Droplet Transportation through an Orifice on Electrode for Digital Microfluidics Modulations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
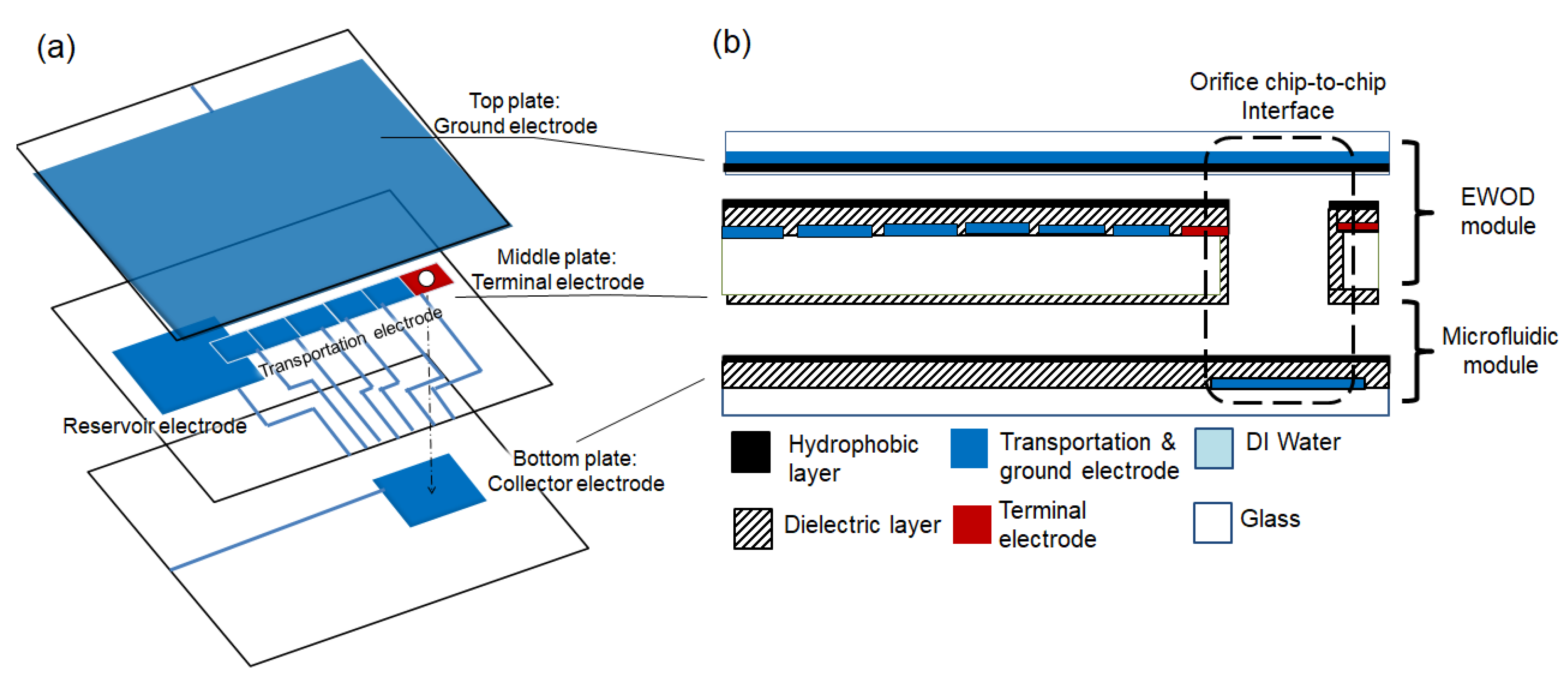
2.1. Device Fabrication
2.2. EWOD Actuation
2.3. Core–Shell Droplets
2.4. Vertical EWOD Configuration
3. Droplet Vertical Insertion
3.1. Three Stages
3.2. Terminal Electrode
4. Capillary Length
5. Results
5.1. Droplet Insertion
5.1.1. Initial to Suspended Stage
5.1.2. Suspended to Final Stage
5.2. Droplet Volume Change during Insertion
5.2.1. Droplet Recovery
5.2.2. Droplet Shell Removal
6. Application Demonstration
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.; Fobel, R.; Wheeler, A.R. Digital microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2012, 5, 413–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.K.; Moon, H.; Kim, C.-J. Creating, Transporting, Cutting, and Merging Liquid Droplets by Electrowetting-Based Actuation for Digital Microfluidic Circuits. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2003, 12, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, W.C.; Kim, C.-J.C. Droplet actuation by electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD): A review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hung, P.-Y.; Jiang, P.-S.; Lee, E.-F.; Fan, S.-K.; Lu, Y.-W. Genomic DNA extraction from whole blood using a digital microfluidic (DMF) platform with magnetic beads. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.-H.; Fan, S.-K.; Kim, C.-J.; Yao, D.-J. EWOD microfluidic systems for biomedical applications. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2014, 16, 965–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.A.; Padhy, P.; Ren, W.; Wu, M.; Hesselink, L. Microparticle transport along a planar electrode array using moving dielectrophoresis. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 034902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kua, C.H.; Lam, Y.C.; Rodriguez, I.; Yang, C.; Youcef-Toumi, K. Dynamic cell fractionation and transportation using moving dielectrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 6975–6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafrenière, N.M.; Shih, S.C.; Abu-Rabie, P.; Jebrail, M.J.; Spooner, N.; Wheeler, A.R. Multiplexed extraction and quantitative analysis of pharmaceuticals from DBS samples using digital microfluidics. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.; Pamula, V.K.; Fair, R.B. An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, M.H.; Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.; Wheeler, A.R. A digital microfluidic electrochemical immunoassay. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsi, M.H.; Choi, K.; Ng, A.H.; Chamberlain, M.D.; Wheeler, A.R. Electrochemiluminescence on digital microfluidics for microRNA analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, H.; Yi, Z.; Yang, R.; Qin, X.; Shen, S.; Zeng, W.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, C. Designing splicing digital microfluidics chips based on polytetrafluoroethylene membrane. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.-K.; Yang, H.; Hsu, W. Droplet-on-a-wristband: Chip-to-chip digital microfluidic interfaces between replaceable and flexible electrowetting modules. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Jones, T.B. Moving droplets between closed and open microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Won, D.-J.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.J. Three-dimensional digital microfluidic manipulation of droplets in oil medium. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malk, R.; Rival, A.; Fouillet, Y.; Davoust, L. EWOD in coplanar electrode configurations. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Nanochannels, Microchannels, and Minichannels, Montreal, QC, Canada, 1–5 August 2010; pp. 239–248. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, B.F.; Garrell, R.L. Digital microfluidic system with vertical functionality. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1655–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sen, P.; Kim, C.-J.C. Capillary spreading dynamics of electrowetted sessile droplets in air. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4302–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsi, S.; Valiadi, M.; Tsaloglou, M.