Coexisting Firing Patterns in an Improved Memristive Hindmarsh–Rose Neuron Model with Multi-Frequency Alternating Current Injection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Description
3. AC-Induced Complex Dynamical Behaviors under Single Excitation
3.1. Coexisting Asymmetric Firings When Changes
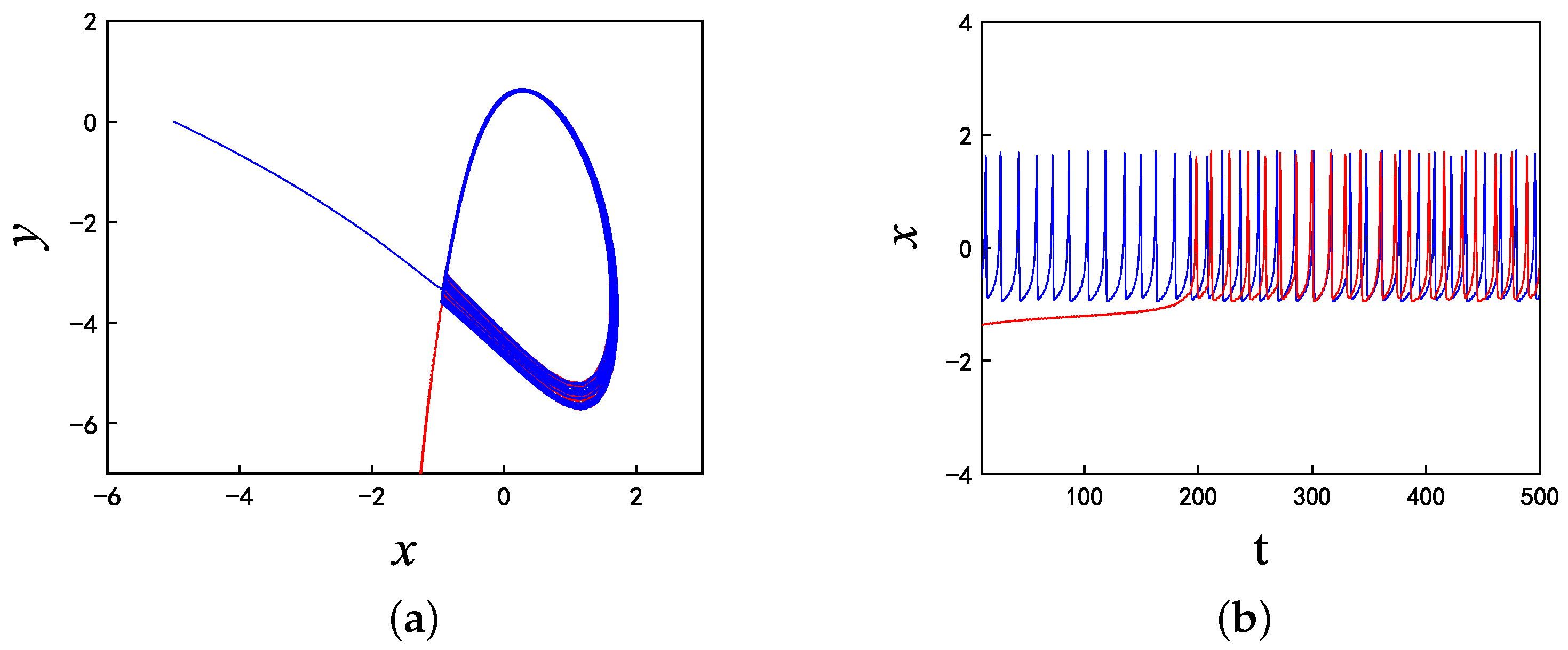
3.2. Coexisting Firing Patterns When Changes
