Bioinspiration and Biomimetic Art in Robotic Grippers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
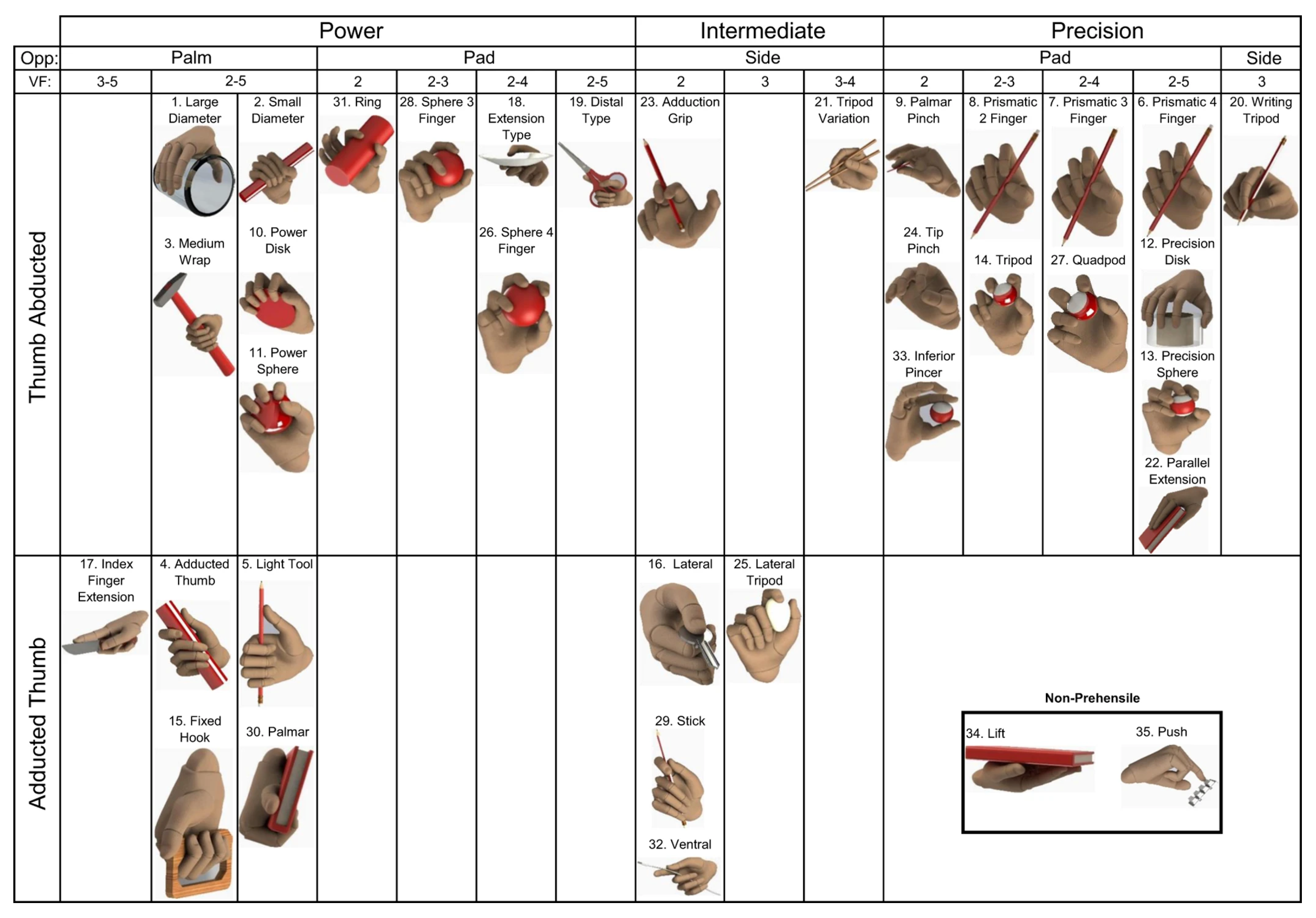
1.1. Grasping Taxonomy
1.2. Number of Objects
2. Human-Hand-like Grippers
2.1. Traditional Rigid-Link Grippers
2.1.1. Two-Finger Grippers
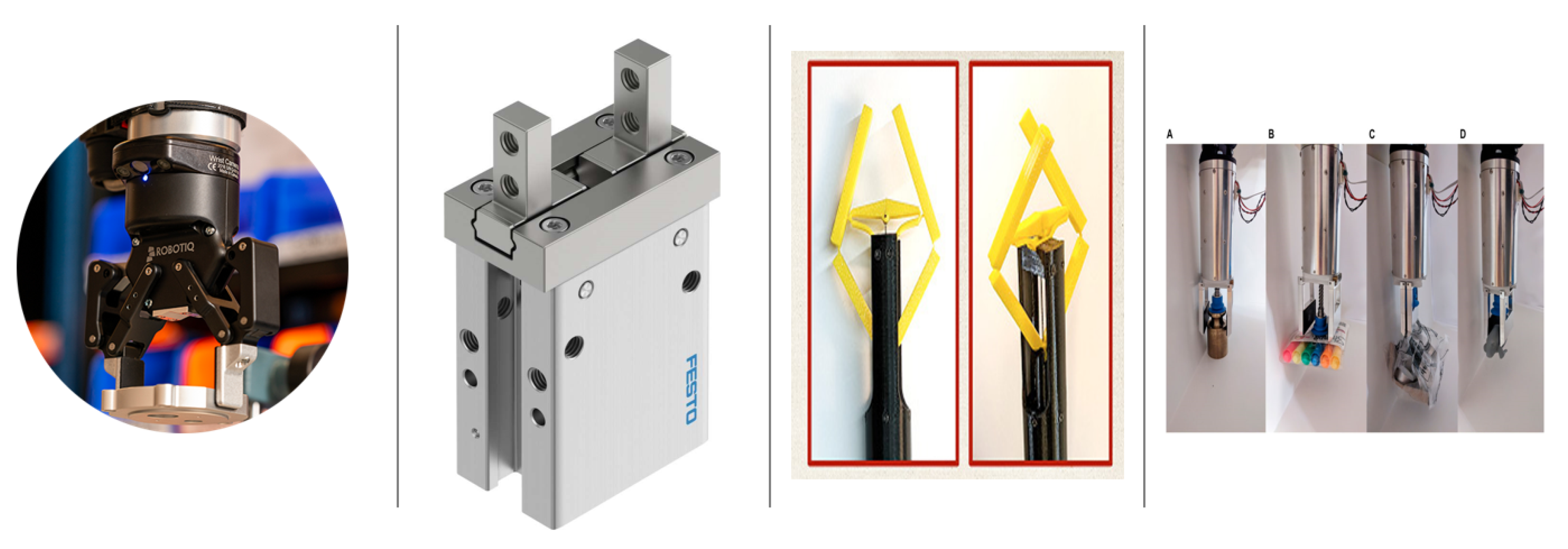

2.1.2. Three-Finger Grippers
2.1.3. Multi-Finger Grippers
2.2. Soft Grippers
2.2.1. Soft Grippers with Gripping by Actuation
2.2.2. Soft Grippers with Gripping by Controlled Stiffness
2.2.3. Soft Grippers with Gripping by Controlled Adhesion
3. Animal-Inspired Grippers
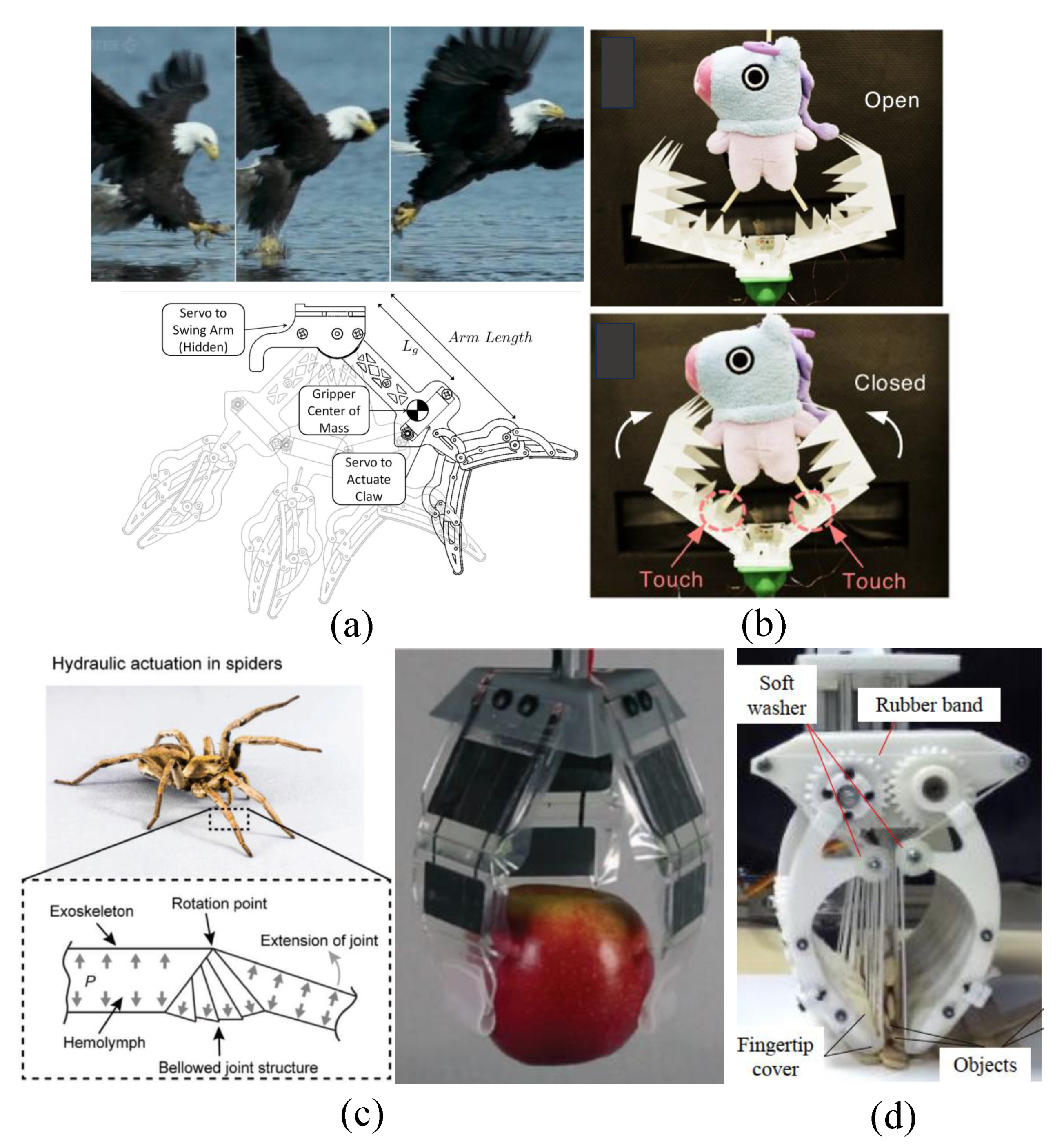
3.1. Clamp Grasp
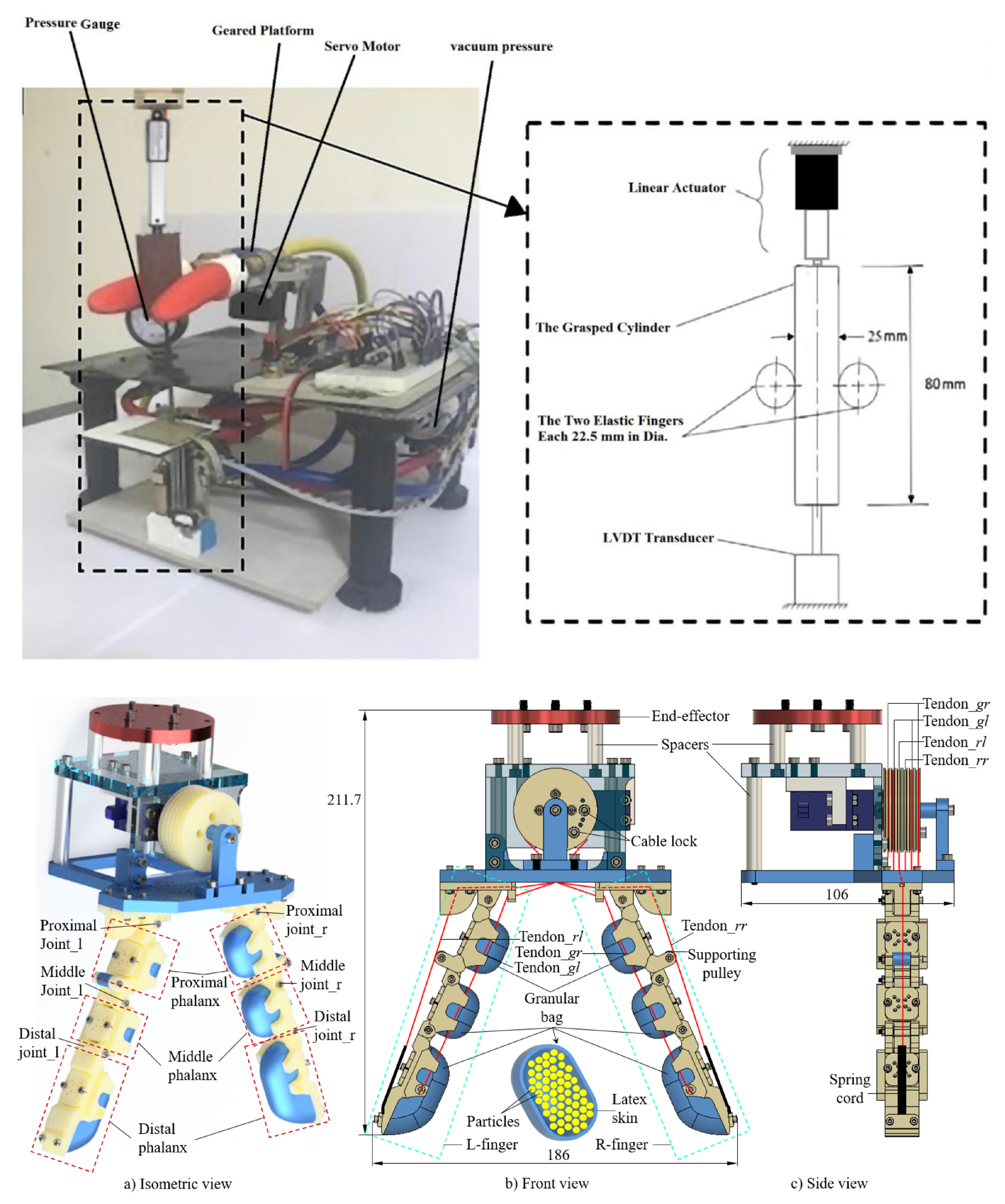
3.2. Sucking Grasp
3.3. Wrapping Grasp
3.3.1. Elephant Trunk
3.3.2. Tentacle-Inspired Grippers
3.3.3. Serpentes-Inspired and Mammal-Inspired (Spine-like) Grippers
3.4. Dry Adhesion Grasping
3.5. Wet Adhesion Grasping

3.6. Lock and Hook Grasping
3.7. Swallowing Grasp
4. Plant-Inspired Grippers

5. Summary
5.1. Actuators
5.2. Applications
5.2.1. Applications of B-I Soft Grippers
5.2.2. Applications of B-I Rigid Grippers
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.; Kim, S. Soft robot review. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, D.M.; Mândru, S.D.; Biriș, C.M.; Petrașcu, O.L.; Morariu, F.; Ianosi-Andreeva-Dimitrova, A. Soft Robotics: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Micromachines 2023, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, F.; Waqas, M.; Jawed, B.; Soomro, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Hina, A.; Khan, U.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, K.H. Decade of bio-inspired soft robots: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 073002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Cacucciolo, V.; Floreano, D.; Shea, H. Soft Robotic Grippers. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1707035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.; Culha, U.; Giardina, F.; Guenther, F.; Rosendo, A.; Iida, F. Soft Manipulators and Grippers: A Review. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, G.D.; Goh, G.L.; Lyu, Z.; Ariffin, M.Z.; Yeong, W.Y.; Lum, G.Z.; Campolo, D.; Han, B.S.; Wong, H.Y.A. 3D Printing of Robotic Soft Grippers: Toward Smart Actuation and Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, Z. Soft-rigid coupling grippers: Collaboration strategies and integrated fabrication methods. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, D.; Walker, I.D. Soft robotics: Biological inspiration, state of the art, and future research. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2008, 5, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudabayev, A.; Rysbek, Z.; Khassenova, R.; Varol, H.A. Human grasping database for activities of daily living with depth, color and kinematic data streams. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feix, T.; Romero, J.; Schmiedmayer, H.B.; Dollar, A.M.; Kragic, D. The GRASP Taxonomy of Human Grasp Types. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2016, 46, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stival, F.; Atzori, M. A quantitative taxonomy of human hand grasps. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2018, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiers, A.J.; Liarokapis, M.V.; Calli, B.; Dollar, A.M. Single-Grasp Object Classification and Feature Extraction with Simple Robot Hands and Tactile Sensors. