Friction Behavior of Rough Surfaces on the Basis of Contact Mechanics: A Review and Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Progress of Contact Modeling for Single Asperity
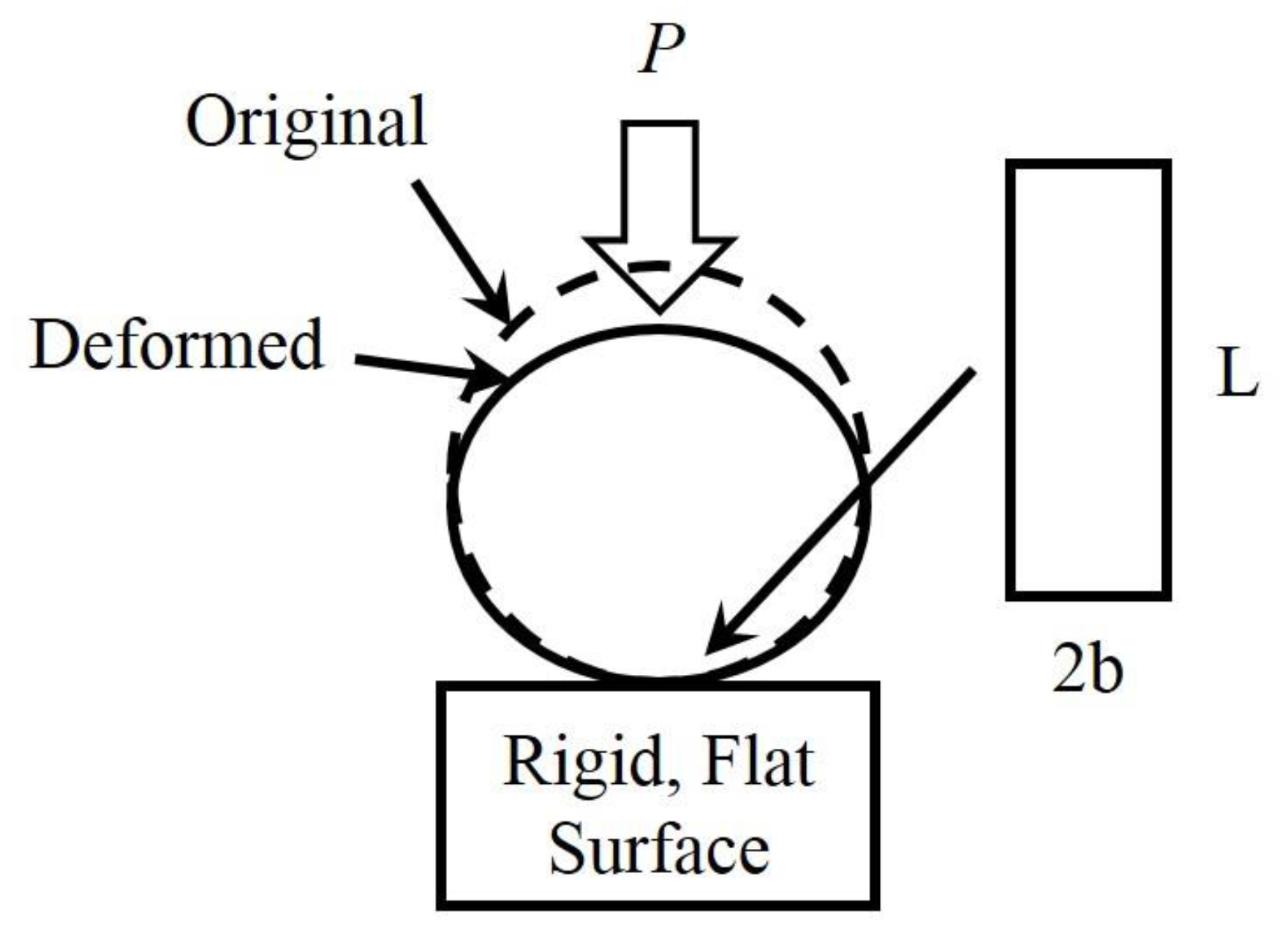
2.1. Two-Dimensional Contact Model
2.2. Three-Dimensional Contact Model for Spherical Shape
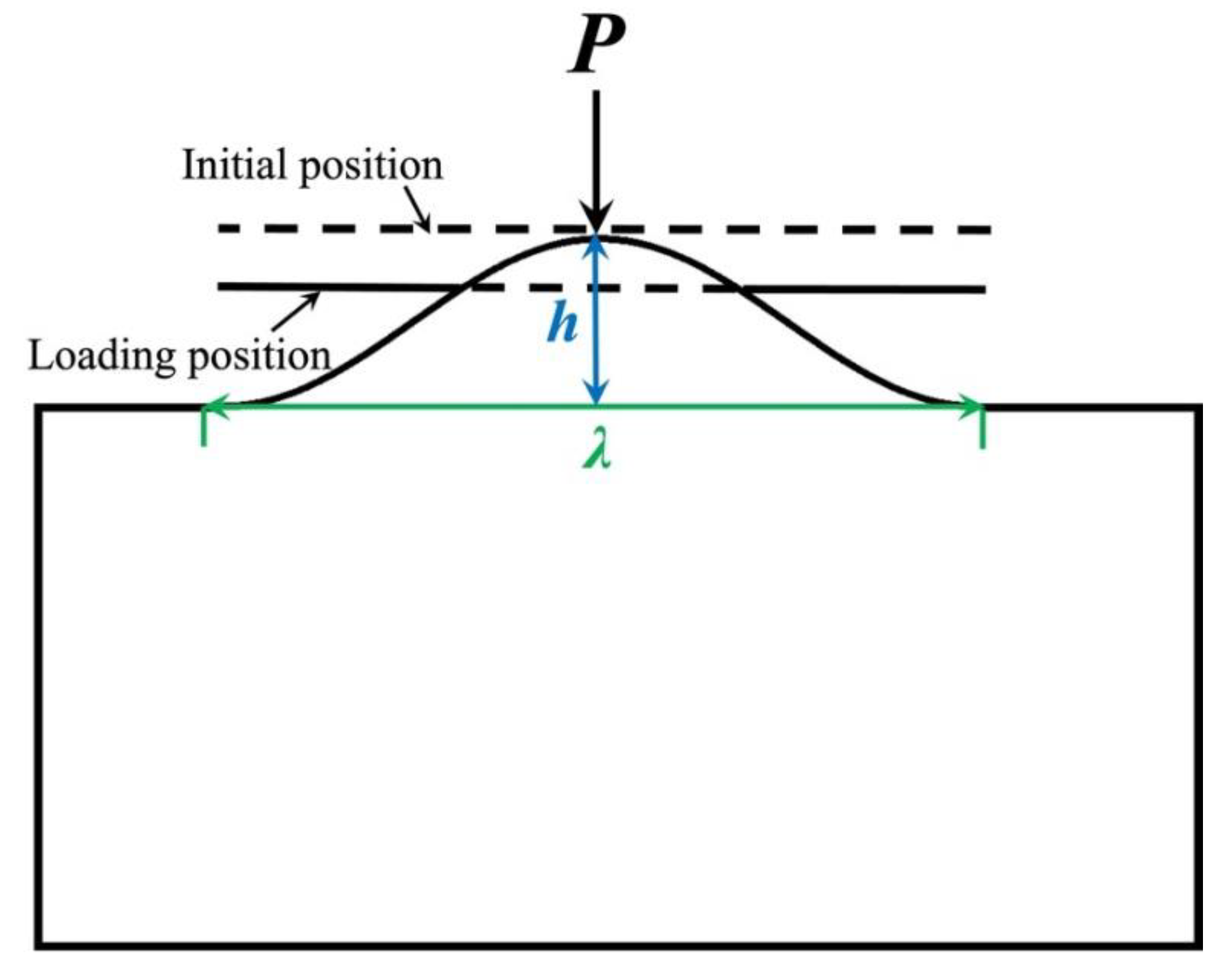
2.3. Three-Dimensional Contact Model for Sinusoidal Profile
3. Study on Contact between Rough Surfaces
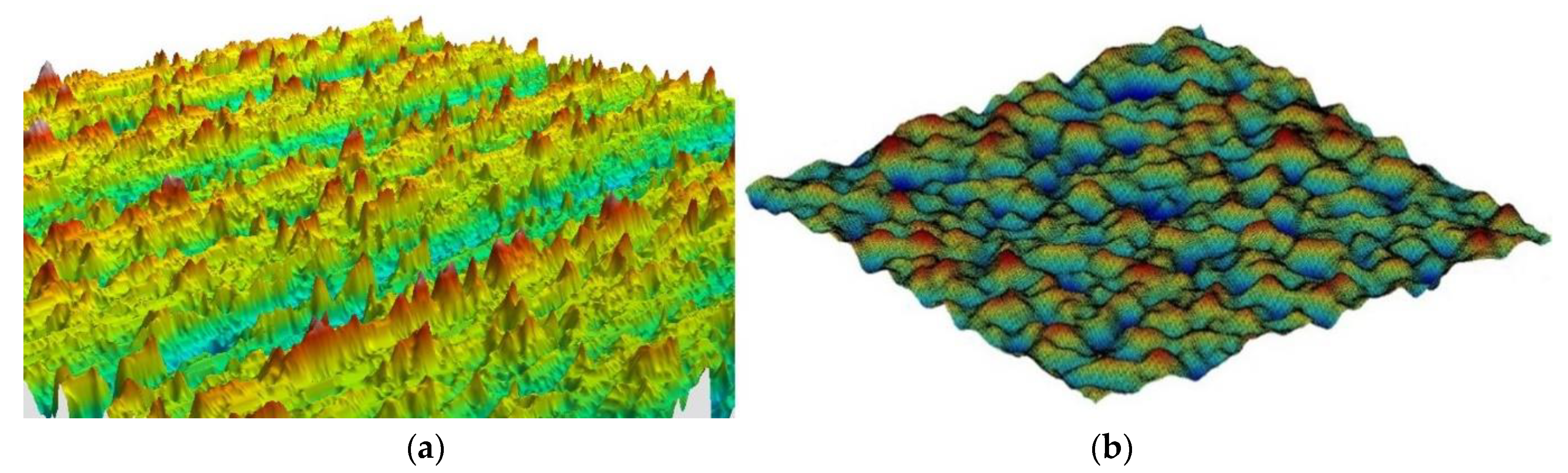
3.1. Surface Roughness
3.2. Rough Surface Research Based on Statistical Model
3.3. Fractal Modeling Method for Rough Surface
4. Research Progress on Interface Sliding and Friction Behavior
4.1. Friction and Slip Behaviors of a Single Asperity
4.2. Examples of Interface Friction Behavior Standing on Contact Mechanics
4.3. Experimental Methods for Friction Studies
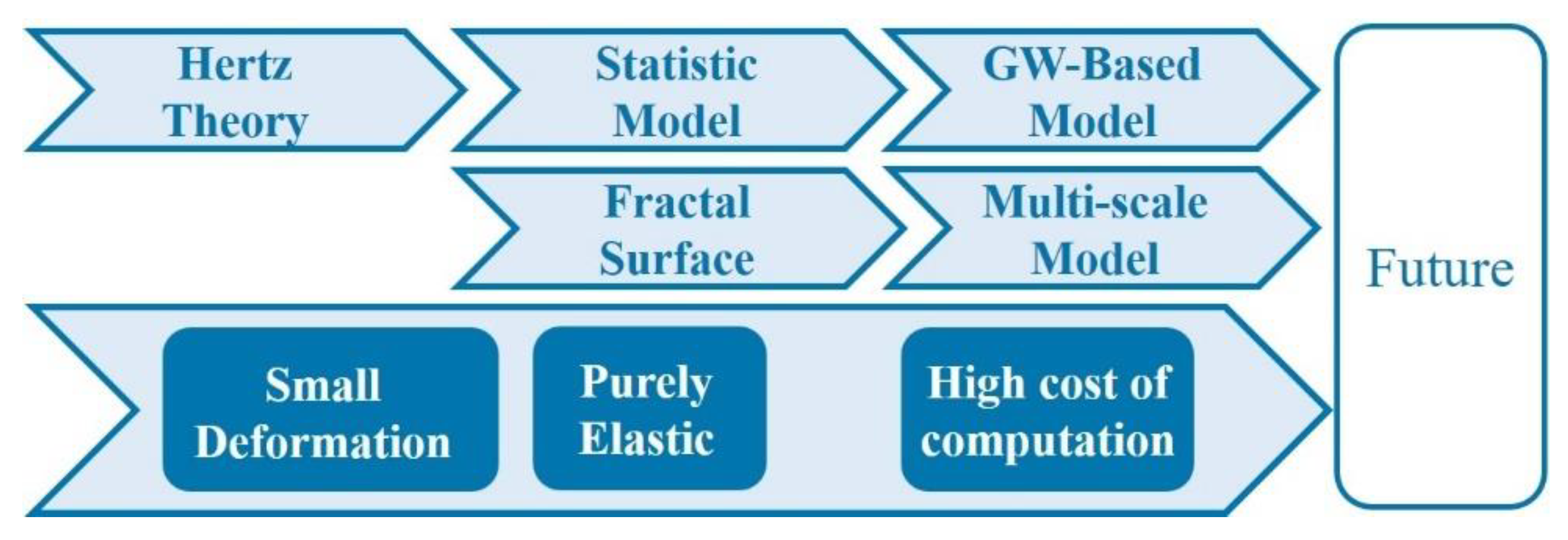
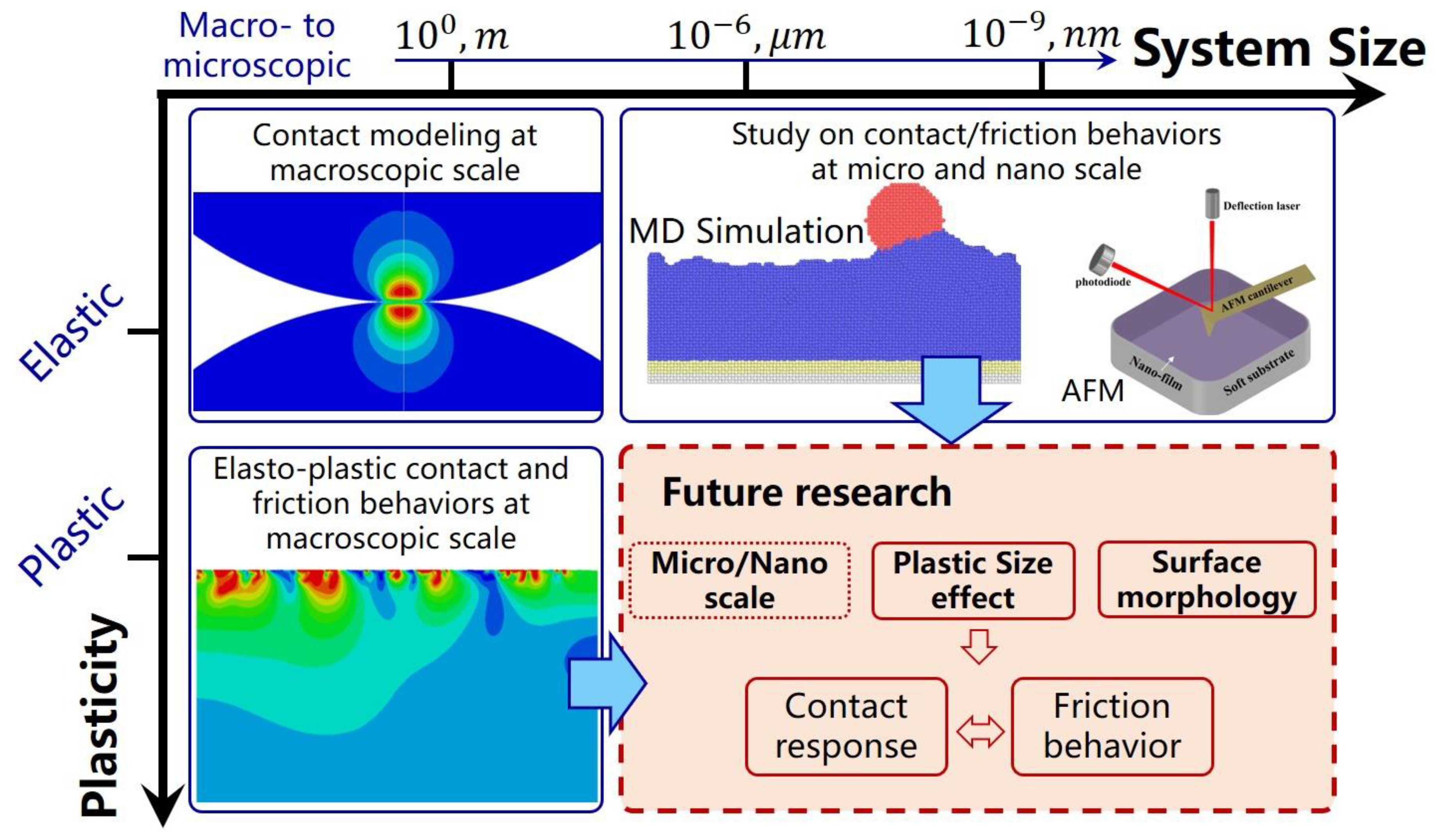
5. Prospects of Research Themes in Contact and Friction Behaviors of Rough Surfaces
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulkarni, S.M.; Hahn, G.T.; Rubin, C.A.; Bhargava, V. Elasto-Plastic Finite Element Analysis of Repeated Three-Dimensional, Elliptical Rolling Contact With Rail Wheel Properties. J. Tribol. 1991, 113, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamiş, M.B.; Selçukxin, B. Analysis of the Friction behaviour of bolted joints. Wear 1993, 166, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Micro/nanotribology and its applications to magnetic storage devices and MEMS. Tribol. Int. 1995, 28, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brot, C.; Etsion, I.; Kligerman, Y. A contact model for a creeping sphere and a rigid flat. Wear 2008, 265, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbe-Valloire, F.; Prat, M. A model for face-turned surface microgeometry: Application to the analysis of metallic static seals. Wear 2008, 264, 980–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. Influence of tribology on global energy consumption, costs and emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Wang, X.; Saha, S.; Xu, Y.; Sharma, A.; Jackson, R.L. A review of elastic–plastic contact mechanics. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2017, 69, 060804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.L.; Ghaednia, H.; Pope, S. A Solution of Rigid–Perfectly Plastic Deep Spherical Indentation Based on Slip-Line Theory. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 58, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, I. A Transient Dynamic Analysis of Mechanical Seals Including Asperity Contact and Face Deformation. Tribol. Trans. 2002, 45, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, G.; Baronet, C. Elastoplastic indentation of a half-space by an infinitely long rigid circular cylinder. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1971, 13, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinar, A.; Sinclair, G. Quasi-static normal indentation of an elasto-plastic half-space by a rigid circular cylinder of infinite length. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1986, 22, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesarovic, S.; Fleck, N.A. Frictionless indentation of dissimilar elastic–plastic spheres. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2000, 37, 7071–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Jackson, R.L. A Finite Element Study of an Elasto-Plastic Disk or Cylindrical Contact Against a Rigid Flat in Plane Stress with Bilinear Hardening. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xu, C.; Wan, Q. Modeling Tangential Contact of Rough Surfaces With Elastic- and Plastic-Deformed Asperities. J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 051401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yastrebov, V.; Cailletaud, G.; Noël, S.; Mballa, F.S.M.; Proudhon, H.; Houzé, F.; Testé, P. Three-level multi-scale modeling of electrical contacts sensitivity study and experimental validation. In Proceedings of the 61st IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, San Diego, CA, USA, 11–14 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.L.; Kogut, L. Electrical Contact Resistance Theory for Anisotropic Conductive Films Considering Electron Tunneling and Particle Flattening. IEEE Trans. Components Packag. Technol. 