Screen-Printed Wearable Sweat Sensor for Cost-Effective Assessment of Human Hydration Status through Potassium and Sodium Ion Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials, Reagents, and Equipment
2.2. Design and Fabrication of the Sensors
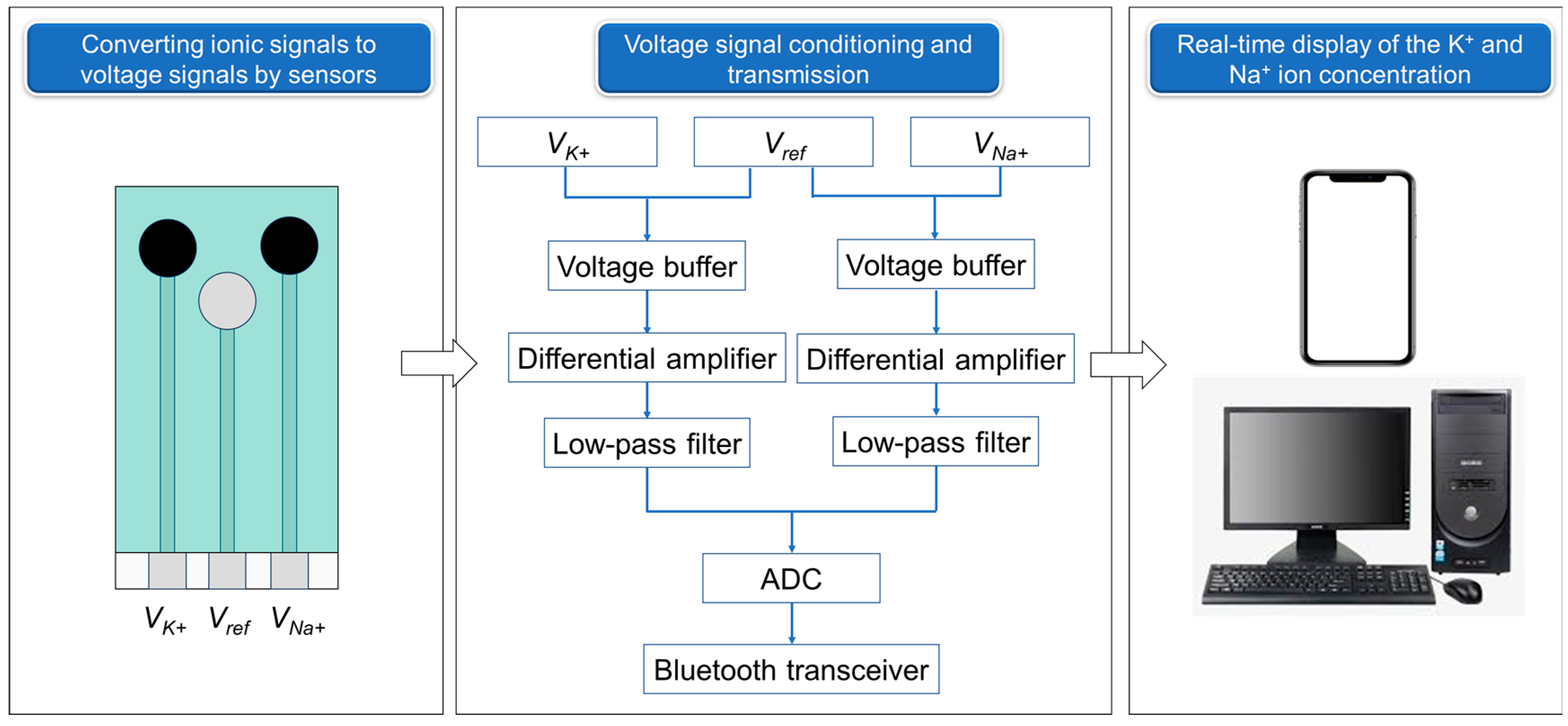
2.2.1. Overall Design
2.2.2. Structure of the Sensor
2.2.3. Fabrication of the Substrate Electrodes
2.2.4. Preparation of the Ion Selective Membranes and the Reference Electrode
2.2.5. Signal Treatment
2.3. Performance of the Substrate Electrodes
2.4. Detection Performance of the Sensors
2.4.1. Sensitivity and Linearity
2.4.2. Repeatability
2.4.3. Interference Resistance
2.4.4. Mechanical Deformation Resistance
2.4.5. Stability
2.4.6. Storage Stability
2.5. On-Body Trials
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Electrical and Electrochemical Performance of Screen-Printed Substrate Electrodes
3.1.1. Electrical Performance
3.1.2. Electrochemical Performance
3.2. Detection Performance of the Sensor
3.2.1. Sensitivity and Linearity
3.2.2. Repeatability
3.2.3. Interference Resistance
3.2.4. Mechanical Deformation Resistance
3.2.5. Stability
3.2.6. Storage Stability
3.3. On-Body Trials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, L.E. Rehydration during endurance exercise: Challenges, research, options, methods. Nutrients 2021, 13, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Song, Z.; Cai, H.; Fang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Wearable and flexible electrochemical sensors for sweat analysis: A review. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzberg, H.D. Case studies in management of muscle cramps. Neurol. Clin. 2020, 38, 679–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Wei, G.; Liu, A.; Huo, F.; Zhang, Z. A review of sampling, energy supply and intelligent monitoring for long-term sweat sensors. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, E.T.; Cotter, J.D.; Kilding, A.E. Methods for improving thermal tolerance in military personnel prior to deployment. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlot, K. Negative energy balance during military training: The role of contextual limitations. Appetite 2021, 164, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, T.J.; Wardle, S.L.; Greeves, J.P. Energy deficiency in soldiers: The risk of the athlete triad and relative energy deficiency in sport syndromes in the military. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlotman, T.E.; Lehnhardt, K.R.; Abercromby, A.F.; Easter, B.D.; Downs, M.E.; Akers, L.K.S.; Convertino, V.A. Bridging the gap between military prolonged field care monitoring and exploration spaceflight: The compensatory reserve. NPJ Microgravity 2019, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barley, O.R.; Chapman, D.W.; Abbiss, C.R. Reviewing the current methods of assessing hydration in athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.W.; Seo, S.P.; Ha, Y.-S.; Kim, W.T.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yun, S.-J.; Kim, W.-J.; Lee, S.-C. Twenty-four-hour urine osmolality as a representative index of adequate hydration and a predictor of recurrence in patients with urolithiasis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostelnik, S.B.; Davy, K.P.; Hedrick, V.E.; Thomas, D.T.; Davy, B.M. The validity of urine color as a hydration biomarker within the general adult population and athletes: A systematic review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2021, 40, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liska, D.; Mah, E.; Brisbois, T.; Barrios, P.L.; Baker, L.B.; Spriet, L.L. Narrative review of hydration and selected health outcomes in the general population. Nutrients 2019, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-M.; Li, Y.