Effect of the Thermal History on the Crystallinity of Poly (L-lactic Acid) During the Micromolding Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation with Different Thermal History in the Micromolding Process
2.3. Microneedle Fabrication Using the Micromolding Process
2.4. Characterization
3. Results
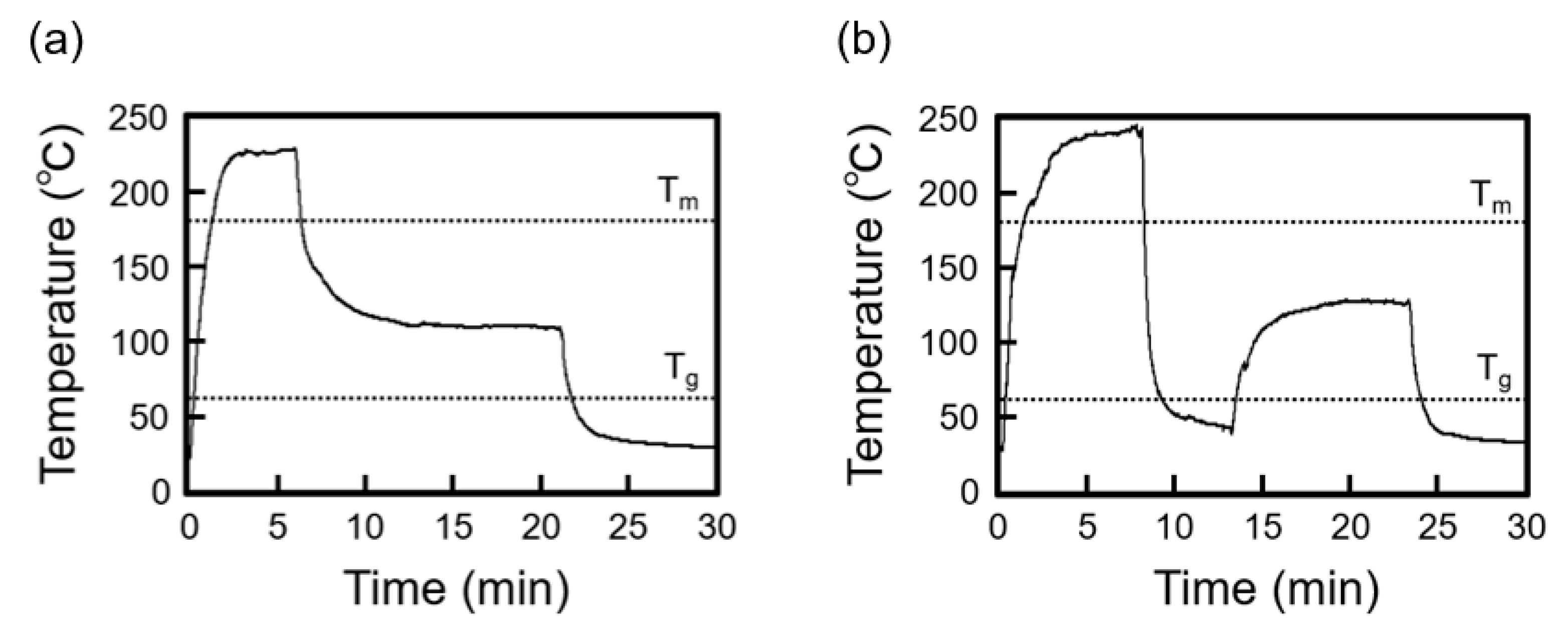
3.1. Thermal History
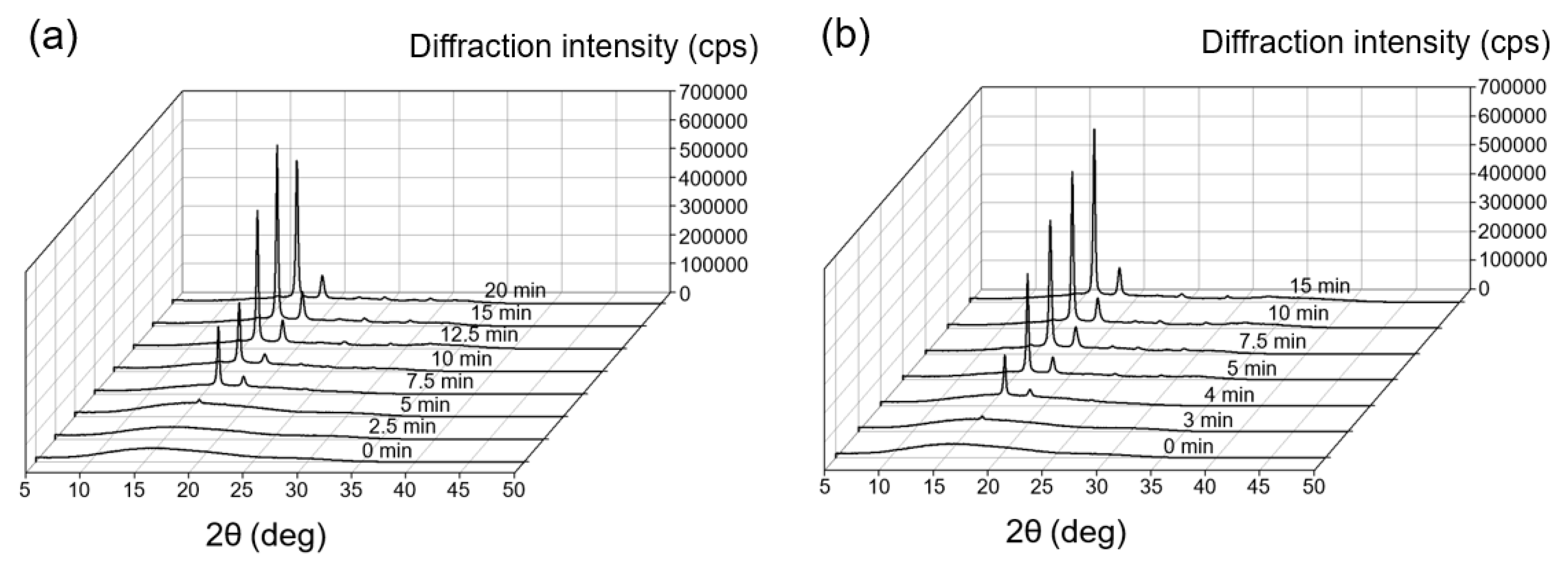
3.2. Crystallinity
3.3. Crystallization Kinetics
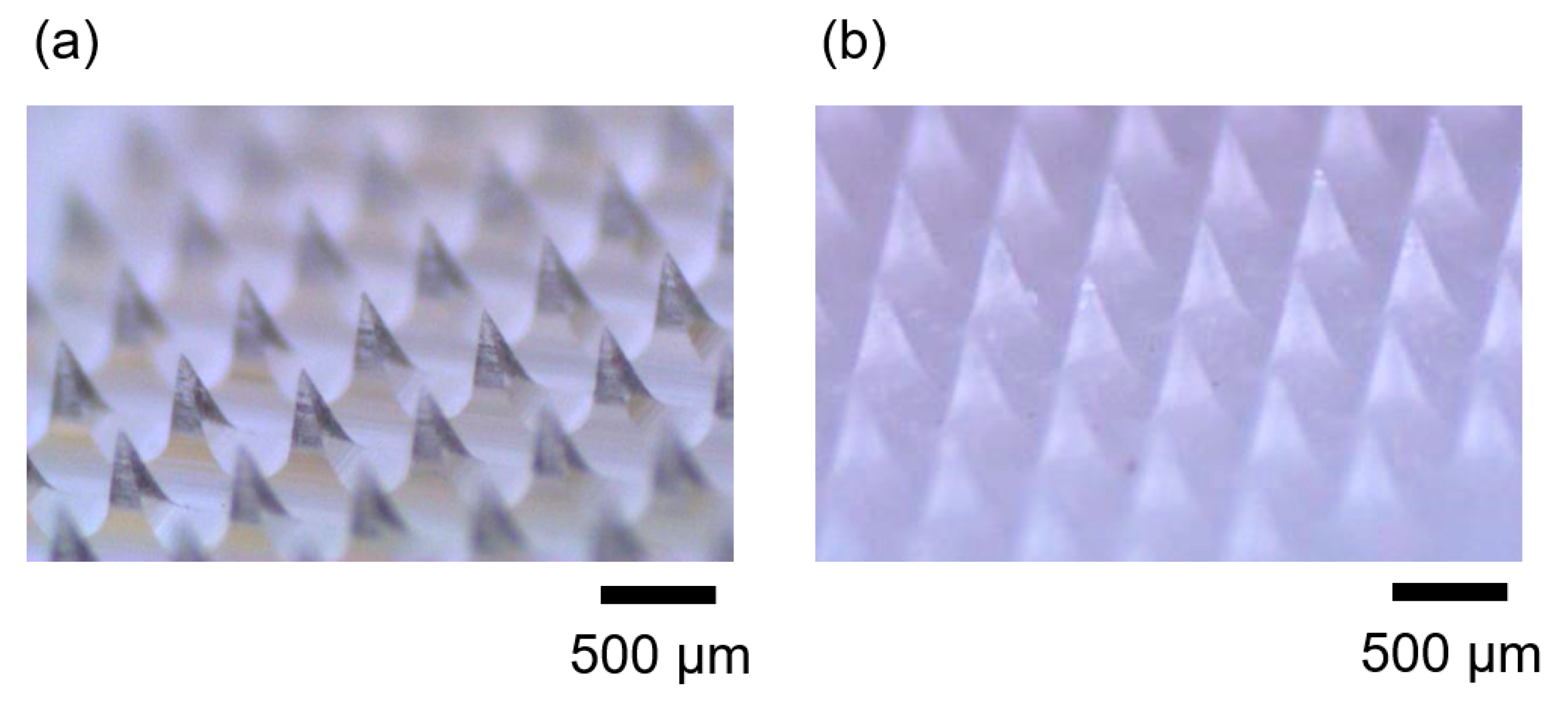
3.4. Demonstration of Microneedle Fabrication with Different Thermal History
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamshidian, M.; Tehrany, E.A.; Imran, M.; Jacquot, M.; Desobry, S. Poly-lactic acid: Production, applications, nanocomposites, and release studies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 552–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergård, A.; Stolt, M. Properties of lactic acid based polymers and their correlation with composition. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1123–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckele, M.; Schomburg, W. Review on micro molding of thermoplastic polymers. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2003, 14, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mayes, R.H.; Chen, G.E.; Xie, H.; Chan, P.S. Effects of process parameters on the micro molding process. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2003, 43, 1542–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giboz, J.; Copponnex, T.; Mélé, P. Microinjection molding of thermoplastic polymers: A review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, R96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, D.; Hyon, S.-H.; Ikada, Y. Degradation of high molecular weight poly (L-lactide) in alkaline medium. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, E.W.; Sterzel, H.J.; Wegner, G. Investigation of the structure of solution grown crystals of lactide copolymers by means of chemical reactions. Kolloid Z. Z. Polym. 1973, 251, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Nakahara, K.; Ikarashi, K. Poly (L-Lactide), 8. High-Temperature Hydrolysis of Poly (L-Lactide) Films with Different Crystallinities and Crystalline Thicknesses in Phosphate-Buffered Solution. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2001, 286, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Mizuno, A.; Ikada, Y. Properties and morphology of poly (L-lactide). III. Effects of initial crystallinity on long-term in vitro hydrolysis of high molecular weight poly (L-lactide) film in phosphate-buffered solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 77, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H. Hydrolytic Degradation. In Poly(Lactic Acid); Grossman, R.F., Nwabunma, D., Auras, R., Lim, L.-T., Selke, S.E.M., Tsuji, H., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 343–381. [Google Scholar]
- Renouf-Glauser, A.C.; Rose, J.; Farrar, D.F.; Cameron, R.E. The effect of crystallinity on the deformation mechanism and bulk mechanical properties of PLLA. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5771–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, G.; Cella, G.D.; Bastioli, C. Effect of molecular weight and crystallinity on poly (lactic acid) mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 59, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y.; Takehara, H.; Ichiki, T. Mechanical strength evaluation of crystalline poly (L-lactic acid) fabricated by replica micromolding for bioabsorbable microneedle devices. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, SDDK05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.M.; Lee, E.C. Improving mechanical performance of injection molded PLA by controlling crystallinity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2246–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iozzino, V.; Meo, A.D.; Pantani, R. Micromolded polylactic acid with selective degradation rate. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krepker, M.; Prinz-Setter, O.; Shemesh, R.; Vaxman, A.; Alperstein, D.; Segal, E. Antimicrobial carvacrol-containing polypropylene films: Composition, structure and function. Polymers 2018, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tashiro, K.; Tsuji, H.; Domb, A.J. Disorder-to-order phase transition and multiple melting behavior of poly (L-lactide) investigated by simultaneous measurements of WAXD and DSC. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, I. Modified avrami equation for the bulk crystallization kinetics of spherulitic polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Gen. Pap. 1965, 3, 3067–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Liu, X.; Lu, K. An explanation to the anomalous Avrami exponent. Scr. Mater. 