Growth of Less than 20 nm SnO Nanowires Using an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template for Gas Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
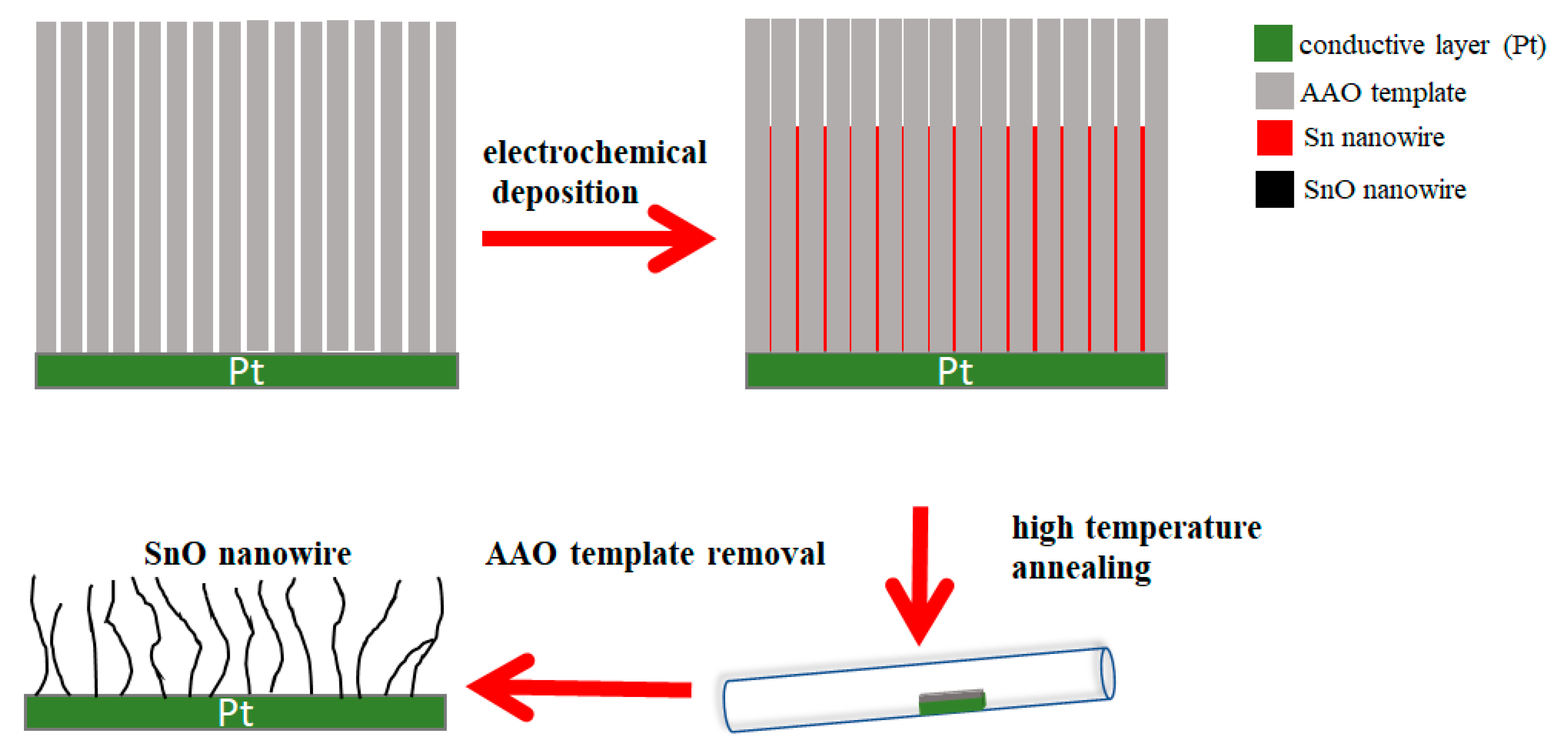
2. Synthesis Procedure and Methods
2.1. Synthesizing Procedure of AAO Template
2.2. Synthesizing Procedure of SnO Nanowires
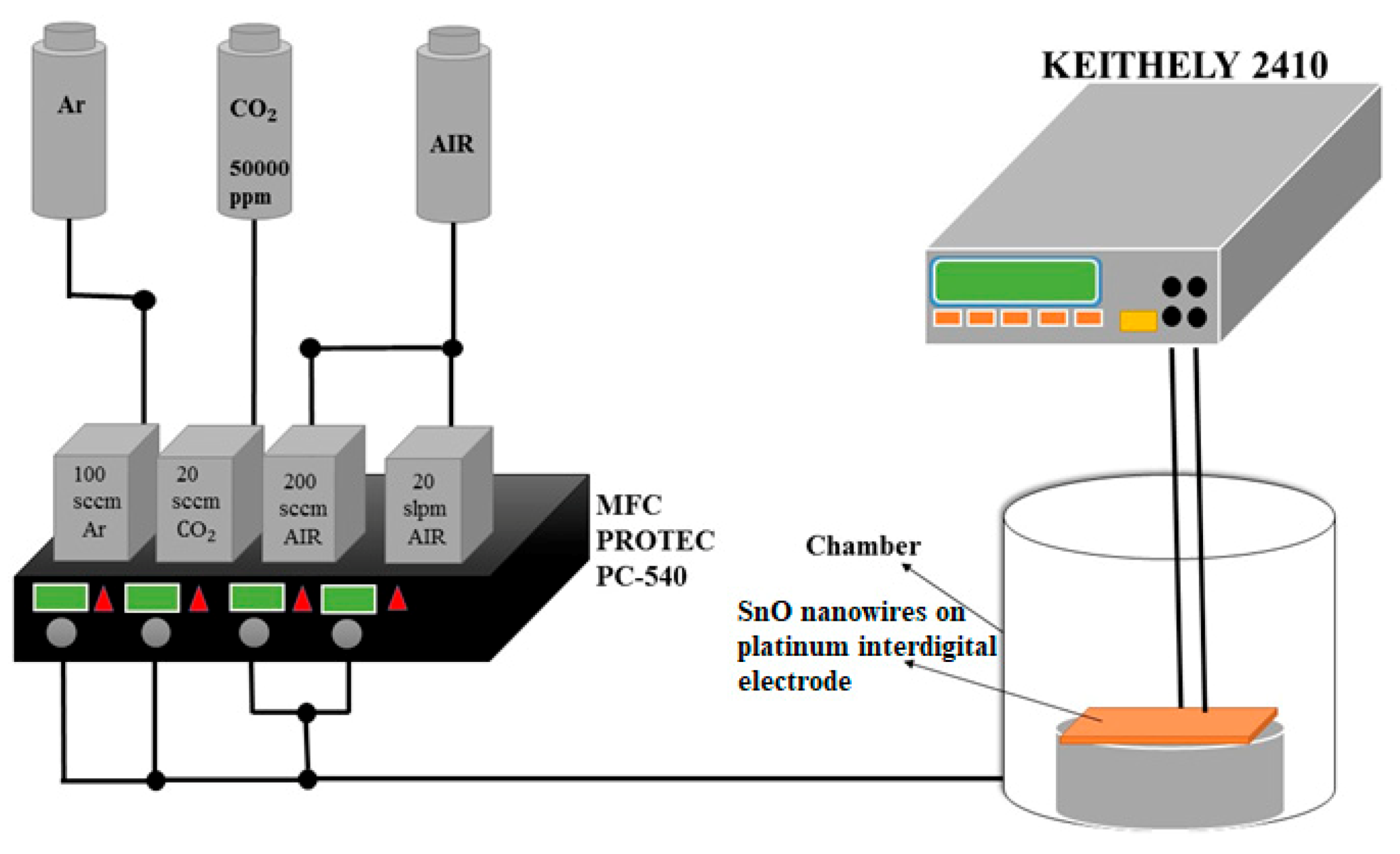
2.3. A Gas-Sensor and Equipment for Sensing CO2
3. Results
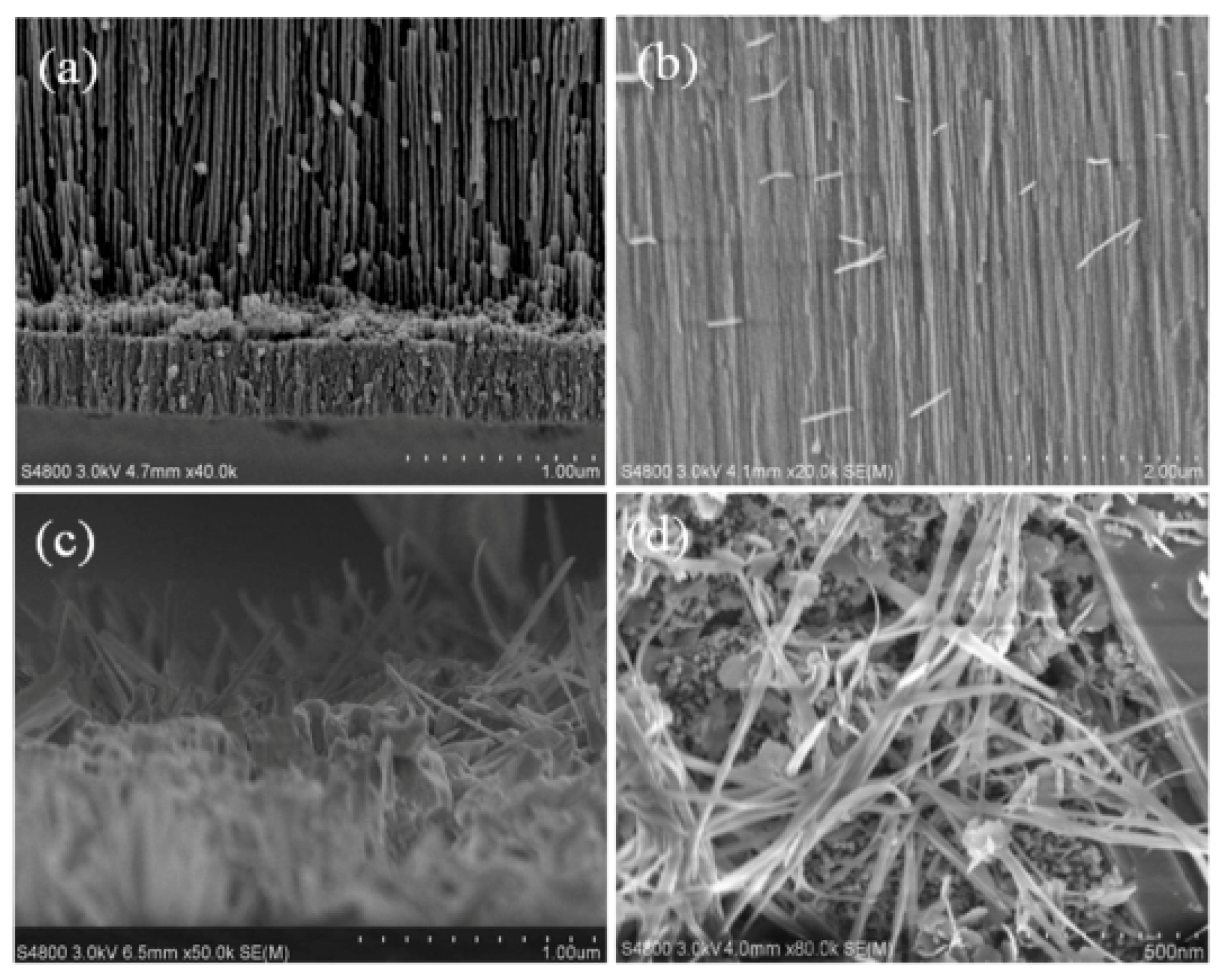
3.1. Synthesizing the AAO Template
3.2. Synthesizing the SnO Nanowires
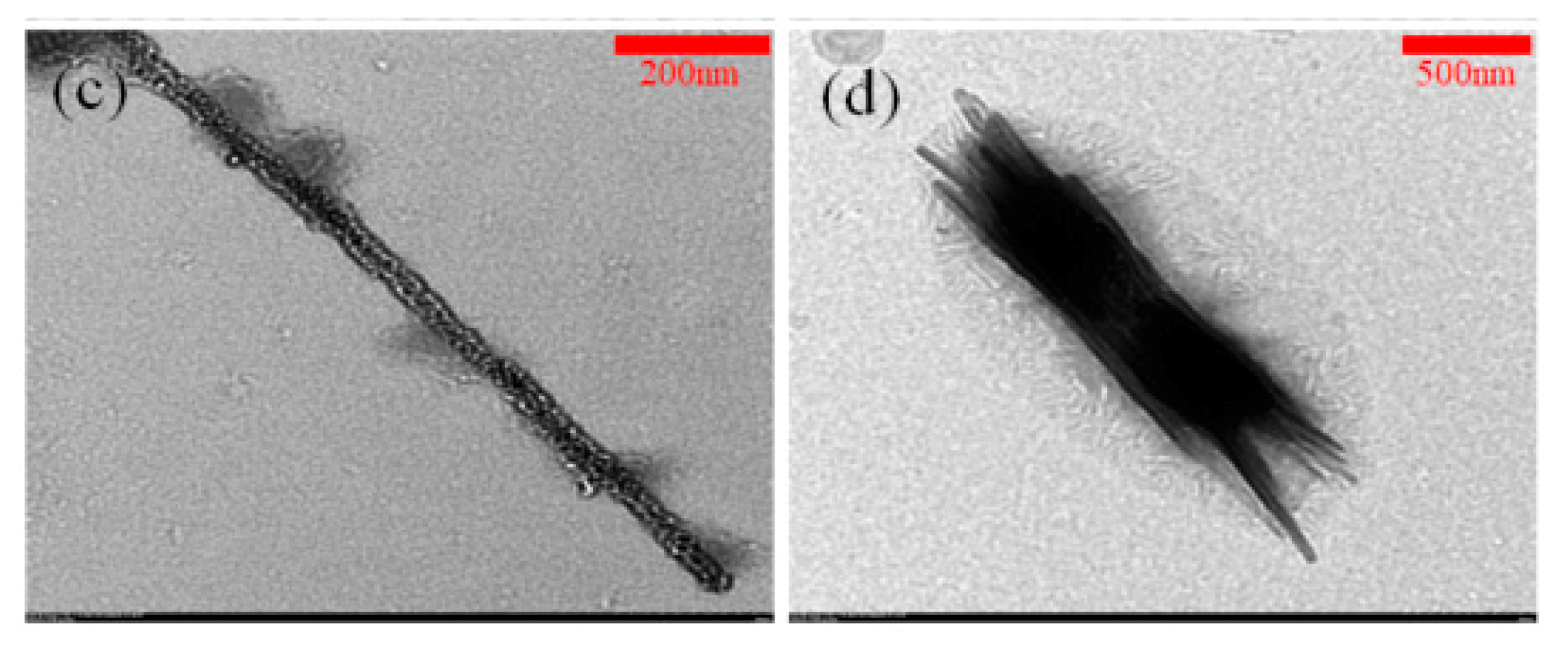
3.3. Analysis of the SnO Nanowires
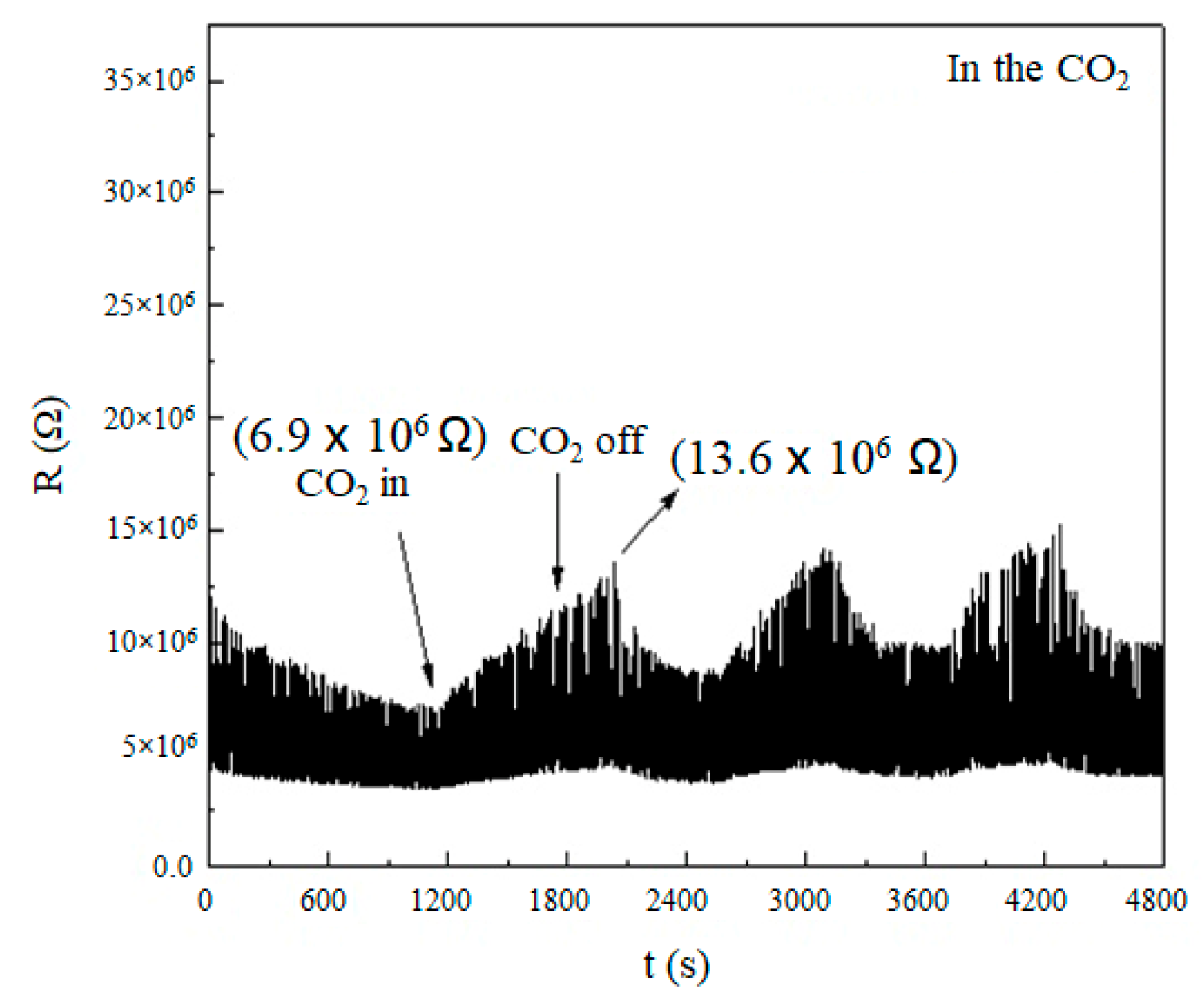
3.4. Sensing the CO2 by Using the SnO Nanowires
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salah, N.; Al-Shawafi, W.M.; Habib, S.S.; Azam, A.; Alshahrie, A. Growth-controlled from SnO2 nanoparticles to SnO nanosheets with tunable properties. Mater. Des. 2016, 103, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhu, Z. Study on the structure feature of SnO micro/nanostructure with interesting distribution characteristic of concentric annulus. Mater. Lett. 2017, 186, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezalou, S.; Öznülüer, T.; Demir, Ü. One-pot electrochemical fabrication of single-crystalline SnO nanostructures on Si and ITO substrates for catalytic, sensor and energy storage applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 448, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-R.; Lee, I.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, K.-C. Growth of free-standing SnO nanostructures on single layer graphene. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalane, C.M.; Kanimozhi, K.; Arularasu, M.; Ramalingam, G.; Kaviyarasu, K. Self-cleaning mechanism of synthesized SnO2/TiO2 nanostructure for photocatalytic activity application for waste water treatment. Surfaces Interfaces 2019, 17, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalathas, A.P.; Alkaisi, M.M. Nanostructures for light trapping in thin film solar cells. Micromachines 2019, 10, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samà, J.; Prades, J.D.; Casals, O.; Barth, S.; Gracia, I.; Cané, C.; Domènech-Gil, G.; Hernández-Ramírez, F.; Romano-Rodríguez, A. Low-cost fabrication of zero-power metal oxide nanowire gas sensors: Trends and challenges. Procedia Eng. 2015, 120, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vallejos, S.; Grácia, I.; Chmela, O.; Figueras, E.; Hubálek, J.; Cané, C. Chemoresistive micromachined gas sensors based on functionalized metal oxide nanowires: Performance and reliability. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schipani, F.; Miller, D.R.; Ponce, M.A.; Aldao, C.M.; Akbar, S.A.; Morris, P.A.; Xu, J.C. Conduction mechanisms in SnO2 single-nanowire gas sensors: Animpedance spectroscopy study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelfhout, R.; Strijckmans, K.; Depla, D. Anomalous effects in the aluminum oxide sputtering yield. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 155202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Kuo, T.-Y.; Chen, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Pour Yazdi, M.A.; Billard, A. Contribution of enhanced ionization to the optoelectronic properties of p-type NiO films deposited by high power impulse magnetron sputtering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 5285–5291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Beainou, R.; Martin, N.; Potin, V.; Pedrosa, P.; Pour Yazdi, M.A.; Billard, A. Correlation between structure and electrical resistivity of W-Cu thin films prepared by GLAD co-sputtering. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2017, 313, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depla, D.; Buyle, G.; Haemers, J.; De Gryse, R. Discharge voltage measurements during magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coatings Technol. 2006, 200, 4329–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graaf, A.; van Deelen, J.; Poodt, P.; van Mol, T.; Spee, K.; Grob, F.; Kuypers, A. Development of atmospheric pressure CVD processes for high-quality transparent conductive oxides. Energy Procedia 2010, 2, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rho, W.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Han, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Jun, B.H. Au-embedded and carbon-doped freestanding TiO2 nanotube arrays in dye-sensitized solar cells for better energy conversion efficiency. Micromachines 2019, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-C.; Lee, D.-H.; Maeng, S. Synthesis of novel pure SnO nanostructures by thermal evaporation. Mater. Lett. 2012, 86, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, M.; Usui, H.; Sakaguchi, H. Electrochemical Na-insertion/extraction properties of SnO thick-film electrodes prepared by gas-depositionitle of the article. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tariq, Z.; Butt, F.K.; Rehman, S.U.; Haq, B.U.; Aleem, F.; Li, C. First-principles study of electronic and optical properties of sulfur doped tin monoxide: A potential applicant for optoelectronic devices. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 7495–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Zhu, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, W.; Bai, L. Formaldehyde sensing properties of SnO–graphene composites prepared via hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2015, 31, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kushwaha, N.; Mittal, J. Superior, rapid and reversible sensing activity of graphene-SnO hybrid film for low concentration of ammonia at room temperature. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.-S.; Park, M.-J.; Kwon, S.-H.; Joo, H.-J.; Song, S.-H.; Kwon, H.-I. Low temperature NO2 sensing properties of RF-sputtered SnO-SnO2 heterojunction thin-film with p-type semiconducting behavior. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 17283–17289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Fan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Xiang, Q.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. A low temperature formaldehyde gas sensor based on hierarchical SnO/SnO2 nano-flowers assembled from ultrathin nanosheets: Synthesis, sensing performance and mechanism. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2019, 294, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, P.G.; Altimari, P.; Rubino, A.; Pagnanelli, F. Electrodeposition of cobalt nanowires into alumina templates generated by one-step anodization. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, P.G.; Farina, L.; Zanoni, R.; Altimari, P.; Cojocariu, I.; Rubino, A.; Navarra, M.A.; Panero, S.; Pagnanelli, F. Electrochemical synthesis of nanowire anodes from spent lithium ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 319, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.R.; Miura, N. Electrochemical synthesis and characterization of nanostructured tin oxide for electrochemical redox supercapacitors. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q. Controlled fabrication of SnO2 arrays of well-aligned nanotubes and nanowires. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadava, Y.; Denicoló, G.; Arias, A.; Roman, L.; Hümmelgen, I. Preparation and characterization of transparent conducting tin oxide thin film electrodes by chemical vapour deposition from reactive thermal evaporation of SnCl2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1997, 48, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, P.K.; Borthakur, A.; Saikia, P.K. Structural, optical and electrical properties of tin oxide thin film deposited by APCVD method. Indian J. Phys. 2011, 85, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Xue, C.; Wu, Y.; Tai, R. Preparation and characterization of p-type transparent conducting SnO thin films. Mater. Lett. 2012, 139, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraveo-Frescas, J.A.; Alshareef, H.N. Transparent p-type SnO nanowires with unprecedented hole mobility among oxide semiconductors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 222103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.-B.; Wu, P.-F.; Lin, H.-S.; Lin, Y.-T.; Lee, H.-W.; Kao, C.-T.; Liao, W.-H.; Young, S.-L. Synthesis and characterization of single-crystalline zinc tin oxide nanowires. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.-B.; Wu, P.-F.; Lin, Y.-T.; Kao, C.-T.; Chen, C.-J.; Cheng, F.-C.; Liu, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-S.; Lee, H.