Evaluation of Physiological State of Pen Shell Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758) by a Non-Invasive Heart Rate Recording under Short-Term Hyposalinity Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection and Relocation
2.2. Heart Rate Analyses
2.2.1. Heart Rate Recording
2.2.2. Hyposalinity Test
2.2.3. Calculations of Trec and CV
2.3. Statistical Analyses
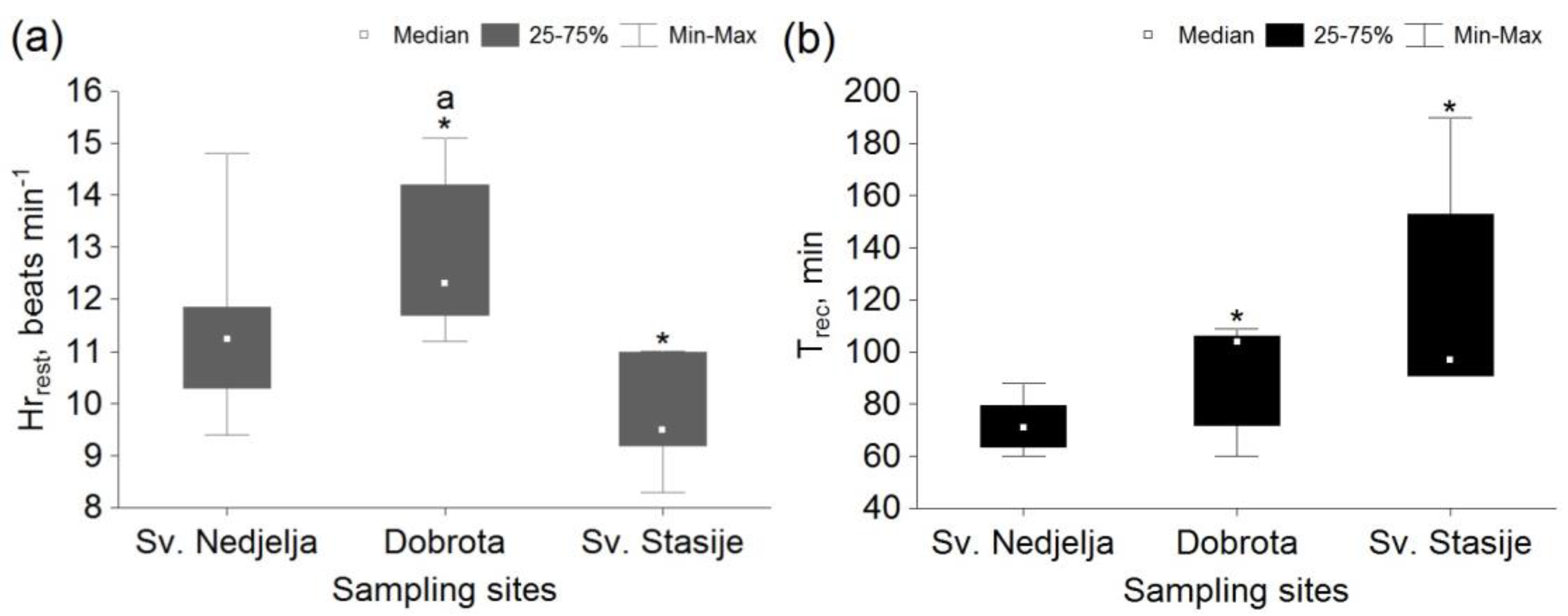
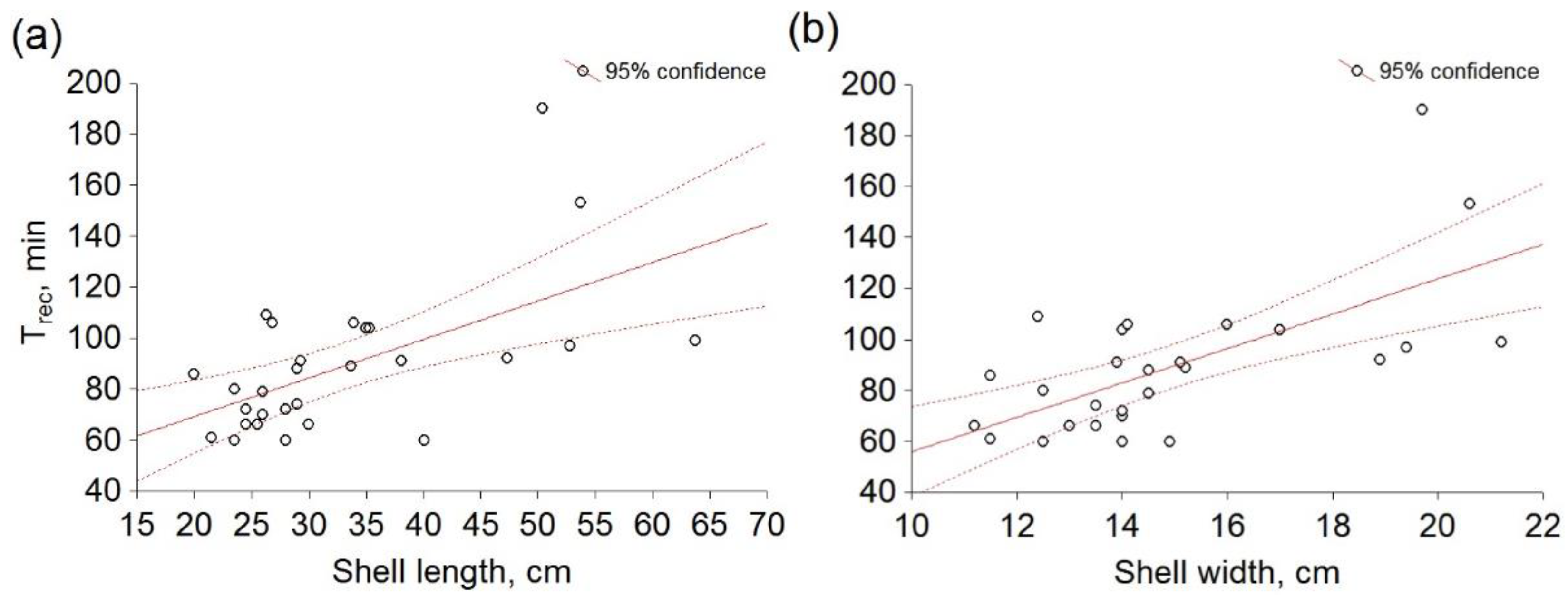
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attrill, M.J. A testable linear model for diversity trends in estuaries. J. Anim. Ecol. 2002, 71, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippart, C.J.; Anadón, R.; Danovaro, R.; Dippner, J.W.; Drinkwater, K.F.; Hawkins, S.J.; Oguzg, T.; O’Sullivanh, G.; Reid, P.C. Impacts of cli-mate change on European marine ecosystems: Observations, expectations and indicators. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2011, 400, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peteiro, L.G.; Woodin, S.; Wethey, D.; Costas-Costas, D.; Martínez-Casal, A.; Olabarria, C.; Vázquez, E. Responses to salinity stress in bivalves: Evidence of ontogenetic changes in energetic physiology on Cerastoderma edule. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmozaffar, S.; Jahromi, S.T.; Rameshi, H.; Sadeghi, A.; Bagheri, T.; Behzadi, S.; Gozari, M.; Zahedi, M.R.; Lazarjani, S.A. The role of salinity in physiological responses of bivalves. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 12, 1548–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, V.J.; Kharazova, A.D. Mechanisms of salinity adaptations in marine molluscs. In Interactions and Adaptation Strategies of Marine Organisms; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 115–126. [Google Scholar]
- Depledge, M.; Andersen, B. A computer-aided physiological monitoring system for continuous, long-term recording of cardiac activity in selected invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1990, 96, 473–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.; Berger, V.; Khalaman, V. The effect of salinity change on the heart rate of Mytilus edulis specimens from different ecological zones. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2005, 318, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.N.; Komendantov, A.J.; Smurov, A.O. Effect of salinity change on cardiac activity in Hiatella arctica and Modiolus modiolus, in the White Sea. Polar Biol. 2012, 35, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.; Fokina, N.; Ruokolainen, T. Changes of heart rate and lipid composition in Mytilus edulis and Modiolus modiolus caused by crude oil pollution and low salinity effects. J. Xenobiotics 2021, 11, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarà, G.; De Pirro, M. Heart beat rate adaptations to varying salinity of two intertidal Mediterranean bivalves: The invasive Brachidontes pharaonis and the native Mytilaster minimus. Ital. J. Zool. 2011, 78, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotov, V.P.