Electrochemical Biosensors for Determination of Colorectal Tumor Biomarkers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Challenges in CRC Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapeutic Response Evaluation
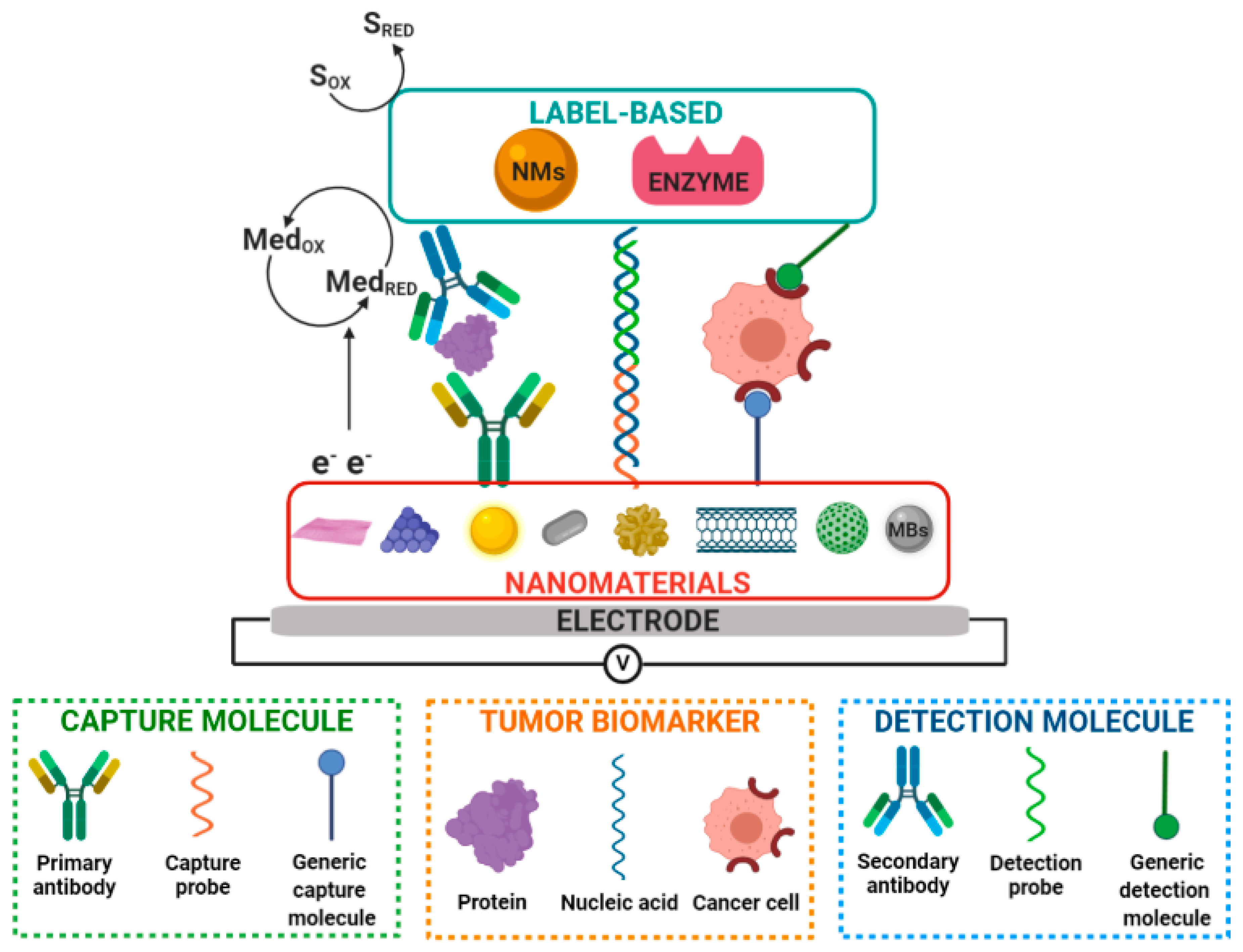
3. Nanobioengineered Electrochemical Biosensors
4. Electrochemical Biosensing of Biomarkers Associated with CRC
4.1. Electrochemical Biosensing of Nucleic Acid Biomarkers of CRC
4.2. Electrochemical Biosensing of Protein Biomarkers of CRC
4.3. Electrochemical Biosensing of CRC-Associated Cells
4.4. Electrochemical Multibiosensing of CRC-Associated Biomarkers
5. Current Challenges and Future Perspectives in Electrochemical Biosensing of CRC-Associated Biomarkers
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GLOBOCAN. Global Colorectal Cancer Statistics 2018; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fearon, E.R.; Vogelstein, B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell 1990, 61, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppedè, F.; Lopomo, A.; Spisni, R.; Migliore, L. Genetic and epigenetic biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A.; Boland, C.R. Epigenetics of Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1442–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. Systematic review of blood diagnostic markers in colorectal cancer. Tech. Coloproctol. 2018, 22, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yörüker, E.E.; Holdenrieder, S.; Gezer, U. Blood-based biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of colorectal cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 455, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Hsieh, J.S.; Chang, M.Y.; Huang, T.J.; Chen, F.M.; Cheng, T.L.; Alexandersen, K.; Huang, Y.S.; Tzou, W.S.; Lin, S.R. Molecular detection of APC, K-ras, and p53 mutations in the serum of colorectal cancer patients as circulating biomarkers. World J. Surg. 2004, 28, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Li, X.F.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, W.Z. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR detection for CEA, CK20 and CK19 mRNA in peripheral blood of colorectal cancer patients. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 2006, 7, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, C.; Hu, L.; Xia, L.; Li, Y. Quantitative Real-time RT–PCR Detection for Survivin, CK20 and CEA in Peripheral Blood of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 38, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouma, A.; Aggeli, C.; Lembessis, P.; Zografos, G.N.; Korkolis, D.P.; Pectasides, D.; Skondra, M.; Pissimissis, N.; Tzonou, A.; Koutsilieris, M. Multiplex RT-PCR-based detections of CEA, CK20 and EGFR in colorectal cancer patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5965–5974. [Google Scholar]
- Herbst, A.; Rahmig, K.; Stieber, P.; Philipp, A.; Jung, A.; Ofner, A.; Crispin, A.; Neumann, J.; Lamerz, R.; Kolligs, F.T. Methylation of NEUROG1 in Serum Is a Sensitive Marker for the Detection of Early Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GLOBOCAN. Cancer Tomorrow: Colon Cancer Incidence and Mortality; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Worm Ørntoft, M.B. Review of Blood-Based Colorectal Cancer Screening: How Far Are Circulating Cell-Free DNA Methylation Markers From Clinical Implementation? Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2018, 17, e415–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, V.; Kalita, J.; Pal, M. Predictive and prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer: A systematic review of recent advances and challenges. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colorectal Cancer Screening Tests. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/screening-tests-used.html (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Colorectal Cancer Screening (PDQ®)–Patient Version. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colorectal-screening-pdq (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Issa, I.A.; NouredDine, M. Colorectal cancer screening: An updated review of the available options. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 5086–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tests to Diagnose and Stage Colorectal Cancer Blood Tests Proctoscopy. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/how-diagnose%0A2020-02-05 (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Tumor Markers. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/diagnosis-staging/diagnosis/tumor-markers-fact-sheet (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Gonzalez-Pons, M.; Cruz-Correa, M. Colorectal Cancer Biomarkers: Where Are We Now? BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 149014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Regueiro, C.R. AGA Future Trends Committee report: Colorectal cancer: A qualitative review of emerging screening and diagnostic technologies. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1083–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, N.L.; Hayes, D.F. Cancer biomarkers. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heichman, K.A. Blood-based testing for colorectal cancer screening. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ColonSentry® Website. Available online: https://www.stagezerolifesciences.com/colonsentry-science.html (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Chao, S.; Pilez, T.; Stamatiou, D.; Ying, J.; Burakoff, R.; Mell, L.D. Stability of The ColonSentry® Colon Cancer Risk Stratification Test. Int. J. Dis. Markers 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, B.T.; Kisiel, J.; Ahlquist, D.A.; Grady, W.M. Molecular markers for colorectal cancer screening. Gut 2015, 64, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FDA. Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) Cologuard; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2014.
