Experimental Investigation on Ultrasonic Atomization Assisted Turning of Titanium Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Experiment Conditions
2.2. Experiment Design
3. Results and Discussion
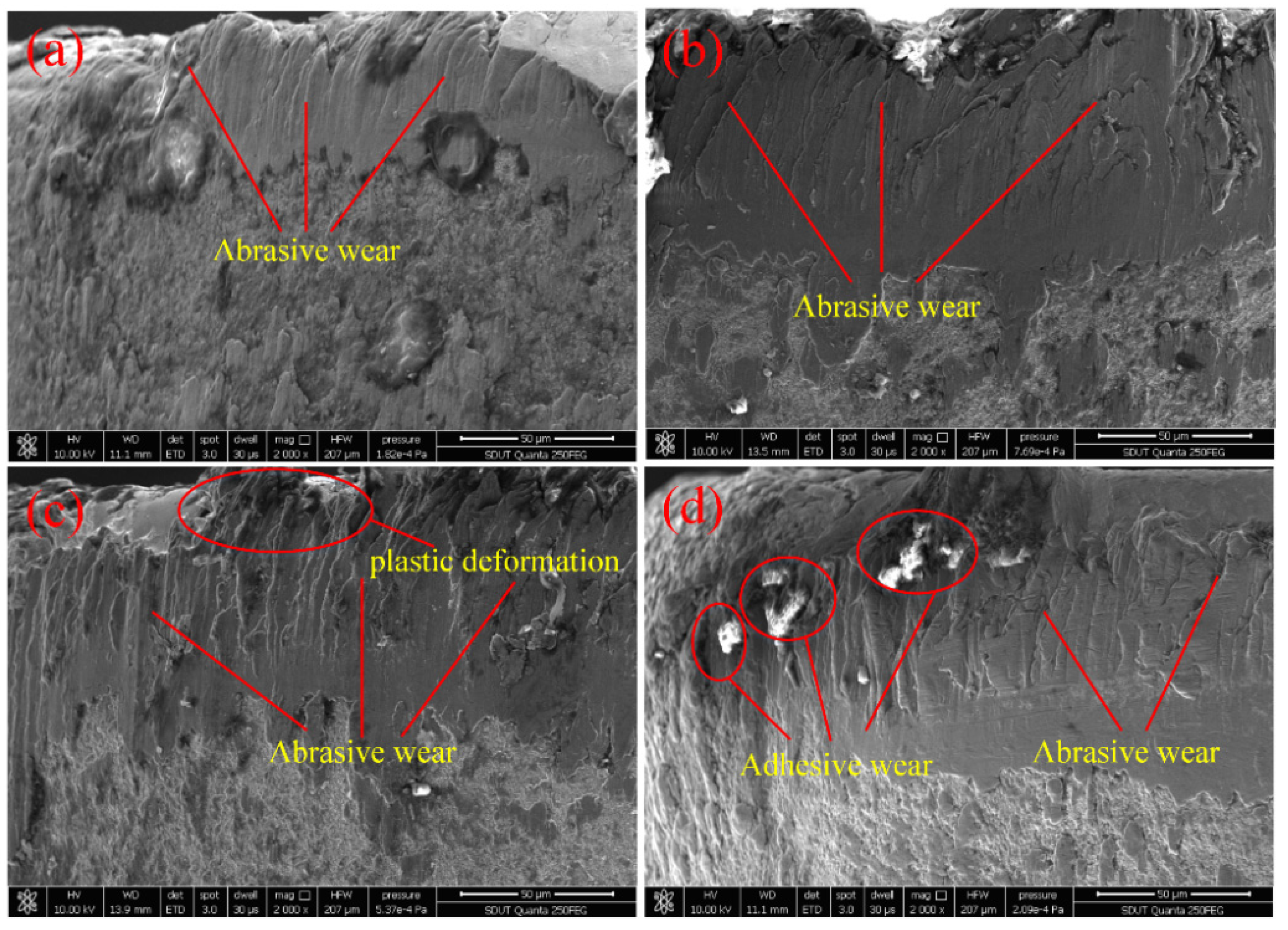
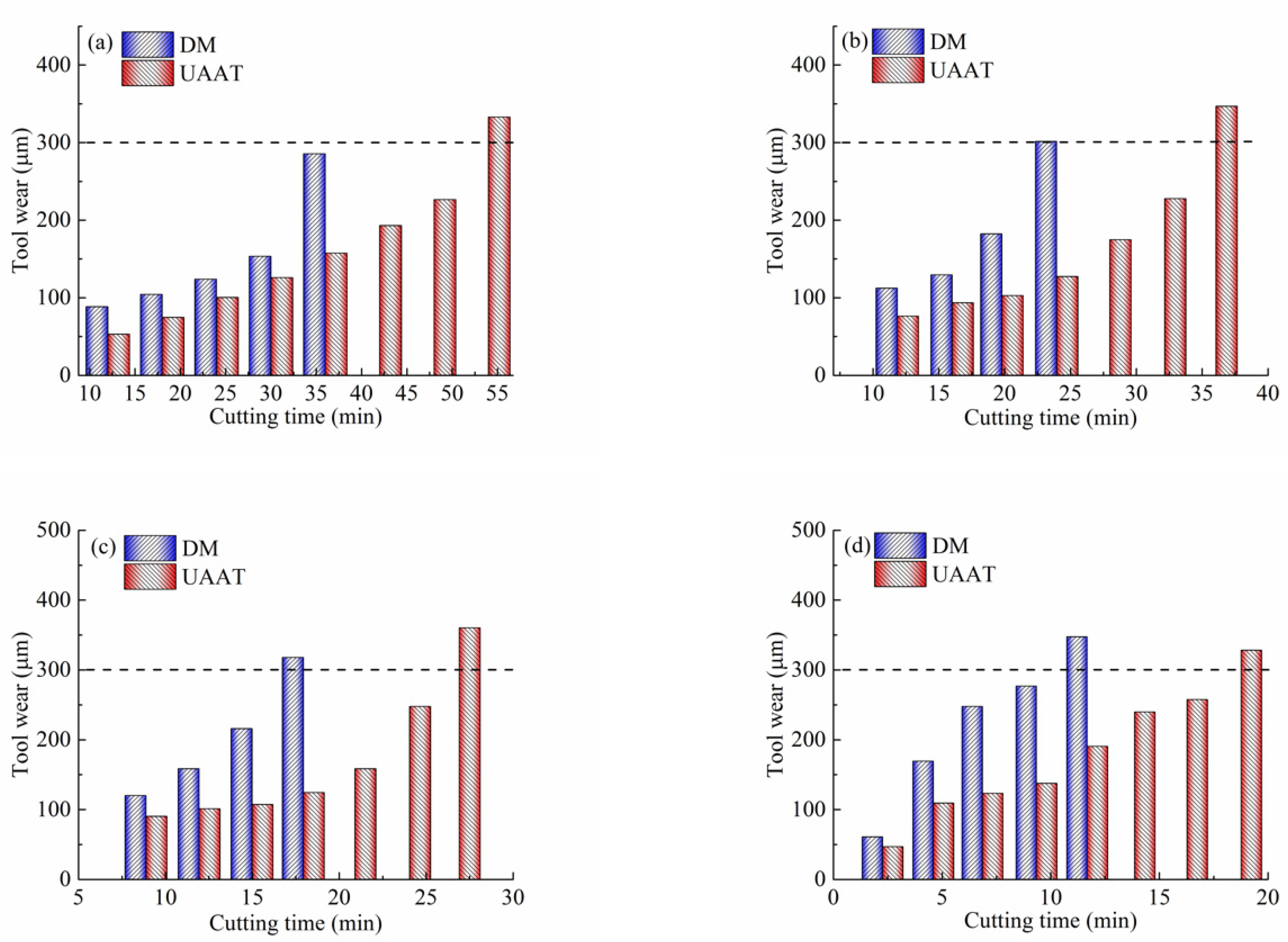
3.1. Tool Wear
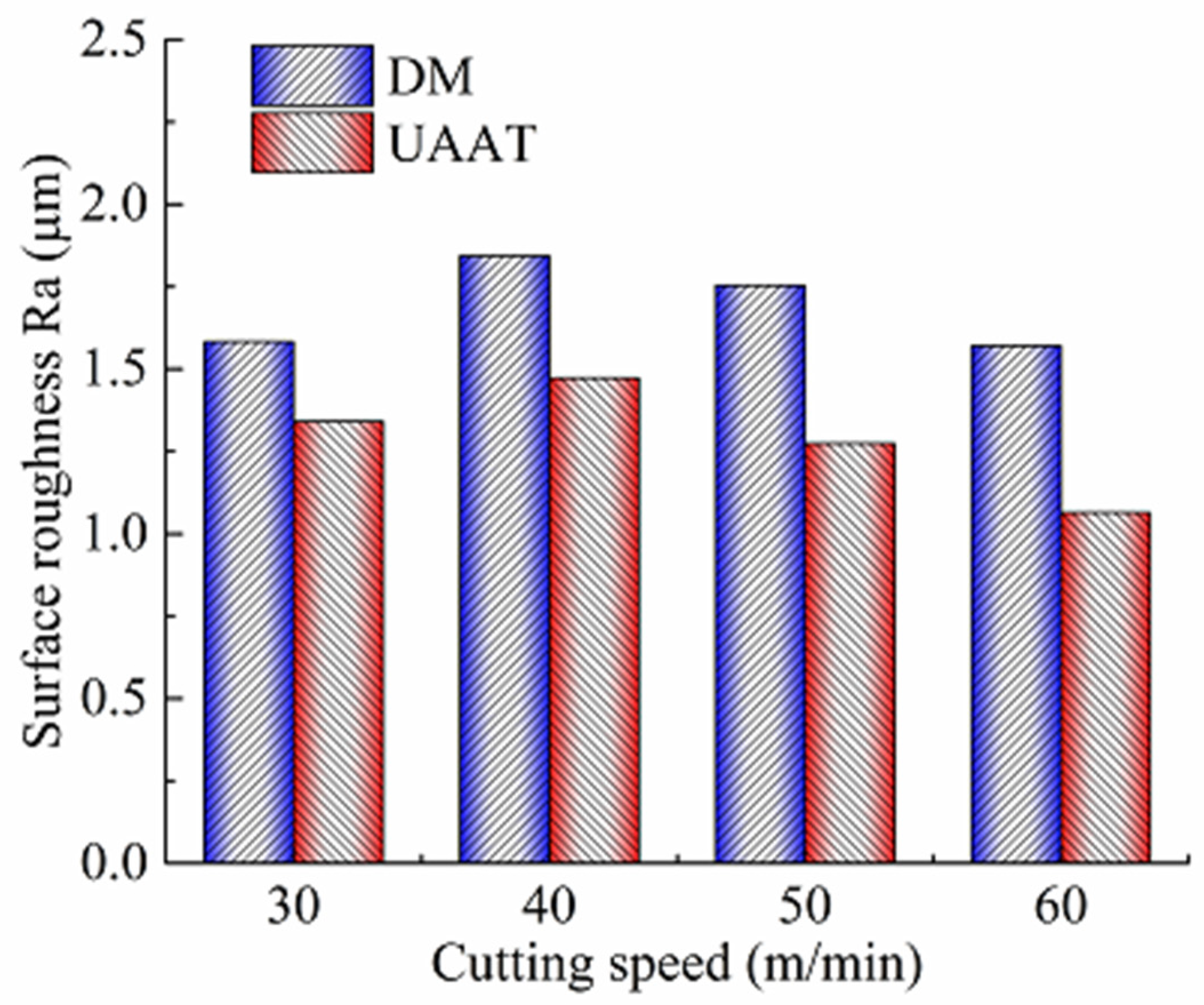
3.2. Surface Roughness
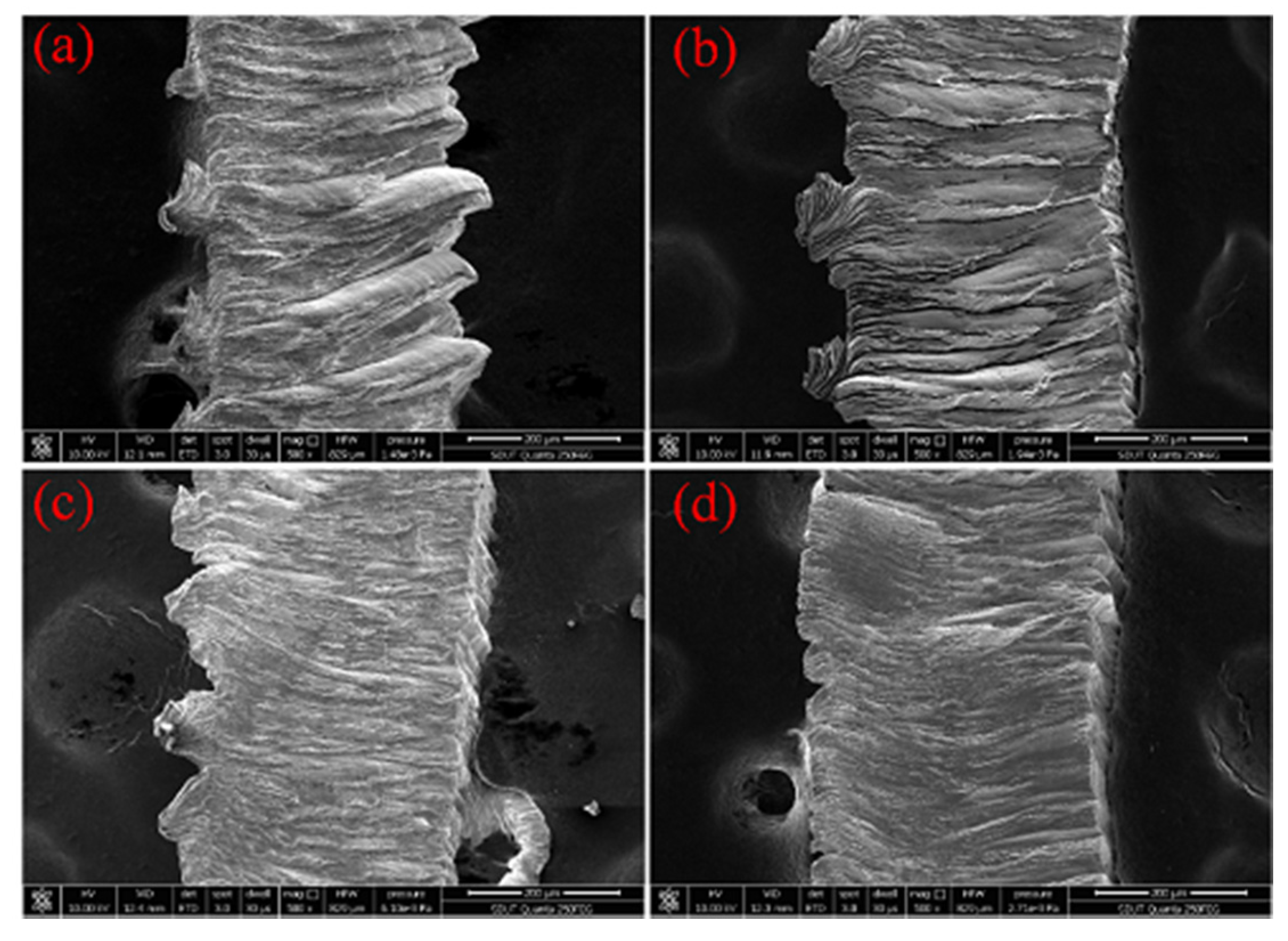
3.3. Chip Morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shalaby, M.A.; Veldhuis, S.C. Some observations on flood and dry finish turning of the Ti-6Al-4V aerospace alloy with carbide and PCD tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 99, 2939–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Z. Tool wear behaviors and corresponding machined surface topography during high-speed machining of Ti-6Al-4V with fine grain tools. Tribol. Int. 2018, 121, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, M.; Azarhoushang, B.; Shamray, S.; Krajnik, P. The effect of dressing parameters on micro-grinding of titanium alloy. Precis. Eng. 2018, 51, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Bai, Q.; Tong, Z. Dislocation Dynamics-Based Modeling and Simulations of Subsurface Damages Microstructure of Orthogonal Cutting of Titanium Alloy. Micromachines 2017, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.; Ismail, L. Thermal analysis of micro milling titanium alloy Ti–6Al–4V. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 229, 659–667. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, X.; Li, G.; Jiang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, Q. Improved toughness of layered architecture TiAlN/CrN coatings for titanium high speed cutting. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 5629–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Liao, W.; Dong, Q.; Sun, L. Friction and wear on titanium alloy surface machined by ultrasonic vibration-assisted milling. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.D.; Sun, Y.; Wen, X.L.; Wang, C.; Gao, Q. Experimental study on surface integrity of Ti-6Al-4V machined by LS-WEDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 88, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Huang, C.; Wen, L.; Zhang, W. Influence of Ultrasonic Surface Rolling on Microstructure and Wear Behavior of Selective Laser Melted Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials 2017, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.; Wu, D.; Ma, L.; Tan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, J. Surface integrity evolution and fatigue evaluation after milling mode, shot-peening and polishing mode for TB6 titanium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Yu, H.O.; Wang, W.K.; Li, Y.P. Comparative Study on Tool Wear of PCBN and Carbide Tools in High Speed Turning of TC4 Titanium Alloy. Modul. Mach. Tool Autom. Manuf. Tech. 2015, 5, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.J.; Qu, S.G.; Pan, Y.X.; Li, X.Q.; Li, F.L. Effects of cutting parameters on dry machining Ti-6Al-4V alloy with ultra-hard tools. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 79, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Patwa, R.; Shin, Y.C. Laser-assisted machining of Inconel 718 with an economic analysis. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.Y.; Shin, Y.C. Improved machinability of SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composited via laser-assisted micromachining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Shen, N.; Shin, Y.C. Thermal and mechanical modeling analysis of laser-assisted micro-milling of difficult-to-machine alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhateeb, M.G.; Shin, Y.C. Investigation of the Machining Behavior of Ti6Al4V/TiC Composites During Conventional and Laser-Assisted Machining. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2019, 141, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.-T.; Woo, W.-S.; Lee, C.-M. A study on the machining characteristics of induction and laser-induction assisted machining of AISI 1045 steel and Inconel. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 34, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.-S.; Woo, W.-S.; Lee, C.