Manufacturing of Porous Glass by Femtosecond Laser Welding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Manufacturing Processes
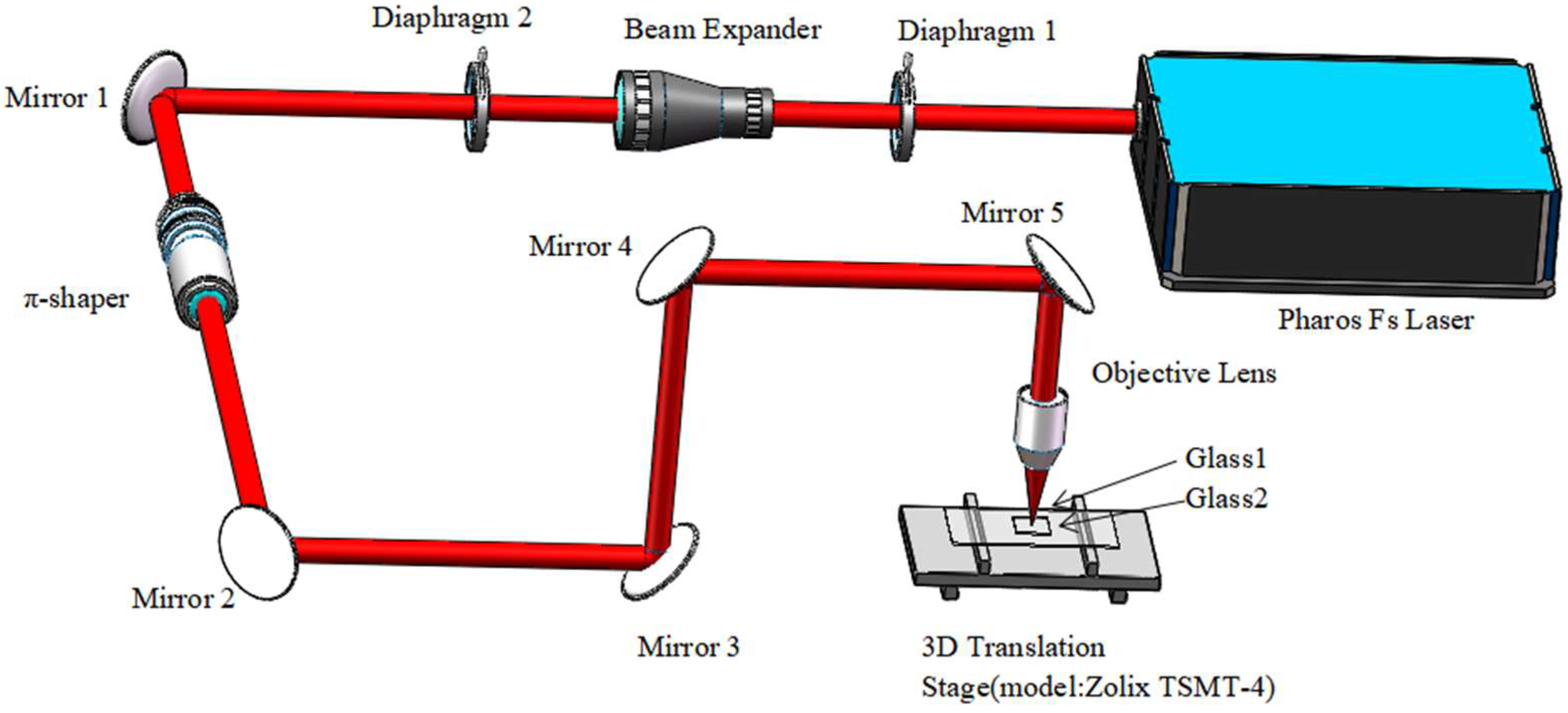
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Manufacturing Processes
3. Mechanism
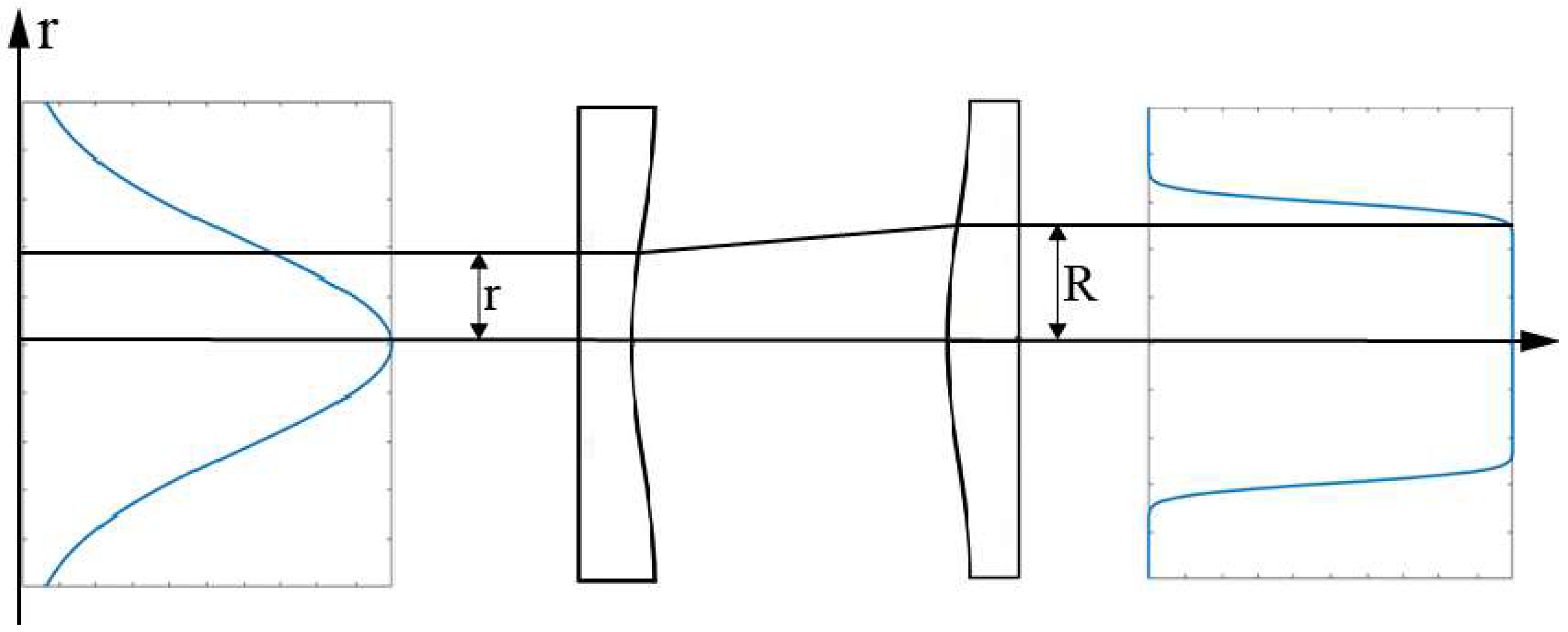
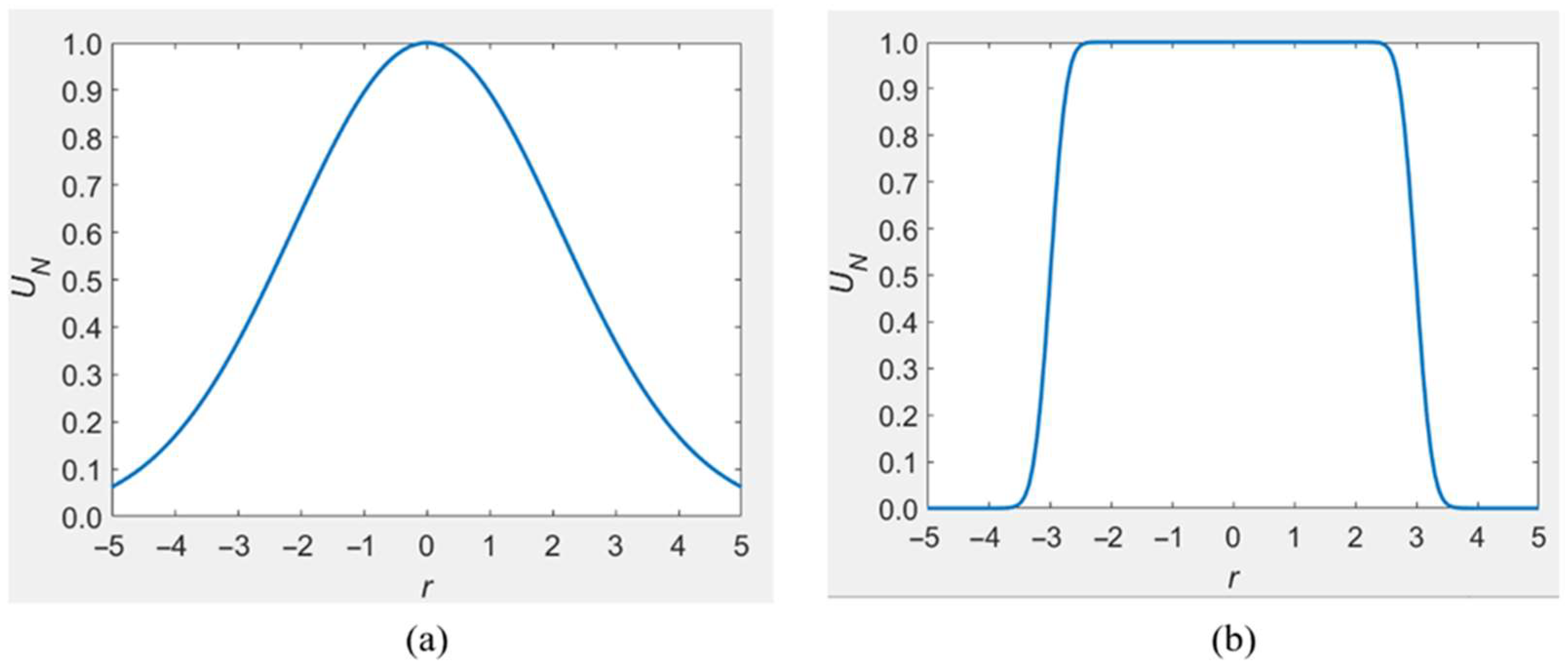
3.1. Comparison of a Gaussian Beam and a Flattened Gaussian Beam
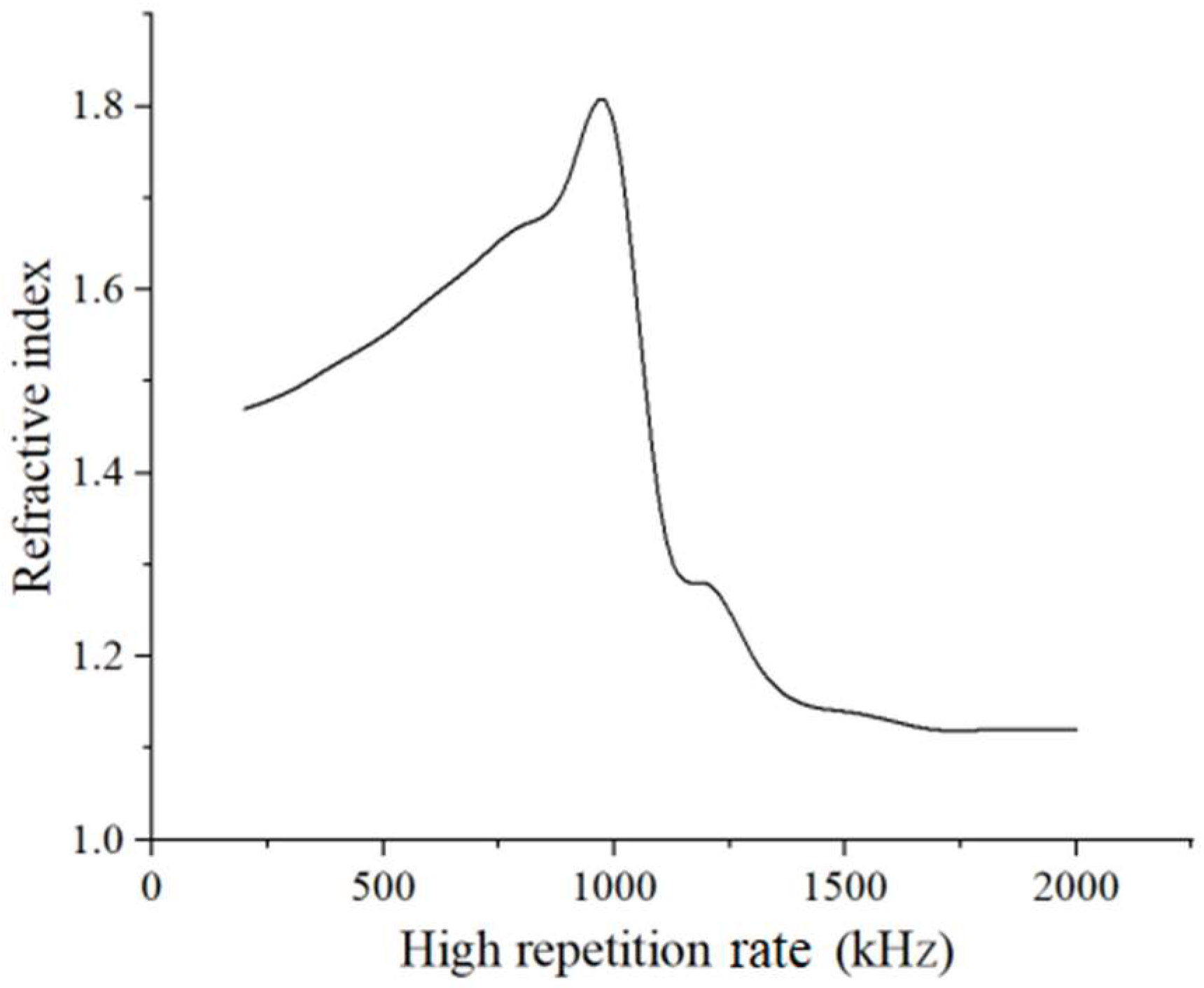
3.2. Formation of Multiple Refractive Indices
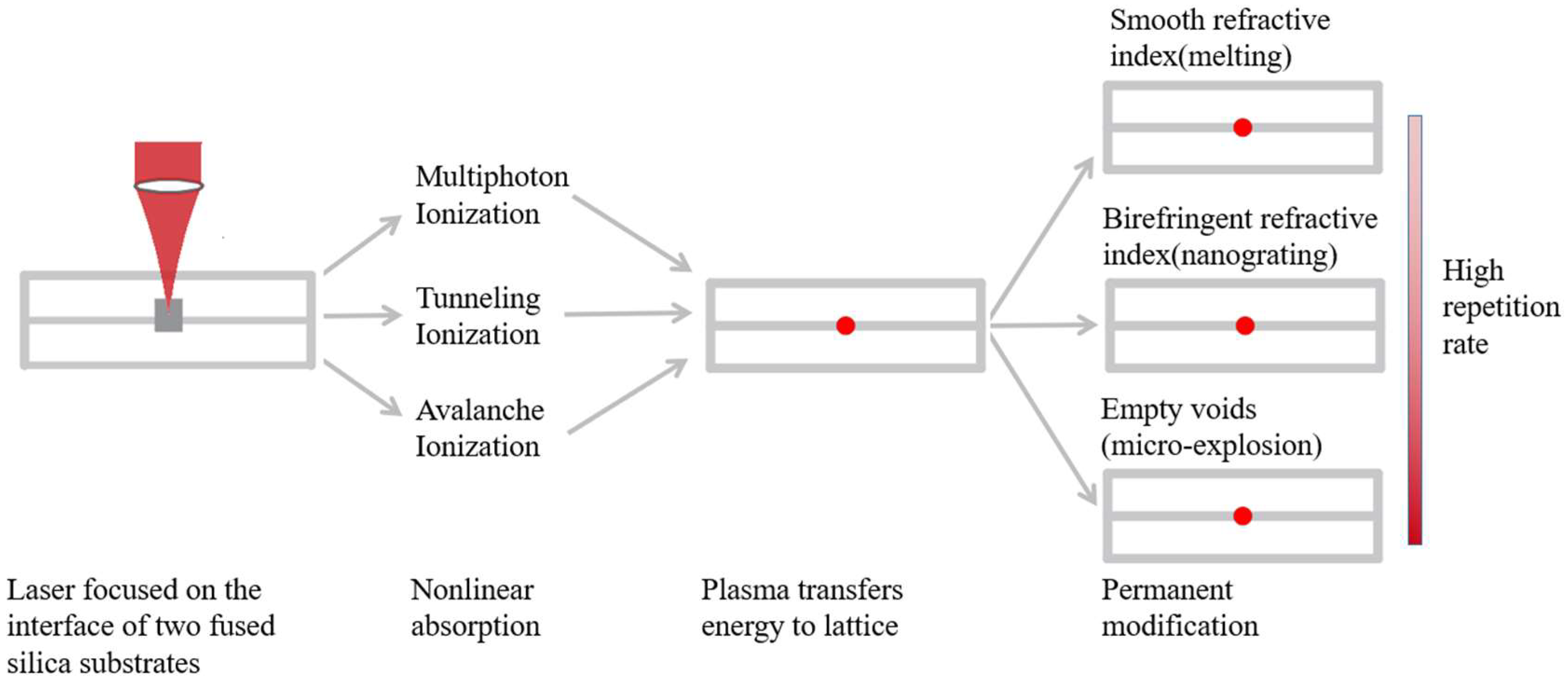
3.3. Three Modification Physics
4. Results and Discussion
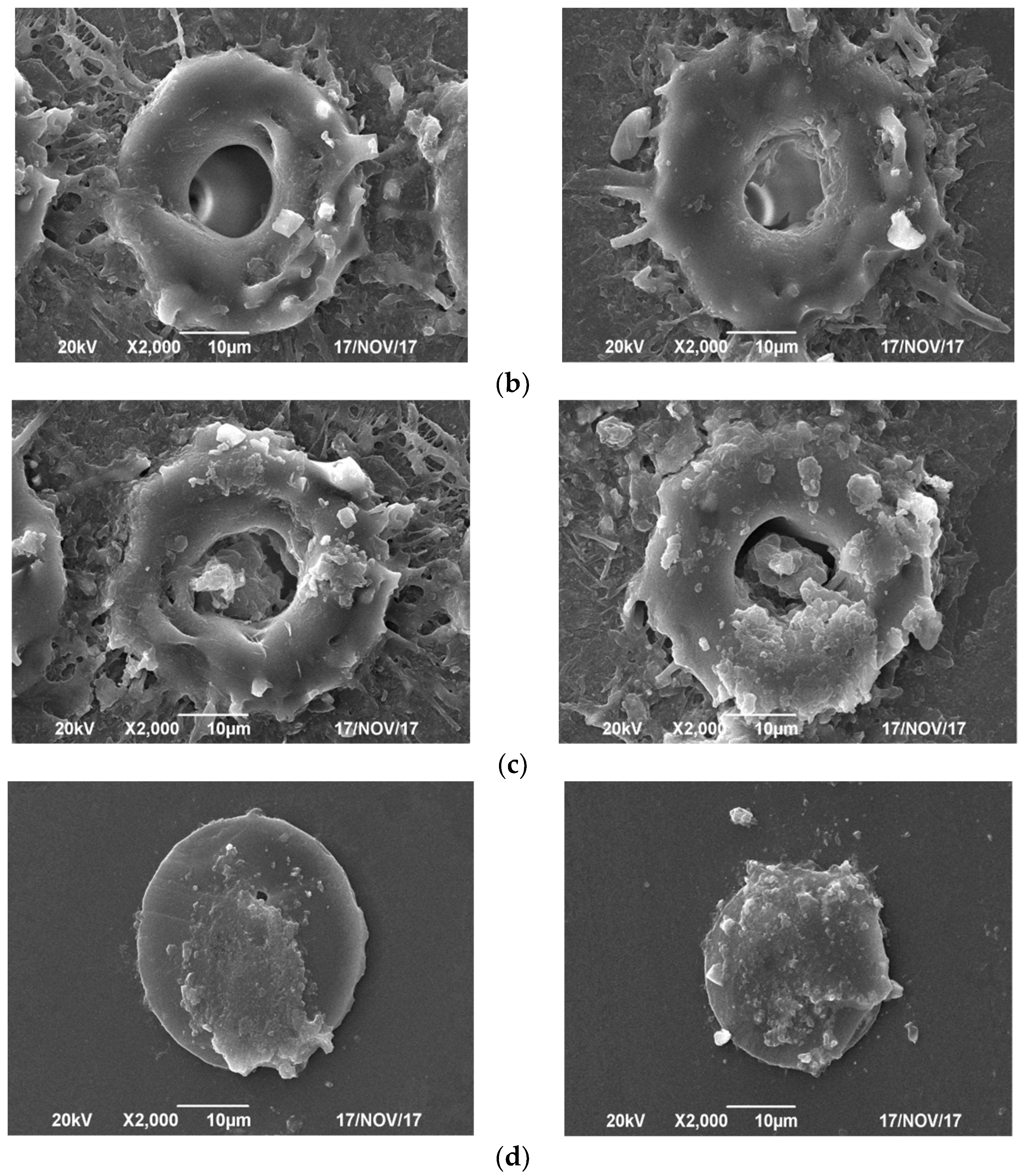
4.1. Results and Discussion of the Welding Spot Structure
4.2. Corresponding Functions of Porous Glass
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janowski, F.; Enke, D. Porous Glasses. In Handbook of Porous Solids; Wiley Online Library, 2002; pp. 1432–1542. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9783527618286.ch22 (accessed on 15 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Hood, H.P.; Nordberg, M.E. Method of Treating Borosilicate Glasses; Corning Inc.: Corning, NY, USA, 