Design of a Tribotester Based on Non-Contact Displacement Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
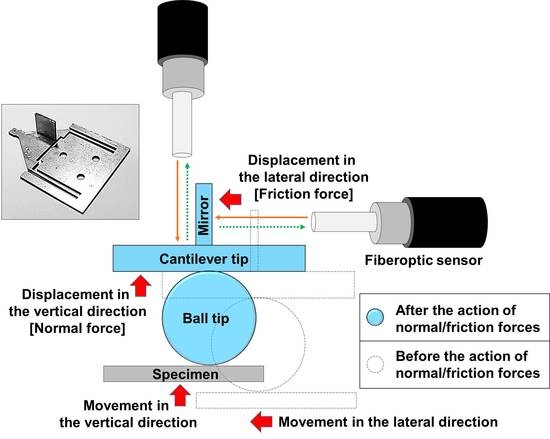
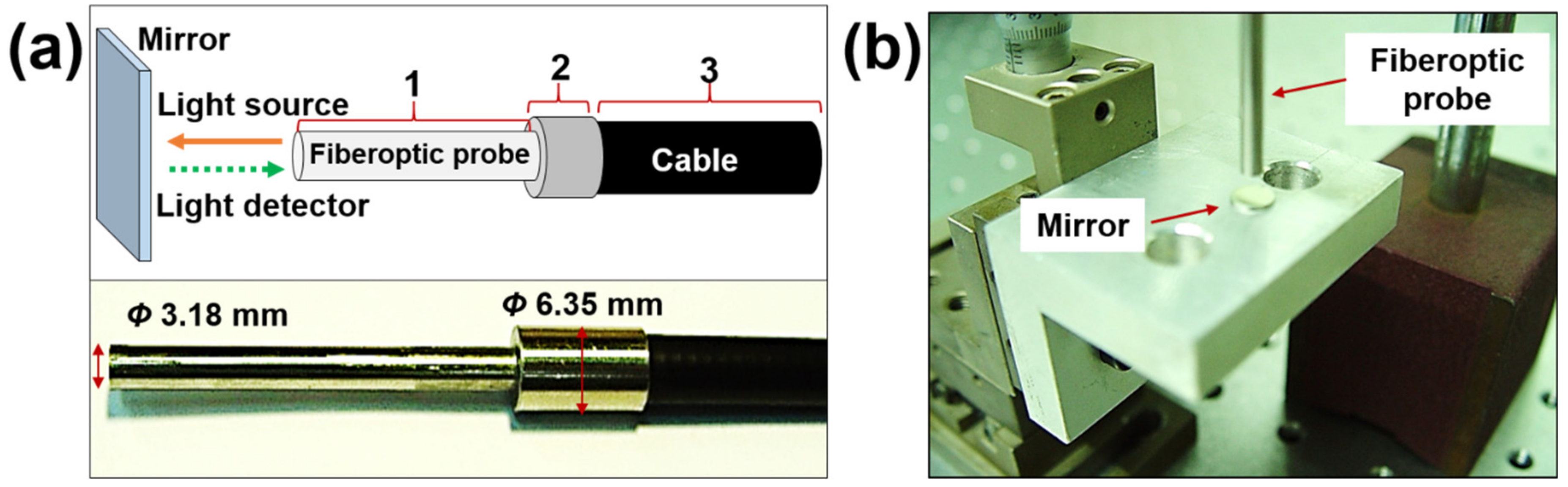
2.1. Fiberoptic Sensor [26,27,28]
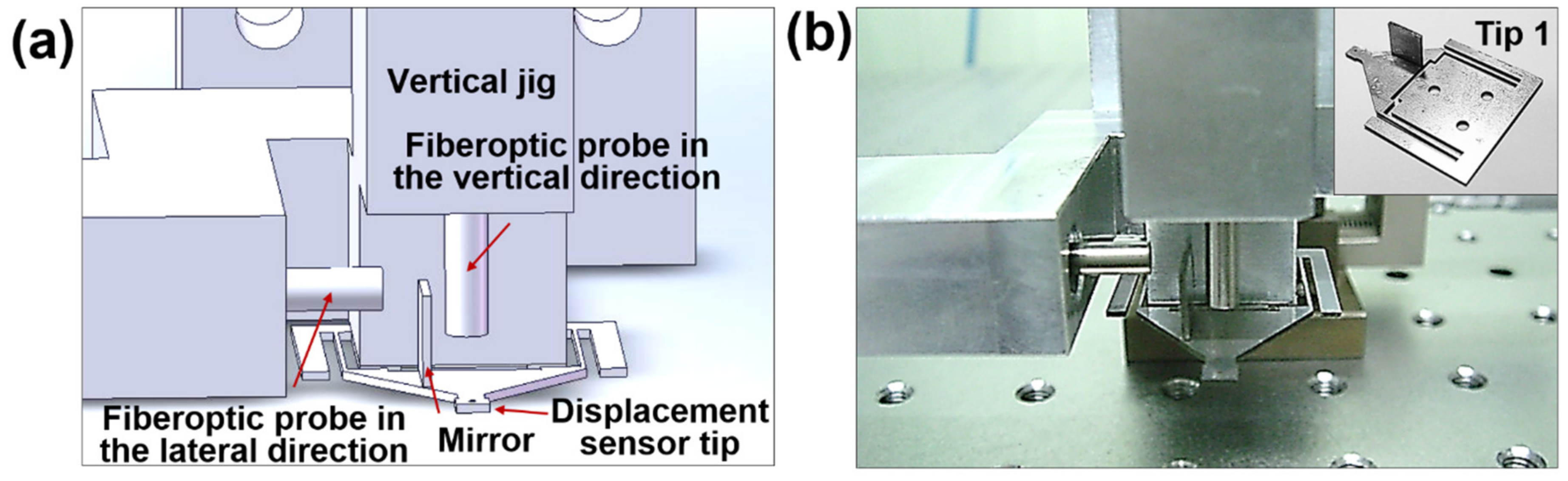
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Sensor Calibration
2.4. Experiment Conditions
3. Results
3.1. Friction and Wear Test
3.2. Tip Design Considering the Coupling Effect
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, H. Self-lubricanting slippery surface with wettability gradients for anti-sticking of electrosurgical scalpel. Micromachines 2018, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendhran, N.; Palanisamy, S.; Periyasamy, P.; Venkatachalam, R. Enhancing of the tribological characteristics of the lubricant oils using Ni-promoted MoS2 nanosheets as nano-additives. Tribol. Int. 2018, 118, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Graphene: a new emerging lubricant. Mater. Today 2014, 17, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, M.; Kang, K.H.; Kim, C.L.; Kim, D.E. Selective release of less defective graphene during sliding of an incompletely reduced graphene oxide coating on steel. Carbon 2018, 134, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Wan, H.; Chen, L.; Ye, Y.; Zhou, H.; Chen, J. Fabrication and tribological behaviors of a novel environmental friendly water-based PAI-PTFE-LaF3 bonded solid lubricating composite coating. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penkov, O.V.; Khadem, M.; Nieto, A.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, D.E. Design and construction of a micro-tribotester for precise in-situ wear measurements. Micromachines 2017, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.L.; Penkov, O.V.; Shin, D.G.; Kim, D.E. Investigation of micro-abrasion characteristics of thin metallic coatings by in-situ SEM scratch test. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 17, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, D.L.; Sawyer, W.G. Addressing practical challenges of low friction coefficient measurements. Tribol. Lett. 2009, 35, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samyn, P.; Kalacska, G.; Keresztes, R.; Zsidai, L.; Baets, P.D. Design of a tribotester for evaluation of polymer components under static and dynamic sliding conditions. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2007, 221, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wu, H.; Su, C.; Wen, S. Measurement of static and dynamic friction coefficients of sidewalls of bulk-microfabricated MEMS devices with an on-chip micro-tribotester. Sens. Actuators A 2007, 135, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binggeli, M.; Christoph, R.; Hintermann, H.E.; Marti, O. Atomic-scale tribometer for friction studies in a controlled atmosphere. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1993, 62, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.S.; Singh, R.A.; Oh, H.J.; Kong, H. The effect of contact area on nano/micro-scale friction. Wear 2005, 259, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, A.; Ahmed, S.I.-U.; Scherge, M.; Schaefer, J.A. Nanofriction mechanisms derived from the dependence of friction on load and sliding velocity from air to UHV on hydrophilic silicon. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 20, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yastrebov, V.A.; Anciaux, G.; Molinari, J.F. From infinitesimal to full contact between rough surfaces: Evolution of the contact area. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 52, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, G.; Bottiglione, F. Asperity contact theories: Do they predict linearity between contact area and load? J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 2555–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Contact mechanics of rough surfaces in tribology: Multiple asperity contact. Tribol. Lett. 1998, 4, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Ai, X. Point contact EHL based on optically measured three-dimensional rough surfaces. J. Tribol. 1997, 119, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneta, M.; Sakai, T.; Nishikawa, H. Effects of surface roughness on point contact EHL. Tribol. Trans. 1993, 36, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wu, T.; Huo, Y.; Yang, H. In-situ characterization of three dimensional worn surface under sliding-rolling contact. Wear 2019, 426–427, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Gao, S.; Yao, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, F.; Chen, H.J. Tribological behavior of polytetrafluoroethylene under unidirectional rotation, reciprocating sliding, and torsion motion. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 60, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, P.; Blomberg, A. Alumina in unlubricated sliding point, line and plane contacts. Wear 1993, 170, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.M.; Seo, J.; Jang, H.; Seo, J.H. Optimizing grafting thickness of zwitterionic sulfobetaine polymer on cross-linked polyethylene surface to reduce friction coefficient. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 452, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duminica, F.-D.; Belchi, R.; Libralesso, L.; Mercier, D. Investigation of Cr(N)/DLC multilayer coatings elaborated by PVD for high wear resistance and low friction applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 337, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, H.; Mohammadali, M. A distributed mechanical joint contact model with slip/slap coupling effects. Mech. Syst. Sig. Process. 