A Novel Monopolar Cross-Scale Nanopositioning Stage Based on Dual Piezoelectric Stick-Slip Driving Principle
Abstract
1. Introduction
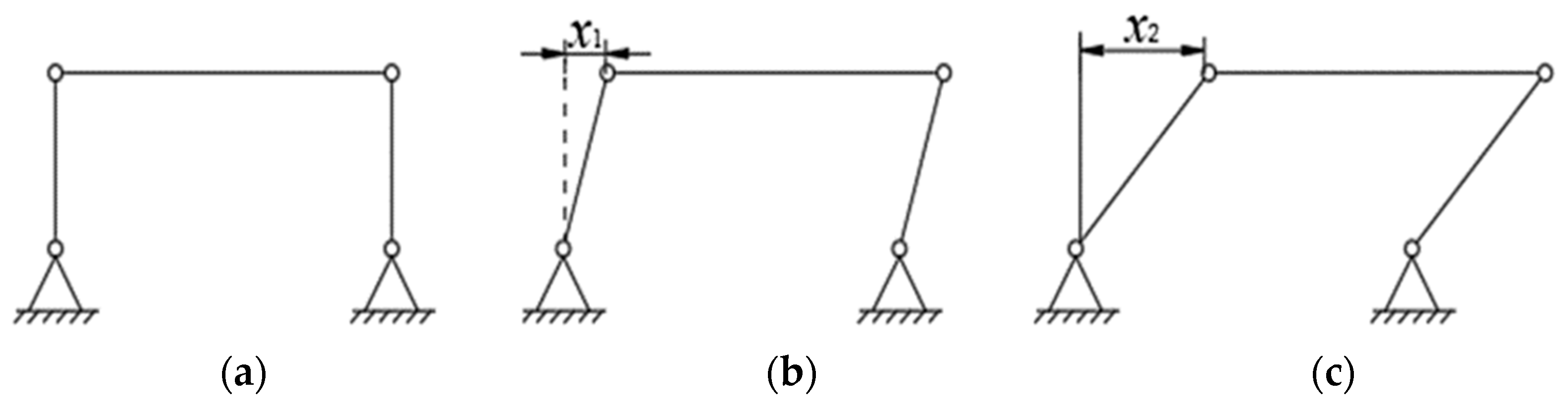
2. Principles of Movement
3. Design and Analysis
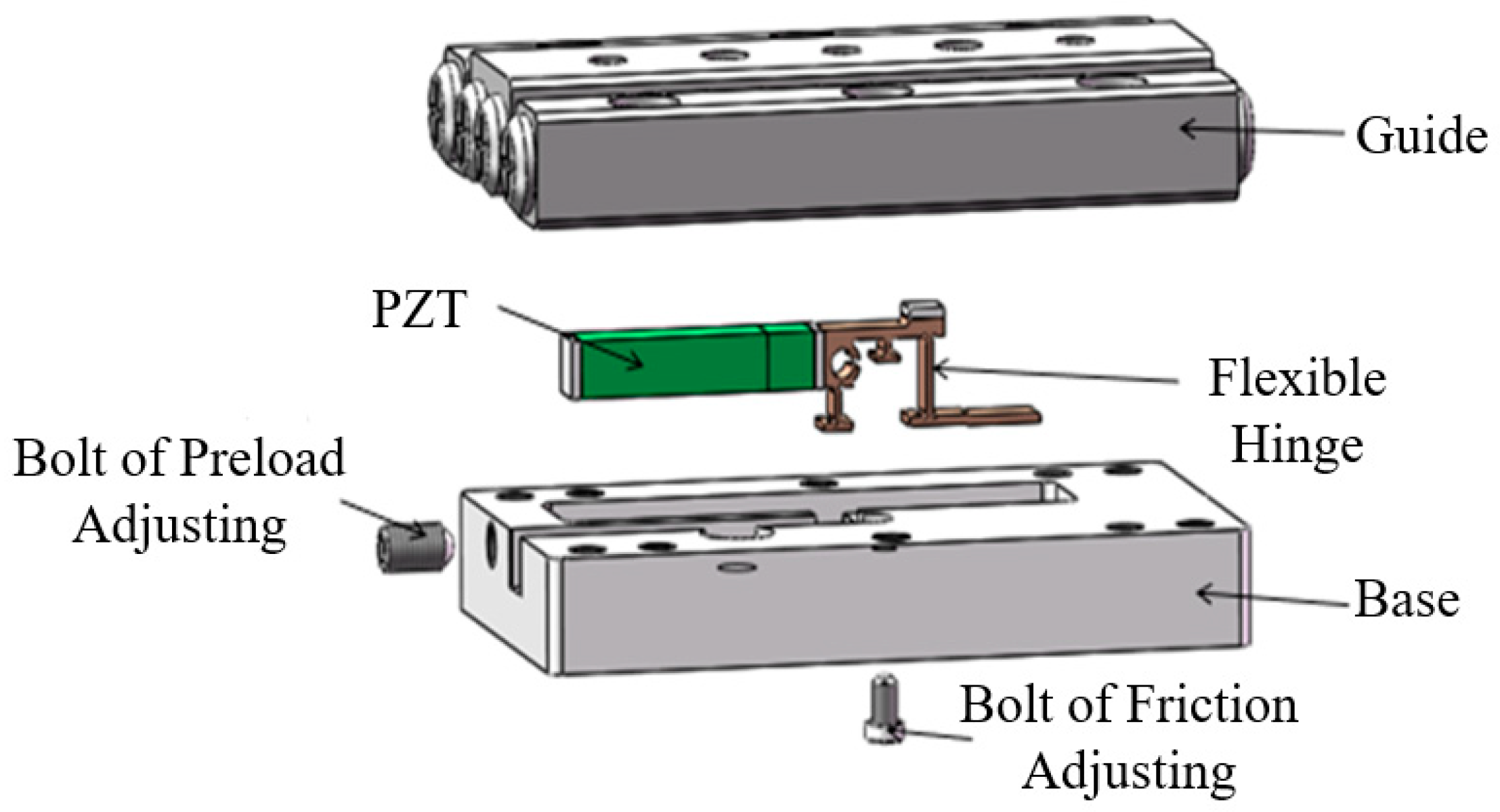
3.1. Design of Overall Structure
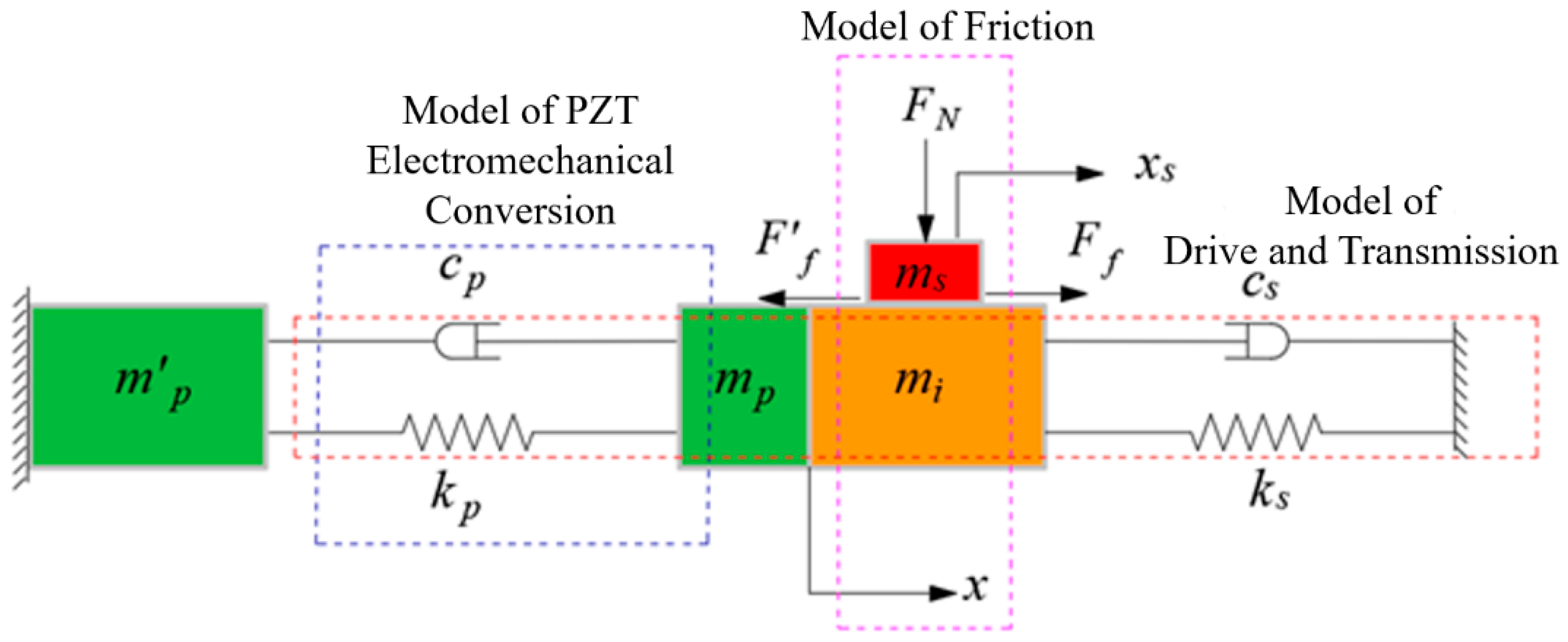