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Strochilo, A.G. Study of contractile activity of the crayfish heart with the aid of a new non-invasive technique. J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2000, 36, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Lehtonen, K.K.; Kurakin, A.S. Experiences on ecological status assessment of the Gulf of Bothnia different sites based on cardiac activity biomarkers of caged mussels (Mytilus edulis). In Proceedings of the ICES Annual Science Conference, Gdańsk, Poland, 19–23 September 2011; Volume 19, p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Martinović, R.; Kurakin, A.S.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Gačić, Z.; Kljajić, Z. Preliminary results of sea water quality assessment based on physiological biomarkers in part of the Boka Kotorska Bay. Water Res. Manag. 2013, 3, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Turja, R.; Höher, N.; Snoeijs, P.; Baršienė, J.; Butrimavičienė, L.; Kuznetsova, T.; Kholodkevich, S.; Devier, M.-H.; Budzinski, H.; Lehtonen, K.K. A multibiomarker approach to the assessment of pollution impacts in two Baltic Sea coastal areas in Sweden using caged mussels (Mytilus trossulus). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kholodkevich, S.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Kurakin, A.S.; Lips, U.; Kolesova, N.; Lehtonen, K.K. Applicability of a bioelectronic cardiac monitoring system for the detection of biological effects of pollution in bioindicator species in the Gulf of Finland. J. Mar. Syst. 2017, 171, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodkevich, S.; Sharov, A.; Kuznetsova, T.; Kurakin, A.; Joksimović, D.; Nikolić, M. Physiological testing of Mytilus galloprovincialis for the environmental assessing of coastal marine areas: A case study in Boka Kotorska Bay (the Adriatic Sea). Chem. Ecol. 2019, 35, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Chuiko, G.M.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Gapeeva, M.V.; Lozhkina, R.A. Quality Assessment of Freshwater Ecosystems by the Functional State of Bivalved Mollusks. Water Resour. 