-W. Synthesis and optical properties of single-crystalline indium zinc oxide (IZO) nanowires via co-deposition and oxidation methods. Vacuum 2015, 115, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-B.; Wu, P.-F.; Lin, Y.-T.; Chen, C.-J.; Kao, C.-T.; Lin, H.-S.; Lee, H.-W.; Liu, H.-H.; Lee, M.-W.; Chen, C.-Y.; et al. Preparation and characterization of single crystalline In-Sn oxide nanowires. Vacuum 2015, 117, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M. ρ-N heterostructural sensor with SnO-SnO2 for fast NO2 sensing response properties at room temperature. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willa, C.; Yuan, J.; Niederberger, M.; Koziej, D. When Nanoparticles meet Poly(Ionic Liquid)s: Chemoresistive CO2 sensing at room temperature. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2537–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinives, S.; Sarkar, T.; Hernández, R.; Mulchandani, A. A miniature chemiresistor sensor for carbon dioxide. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 874, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafiz, S.M.; Ritikos, R.; Whitcher, T.J.; Razib, N.M.; Bien, D.C.S.; Chanlek, N.; Nakajima, H.; Saisopa, T.; Songsiriritthigul, P.; Huang, N.M.; et al. A practical carbon dioxide gas sensor using room-temperature hydrogen plasma reduced graphene oxide. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 2049–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Star, A.; Han, T.-R.; Joshi, V.; Gabiel, J.-C.P.; Grüner, G. Nanoelectronic carbon dioxide sensors. Vacuum 2015, 115, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Materials | T (°C) | Concentration (ppm) | Sensitivity (% ppm−1) | Response Time (min) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly- nanoparticle (ionic liquid) | Room temperature | 150–2400 | ~0.004 | 35 min | [35] |
