d) Time course and dose response of morphine for cold and mechanical allodynia. NS and three different doses of morphine (0.5, 2, and 5 mg/kg) were injected intraperitoneally (n = 8/group). “Pre” refers to the assessment made before the injection of oxaliplatin. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M.; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. NS by Bonferroni post-test after one-way ANOVA.
Figure 2.
Time course of dose-dependent effects of BVA or morphine on oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia in mice. (a,b) Time course and dose response of BVA for cold and mechanical allodynia. Normal saline (NS, control) and three different doses of BVA (0.25, 1, and 2.5 mg/kg) were subcutaneously administered at ST36 acupoint (n = 8/group). (c,d) Time course and dose response of morphine for cold and mechanical allodynia. NS and three different doses of morphine (0.5, 2, and 5 mg/kg) were injected intraperitoneally (n = 8/group). “Pre” refers to the assessment made before the injection of oxaliplatin. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M.; * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. NS by Bonferroni post-test after one-way ANOVA.
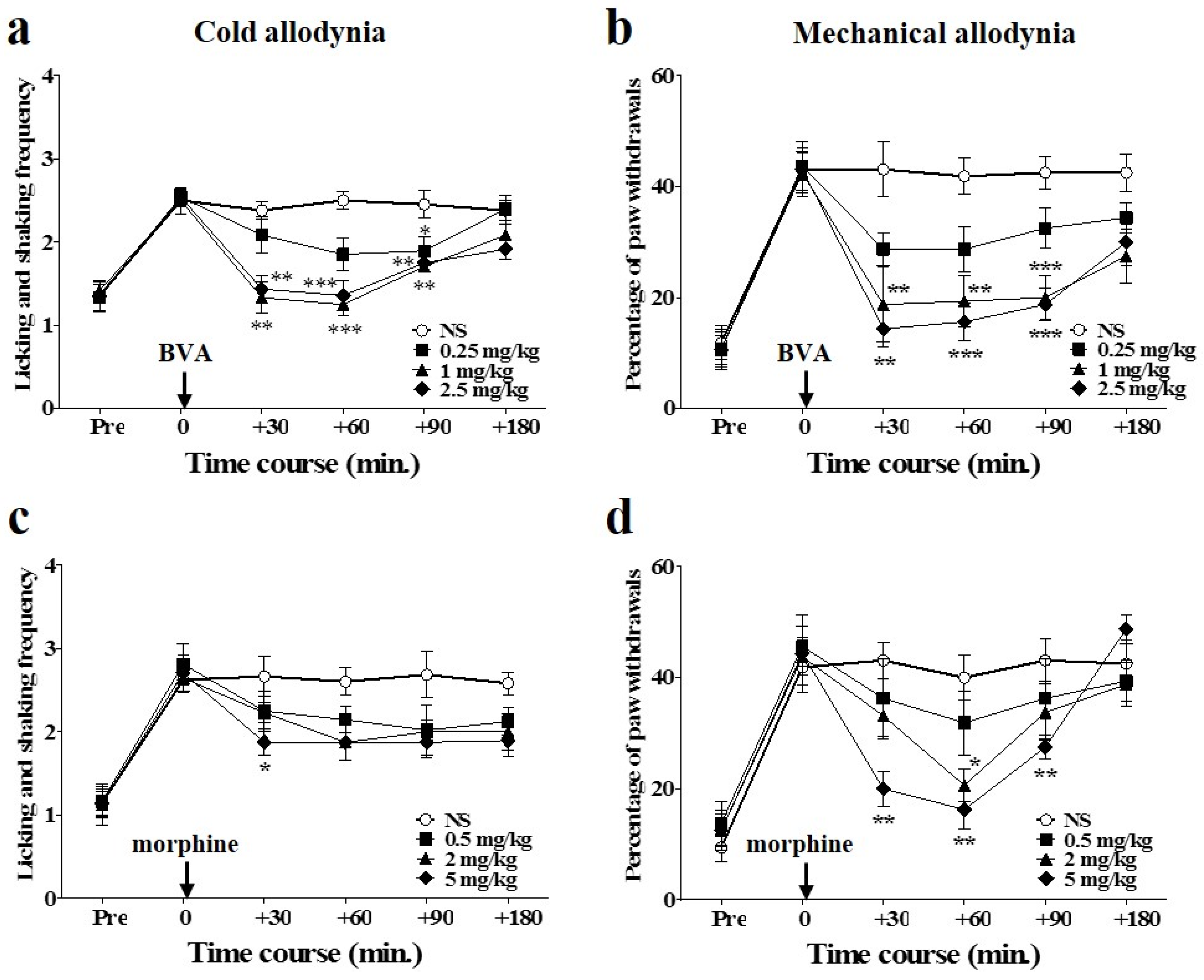
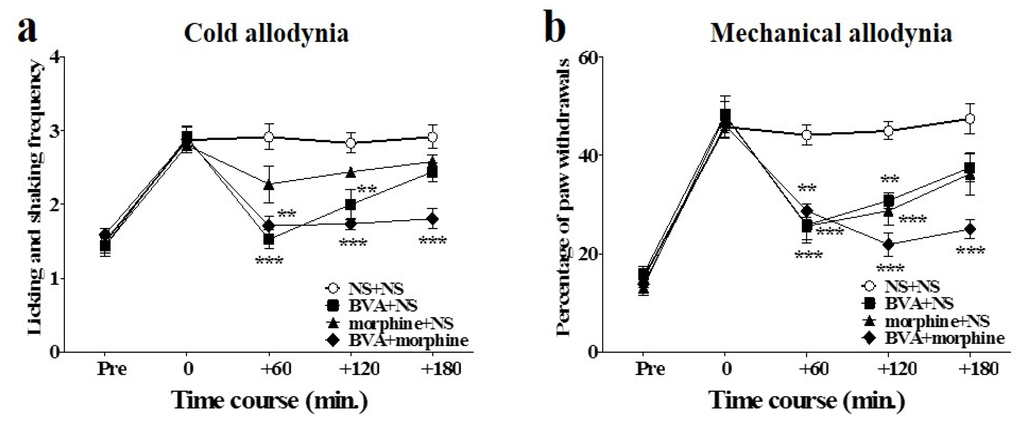
Figure 3.