- FDA. Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) Epi proColon®; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2016.
- Epi proColon ® Website. Available online: https://www.epiprocolon.com/ (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- Świderska, M.; Choromańska, B.; Da̧browska, E.; Konarzewska-Duchnowska, E.; Choromańska, K.; Szczurko, G.; Myśliwiec, P.; Dadan, J.; Ładny, J.R.; Zwierz, K. The diagnostics of colorectal cancer. Contemp. Oncol. 2014, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Stiksma, J.; Grootendorst, D.C.; Van Der Linden, P.W.G. CA 19-9 As a Marker in Addition to CEA to Monitor Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2014, 13, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, M.J. Carcinoembryonic Antigen as a Marker for Colorectal Cancer: Is It Clinically Useful? Clin. Chem. 2001, 47, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirwan, A.; Utratna, M.; O’Dwyer, M.E.; Joshi, L.; Kilcoyne, M. Glycosylation-Based Serum Biomarkers for Cancer Diagnostics and Prognostics. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FDA. PMA P110027: Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) Therascreen® KRAS RGQ PCR Kit 2014; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2014.
- FDA. PMA P140023: Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) Cobas® KRAS Mutation Test; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2015.
- FDA. PMA P170019: Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) FoundationOne CDx; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2017.
- FDA. PMA P160038: Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) PraxisTM Extended RAS Panel; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2017.
- CellSearch Website. Available online: https://www.cellsearchctc.com/ (accessed on 8 January 2020).
- FDA. K071729 Substantial Equivalence Determination Decision Summary CellSearch; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2007.
- Negin, B.P.; Cohen, S.J. Circulating tumor cells in colorectal cancer: Past, present, and future challenges. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2010, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Füzéry, A.K.; Levin, J.; Chan, M.M.; Chan, D.W. Translation of proteomic biomarkers into FDA approved cancer diagnostics: Issues and challenges. Clin. Proteom. 2013, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FDA. Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) Therascreen® KRAS RGQ PCR Kit 2012; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2012.
- FDA. K050245 Substantial Equivalence Determination Decision Summary CellSearch; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2005.
- FDA. K073338 Substantial Equivalence Determination Decision Summary CellSearch; FDA: White Oak, MD, USA, 2008.
- Villar-Vázquez, R.; Padilla, G.; Fernández-Aceñero, M.J.; Suárez, A.; Fuente, E.; Pastor, C.; Calero, M.; Barderas, R.; Casal, J.I. Development of a novel multiplex beads-based assay for autoantibody detection for colorectal cancer diagnosis. Proteomics 2016, 16, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Guzmán-Aránguez, A.; Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Poves, C.; Fernandez-Aceñero, M.J.; Montero-Calle, A.; Solís-Fernández, G.; Fernandez-Diez, S.; Camps, J.; et al. Multiplexed monitoring of a novel autoantibody diagnostic signature of colorectal cancer using HaloTag technology-based electrochemical immunosensing platform. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3022–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical Biosensors: Recommended Definitions and Classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alzate, D.; Cajigas, S.; Robledo, S.; Muskus, C.; Orozco, J. Genosensors for differential detection of Zika virus. Talanta 2020, 210, 120648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.; Medlin, L.K. Electrochemical performance of a DNA-based sensor device for detecting toxic algae. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 153, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.; Jiménez-Jorquera, C.; Fernández-Sánchez, C. Gold nanoparticle-modified ultramicroelectrode arrays for biosensing: A comparative assessment. Bioelectrochemistry 2009, 75, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vásquez, G.; Rey, A.; Rivera, C.; Iregui, C.; Orozco, J. Amperometric biosensor based on a single antibody of dual function for rapid detection of Streptococcus agalactiae. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors—Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziąbowska, K.; Czaczyk, E.; Nidzworski, D. Application of electrochemical methods in biosensing technologies. In Biosensing Technologies for the Detection of Pathogens—A Prospective Way for Rapid Analysis; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harvey, D. Electrochemical Methods. In Analytical Chemistry 2.0; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 667–782. [Google Scholar]
- Labib, M.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Electrochemical Methods for the Analysis of Clinically Relevant Biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9001–9090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazaca, L.C.; Ribovski, L.; Janegitz, B.C.; Zucolotto, V. Nanostructured materials and nanoparticles for point of care (POC) medical biosensors. In Medical Biosensors for Point of Care (POC) Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 229–254. [Google Scholar]
- Yunus, S.; Jonas, A.M.; Lakard, B. Potentiometric Biosensors. In Encyclopedia of Biophysics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1941–1946. [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald, J.R. Impedance spectroscopy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 20, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Davis, J.J.; Bueno, P.R. Fundamentals and applications of impedimetric and redox capacitive biosensors. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. 2014, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belicky, T.; Katrlik, J.; Tkac, J. Glycan and lectin biosensors. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Palecek, E.; Tkác, J.; Bartosík, M.; Bertók, T.; Ostatná, V.; Palecek, J. Electrochemistry of nonconjugated proteins and glycoproteins. Toward sensors for biomedicine and glycomics. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 2045–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hushegyi, A.; Bertok, T.; Damborsky, P.; Katrlik, J.; Tkac, J. An ultrasensitive impedimetric glycan biosensor with controlled glycan density for detection of lectins and influenza hemagglutinins. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7474–7477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blsakova, A.; Kveton, F.; Tkac, J. Glycan-modified interfaces in biosensing: An electrochemical approach. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2019, 14, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, T.; Ogawa, K.; Sumita, D.; Kondo, M.; Shimomura, M. Amperometric glucose sensing with polyaniline/poly(acrylic acid) composite film bearing glucose oxidase and catalase based on competitive oxygen consumption reactions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 811, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; Pingarrón, M.J. Non-Invasive Breast Cancer Diagnosis through Electrochemical Biosensing at Different Molecular Levels. Sensors 2017, 17, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aziz, M.A.; Oyama, M. Nanomaterials in electrochemical biosensor. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 995, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro-Garcia, A.; Merkoçi, A. Nanobiosensors in diagnostics. Nanobiomedicine 2016, 3, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Krauss, T.F. Label-free affinity biosensor arrays: Novel technology for molecular diagnostics. Expert Rev. Med. Device 2017, 14, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rhouati, A.; Catanante, G.; Nunes, G.; Hayat, A.; Marty, J.L. Label-free aptasensors for the detection of mycotoxins. Sensors 2016, 16, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shamsi, M.H. Biosensors-on-chip: A topical review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pomales, G.; Zangmeister, R.A. Recent advances in electrochemical glycobiosensing. Int. J. Electrochem. 2011, 2011, 825790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yagati, A.K.; Go, A.; Chavan, S.G.; Baek, C.; Lee, M.-H.; Min, J. Nanostructured Au-Pt hybrid disk electrodes for enhanced parathyroid hormone detection in human serum. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 128, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supraja, P.; Sudarshan, V.; Tripathy, S.; Agrawal, A.; Singh, S.G. Label free electrochemical detection of cardiac biomarker troponin T using ZnSnO3 perovskite nanomaterials. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Dutta, H.S.; Gogoi, S.; Devi, R.; Khan, R. Nanostructured MoS2-Based Advanced Biosensors: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Povedano, E.; Vargas, E.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Pedrero, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Comparison of Different Strategies for the Development of Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Nucleic Acid Biosensors Using Neither Nanomaterials nor Nucleic Acid Amplification. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.; Alzate, M.; Gallego, J.; Orozco, J. Electroanalysis of an Iron@Graphene-Carbon Nanotube Hybrid Material. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Umar, M.; Saifi, A.; Kumar, S.; Augustine, S.; Srivastava, S.; Malhotra, B.D. Electrochemical paper based cancer biosensor using iron oxide nanoparticles decorated PEDOT:PSS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1056, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.R.; Kaushik, A.; Agrawal, V.V.; Malhotra, B.D. Nanostructured metal oxide-based biosensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2011, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Chen, Y.; Niu, X.; Pan, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. High-performance electrochemical biosensor for nonenzymatic H2O2 sensing based on Au@C-Co3O4 heterostructures. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ahammad, A.J.S.; Jin, J.-H.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, J.-J. A Comprehensive Review of Glucose Biosensors Based on Nanostructured Metal-Oxides. Sensors 2010, 10, 4855–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Juřík, T.; Kovář, D.; Trnková, L.; Skládal, P. Nanoparticle-Based Immunochemical Biosensors and Assays: Recent Advances and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9973–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothipor, C.; Wiriyakun, N.; Putnin, T.; Ngamaroonchote, A.; Jakmunee, J.; Ounnunkad, K.; Laocharoensuk, R.; Aroonyadet, N. Highly sensitive biosensor based on graphene–poly (3-aminobenzoic acid) modified electrodes and porous-hollowed-silver-gold nanoparticle labelling for prostate cancer detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamabadi, P.F.; Heydari-Bafrooei, E. Impedimetric aptasensing of the breast cancer biomarker HER2 using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticles in a composite consisting of electrochemically reduced graphene oxide and single-walled carbon nanotubes. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, D.G.; Kandasubramanian, B. Progress in the Development of Intrinsically Conducting Polymer Composites as Biosensors. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, D.; Pimentel, A.; Gonçalves, A.; Pereira, S.; Branquinho, R.; Barquinha, P.; Fortunato, E.; Martins, R. Metal oxide nanostructures for sensor applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahato, K.; Maurya, P.K.; Chandra, P. Fundamentals and commercial aspects of nanobiosensors in point-of-care clinical diagnostics. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcarius, A.; Minteer, S.D.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Merkoçi, A. Nanomaterials for bio-functionalized electrodes: Recent trends. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 4878–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centelles, J.J. General Aspects of Colorectal Cancer. ISRN Oncol. 2012, 2012, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, M.A.; Kouzarides, T. Cancer epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell 2012, 150, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lao, V.V.; Grady, W.M. Epigenetics and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 8, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Jiang, J.H.; Shen, G.L.; Yu, R.Q. A nano-porous CeO2/Chitosan composite film as the immobilization matrix for colorectal cancer DNA sequence-selective electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2006, 70, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KRAS. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/content/gene/kras/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- KRAS Gene. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/mortality (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Leng, K.; Li, J.; Zheng, F.; Shen, G.; Yu, R. A sequence-selective electrochemical DNA biosensor based on HRP-labeled probe for colorectal cancer DNA detection. Anal. Lett. 2008, 41, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shu, G.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Tang, M. Electrochemical biosensor based on functional composite nanofibers for detection of K-ras gene via multiple signal amplification strategy. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 466, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ogaidi, A.J.M.; Stefan-van Staden, R.I.; Gugoasa, L.A.; Rosu, M.C.; Socaci, C. Electrochemical Determination of the KRAS Genetic Marker for Colon Cancer with Modified Graphete and Graphene Paste Electrodes. Anal. Lett. 2018, 51, 2820–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KRAS Mutation. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/content/alteration/kras-mutation/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Misale, S.; Yaeger, R.; Hobor, S.; Scala, E.; Janakiraman, M.; Liska, D.; Valtorta, E.; Schiavo, R.; Buscarino, M.; Siravegna, G.; et al. Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature 2012, 486, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petit, J.; Carroll, G.; Gould, T.; Pockney, P.; Dun, M.; Scott, R.J. Cell-free DNA as a Diagnostic Blood-Based Biomarker for Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 236, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KRAS G12D. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/content/alteration/kras-g12d/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Vaughn, C.P.; ZoBell, S.D.; Furtado, L.V.; Baker, C.L.; Samowitz, W.S. Frequency of KRAS, BRAF, and NRAS Mutations in Colorectal Cancer. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2011, 50, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.F.; Ma, R.N.; Sun, F.; Jia, L.P.; Zhang, W.; Shang, L.; Xue, Q.W.; Jia, W.L.; Wang, H.S. A versatile label-free electrochemical biosensor for circulating tumor DNA based on dual enzyme assisted multiple amplification strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Xiang, J. Detection of KRAS G12D point mutation level by anchor-like DNA electrochemical biosensor. Talanta 2019, 198, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BRAF. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/content/gene/braf/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- BRAF V600E. Available online: https://www.mycancergenome.org/content/alteration/braf-v600e/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Situ, B.; Cao, N.; Li, B.; Liu, Q.; Lin, L.; Dai, Z.; Zou, X.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yan, X.; et al. Sensitive electrochemical analysis of BRAF V600E mutation based on an amplification-refractory mutation system coupled with multienzyme functionalized Fe3O4/Au nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 43, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlobec, I.; Kovac, M.; Erzberger, P.; Molinari, F.; Bihl, M.P.; Rufle, A.; Foerster, A.; Frattini, M.; Terracciano, L.; Heinimann, K.; et al. Combined analysis of specific KRAS mutation, BRAF and microsatellite instability identifies prognostic subgroups of sporadic and hereditary colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2569–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrilia, N.; Kollias, A.; Manolopoulos, L.; Syrigos, K. Cell adhesion molecules: Role and clinical significance in cancer. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulati, P.; Mishra, P.; Khanuja, M.; Narang, J.; Islam, S.S. Nano-moles detection of tumor specific biomarker DNA for colorectal cancer detection using vertically aligned multi-wall carbon nanotubes based flexible electrodes. Process. Biochem. 2020, 90, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Añorga, L.; Rebollo, A.; Herrán, J.; Arana, S.; Bandrés, E.; García-Foncillas, J. Development of a DNA microelectrochemical biosensor for CEACAM5 detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1368–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Gamella, M.; Pedrero, M.; Barderas, R.; Peláez-García, A.; Mendiola, M.; Hardisson, D.; Feliú, J.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; et al. Amperometric bioplatforms to detect regional DNA methylation with single-base sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccini, A.; Berger, M.D.; Naseem, M.; Tokunaga, R.; Battaglin, F.; Cao, S.; Hanna, D.L.; McSkane, M.; Soni, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Colorectal cancer: Epigenetic alterations and their clinical implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Rev. Cancer 2017, 1868, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toiyama, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Fleshman, J.; Richard, C.; Goel, A. MicroRNAs as potential liquid biopsy biomarkers in colorectal Cancer: A systematic review. BBA Rev. Cancer 2018, 1870, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; Meng, X.; Yin, H.; Ai, S. Amplified electrochemical microRNA biosensor using a hemin-G-quadruplex complex as the sensing element. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7140–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boriachek, K.; Umer, M.; Islam, M.N.; Gopalan, V.; Lam, A.K.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. An amplification-free electrochemical detection of exosomal miRNA-21 in serum samples. Analyst 2018, 143, 1662–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öbrink, B. CEA adhesion molecules: Multifunctional proteins with signal-regulatory properties. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dnistrian, A.M.; Schwartz, M.K.; Greenberg, E.J.; Smith, C.A.; Schwartz, D.C. CA 15-3 and carcinoembryonic antigen in the clinical evaluation of breast cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 1991, 200, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.Y.; Chin, S.F.; Low, T.Y.; Jamal, R. Probing the colorectal cancer proteome for biomarkers: Current status and perspectives. J. Proteom. 2018, 187, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborla, N.; Fragoso, A.; Kemmner, W.; Latta, D.; Nllsson, O.; Botero, M.L.; Drese, K.; O’Sulllivan, C.K. Amperometric immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen in colon cancer samples based on monolayers of dendritic bipodal scaffolds. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Truta, L.A.A.N.A.; Sales, M.G.F. Biomimetic materials assembled on a photovoltaic cell as a novel biosensing approach to cancer biomarker detection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavares, A.P.M.; Truta, L.A.A.N.A.; Moreira, F.T.C.; Carneiro, L.P.T.; Sales, M.G.F. Self-powered and self-signalled autonomous electrochemical biosensor applied to cancinoembryonic antigen determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 140, 111320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.T.C.; Sales, M.G.F. Autonomous biosensing device merged with photovoltaic technology for cancer biomarker detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 855, 113611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, S.; Li, J. Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: Current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2922–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Current advancement in immunosensing of p53 tumor suppressor protein based on nanomaterials: Analytical approach. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Kashaninejad, N.; Masud, M.K.; Yamauchi, Y.; Nguyen, N.T.