Study on the Influence of Central Hole Diameter in a Wire Mesh Electrode on Ionic Wind Characteristics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
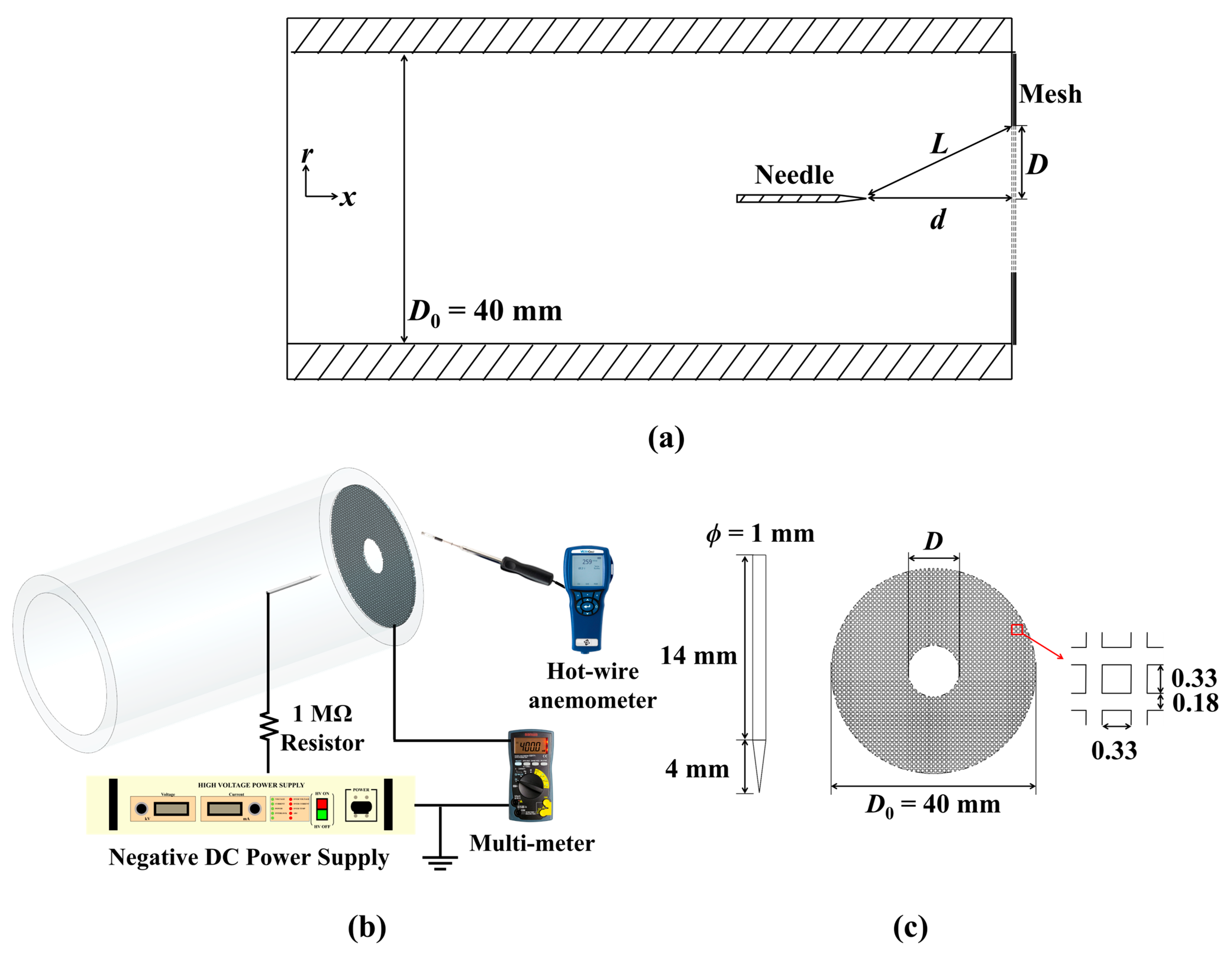
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
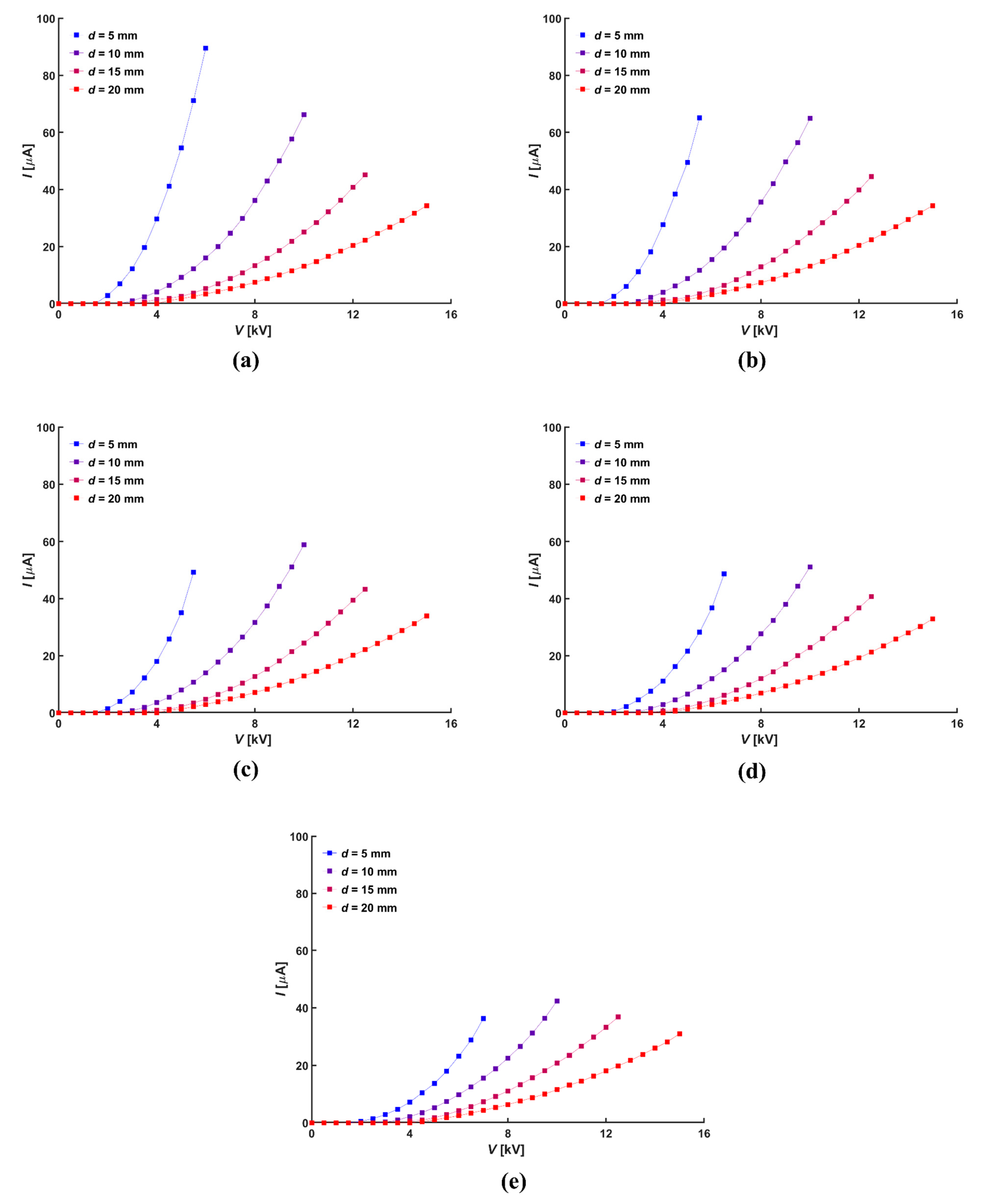
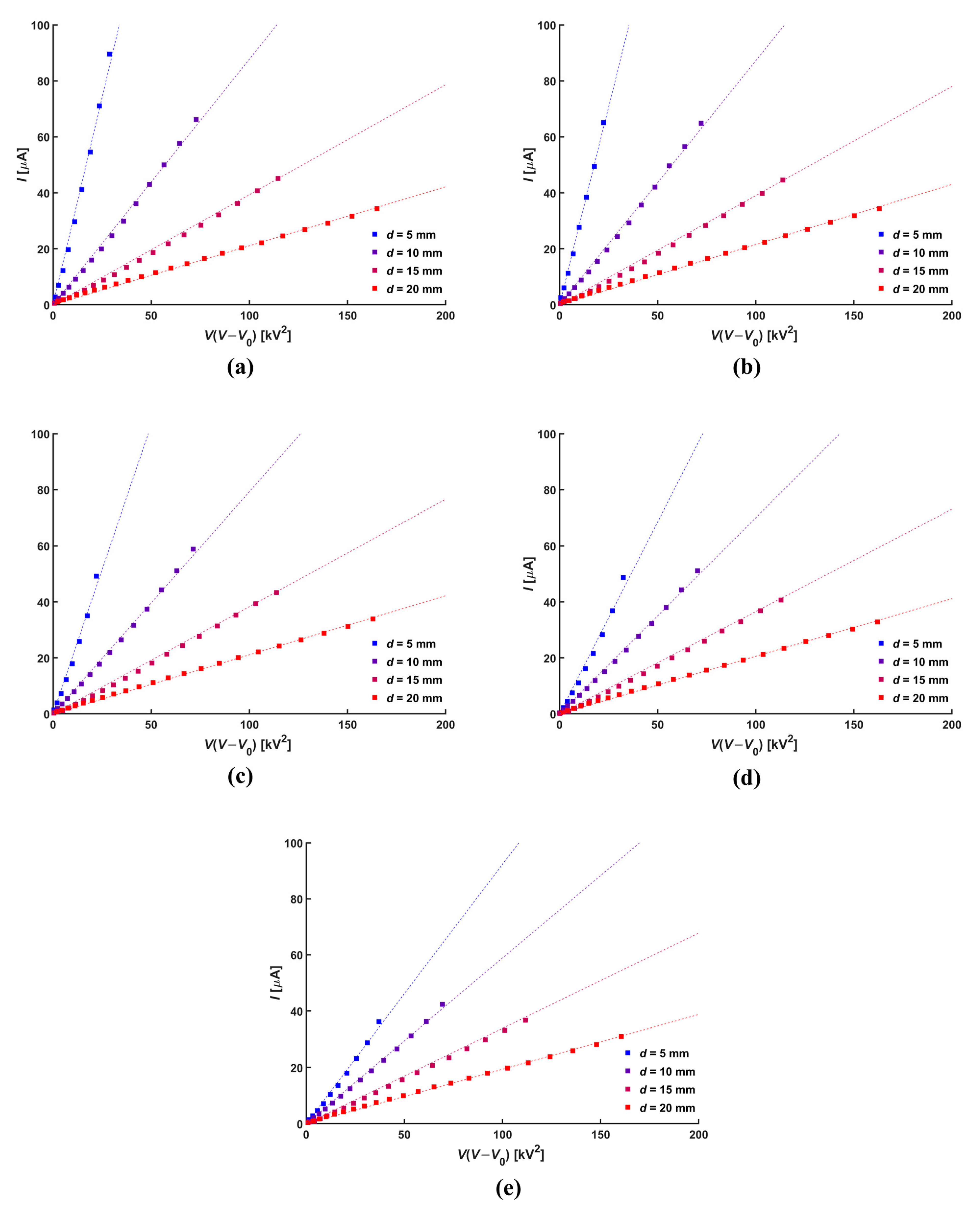
3.1. Electrical Characteristics
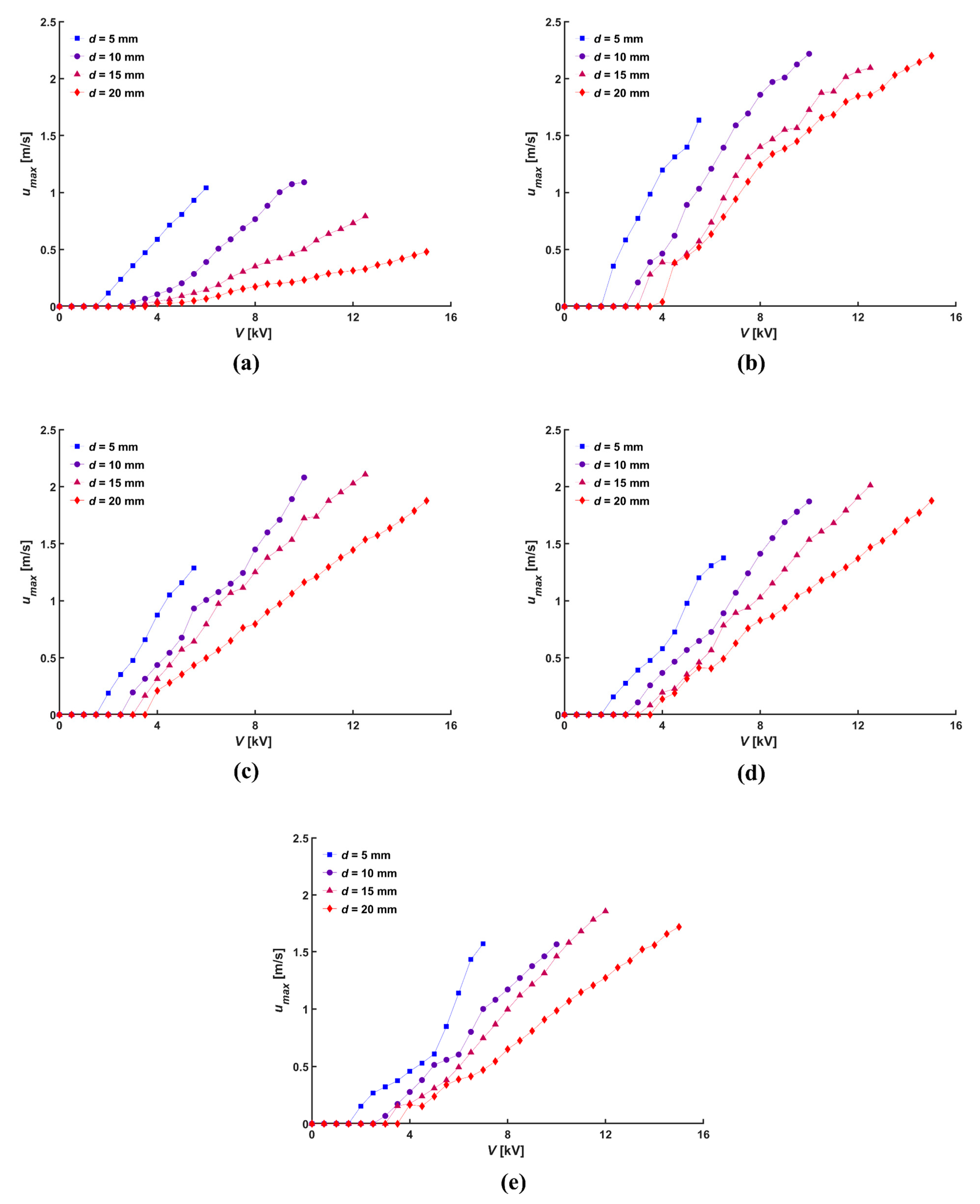
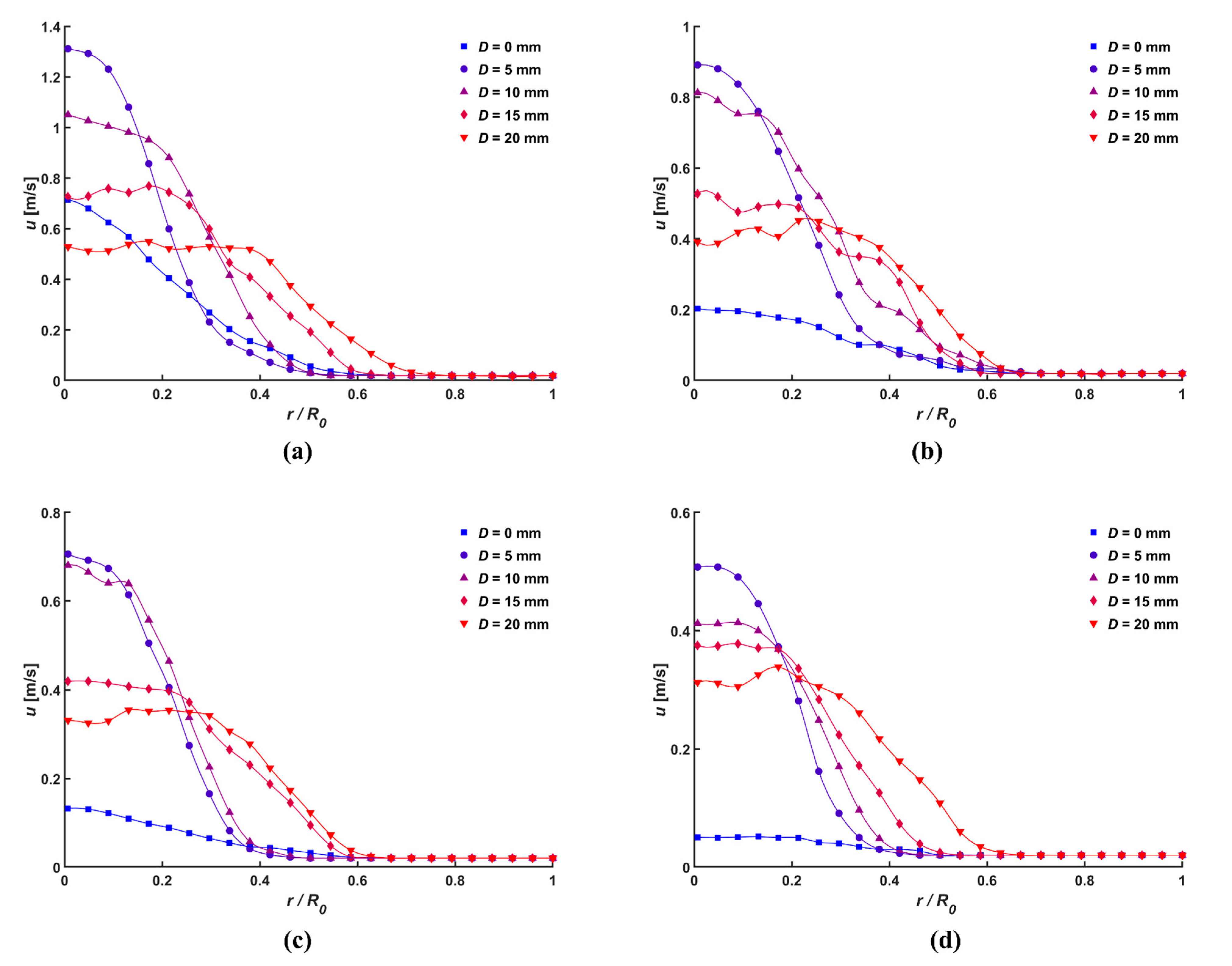
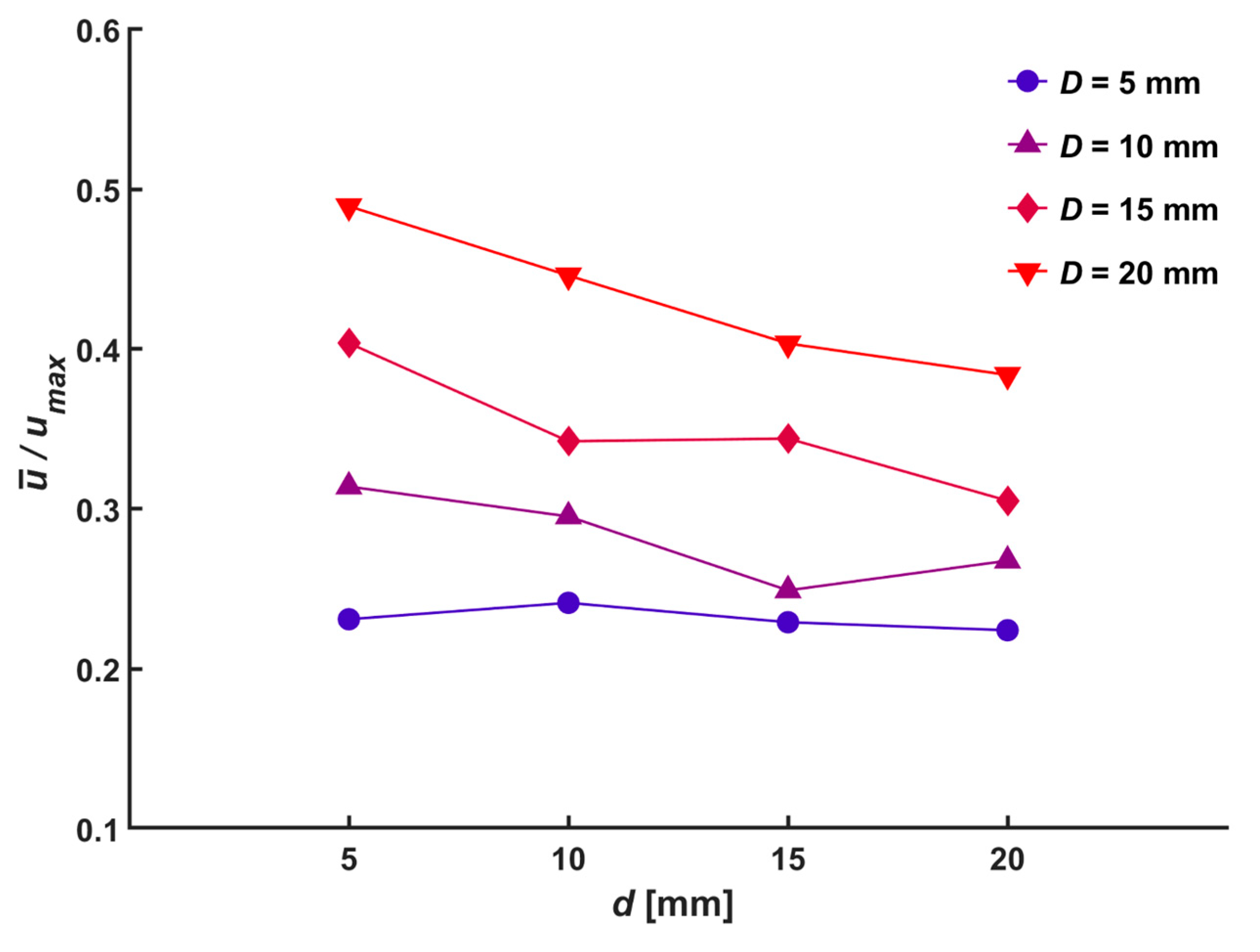
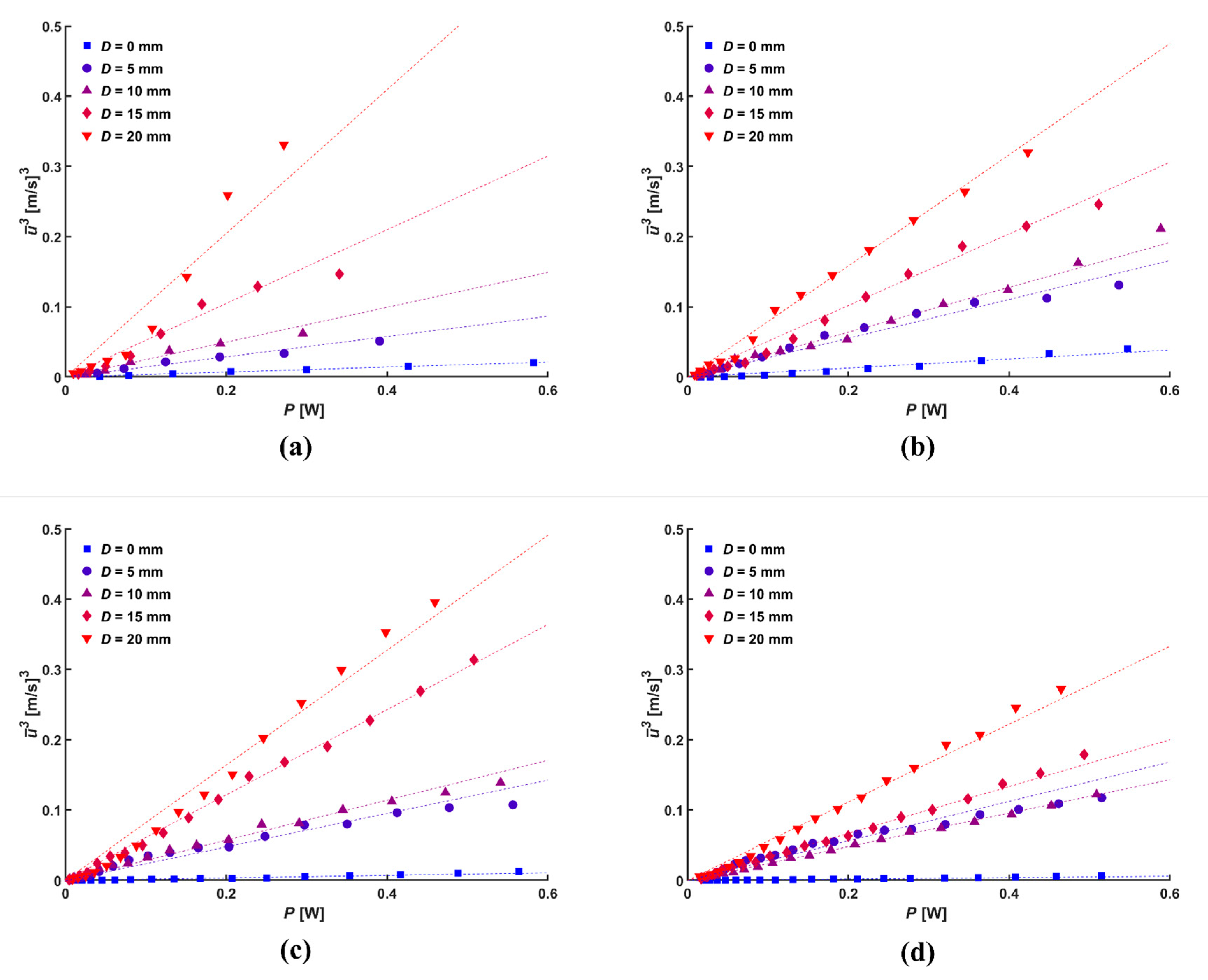
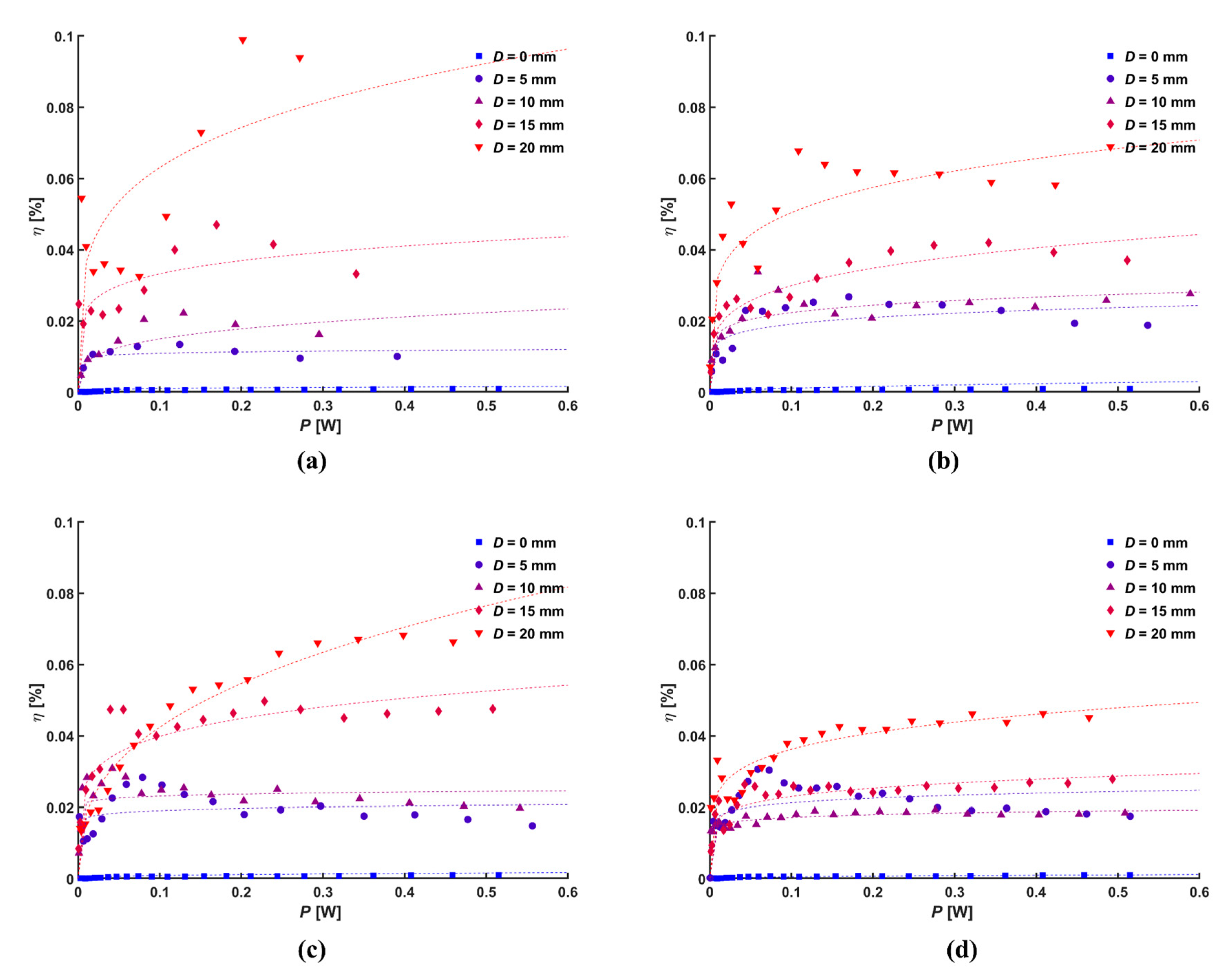
3.2. Flow Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, J.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.; Wu, X.; Ren, Q.; Zhang, J. A review on recent advances and challenges of ionic wind produced by corona discharges with practical applications. J. Phys. D 2021, 55, 153002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Adamiak, K. EHD flow produced by electric corona discharge in gases: From fundamental studies to applications (a review). Part. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Heo, H.; Sohn, D.K.; Ko, H.S. Control of electrohydrodynamic (EHD) flow by secondary electric potential. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 186, 122490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.H.; Tang, F.; Wang, C.; Cui, X. Oscillatory Motion of Water Droplets Both in Oil and on Superhydrophobic Surface under Corona Discharge. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Heo, H.; Sohn, D.K.; Ko, H.S. Analysis and optimization of the electrohydrodynamic (EHD) flow with a wire-to-two-cylinder configuration for convective heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 182, 121959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Kong, L.; Zhang, J. Experimental investigation on flow and heat transfer characteristics of a needle-cylinder type ionic wind generator for LED cooling. Energies 2018, 11, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Guan, Y.; Wu, J. Experimental study of heat transfer enhancement with point-to-ring corona discharge. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 184, 122273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, T.X.; Tran, C.D.; Bui, T.T.; Phan, H.T. A study of angular rate sensing by corona discharge ion wind. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 277, 169–180. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q.; Zhou, S.; Hu, R.; Zheng, H.; Pan, J.; Tang, J. Generation and Transport of Dielectric Droplets along Microchannels by Corona Discharge. Micromachines 2020, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prehn, F.; Timmermann, E.; Kettlitz, M.; Schaufler, K.; Günther, S.; Hahn, V. Inactivation of airborne bacteria by plasma treatment and ionic wind for indoor air cleaning. Plasma Process. Polym. 