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2016, 9, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Harada, K. Grasp and Manipulation of Multiple Objects. In Robotics Research; Springer: London, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.V.; Bui, T.H. Towards Safely Grasping Group Objects by Hybrid Robot Hand. In Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation Engineering (RCAE), Wuhan, China, 4–6 November 2021; pp. 389–393. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Nguyen, P.N.; Nguyen, T.; Le, T.L. Hybrid robot hand for stably manipulating one group objects. Arch. Mech. Eng. 2022, 69, 375–391. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Sunil Bohra, D.; Han, B.S.; Chow, W.T. Towards Flexible Manipulation with Wiring-Base Robot Hand. In Robot Intelligence Technology and Applications 7, RiTA 2022; Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 642. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Chow, W.T. Wiring-Claw Gripper for Soft-Stable Picking up Multiple Objects. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 3972–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agboh, W. Learning to Efficiently Plan Robust Frictional Multi-Object Grasps. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.07420. [Google Scholar]
- Agboh, W.C.; Ichnowski, J.; Goldberg, K.; Dogar, M.R. Multi-Object Grasping in the Plane. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.00229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Amatova, E.; Chen, T. Multi-Object Grasping–Types and Taxonomy. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.15276. [Google Scholar]
- Kapandji, I. The Physiology of the Joints: Lower Limb; Edinburgh Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, G. The mechanical structure of the artificial limbs. In Replacement Links and Work Aids: For War Disabled and Accident Victims; Julius Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1919; pp. 321–661. [Google Scholar]
- Napier, J.R. The prehensile movements of the human hand. J. Bone Jt. Surgery Br. Vol. 1956, 38, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadikhoshkho, Z.; Zareinia, K.; Janabi-Sharifi, F. A Brief Review on Robotic Grippers Classifications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Canadian Conference of Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Edmonton, AB, Canada, 5–8 May 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ren, L.; Chen, Y.; Niu, S.; Han, Z.; Ren, L. Bio-Inspired Soft Grippers Based on Impactive Gripping. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deimel, R.; Brock, O. A novel type of compliant and underactuated robotic hand for dexterous grasping. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2016, 35, 161–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.G.; Grioli, G.; Farnioli, E.; Serio, A.; Piazza, C.; Bicchi, A. Adaptive synergies for the design and control of the Pisa/IIT SoftHand. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.H.; Farley, C.T.; Full, R.J.; Koehl, M.; Kram, R.; Lehman, S. How animals move: An integrative view. Science 2000, 288, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J. Dexterous robotic grasping of delicate fruits aided with a multi-sensory e-glove and manual grasping analysis for damage-free manipulation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 190, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, A.M.; Howe, R.D. The Highly Adaptive SDM Hand: Design and Performance Evaluation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisman, J.; Kanojia, C.; Zeid, I. Graspar: A flexible, easily controllable robotic hand. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 1996, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odhner, L.U.; Jentoft, L.P.; Claffee, M.R.; Corson, N.; Tenzer, Y.; Ma, R.R.; Buehler, M.; Kohout, R.; Howe, R.D.; Dollar, A.M. A compliant, underactuated hand for robust manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 736–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocarlie, M.; Hicks, F.M.; Holmberg, R.; Hawke, J.; Schlicht, M.; Gee, J.; Stanford, S.; Bahadur, R. The Velo gripper: A versatile single-actuator design for enveloping, parallel and fingertip grasps. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2014, 33, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Schunk, H. Grippers in Motion. In Grippers in Motion; Wolf, A., Schunk, H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birglen, L.; Laliberté, T.; Gosselin, C. Underactuated Robotic Hands; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, S.; Umetani, Y. The development of soft gripper for the versatile robot hand. Mech. Mach. Theory 1978, 13, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2F-85 and 2F-140 Grippers. Available online: https://robotiq.com/products/2f85-140-adaptive-robot-gripper (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Festo. Mechanical Grippers. Available online: https://www.festo.com/hk/en/c/products/industrial-automation/pneumatic-grippers/mechanical-grippers-id_pim415/ (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Bullock, I.M.; Dollar, A.M. Classifying human manipulation behavior. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, Zurich, Switzerland, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, I.M.; Ma, R.R.; Dollar, A.M. A hand-centric classification of human and robot dexterous manipulation. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2012, 6, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iberall, T. Human Prehension and Dexterous Robot Hands. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1997, 16, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchi, A.; Marigo, A. Dexterous grippers: Putting nonholonomy to work for fine manipulation. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2002, 21, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Cannella, F.; Canali, C.; D’Imperio, M.; Hauptman, T.; Sofia, G.; Caldwell, D. A study on data-driven in-hand twisting process using a novel dexterous robotic gripper for assembly automation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 September 2014; pp. 4470–4475. [Google Scholar]
- Tincani, V.; Grioli, G.; Catalano, M.G.; Garabini, M.; Grechi, S.; Fantoni, G.; Bicchi, A. Implementation and control of the velvet fingers: A dexterous gripper with active surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 2744–2750. [Google Scholar]