3.3. Influence of Coupling Strength k on Dynamics
4. Different Firing Patterns Are Driven by High–Low-Frequency Current
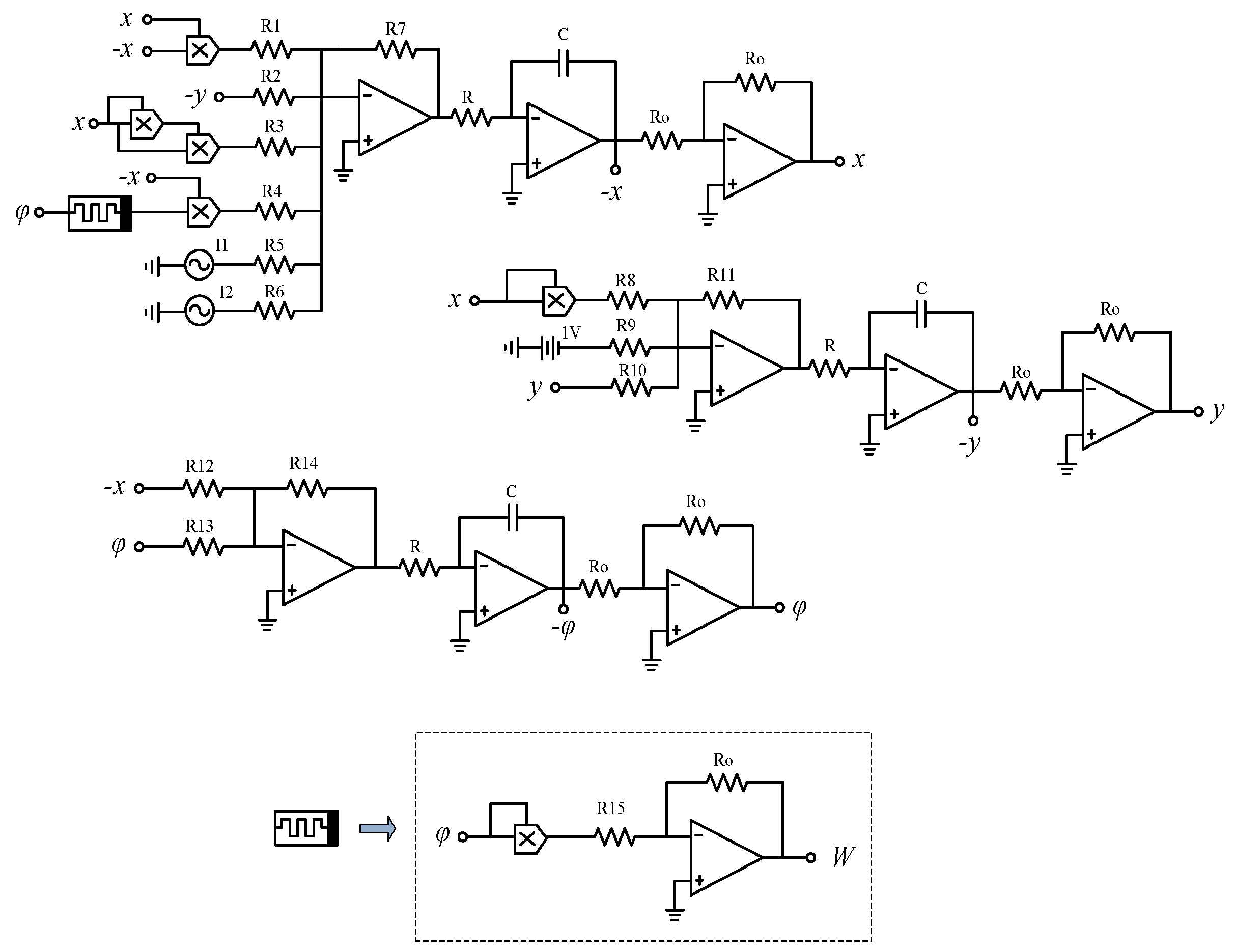
5. Circuit Implementation
- Variable-scale reduction transformation. Since the range of the attractor does not exceed the dynamic range of V, variable-scale reduction transformation of variety is not required.