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. Autoantibodies as diagnostic and prognostic cancer biomarker: Detection techniques and approaches. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 139, 111315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campuzano, S.; Pedrero, M.; González-Cortés, A.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical biosensors for autoantibodies in autoimmune and cancer diseases. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Guzman-Aranguez, A.; Poves, C.; Fernandez-Acenero, M.J.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Montiel, V.R.V.; Domínguez, G.; Frutos, L.S.; Rodríguez, N.; Villalba, M.; et al. Toward liquid biopsy: Determination of the humoral immune response in cancer patients using halotag fusion protein-modified electrochemical bioplatforms. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12339–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Masud, M.K.; Islam, M.N.; Gopalan, V.; Lam, A.K.Y.; Tanaka, S.; Nguyen, N.T.; Hossain, M.S.; Li, C.; Yamauchi, M.Y.; et al. Gold-loaded nanoporous iron oxide nanocubes: A novel dispersible capture agent for tumor-associated autoantibody analysis in serum. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 8805–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attallah, A.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; El-Sayed, A.M.; Tabll, A.A. Detection of serum p53 protein in patients with different gastrointestinal cancers. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2003, 27, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, M.; Aydın, E.B.; Sezgintürk, M.K. A disposable immunosensor using ITO based electrode modified by a star-shaped polymer for analysis of tumor suppressor protein p53 in human serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Duuren, J.B.J.H.; Müsken, M.; Karge, B.; Tomasch, J.; Wittmann, C.; Häussler, S.; Brönstrup, M. Use of Single-Frequency Impedance Spectroscopy to Characterize the Growth Dynamics of Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasem, K.; Gopalan, V.; Salajegheh, A.; Lu, C.-T.; Smith, R.A.; Lam, A.K.-Y. The roles of JK-1 (FAM134B) expressions in colorectal cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 326, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Gopalan, V.; Wahab, R.; Smith, R.A.; Qiao, B.; Lam, A.K.-Y. Stage dependent expression and tumor suppressive function of FAM134B (JK1) in colon cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, F.; Haque, M.H.; Yadav, S.; Islam, M.N.; Gopalan, V.; Nguyen, N.T.; Lam, A.K.; Shiddiky, M.J.A. An electrochemical method for sensitive and rapid detection of FAM134B protein in colon cancer samples. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Regiart, M.; Fernández-Baldo, M.A.; Villarroel-Rocha, J.; Messina, G.A.; Bertolino, F.A.; Sapag, K.; Timperman, A.T.; Raba, J. Microfluidic immunosensor based on mesoporous silica platform and CMK-3/poly-acrylamide-co-methacrylate of dihydrolipoic acid modified gold electrode for cancer biomarker detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 963, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proença, C.A.; Baldo, T.A.; Freitas, T.A.; Materón, E.M.; Wong, A.; Durán, A.A.; Melendez, M.E.; Zambrano, G.; Faria, R.C. Novel enzyme-free immunomagnetic microfluidic device based on Co0.25Zn0.75Fe2O4 for cancer biomarker detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1071, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.G.; Fernández-baldo, M.A.; Serrano, M.J.; Messina, G.A.; Lorente, J.A.; Raba, J. Epithelial cancer biomarker EpCAM determination in peripheral blood samples using a microfluidic immunosensor based in silver nanoparticles as platform. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2015, 221, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, K.; Ortega, F.G.; Messina, G.A.; Sanz, M.I.; Fernández-baldo, M.A.; Raba, J. Integrated bio-affinity nano-platform into a micro fluidic immunosensor based on monoclonal bispecific trifunctional antibodies for the electrochemical determination of epithelial cancer biomarker. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 464, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-H.; Sun, R.; Zhou, X.-M.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Lu, J.-B.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, L.-S.; Yang, X.-Z.; Shi, L.; Xiao, R.-W.; et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule overexpression regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Chen, W. A Polyamidoamine Dendrimer-Based Electrochemical Immunosensor for Label-Free Determination of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule- Expressing Cancer Cells. Sensors 2019, 19, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.M.; Ryu, M.Y.; Yun, J.W.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.P. Electrochemical peptide sensor for diagnosing adenoma-carcinoma transition in colon cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; Ryu, M.Y.; Lee, G.B.; Park, J.P. Selection of High Affinity Peptides for Prediction of Colorectal Adenoma–to-Carcinoma Progression. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 1140–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.; Chandra, P.; Koo, J.P.; Shim, Y.B. Development of a bifunctional nanobiosensor for screening and detection of chemokine ligand in colorectal cancer cell line. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Xu, Z.-Q.; Zong, Y.-P.; Ou, B.-C.; Shen, X.-H.; Feng, H.; Zheng, M.-H.; Zhao, J.-K.; Lu, A.-G. CXCL5 induces tumor angiogenesis via enhancing the expression of FOXD1 mediated by the AKT/NF-κB pathway in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiddiky, M.J.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Shim, Y.-B. Hydrazine-Catalyzed Ultrasensitive Detection of DNA and Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6886–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, M.; Toiyama, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Saigusa, S.; Okugawa, Y.; Hiro, J.; Uchida, K.; Mohri, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M. CXCL5, a promoter of cell proliferation, migration and invasion, is a novel serum prognostic marker in patients with colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez-Redín, G.; Furuta, R.H.M.; Wilson, D.; Shimizu, F.M.; Materon, E.M.; Arantes, L.M.R.B.; Melendez, M.E.; Carvalho, A.L.; Reis, R.M.; Chaur, M.N.; et al. Screen-printed interdigitated electrodes modified with nanostructured carbon nano-onion films for detecting the cancer biomarker CA19-9. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Povedano, E.; Montiel, V.R.V.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical immunosensor for IL-13 Receptor α2 determination and discrimination of metastatic colon cancer cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 117, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serafín, V.; Valverde, A.; Martínez-García, G.; Martínez-Periñán, E.; Comba, F.