- Samuels, M.; Lu, L.; Wang, C. Two-finger Multi-DOF Folding Robot Grippers. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeve, A.; Ven, O.; Vogel, J.; Breedveld, P.; Dankelman, J. Vacuum packed particles as flexible endoscope guides with controllable rigidity. Granul. Matter 2010, 12, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courchesne, J.; Cardou, P.; Rachide Onadja, P.A. A compact underactuated gripper with two fingers and a retractable suction cup. Front. Robot. AI 2023, 10, 1066516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, W.T. BarrettHand Grasper: Programmably Flexible Part Handling and Assembly. In Humanoid Robotics: A Reference; Goswami, A., Vadakkepat, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, S.B.; Dollar, A.M. An Adaptive Three-Fingered Prismatic Gripper with Passive Rotational Joints. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2016, 1, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocarlie, M.; Miller, A.; Allen, P. Grasp analysis using deformable fingers. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; pp. 4122–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanafusa, H.; Asada, H.H. A robot hand with elastic fingers and its application to assembly process. IFAC-PapersOnLine 1977, 10, 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A. Shape for Contact. Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sompur, V.; Thondiyath, A.; SKM, V. Design and Development of a Bio-Inspired Novel 3-Fingered Gripper Platform. In Proceedings of the AIR2021: Advances in Robotics-5th International Conference of the Robotics Society, New York, NY, USA, 1 June 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.; Iversen, E.; Knutti, D.; Johnson, R.; Biggers, K. Design of the Utah/MIT dextrous hand. In Proceedings of the 1986 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–10 April 1986; Volume 3, pp. 1520–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen, S.C.; Wood, J.E.; Knutti, D.; Biggers, K.B. The UTAH/MIT dextrous hand: Work in progress. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1984, 3, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggers, K.; Jacobsen, S.; Gerpheide, G. Low level control of the Utah/MIT dextrous hand. In Proceedings of the 1986 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–10 April 1986; Volume 3, pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Salisbury, J.K.; Craig, J.J. Articulated Hands: Force Control and Kinematic Issues. Int. J. Robot. Res. 1982, 1, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jau, B. Dexterous telemanipulation with four fingered hand system. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 1995 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nagoya, Japan, 21–27 May 1995; Volume 1, pp. 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulos, K.; Van Riper, J.; Zink, A.; Stephanou, H. Kinematic analysis and position/force control of the Anthrobot dextrous hand. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 1997, 27, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekey, G.A.; Tomovic, R.; Zeljkovic, I. Control architecture for the Belgrade/USC hand. In Dextrous Robot Hands; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rosheim, M.E. Robot Evolution: The Development of Anthrobotics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.R.; Huang, H.P. Integrating fuzzy control of the dexterous National Taiwan University (NTU) hand. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 1996, 1, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfass, J.; Hirzinger, G.; Knoch, S.; Liu, H. DLR’s multisensory articulated hand. I. Hard- and software architecture. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Cat. No. 98CH36146), Leuven, Belgium, 20 May 1998; Volume 3, pp. 2081–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meusel, P.; Seitz, N.; Willberg, B.; Hirzinger, G.; Jin, M.; Liu, Y.; Wei, R.; Xie, Z. The modular multisensory DLR-HIT-Hand. Mech. Mach. Theory 2007, 42, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, K.; Meusel, P.; Seitz, N.; Hirzinger, G.; Jin, M.; Liu, Y.; Fan, S.; Lan, T.; Chen, Z. Multisensory five-finger dexterous hand: The DLR/HIT Hand II. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 3692–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Komatsu, T.; Uchiyama, K. Dexterous anthropomorphic robot hand with distributed tactile sensor: Gifu hand II. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2002, 7, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Eppner, C.; Levine, S.; Abbeel, P. Learning Dexterous Manipulation for a Soft Robotic Hand from Human Demonstrations. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 3786–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, P.; Kumar, S.; Sahin, F. Design of a Soft Robotic Gripper for Improved Grasping with Suction Cups. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), Bari, Italy, 6–9 October2019; pp. 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Kawamura, S.; Hirai, S. Comparison of different soft grippers for lunch box packaging. Robot. Biomimetics 2017, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petković, D.; Issa, M.; Pavlović, N.D.; Zentner, L.; Ćojbašić, Ž. Adaptive neuro fuzzy controller for adaptive compliant robotic gripper. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 13295–13304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petković, D.; Pavlović, N.D.; Shamshirband, S.; Badrul Anuar, N. Development of a new type of passively adaptive compliant gripper. Ind. Robot. Int. J. 2013, 40, 610–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belzile, B.; Birglen, L. A compliant self-adaptive gripper with proprioceptive haptic feedback. Auton. Robot. 2014, 36, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Huang, G.F.; Chiu, C.H.; Pai, T.Y. Topology synthesis and optimal design of an adaptive compliant gripper to maximize output displacement. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2018, 90, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Hirose, S.; Yoshinada, H. Design and experiments for a coupled tendon-driven manipulator. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1993, 13, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Dollar, A. Yale OpenHand Project: Optimizing Open-Source Hand Designs for Ease of Fabrication and Adoption. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2017, 24, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfagharian, A.; Gharaie, S.; Gregory, J.; Bodaghi, M.; Kaynak, A.B.; Nahavandi, S. A Bioinspired Compliant 3D-Printed Soft Gripper. Soft Robot. 2021, 9, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manti, M.; Cacucciolo, V.; Cianchetti, M. Stiffening in Soft Robotics: A Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2016, 23, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beddow, L.; Wurdemann, H.; Kanoulas, D. A Caging Inspired Gripper using Flexible Fingers and a Movable Palm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 7195–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Gerez, L.; Chapman, J.; Liarokapis, M. A Tendon-Driven, Preloaded, Pneumatically Actuated, Soft Robotic Gripper with a Telescopic Palm. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), New Haven, CT, USA, 15 May–15 July 2020; pp. 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Ismail, A. On the development of a new pneumatic versatile gripper. Proc. JFPS Int. Symp. Fluid Power 1993, 1993, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollar, A.M.; Howe, R.D. The SDM Hand: A Highly Adaptive Compliant Grasper for Unstructured Environments. In Experimental Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoga, K.; Goldenberg, A. Soft materials for robotic fingers. In Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Nice, France, 12–14 May 1992; Volume 2, pp. 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutkosky, M.; Jourdain, J.; Wright, P. Skin materials for robotic fingers. In Proceedings of the 1987 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Raleigh, NC, USA, 31 March–3 April 1987; Volume 4, pp. 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Todorov, E. Design of a highly biomimetic anthropomorphic robotic hand towards artificial limb regeneration. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, W.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Purnawali, H.; Tang, C. Stimulus-responsive shape memory materials: A review. Mater. Des. 2012, 33, 577–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkman, G. Advances in shape memory polymer actuation. Mechatronics 2000, 10, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, C.C.; Lin, C.M.; Fan, C.H. A Self-Sensing Microgripper Module with Wide Handling Ranges. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, J.-y.; Wakimoto, S.; Satoh, T.; Saga, N.; Suzumori, K. Design of a variable-stiffness robotic hand using pneumatic soft rubber actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, J.; Lipson, H. The JamHand: Dexterous manipulation with minimal actuation. Soft Robot. 2017, 4, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, O.; Youssef, G.; Nacy, S.; Jameel Al-Tamimi, A.N.; Hussein, O.; Abbood, W.T.; Abdullah, O.I.; AL-Karkhi, N.K. A Systematic Approach to Stable Grasping of a Two-Finger Robotic Hand Activated by Jamming of Granular Media. Electronics 2023, 12, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Dhyan, S.B.; Han, B.S.; Chow, W.T. Universally Grasping Objects with Granular—Tendon Finger: Principle and Design. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.; Bruzewicz, D.; Weibel, D.; Whitesides, G. Microsolidics: Fabrication of three-dimensional metallic microstructures in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintake, J.; Schubert, B.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H.; Floreano, D. Variable stiffness actuator for soft robotics using dielectric elastomer and low-melting-point alloy. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Niu, X.; Yu, Z.; Hu, W.; Brochu, P.; Pei, Q. Compliant silver nanowire-polymer composite electrodes for bistable large strain actuation. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besse, N.; Rosset, S.; Zarate, J.J.; Shea, H. Flexible active skin: Large reconfigurable arrays of individually addressed shape memory polymer actuators. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, K.; Sugitani, K.; Morimoto, N.; Sakaguchi, S.; Noritsugu, T.; Mukai, T. Pneumatic artificial rubber muscle using shape-memory polymer sheet with embedded electrical heating wire. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 125005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, D.K.; Sakhaei, A.H.; Layani, M.; Zhang, B.; Ge, Q.; Magdassi, S. Highly stretchable and UV curable elastomers for digital light processing based 3D printing. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrasher, C.J.; Schwartz, J.J.; Boydston, A.J. Modular elastomer photoresins for digital light processing additive manufacturing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39708–39716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ahn, S. Non-intrusive load monitoring system for anomaly detection based on energy disaggregation by cascading semi-supervised learning and deep learning methods. Soft Robot. 2017, 3, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzeh, A.; Paik, J. Grasp Mode and Compliance Control of an Underactuated Origami Gripper Using Adjustable Stiffness Joints. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 2165–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzeh, A.; Paik, J. An under-actuated origami gripper with adjustable stiffness joints for multiple grasp modes. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 055035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzeh, A.; Salerno, M.; Paik, J. Stiffness Control with Shape Memory Polymer in Underactuated Robotic Origamis. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hao, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, Z. A novel design of shape-memory alloy-based soft robotic gripper with variable stiffness. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881420907813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Aswal, V.K.; Sastry, P.U.; Rana, D.; Maiti, P. Reversible Bidirectional Shape Memory Effect in Polyurethanes through Molecular Flipping. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 4889–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Su, H.-J. Modeling and Validation of a Novel Bending Actuator for Soft Robotics Applications. Soft Robot. 2016, 3, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinpoor, M.; Bar-Cohen, Y.; Simpson, J.O.; Smith, J. Ionic polymer-metal composites (IPMCs) as biomimetic sensors, actuators and artificial muscles—A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzumori, K.; Iikura, S.; Tanaka, H. Applying a flexible microactuator to robotic mechanisms. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 1992, 12, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilievski, F.; Mazzeo, A.D.; Shepherd, R.F.; Chen, X.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft robotics for chemists. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Takemura, K.; Yokota, S.; Edamura, K. A robot hand using electro-conjugate fluid. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 5923–5928. [Google Scholar]