-M. A study on the machining characteristics and energy efficiency of Ti-6Al-4V in laser-assisted trochoidal milling. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 5, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejjani, R.; Shi, B.; Attia, H.; Balazinski, M. Laser assisted turning of Titanium Metal Matrix Composite. CIRP Ann. 2011, 60, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Melkote, S.N. Characterization of a hybrid laser-assisted mechanical micromachining (LAMM) process for a difficult-to-machine material. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Pfefferkorn, F. Effect of Laser Preheating the Workpiece on Micro end Milling of Metals. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2008, 130, 011004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.M.; Hou, X.B.; Wang, L.; Chen, B.C. Experimental investigation on the compatibility of nanoparticles with vegetable oils for nanofluid minimum quantity lubrication machining. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niketh, S.; Samuel, G.L. Drilling performance of micro textured tools under dry, wet and MQL condition. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 32, 254–268. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Yu, T.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, W. Parameter optimization during minimum quantity lubrication milling of TC4 alloy with graphene-dispersed vegetable-oil-based cutting fluid. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1508–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Pérez, J.; Cantero, J.L.; Díaz-Álvarez, J.; Miguélez, M.H. Hybrid Composite-Metal Stack Drilling with Different Minimum Quantity Lubrication Levels. Materials 2019, 12, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bermingham, M.; Sim, W.; Kent, D.; Gardiner, S.; Dargusch, M. Tool life and wear mechanisms in laser assisted milling Ti–6Al–4V. Wear 2015, 322, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khmelev, V.N.; Shalunov, A.; Golykh, R.N.; Nesterov, V.; Dorovskikh, R.S.; Shalunova, A.V. Providing the Efficiency and Dispersion Characteristics of Aerosols in Ultrasonic Atomization. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2017, 90, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, T.; Sekiguchi, K.; Sankoda, K.; Namiki, N.; Nii, S. Effect of ultrasonic frequency on size distributions of nanosized mist generated by ultrasonic atomization. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 37, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmoro, A.; d’Amore, M.; Barba, A.A. Droplet size prediction in the production of drug delivery microsystems by ultrasonic atomization. Transl. Med. 2013, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, T.; Yu, T.B.; Shi, J.S.; Zhao, J. Study on polishing slurry waste reduction in polishing