Time course of the effect of combined administration of BVA and morphine on oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia in mice. BVA (1 mg/kg, s.c., ST36) and morphine (2 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered simultaneously. Effect on cold (n = 6–8/group) (a) and mechanical (n = 6–8/group) (b) allodynia were assessed using the acetone and von Frey filament test, respectively. NS was administered subcutaneously at ST36, when used with morphine, and administered intraperitoneally when used with BVA. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M.; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control (NS + NS); by Bonferroni post-test after one-way ANOVA.
Figure 3.
Time course of the effect of combined administration of BVA and morphine on oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia in mice. BVA (1 mg/kg, s.c., ST36) and morphine (2 mg/kg, i.p.) were administered simultaneously. Effect on cold (n = 6–8/group) (a) and mechanical (n = 6–8/group) (b) allodynia were assessed using the acetone and von Frey filament test, respectively. NS was administered subcutaneously at ST36, when used with morphine, and administered intraperitoneally when used with BVA. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M.; ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control (NS + NS); by Bonferroni post-test after one-way ANOVA.
2.4. Involvement of Spinal Opioidergic and 5-HT3 Receptors but not of α2-Adrenergic Receptors in the Combination Effect of BVA and Morphine on Oxaliplatin-Induced Allodynia in Mice
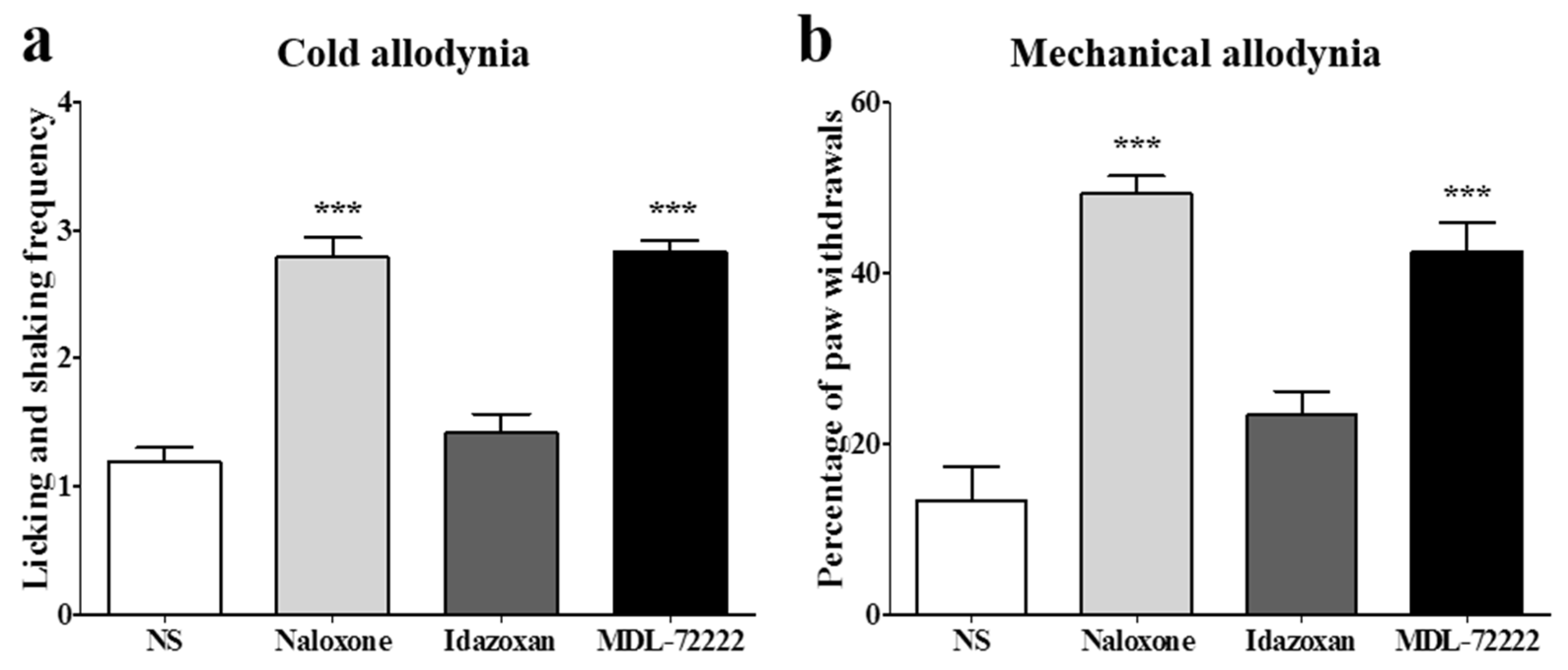