2007, 30, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Jackson, R.L.; Gao, J. A third body contact model for particle contaminated electrical contacts. In Proceedings of the 60th IEEE Holm Conference on Electrical Contacts, New Orleans, LA, USA, 12–15 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaednia, H.; Jackson, R.L. On the effect of nanoparticles on the real area of contact. Friction and Wear. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 041603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follansbee, P.; Sinclair, G. Quasi-static normal indentation of an elasto-plastic half-space by a rigid sphere—I: Analysis. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1984, 20, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, G.B.; Follansbee, P.S.; Johnson, K.L. Quasi-static normal indentation of an elasto-plastic half-space by a rigid sphere—II. Results. Int. J. Solids Struct. 1985, 21, 865–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.; Kogut, L. A Comparison of Flattening and Indentation Approaches for Contact Mechanics Modeling of Single Asperity Contacts. J. Tribol. 2005, 128, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-R.; Etsion, I.; Bogy, D.B. Static Friction Coefficient Model for Metallic Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 1988, 110, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Maietta, D.M.; Chang, L. An Asperity Microcontact Model Incorporating the Transition From Elastic Deformation to Fully Plastic Flow. J. Tribol. 1999, 122, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Etsion, I. Elastic-Plastic Contact Analysis of a Sphere and a Rigid Flat. J. Appl. Mech. 2002, 69, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B.; Sahoo, P. Effect of Strain Hardening on Elastic-Plastic Contact of a Deformable Sphere against a Rigid Flat under Full Stick Contact Condition. Adv. Tribol. 2012, 2012, 472794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Pope, S.A.; Jackson, R.L.; Marghitu, D.B. A comprehensive study of the elasto-plastic contact of a sphere and a flat. Tribol. Int. 2015, 93, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisis, T.; Gourgiotis, P.; Baxevanakis, K.; Georgiadis, H. Some basic contact problems in couple stress elasticity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 2084–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuriya, A.N.; Bhandakkar, T.K. Plane strain indentation on finite thickness bonded layer in couple stress elasticity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2017, 108, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourgiotis, P.; Zisis, T.; Giannakopoulos, A.; Georgiadis, H. The Hertz contact problem in couple-stress elasticity. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2019, 168, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zeng, F.; Yuan, B.; Wang, Y. An approximate model to describe the size effects of spherical contact tests, based on a modified couple stress elasticity. Acta Mech. 2021, 232, 4363–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Gibson, R.; Thomas, T. The elastic contact of a rough surface. Wear 1975, 35, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, J.H. An Elliptic Elastic-Plastic Asperity Microcontact Model for Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 1998, 120, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, Y.-R.; Wang, P.-Y. An Elliptical Microcontact Model Considering Elastic, Elastoplastic, and Plastic Deformation. J. Tribol. 2003, 125, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, C. An improved simplified model of rough surface profile. Tribol. Int. 2018, 125, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourani, A. A New Three-Dimensional Numerical Model of Rough Contact: Influence of Mode of Surface Deformation on Real Area of Contact and Pressure Distribution. J. Tribol. 