A Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Camera Based on Negative Pressure Forming Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Lens
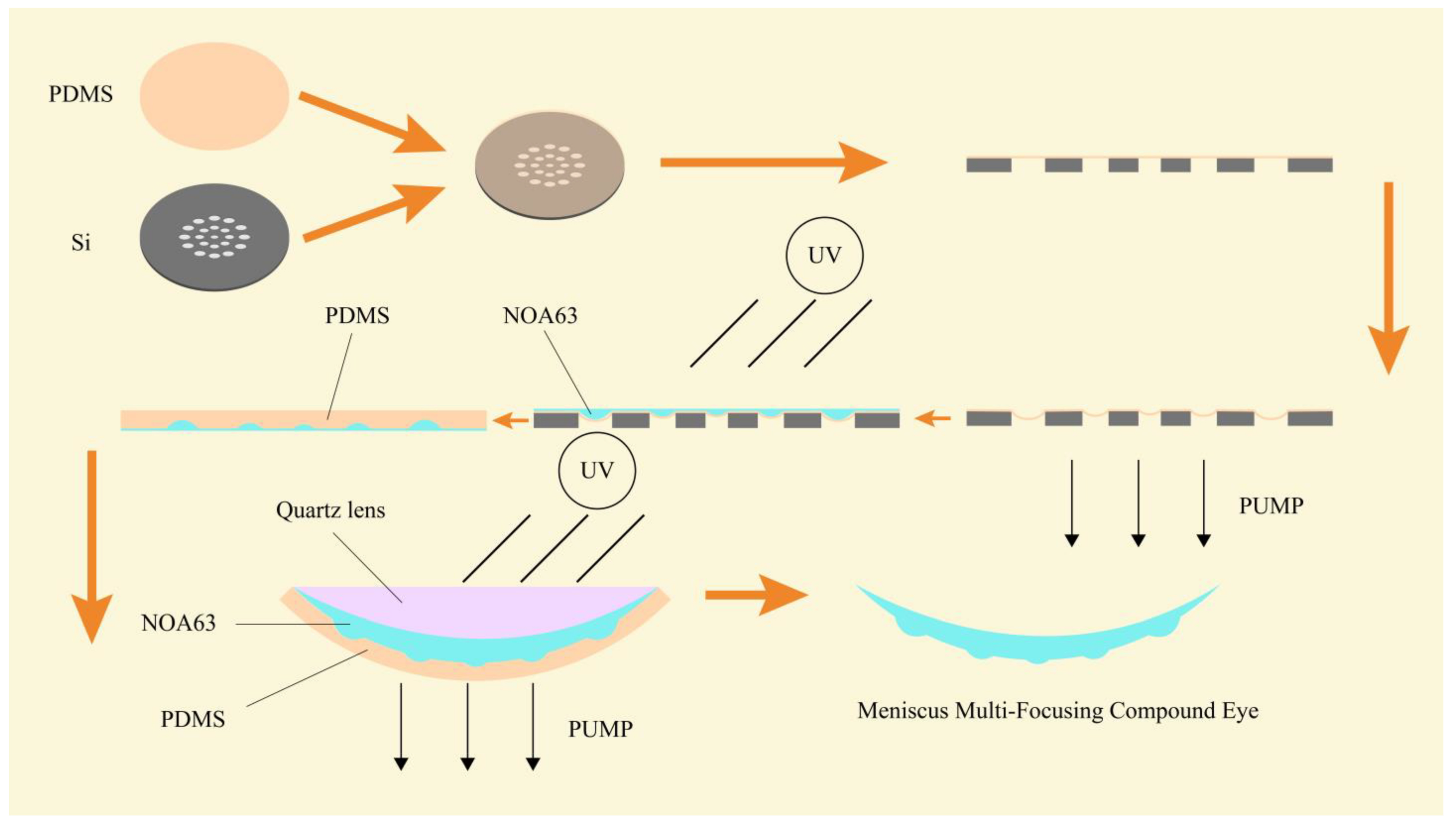
2.2. Preparation of Multifocal Meniscus Compound Eye
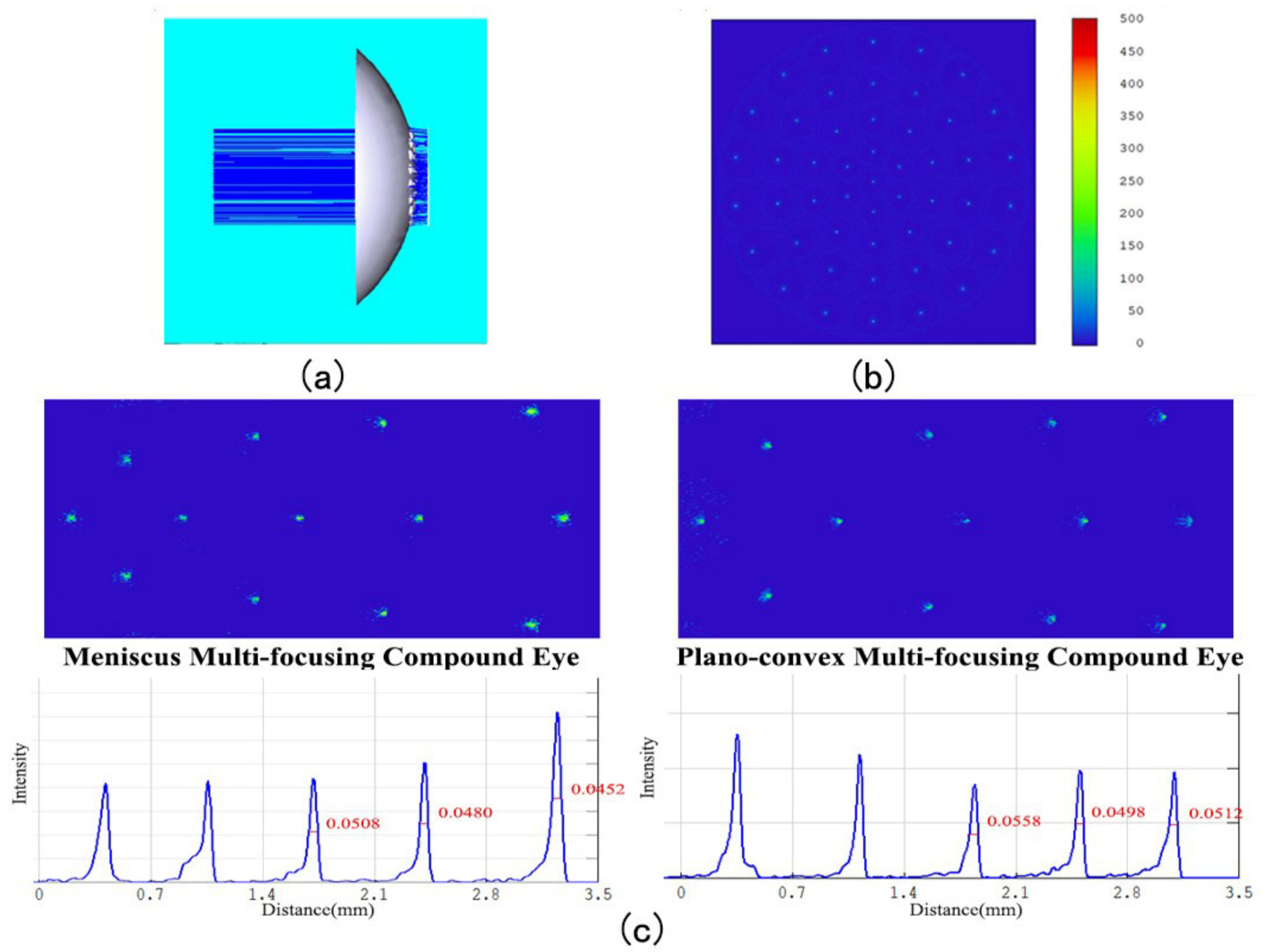
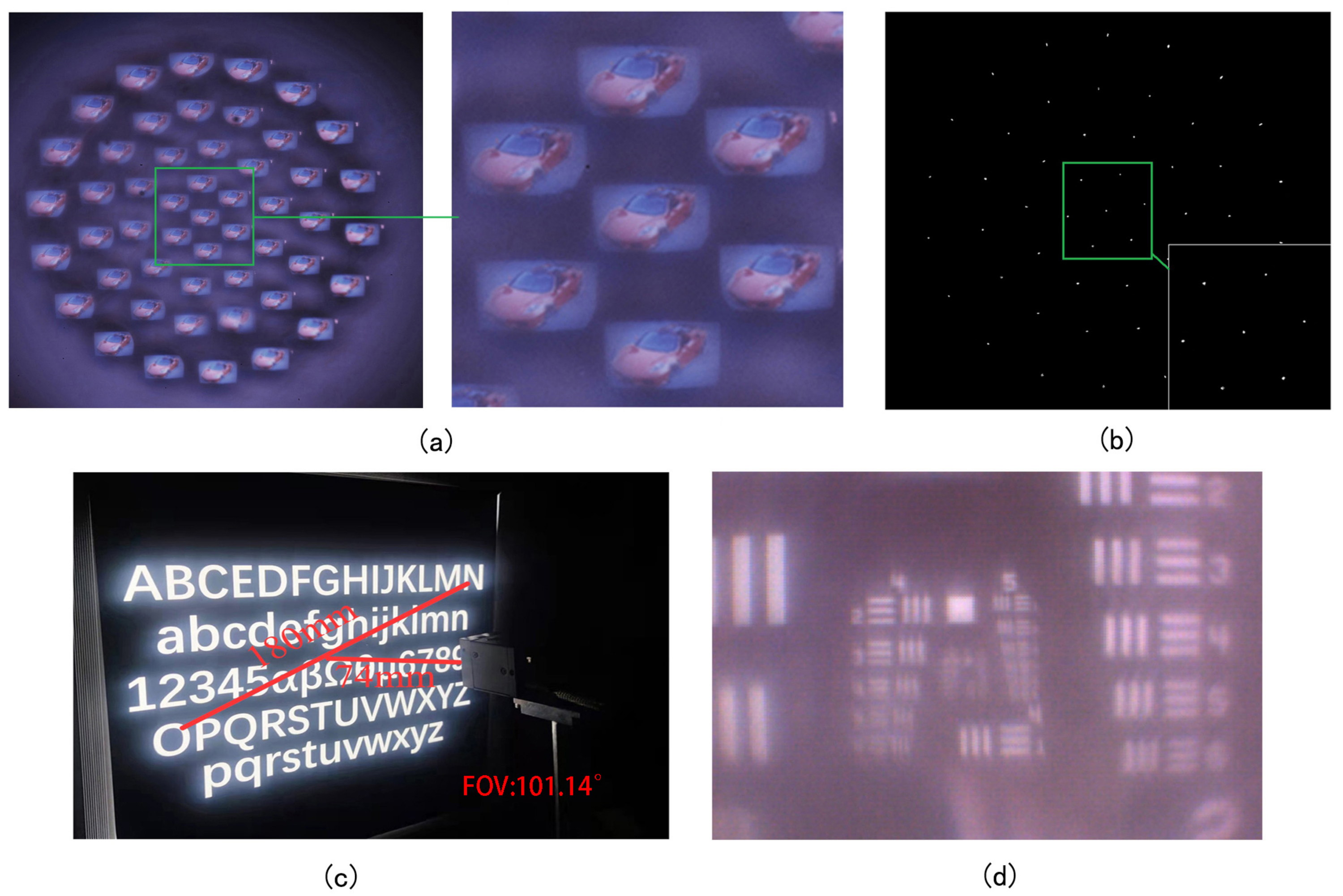
2.3. Measurement and Characterization of Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Lens
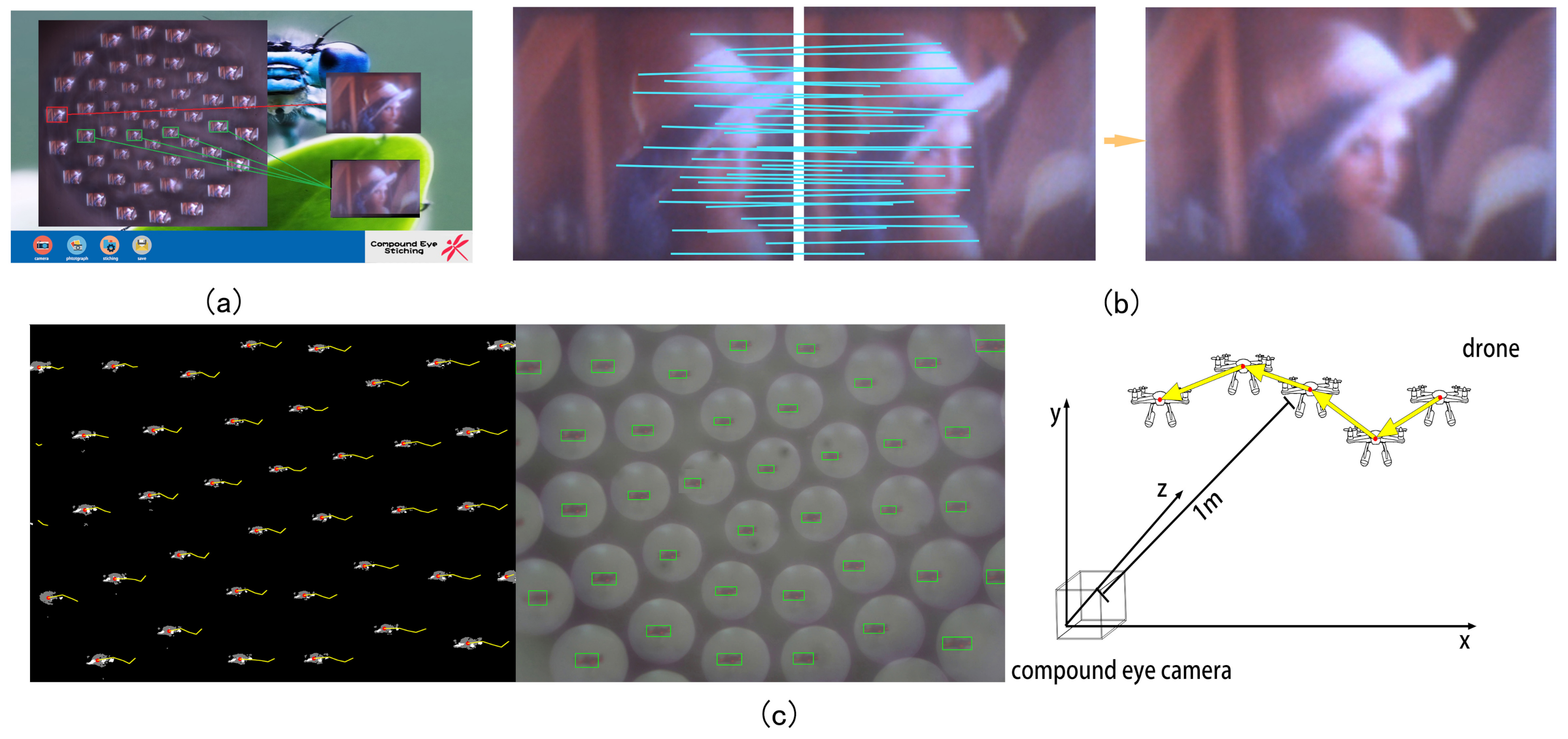
2.4. System Application of Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Lens
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q. Review of state-of-the-art artificial compound eye imaging systems. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2019, 14, 031002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannier, J.; Schoenemann, B.; Gillot, T.; Charbonnier, S.; Clarkson, E. Exceptional preservation of eye structure in arthropod visual predators from the Middle Jurassic. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randel, N.; Jékely, G. Phototaxis and the origin of visual eyes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, E.R.; Dornan, C.; Sendova-Franks, A.B.; Franks, N.R. Asymmetric ommatidia count and behavioural lateralization in the ant Temnothorax albipennis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Fan, F. Design and fabrication of a multi-focusing artificial compound eyes with negative meniscus substrate. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2017, 27, 045011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, H.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chen, F.; Zhang, F.; Du, G.; Yong, J.; Hou, X. Direct fabrication of compound-eye microlens array on curved surfaces by a facile femtosecond laser enhanced wet etching process. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 221109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Cai, Y.; Xu, C.; Pang, H.; Cao, A.; Fu, Y.; Deng, Q. Fabrication of Multifocal Microlens Array by One Step Exposure Process. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, S.; Arzenbacher, K.; Gissibl, T.; Giessen, H.; Herkommer, A.M. 3D-printed eagle eye: Compound microlens system for foveated imaging. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wang, J.N.; Niu, L.G.; Zhang, X.L.; Wu, S.Z.; Chen, Q.D.; Lee, L.P.; Sun, H.B. Bioinspired fabrication of high-quality 3D artificial compound eyes by voxel-modulation femtosecond laser writing for distortion-free wide-field-of-view imaging. