High Permeability Photosintered Strontium Ferrite Flexible Thin Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Strontium Hexaferrite
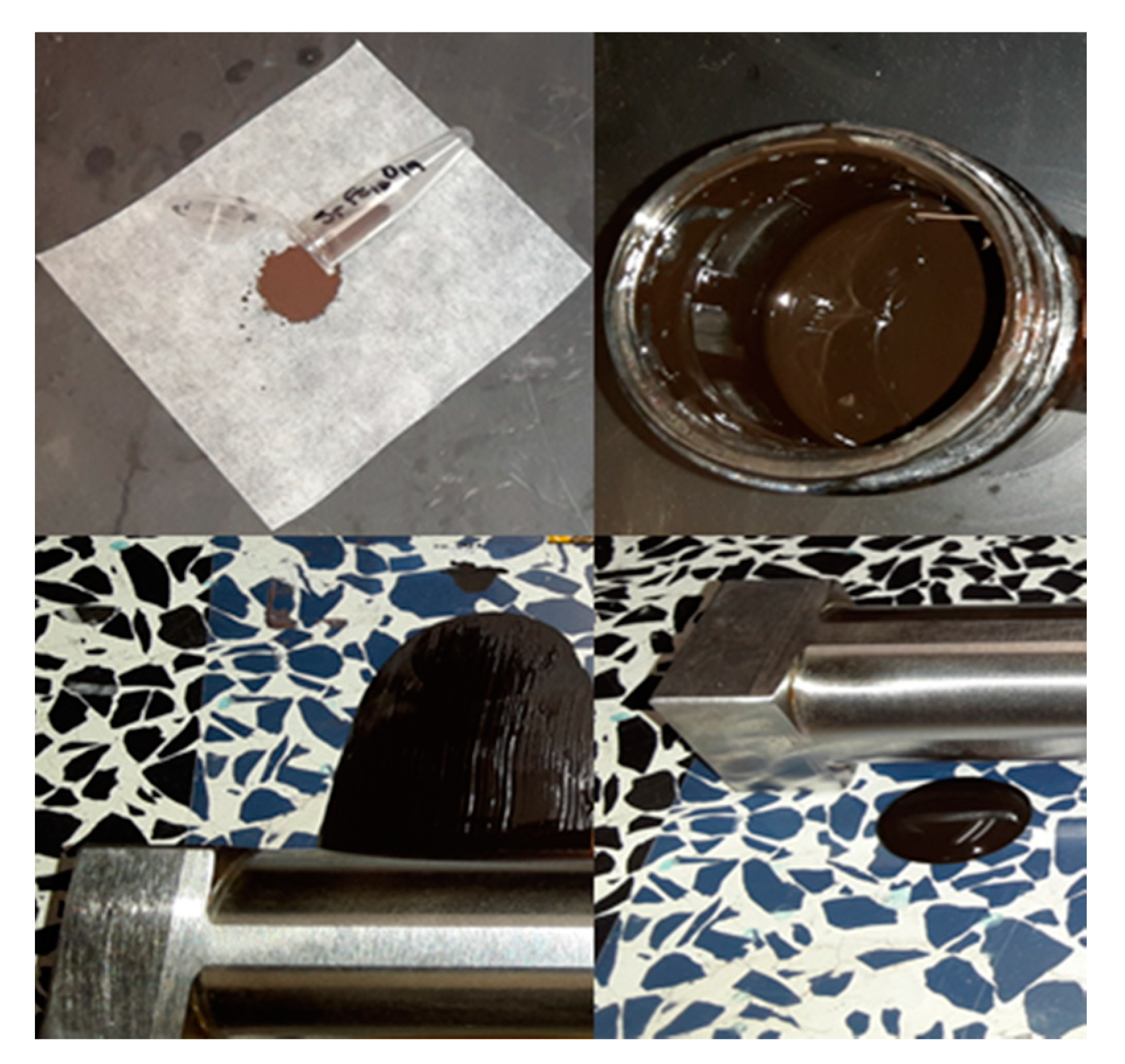
2.2. Paste Formulation and Application of Strontium Ferrite Thin Films
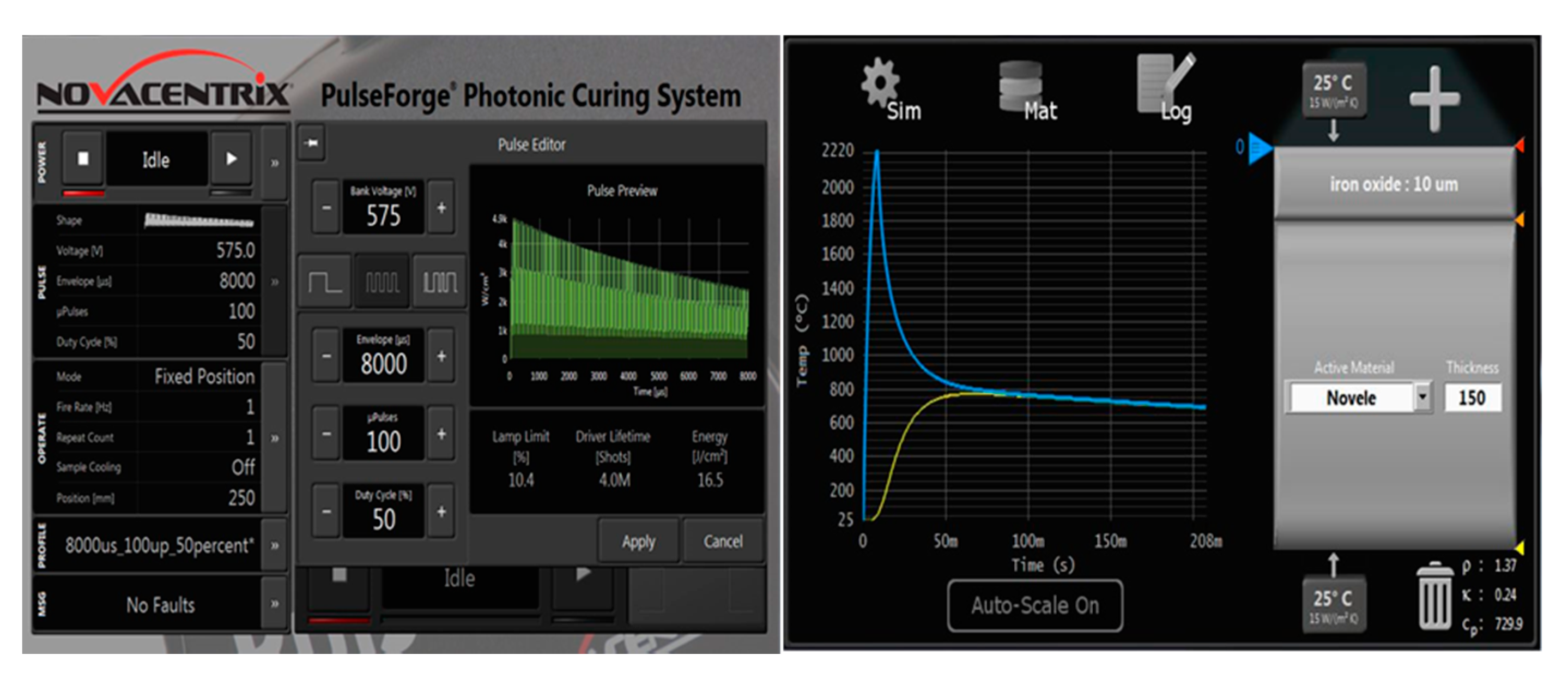
2.3. Photosintering of Strontium Ferrite Thin Films
3. Results
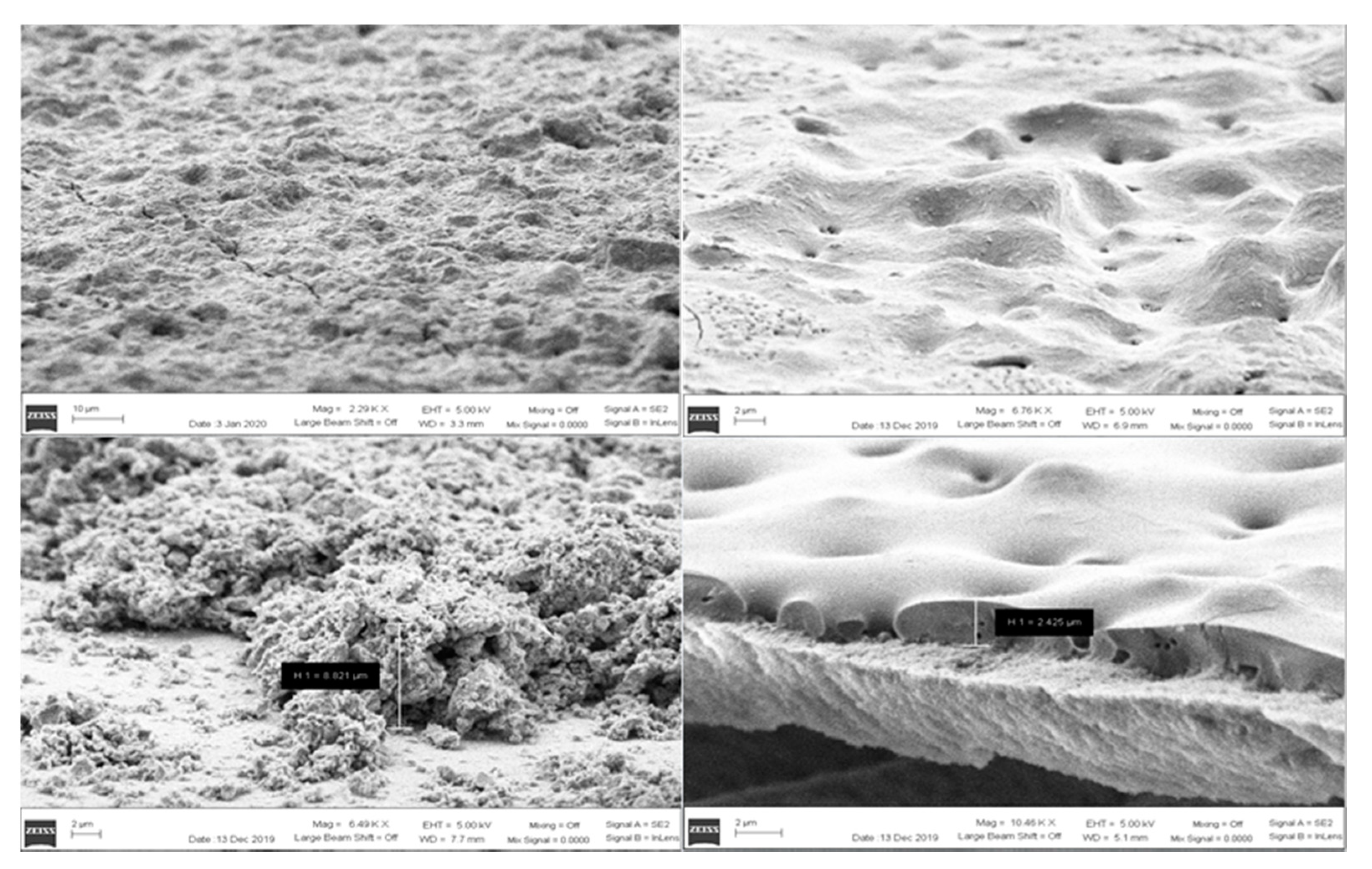
3.1. DC Characterization
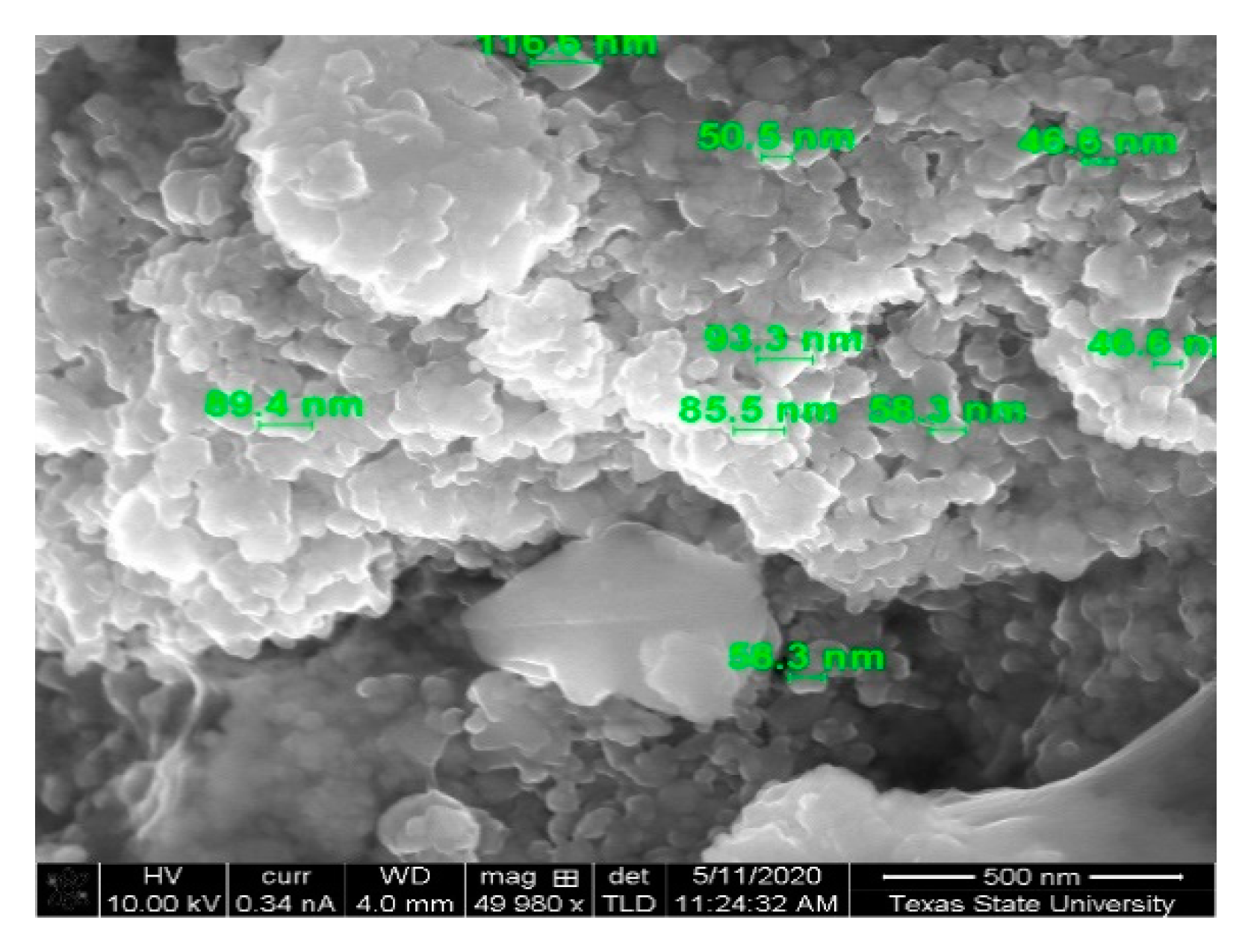
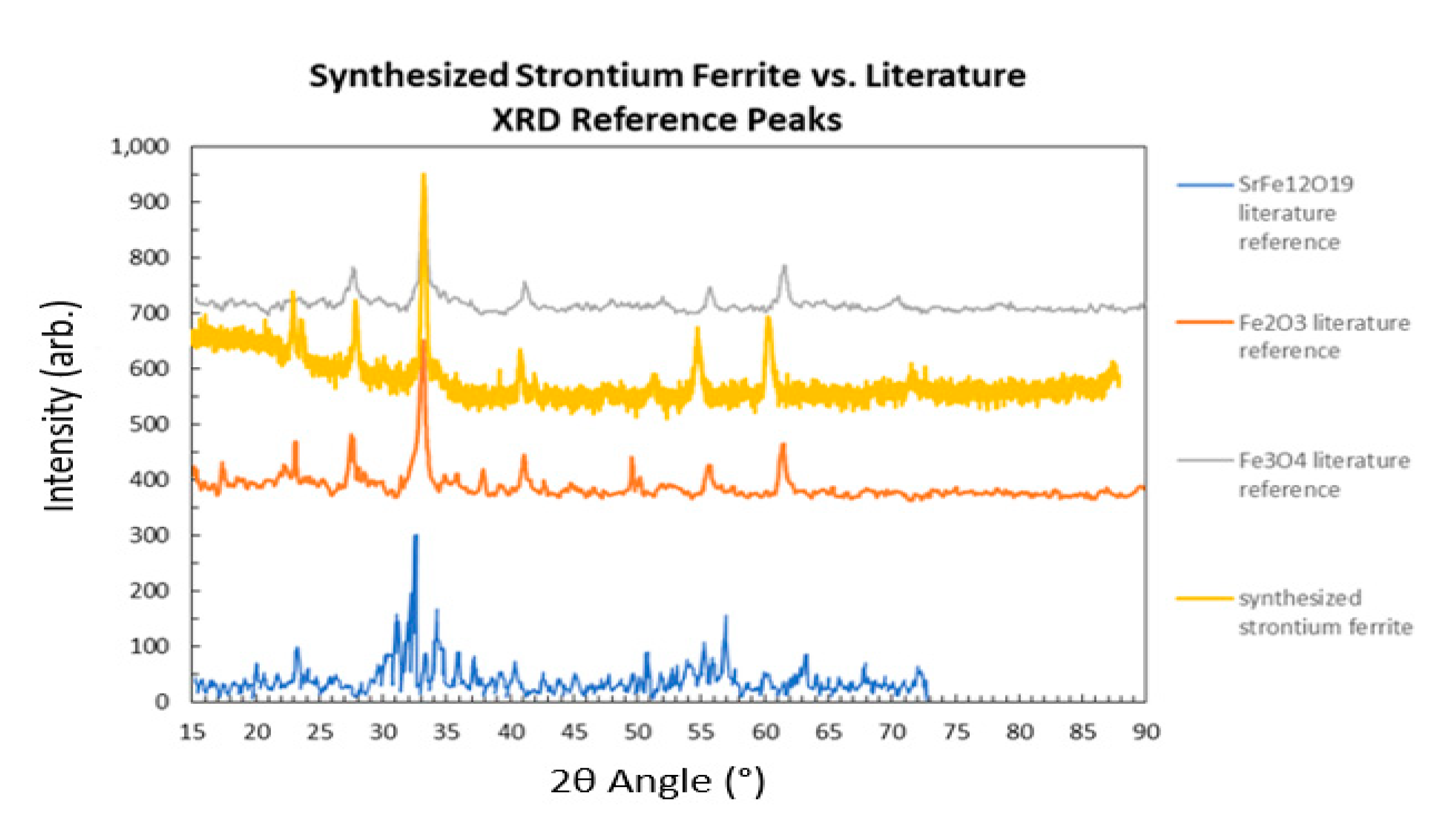
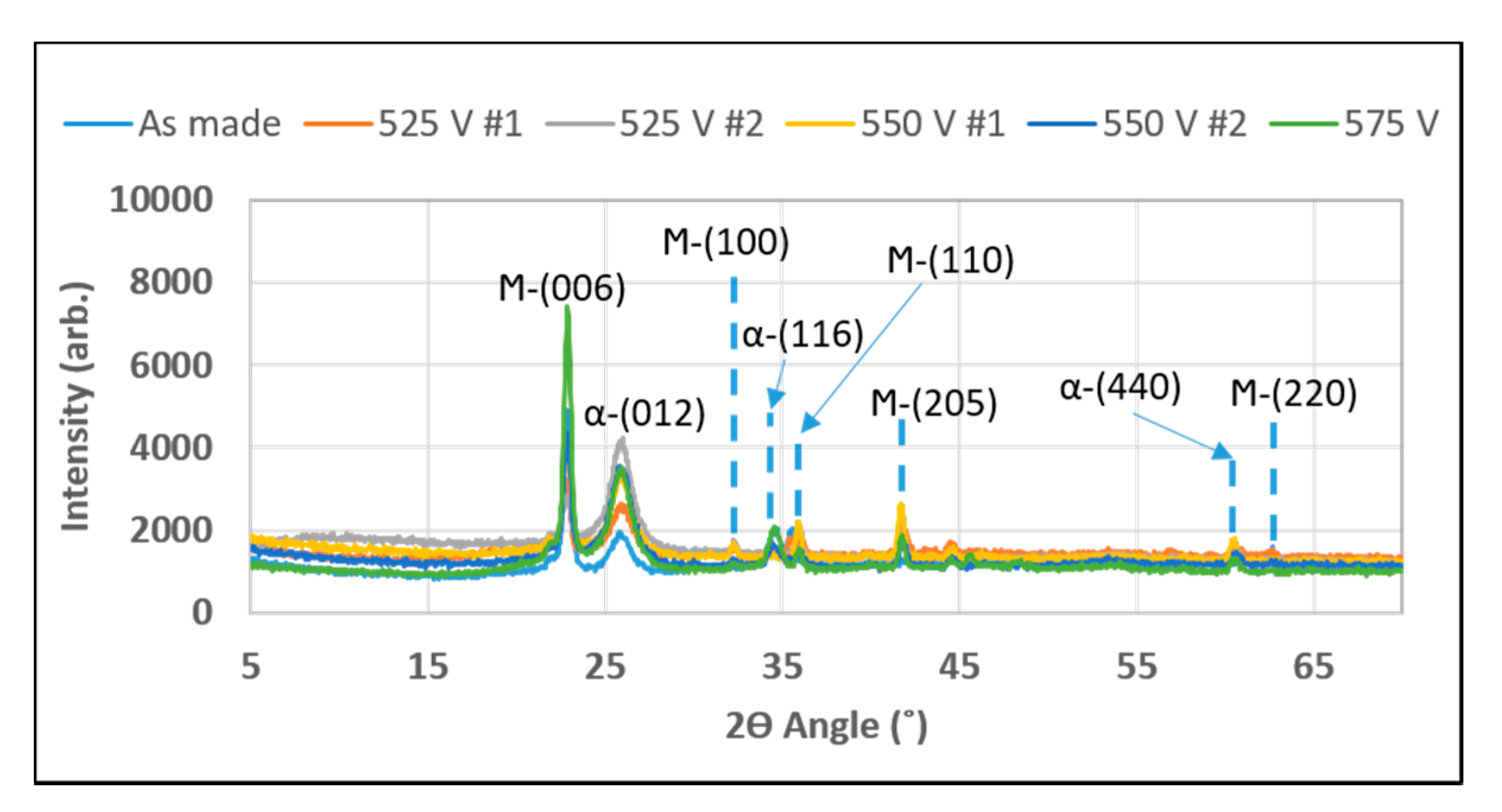
3.1.1. XRD Analysis
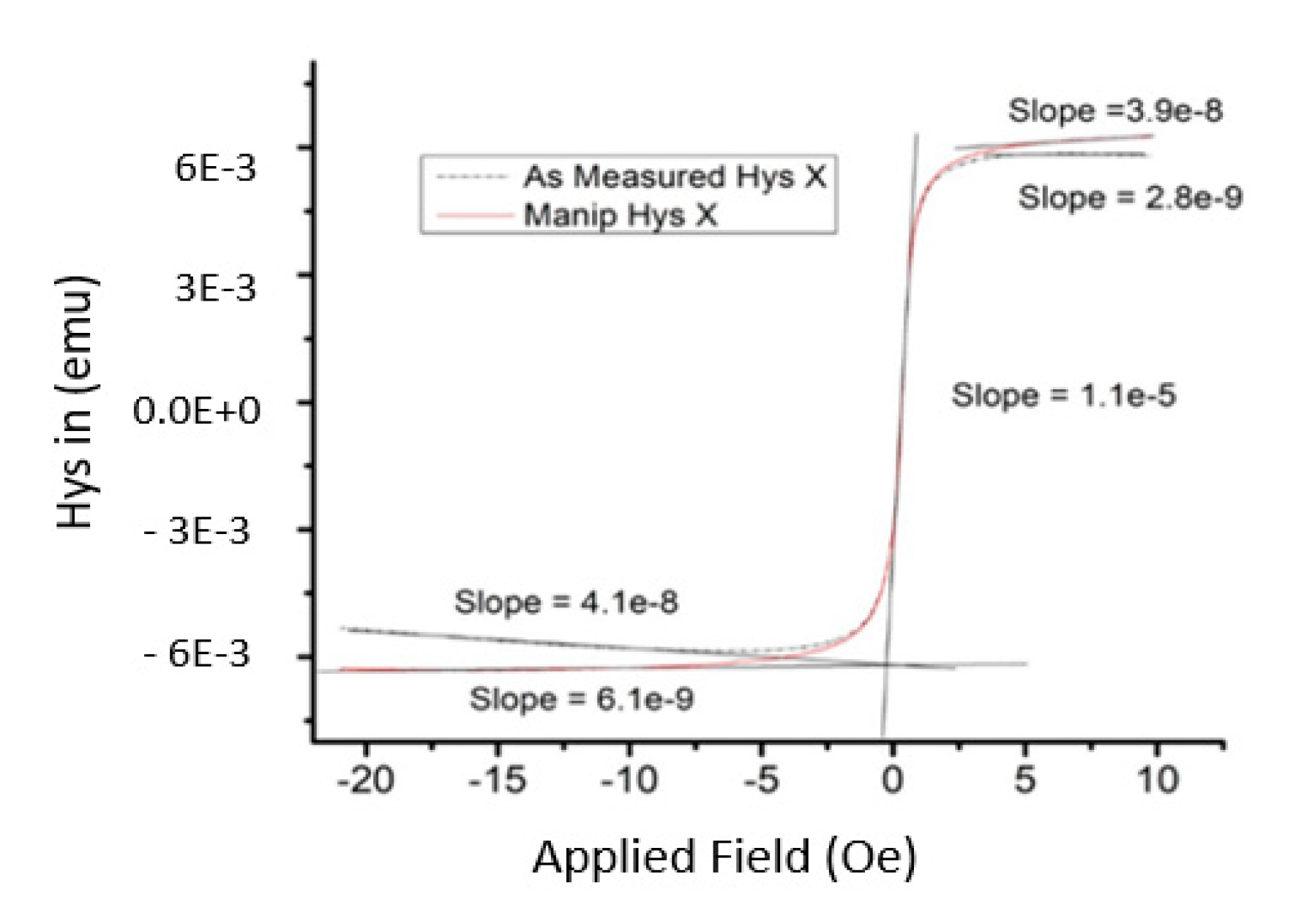
3.1.2. VSM Analysis of Permeability
3.1.3. Hermes Probe Station Analysis
3.2. Microwave Frequency Characterization
