Dielectrophoretic Separation of Particles Using Microfluidic Chip with Composite Three-Dimensional Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mathematical Model for Particle Trajectory
2.2. Experiment
2.2.1. Dispersion of Ag Powder
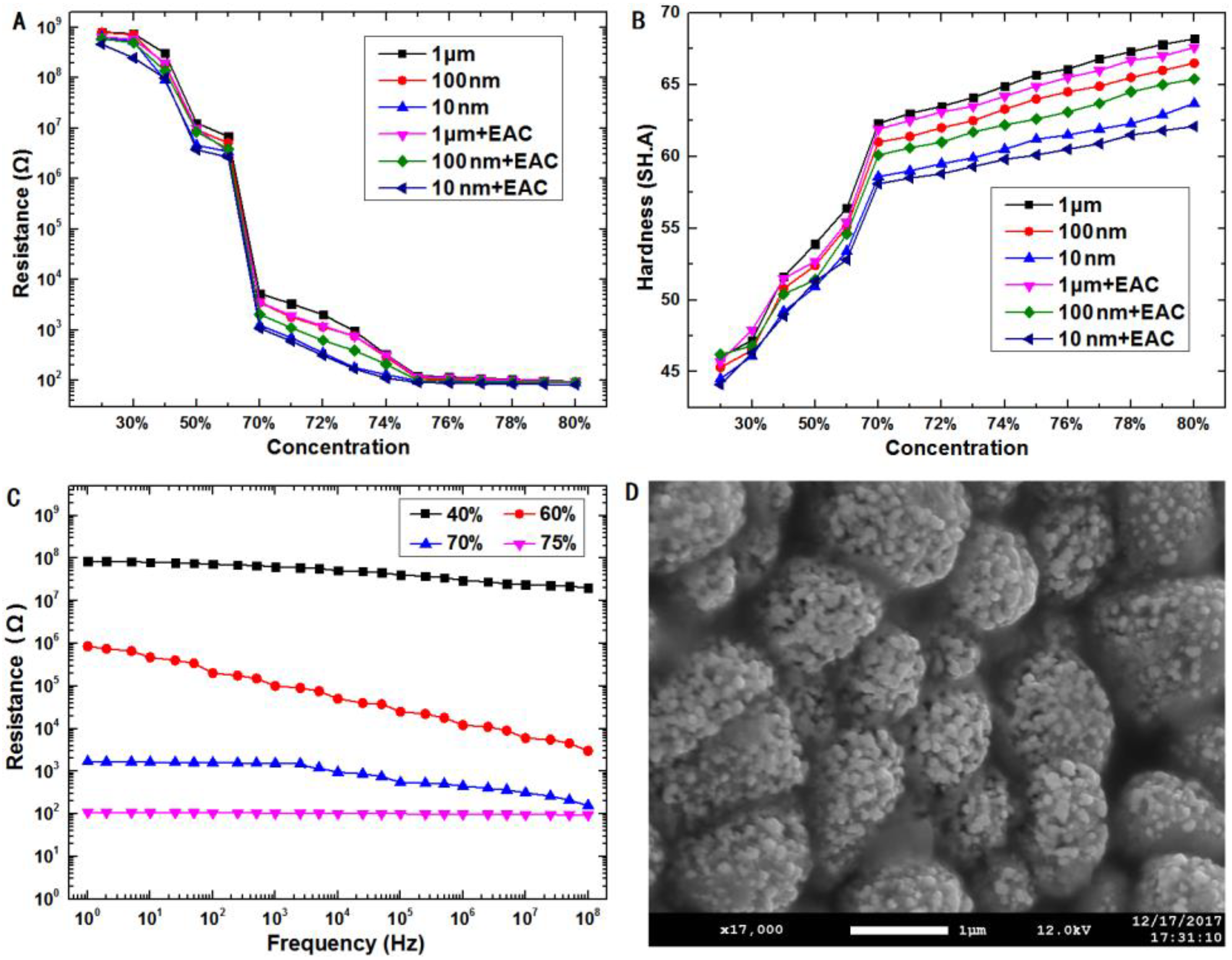
2.2.2. Performance Evaluation of Composite Material
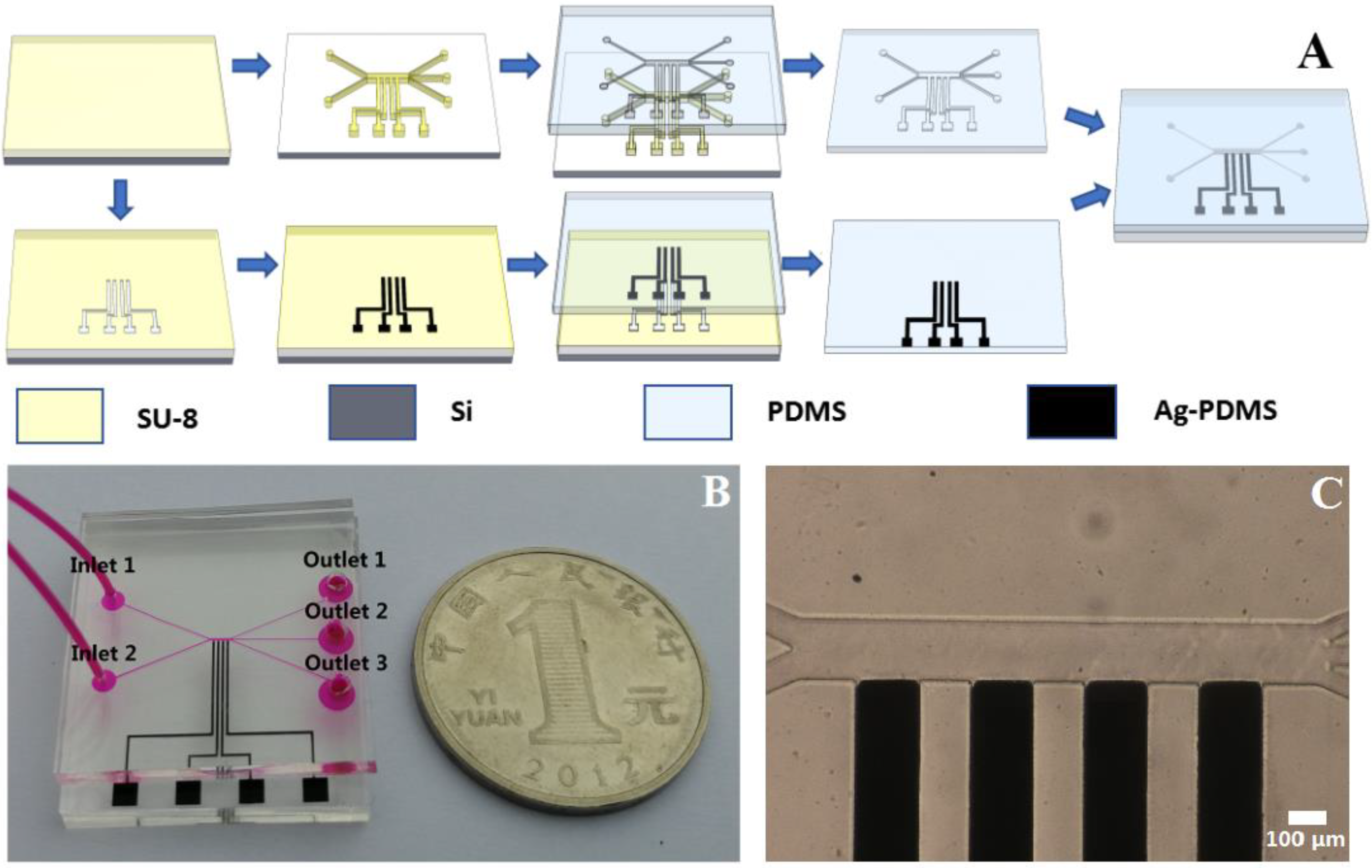
2.2.3. Microfabrication
2.2.4. Experimental Solutions
2.2.5. Experimental Manipulation and Visualization
3. Results and Discussion
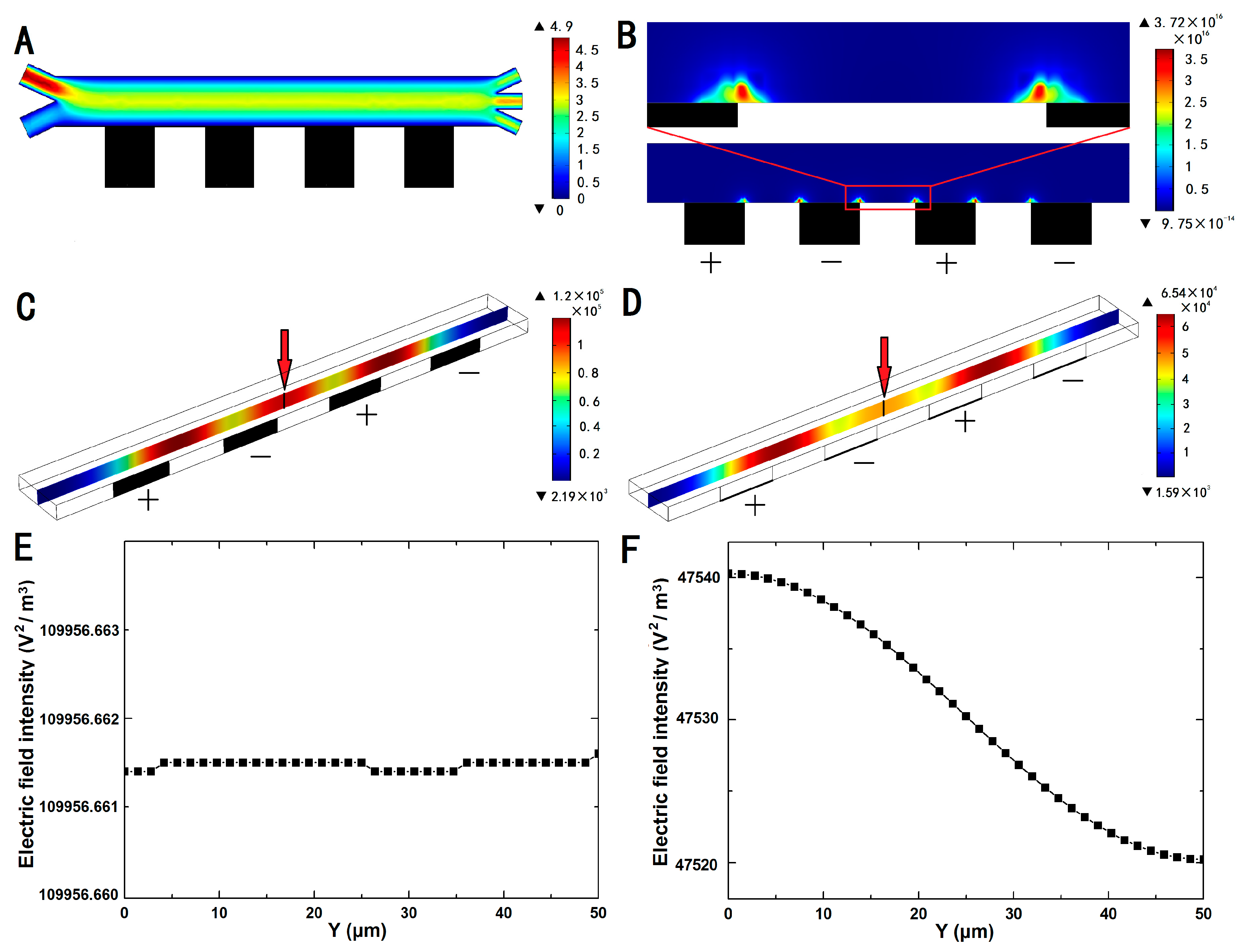
3.1. Numerical Simulation
3.2. Effect of Voltage on Separation
3.3. Effect of Flow Rate on Separation
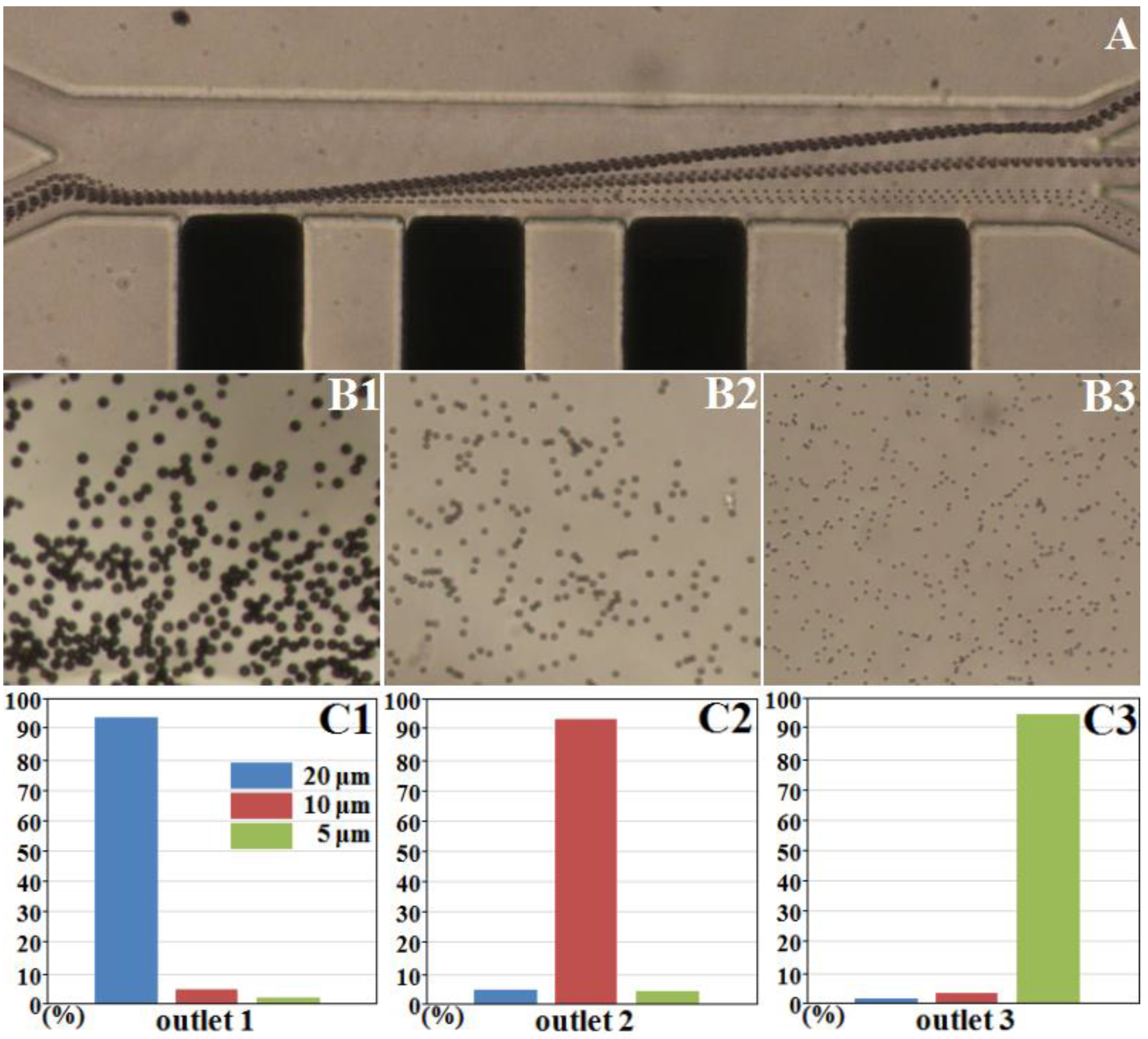
3.4. Separation of Three Different Polystyrene Particles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jellema, L.C.; Mey, T.; Koster, S.; Verpoorte, E. Charge-based particle separation in microfluidic devices using combined hydrodynamic and electrokinetic effects. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Biswas, K.; Das, S. A microfluidic device for continuous manipulation of biological cells using dielectrophoresis. Med. Eng. Phys. 2014, 36, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Canter, R.C.; Keten, G.; Vedantam, P.; Tzeng, T.-R.J.; Xuan, X. Continuous-flow particle and cell separations in a serpentine microchannel via curvature-induced dielectrophoresis. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2011, 11, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejad, H.R.; Samiei, E.; Ahmadi, A.; Hoorfar, M. Gravity-driven hydrodynamic particle separation in digital microfluidic systems. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 35966–35975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Patel, S.; Xuan, X. Three-Dimensional Reservoir-Based Dielectrophoresis (rDEP) for Enhanced Particle Enrichment. Micromachines 2018, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttawut, L.; Chun, Y. AC-dielectrophoretic characterization and separation of submicron and micron particles using sidewall AgPDMS electrodes. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 012807. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, T.; Maruyama, H.; Honda, A.; Arai, F. Virus Enrichment for Single Virus Infection by Using 3D Insulator Based Dielectrophoresis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.S.W.; Mitchell, P.D.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. Image-based sorting and negative dielectrophoresis for high purity cell and particle separation. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 2718–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Hou, L.; Jiang, H. High-Throughput Separation, Trapping, and Manipulationof Single Cells and Particles by Combined Dielectrophoresis at a BipolarElectrode Array. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11461–11469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbaros, C.; Yuejun, K.; Zhemin, W.; Dongqing, L. Continuous particle separation by size via AC-dielectrophoresis using a lab-on-a-chip device with 3-D electrodes. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 766–772. [Google Scholar]
- Chiou, P.Y.; Ohta, A.T.; Wu, M.C. Massively parallel manipulation of single cells and microparticles using optical images. Nature 2005, 436, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.J.; Yobas, L.; Lee, G.Y.H.; Ong, C.N.; Lim, C.T. Microdevice for the isolation and enumeration of cancer cells from blood. Biomed. Microdevices 2009, 11, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFaul, S.M.; Lin, B.K.; Ma, H. Cell separation based on size and deformability using microfluidic funnel ratchets. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2369–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devendra, R.; Drazer, G. Gravity Driven Deterministic Lateral Displacement for Particle Separation in Microfluidic Devices. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 10621–10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttawut, L.; Chun, Y.; Yee Cheong, L. Continuous sorting and separation of microparticles by size using AC dielectrophoresis in a PDMS microfluidic device with 3-D conducting PDMS composite electrodes. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2622–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiefard, N.; Sasanpour, P.; Fardindoost, S.; Irajizad, A. A novel approach for microparticle separation based on dielectrophoresis method. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2019, 5, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.X.; Poon, R.Y.C.; Wong, C.S.C.; Yobas, L. Label-free enumeration of colorectal cancer cells from lymphocytes performed at a high cell-loading density by using interdigitated ring-array microelectrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-H.; Huang, C.-T.; Wu, H.-H.; Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, A.S.; Jen, C.-P. Isolating and Concentrating Rare Cancerous Cells in Large Sample Volumes of Blood by Using Dielectrophoresis and Stepping Electric Fields. Biochip J. 2014, 8, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, X.; Jia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, H. A simplified microfluidic device for particle separation with two consecutive steps: Induced charge electroosmotic prefocusing and dielectrophoretic separation. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9583–9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazzam, A.; Mathew, B.; Alhammadi, F. Novel microfluidic device for the continuous separation of cancer cells using dielectrophoresis. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Ng, C.N.; Chau, M.L.; Yobas, L. Railing cells along 3D microelectrode tracks for continuous-flow dielectrophoretic sorting. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3760–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirmohammadli, V.; Manavizadeh, N. Application of Differential Electrodes in a Dielectrophoresis-Based Device for Cell Separation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2019, 66, 4075–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Yang, J.; Qian, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zheng, X. A cell electrofusion microfluidic device integrated with 3D thin-film microelectrode arrays. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 034121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, J.; Joo, S.W.; Qian, S.Z. A cell electrofusion microfluidic chip with micro-cavity microelectrode array. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2013, 15, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, P.; Kumar, V.; Belgamwar, S.U.; Sharma, N.N. Microfluidic Device for Cell Trapping with Carbon Electrodes Using Dielectrophoresis. Biomed. Microdevices 2018, 20, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Cai, B.; Yu, X.L.; Guo, S.S.; Zhao, X.Z. One-step fabrication of 3D silver paste electrodes into microfluidic devices for enhanced droplet-based cell sorting. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 057134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewpiriyawong, N.; Kandaswamy, K.; Yang, C.; Ivanov, V.; Stocker, R. Microfluidic Characterization and Continuous Separation of Cells and Particles Using Conducting Poly(dimethyl siloxane) Electrode Induced Alternating Current-Dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 9579–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Ren, Y.; Jiang, H. Continuous dielectrophoretic particle separation using a microfluidic device with 3D electrodes and vaulted obstacles. Electrophoresis 2015, 36, 1744–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Mavrogiannis, N.; Ibo, M.; Crivellari, F.; Gagnon, Z.R. Microfluidic free-flow zone electrophoresis and isotachophoresis using carbon black nano-composite PDMS sidewall membranes. Electrophoresis 2016, 38, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Han, X.W.; Yang, J.; Hu, N. Multi-Stage Particle Separation based on Microstructure Filtration and Dielectrophoresis. Micromachines 2019, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Larasati; Duncker, B.P.; Li, D. Continuous