2020, 17, 2000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermann, E.; Prehn, F.; Schmidt, M.; Höft, H.; Brandenburg, R.; Kettlitz, M. Indoor air purification by dielectric barrier discharge combined with ionic wind: Physical and microbiological investigations. J. Phys. D 2018, 51, 164003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.S.; Pister, K.S. Geometric optimization of microfabricated silicon electrodes for corona discharge-based electrohydrodynamic thrusters. Micromachines 2017, 8, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.C.; Wen, T.Y. The effects of inlet blockage and electrical driving mode on the performance of a needle-ring ionic wind pump. Micromachines 2021, 12, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickard, M.; Dunn-Rankin, D. Numerical simulation of a tubular ion-driven wind generator. J. Electrost. 2007, 65, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeili, B.; Chang, J.S.; Harvel, G.D.; Ching, C.Y.; Brocilo, D. Flow characteristics of wire-rod type electrohydrodynamic gas pump under negative corona operations. J. Electrost. 2008, 66, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colas, D.F.; Ferret, A.; Pai, D.Z.; Lacoste, D.A.; Laux, C.O. Ionic wind generation by a wire-cylinder-plate corona discharge in air at atmospheric pressure. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 103306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dramane, B.; Zouzou, N.; Moreau, E.; Touchard, G. Electrostatizc precipitation in wire-to-cylinder configuration: Effect of the high-voltage power supply waveform. J. Electrost. 2009, 67, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- June, M.S.; Kribs, J.; Lyons, K.M. Measuring efficiency of positive and negative ionic wind devices for comparison to fans and blowers. J. Electrost. 