To clarify the analgesic mechanism of combined BVA and morphine administration at the spinal cord level, opioidergic, noradrenergic, and serotonergic antagonists were injected intrathecally 20 min before the treatment. Naloxone (opioid antagonist, 20 μg), idazoxan (α2-adrenergic antagonist, 10 μg), or MDL-72222 (5-HT3 receptor antagonist, 15 μg) was administered in a volume of 5 μL, and the same volume of NS was used for control. Idazoxan, similar to the NS treated group, did not block the anti-allodynic effect of the combined administration of BVA and morphine, showing that spinal α2-adrenergic receptors are not involved in the analgesic effect of BVA and morphine. In contrast, the naloxone pretreated group or the MDL-72222 pretreated group significantly blocked the analgesic effect of BVA and morphine, indicating that spinal opioidergic and 5-HT3 receptors may play a crucial role in the suppressive effect of BVA and morphine on oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia in mice (Figure 4). In each group, mice showed elevated cold and mechanical allodynia signs before the administration of each antagonist (cold-licking and shaking frequency: NS 3.05 ± 0.43; naloxone 3.02 ± 0.29; idazoxan 2.83 ± 0.45; MDL-72222 2.72 ± 0.20, mechanical-percentage of paw withdrawals: NS 46.66 ± 6.05; naloxone 46.42 ± 5.56; idazoxan 49.16 ± 3.76; MDL-72222 46.66 ± 6.83).
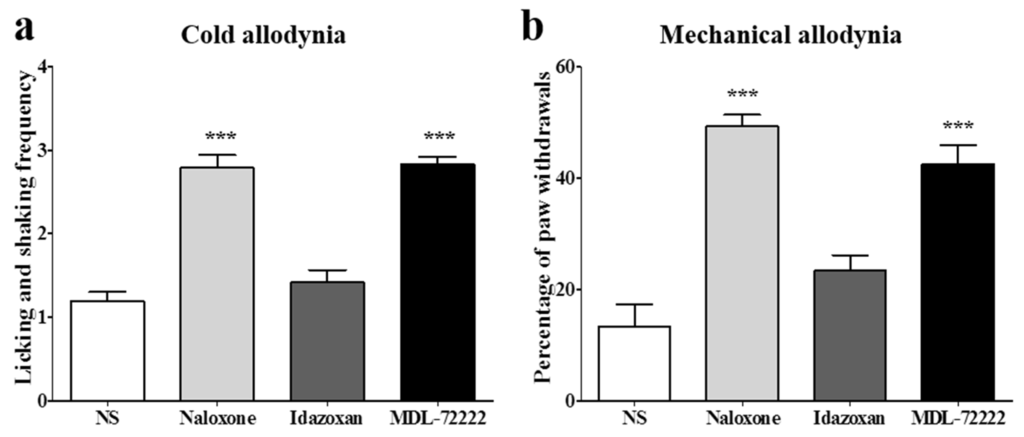
Figure 4.