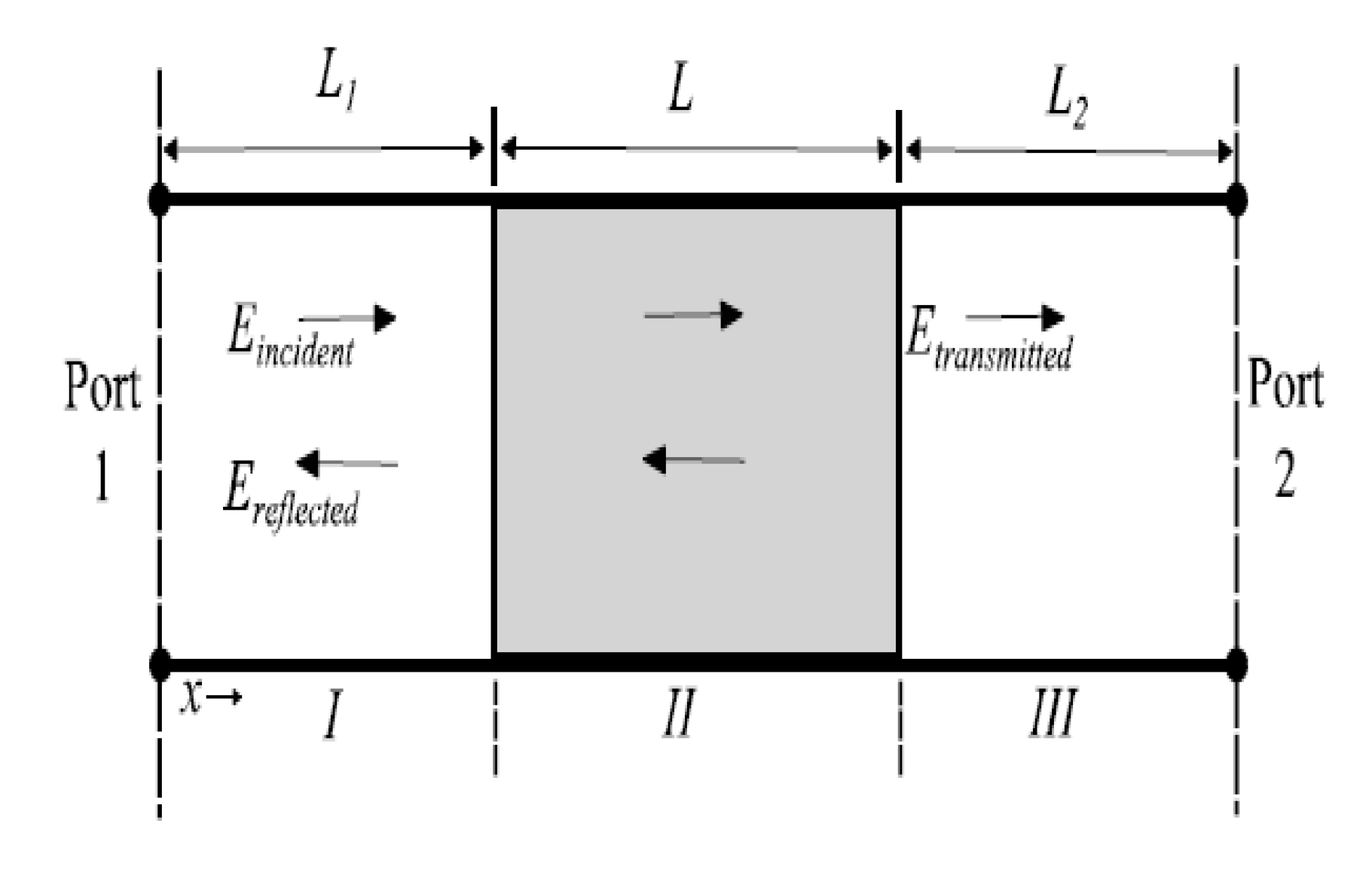
3.2.1. Waveguide Signal Perturbation: Basic Principle
Nicolson–Ross–Weir (NRW) Algorithm
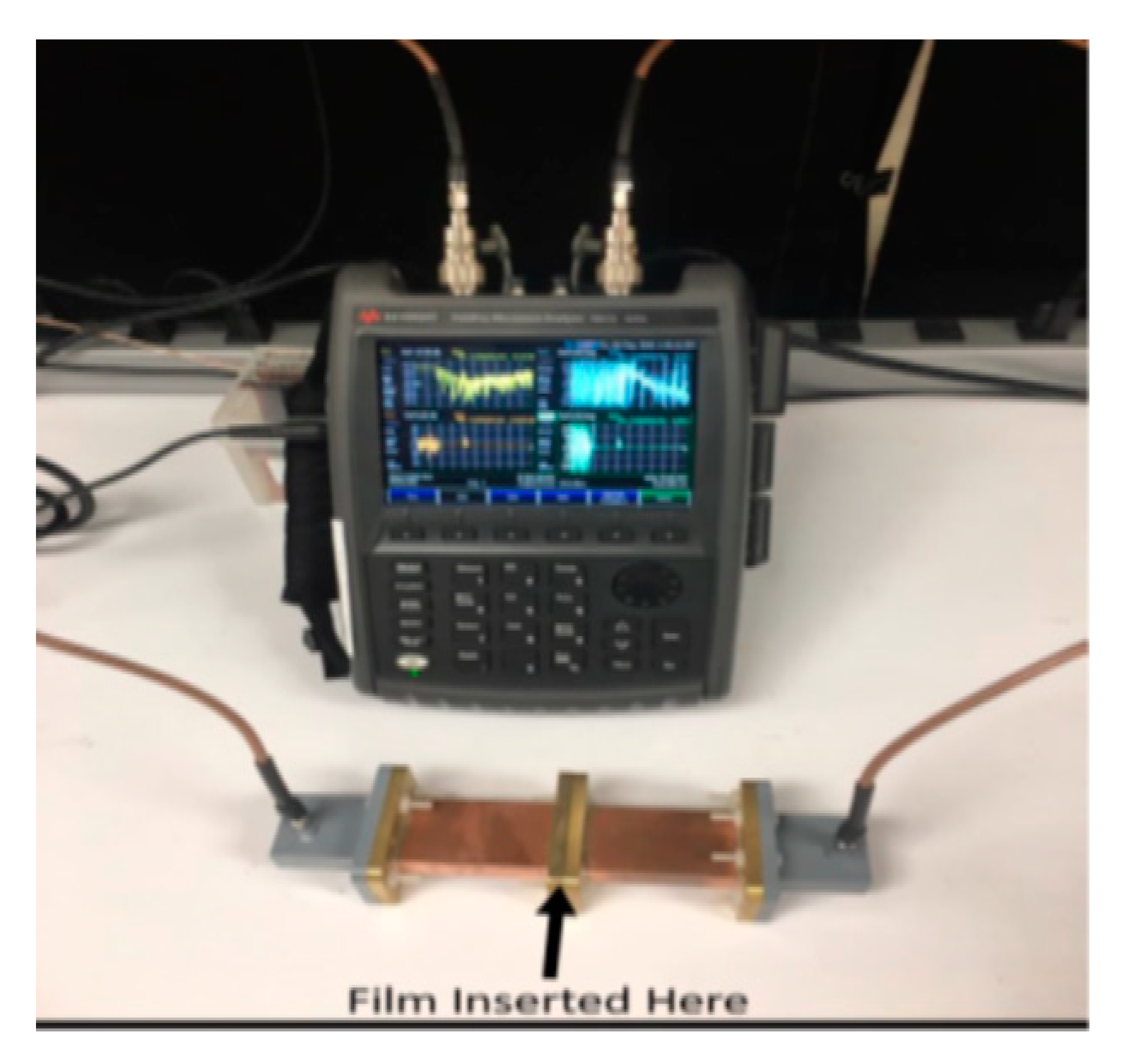
3.2.2. Experimental Setup
3.2.3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frans, T. New Developments in Ferromagnetic Materials. Nature 1948, 161, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Srinivasan, G.; Hunter, S.; Babu, V.S.; Seehra, M.S. Observation of superparamagnetism in rf-sputtered films of zinc ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1995, 146, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Sharma, A.; Afsar, M.N.; Obi, O.