2019, 46, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolic, M.; Kuznetsova, T.; Kholodkevich, S.; Gvozdenovic, S.; Mandic, M.; Joksimovic, D.; Teodorovic, I. Cardiac activity in the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) as a biomarker for assessing sea water quality in Boka Kotorska Bay, South Adriatic Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2019, 20, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavodnik, D.; Hrs-Brenko, M.; Legac, M. Synopsis on the fan shell Pinna nobilis L. in the eastern Adriatic Sea. In Les Espèces Marines à Protéger en Méditerranée; Boudouresque, C.F., Avon, M., Gravez, V., Eds.; GIS Posidonie: Marseille, France, 1991; pp. 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Butler, A.; Vicente, N.; De Gaulejac, B. Ecology of the pterioid bivalves Pinna bicolor Gmelin and Pinna nobilis L. Mar. Life 1993, 3, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, L.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; García-March, J.R.; Deudero, S.; Alvarez, E.; Vicente, N.; Duarte, C.M.; Hendriks, I.E. The pen shell, Pinna nobilis: A review of population status and recommended research priorities in the Mediterranean Sea. Adv. Mar. Biol. 2015, 71, 109–160. [Google Scholar]
- Catanese, G.; Grau, A.; Valencia, J.M.; Garcia-March, J.R.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Alvarez, E.; Deudero, S.; Darriba, S.; Carballal, M.J.; Villalba, A. Haplosporidium pinnae sp. nov., a haplosporidan parasite associated with mass mortalities of the fan mussel, Pinna nobilis, in the Western Mediterranean Sea. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2018, 157, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, F.; Aceto, S.; Pollaro, F.; Miccio, A.; Iaria, C.; Carrasco, N.; Prado, P.; De Vico, G. A mycobacterial disease is associated with the silent mass mortality of the pen shell Pinna nobilis along the Tyrrhenian coastline of Italy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Luis, M.; Álvarez, E.; Barrajón, A.; García-March, J.R.; Grau, A.; Hendriks, I.E.; Jiménez, S.; Kersting, D.; Moreno, D.; Pérez, M.; et al. S.O.S. Pinna nobilis: A Mass Mortality Event in Western Mediterranean Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsanevakis, S.; Tsirintanis, K.; Tsaparis, D.; Doukas, D.; Sini, M.; Athanassopoulou, F.; Κolygas, M.N.; Tontis, D.; Koutsoubas, D.; Bakopoulos, V. The cryptogenic parasite Haplosporidium pinnae invades the Aegean Sea and causes the collapse of Pinna nobilis populations. Aquat. Invasions 2019, 14, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersting, D.; Benabdi, M.; Čižmek, H.; Grau, A.; Jimenez, C.; Katsanevakis, S.; Öztürk, B.; Tuncer, S.; Tunesi, L.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; et al. Pinna nobilis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019; IUCN Red List: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanellas-Reboredo, M.