monodrystalline silicon based on ultrasonic atomization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yi, S.; Sun, S.; Ding, S. Wear mechanisms and performance of abrasively ground polycrystalline diamond tools of different diamond grains in machining titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yi, S.; Wen, C.; Ding, S. Wear Mechanism and Modeling of Tribological Behavior of Polycrystalline Diamond Tools When Cutting Ti6Al4V. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2018, 140, 121011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, S.; Li, G.; Ding, S.; Mo, J. Performance and mechanisms of graphene oxide suspended cutting fluid in the drilling of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, J. Effects of continuous minimum quantity lubrication with ultrasonic vibration in turning of titanium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
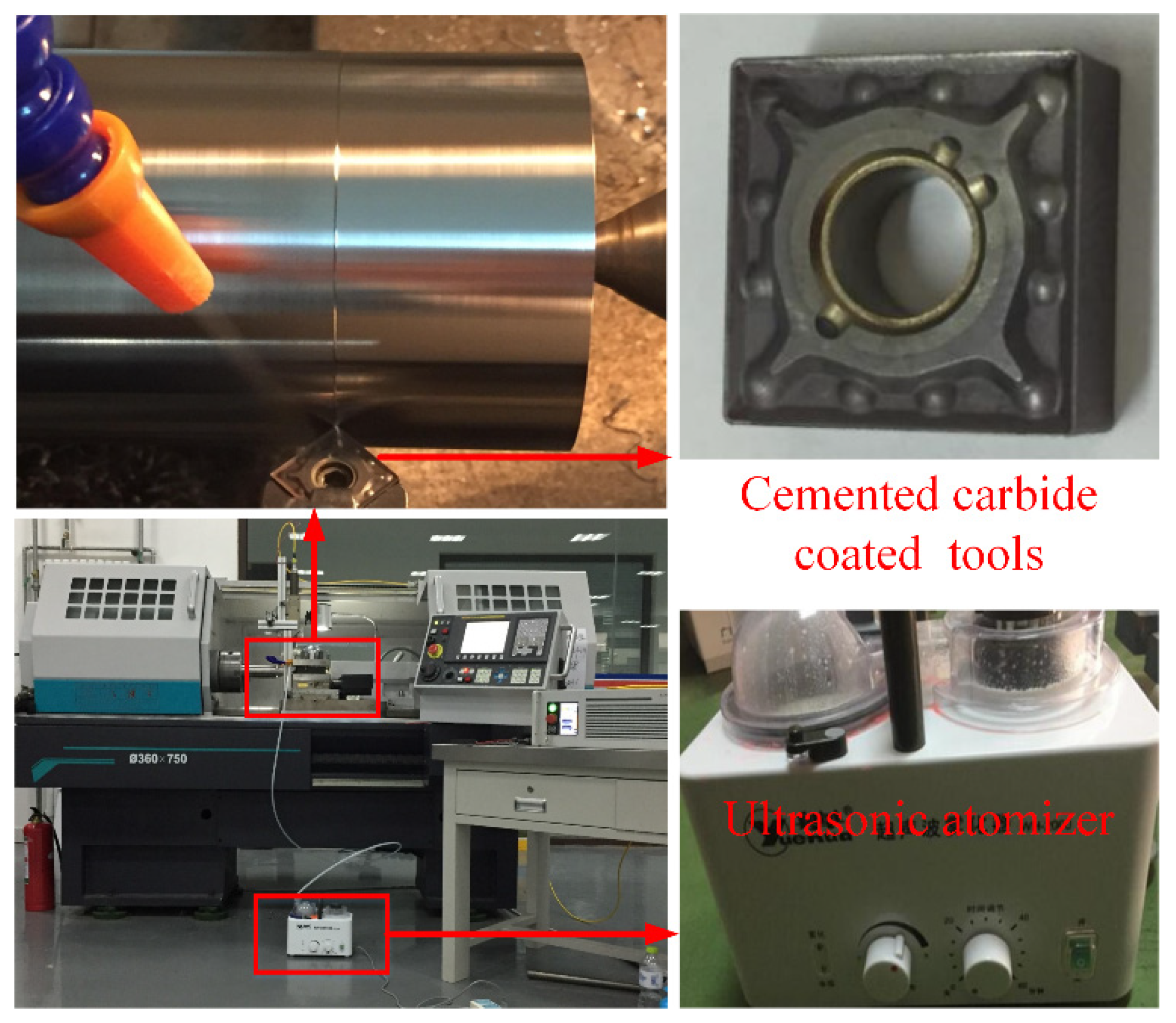



| Element | Ti | Al | V | Fe | O | C | N | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition (wt %) | Balance | 5.5–6.8 | 3.5–4.5 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.015 |
| Property | ρ (g/m3) | σT (MPa) | σY (MPa) | δ (%) | H (HV) | λ (W/m∙K) | E (GPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 4430 | 990 | 830 | 14 | 312 | 7.9 | 114 |
| Angle Types | Value (°) |
|---|---|
| Principal deflection angle | 45 |
| Auxiliary deflection angle | 45 |