3.2. Drive System Modeling and Analysis
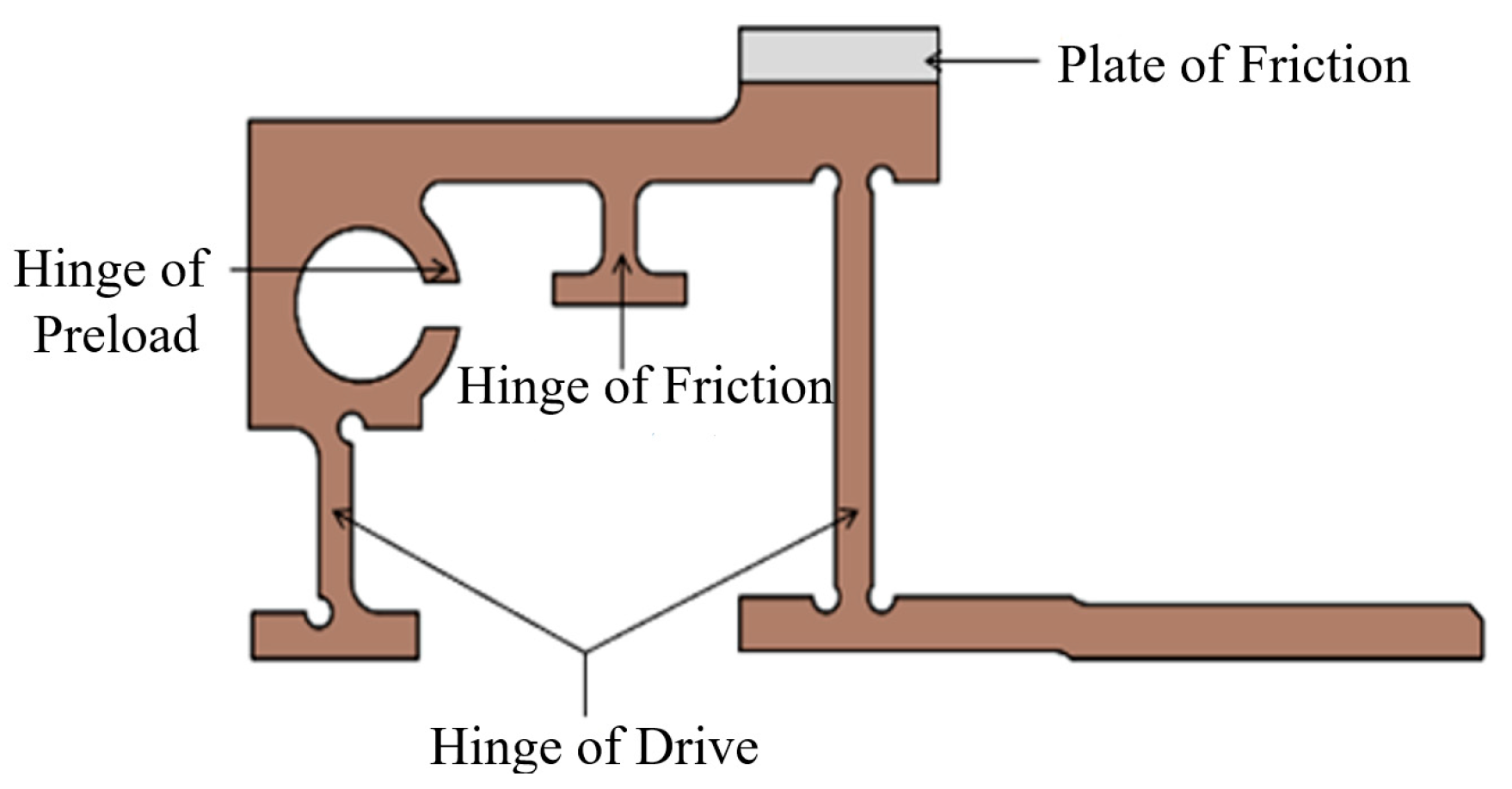
3.3. Design of Flexible Hinge Structure
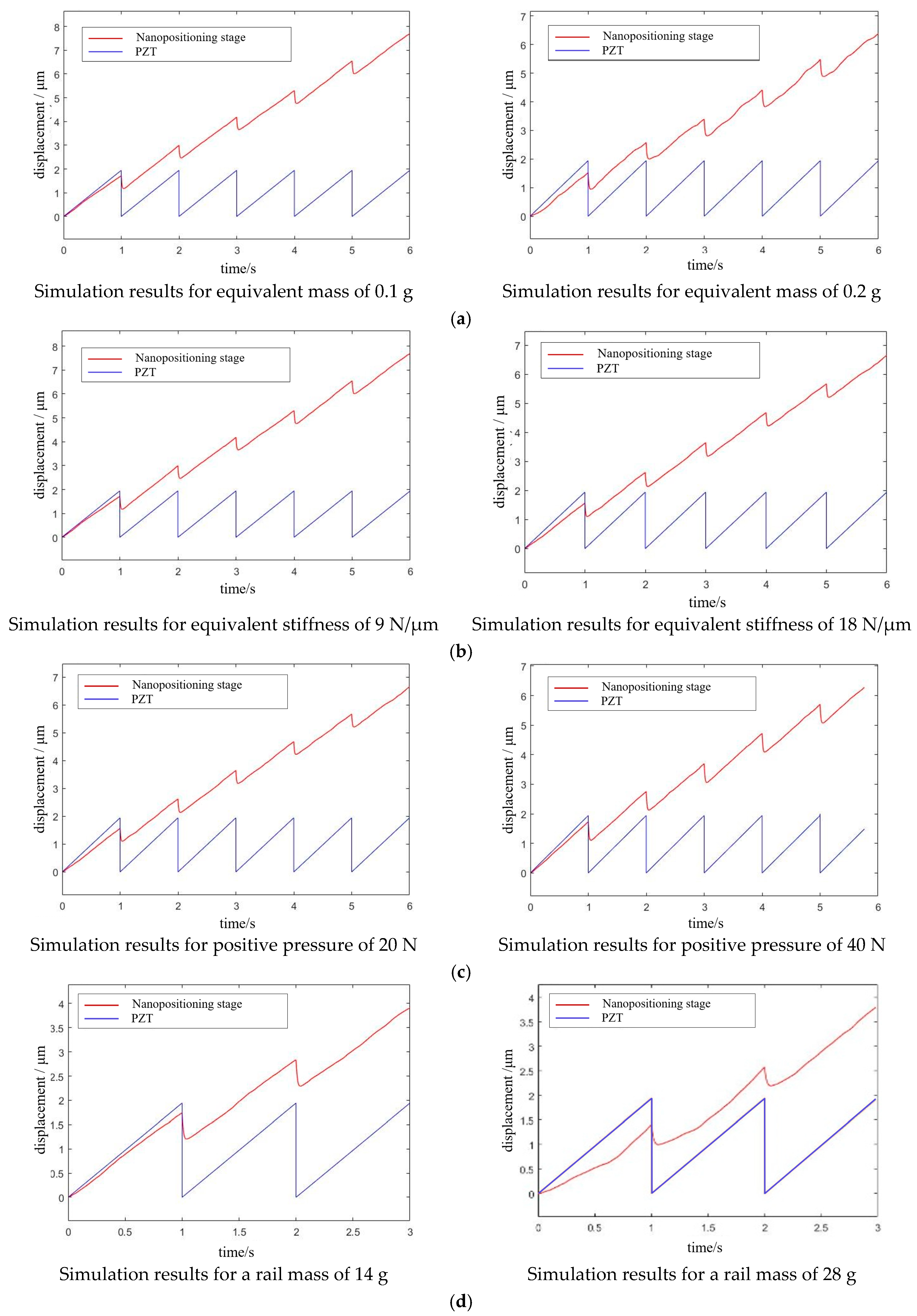
3.4. Analysis and Simulation of Flexible Hinge Structure
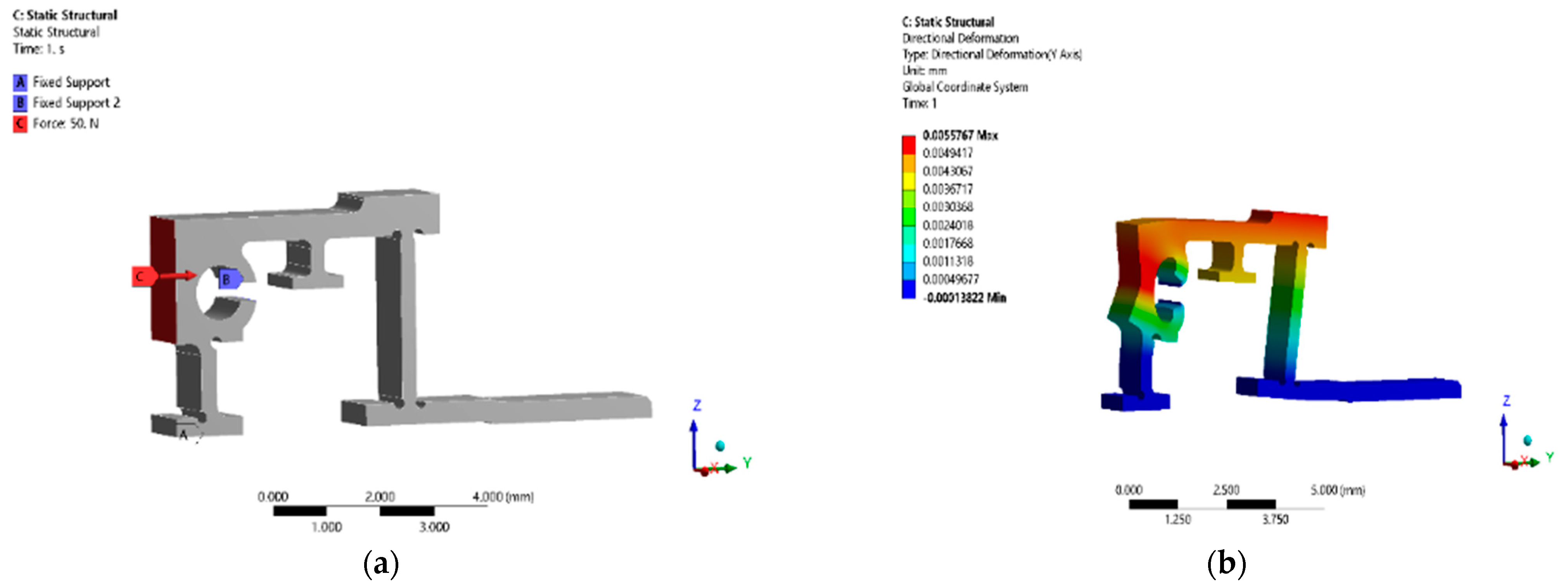
- Stiffness problem. Too little stiffness will increase the deformation under the preload force affecting its life, reducing return speed, and lowering the dynamic response speed; too much stiffness will increase the resistance to the piezoelectric stack, and the output displacement transferred to the guide will be reduced, lowering the movement speed of the positioning stage.