Cell Characterization and Separation by Microfluidic Alternating Current Dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 6304–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Zheng, X.L.; Hu, N.; Yang, J.; Luo, H.Y.; Jiang, F.; Liao, Y.J. Research Progress on Microfluidic Chip of Cell Separation Based on Dielectrophoresis. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.L.; Kuo, M.Y.; Juang, Y.J. Development of flow through dielectrophoresis microfluidic chips for biofuel production: Sorting and detection of microalgae with different lipid contents. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 064120–064122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, X.; Zhu, J.; Church, C. Particle focusing in microfluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.Z.; Peng, S.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Wen, W.J.; Sheng, P. Characterizing and Patterning of PDMS-Based Conducting Composites. Adv. Mater. 2010, 19, 2682–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Chen, J.; Cao, X.; Dong, H. Combining 3D sidewall electrodes and contraction/expansion microstructures in microchip promotes isolation of cancer cells from red blood cells. Talanta 2019, 196, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, H.; Neuzil, P. DEP-on-a-Chip: Dielectrophoresis Applied to Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines 2019, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Mao, X.; Ahmed, D.; Colletti, A.; Huang, T.J. Focusing microparticles in a microfluidic channel with standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip 2008, 8, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, T.; Takei, M. Microfluidic device embedding electrodes for dielectrophoretic manipulation of cells—A review. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Agarwal, P.