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Barderas, R.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Graphene quantum dots-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as nanocarriers in electrochemical immunosensing. Determination of IL-13 receptor α2 in colorectal cells and tumor tissues with different metastatic potential. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Serafín, V.; Montero-Calle, A.; González-Cortés, A.; Barderas, R.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Carbon/Inorganic Hybrid Nanoarchitectures as Carriers for Signaling Elements in Electrochemical Immunosensors: First Biosensor for the Determination of the Inflammatory and Metastatic Processes Biomarker RANK-ligand. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renema, N.; Navet, B.; Heymann, M.F.; Lezot, F.; Heymann, D. RANK-RANKL signalling in cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.; Yang, L.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y. Cadherin Signaling in Cancer: Its Functions and Role as a Therapeutic Target. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, N.; Perraud, A.; Blondy, S.; Jauberteau, M.O.; Battu, S.; Mathonnet, M. E-cadherin: A potential biomarker of colorectal cancer prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 4571–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartolomé, R.A.; Barderas, R.; Torres, S.; Fernandez-Aceñero, M.J.; Mendes, M.; García-Foncillas, J.; Lopez-Lucendo, M.; Casal, J.I. Cadherin-17 interacts with α2β1 integrin to regulate cell proliferation and adhesion in colorectal cancer cells causing liver metastasis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1658–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Seol, J.A.; Choi, H.J.; Roh, Y.H.; Choi, P.J.; Lee, K.E.; Roh, M.S. Comparison of cadherin-17 expression between primary colorectal adenocarcinomas and their corresponding metastases: The possibility of a diagnostic marker for detecting the primary site of metastatic tumour. Histopathology 2011, 58, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-San Martín, C.; Pedrero, M.; Manuel de Villena, F.J.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Rodríguez, N.; Domínguez, G.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Disposable Amperometric Immunosensor for the Determination of the E-Cadherin Tumor Suppressor Protein in Cancer Cells and Human Tissues. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Povedano, E.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Rodríguez, N.; Domínguez, G.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Determination of Cadherin-17 in Tumor Tissues of Different Metastatic Grade Using a Single Incubation-Step Amperometric Immunosensor. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11161–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, T.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Augustine, S.; Yadav, B.K.; Malhotra, B.D. Protein functionalised self assembled monolayer based biosensor for colon cancer detection. Talanta 2019, 201, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadighbayan, D.; Sadighbayan, K.; Tohid-kia, M.R.; Khosroushahi, A.Y.; Hasanzadeh, M. Development of electrochemical biosensors for tumor marker determination towards cancer diagnosis: Recent progress. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tertis, M.; Leva, P.I.; Bogdan, D.; Suciu, M.; Graur, F.; Cristea, C. Impedimetric aptasensor for the label-free and selective detection of Interleukin-6 for colorectal cancer screening. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagawa, H.; Sone, S.; Takahashi, Y.; Haku, T.; Yano, S.; Shinohara, T.; Ogura, T. Serum levels of interleukin 6 in patients with lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 71, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundling, K.E.; Lowe, A.C. Circulating Tumor Cells: Overview and Opportunities in Cytology. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2019, 26, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasova, P.; Pinkas, M.; Kolostova, K.; Gurlich, R.; Bobek, V. Circulating tumor cells in different stages of colorectal cancer. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2017, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, W.-C.; Wu, M.-H.; Chang, P.-H.; Hsu, H.-C.; Chang, G.; Huang, W.-K.; Wu, C.-E.; Chia-Hsun Hsieh, J. A Prognostic Model Based on Circulating Tumour Cells is Useful for Identifying the Poorest Survival Outcome in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci 2018, 14, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sastre, J.; Maestro, M.L.; Gomez-Espana, A.; Rivera, F.; Valladares, M.; Massuti, B.; Benavides, M.; Gallen, M.; Marcuello, E.; Abad, A.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cell Count Is a Prognostic Factor in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving First-Line Chemotherapy Plus Bevacizumab: A Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors Study. Oncologist 2012, 17, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vafaei, S.; Fattahi, F.; Ebrahimi, M.; Janani, L.; Shariftabrizi, A.; Madjd, Z. Common molecular markers between circulating tumor cells and blood exosomes in colorectal cancer: A systematic and analytical review. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8669–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagrath, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Maheswaran, S.; Bell, D.W.; Irimia, D.; Ulkus, L.; Smith, M.R.; Kwak, E.L.; Digumarthy, S.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 2007, 450, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maltez-Da Costa, M.; De La Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Nogués, C.; Barrios, L.; Ibáñez, E.; Merkoçi, A. Simple monitoring of cancer cells using nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4164–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, M.A.; Amoabediny, G.; Tajik, P.; Hosseini, M.; Ghafar-Zadeh, E. An apta-biosensor for colon cancer diagnostics. Sensors 2015, 15, 22291–22303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, A.; Zhang, C.; Liang, G.; Feng, W.; Tian, Z.; Jing, C. Hyaluronate-functionalized graphene for label-free electrochemical cytosensing. Micromachines 2018, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina, M.; Vélez, D.; Asenjo, J.A.; Egea, G.; Real, F.X.; Gil, J.; Subiza, J.L. Human colon adenocarcinomas express a MUC1-associated novel carbohydrate epitope on core mucin glycans defined by a monoclonal antibody (A10) raised against murine Ehrlich tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Tanimoto, T.; Tanaka, S.; Haruma, K.; Yoshihara, M.; Sumii, K.; Kajiyama, G.; Shimamoto, F.; Kohno, N. MUC1 expression in intramucosal colorectal neoplasms. Possible involvement in histogenesis and progression. Oncology 1999, 56, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Ye, D.