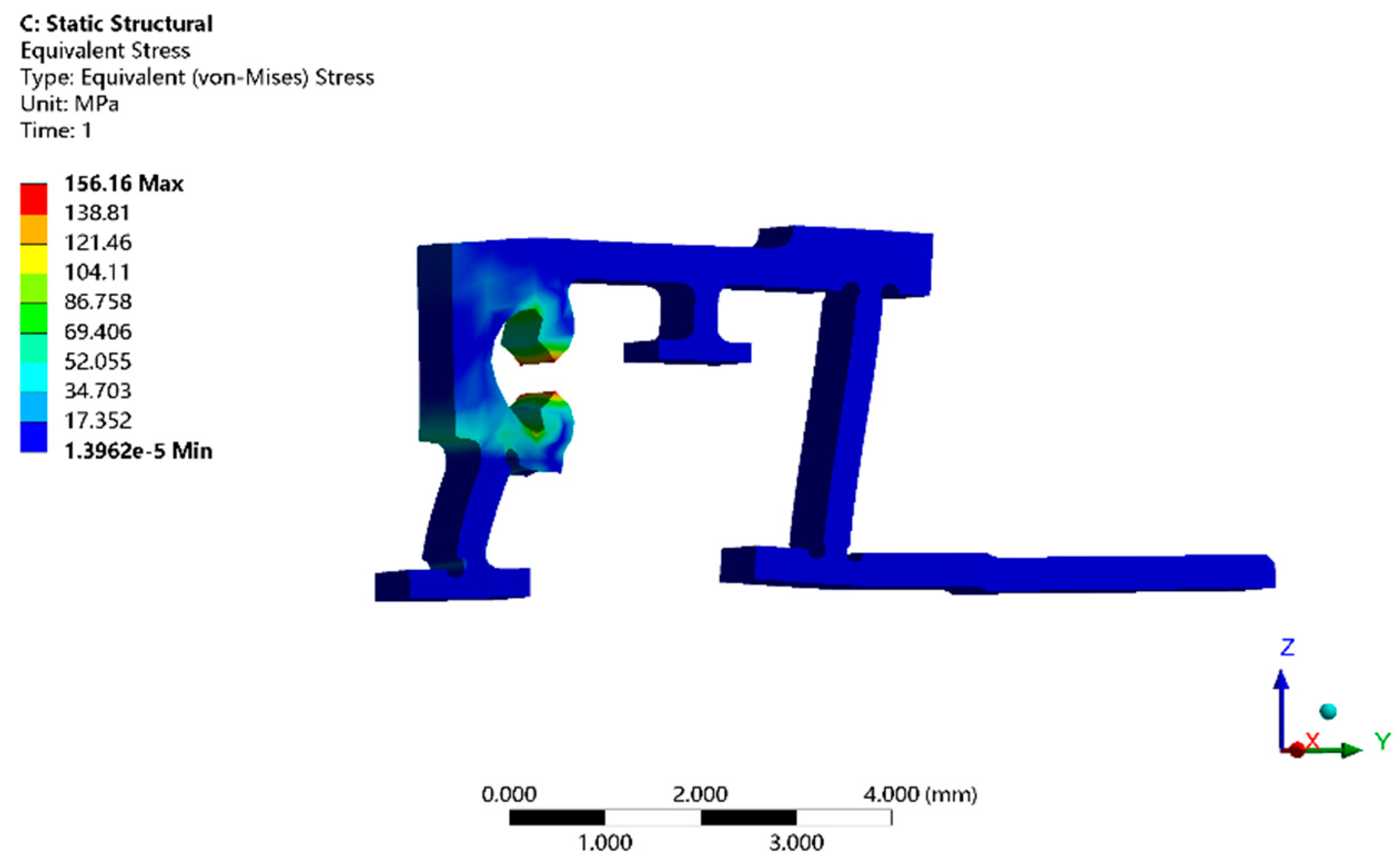
- Strength problem. Flexible hinges mainly use the small deformation and self-return characteristics generated by elastic materials to improve the displacement resolution; too little strength will cause plastic deformation or even fatigue damage due to alternating loads.
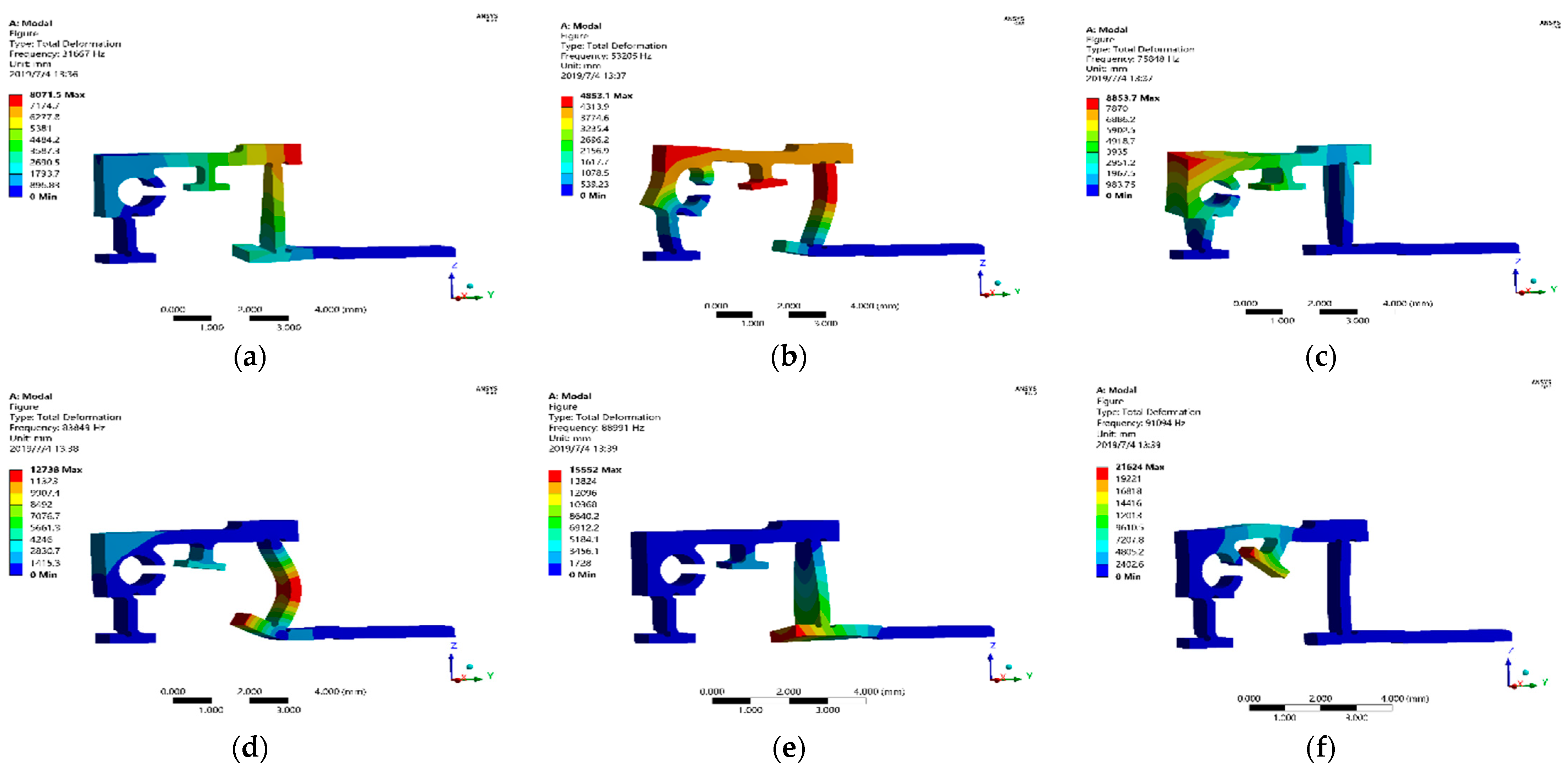
- Resonant frequency problem. The PZT achieves periodic vibration under the excitation of a sawtooth wave voltage signal. If the working frequency of the PZT is greater than or equal to the frequency of any mode of the flexible hinge, it will cause the flexible hinge to produce a self-excitation or resonance phenomenon with the PZT, resulting in unstable stage motion.