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2014, 2, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Chang, S.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.M.; Song, Y.M. High-Identical Numerical Aperture, Multifocal Microlens Array through Single-Step Multi-Sized Hole Patterning Photolithography. Micromachines 2020, 11, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hou, W.J.; Jiang, L.J.; Gao, Y.; Fan, L.S.; Jiang, L.; Silvain, J.F.; Lu, Y.F. Direct writing of graphene patterns on insulating substrates under ambient conditions. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.; Hawkins, A.R. The photonic integration of non-solid media using optofluidics. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gissibl, T.; Thiele, S.; Herkommer, A.; Giessen, H. Sub-micrometre accurate free-form optics by three-dimensional printing on single-mode fibres. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gissibl, T.; Thiele, S.; Herkommer, A.; Giessen, H. Two-photon direct laser writing of ultracompact multi-lens objectives. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, S.; Gissibl, T.; Giessen, H.; Herkommer, A.M. Ultra-compact on-chip LED collimation optics by 3D femtosecond direct laser writing. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 3029–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.I.; Kim, K.; Yang, S.; won Jang, K.; Jeong, K.H. Multifocal microlens arrays using multilayer photolithography. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 9082–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, D.; Duparré, J.; Zeitner, U.D.; Tünnermann, A. Laser lithographic fabrication and characterization of a spherical artificial compound eye. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 3067–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Kang, E.K.; Ju, G.W.; Song, Y.M.; Lee, Y.T. Shape-controllable, bottom-up fabrication of microlens using oblique angle deposition. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 3328–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y.; Chi, J.; Xu, W.; Xiang, Y. Bio-inspired spherical compound eye camera for simultaneous wide-band and large field of view imaging. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 20952–20962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Li, M.; Shen, L.; Qiu, J.; Zhou, Y. Flexible fabrication of biomimetic compound eye array via two-step thermal reflow of simply pre-modeled hierarchic microstructures. Opt. Commun. 2017, 393, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Deng, Y.; Hao, P.; Fan, J.; Chi, M.; Wu, Y. Polymeric microlens array fabricated with PDMS mold-based hot embossing. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2014, 24, 095028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, A.; Duparré, J.; Dannberg, P.; Bräuer, A.; Tünnermann, A. Artificial neural superposition eye. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 11922–11933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duparré, J.; Schreiber, P.; Matthes, A.; Pshenay-Severin, E.; Bräuer, A.; Tünnermann, A.; Völkel, R.; Eisner, M.; Scharf, T. Microoptical telescope compound eye. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Maciel, M.; Rocha, R.P.; Carmo, J.P.; Correia, J.H. Measurement and statistical analysis toward reproducibility validation of AZ4562 cylindrical microlenses obtained by reflow. Measurement 2014, 49, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-K.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, M.; Bae, J.M.; Mahmud, I.; Kim, H.-R. Design and fabrication of multi-focusing microlens array with different numerical apertures by using thermal reflow method. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2014, 18, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherng, Y.-S.; Su, G.-D.J. Fabrication of polydimethylsiloxane microlens array on spherical surface using multi-replication process. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2013, 24, 015016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Wei, H.; Hao, X.; Wang, D.; Dai, Y.; Shi, J. Direct fabrication of microlens arrays with high numerical aperture by ink-jetting on nanotextured surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, G.; Zhang, C.; Yang, D.; Wang, Z. Theoretical Design of a Bionic Spatial 3D-Arrayed Multifocal Metalens. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Qu, P.; He, S.; Wang, X.; Si, J.; Hou, X. Fabrication of bioinspired omnidirectional and gapless microlens array for wide field-of-view detections. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 133701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Xin, W.; Ye, X.; Xiao, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Yin, P. Hierarchical Artificial Compound Eyes with Wide Field-of-View and Antireflection Properties Prepared by Nanotip-Focused Electrohydrodynamic Jet Printing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 60625–60635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdo, S.; Diaspro, A.; Duocastella, M. Microlens fabrication by replica molding of frozen laser-printed droplets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 418, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Jeong, K.-H. Monolithic polymer microlens arrays with high numerical aperture and high packing density. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 2160–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, Q.; Wu, D.; Yu, W. Biomimetic multispectral curved compound eye camera for real-time multispectral imaging in an ultra-large field of view. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 33346–33356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Mei, X.; Pan, A. Designable Ultratransparent and Superhydrophobic Surface of Embedded Artificial Compound Eye with Extremely Low Adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 53557–53567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Allen, Y.Y. Development of a 3D artificial compound eye. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 18125–18137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.-X.; Zheng, J.-X.; Qi, J.-Y.; Guo, M.-R.; Gao, B.-R.; Liu, X.-Q. Integration of Multifocal Microlens Array on Silicon Microcantilever via Femtosecond-Laser-Assisted Etching Technology. Micromachines 2022, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Lyu, J.; Sun, H.; Cui, X.; Wang, T.; Lu, M. Fabrication of a chirped artificial compound eye for endoscopic imaging fiber bundle by dose-modulated laser lithography and subsequent thermal reflow. Opt. Eng. 2015, 54, 033105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-H.; Chao, C.-K.; Hung, S.-Y. A novel fabrication method of micro-needle mold by using the micro-lens mask through contact printing. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.Y.; Park, J.J.; Ye, S.J.; Hyun, W.J.; Im, H.-G.; Bae, B.