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S.; Kong, J. A novel aptasensor based on MUC-1 conjugated CNSs for ultrasensitive detection of tumor cells. Analyst 2014, 139, 4917–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Lee, M. Increasing the α 2, 6 sialylation of glycoproteins may contribute to metastatic spread and therapeutic resistance in colorectal cancer. Gut Liver 2013, 7, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Ding, J. Sialylation is involved in cell fate decision during development, reprogramming and cancer progression. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Yang, D.P.; Ye, D.; Zhang, X.; Fang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Kong, J. Protein-inorganic hybrid nanoflowers as ultrasensitive electrochemical cytosensing Interfaces for evaluation of cell surface sialic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashkavayi, A.B.; Raoof, J.B.; Ojani, R.; Kavoosian, S. Ultrasensitive electrochemical aptasensor based on sandwich architecture for selective label-free detection of colorectal cancer (CT26) cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymani, J.; Hasanzadeh, M.; Somi, M.H.; Shadjou, N.; Jouyban, A. Highly sensitive and specific cytosensing of HT 29 colorectal cancer cells using folic acid functionalized-KCC-1 nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 132, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidi, M.R.; Karami, P.; Johari-Ahar, M.; Omidi, Y. Direct detection of tryptophan for rapid diagnosis of cancer cell metastasis competence by an ultra-sensitive and highly selective electrochemical biosensor. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 7910–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragones, H.; Schreiber, D.; Inberg, A.; Berkh, O.; Kósa, G.; Freeman, A.; Shacham-Diamand, Y. Disposable electrochemical sensor prepared using 3D printing for cell and tissue diagnostics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameer, A.S. Colorectal Cancer: Molecular Mutations and Polymorphisms. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, B.Y.; Cho, J.; Hong, H.K.; Bae, J.S.; Park, W.Y.; Joung, J.G.; Cho, Y.B. Exome and transcriptome sequencing identifies loss of PDLIM2 in metastatic colorectal cancers. Cancer Manag. Res. 2017, 9, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fung, K.Y.C.; Tabor, B.; Buckley, M.J.; Priebe, I.K.; Purins, L.; Pompeia, C.; Brierley, G.V.; Lockett, T.; Gibbs, P.; Tie, J.; et al. Blood-based protein biomarker panel for the detection of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S. Tumor markers in clinical practice: General principles and guidelines. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2009, 30, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.; Song, P.; Zhou, G.; Zuo, X.; Aldalbahi, A.; Lou, X.; Shi, J.; Fan, C. Electrochemical detection of nucleic acids, proteins, small molecules and cells using a DNA-nanostructure-based universal biosensing platform. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1244–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; ben Hassine, A.; Serafín, V.; Muñoz-San Martín, C.; Pedrero, M.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Gamella, M.; Raouafi, N.; Barderas, R.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; et al. Dual Amperometric Immunosensor for Improving Cancer Metastasis Detection by the Simultaneous Determination of Extracellular and Soluble Circulating Fraction of Emerging Metastatic Biomarkers. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafín, V.; Valverde, A.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Simultaneous amperometric immunosensing of the metastasis-related biomarkers IL-13Rα2 and CDH-17 by using grafted screen-printed electrodes and a composite prepared from quantum dots and carbon nanotubes for signal amplification. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
















| Clinical Purpose | Type of Biomarker | Tumor Marker | Specimen Type | Commercially Available Test | Detection Method | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation of the risk/probability of a patient having CRC | Messenger RNA (mRNA) | ANXA3, CLEC4D, LMNB1, PRRG4, TNFAIP6, VNN1, IL2RB | Blood | ColonSentry® | qPCR | [25,26,27] |
| Screening for average-risk adults | Mutant and methylated DNA, and FIT | - | Stool | a CologuardTM | For DNA markers: qPCR For Hemoglobine: ELISA | [28,29] |
| Methylated DNA | SEPT9 | Blood | b Epi proColon® | qPCR | [25,30,31] | |
| Diagnostic | Glycoprotein | c TAG-72 | Serum | NA | - | [32] |
| Conjugated polypeptide | TPS | Serum | NA | - | [32] | |
| Prognosis | Tetrasaccharide | d CA-19.9 | Serum | NA | Immunoassay | [32,33] |
| Evaluation of recurrence after tumor resection | Glycoprotein | e CEA | Serum | NA | Immunoassay | [25,32,34,35] |
| Therapeutic-response (5-Fluorouracil-based chemotherapy) | Conjugated polypeptide | TPS | Serum | NA | - | [32] |
| Glycoprotein | e CEA | Serum | NA | Immunoasay | [25,32,34,35] | |
| Therapeutic-response (cetuximab and panitumumab-based therapy) | DNA | Mutations in KRAS gene | DNA samples extracted from FFPE tumor tissue | f Therascreen KRAS RGQ PCR Kit | qPCR | [36] |
| Mutations in codons 12 and 13 of the KRAS gene | DNA samples extracted from FFPE tumor tissue | g Cobas KRAS Mutation Test | qPCR | [37] | ||
| For cetuximab: KRAS wild-type (absence of mutations in codons 12 and 13) For panitumumab: KRAS (exons 2, 3, and 4) and NRAS (exons 2, 3, and 4) | DNA samples extracted from FFPE tumor tissue | h FoundationOne CDx | - | [38] | ||
| Therapeutic-response (panitumumab-based therapy) | DNA | Mutations from exons 2, 3, and 4 of both KRAS and NRAS gen | DNA samples extracted from FFPE tumor tissue | i Praxis Extended RAS Panel | qPCR | [39] |
| Follow-up of metastatic patients | Circulating tumor cell | Epithelial cells | Blood | j CellSearch™ | Fluorescence detection after immunomagnetic capture | [6,40,41,42] |
| Type of Biomarker | Biomarker | Clinical Purpose | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic | Prognosis | Therapeutic Response Evaluation | ||||
| Genetic | Genes | SEPT9 | X | [5] | ||
| Mutation gene | APC, KRAS, TP53 | X | X | X | [6,7] | |
| Transcript | mRNA | CEA, cytokeratin 20, survivin, EGFR | X | X | [8,9,10] | |
| Epigenetic | Hypermethylated DNA | MLH1, DAPK, RUNX3, ALX4, SEPT9, Vimentin, NEUROG1 | X | [4,11] | ||
| HLTF, HPP1, DFNA5 | X | [6] | ||||
| Hypomethylated DNA | LINE-1 | X | [5] | |||
| miRNA | miRNA-15b, miRNA-18a, miRNA-19b, miRNA-20a, miRNA-21, miRNA-29a, miRNA-29b, miRNA-155, miRNA-194, miRNA-221, miRNA-335, miRNA-365, miRNA-1290 | X | [4,5,6] | |||
| miRNA-141, miRNA-200c | X | [4] | ||||
| miRNA-27b, miRNA-130b, miRNA-148a, miRNA-326, miRNA-484 | X | [6] | ||||
| miRNA-19a, miRNA-106a | X | X | [5,6] | |||
| Histones modification | H3K9me3, H4K20me3, H3K27me3 | X | [5] | |||