1996, 34, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battegazzore, D.; Bocchini, S.; Frache, A. Crystallization kinetics of poly (lactic acid)-talc composites. Express Polym. Lett. 2011, 5, 849–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, H.; Dean, K.; Chen, L. Cold crystallization and postmelting crystallization of PLA plasticized by compressed carbon dioxide. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2008, 46, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, R.V.; Muller, A.J.; Raquez, J.M.; Dubois, P. Crystallization kinetics and morphology of biodegradable double crystalline PLLA-b-PCL diblock copolymers. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 4149–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, F.; Nishikawa, K.; Inoue, Y.; Yazawa, K. Nucleation enhancement effect in poly (l-lactide)(PLLA)/poly (ϵ-caprolactone)(PCL) blend induced by locally activated chain mobility resulting from limited miscibility. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8335–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Crystallization behavior and morphology of polylactic acid (PLA) with aromatic sulfonate derivative. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, A.; Umemoto, S.; Ishihara, N.; Okui, N. Influence of thermal history on primary nucleation and crystal growth rates of isotactic polystyrene. Polymer 2006, 47, 5531–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal drug delivery: Innovative pharmaceutical developments based on disruption of the barrier properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsioris, K.; Raja, W.K.; Pritchard, E.M.; Panilaitis, B.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Fabrication of silk microneedles for controlled-release drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, S.; Ito, Y.; Kiyohara, T.; Kataoka, M.; Ochiai, M.; Takada, K. Antigen-loaded dissolving microneedle array as a novel tool for percutaneous vaccination. Vaccine 2012, 30, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraishi, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Hirobe, S.; Okada, N.; Nakagawa, S. Performance and characteristics evaluation of a sodium hyaluronate-based microneedle patch for a transcutaneous drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Okamoto, H.; Kawai, Y.