2016, 80, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuberger, M.; Drummond, C.; Israelachvili, J. Coupling of normal and transverse motions during frictional sliding. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 5038–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Feng, F.; Chen, D.; Lin, W.; Chen, S.-C. Precision non-contact displacement sensor based on the near-field characteristics of fiber specklegrams. Sens. Actuator A 2019, 296, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrzywnicka, A.; Śniadek, P.; Małyszka, N.; Lizanets, D.; Kubicki, W.; Pawlak, P.; Walczak, R. MEMS cytometer for porcine oocyte deformation measurement. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2019, 29, 095004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammer, A.S.; Olgac, N. Delayed resonator concept for vibration suppression using piezoelectric networks. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 115008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohyama, S.; Takahashi, H.; Yoshida, S.; Onoe, H.; Hirayama-Shoji, K.; Tsukagoshi, T.; Takahata, T.; Shimoyama, I. Spring constant measurement using a MEMS force and displacement sensor utilizing paralleled piezoresistive cantilevers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 045013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lantz, M.A.; O’Shea, S.J.; Hoole, A.C.F.; Welland, M.E. Lateral stiffness of the tip and tip-sample contact in frictional force microscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1997, 70, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.R.; Etsion, I.; Bogy, D.B. Static friction coefficient model for metallic rough surfaces. J. Tribol. 1988, 110, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, A.Y.; Polycarpou, A.A.; Conry, T.F. Detailed surface roughness characterization of engineering surfaces undergoing tribological testing leading to scuffing. Wear 2003, 255, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, C.-L.; Sung, Y.-G. Design of a Tribotester Based on Non-Contact Displacement Measurements. Micromachines 2019, 10, 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110748
Kim C-L, Sung Y-G. Design of a Tribotester Based on Non-Contact Displacement Measurements. Micromachines. 2019; 10(11):748. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110748
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Chang-Lae, and Yoon-Gyung Sung. 2019. "Design of a Tribotester Based on Non-Contact Displacement Measurements" Micromachines 10, no. 11: 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110748
APA StyleKim, C.-L., & Sung, Y.-G. (2019). Design of a Tribotester Based on Non-Contact Displacement Measurements. Micromachines, 10(11), 748. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10110748