2014, 137, 011401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.; Greenwood, J.; Higginson, J. The contact of elastic regular wavy surfaces. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1985, 27, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, C.Y.; Bhushan, B. Comparison of surface roughness measurements by stylus profiler, AFM and non-contact optical profiler. Wear 1995, 190, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yastrebov, V.A.; Anciaux, G.; Molinari, J.-F. From infinitesimal to full contact between rough surfaces: Evolution of the contact area. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 52, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Xu, Y.; Jackson, R.L. Perfectly Elastic Axisymmetric Sinusoidal Surface Asperity Contact. J. Tribol. 2016, 138, 031401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Dikken, R.J.; Nicola, L.; Van Der Giessen, E. Plastic Ploughing of a Sinusoidal Asperity on a Rough Surface. J. Appl. Mech. 2015, 82, 071006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bower, A.; Kim, K.-S.; Lev, L.; Cheng, Y. The behavior of an elastic–perfectly plastic sinusoidal surface under contact loading. Wear 2006, 261, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Van der Giessen, E.; Nicola, L. Plastic flattening of a sinusoidal metal surface: A discrete dislocation plasticity study. Wear 2012, 296, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Krithivasan, V.; Jackson, R.L. An analysis of three-dimensional elasto-plastic sinusoidal contact. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 27, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William. Plastic deformation of a sinusoidal surface. Wear 2007, 264, 60–68. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Proudhon, H. Finite element analysis of frictionless contact between a sinusoidal asperity and a rigid plane: Elastic and initially plastic deformations. Mech. Mater. 2014, 77, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Proudhon, H. Finite element analysis of contact deformation regimes of an elastic-power plastic hardening sinusoidal asperity. Mech. Mater. 2016, 103, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, A.Y.; Polycarpou, A.A.; Conry, T.F. Detailed surface roughness characterization of engineering surfaces undergoing tribological testing leading to scuffing. Wear 2003, 255, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltombe, R.; Kubiak, K.J.; Bigerelle, M. How to select the most relevant 3D roughness parameters of a surface. Scanning 2013, 36, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodich, F.M.; Pepelyshev, A.; Savencu, O. Statistical approaches to description of rough engineering surfaces at nano and microscales. Tribol. Int. 2016, 103, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, E.J.; Firestone, F.A. Specifying surface quality. Mech. Eng. 1933, 65, 569–572. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse, D.J.; Archard, J.F. The properties of random surfaces of significance in their contact. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1970, 316, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Scott, P.J.; Whitehouse, D.J.; Blunt, L. Paradigm shifts in surface metrology. Part I. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2007, 463, 2049–2070. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Leach, R.K.; Petzing, J.; Coupland, J.M. Surface measurement errors using commercial scanning white light interferometers. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 19, 015303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, U.; Haefke, H.; Reimann, P.; Güntherodt, H.-J. Tip artefacts in scanning force microscopy. J. Microsc. 1994, 173, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechenault, F.; Pallares, G.; George, M.; Rountree, C.; Bouchaud, E.; Ciccotti, M. Effects of Finite Probe Size on Self-Affine Roughness Measurements. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 025502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Williamson, J.B.P. Contact Nominally Flat Surfaces. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1966, 295, 300–319. [Google Scholar]