-J.; Han, D.; Zhu, H.-C.; Xue, C.-D.; Chui, H.-C.; Cao, T.; Qin, K.-R. A capillary-evaporation micropump for real-time sweat rate monitoring with an electrochemical sensor. Micromachines 2019, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Ishihara, T.; Kuwabara, K.; Amano, T.; Togo, H. Wearable Microfluidic Sensor for the Simultaneous and Continuous Monitoring of Local Sweat Rates and Electrolyte Concentrations. Micromachines 2022, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xu, K.; Xu, H.; Huang, A.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.e.; Lu, K.; Wan, F.; Bai, Z. A One-Dollar, Disposable, Paper-Based Microfluidic Chip for Real-Time Monitoring of Sweat Rate. Micromachines 2022, 13, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasier, N.; Eckstein, J. Sweat as a source of next-generation digital biomarkers. Digit. Biomark. 2019, 3, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Benzigar, M.R.; Subramony, J.A.; Lovell, N.H.; Liu, G. Advances in sweat wearables: Sample extraction, real-time biosensing, and flexible platforms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34337–34361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Duan, W.; Jin, Y.; Wo, F.; Xi, F.; Wu, J. Ratiometric fluorescent nanohybrid for noninvasive and visual monitoring of sweat glucose. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Paz, E.; Saha, T.; Del Caño, R.; Seker, S.; Kshirsagar, N.; Wang, J. Non-invasive monitoring of interstitial fluid lactate through an epidermal iontophoretic device. Talanta 2023, 254, 124122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, S.M.; Choi, J.; Won, P.; Ko, S.H. Challenges and strategies in developing an enzymatic wearable sweat glucose biosensor as a practical point-of-care monitoring tool for type II diabetes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.; Wunderlich, L.; Weinzierl, F.; Lei, Y.; Duerkop, A.; Alshareef, H.N.; Baeumner, A.J. Electrochemical multi-analyte point-of-care perspiration sensors using on-chip three-dimensional graphene electrodes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirovano, P.; Dorrian, M.; Shinde, A.; Donohoe, A.; Brady, A.J.; Moyna, N.M.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D.; McCaul, M. A wearable sensor for the detection of sodium and potassium in human sweat during exercise. Talanta 2020, 219, 121145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Hu, C.; Liu, W.; Shen, G. Progress and perspectives in designing flexible microsupercapacitors. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Chen, D.; Shen, G. Wearable sweat monitoring system with integrated micro-supercapacitors. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Q.; Yap, L.W.; Wang, R.; Gong, S.; Guo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, Q.; Wang, J.; Simon, G.P.; Cheng, W. Vertically aligned gold nanowires as stretchable and wearable epidermal ion-selective electrode for noninvasive multiplexed sweat analysis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4647–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.; Mohammadifar, M.; Choi, S. A single-use, self-powered, paper-based sensor patch for detection of exercise-induced hypoglycemia. Micromachines 2017, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, S.A.; De la Paz, E.; Del Caño, R.; Seker, S.; Saha, T.; Wang, J.; Jaramillo-Botero, A. Non-invasive in-vivo glucose-based stress monitoring in plants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 231, 115300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kare, S.P.; Das, D.; Chaudhury, K.; Das, S. Hand-drawn electrode based disposable paper chip for artificial sweat analysis using impedance spectroscopy. Biomed. Microdevices 2021, 23, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, K.; Long, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, F.; Gong, W. A flexible nonenzymatic sweat glucose sensor based on Au nanoflowers coated carbon cloth. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 388, 133798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T.; Songkakul, T.; Knisely, C.T.; Yokus, M.A.; Daniele, M.A.; Dickey, M.D.; Bozkurt, A.; Velev, O.D. Wireless wearable electrochemical sensing platform with zero-power osmotic sweat extraction for continuous lactate monitoring. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadifar, M.; Tahernia, M.; Yang, J.H.; Koh, A.; Choi, S. Biopower-on-Skin: Electricity generation from sweat-eating bacteria for self-powered E-Skins. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahernia, M.; Mohammadifar, M.; Liu, L.; Choi, S. A disposable, papertronic three-electrode potentiostat for monitoring bacterial electrochemical activity. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 24717–24723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonla, C.; Del Caño, R.; Sakdaphetsiri, K.; Saha, T.; De la Paz, E.; Düsterloh, A.; Wang, J. Disposable screen-printed electrochemical sensing strips for rapid decentralized measurements of salivary ketone bodies: Towards therapeutic and wellness applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 220, 114891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Sun, N.; Lai, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.; Zhao, X.; Feng, L. Paper-Based Sandwich-Structured Wearable Sensor with Sebum Filtering for Continuous Detection of Sweat pH. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.; Ahamed, A.; Cheong, Y.H.; Zhao, K.; Ding, R.; Lisak, G. Non-equilibrium potentiometric sensors integrated with metal modified paper-based microfluidic solution sampling substrates for determination of heavy metals in complex environmental samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1197, 339495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisak, G.; Arnebrant, T.; Ruzgas, T.; Bobacka, J. Textile-based sampling for potentiometric determination of ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 877, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Zhao, K.; Ding, R.; Chan, W.P.; Yang, M.; Yip, J.S.Q.; Lisak, G. Ion-selective membrane modified microfluidic paper-based solution sampling substrates for potentiometric heavy metal detection. Analyst 2022, 147, 4500–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Lisak, G. Sponge-based microfluidic sampling for potentiometric ion sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1091, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, R.; Krikstolaityte, V.; Lisak, G. Inorganic salt modified paper substrates utilized in paper based microfluidic sampling for potentiometric determination of heavy metals. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 290, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Ma, X.; Fan, L.; Xin, J.H.; Yu, H. Weavable, large-scaled, rapid response, long-term stable electrochemical fabric sensor integrated into clothing for monitoring potassium ions in sweat. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Bao, Y.; Han, T.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Z. A wearable electrochemical sensor based on β-CD functionalized graphene for pH and potassium ion analysis in sweat. Talanta 2022, 245, 123481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Cao, Q.; Mao, X.; Pan, W.; Tu, T.; Fang, L.; Ye, X. An integrated paper-based microfluidic device for real-time sweat potassium monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 9642–9648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.B. Sweating rate and sweat sodium concentration in athletes: A review of methodology and intra/interindividual variability. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.; Burns, A.; Lenigk, R.; Gettings, R.; Ashe, J.; Porter, A.; McCaul, M.; Barrett, R.; Diamond, D.; White, P. A wearable patch for continuous monitoring of sweat electrolytes during exertion. Lab A Chip 2018, 18, 2632–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Emaminejad, S.; Nyein, H.Y.Y.; Challa, S.; Chen, K.; Peck, A.; Fahad, H.M.; Ota, H.; Shiraki, H.; Kiriya, D. Fully integrated wearable sensor arrays for multiplexed in situ perspiration analysis. Nature 2016, 529, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Liang, B.; Mao, X.; Wei, J.; Tu, T.; Fang, L.; Ye, X. A Smartwatch Integrated with a Paper-based Microfluidic Patch for Sweat Electrolytes Monitoring. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Electrodes | Types | Average Resistance (Ω) | Standard Deviation of Resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|---|---|
| K+ ISE | chip-to-chip (n = 5) | 76.68 | 2.93 |
| batch-to-batch (n = 5) | 76.56 | 4.33 | |
| Na+ ISE | chip-to-chip (n = 5) | 76.48 | 2.11 |
| batch-to-batch (n = 5) | 76.36 | 4.64 | |
| Ag/AgCl RE | chip-to-chip (n = 5) | 1.22 | 0.08 |
| batch-to-batch (n = 5) | 1.21 | 0.27 |
| K+ ISE | Na+ ISE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run-to-Run (n = 5) | Chip-to-Chip (n = 5) | Run-to-Run (n = 5) | Chip-to-Chip (n = 5) | |
| average slope (mV/decade) | 54.859 | 54.159 | 55.068 | 55.106 |
| standard deviation of slope (mV/decade) | 0.674 | 1.086 | 0.318 | 0.395 |
| average base potential a (mV) | 201.582 | 199.28 | 212 | 212.496 |
| standard deviation of base potential (mV) | 1.160 | 4.580 | 1.603 | 4.198 |
| Weight before Exercise (kg) | Weight after Exercise (kg) | s. r. a Time (s) of K+ ISE | min. con. b of K+ (mM) | s. r. Time (s) of Na+ ISE | max. con. c of Na+ (mM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st day | 79.35 | 78.59 | 501 | 4.05 | 498 | 100.01 |
| 2nd day | 79.41 | 78.75 | 512 | 4.11 | 508 | 99.55 |
| 3rd day | 79.22 | 78.61 | 522 | 4.28 | 516 | 97.09 |
| 4th day | 79.01 | 78.44 | 537 | 4.39 | 532 | 96.38 |
| 5th day | 79.09 | 78.53 | 546 | 4.69 | 542 | 95.18 |
| 6th day | 78.92 | 78.37 | 558 | 4.77 | 553 | 94.76 |
| 7th day | 78.84 | 78.30 | 567 | 5.10 | 562 | 89.55 |
| 8th day | 78.79 | 78.27 | 576 | 5.20 | 575 | 88.16 |
| 9th day | 78.81 | 78.29 | 588 | 5.36 | 586 | 83.61 |
| 10th day | 78.71 | 78.19 | 597 | 5.47 | 595 | 81.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Sun, N.; Lai, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wu, J.; Zhou, W. Screen-Printed Wearable Sweat Sensor for Cost-Effective Assessment of Human Hydration Status through Potassium and Sodium Ion Detection. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081497
Yang M, Sun N, Lai X, Li Y, Zhao X, Wu J, Zhou W. Screen-Printed Wearable Sweat Sensor for Cost-Effective Assessment of Human Hydration Status through Potassium and Sodium Ion Detection. Micromachines. 2023; 14(8):1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081497
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Mingpeng, Nan Sun, Xiaochen Lai, Yanjie Li, Xingqiang Zhao, Jiamin Wu, and Wangping Zhou. 2023. "Screen-Printed Wearable Sweat Sensor for Cost-Effective Assessment of Human Hydration Status through Potassium and Sodium Ion Detection" Micromachines 14, no. 8: 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081497
APA StyleYang, M., Sun, N., Lai, X., Li, Y., Zhao, X., Wu, J., & Zhou, W. (2023). Screen-Printed Wearable Sweat Sensor for Cost-Effective Assessment of Human Hydration Status through Potassium and Sodium Ion Detection. Micromachines, 14(8), 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081497