1942. [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovich, E. Preparation of glass by sintering. J. Mater. Sci. Rev. 1985, 20, 4259–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, M.D.; Tseng, T.-Y. Preparation of SiO2 Glass from Model Powder Compacts: II, Sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1984, 67, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighzadeh, A.; Ghoranneviss, M.; Elahi, A.S. Application of partial sintering of waste glasses for preparation of porous glass bodies. J. Porous Mater. 2014, 21, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazawa, T.; Tanaka, H.; Eguchi, K. Preparation of porous glass hollow fibre from glass based on SiO2-B2O3-RO-ZrO2 (R = Ca, Zn) system. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1994, 13, 494–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubu, T.; Yamane, M. Preparation of porous glass-ceramics of the TiO2-SiO2 system. J. Mater. Sci. 1985, 20, 4309–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, J.J.; Allersma, T. Thermally Stable and Crush Resistant Microporous Glass Catalyst Supports and Methods of Making; PPG Industries Inc.: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.M.M.; Vasconcelos, W.L. Properties of porous silica glasses prepared via sol–gel process. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2000, 273, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Oliver, C.J.R.; James, P.F.; Rawson, H. Silica and silica-titania glasses prepared by the sol-gel process. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1982, 48, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awschalom, D.; Warnock, J. Supercooled liquids and solids in porous glass. Phys. Rev. B 1987, 35, 6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Eaton, S.M.; Li, J.; Nejadmalayeri, A.H.; Herman, P.R. Type II high-strength Bragg grating waveguides photowritten with ultrashort laser pulses. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 4182–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xie, X.; Zhao, X.; Ma, L.; Lei, L.; Qiu, J.; Nie, Z. Polarization-dependent microstructural evolution induced by a femtosecond laser in an aluminosilicate glass. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 10265–10274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, P.; Yan, X.; Leng, N.; Xu, C.; Xiao, H.; Lu, Y. High-throughput rear-surface drilling of microchannels in glass based on electron dynamics control using femtosecond pulse trains. Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 2781–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerr, F.; Thienpont, H. Refractive laser beam shaping by means of a functional differential equation based design approach. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 8001–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, F. Flattened gaussian beams. Opt. Commun. 1994, 107, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homoelle, D.; Wielandy, S.; Gaeta, A.L.; Borrelli, N.F.; Smith, C. Infrared photosensitivity in silica glasses exposed to femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 1311–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Will, M.; Nolte, S.; Chichkov, B.N.; Tünnermann, A. Optical properties of waveguides fabricated in fused silica by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 4360–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osellame, R.; Chiodo, N.; Valle, G.D.; Cerullo, G.; Ramponi, R.; Laporta, P.; Killi, A.; Morgner, U.; Svelto, O. Waveguide lasers in the C-band fabricated by laser inscription with a compact femtosecond oscillator. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2006, 12, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Watanabe, W.; Nolte, S.; Schaffer, C.B. Ultrafast Processes for Bulk Modification of Transparent Materials. MRS Bull. 2006, 31, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, M.-H.; Huang, S.-Z.; Chen, L.-H.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.-Y.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Su, B.-L. Applications of hierarchically structured porous materials from energy storage and conversion, catalysis, photocatalysis, adsorption, separation, and sensing to biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3479–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasu, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Sugimoto, W.; Murakami, Y. Effects of the surface area of carbon support on the characteristics of highly-dispersed Pt-Ru particles as catalysts for methanol oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 3861–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Iwaishi, S.