- Time-scale transformation:
- Differential–integral conversion:
- Because the inverse addition proportional arithmetic unit is used in the circuit, the Equation (14) is normalized to:where the memductance function equivalent circuit is
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952, 117, 500–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzHugh, R. Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1961, 1, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.; Lecar, H. Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 1981, 35, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindmarsh, J.L.; Rose, R.M. A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 1982, 296, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopfield, J.J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-state neurons. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3088–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandi-Mehran, N.; Jafari, S.; Hashemi Golpayegani, S.M.R.; Nazarimehr, F.; Perc, M. Different synaptic connections evoke different firing patterns in neurons subject to an electromagnetic field. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 1809–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.J.; Luo, T.Q.; Lu, H.W.; Wang, Y. Bifurcation study of neuron firing activity of the modified Hindmarsh-Rose model. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Wang, C.; Ren, G.; Ma, J.; Song, X. Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 85, 1479–1490. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, S.; Bao, B.; Volos, C.; Nazarimehr, F.; Bao, H. Collective behavior of nonlinear dynamical oscillators. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top 2022, 231, 3957–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiei, M.; Jafari, S.; Parastesh, F.; Ozer, M.; Kapitaniak, T.; Perc, M. Time delayed chemical synapses and synchronization in multilayer neuronal networks with ephaptic inter-layer coupling. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2020, 84, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Vignesh, D.; Rondoni, L.; Banerjee, S. Chaos and multi-layer attractors in asymmetric neural networks coupled with discrete fractional memristor. Neural Netw. 2023, 167, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, K. A discrete memristive neural network and its application for character recognition. Neurocomputing 2023, 523, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prezioso, M.; Merrikh-Bayat, F.; Hoskins, B.D.; Adam, G.C.; Likharev, K.K.; Strukov, D.B. Training and operation of an integrated neuromorphic network based on metal-oxide memristors. Nature 2015, 521, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; An, M.; He, S.; Zhang, X.; Iu, H.H.C.; Li, Z. Two-dimensional memristive hyperchaotic maps with different coupling frames and its hardware implementation. Chaos 2023, 33, 073129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Wu, H. Memristor Initial-Offset Boosting in Memristive HR Neuron Model with Hidden Firing Patterns. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2020, 30, 2030029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Hu, A.; Liu, W.; Bao, B. Hidden Bursting Firings and Bifurcation Mechanisms in Memristive Neuron Model with Threshold Electromagnetic Induction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 31, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, M.; Ma, M. Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 1455–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Hong, Q.; Sun, Y. A Multi-Stable Memristor and its Application in a Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2020, 67, 3472–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Wang, Z. Modeling and dynamics of double Hindmarsh–Rose neuron with memristor-based magnetic coupling and time delay. Chin. Phys. B 2021, 30, 120516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Dong, E. A new locally active memristive synapse-coupled neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 104, 4459–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yao, W. Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 100, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, C. A simple locally active memristor and its application in HR neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 30, 053118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Iu, H.H.C.; Li, Z. Firing activities analysis of a novel small heterogeneous coupled network through a memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 15397–15415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Feudel, U. Control of multistability. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 540, 167–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Huang, D.; Lai, Y.C. Multistability, chaos, and random signal generation in semiconductor superlattices. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 062204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lin, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, C.; Deng, Q. Research Progress on Chaos, Memory and Neural Network Circuits Based on Memristor. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2020, 42, 795–810. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Xu, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhou, P. The Electrical Activity of Neurons Subject to Electromagnetic Induction and Gaussian White Noise. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2017, 27, 1750030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Hu, A.; Liu, W. Bipolar Pulse-Induced Coexisting Firing Patterns in Two-Dimensional Hindmarsh–Rose Neuron Model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2019, 29, 1950006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, G.; Tang, J.; Jin, W. Energy dependence on modes of electric activities of neuron driven by multi-channel signals. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 1967–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, W.; Yi, M.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Q.; Zhan, X.; Jia, Y. Vibrational resonance induced by transition of phase-locking modes in excitable systems. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 016209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Jia, Y. Effects of patch temperature on spontaneous action potential train due to channel fluctuations: Coherence resonance. BioSystems 2005, 81, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Jia, Y.; Liu, W.; Yang, L. Mixed Stimulus-Induced Mode Selection in Neural Activity Driven by High and Low Frequency Current under Electromagnetic Radiation. Complexity 2017, 2017, 7628537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, L. Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 91, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, K.; Subha, P.A. Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model with memristors. BioSystems 2019, 178, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
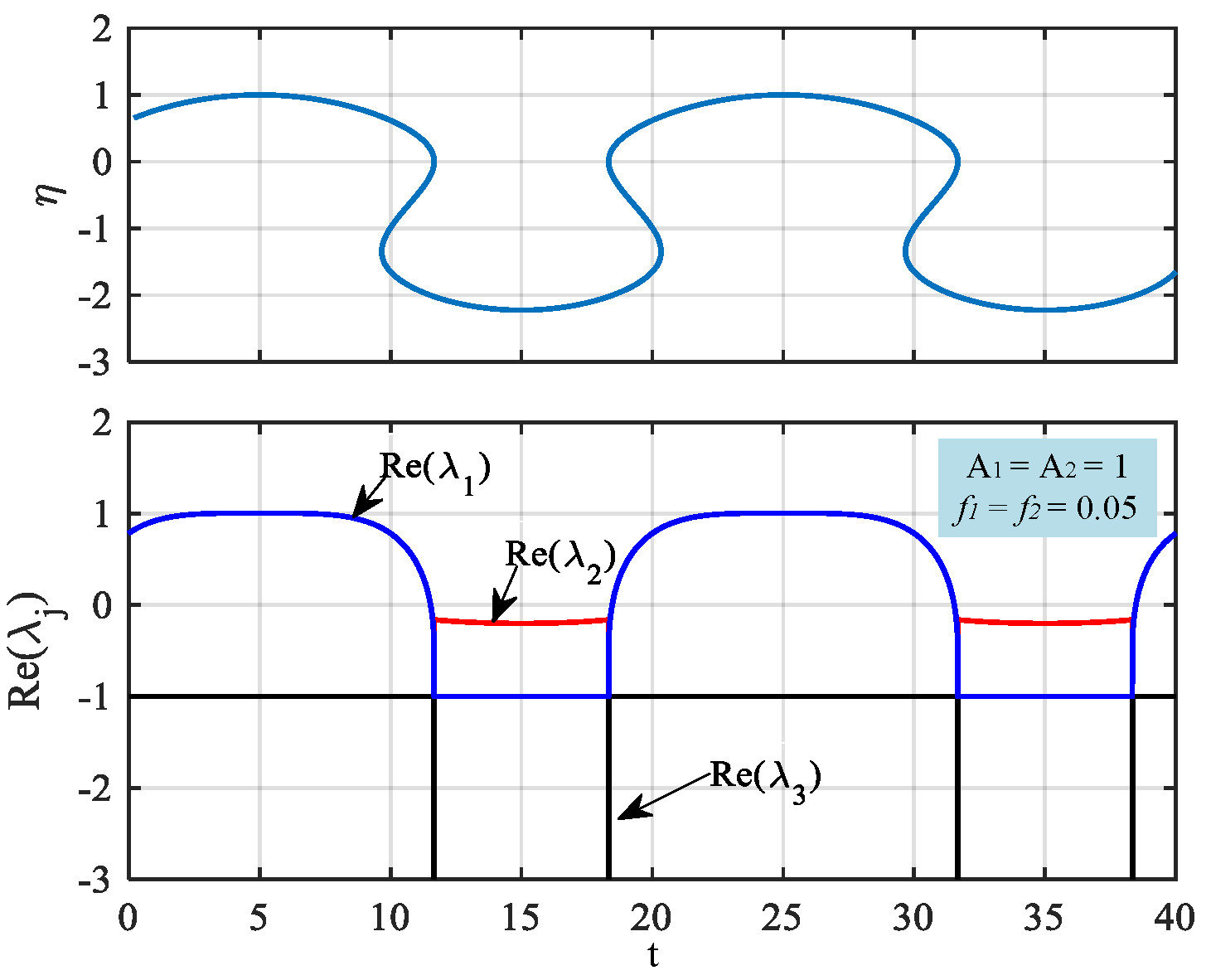
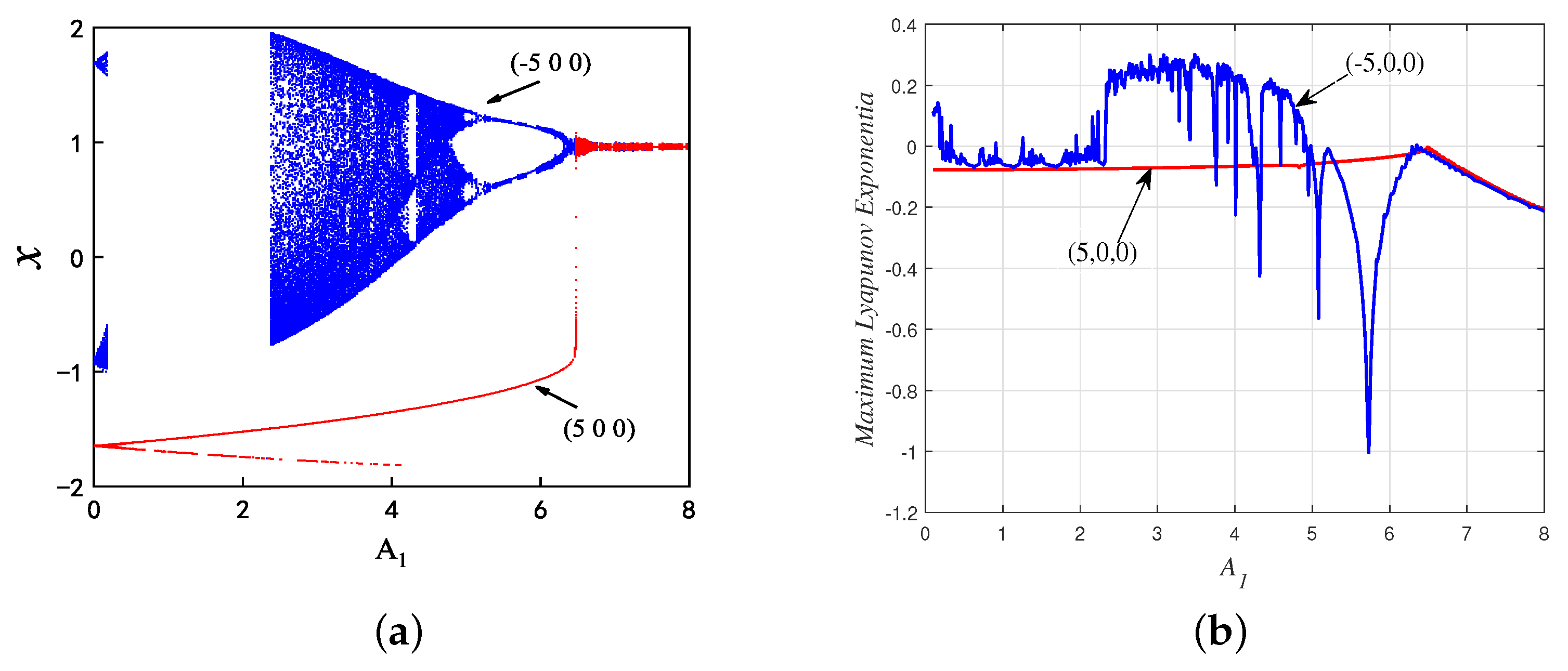


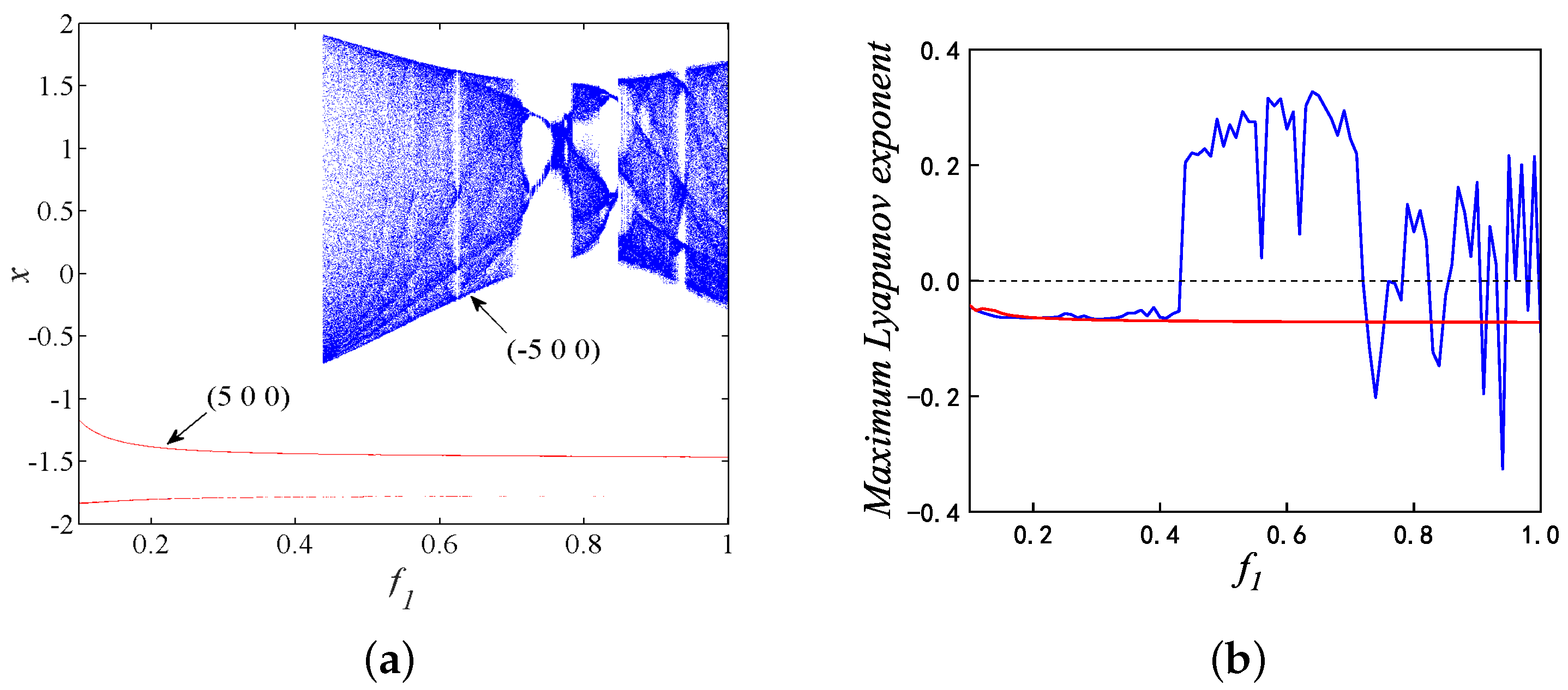
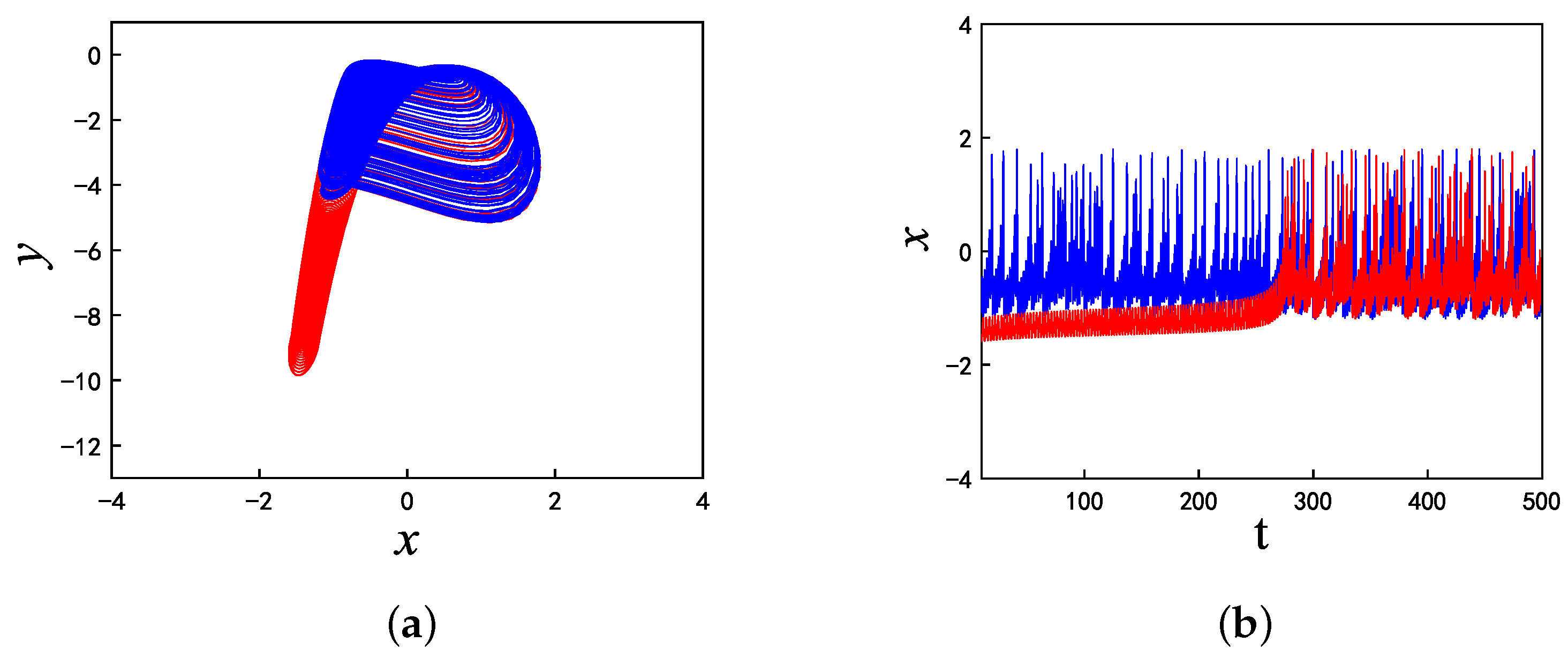


| t | Equilibrium | and | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1, −4, 1) | , | Unstable | |