3.4.1. Stiffness Analysis
3.4.2. Strength Analysis
3.4.3. Modal Analysis
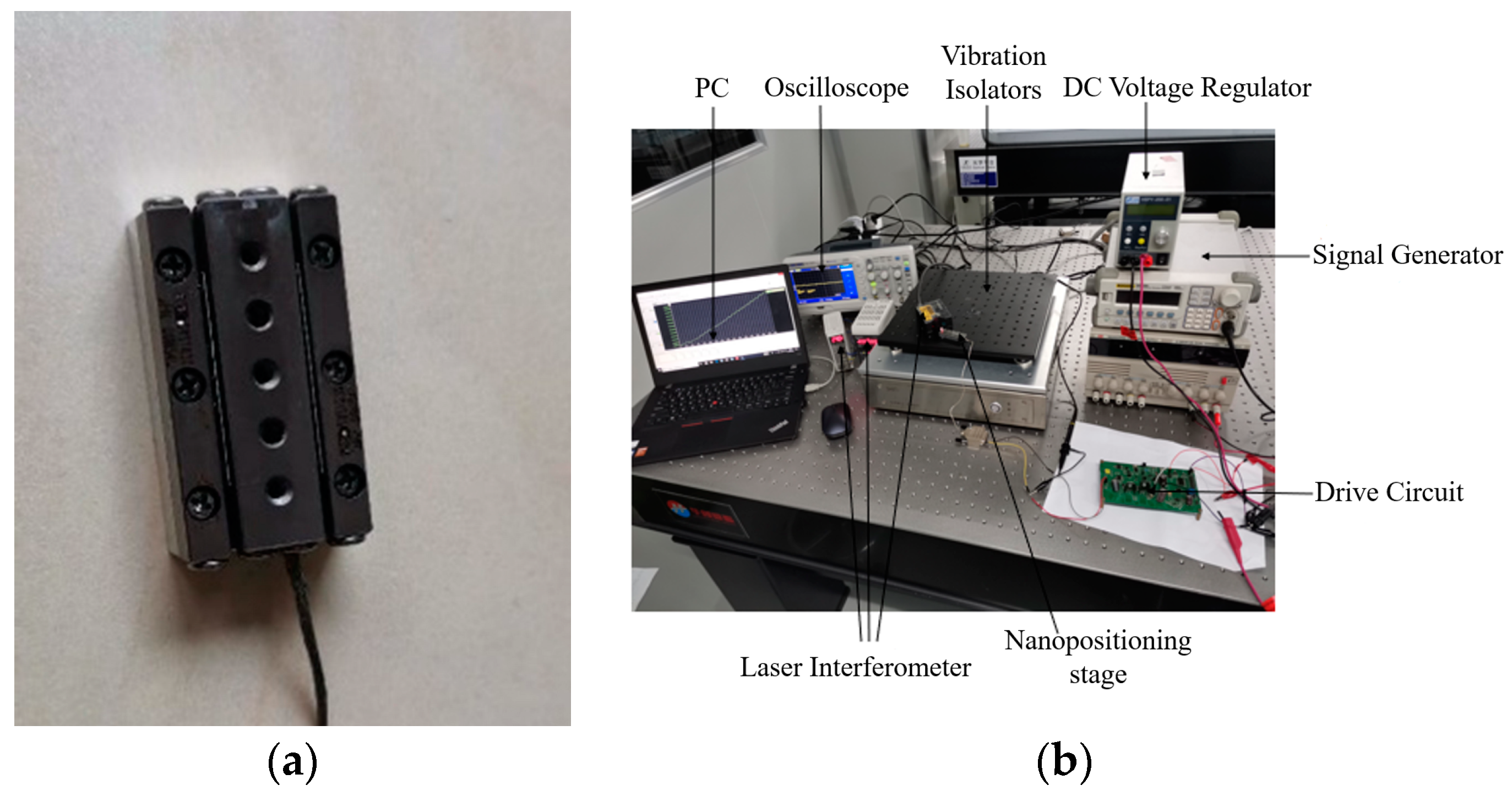
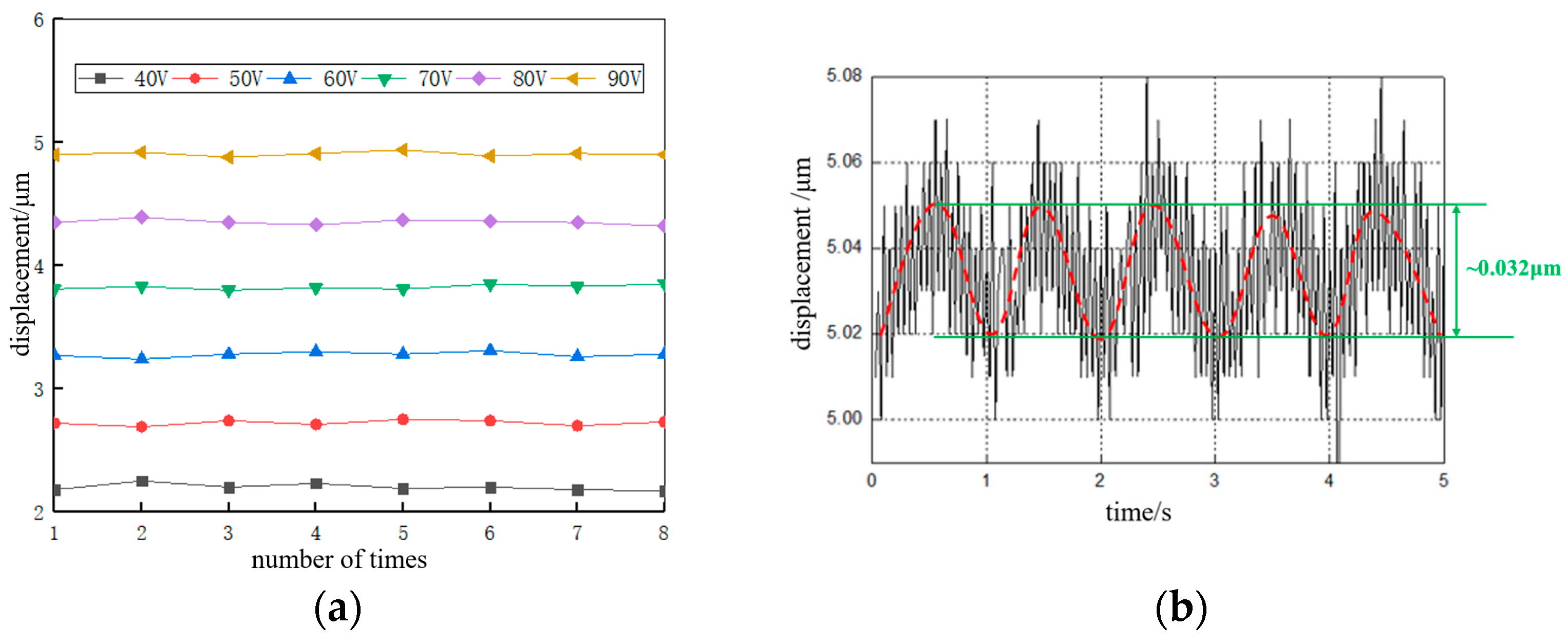
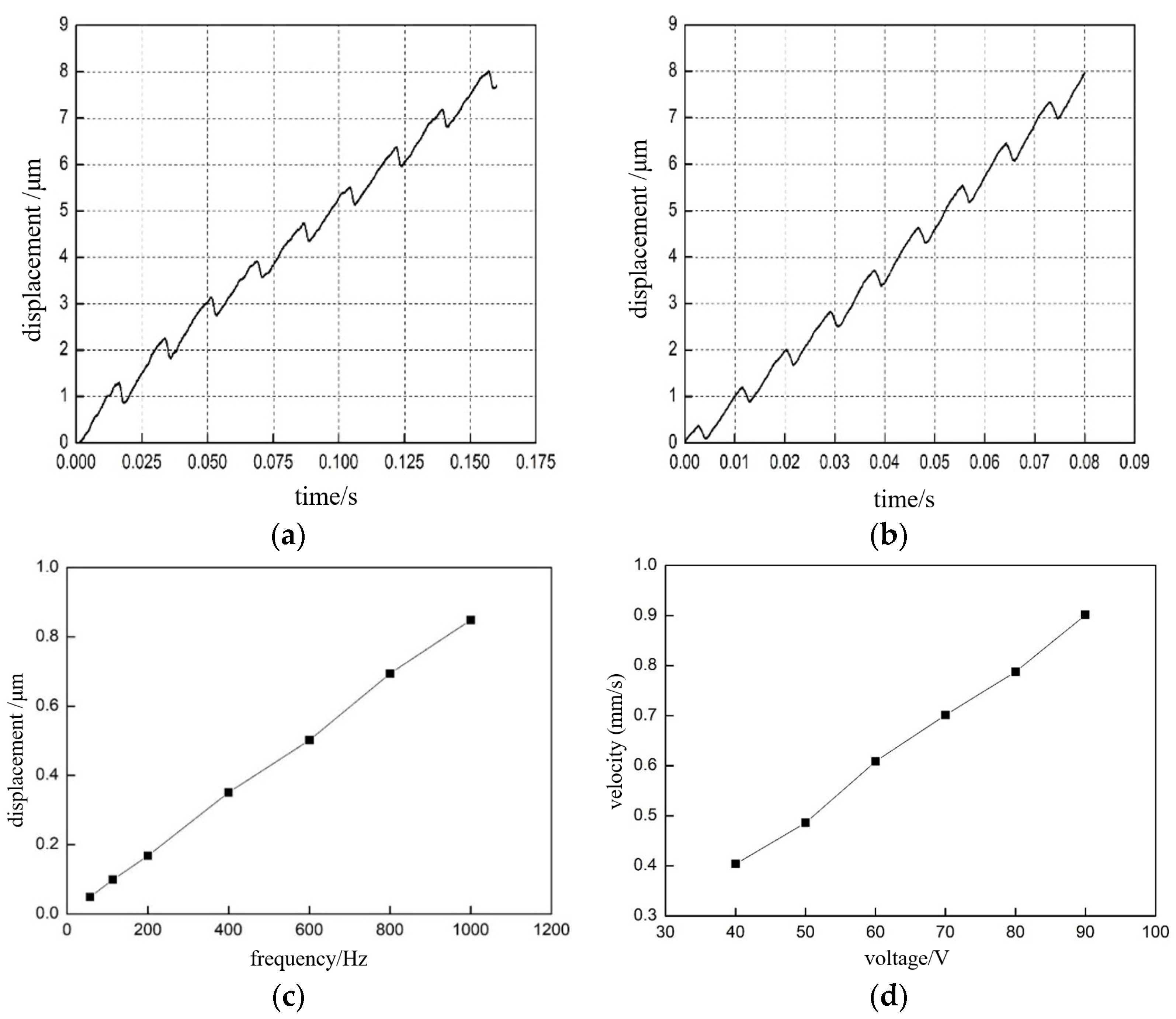
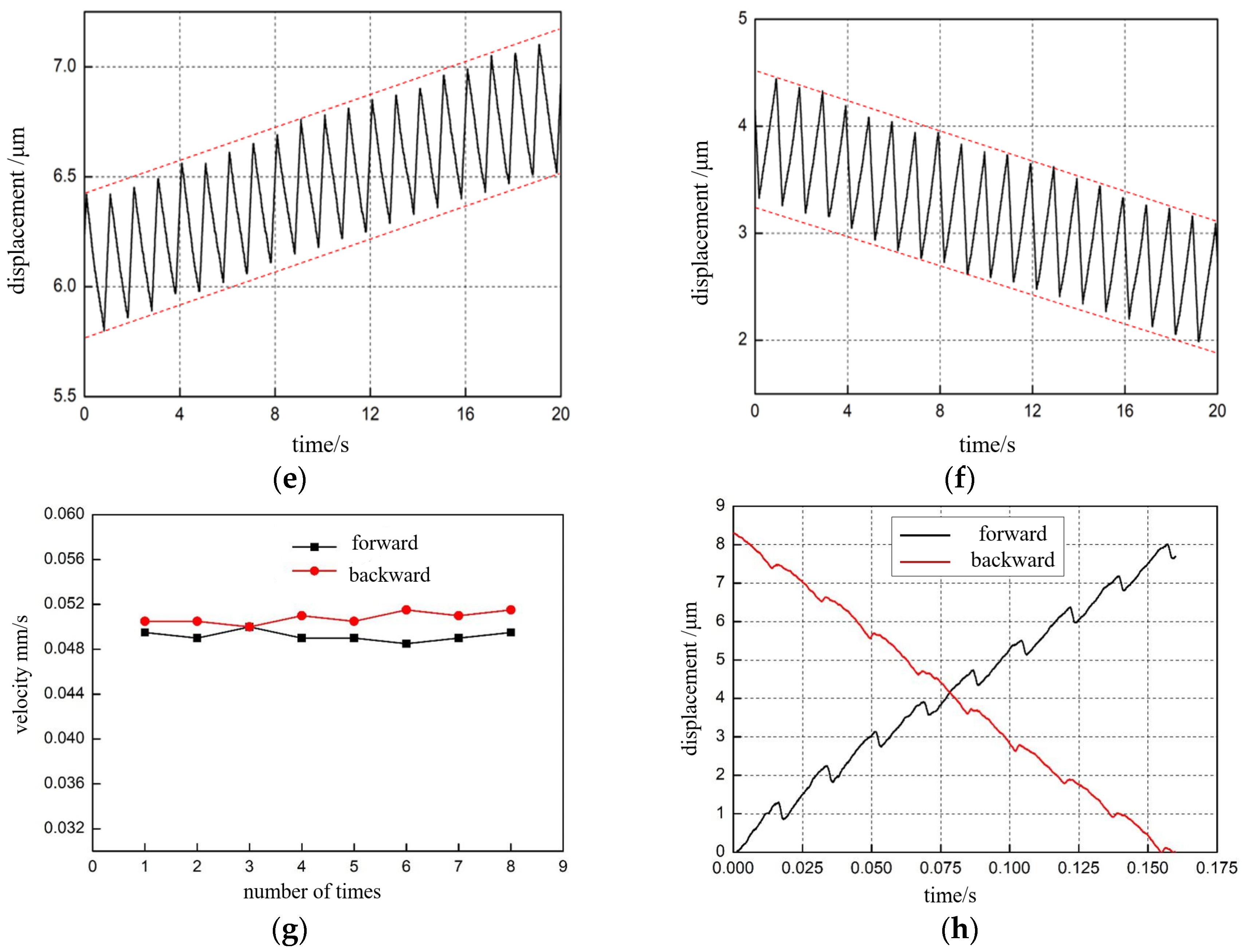
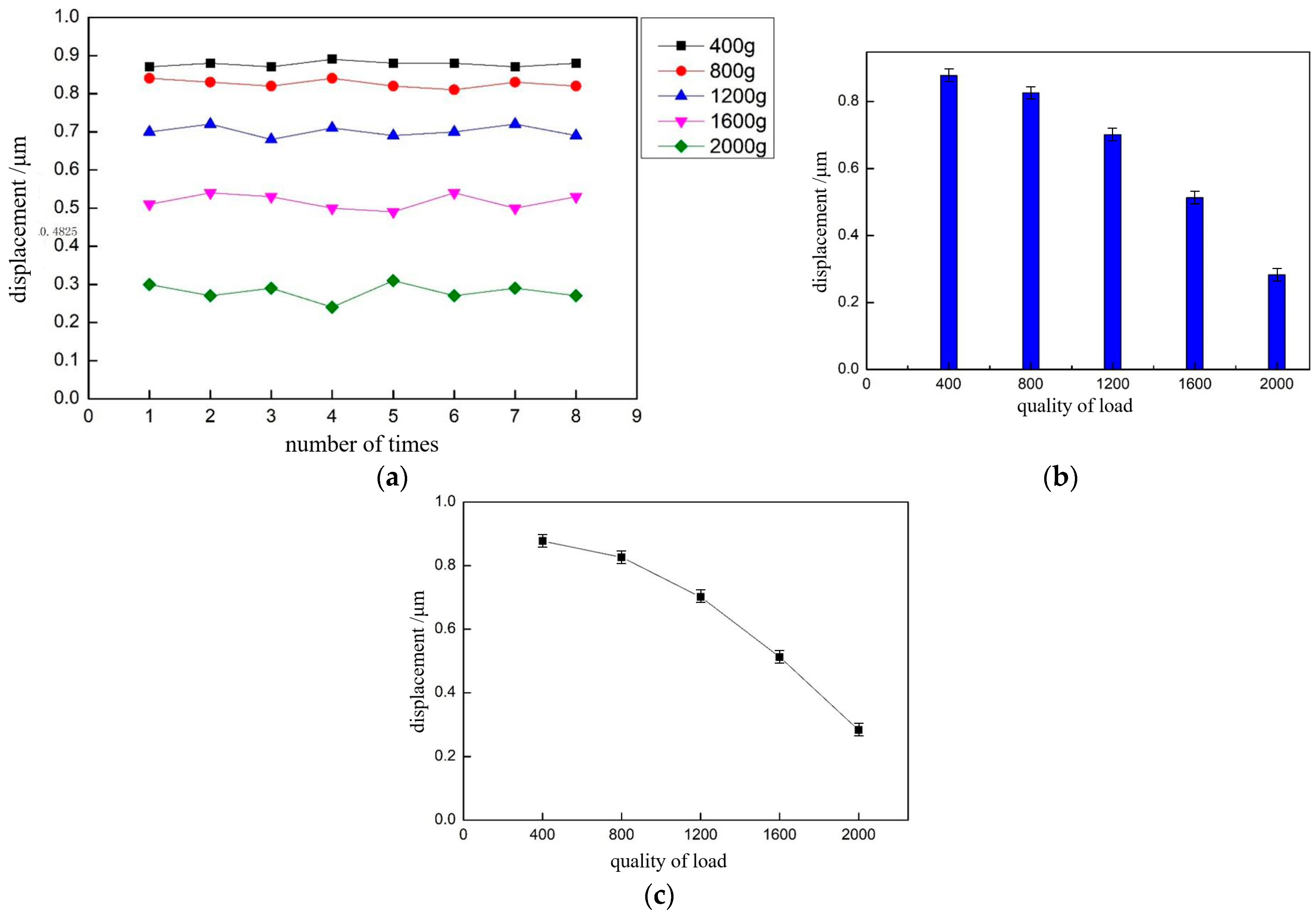
4. Experimental Results
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, B.; Dai, W.; Tao, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X. Excimer Laser-Deposited Na2/3Ni1/4Mn3/4O2 Film Cathode for Stable Sodium-Ion Battery. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumus, E.; Bingol, H.; Zor, E. Nanomaterials-Enriched Sensors for Detection of Chiral Pharmaceuticals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 221, 115031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, F.; Avatefi, M.; Moghadam, N.B.; Asghari, S.; Ekrami, E.; Mahmoudifard, M. A review of graphene quantum dots and their potential biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 08853282221125311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Deng, H.; Wang, J.; Hong, R.; Hu, S.; Hou, H.; Dong, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; et al. Bioresorbable thin-film silicon diodes for the optoelectronic excitation and inhibition of neural activities. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Dai, C.; Sun, Y. Robotic micromanipulation: Fundamentals and applications. Annu. Rev. Contr. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2019, 2, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, D.K.; Shi, C.; Sun, Y. A Review of Nanomanipulation in Scanning Electron Microscopes; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 347–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otnes, G.; Borgström, M.T. Towards High Efficiency Nanowire Solar Cells. Nano Today 2017, 12, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.C.; Pan, J.H.; Lin, D.B.; Ma, J.; Liu, S.Y.; Chang, J.C.; Lin, J.C. EBIC Technique Study for Implant Doping Problem in Failure Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits (IPFA), Singapore, 15 September–15 October 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Crouzier, L.; Delvallée, A.; Ducourtieux, S.; Devoille, L.; Noircler, G.; Ulysse, C.; Taché, O.; Barruet, E.; Tromas, C.; Feltin, N. Development of a new hybrid approach combining AFM and SEM for the nanoparticle dimensional metrology. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Chen, B.K.