Involvement of spinal opioidergic and 5-HT3, but not of α2-adrenergic receptors, in the combination effect of BVA and morphine on oxaliplatin-induced allodynia in mice. The behavioral tests for cold (a) and mechanical (b) allodynia were performed. Twenty min after the pretreatment with antagonists, BVA (1 mg/kg) and morphine (2 mg/kg) were administered. Assessment was made 60 min after the BVA and morphine treatment. NS (i.t., n = 6). Naloxone (20 μg, i.t., n = 7). Idazoxan (10 μg, i.t., n = 6). MDL-72222 (15 μg, i.t., n = 6). Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M.; *** p < 0.001 vs. NS; by Bonferroni post-test after one-way ANOVA.
Figure 4.
Involvement of spinal opioidergic and 5-HT3, but not of α2-adrenergic receptors, in the combination effect of BVA and morphine on oxaliplatin-induced allodynia in mice. The behavioral tests for cold (a) and mechanical (b) allodynia were performed. Twenty min after the pretreatment with antagonists, BVA (1 mg/kg) and morphine (2 mg/kg) were administered. Assessment was made 60 min after the BVA and morphine treatment. NS (i.t., n = 6). Naloxone (20 μg, i.t., n = 7). Idazoxan (10 μg, i.t., n = 6). MDL-72222 (15 μg, i.t., n = 6). Data are presented as the mean ± S.E.M.; *** p < 0.001 vs. NS; by Bonferroni post-test after one-way ANOVA.
3. Discussion
Peripheral neuropathy occurring soon after the administration of oxaliplatin is a serious side effect that limits the use of the drug. Anticonvulsants and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors are recommended as first-line treatments, but even these drugs can cause side effects, such as sedation, dizziness, and cardiac complications. Thus, there is a need for better therapeutic options [31,32].
BVA is a therapeutic method generally used in Korea. It has been reported to effectively attenuate neuropathic pain in different animal models via noradrenergic and/or serotonergic pathways [17,18,33], and the results of a clinical trial have demonstrated that BVA can be efficacious in CIPN [16]. Morphine, although polemics exist [24,25,26], has been demonstrated to significantly alleviate neuropathic pain [28,34] and oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy [29]. These results let us hypothesize that BVA, along with morphine, might be effective for oxaliplatin-induced cold and mechanical allodynia.
In this article, firstly, we observed the time course and dose response of the separate BVA and morphine effect on oxaliplatin-induced allodynia in mice. BVA doses of 1 and 2.5 mg/kg had a statistically significant effect on both cold and mechanical allodynia. However, a high dose of BVA induced a side effect (i.e., swelling at the injected area) in a subset of mice as observed in our previous study [17], suggesting that a BVA dose of 1 mg/kg is the most effective dose without any side effects, as reported in another article [21]. In our experiments, 0.25 mg/kg dose of BVA had a less significant effect than 1 or 2.5 mg/kg dose of BVA, unlike the previous data, where the lowest dose of BVA (0.25 mg/kg) had a greater effect than higher doses (1 or 2.5 mg/kg) [17]. This discrepancy may be due to the differences in the area of behavioral test (hind paw vs. tail), location of acupoint (ST36 vs. GV3), and animal strain (mice vs. rats). In addition, we found that morphine dose-dependently attenuated the allodynia elicited by oxaliplatin in mice. Its analgesic effects were greater on mechanical allodynia than on cold allodynia. In the acetone test for cold allodynia, only the 5 mg/kg treated group showed a significant decrease in allodynia at 30 min after the treatment. In the von Frey filament test, both the 2 and 5 mg/kg doses significantly attenuated allodynia, but these effects were not maintained until 180 min after the injection. Although no behavioral oddity such as sedation was observed in the 5 mg/kg group in these experiments, an article reported that a statistically significant reduction in spontaneous locomotor activity was observed in 5 mg/kg of morphine injected mice [35].
Secondly, we demonstrated that the combination treatment of medium doses of BVA (1 mg/kg) and morphine (2 mg/kg) can markedly reduce cold and mechanical allodynia induced by a single injection of oxaliplatin in mice. The combination treatment of BVA and morphine had an analgesic effect that lasted longer (180 min) than the effect of the highest doses of BVA or morphine (2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg, respectively). Furthermore, no side effect such as swelling was observed unlike in mice injected with the highest dose of BVA. Thus, we propose that the combination of medium doses of BVA and morphine can be an effective treatment method, without any side effects, in oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain.