- Tingting, Z.; Feng, Y.T.; Min, W. An extended Greenwood-Williamson model based normal interaction law for discrete element modelling of spherical particles with surface roughness. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2018, 42, 1624–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Beheshti, A.; Polycarpou, A.A. Rough Surface Normal Nanocontact Stiffness: Experimental Measurements and Rough Surface Contact Model Predictions. J. Appl. Mech. 2017, 84, 031006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zou, Y. A Comparative Study on Equivalent Modeling of Rough Surfaces Contact. J. Tribol. 2018, 140, 041402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, A.; Khonsari, M.M. On the Contact of Curved Rough Surfaces: Contact Behavior and Predictive Formulas. J. Appl. Mech. 2014, 81, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M. A note on the possibility of roughness enhancement of adhesion in Persson’s theory. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 121, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jackson, R.; Green, I. On the Modeling of Elastic Contact between Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 2011, 54, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.L.; Green, I. A statistical model of elasto-plastic asperity contact between rough surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2005, 39, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chang, L. A Model of Asperity Interactions in Elastic-Plastic Contact of Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 2000, 123, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M.; Greenwood, J.A.; Paggi, M. Inclusion of “interaction” in the Greenwood and Williamson contact theory. Wear 2008, 265, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Van der Giessen, E.; Vakis, A.I. Erratum: Asperity interaction and substrate deformation in statistical summation models of contact between rough surfaces. J. Appl. Mech. 2016, 83, 087001. [Google Scholar]
- Ciavarella, M.; Delfine, V.; Demelio, G. A “re-vitalized” Greenwood and Williamson model of elastic contact between fractal surfaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2006, 54, 2569–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, C.-D.; Katta, R.R.; Lee, J.; Polycarpou, A.A. Effect of asperity interactions on rough surface elastic contact behavior: Hard film on soft substrate. Tribol. Int. 2010, 43, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, S.; Eriten, M.; Polycarpou, A.A. An Improved Model of Asperity Interaction in Normal Contact of Rough Surfaces. J. Appl. Mech. 2012, 80, 011025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yao, Q.; Li, Q.; Feng, X.-Q.; Gao, H. Contact stiffness of regularly patterned multi-asperity interfaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 111, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Van der Giessen, E.; Liu, X. Strain gradient plasticity analysis of elasto-plastic contact between rough surfaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 96, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Vakis, A.; Liu, X.; Van der Giessen, E. Statistical model of rough surface contact accounting for size-dependent plasticity and asperity interaction. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2017, 106, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Contact analysis between rough surfaces considering the size-affected deformation behaviour of multi-scale asperities. Tribol. Int. 2022, 172, 107592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S. A Three-Dimensional Thermal-Mechanical Asperity Contact Model for Two Nominally Flat Surfaces in Contact. J. Tribol. 2000, 123, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.L. The Effect of Scale-Dependent Hardness on Elasto-Plastic Asperity Contact between Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 2006, 49, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.; Putignano, C.; Ciavarella, M. A Greenwood & Williamson theory for line contact. Wear 2011, 270, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müser, M.H.; Dapp, W.B.; Bugnicourt, R.; Sainsot, P.; Lesaffre, N.; Lubrecht, T.A.; Persson, B.N.J.; Harris, K.; Bennett, A.; Schulze, K.; et al. Meeting the Contact-Mechanics challenge. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M. A comment on “Meeting the Contact-Mechanics challenge” by Muser et al. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müser, M.H. Response to “A comment on Meeting the Contact-(Mechanics) challenge”. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpick, R.W. The contact sport of rough surfaces. Science 2018, 359, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignano, C.; Afferrante, L.; Carbone, G.; Demelio, G. A new efficient numerical method for contact mechanics of rough surfaces. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putignano, C.; Afferrante, L.; Carbone, G.; Demelio, G. The influence of the statistical properties of self-affine surfaces in elastic contacts: A numerical investigation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2012, 60, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yastrebov, V.A.; Anciaux, G.; Molinari, J.-F. On the accurate computation of the true contact-area in mechanical contact of random rough surfaces. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xia, Y.; Scarpa, F.; Hong, J.; Ma, Y. Interfacial contact stiffness of fractal rough surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, B.N.J. Elasto-plastic contact between randomly rough surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Bucher, F.; Chiaia, B. Elastic contact between randomly rough surfaces: Comparison of theory with numerical results. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 184106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Jackson, R.L. A Comparison of Contact Modeling Utilizing Statistical and Fractal Approaches. J. Tribol. 2005, 128, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Bhushan, B. Fractal Model of Elastic-Plastic Contact Between Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 1991, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Komvopoulos, K. Contact analysis of elastic-plastic fractal surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 3617–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, C. Research on fractal model of normal contact stiffness for mechanical joint considering asperity interaction. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 134, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Gan, L. A revised Majumdar and Bushan model of elastoplastic contact between rough surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 425, 1138–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, L. A Normal Contact Stiffness Model of Joint Surface Based on Fractal Theory. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2019, 119, 459–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.C.; Lin, J.F. Fractal Model Developed for Elliptic Elastic-Plastic Asperity Microcontacts of Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 2004, 126, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L. A fractal contact model of rough surfaces considering detailed multi-scale effects. Tribol. Int. 2022, 176, 107920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S. Multi-stage contact model between fractal rough surfaces based on multi-scale asperity deformation. Appl. Math. Model. 2022, 109, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A. Engineering Tribology; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Katano, Y.; Nakano, K.; Otsuki, M.; Matsukawa, H. Novel Friction Law for the Static Friction Force based on Local Precursor Slipping. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, srep06324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.L.; Dimaki, A.; Psakhie, S.; Popov, M. On the role of scales in contact mechanics and friction between elastomers and randomly rough self-affine surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, O.; Fineberg, J. Static Friction Coefficient Is Not a Material Constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 254301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayfidinov, K.; Cezan, S.D.; Baytekin, B.; Baytekin, H.T. Minimizing Friction. Wear. and energy losses by eliminating contact charging. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, K. Lowering coefficient of friction in Cu alloys with stable gradient nanostructures. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1601942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapperi, S. Looking at How Things Slip. Science 2010, 330, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.D. Compliance of Elastic Bodies in Contact. J. Appl. Mech. 1949, 16, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, G.M. Explicit Equations for the Stresses beneath a Sliding Spherical Contact. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1983, 197, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Etsion, I. A Semi-Analytical Solution for the Sliding Inception of a Spherical Contact. J. Tribol. 2003, 125, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizmer, V.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. The effect of contact conditions and material properties on the elasticity terminus of a spherical contact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2006, 43, 5736–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zait, Y.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. Unloading of an elastic–plastic spherical contact under stick contact condition. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Kligerman, Y.; Kadin, Y. Unloading of an elastic–plastic loaded spherical contact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 3716–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronen, S.; Goltsberg, R.; Etsion, I. A comparison of stick and slip contact conditions for a coated sphere compressed by a rigid flat. Friction 2017, 5, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizmer, V.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. Elastic–plastic spherical contact under combined normal and tangential loading in full stick. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 25, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Shi, X. Numerical Investigation of Adhesive Wear and Static Friction Based on the Ductile Fracture of Junction. J. Appl. Mech. 2013, 80, 041032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wu, A.; Zhu, C.; Qu, S. Effects of load configuration on partial slip contact between an elastic-plastic sphere and a rigid flat. Tribol. Int. 2013, 61, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Shi, X.; Polycarpou, A.A. An Elastic-Plastic Spherical Contact Model Under Combined Normal and Tangential Loading. J. Appl. Mech. 2012, 79, 051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X. On Slip Inception and Static Friction for Smooth Dry Contact. J. Appl. Mech. 2014, 81, 121005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Liu, C.; Huang, G.; Jiang, D.; Jin, J. Nano-sized single-asperity friction behavior: Insight from molecular dynamics simulations. Eur. J. Mech.-A/Solids 2022, 96, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Scheibert, J.; Gadegaard, N.; Mulvihill, D.M. An asperity-based statistical model for the adhesive friction of elastic nominally flat rough contact interfaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 164, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.; Pusterhofer, M.; Summer, F.; Grün, F. Validation of statistic and deterministic asperity contact models using experimental Stribeck data. Tribol. Int. 2021, 165, 107329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, H.; Tavakoli, E.; Ahmadian, H. Modeling polymer-metal frictional interface using multi-asperity contact theory. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 164, 108227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, L.; Qu, P.; Li, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Z. A multiscale soft-contact modelling method for rough surfaces in contact with coupled slipping/sliding and rolling. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, S.; Beheshti, A. Asperity-based contact and static friction with provision for creep: A review. Surfaces Interfaces 2021, 24, 101144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Li, Z.-M.; Liu, T.; Zhao, G.; Jing, J.; Yuan, W. A novel multiscale model for contact behavior analysis of rough surfaces with the statistical approach. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 212, 106808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergel, J.C.; Scheibert, J.; Sauer, R.A. Contact with coupled adhesion and friction: Computational framework, applications, and new insights. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2020, 146, 104194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Batou, A.; Ouyang, H. An Isogeometric analysis based method for frictional elastic contact problems with randomly rough surfaces. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2022, 394, 114865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouvry, S.; Wendler, B.; Liskiewicz, T.; Dudek, M.; Kolodziejczyk, L. Fretting wear analysis of TiC/VC multilayered hard coatings: Experiments and modelling approaches. Wear 2004, 257, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, M.; Mulvihill, D.; Nowell, D.; Hills, D. Measurements of pressure and area dependent tangential contact stiffness between rough surfaces using digital image correlation. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, M.E.; Mulvihill, D.M.; Nowell, D.; Hills, D.A. Determination of the Frictional Properties of Titanium and Nickel Alloys Using the Digital Image Correlation Method. Exp. Mech. 2010, 51, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, D.; Kartal, M.; Olver, A.; Nowell, D.; Hills, D. Investigation of non-Coulomb friction behaviour in reciprocating sliding. Wear 2011, 271, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, X.; Lu, K. Friction mechanism in the running-in stage of copper: From plastic deformation to delamination and oxidation. Tribol. Int. 2017, 115, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, E.E.; Polycarpou, A.A. The effect of surface roughness on the transfer of polymer films under unlubricated testing conditions. Wear 2015, 326–327, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridrici, V.; Fouvry, S.; Kapsa, P. Fretting Wear behavior of a Cu–Ni–In plasma coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 163–164, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, T.; Kagami, J.; Kawaguchi, T.; Hatazawa, T. Micro-displacement characteristics under tangential force. Wear 2000, 241, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, S.; Akay, A.; Gola, M.M. Measurement of Tangential Contact Hysteresis During Microslip. J. Tribol. 2004, 126, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Królikowski, J.; Szczepek, J. Prediction of contact parameters using ultrasonic method. Wear 1991, 148, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer-Joyce, R.; Drinkwater, B.W.; Quinn, A.M. The Use of Ultrasound in the Investigation of Rough Surface Interfaces. J. Tribol. 2000, 123, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltazar, A.; Rokhlin, S.I.; Pecorari, C. On the relationship between ultrasonic and micromechanical properties of contacting rough surfaces. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2002, 50, 1397–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Valadez, M.; Baltazar, A.; Dwyer-Joyce, R. Study of interfacial stiffness ratio of a rough surface in contact using a spring model. Wear 2010, 268, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, D.A.; Nowell, D. Mechanics of fretting fatigue-Oxford’s contribution. Tribol. Int. 2014, 76, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, D.M.; Brunskill, H.; Kartal, M.E.; Dwyer-Joyce, R.S.; Nowell, D. A Comparison of Contact Stiffness Measurements Obtained by the Digital Image Correlation and Ultrasound Techniques. Exp. Mech. 2013, 53, 1245–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, D.; Kartal, M.; Nowell, D.; Hills, D. An elastic–plastic asperity interaction model for sliding friction. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 1679–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriten, M.; Polycarpou, A.A.; Bergman, L.A. Surface Roughness Effects on Energy Dissipation in Fretting Contact of Nominally Flat Surfaces. J. Appl. Mech. 2010, 78, 021011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, O.; Mall, S. Effects of slip on fretting behavior: Experiments and analyses. Wear 2004, 256, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.; Wahab, M.A. Finite element analysis of fretting wear under variable coefficient of friction and different contact regimes. Tribol. Int. 2017, 107, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muser, M.H. How static is static Friction? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13187–13188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, O.; Cohen, G.; Fineberg, J. The Dynamics of the Onset of Frictional Slip. Science 2010, 330, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpick, R.W. Controlling Friction. Science 2006, 313, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Service, R.F. The Power of Friction. Science 2013, 339, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etsion, I. Comment on Leonardo da Vinci’s Friction Experiments: An Old Story Acknowledged and Repeated. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 58, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, V.L. Is Tribology Approaching Its Golden Age? Grand Challenges in Engineering Education and Tribological Research. Front. Mech. Eng. 2018, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Etsion, I. A Static Friction Model for Elastic-Plastic Contacting Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 2004, 126, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, D.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. A Model for Contact and Static Friction of Nominally Flat Rough Surfaces Under Full Stick Contact Condition. J. Tribol. 2008, 130, 031401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Etsion, I.; Talke, F.E. Contact Area and Static Friction of Rough Surfaces With High Plasticity Index. J. Tribol. 2010, 132, 031401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, A.; Huang, S. Effect of loading induced anisotropy on the shear behavior of rough interfaces. Tribol. Int. 2011, 44, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Wan, Q.; Guo, X. Plane Contact and Partial Slip Behaviors of Elastic Layers With Randomly Rough Surfaces. J. Appl. Mech. 2015, 82, 091006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakis, A.; Yastrebov, V.; Scheibert, J.; Nicola, L.; Dini, D.; Minfray, C.; Almqvist, A.; Paggi, M.; Lee, S.; Limbert, G.; et al. Modeling and simulation in tribology across scales: An overview. Tribol. Int. 2018, 125, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Quan, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Han, B.; Liu, G. Influence of Nanoscale Textured Surfaces and Subsurface Defects on Friction Behaviors by Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Nanomaterials. 2019, 9, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





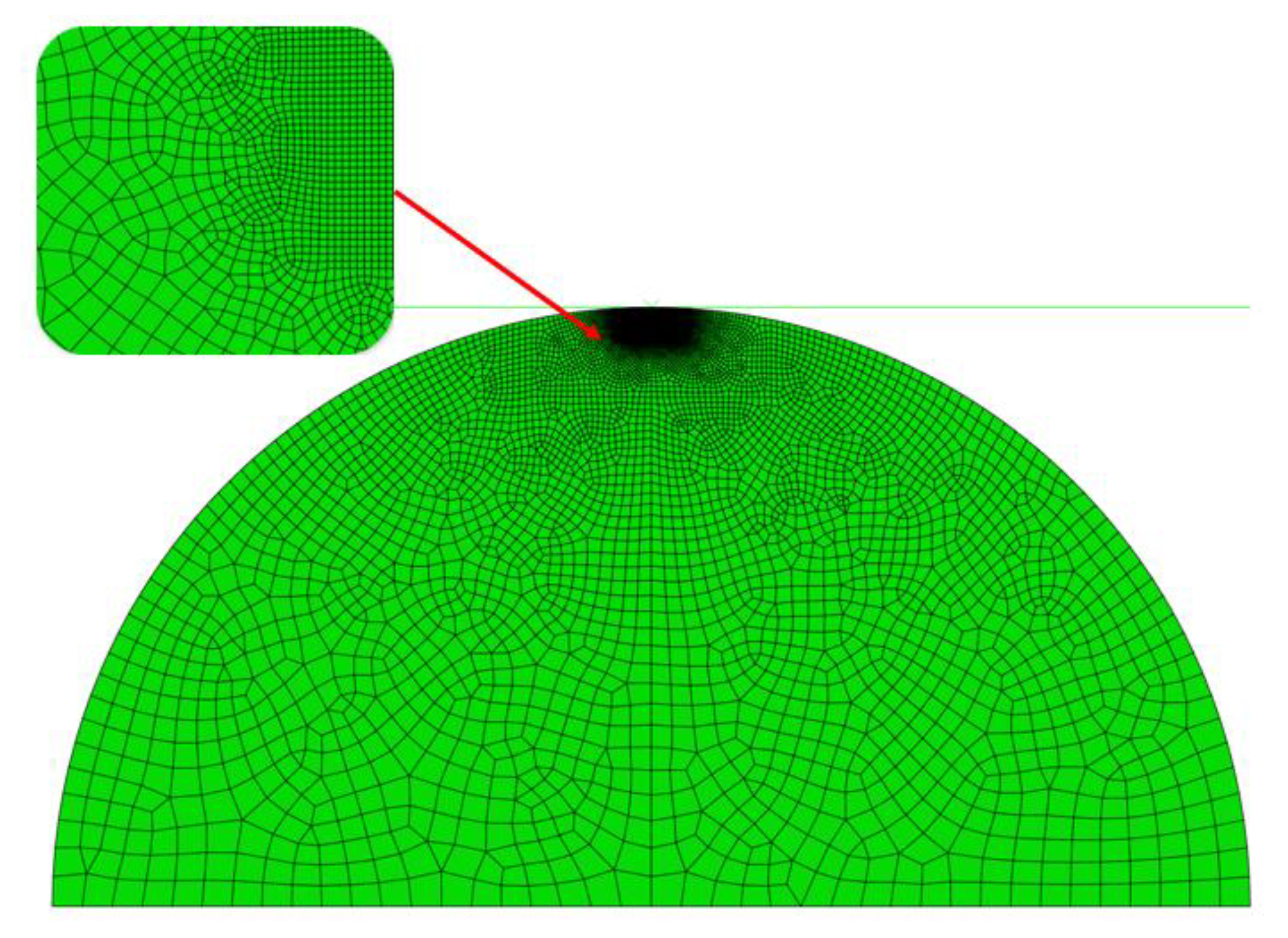

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Friction Behavior of Rough Surfaces on the Basis of Contact Mechanics: A Review and Prospects. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111907
Zhang S, Li D, Liu Y. Friction Behavior of Rough Surfaces on the Basis of Contact Mechanics: A Review and Prospects. Micromachines. 2022; 13(11):1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111907
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Siyuan, Dawei Li, and Yanwei Liu. 2022. "Friction Behavior of Rough Surfaces on the Basis of Contact Mechanics: A Review and Prospects" Micromachines 13, no. 11: 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111907
APA StyleZhang, S., Li, D., & Liu, Y. (2022). Friction Behavior of Rough Surfaces on the Basis of Contact Mechanics: A Review and Prospects. Micromachines, 13(11), 1907. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13111907