| Other non-coding RNA | NEAT1_v1, NEAT1_v2 | X | [5] | |||
| Protein | Antibodies | Autoantibody-p53, Anti-p53, Anti-IMPDH2, Anti-MDM2, Anti-MAGEA4, FnIgA, FnIgG, Autoantibody-GTF2B, Autoantibody-MAPKAPK3, Autoantibody-PIM1, Autoantibody-PKN1, Autoantibody-SRC, Autoantibody-STK4, Autoantibody-SULF1 | X | [5,47,48] | ||
| Proteins | RBP4, THBS, TFF3, CEA, COL3A1, COL10A1, EGFR, CA11-19, MIC-1, GDF15, IL-6, IL-8, AZGP1, Angiopoetin-2, CL-L1, M-ficolin, MAp44, IGFBP2, DKK3, PKM2, CA19-9, CA50, CA72-4, p53, sFasL, VEGF | X | [5,6] | |||
| Cell | Circulating tumor cell (CTC) | CTC | X | [6] | ||
| Biomarker | Electrode Support | Detection Method/ Redox Probe | Dynamic Linear Range | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Test Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene sequence-associated with CRC | GCE/(CeO2-CHIT) | DPV/Methylene blue | 1.59 × 10−11 to 1.16 × 10−7 M | 1.0 × 10−11 mol L−1 | NA | [95] |
| KRAS | Au | Amperometry/ HQ | 1.17 × 10−11 to 1.17 × 10−7 M | 5.85 × 10−12 M | NA | [98] |
| GCE | DVP/AuCl4- | 0.1 to 100 pM | 30 fM | Cell line SW480 | [99] | |
| Phthalocyanine-BODIPY dye/Graphite | DVP/No reported | 1.54 × 10−4 to 1.92 × 10−2 µg mL−1 | 2.06 × 10−6 µg mL−1 | Blood | [100] | |
| A1/PtTiO2-reduced graphene oxide | 3.07 × 10−7 to 3.84 × 10−3 µg mL−1 | 8.67 × 10−10 µg mL−1 | ||||
| A2/PtTiO2-reduced graphene oxide | 3.84 × 10−8 to 0.48 µg mL−1 | 2.94 × 10−5 µg mL−1 | ||||
| KRAS mutation (KRAS G12D) | Au | DPV/Methylene blue | 0.01 fM to 1 pM | 2.4 aM | Plasma | [106] |
| Au | SWV/Methylene blue | 5.92 pM to 10 nM for t-DNA 100 pM to 10 nM for M-DNA | Not reported | Serum | [107] | |
| BRAF mutation (BRAF V600E) | SPCE | DPV/AA | 50–0.8% of V600E alleles | Not reported | Cell line HT29 | [110] |
| CEACAM5 | Au | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | NA | [114] |
| PET/VA-MWCNTs-COOH | CV/Methylene blue | 50 to 250 µM | 0.92 µM | Cell line T84 | [113] | |
| 5-hmC MGMT | SPCE | Amperometry/HQ | 77 to 7500 pM (ProtA-polyHRP80) | 23 pM | Cell lines SW480 SW620 Colorectal tissues | [115] |
| 44 to 5000 pM (Histostar) | 13 pM | |||||
| miRNA-21 | Au/AuNPs | Amperometry/ hemin-G-quadruplex complex | 5 to 5000 pM | 3.96 pM | Cell line HT29 | [118] |
| SPAuE | DPV/[Fe(CN)6]4−/3− | 1.0 pM to 10 nM | 1.0 pM | Cell line SW-48 Serum | [119] |
| Biomarker | Electrode Support | Detection Method/ Redox Probe | Dynamic Linear Range | Limit of Detection (LOD) | Tested Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEA | Au | DPV/HQ | 0 to 200 ng mL−-1 | 0.2 ng mL−1 | Serum | [123] |
| (FTO) glass | EIS/(I−/I3−) | 0.125 to 7.5 pg mL−1 | 0.0832 pg mL−1 | Urine | [124] | |
| (FTO) glass | Voltammetry/(I−/I3−) | 10 ng mL−1 to 100 µg mL−1 | 0.14 ng mL−1 | Urine | [125] | |
| (FTO) glass | Power/(I−/I3−) | 0.025 to 0.75 ng mL−1 | 0.10 pg mL−1 | Urine | [126] | |
| Autoantibodies-p53 | SPCE | Amperometry/HQ | 1.1 to 5 U mL−1 | 0.34 U mL−1 | Serum | [131] |
| SPAuE/(Au@NPFe2O3 NC) | Amperometry/TMB | 0.02 to 14 U mL−1 | 0.02 U mL−1 | Serum | [132] | |
| p53 | ITO/StarPGMA | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]4−/3− | 0.02 to 4 pg mL−1 | 7 fg mL−1 | Serum | [134] |
| FAM134B | SPCE/Extravidin | DPV/[Fe(CN)6]4−/3− | 0.01 to 100 ng μL−1 | 10 pg μL−1 | Cell lines SW480 SW48 HCT116 Serum | [138] |
| EpCAM | Au/AgNPs-CHIT | Amperometry/(4-TBC) | Not reported | 2.7 pg mL−1 | Peripheral blood | [141] |
| Au/AgNPs-PVA | Amperometry/(4-TBC) | 2 to 2000 pg mL−1 | 0.8 pg mL−1 | Peripheral blood | [142] | |
| LRG1 | Au | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]4−/3− | 0 to 0.25 μg mL−1 | 0.025 μg mL−1 | Plasma | [145] |
| CXCL5 | GCE | Amperometry/Hydrazine | 0.1 to 10 ng mL−1 | 0.078 ng mL−1 | Cell line HT29 Serum | [147] |
| CA19-9 | SPIDE/CNO-GO | EIS/Phosphate Buffer | 0.3 to 100 U mL−1 | 0.12 U mL−1 | Cell line HT29 | [151] |
| ET-1 | Au | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | 2 to 100 pg mL−1 | 0.34 pg mL−1 | NA | [162] |
| IL-13Rα2 | SPCE | Amperometry/HQ | 3.9 to 100 ng mL−1 | 1.2 ng mL−1 | Cell lines SW480 SW620 KM12C KM12SM | [152] |
| SPCE/pABA/strep | Amperometry/HQ | 2.7 to 100 ng mL−1 | 0.8 ng mL−1 | Cell lines SW480 SW620 KM12C KM12SM Colorectal tissues | [153] | |
| RANKL | SPCE/pABA/strep | Amperometry/HQ | 10.4 to 1000 ng mL−1 | 3.1 ng mL−1 | Serum | [154] |
| E-cad | SPCE | Amperometry/HQ | 0.5 to 25 ng mL−1 | 0.16 ng mL−1 | Cell lines SW480 SW620 KM12C KM12SM Colorectal tissues | [160] |
| CDH17 | SPCE | Amperometry/HQ | 4.8 to 1000 ng mL−1 | 1.43 ng mL−1 | Cell lines SW480 SW620 KM12C KM12SM Colorectal tissues | [161] |
| IL-6 | GCE/pABA/pATP/AuNPs | EIS//[Fe(CN)6]4−/3− | 5 pg mL−1 to 100 ng mL−1 | 1.6 pg mL−1 | Serum | [164] |
| Biomarker | Electrode Support | Detection Method/ Redox Probe | Dynamic Linear Range [cells mL−1] | Limit of Detection (LOD) [cells mL−1] | Test Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caco2 | SPCE | Amperometry/HCl | 1 × 104 to 5 × 104 cells | 2.2 × 102 cells | Cell culture | [172] |
| HCT116 | SPAuE | CV/[Fe(CN)6]3− | 1 to 100 | 7 | Cell culture | [173] |
| GCE/(NH2/GO) | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | 5 × 102 to 5 × 106 | 100 | Cell culture | [174] | |
| DLD-1 | GCE/CNSs | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | 1.25 × 102 to 1.25 × 106 | 40 | Cell culture | [177] |
| GCE/BSA-AgNFs | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | 1.35 × 102 to 1.35 × 107 | 40 | Cell culture | [180] | |
| CT26 | SPCE/AuNPs/SBA-15-pr-NH2 | EIS/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | 10 to 1 × 105 | 2 | Cell culture | [181] |
| HT29 | GCE/KCC-1- NH2 | SWV/DPV/[Fe(CN)6]3−/4− | 50 to 1.2 × 104 | Not reported | Cell culture | [182] |
| Au/MWCNTs-COOH | CC-PSA/Trp | 0.0001 to 10 mM | 64 pM | Cell culture | [183] | |
| Colo320 HCT116 | Carbon/Gold | Amperometry/ p-aminophenol | 0.25 to 10 µg mL−1 | Not reported | Cell culture | [184] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quinchia, J.; Echeverri, D.; Cruz-Pacheco, A.F.; Maldonado, M.E.; Orozco, J. Electrochemical Biosensors for Determination of Colorectal Tumor Biomarkers. Micromachines 2020, 11, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040411
Quinchia J, Echeverri D, Cruz-Pacheco AF, Maldonado ME, Orozco J. Electrochemical Biosensors for Determination of Colorectal Tumor Biomarkers. Micromachines. 2020; 11(4):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040411
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuinchia, Jennifer, Danilo Echeverri, Andrés Felipe Cruz-Pacheco, María Elena Maldonado, and Jahir Orozco. 2020. "Electrochemical Biosensors for Determination of Colorectal Tumor Biomarkers" Micromachines 11, no. 4: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040411
APA StyleQuinchia, J., Echeverri, D., Cruz-Pacheco, A. F., Maldonado, M. E., & Orozco, J. (2020). Electrochemical Biosensors for Determination of Colorectal Tumor Biomarkers. Micromachines, 11(4), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11040411