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; Mourre, B.; Álvarez, E.; Deudero, S.; Amores, Á.; Addis, P.; Ballesteros, E.; Barrajón, A.; Coppa, S.; et al. Tracking a mass mortality outbreak of pen shell Pinna nobilis populations: A collaborative effort of scientists and citizens. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simide, R.; Couvray, S.; Vicente, N. Présence de Pinna nobilis (L. 1758) dans l’étang littoral de Diana (Corse). Marinelife-revue.fr 2019, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Foulquié, M.; de la Grandrive, R.D.; Dalias, N.; Vicente, N. Inventaire et état de santé des populations de Pinna nobilis (L. 1758) dans l’étang de Thau (Hérault, France). Marinelife-revue.fr 2020, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Peyran, C.; Morage, T.; Nebot-Colomer, E.; Iwankow, G.; Planes, S. Unexpected residual habitats raise hope for the survival of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis along the Occitan coast (Northwest Mediterranean Sea). Endanger. Species Res. 2022, 48, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellafiore, D.; Guarnieri, A.; Grilli, F.; Penna, P.; Bortoluzzi, G.; Giglio, F.; Pinardi, N. Study of the hydrodynamical processes in the Boka Kotorska Bay with a finite element model. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2011, 52, 298–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-March, J.R.; Sanchís Solsona, M.Á.; García-Carrascosa, A.M. Shell gaping behaviour of Pinna nobilis L.; 1758: Circadian and circalunar rhythms revealed by in situ monitoring. Mar. Biol. 2008, 153, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-March, J.R.; Jiménez, S.; Sanchis, M.A.; Monleon, S.; Lees, J.; Surge, D.; Tena-Medialdea, J. In situ biomonitoring shows seasonal patterns and environmentally mediated gaping activity in the bivalve, Pinna nobilis. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandis, S.; Garcia-March, J.; Sanchis, M.Á.; Monleón, S.; Vicente, N.; Tena, J. Temperature regulates the switch be-tween light-synchronized and unsynchronized activity patterns in the subtidal bivalve Pinna nobilis. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2018, 19, 366–375. [Google Scholar]
- Trigos, S.; García-March, J.R.; Vicente, N.; Tena, J.; Torres, J. Respiration rates of the fan mussel Pinna nobilis at different temperatures. J. Molluscan Stud. 2014, 81, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Giannetto, A.; Natalotto, A.; Parrino, V.; Mauceri, A.; Spanò, N. Pen shell Pinna nobilis L. (Mollusca: Bivalvia) from different peculiar environments: Adaptive mechanisms of osmoregulation and neurotransmission. Eur. Zool. J. 2019, 86, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čižmek, H.; Čolić, B.; Gračan, R.; Grau, A.; Catanese, G. An emergency situation for pen shells in the Mediterranean: The Adriatic Sea, one of the last Pinna nobilis shelters, is now affected by a mass mortality event. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 173, 107388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mačić, V.; Hernandis Caballero, S.; Vicente, N.; García March, J.R.; Tena Medialdea, J.; Martinović, R.; Joksimović, D.; Drakulović, D.; Petović, S. Exceptionally high density of Pinna nobilis L. 1758 in the Boka Kotorska Bay (Montenegro). In Proceedings of the 13rd European Conference on Scientific Diving, Funchal, Madeira, Portugal, 22–23 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Marrocco, V.; Zangaro, F.; Sicuro, A.; Pinna, M. A scaling down mapping of Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758) through the combination of scientific literature, NATURA 2000, grey literature and citizen science data. Nat. Conserv. 2019, 33, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-March, J.R.; Vicente, N. Protocol to Study and Monitor Pinna nobilis Populations within Marine Protected Areas; MEPA: La Valette, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Trigos-Santos, S.; Vicente, N. Transplantation protocol for the fan mussel Pinna nobilis in different types of substrate. Mar. Life 2016, 18, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda, D.; Esparza, A.; Ghamari, M.; Soltanpur, C.; Nazeran, H. A review on wearable photoplethysmography sensors and their potential future applications in health care. Int. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 4, 195. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, T.; Maeda, Y.; Sekine, M.; Yoshida, M. Wearable Photoplethysmographic Sensors—Past and Present. Electronics 2014, 3, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholodkevich, S.V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Kurakin, A.S.; Kornienko, E.L.; Fedotov, V.P. Real time biomonitoring of surface water toxicity level at water supply stations. Environ. Bioindic. 2008, 3, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, R.D.; Depledge, M.H. Physiological responses: Their measurement and use as environmental biomarkers in ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicology 1999, 8, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System), Version 7. 2004. Available online: www.statsoft.com (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Martinović, R.; Kolarević, S.; Kračun-Kolarević, M.; Kostić, J.; Marković, S.; Gačić, Z.; Kljajić, Z.; Vuković-Gačić, B. Genotoxic potential and heart rate disorders in the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis exposed to Superdispersant-25 and dispersed diesel oil. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 108, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, R.; Kolarević, S.; Kračun-Kolarević, M.; Kostić, J.; Jokanović, S.; Gačić, Z.; Joksimović, D.; Đurović, M.; Kljajić, Z.; Vuković-Gačić, B. Comparative assessment of cardiac activity and DNA damage in haemocytes of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis in exposure to tributyltin chloride. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 47, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarykhta, V.V.; Kuznetsova, T.V.; Sharov, A.N.; Kholodkevich, S.V.; Zhaohan, Z.; Yujie, F. Cardiac Activity in the Bivalve Mollusc Cristaria plicata from the River Songhua (China). J. Evol. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 55, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S. Ecophysiological aspects of cardiac activity in the subtropical mussel Perna viridis (L.) (Bivalvia: Mytilidae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2002, 267, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Bao, Z.; Wang, S. Development of Novel Cardiac Indices and Assessment of Factors Affecting Cardiac Activity in a Bivalve Mollusc Chlamys farreri. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braby, C.E.; Somero, G.N. Following the heart: Temperature and salinity effects on heart rate in native and invasive species of blue mussels (genus Mytilus). J. Exp. Biol. 2006, 209, 2554–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depledge, M.H.; Lundebye, A.K. Physiological monitoring of contaminant effects in individual rock crabs, Hemigrapsus edwardsi: The ecotoxicological significance of variability in response. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1996, 113, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksimović, D.; Perošević, A.; Castelli, A.; Pestorić, B.; Šuković, D.; Đurović, D. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface sediments of the Montenegrin coast: A 10-year review. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2598–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joksimović, D.; Stanković, S. Accumulation of trace metals in marine organisms of the southeastern Adriatic coast, Montenegro. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2012, 77, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, R.; Petović, S.; Joksimović, D.; Bunet, R.; Couvray, S.; Kirchhofer, D.; Simide, R.; Garcia-March, J.R.; Tena-Medialdea, J.; Castelli, A.; et al. Recruitment and Growth of the Fan Mussel Pinna nobilis in the Montenegrin Adriatic Coast and Comparison with the Western Mediterranean. In The Montenegrin Adriatic Coast; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-March, J.R.; Tena, J.; Henandis, S.; Vázquez-Luis, M.; López, D.; Téllez, C.; Prado, P.; Navas, J.I.; Bernal, J.; Catanese, G.; et al. Can we save a marine species affected by a highly infective, highly lethal, waterborne disease from extinction? Biol. Conserv. 