Thirdly, in the following study, which was conducted to clarify the mechanism of the analgesic effect of the combined treatment of BVA and morphine, opioid and 5-HT3 receptors but not α2-adrenergic receptors were found to mediate the effect at the spinal level. These results were somewhat unexpected because, hitherto, only a limited number of studies have concentrated on the role of serotonergic receptors [22], compared to the numerous articles that have focused on α2-adrenergic receptors [21,36,37,38,39], and the analgesic pathways of BVA in various types of pain. However, experiments conducted in our laboratory demonstrated that intrathecal injections of noradrenergic antagonists partially blocked the analgesic effects of BVA on oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia in rats [17], whereas serotonergic antagonists completely blocked the effects [18]. Thus, it can be suggested that the serotonergic analgesic system rather than the noradrenergic system plays an important role in the effect of BVA, at least on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain.
As mentioned in the “Introduction” section, BVA and morphine have been known to modulate two distinct analgesic pathways: BVA via noradrenergic and/or serotonergic receptors [22], and morphine via opioidergic receptors [23]. However, in our results, pre-treatment with naloxone or MDL-72222 completely, not partially, blocked the analgesic effect of the combined treatment of BVA and morphine. Although we could not understand all the details of the process, these results let us speculate that other pathways may be involved in the analgesic effect of the combination treatment of BVA and morphine. Actually, complex interrelationships between opioid and serotonergic systems at the spinal or supraspinal level have been suggested. For example, it has been suggested that enkephalinergic dorsal horn neurons express 5-HT3 receptors, and that at least some part of the analgesia produced by 5-HT at the spinal level is due to 5-HT3 receptors located on the intrinsic neurons in the dorsal horn [40,41]. Some articles supported this suggestion by demonstrating that the analgesic effect of intrathecally administered 5-HT3 receptor agonist 2-methylserotonin was attenuated by the opioid antagonist naloxone [42,43]. Furthermore, microinjection of morphine into the periaqueductal gray has been found to evoke the release of serotonin from the spinal cord [44].
In conclusion, intermediate doses of BVA (1 mg/kg) and morphine (2 mg/kg), when administered simultaneously, significantly attenuated cold and mechanical allodynia induced by a single administration of oxaliplatin in mice. This combination of BVA and morphine at intermediate doses had a greater and longer effect than either BVA or morphine alone at the highest dose (i.e., 2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg, respectively). This analgesic effect was significantly blocked by intrathecally administered naloxone and MDL-72222, but not by idazoxan, demonstrating that opioidergic and 5-HT3 receptors, but not α2-adrenergic receptors, mediate the effect at the spinal level.
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals
Male C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old) were purchased from Daehan Biolink (Chungbuk, Korea) and they were housed in cages with water and food available ad libitum. The room was maintained with 12 h-light/dark cycle (a light cycle; 08:00–20:00, a dark cycle; 20:00–08:00) and kept at 23 ± 2 °C. All animals were acclimated in their cages for one week prior to any experiments. All procedures involving animals were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Kyung Hee University (KHUASP(SE)-15-024).
4.2. Oxaliplatin Administration
Oxaliplatin (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was dissolved in a 5% glucose solution at a concentration of 2 mg/mL and was intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected at a dose of 6 mg/kg [4,45]. The same volume of 5% glucose solution was used in the control group.
4.3. Behavioral Test
Behavioral tests were conducted before and after oxaliplatin administration to observe whether cold and mechanical allodynia were induced in mice. For a week before the start of experiments, each mouse was habituated to handling procedures and to all testing procedures by investigators. The experimenters were blinded to oxaliplatin and any other treatments. Cold and mechanical sensitivities were measured using acetone and von Frey filaments, respectively [45]. Mice were placed on a wire mesh floor covered with a clear plastic box (12 × 8 × 6 cm), and were habituated for 30 min prior to each testing. Acetone (10 μL, Reagents Chemical Ltd., Gyonggi-do, Korea) was sprayed three times onto the plantar skin of each hind paw, and the frequencies of licking and shaking of the affected paw was counted after the acetone spray, for 30 s [46]. It is possible that acetone induces some behavioral responses in naïve mice; however, as shown in our experiments, mice that received a single injection of oxaliplatin showed a significantly increased level of response to acetone, compared to the vehicle injected control mice.