-S.; Park, O.O. Novel microlens arrays with embedded Al2O3 nanoparticles for enhancing efficiency and stability of flexible polymer light-emitting diodes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 65450–65458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Qiu, S.; Jin, W.; Xue, J. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Method for Bionic Compound-Eye System Based on MVSNet Network. Electronics 2022, 11, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Barrett, S.; Wright, C.; Wilcox, M. A bio-inspired apposition compound eye machine vision sensor system. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2009, 4, 046002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.C.; Stoykovich, M.P.; Song, J.; Malyarchuk, V.; Choi, W.M.; Yu, C.-J.; Geddes, J.B., III; Xiao, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y. A hemispherical electronic eye camera based on compressible silicon optoelectronics. Nature 2008, 454, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogal, O.; Leblebici, Y. An insect eye inspired miniaturized multi-camera system for endoscopic imaging. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 11, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrinos, D.; Möller, R.; Labhart, T.; Pfeifer, R.; Wehner, R. A mobile robot employing insect strategies for navigation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2000, 30, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; He, W.; Wei, D.; Hu, C.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, C. Depth-of-Field-Extended Plenoptic Camera Based on Tunable Multi-Focus Liquid-Crystal Microlens Array. Sensors 2020, 20, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C.; Bachman, H.; Becker, R.; Mai, J.; Jiao, Z.; Li, W.; Zheng, L.; Wan, X. Biomimetic apposition compound eye fabricated using microfluidic-assisted 3D printing. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liao, W.; Xu, Z.; Yu, W. SCECam: A spherical compound eye camera for fast location and recognition of objects at a large field of view. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 32333–32345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.-L.; Pan, J.-G.; Su, G.