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y. Robotic probing of nanostructures inside scanning electron microscopy. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2014, 30, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Experimental study on load characteristics of macro-micro dual-drive precision positioning mechanism. In Intelligent Robotics and Applications; Huang, Y., Wu, H., Liu, H., Yin, Z., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 464–471. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Sun, L. Design of a control system for a macro-micro dual-drive high acceleration high precision positioning stage for IC packaging. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2009, 52, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Tian, X.; Zhang, D.; Liu, X. Design of a piezo-driven inchworm flexure stage for precision positioning. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2016, 50, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Chu, X.; Yuan, S.; Zhong, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, S. Development of an ultrasonic linear motor with ultra-positioning capability and four driving feet. Ultrasonics 2016, 72, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, F.; Zhu, J.; Pang, M.; Ru, C. Long-stroke nanopositioning stage driven by piezoelectric motor. J. Sens. 2014, 2014, 926314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Jin, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, L. Double closed-loop control of a trans-scale precision positioning stage based on the inertial stick–slip driving. Sens. Actuators A 2019, 297, 111547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, J.; Salarieh, H.; Vossoughi, G. Study of a piezo-electric actuated vibratory micro-robot in stick-slip mode and investigating the design parameters. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 1927–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Sangchap, M.; Tahmasebipour, M.; Tahmasebipour, Y. A linear inchworm piezomotor with a new configuration: Design considerations, fabrication and characterization. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2022, 46, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Fan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Hong, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, D. Design and experimental research of a novel stick-slip type piezoelectric actuator. Micromachines 2017, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Quan, Q.; Tian, X. Optimization and analysis of a u-shaped linear piezoelectric ultrasonic motor using longitudinal transducers. Sensors 2018, 18, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, D.