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; He, X. Continuous On-Chip Cell Separation Based on Conductivity-Induced Dielectrophoresis with 3D Self-Assembled Ionic Liquid Electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylon-Cardiel, J.L.; Jesus-Perez, N.M.; Chavez-Santoscoy, A.V.; Lapizco-Encinas, B.H. Controlled microparticle manipulation employing low frequency alternating electric fields in an array of insulators. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cottet, J.; Vaillier, C.; François, B.; Frénéa-Robin, M.; Renaud, P. A reproducible method for μm precision alignment of PDMS microchannels with on-chip electrodes using a mask aligner. Biomicrofluidics 2017, 11, 064111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puttaswamy, S.V.; Fishlock, S.J.; Steele, D.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C.; McLaughlin, J. Versatile microfluidic platform embedded with sidewall three-dimensional electrodes for cell manipulation. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2019, 5, 055003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J.; Tian, T.; Liao, Y. Dielectrophoretic Separation of Particles Using Microfluidic Chip with Composite Three-Dimensional Electrode. Micromachines 2020, 11, 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070700
Chen L, Liu X, Zheng X, Zhang X, Yang J, Tian T, Liao Y. Dielectrophoretic Separation of Particles Using Microfluidic Chip with Composite Three-Dimensional Electrode. Micromachines. 2020; 11(7):700. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070700
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Li, Xing Liu, Xiaolin Zheng, Xiaoling Zhang, Jun Yang, Tian Tian, and Yanjian Liao. 2020. "Dielectrophoretic Separation of Particles Using Microfluidic Chip with Composite Three-Dimensional Electrode" Micromachines 11, no. 7: 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070700
APA StyleChen, L., Liu, X., Zheng, X., Zhang, X., Yang, J., Tian, T., & Liao, Y. (2020). Dielectrophoretic Separation of Particles Using Microfluidic Chip with Composite Three-Dimensional Electrode. Micromachines, 11(7), 700. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070700