-I.; Yanagimoto, Y.; Kai, T. Hydrogenation of 1-hexenes and 1-octenes over nickel catalyst supported on porous glass prepared from borosilicate glass. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 1997, 14, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zook, J.D. An overview of optical data storage technology. Proc. IEEE 1975, 63, 1207–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Miura, K.; Hirao, K. Three-dimensional optical memory using glasses as a recording medium through a multi-photon absorption process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 37, 2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, Y. Angle-independent structural coloured amorphous arrays. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 23299–23309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, A.; Chu, C.; Zhou, S.; Guo, J.; Chen, T.; Xu, G. Electric field induced structural color changes of SiO2@ TiO2 core–shell colloidal suspensions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 1990–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glezer, E.; Milosavljevic, M.; Huang, L.; Finlay, R.; Her, T.-H.; Callan, J.P.; Mazur, E. Three-dimensional optical storage inside transparent materials. Opt. Lett. 1996, 21, 2023–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, H.; Pan, J.; Zheng, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q. Manufacturing of Porous Glass by Femtosecond Laser Welding. Micromachines 2022, 13, 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050765
Tan H, Pan J, Zheng X, Fu X, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Huang Q. Manufacturing of Porous Glass by Femtosecond Laser Welding. Micromachines. 2022; 13(5):765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050765
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Hua, Jiahui Pan, Xiaojia Zheng, Xiaoquan Fu, Yuxun Zhang, Yanxing Liu, and Qiheng Huang. 2022. "Manufacturing of Porous Glass by Femtosecond Laser Welding" Micromachines 13, no. 5: 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050765
APA StyleTan, H., Pan, J., Zheng, X., Fu, X., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., & Huang, Q. (2022). Manufacturing of Porous Glass by Femtosecond Laser Welding. Micromachines, 13(5), 765. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13050765