2020, 243, 108498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhmet, I.; Nikolaev, K.; Levakin, I.; Ekimov, D. Influence of Himasthla elongata (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) metacercariae on heart rate in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 166, 107220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskin, H.H.; Ford, S.E. Haplosporidium nelsoni (MSX) on delaware bay seed oyster beds: A host-parasite relationship along a salinity gradient. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1982, 40, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
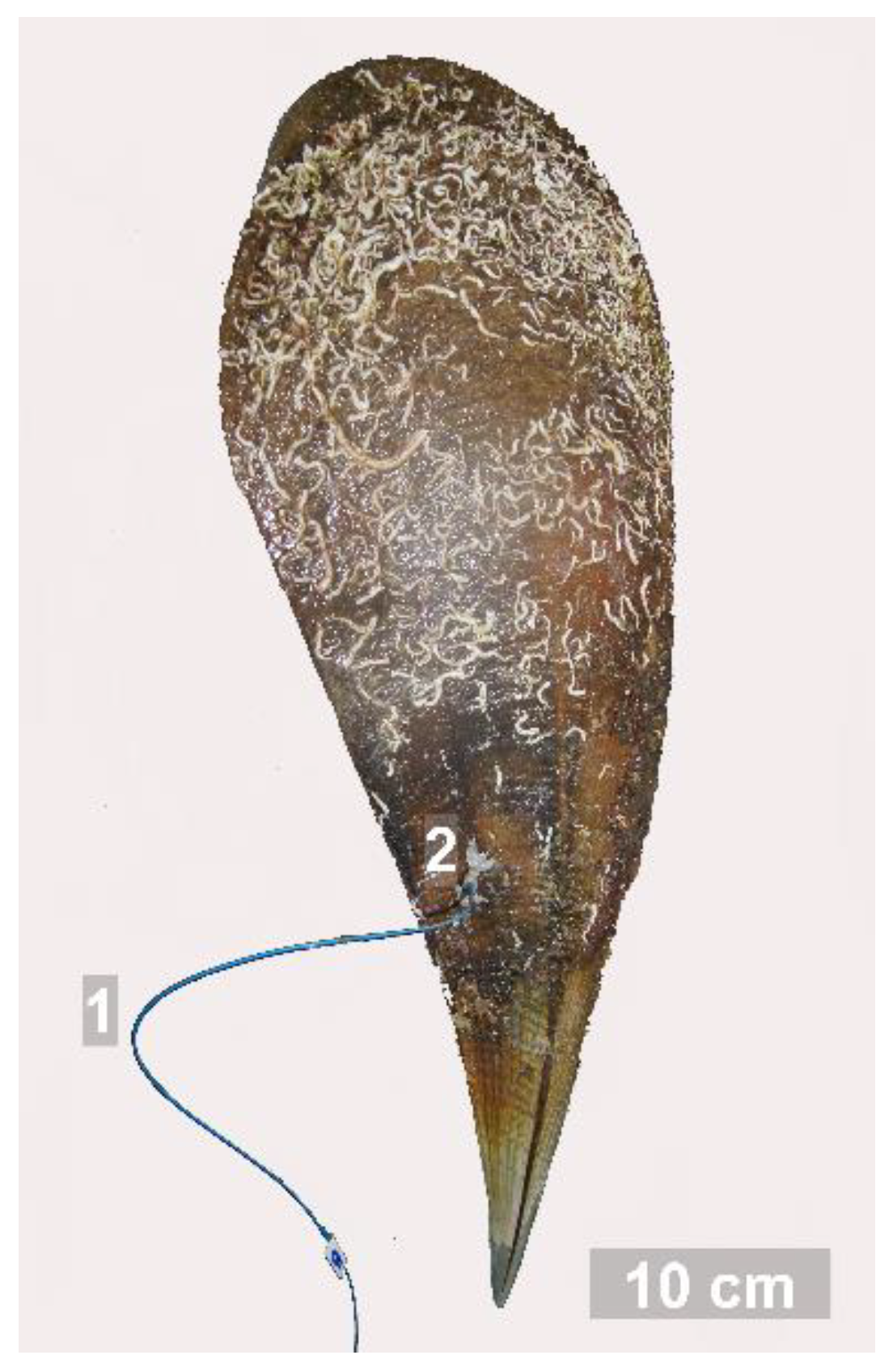




| Sampling Sites | Exp. No. | Temp. (°C) | Background Salinity (‰) | Salinity Reduction (‰) | Salinity Restoration (‰) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sv. Nedjelja | I | 19.4 | 36 | 19.2 | 36.3 |
| II | 20.3 | 34.8 | 18.3 | 35.6 | |
| Dobrota | I | 20.1 | 29.3 | 15 | 30 |
| II | 22.3 | 35.3 | 17.8 | 35 | |
| Sv. Stasije | I | 19.5 | 32.4 | 17.1 | 33.1 |
| II | 21.4 | 33.5 | 16.6 | 33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinović, R.; Joksimović, D.; García-March, J.R.; Vicente, N.; Gačić, Z. Evaluation of Physiological State of Pen Shell Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758) by a Non-Invasive Heart Rate Recording under Short-Term Hyposalinity Test. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091549
Martinović R, Joksimović D, García-March JR, Vicente N, Gačić Z. Evaluation of Physiological State of Pen Shell Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758) by a Non-Invasive Heart Rate Recording under Short-Term Hyposalinity Test. Micromachines. 2022; 13(9):1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091549
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinović, Rajko, Danijela Joksimović, José Rafael García-March, Nardo Vicente, and Zoran Gačić. 2022. "Evaluation of Physiological State of Pen Shell Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758) by a Non-Invasive Heart Rate Recording under Short-Term Hyposalinity Test" Micromachines 13, no. 9: 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091549
APA StyleMartinović, R., Joksimović, D., García-March, J. R., Vicente, N., & Gačić, Z. (2022). Evaluation of Physiological State of Pen Shell Pinna nobilis (Linnaeus, 1758) by a Non-Invasive Heart Rate Recording under Short-Term Hyposalinity Test. Micromachines, 13(9), 1549. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13091549