2011, 69, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, A.M.; Cademartiri, L.; Whitesides, G.M.; Bishop, K.J. Electric winds driven by time oscillating corona discharges. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 143302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.D.; Hwang, D.H.; Geum, S.T. An EHD gas pump utilizing a ring/needle electrode. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2009, 16, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, E.; Touchard, G. Enhancing the mechanical efficiency of electric wind in corona discharges. J. Electrost. 2008, 66, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranshahi, K.; Martynenko, A.; Defraeye, T. Cutting-down the energy consumption of electrohydrodynamic drying by optimizing mesh collector electrode. Energy 2020, 208, 118168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, T.; Cai, Y.X.; Wang, J.B.; Wang, J. Development and application of a solid-state fan for enhanced heat dissipation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 169, 114922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K. An empirical formula for negative corona discharge current in point-grid electrode geometry. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 96, 2472–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bahy, M.M.; Abouelsaad, M.; Abdel-Gawad, N.; Badawi, M. Onset voltage of negative corona on stranded conductors. J. Phys. D. 2007, 40, 3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, J.S. Electricity in Gases; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1915. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Park, D.; Noh, K.C.; Hwang, J. Velocity and energy conversion efficiency characteristics of ionic wind generator in a multistage configuration. J. Electrost. 2010, 68, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, J.H.; Sohn, D.K.; Ko, H.S. Study on the Influence of Central Hole Diameter in a Wire Mesh Electrode on Ionic Wind Characteristics. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081614
Chung JH, Sohn DK, Ko HS. Study on the Influence of Central Hole Diameter in a Wire Mesh Electrode on Ionic Wind Characteristics. Micromachines. 2023; 14(8):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081614
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Ji Hong, Dong Kee Sohn, and Han Seo Ko. 2023. "Study on the Influence of Central Hole Diameter in a Wire Mesh Electrode on Ionic Wind Characteristics" Micromachines 14, no. 8: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081614
APA StyleChung, J. H., Sohn, D. K., & Ko, H. S. (2023). Study on the Influence of Central Hole Diameter in a Wire Mesh Electrode on Ionic Wind Characteristics. Micromachines, 14(8), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14081614