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, N. Permittivity and permeability measurement of spin-spray deposited Ni-Zn-ferrite thin film sample. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 4085–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngs, I.; Bowler, N.; Lymer, K.P.; Hussain, S. Dielectric relaxation in metal-coated particles: The dramatic role of nano-scale coatings. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamps, R.L. Dynamic magnetic properties of ferroic films, multilayers, and patterned elements. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 2380–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, K.; Leiste, H.; Krüger, K. Ferromagnetic resonance frequency increase and resonance line broadening of a ferromagnetic Fe–Co–Hf–N film with in-plane uniaxial anisotropy by high-frequency field perturbation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 345, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.N. (Ed.) A Guide to the Characterisation of dielectric materials at RF and microwave frequencies; The Institute of Measurement & Control (UK) & NPL: London, UK, 2003; ISBN 0904457389. Available online: http://eprintspublications.npl.co.uk/id/eprint/2905 (accessed on 31 December 2020).
- Nicolson, A.M.; Ross, G.F. Measurement of the intrinsic properties of materials by time domain techniques. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 1970, 19, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weir, W.B. Automatic measurement of complex dielectric constant and permeability at microiwave frequencies. Proc. IEEE 1974, 62, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoor, A.Y.; Afsar, M.N. Complex permittivity and permeability of barium and strontium ferrite powders in X, KU, and K-band frequency ranges. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 10F105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Rai, R.C.; Podraza, N.J.; Denev, S.; Ramirez, M.; Chu, Y.H.; Martin, L.W.; Ihlefeld, J.; Heeg, T.; Schubert, J.; et al. Linear and nonlinear optical properties of Bi FeO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 121915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inaba, K. High