-D.J. One-lens camera using a biologically based artificial compound eye with multiple focal lengths. Optica 2019, 6, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, G.; Liu, Y.; Tao, K.; Xing, H.; Huang, R.; Chi, M.; Zhou, W.; Wu, Y. Fabrication and characterization of curved compound eyes based on multifocal microlenses. Micromachines 2020, 11, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Lian, G.; Liu, Y.; Xing, H.; Xing, Y.; Su, X.; Feng, X.; Wu, Y. Design and integration of the single-lens curved multi-focusing compound eye camera. Micromachines 2021, 12, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuard, D.; Tzvetkova-Chevolleau, T.; Decossas, S.; Tracqui, P.; Schiavone, P. Optimization of poly-di-methyl-siloxane (PDMS) substrates for studying cellular adhesion and motility. Microelectron. Eng. 2008, 85, 1289–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z. Polydimethylsiloxane Mechanical Properties Measured by Macroscopic Compression and Nanoindentation Techniques; University of South Florida: Tampa, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]





| Unit (mm) | Diameter dn | Height hn | Focal Length fn |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.500 | 0.090 | 0.709 |
| 2 | 0.520 | 0.097 | 0.717 |
| 3 | 0.560 | 0.109 | 0.736 |
| 4 | 0.660 | 0.131 | 0.801 |
| 5 | 0.880 | 0.226 | 0.980 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Yu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Shu, F.; Peng, L.; Wu, Y. A Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Camera Based on Negative Pressure Forming Technology. Micromachines 2023, 14, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020420
Feng X, Liu Y, Dong J, Yu Y, Xing Y, Shu F, Peng L, Wu Y. A Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Camera Based on Negative Pressure Forming Technology. Micromachines. 2023; 14(2):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020420
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xin, Yongshun Liu, Junyu Dong, Yongjian Yu, Yi Xing, Fengfeng Shu, Lanxin Peng, and Yihui Wu. 2023. "A Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Camera Based on Negative Pressure Forming Technology" Micromachines 14, no. 2: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020420
APA StyleFeng, X., Liu, Y., Dong, J., Yu, Y., Xing, Y., Shu, F., Peng, L., & Wu, Y. (2023). A Meniscus Multifocusing Compound Eye Camera Based on Negative Pressure Forming Technology. Micromachines, 14(2), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14020420