-N.; Parry-Jones, L.; Jacobs, A.; Watson, R.; Turner, C.; Amos, R.; Hadwen, B.; Buse, J. Rapid and sensitive detection of antibiotic resistance on a programmable digital microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rival, A.; Jary, D.; Delattre, C.; Fouillet, Y.; Castellan, G.; Bellemin-Comte, A.; Gidrol, X. An EWOD-based microfluidic chip for single-cell isolation, mRNA purification and subsequent multiplex qPCR. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3739–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Sadeghi, S.; Shah, G.J.; Chen, S.; Keng, P.Y.; van Dam, R.M. Accurate dispensing of volatile reagents on demand for chemical reactions in EWOD chips. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3331–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, Y.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.-B. Hierarchical micro/nano structures for super-hydrophobic surfaces and super-lyophobic surface against liquid metal. Micro Nano Syst. Lett. 2014, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brassard, D.; Malic, L.; Normandin, F.; Tabrizian, M.; Veres, T. Water-oil core-shell droplets for electrowetting-based digital microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raccurt, O.; Berthier, J.; Clementz, P.; Borella, M.; Plissonnier, M. On the influence of surfactants in electrowetting systems. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Saar, K.L.; Jacquat, R.; Hong, L.; Levin, A.; Gang, H.; Ye, R.; Mu, B.; Knowles, T.P. Mechanism of biosurfactant adsorption to oil/water interfaces from millisecond scale tensiometry measurements. Interface Focus 2017, 7, 20170013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhuri, R.G.; Paria, S. Dynamic contact angles on PTFE surface by aqueous surfactant solution in the absence and presence of electrolytes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 337, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbatan, T.; Shen, W. Measurement of the surface tension of liquid marbles. Langmuir 2011, 27, 12923–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, E.; Young, P.; Mohseni, K. Electrostatic force calculation for an EWOD-actuated droplet. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2007, 3, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarts, D. Capillary Length in a Fluid− Fluid Demixed Colloid− Polymer Mixture. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 7407–7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berthier, J. Micro-Drops and Digital Microfluidics, 2nd ed.; William Andrew: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor, C.K.; Batchelor, G. An Introduction to Fluid Dynamics; Cambridge University Press: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, J.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.; Shin, B.; Bae, J.; Kim, H.-Y. Interfacial waves generated by electrowetting-driven contact line motion. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, A.; Haage, G.; Renzow, D. The temperature dependence of contact angles polytetrafluoroethylene/N-alkanes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1971, 35, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Configuration | γLG(L) (mN/m) (Liquid–Gas (Liquid)) | γLS (mN/m) Liquid–Solid | λc (mm) | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Droplet I | Water–air droplet | 76 | 92 | 2.7 | General Purpose |
| Droplet II | Core: Water Shell: oil (hexadecane) | 36 | 92 | 3.2 | Lower the surface tension/prevent evaporation |
| Droplet III | Core: water + Tween20 Shell: oil (hexadecane) | 7 | 22 | 1.8 | Much smaller surface tension/prevent evaporation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, T.-C.; Lu, Y.-W. Droplet Transportation through an Orifice on Electrode for Digital Microfluidics Modulations. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111385
Chu T-C, Lu Y-W. Droplet Transportation through an Orifice on Electrode for Digital Microfluidics Modulations. Micromachines. 2021; 12(11):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111385
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Ting-Chia, and Yen-Wen Lu. 2021. "Droplet Transportation through an Orifice on Electrode for Digital Microfluidics Modulations" Micromachines 12, no. 11: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111385
APA StyleChu, T.-C., & Lu, Y.-W. (2021). Droplet Transportation through an Orifice on Electrode for Digital Microfluidics Modulations. Micromachines, 12(11), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12111385