| (−2.02, −19.402, −2.02) | , , | Stable | |
| 15 | (−2.22, −23.642, −2.22) | , , | Stable |
| LEs | Firing Patterns | |
|---|---|---|
| LE1 = −0.0536 LE2 = −1.0056 LE3 = −16.7675 | = 0.002 |  |
| LE1 = −0.1018 LE2 = −1.0062 LE3 = −17.9204 | = 0.02 |  |
| LE1 = −0.0129 LE2 = −1.0062 LE3 = −16.8427 | = 0.04 |  |
| LE1 = 0.0276 LE2 = −1.0065 LE3 = −14.0263 | = 0.07 | 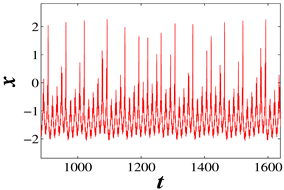 |
| Parameters | Significations | Value |
|---|---|---|
| R, | Resistance | 2 k |
| Resistance | 3 k | |
| , | Resistance | 10 k |
| Resistance | 30 k | |
| , , , , , , | Resistance | 100 k |
| , , , | Resistance | 300 k |
| C | Capacitor | 50 nF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Ding, J.; Deng, B.; He, S.; Iu, H.H.-C. Coexisting Firing Patterns in an Improved Memristive Hindmarsh–Rose Neuron Model with Multi-Frequency Alternating Current Injection. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122233
Wang M, Ding J, Deng B, He S, Iu HH-C. Coexisting Firing Patterns in an Improved Memristive Hindmarsh–Rose Neuron Model with Multi-Frequency Alternating Current Injection. Micromachines. 2023; 14(12):2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122233
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mengjiao, Jie Ding, Bingqing Deng, Shaobo He, and Herbert Ho-Ching Iu. 2023. "Coexisting Firing Patterns in an Improved Memristive Hindmarsh–Rose Neuron Model with Multi-Frequency Alternating Current Injection" Micromachines 14, no. 12: 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122233
APA StyleWang, M., Ding, J., Deng, B., He, S., & Iu, H. H.-C. (2023). Coexisting Firing Patterns in an Improved Memristive Hindmarsh–Rose Neuron Model with Multi-Frequency Alternating Current Injection. Micromachines, 14(12), 2233. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14122233