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Hirobe, S.; Okada, N.; Nakagawa, S. Vaccine efficacy of transcutaneous immunization with amyloid β using a dissolving microneedle array in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 266, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirobe, S.; Azukizawa, H.; Hanafusa, T.; Matsuo, K.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Katayama, I.; Okada, N.; Nakagawa, S. Clinical study and stability assessment of a novel transcutaneous influenza vaccination using a dissolving microneedle patch. Biomaterials 2015, 57, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusamori, K.; Katsumi, H.; Sakai, R.; Hayashi, R.; Hirai, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Hitomi, K.; Quan, Y.; Kamiyama, F.; Sumida, S.I.; et al. Development of a drug-coated microneedle array and its application for transdermal delivery of interferon alpha. Biofabrication 2016, 8, 015006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.; Boopathy, A.V.; Lam, L.K.; Moynihan, K.D.; Welch, M.E.; Bennett, N.R.; Turvey, M.E.; Thai, N.; Love, J.C.; Hammond, P.T.; et al. Cell and fluid sampling microneedle patches for monitoring skin-resident immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaar2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takehara, H.; Hadano, Y.; Kanda, Y.; Ichiki, T. Effect of the Thermal History on the Crystallinity of Poly (L-lactic Acid) During the Micromolding Process. Micromachines 2020, 11, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050452
Takehara H, Hadano Y, Kanda Y, Ichiki T. Effect of the Thermal History on the Crystallinity of Poly (L-lactic Acid) During the Micromolding Process. Micromachines. 2020; 11(5):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050452
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakehara, Hiroaki, Yuki Hadano, Yukihiro Kanda, and Takanori Ichiki. 2020. "Effect of the Thermal History on the Crystallinity of Poly (L-lactic Acid) During the Micromolding Process" Micromachines 11, no. 5: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050452
APA StyleTakehara, H., Hadano, Y., Kanda, Y., & Ichiki, T. (2020). Effect of the Thermal History on the Crystallinity of Poly (L-lactic Acid) During the Micromolding Process. Micromachines, 11(5), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050452