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cai, H. Design and simulation of a macro-micro dual-drive high acceleration precision XY-stage for IC bonding technology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Packaging Technology, Shenzhen, China, 30 August–2 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Kaneko, J.; Azuma, T.; Ito, S.; Gao, W.; Lu, T.-F. Design and construction of the motion mechanism of an XY micro-stage for precision positioning. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 201, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Huo, Z.; Wang, F.; Liang, C.; Shi, B.; Zhang, D. A novel friction-actuated 2-DOF high precision positioning stage with hybrid decoupling structure. Mech. Mach. Theory 2022, 167, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.S.; Werner, C.; Slipets, R.; Larsen, P.E.; Hwang, I.-S.; Chang, T.-J.; Danzebrink, H.U.; Huang, K.-Y.; Hwu, E.-T. Low-cost, open-source XYZ nanopositioner for high-precision analytical applications. HardwareX 2022, 11, e00317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; He, M.; Li, H.; Lu, X.; Zhao, H.; Gao, H. A Novel Trapezoid-Type Stick–Slip Piezoelectric Linear Actuator Using Right Circular Flexure Hinge Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 5545–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, H.; Zhao, H. A Piezoelectric-Driven Linear Actuator by Means of Coupling Motion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 2458–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Ning, P.; Gao, Q.; Yu, Y.; Lu, X.; Yang, S.; Cheng, T. A flexure hinged piezoelectric stick–slip actuator with high velocity and linearity for long-stroke nano-positioning. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 075017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotondrabe, M.; Haddab, Y.; Lutz, P. Development, modeling, and control of a micro-/nanopositioning 2-dof stick–slip device. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2009, 14, 733–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.attocube.com/en/products/nanopositioners/low-temperature-nanopositioners/anpx101reslt-linear-x-nanopositioner (accessed on 20 October 2022).