Mechanical sensitivity was measured by the von Frey filament test [47]. Mice were placed on the same wire mesh floor covered with a clear plastic box as mentioned above, and the von Frey filament (Linton Instrumentation, Norfolk, UK) with a bending force of 0.4 g was applied ten times to the mid plantar skin (avoiding the base of the tori) of each hind paw, and each application was held for 3 s [48]. The number of withdrawal responses to the von Frey filament applications from both hind paws was counted and then expressed as an overall percentage response.
4.4. BVA and Morphine Treatment
BV from Apis mellifera (Sigma) was dissolved in NS. BV was subcutaneously injected into the right Zusanli acupoint (ST36) located on the lateral side of the stifle joint adjacent to the anterior tubercle of the tibia as previously described [36,49]. Morphine hydrochloride (Myungmoon Pharm., Seoul, Korea) was diluted in NS and was injected intraperitoneally. In order to determine the effective dose of BVA or morphine, mice showing significant cold and mechanical allodynia signs were divided randomly into four groups. BVA at doses of 0.25, 1.0, and 2.5 mg/kg was injected into ST36 acupoint in a volume of 20 μL. In the control group, the same volume of NS was injected subcutaneously into the same acupoint. For morphine, doses of 0.5, 2, and 5 mg/kg were injected intraperitoneally in a volume of 0.2 mL. Control group mice received the same volume of NS, intraperitoneally.
4.5. Antagonist Treatment
In order to reveal the spinal analgesic mechanism of simultaneously injected BVA and morphine in oxaliplatin-administered mice, the antagonists were injected intrathecally. Opioid receptor antagonist naloxone (Sigma; 20 μg), selective α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist idazoxan (Sigma; 10 μg), or 5-HT3 antagonist MDL-72222 (Tocris, Cookson, UK, 3-tropanyl-3,5-dichlorobenzoate, 15 μg) were injected 20 min prior to the combination treatment of BVA and morphine.
Naloxone and idazoxan were dissolved in NS. MDL-72222 was dissolved in 20% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). The needle of a Hamilton syringe was inserted into the subarachnoid space between lumbar vertebrae L5 and L6. A flick of the mouse’s tail provided a reliable indicator that the needle had penetrated the dura mater. The syringe was held in position for a few seconds after the injection of a volume of 5 μL. The dose of each antagonist was determined based on previously published studies showing the selective and effective antagonistic action [38,50,51,52].
4.6. Statistical Analysis
The data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. and were analyzed by the paired, unpaired t-test, or one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni multiple comparison test was performed to determine the statistically significant differences among the groups. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2013R1A1A1012403).
Author Contributions
Sun Kwang Kim conceived and designed the study. Woojin Kim, Min Joon Kim and Donghyun Go performed the experiments. Woojin Kim, Heung Sik Na and Sun Kwang Kim analyzed and interpreted the data. Woojin Kim, Byung-Il Min, Heung Sik Na and Sun Kwang Kim wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Screnci, D.; McKeage, M.; Galettis, P.; Hambley, T.; Palmer, B.; Baguley, B. Relationships between hydrophobicity, reactivity, accumulation and peripheral nerve toxicity of a series of platinum drugs. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in globocan 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arany, I.; Safirstein, R.L. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin. Nephrol. 2003, 23, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, B.; Coudoré-Civiale, M.-A.; Balayssac, D.; Eschalier, A.; Coudoré, F.; Authier, N. Behavioral and immunohistological assessment of painful neuropathy induced by a single oxaliplatin injection in the rat. Toxicology 2007, 234, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamelin, E.; Gamelin, L.; Bossi, L.; Quasthoff, S. Clinical aspects and molecular basis of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity: Current management and development of preventive measures. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasetto, L.M.; D’Andrea, M.R.; Rossi, E.; Monfardini, S. Oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity: How and why? Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2006, 59, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehky, T.J.; Leonard, G.D.; Wilson, R.H.; Grem, J.L.; Floeter, M.K. Oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity: Acute hyperexcitability and chronic neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2004, 29, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Barton, D.; Kottschade, L.; Grothey, A.; Loprinzi, C. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Prevention and treatment strategies. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyriou, A.A.; Polychronopoulos, P.; Iconomou, G.; Chroni, E.; Kalofonos, H.P. A review on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral nerve damage. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Lee, B.; Seo, J. A case of the reduction of cervical disc protrusion on the ct scanning after 5 months by oriental medical treatments added by bee venom acupuncture. J. Kor. AM Meridian Pointol. Soc. 2001, 18, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Yook, T.-H.; Song, B.-Y.; Lee, D.-H. Clinical report of oriental medicine treatment with bee venom therapy of progressive muscle atrophy 1 patient. J. Pharmacopunct. 2000, 3, 119–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.-Y.; Shim, S.-R.; Rhee, H.Y.; Park, H.-J.; Jung, W.-S.; Moon, S.-K.; Park, J.-M.; Ko, C.-N.; Cho, K.-H.; Park, S.-U. Effectiveness of acupuncture and bee venom acupuncture in idiopathic parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Song, H.S.; Lee, C.K.; Hong, J.T. Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-D.; Park, H.-J.; Chae, Y.; Lim, S. An overview of bee venom acupuncture in the treatment of arthritis. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2005, 2, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Pittler, M.H.; Shin, B.-C.; Kong, J.C.; Ernst, E. Bee venom acupuncture for musculoskeletal pain: A review. J. Pain 2008, 9, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Jeon, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-W.; Cho, C.-K.; Kwon, K.-R.; Shin, J.-E.; Sagar, S.; Wong, R.; Yoo, H.-S. Sweet bee venom pharmacopuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J. Acupunct. Meridian Stud. 2012, 5, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.-S.; Moon, H.J.; Li, D.X.; Gil, M.; Min, J.K.; Lee, G.; Bae, H.; Kim, S.K.; Min, B.-I. Effect of bee venom acupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Li, D.X.; Yoon, H.; Go, D.; Quan, F.S.; Min, B.I.; Kim, S.K. Serotonergic mechanism of the relieving effect of bee venom acupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic cold allodynia in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.S. Acupuncture: Neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, S.K.; Min, B.-I. Mechanisms of electroacupuncture-induced analgesia on neuropathic pain in animal model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.H.; Huh, J.E.; Lee, J.D.; Park, D.S. Antinociceptive effect and the mechanism of bee venom acupuncture (apipuncture) on inflammatory pain in the rat model of collagen-induced arthritis: Mediation by α2-adrenoceptors. Brain Res. 2006, 1073–1074, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.W.; Kwon, Y.B.; Han, H.J.; Yang, I.S.; Beitz, A.J.; Lee, J.H. Antinociceptive mechanisms associated with diluted bee venom acupuncture (apipuncture) in the rat formalin test: Involvement of descending adrenergic and serotonergic pathways. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 51, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yekkirala, A.S.; Kalyuzhny, A.E.; Portoghese, P.S. Standard opioid agonists activate heteromeric opioid receptors: Evidence for morphine and [d-ala2-mephe4-glyol5] enkephalin as selective μ–δ agonists. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2009, 1, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arner, S.; Arner, B. Differential effects of epidural morphine in the treatment of cancer-related pain. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1985, 29, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherny, N.; Thaler, H.; Friedlander-Klar, H.; Lapin, J.; Foley, K.; Houde, R.; Portenoy, R. Opioid responsiveness of cancer pain syndromes caused by neuropathic or nociceptive mechanisms a combined analysis of controlled, single-dose studies. Neurology 1994, 44, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portenoy, R.K.; Foley, K.M.; Inturrisi, C.E. The nature of opioid responsiveness and its implications for neuropathic pain: New hypotheses derived from studies of opioid infusions. Pain 1990, 43, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershman, D.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Dworkin, R.H.; Smith, E.M.L.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Gavin, P.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilron, I.; Bailey, J.M.; Tu, D.; Holden, R.R.; Weaver, D.F.; Houlden, R.L. Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.J.; Lim, B.-S.; Lee, D.-I.; Ye, M.S.; Lee, G.; Min, B.-I.; Bae, H.; Na, H.S.; Kim, S.K. Effects of electroacupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic cold hypersensitivity in rats. J. Physiol. Sci. 2014, 64, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, B.; Coudoré, F.; Decalonne, L.; Eschalier, A.; Authier, N. Comparative antiallodynic activity of morphine, pregabalin and lidocaine in a rat model of neuropathic pain produced by one oxaliplatin injection. Neuropharmacology 2008, 55, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ormseth, M.J.; Scholz, B.A.; Boomershine, C.S. Duloxetine in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Patient Preference Adherence 2011, 5, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serpell, M.; Group, N.P.S. Gabapentin in neuropathic pain syndromes: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Pain 2002, 99, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.-Y.; Roh, D.-H.; Choi, J.-W.; Ryu, Y.; Lee, J.-H. Repetitive treatment with diluted bee venom attenuates the induction of below-level neuropathic pain behaviors in a rat spinal cord injury model. Toxins 2015, 7, 2571–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-W.; Chaplan, S.R.; Yaksh, T.L. Systemic and supraspinal, but not spinal, opiates suppress allodynia in a rat neuropathic pain model. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 199, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemberg, K.; Kontinen, V.K.; Viljakka, K.; Kylänlahti, I.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Kalso, E. Morphine, oxycodone, methadone and its enantiomers in different models of nociception in the rat. Anesthesia Analg. 2006, 102, 1768–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, D.-H.; Kwon, Y.-B.; Kim, H.-W.; Ham, T.-W.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Kang, S.-Y.; Han, H.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Beitz, A.J.; Lee, J.-H. Acupoint stimulation with diluted bee venom (apipuncture) alleviates thermal hyperalgesia in a rodent neuropathic pain model: Involvement of spinal alpha 2-adrenoceptors. J. Pain 2004, 5, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-B.; Kang, M.-S.; Han, H.-J.; Beitz, A.J.; Lee, J.-H. Visceral antinociception produced by bee venom stimulation of the zhongwan acupuncture point in mice: Role of α 2 adrenoceptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 308, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.B.; Ham, T.W.; Kim, H.W.; Roh, D.H.; Yoon, S.Y.; Han, H.J.; Yang, I.S.; Kim, K.W.; Beitz, A.J.; Lee, J.H. Water soluble fraction (<10 kda) from bee venom reduces visceral pain behavior through spinal α 2-adrenergic activity in mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2005, 80, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.B.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Roh, D.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Ryu, Y.H.; Choi, S.M.; Han, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.W. Substantial role of locus coeruleus-noradrenergic activation and capsaicin-insensitive primary afferent fibers in bee venom’s anti-inflammatory effect. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 55, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, M.; Yamazaki, H.; Hori, Y. Enkephalinergic neurons express 5-HT3 receptors in the spinal cord dorsal horn: Single cell RT-PCR analysis. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 2749–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Tsuda, M.; Kofuji, T.; Hori, Y. Physiological properties of enkephalin-containing neurons in the spinal dorsal horn visualized by expression of green fluorescent protein in bac transgenic mice. BMC Neurosci. 2011, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, R.; Xie, Y.F.; Qiao, J.T.; Dafny, N. Norepinephrine and serotonin-induced antinociception are blocked by naloxone with different dosages. Brain Res. Bull. 1994, 35, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giordano, J. Analgesic profile of centrally administered 2-methylserotonin against acute pain in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1991, 199, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaksh, T.; Tyce, G. Microinjection of morphine into the periaqueductal gray evokes the release of serotonin from spinal cord. Brain res. 1979, 171, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, K.; Bae, H.; Kim, S.K. Analgesic effects of bee venom derived phospholipase a2 in a mouse model of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain. Toxins 2015, 7, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatters, S.J.; Bennett, G.J. Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel-and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 2004, 109, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, E.K.; Levine, J.D. Comparison of oxaliplatin-and cisplatin-induced painful peripheral neuropathy in the rat. J. Pain 2009, 10, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, K.; Sugawara, T.; Fujishita, K.; Shinozaki, Y.; Matsukawa, T.; Suzuki, T.; Koizumi, S. The astrocyte-targeted therapy by bushi for the neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-W.; Kwon, Y.-B.; Ham, T.-W.; Roh, D.-H.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Yang, I.-S.; Beitz, A.J.; Lee, J.-H. Acupoint stimulation using bee venom attenuates formalin-induced pain behavior and spinal cord fos expression in rats. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.-Y.; Roh, D.-H.; Kwon, Y.-B.; Kim, H.-W.; Seo, H.-S.; Han, H.-J.; Lee, H.-J.; Beitz, A.J.; Lee, J.-H. Acupoint stimulation with diluted bee venom (apipuncture) potentiates the analgesic effect of intrathecal clonidine in the rodent formalin test and in a neuropathic pain model. J. Pain 2009, 10, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omiya, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yuzurihara, M.; Murata, M.; Aburada, M.; Kase, Y.; Takeda, S. Antinociceptive effect of shakuyakukanzoto, a kampo medicine, in diabetic mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2005, 99, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, D.-H.; Kim, H.-W.; Yoon, S.-Y.; Kang, S.-Y.; Kwon, Y.-B.; Cho, K.-H.; Han, H.-J.; Ryu, Y.-H.; Choi, S.-M.; Lee, H.-J. Bee venom injection significantly reduces nociceptive behavior in the mouse formalin test via capsaicin-insensitive afferents. J. Pain 2006, 7, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