| PEI-functionalized PANI film | Room temperature | 50–5000 | ~0.00714 | >10 min | [36] |
| Reduced graphene oxide | Room temperature | 0–1500 | 0.0118 | 4 min | [37] |
| PeI-starch-functionalized CNTs | Room temperature | 0–1500 | 0.000101 | ~15 s (100%) | [38] |
| SnO nanowire | Room temperature | 5000 | 0.000098 | 5 min | this work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, B.-C.; Shi, J.-B.; Lin, H.-S.; Hsu, P.-Y.; Lee, H.-W.; Lin, C.-H.; Lee, M.-W.; Kao, M.-C. Growth of Less than 20 nm SnO Nanowires Using an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template for Gas Sensing. Micromachines 2020, 11, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020153
Zheng B-C, Shi J-B, Lin H-S, Hsu P-Y, Lee H-W, Lin C-H, Lee M-W, Kao M-C. Growth of Less than 20 nm SnO Nanowires Using an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template for Gas Sensing. Micromachines. 2020; 11(2):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020153
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Bo-Chi, Jen-Bin Shi, Hsien-Sheng Lin, Po-Yao Hsu, Hsuan-Wei Lee, Chih-Hsien Lin, Ming-Way Lee, and Ming-Cheng Kao. 2020. "Growth of Less than 20 nm SnO Nanowires Using an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template for Gas Sensing" Micromachines 11, no. 2: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020153
APA StyleZheng, B.-C., Shi, J.-B., Lin, H.-S., Hsu, P.-Y., Lee, H.-W., Lin, C.-H., Lee, M.-W., & Kao, M.-C. (2020). Growth of Less than 20 nm SnO Nanowires Using an Anodic Aluminum Oxide Template for Gas Sensing. Micromachines, 11(2), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020153





