Fumonisin B1 (FB1) Induces Lamellar Separation and Alters Sphingolipid Metabolism of In Vitro Cultured Hoof Explants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
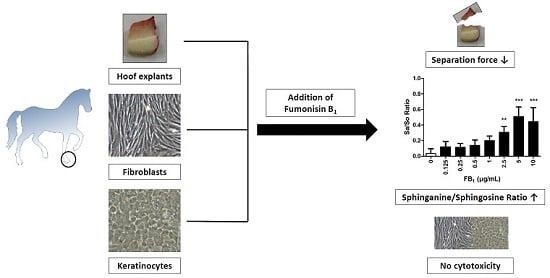
2.1. Cytotoxicity of FB1 on Primary Hoof Cells
2.2. Viability and Separation Force of Control Hoof Explants
2.3. Effect of FB1 on Separation Force
2.4. Effects of FB1 Sphingolipid Metabolism
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Preparation of FB1 Stock Solution
5.2. Ethical Statement
5.3. Animals
5.4. Preparation of Hoof Explants
5.5. Isolation, Cultivation, and Cytotoxicity Tests of Dermal and Epidermal Cells
5.6. Cultivation, Viability, and Lamellar Separation (Force Transducer) of Hoof Explants
5.7. Sphinganine (Sa) and Sphingosine (So) Analysis via LC-MS/MS
5.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ELEM | Equine Leukoencephalomalacia |
| FB1 | Fumonisin B1 |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharides |
| Sa | Sphinganine |
| So | Sphingosine |
| Sa/So ratio | Sphinganine-to-sphingosine ratio |
| WST | Water Soluble Tetrazolium |
References
- USDA. Lameness and laminitis in us horses; USDA Rural Development: Denver, CO, USA, 2000.
- Bailey, S.R.; Adair, H.S.; Reinemeyer, C.R.; Morgan, S.J.; Brooks, A.C.; Longhofer, S.L.; Elliott, J. Plasma concentrations of endotoxin and platelet activation in the developmental stage of oligofructose-induced laminitis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 129, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.M.; Bailey, S.R. A review of recent advances and current hypotheses on the pathogenesis of acute laminitis. Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mungall, B.A.; Pollitt, C.C. Thermolysin activates equine lamellar hoof matrix metalloproteinases. J. Comp. Pathol. 2002, 126, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mungall, B.A.; Kyaw-Tanner, M.; Pollitt, C.C. In vitro evidence for a bacterial pathogenesis of equine laminitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2001, 79, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, J.L.; McDowell, K.J. Tall fescue alkaloids cause vasoconstriction in equine medial palmar artery and vein. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 55. [Google Scholar]
- McDowell, K.J.; Moore, E.S.; Parks, A.G.; Bush, L.P.; Horohov, D.W.; Lawrence, L.M. Vasoconstriction in horses caused by endophyte-infected tall fescue seed is detected with doppler ultrasonography. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 1677–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douthit, T.L.; Bormann, J.M.; Gradert, K.C.; Lomas, L.W.; DeWitt, S.F.; Kouba, J.M. The impact of endophyte-infected fescue consumption on digital circulation and lameness in the distal thoracic limb of the horse. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, K.A.; Riley, R.T. Fumonisin toxicity and mechanism of action: Overview and current perspectives. Food Saf. 2013, 1, 49–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesener, K.; Curtui, V.; Dietrich, R.; Martlbauer, E.; Usleber, E. Mycotoxins in horse feed. Mycotoxin Res. 2010, 26, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasas, W.F.; Kellerman, T.S.; Gelderblom, W.C.; Coetzer, J.A.; Thiel, P.G.; van der Lugt, J.J. Leukoencephalomalacia in a horse induced by fumonisin B1 isolated from Fusarium moniliforme. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1988, 55, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brownie, C.F.; Cullen, J. Characterization of experimentally induced equine leukoencephalomalacia (ELEM) in ponies (Equus caballus): Preliminary report. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1987, 29, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Foreman, J.H.; Constable, P.D.; Waggoner, A.L.; Levy, M.; Eppley, R.M.; Smith, G.W.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Haschek, W.M. Neurologic abnormalities and cerebrospinal fluid changes in horses administered fumonisin B1 intravenously. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2004, 18, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.F.; Ledet, A.E.; Owens, D.L.; Rice, L.G.; Nelson, H.A.; Osweiler, G.D.; Wilson, T.M. Experimental equine leukoencephalomalacia, toxic hepatosis, and encephalopathy caused by corn naturally contaminated with fumonisins. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1993, 5, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Ross, P.F.; Wilson, T.M.; Riley, R.T.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Increases in serum sphingosine and sphinganine and decreases in complex sphingolipids in ponies given feed containing fumonisins, mycotoxins produced by Fusarium moniliforme. J. Nutr. 1992, 122, 1706–1716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, G.W.; Constable, P.D.; Foreman, J.H.; Eppley, R.M.; Waggoner, A.L.; Tumbleson, M.E.; Haschek, W.M. Cardiovascular changes associated with intravenous administration of fumonisin B1 in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2002, 63, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, H.; Nakamura, M.; Kuwano, A.; Kasamatsu, M.; Nagahata, H. Quantities and types of ceramides and their relationships to physical properties of the horn covering the claws of clinically normal cows and cows with subclinical laminitis. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 69, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jovanović, M.; Trailović, D.; Kukolj, V.; Nešić, S.; Marinković, D.; Nedeljković-Trailović, J.; Jakovac, B.; Milićević, D. An outbreak of fumonisin toxicosis in horses in Serbia. World Mycotoxin J. 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.F.; Rice, L.G.; Reagor, J.C.; Osweiler, G.D.; Wilson, T.M.; Nelson, H.A.; Owens, D.L.; Plattner, R.D.; Harlin, K.A.; Richard, J.L.; et al. Fumonisin B1 concentrations in feeds from 45 confirmed equine leukoencephalomalacia cases. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1991, 3, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrillo, G.N.; Rodriguez, F.S.; Gordo, L.G.; de Mendoza Salcedo, M.H.; Cordero, V.R. Clinical and pathological aspects of an outbreak of equine leukoencephalomalacia in spain. J. Veterinary Med. Ser. A 1996, 43, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streit, E.; Naehrer, K.; Rodrigues, I.; Schatzmayr, G. Mycotoxin occurrence in feed and feed raw materials worldwide: Long-term analysis with special focus on Europe and Asia. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2013, 93, 2892–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streit, E.; Schwab, C.; Sulyok, M.; Naehrer, K.; Krska, R.; Schatzmayr, G. Multi-mycotoxin screening reveals the occurrence of 139 different secondary metabolites in feed and feed ingredients. Toxins 2013, 5, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, C.E.; Collins, S.N.; Verheyen, K.L.; Richard Newton, J. Frequency of equine laminitis: A systematic review with quality appraisal of published evidence. Vet. J. 2011, 189, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.M. Conquer laminitis by 2020. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2010, 30, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, K.A.; Riley, R.T.; Moore, N.D.; Burns, T.D. Alkaline cooking (nixtamalisation) and the reduction in the in vivo toxicity of fumonisin-contaminated corn in a rat feeding bioassay. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.H.; Ferreira, F.L.; da Silva, V.N.; Aquino, S.; Correa, B. Effects of aflatoxin B1 and fumonisin B1 on the viability and induction of apoptosis in rat primary hepatocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1944–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramasamy, S.; Wang, E.; Hennig, B.; Merrill, A.H., Jr. Fumonisin B1 alters sphingolipid metabolism and disrupts the barrier function of endothelial cells in culture. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1995, 133, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvano, F.; Russo, A.; Cardile, V.; Galvano, G.; Vanella, A.; Renis, M. DNA damage in human fibroblasts exposed to fumonisin B1. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvano, F.; Campisi, A.; Russo, A.; Galvano, G.; Palumbo, M.; Renis, M.; Barcellona, M.L.; Perez-Polo, J.R.; Vanella, A. DNA damage in astrocytes exposed to fumonisin B1. Neurochem. Res. 2002, 27, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouadio, J.H.; Mobio, T.A.; Baudrimont, I.; Moukha, S.; Dano, S.D.; Creppy, E.E. Comparative study of cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by deoxynivalenol, zearalenone or fumonisin B1 in human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Toxicology 2005, 213, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolleson, W.H.; Dooley, K.L.; Sheldon, W.G.; Thurman, J.D.; Bucci, T.J.; Howard, P.C. The mycotoxin fumonisin induces apoptosis in cultured human cells and in livers and Kidneys of rats. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1996, 392, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tolleson, W.H.; Melchior, W.B., Jr.; Morris, S.M.; McGarrity, L.J.; Domon, O.E.; Muskhelishvili, L.; James, S.J.; Howard, P.C. Apoptotic and anti-proliferative effects of fumonisin B1 in human keratinocytes, fibroblasts, esophageal epithelial cells and hepatoma cells. Carcinogenesis 1996, 17, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolleson, W.H.; Couch, L.H.; Melchior, W.B., Jr.; Jenkins, G.R.; Muskhelishvili, M.; Muskhelishvili, L.; McGarrity, L.J.; Domon, O.; Morris, S.M.; Howard, P.C. Fumonisin B1 induces apoptosis in cultured human keratinocytes through sphinganine accumulation and ceramide depletion. Int. J. Oncol. 1999, 14, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisinger, N.; Schaumberger, S.; Nagl, V.; Hessenberger, S.; Schatzmayr, G. Milk thistle extract and silymarin inhibit lipopolysaccharide induced lamellar separation of hoof explants in vitro. Toxins 2014, 6, 2962–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisinger, N.; Schaumberger, S.; Nagl, V.; Hessenberger, S.; Schatzmayr, G. Concentration dependent influence of lipopolysaccharides on separation of hoof explants and supernatant lactic acid concentration in an ex vivo/in vitro laminitis model. PLoS One 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollitt, C.C.; Pass, M.A.; Pollitt, S. Batimastat (BB-94) inhibits matrix metalloproteinases of equine laminitis. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 1998, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pawlak, E.A.; Johnson, P.J.; Belknap, J.K.; Alfandari, D.; Black, S.J. Expression and activity of collagenases in the digital laminae of horses with carbohydrate overload-induced acute laminitis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodi, M.; Alizadeh, A.M.; Sohanaki, H.; Rezaei, N.; Amini-Najafi, F.; Khosravi, A.R.; Hosseini, S.K.; Safari, Z.; Hydarnasab, D.; Khori, V. Impact of fumonisin B1 on the production of inflammatory cytokines by gastric and colon cell lines. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012, 11, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.T.; An, N.H.; Showker, J.L.; Yoo, H.S.; Norred, W.P.; Chamberlain, W.J.; Wang, E.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Motelin, G.; Beasley, V.R.; et al. Alteration of tissue and serum sphinganine to sphingosine ratio: An early biomarker of exposure to fumonisin-containing feeds in pigs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1993, 118, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, I.; Nagl, V.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Varga, E.; Schwarz, C.; Slavik, V.; Reisinger, N.; Malachova, A.; Cirlini, M.; Generotti, S.; et al. Effects of orally administered fumonisin B1 (FB1), partially hydrolysed FB1, hydrolysed FB1 and N-(1-deoxy-d-fructos-1-yl) FB1 on the sphingolipid metabolism in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 76, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golden, G.M.; Guzek, D.B.; Kennedy, A.H.; McKie, J.E.; Potts, R.O. Stratum corneum lipid phase transitions and water barrier properties. Biochemistry 1987, 26, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fodor, J.; Balogh, K.; Weber, M.; Miklos, M.; Kametler, L.; Posa, R.; Mamet, R.; Bauer, J.; Horn, P.; Kovacs, F.; et al. Absorption, distribution and elimination of fumonisin B1 metabolites in weaned piglets. Food Addit. Contam. A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2008, 25, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Larranaga, M.R.; Anadon, A.; Diaz, M.J.; Fernandez-Cruz, M.L.; Martinez, M.A.; Frejo, M.T.; Martinez, M.; Fernandez, R.; Anton, R.M.; Morales, M.E.; et al. Toxicokinetics and oral bioavailability of fumonisin B1. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1999, 41, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shephard, G.S.; Thiel, P.G.; Sydenham, E.W.; Savard, M.E. Fate of a single dose of 14C-labelled fumonisin B1 in vervet monkeys. Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilkin, P.; Direito, G.; Simas, M.M.; Mallmann, C.A.; Correa, B. Toxicokinetics and toxicological effects of single oral dose of fumonisin B1 containing fusarium verticillioides culture material in weaned piglets. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 185, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, B.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Caha, S.; Moll, W.D.; Schatzmayr, G.; Applegate, T.J. Dose-dependent effects on sphingoid bases and cytokines in chickens fed diets prepared with fusarium verticillioides culture material containing fumonisins. Toxins 2015, 7, 1253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| 24 h | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 (µg/mL) | Mean (N) | SD | p-Value |
| 0 | 21.0 | 8.8 | - |
| 0.125 | 13.4 | 7.1 | 0.007 |
| 0.25 | 13.1 | 9.1 | 0.016 |
| 0.5 | 12.6 | 4.1 | 0.084 |
| 1 | 11.5 | 6.1 | 0.000 |
| 2.5 | 12.7 | 5.6 | 0.003 |
| 5 | 12.9 | 6.4 | 0.004 |
| 10 | 14.3 | 7.7 | 0.005 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reisinger, N.; Dohnal, I.; Nagl, V.; Schaumberger, S.; Schatzmayr, G.; Mayer, E. Fumonisin B1 (FB1) Induces Lamellar Separation and Alters Sphingolipid Metabolism of In Vitro Cultured Hoof Explants. Toxins 2016, 8, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040089
Reisinger N, Dohnal I, Nagl V, Schaumberger S, Schatzmayr G, Mayer E. Fumonisin B1 (FB1) Induces Lamellar Separation and Alters Sphingolipid Metabolism of In Vitro Cultured Hoof Explants. Toxins. 2016; 8(4):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040089
Chicago/Turabian StyleReisinger, Nicole, Ilse Dohnal, Veronika Nagl, Simone Schaumberger, Gerd Schatzmayr, and Elisabeth Mayer. 2016. "Fumonisin B1 (FB1) Induces Lamellar Separation and Alters Sphingolipid Metabolism of In Vitro Cultured Hoof Explants" Toxins 8, no. 4: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040089
APA StyleReisinger, N., Dohnal, I., Nagl, V., Schaumberger, S., Schatzmayr, G., & Mayer, E. (2016). Fumonisin B1 (FB1) Induces Lamellar Separation and Alters Sphingolipid Metabolism of In Vitro Cultured Hoof Explants. Toxins, 8(4), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8040089