Resolution X Ray Diffraction Analyses of (La,Sr)MnO3/ZnO/Sapphire(0001) Double Heteroepitaxial Films. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2013, 3, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, A.; Ghanbari, D.; Nabiyouni, G. Facile synthesis of hexagonal strontium ferrite nanostructures and hard magnetic poly carbonate nanocomposite. Main Group Met. Chem. 2017, 40, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, R.; Rosas, G.; Perez, R. Effect of the surfactant on the growth and oxidation of iron nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2015, 12, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, E.; Rozatian, A.S.; Yousefi, M.H. Synthesis and characterization of SrFe12O19 nanoparticles produced by a low-temperature solid-state reaction method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Ong, C.K.; Neo, C.P.; Varadan, V.V.; Varadan, V.K. Microwave Electronics Measurement and Materials Characterization; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A. The Step by Step Development of NRW Method. In Proceedings of the SBMO/IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and Optoelectronics Conference, Natal, Brazil, 29 October–1 November 2011; pp. 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, A.; Mishra, B.; Foley, A.; Wood, L.; Chen, M.Y. High Permeability Photosintered Strontium Ferrite Flexible Thin Films. Micromachines 2021, 12, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010042
Ahmad A, Mishra B, Foley A, Wood L, Chen MY. High Permeability Photosintered Strontium Ferrite Flexible Thin Films. Micromachines. 2021; 12(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Abid, Bhagyashree Mishra, Andrew Foley, Leslie Wood, and Maggie Yihong Chen. 2021. "High Permeability Photosintered Strontium Ferrite Flexible Thin Films" Micromachines 12, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010042
APA StyleAhmad, A., Mishra, B., Foley, A., Wood, L., & Chen, M. Y. (2021). High Permeability Photosintered Strontium Ferrite Flexible Thin Films. Micromachines, 12(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010042