| Type | Dimension | Nominal Displacement | Maximum Output Force | Stiffness | Static Capacity | Resonant Frequency (kHz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mm3) | (μm) | (N) | (N/μm) | (nF) | ||
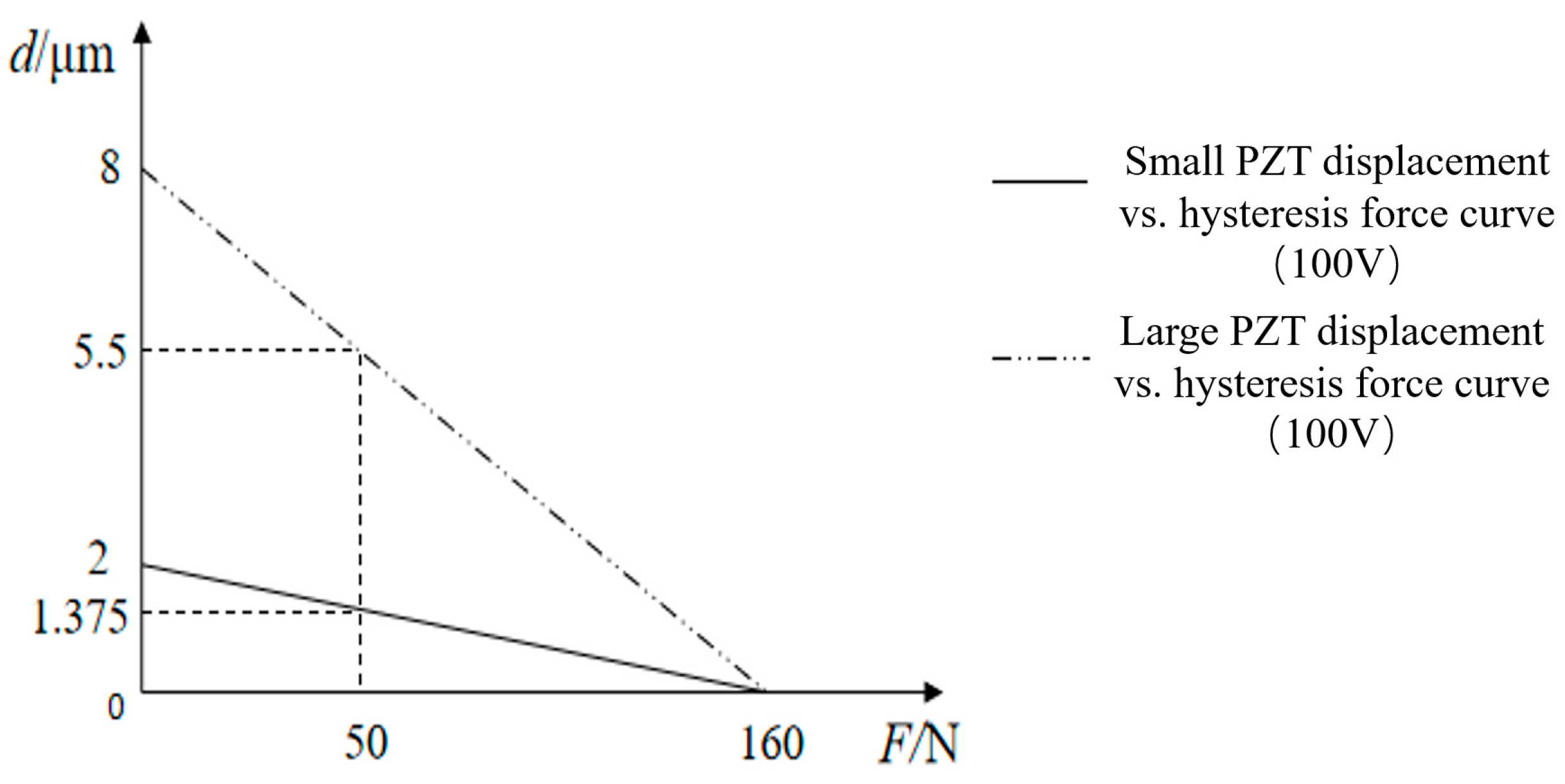
| Large PZT | 2 × 2 × 8 | 8 | 160 | 20 | 88 | 115 |
| Small PZT | 2 × 2 × 2 | 2 | 160 | 80 | 22 | 115 |
| Load Quality & Serial Number | 400 g (μm) | 800 g (μm) | 1200 g (μm) | 1600 g (μm) | 2000 g (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.70 | 0.51 | 0.27 |
| 2 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.54 | 0.29 |
| 3 | 0.87 | 0.82 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.24 |
| 4 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.50 | 0.31 |
| 5 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.49 | 0.27 |
| 6 | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.70 | 0.54 | 0.29 |
| 7 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.72 | 0.50 | 0.27 |
| 8 | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.69 | 0.53 | 0.28 |
| Average value | 0.8775 | 0.8263 | 0.7013 | 0.5175 | 0.28 |
| Error | 0.0070 | 0.0106 | 0.0146 | 0.0198 | 0.0378 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Meng, S.; Wang, Y.; Pang, M.; Hu, Z.; Ru, C. A Novel Monopolar Cross-Scale Nanopositioning Stage Based on Dual Piezoelectric Stick-Slip Driving Principle. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13112008
Zhu J, Meng S, Wang Y, Pang M, Hu Z, Ru C. A Novel Monopolar Cross-Scale Nanopositioning Stage Based on Dual Piezoelectric Stick-Slip Driving Principle. Micromachines. 2022; 13(11):2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13112008
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Junhui, Siyuan Meng, Yong Wang, Ming Pang, Zhiping Hu, and Changhai Ru. 2022. "A Novel Monopolar Cross-Scale Nanopositioning Stage Based on Dual Piezoelectric Stick-Slip Driving Principle" Micromachines 13, no. 11: 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13112008
APA StyleZhu, J., Meng, S., Wang, Y., Pang, M., Hu, Z., & Ru, C. (2022). A Novel Monopolar Cross-Scale Nanopositioning Stage Based on Dual Piezoelectric Stick-Slip Driving Principle. Micromachines, 13(11), 2008. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13112008