| Rake angle | 0 |
| Back angle | 0 |
| Blade inclination angle | 9 |
| Machining Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Cutting speed (m/min) | 30, 40, 50, 60 |
| Feed rate (mm/r) | 0.1 |
| Cutting depth (mm) | 0.4 |
| Volume of output (mL/min) | 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, J.; Huang, B.; Dong, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, X.; Luan, X. Experimental Investigation on Ultrasonic Atomization Assisted Turning of Titanium Alloy. Micromachines 2020, 11, 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020168
Meng J, Huang B, Dong X, Hu Y, Zhao Y, Wei X, Luan X. Experimental Investigation on Ultrasonic Atomization Assisted Turning of Titanium Alloy. Micromachines. 2020; 11(2):168. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020168
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Jianbing, Bingqi Huang, Xiaojuan Dong, Yizhong Hu, Yugang Zhao, Xiuting Wei, and Xiaosheng Luan. 2020. "Experimental Investigation on Ultrasonic Atomization Assisted Turning of Titanium Alloy" Micromachines 11, no. 2: 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020168
APA StyleMeng, J., Huang, B., Dong, X., Hu, Y., Zhao, Y., Wei, X., & Luan, X. (2020). Experimental Investigation on Ultrasonic Atomization Assisted Turning of Titanium Alloy. Micromachines, 11(2), 168. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11020168