- Niiyama, R.; Sun, X.; Sung, C.; An, B.; Rus, D.; Kim, S. Pouch motors: Printable soft actuators integrated with computational design. Soft Robot. 2015, 2, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Ding, N. Design and Implementation of CCRobot-II: A Palm-based Cable Climbing Robot for Cable-stayed Bridge Inspection. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 9747–9753. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, J.; Polin, J.; Sreenath, K.; Kumar, V. Avian-Inspired Grasping for Quadrotor Micro UAVs, Volume 6A: 37th Mechanisms and Robotics Conference. In International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, D. A Two-Finger Soft-Robotic Gripper With Enveloping and Pinching Grasping Modes. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Seo, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, W.J.; Yi, B.J. Design and Implementation of a Multi-Function Gripper for Grasping General Objects. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyonoputro, J.C.; Wan, W.; Akanesuvan, K.; Harada, K. A Double-jaw Hand that Mimics A Mouth of the Moray Eel. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 12–15 December 2018; pp. 1527–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Feliu-Talegon, D.; Acosta, J.; Suarez, A.; Ollero, A. A Bio-Inspired Manipulator with Claw Prototype for Winged Aerial Robots: Benchmark for Design and Control. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Sun, Y. Design and Experiment of a Deformable Bird-inspired UAV Perching Mechanism. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, P.; Guo, G.; Zhang, X. Perching and Grasping Mechanism Inspired by a Bird—Claw. Machines 2022, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Mehta, A. Origami-based integration of robots that sense, decide, and respond. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, N.D.; Linh, H.N.; Thanh-Phong, D.; Ngoc, L.C. Multi-objective optimization design for a sand crab-inspired compliant microgripper. Microsyst. Technol. 2019, 25, 3991–4009. [Google Scholar]
- Kellaris, N.; Rothemund, P.; Zeng, Y.; Mitchell, S.K.; Smith, G.M.; Jayaram, K.; Keplinger, C. Spider-Inspired Electrohydraulic Actuators for Fast, Soft-Actuated Joints. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooks, W. Fin Ray® Effect Inspired Soft Robotic Gripper: From the RoboSoft Grand Challenge toward Optimization. Front. Robot. AI 2016, 3, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suder, J.; Bobovský, Z.; Mlotek, J.; Vocetka, M.; Oščádal, P.; Zeman, Z. Structural Optimization Method of a FinRay Finger for the Best Wrapping of Object. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Kang, R. Design of a Flexible Capture Mechanism Inspired by Sea Anemone for Non-cooperative Targets. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2022, 34, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Song, R.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, L.; Liu, F.; Jiang, P.; Sindersberger, D.; Monkman, G.J.; Guo, J. Bio-Inspired Shape-Adaptive Soft Robotic Grippers Augmented with Electroadhesion Functionality. Soft Robot. 2019, 6, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kier, W.M.; Stella, M.P. The arrangement and function of octopus arm musculature and connective tissue. J. Morphol. 2007, 268, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, E.B.L.; Hanlon, R.T. Octopus arms exhibit exceptional flexibility. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, F.W. Octopus sucker-arm coordination in grasping and manipulation. Am. Malacol. Bull. 2008, 24, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.N.; Hochner, B.; Kuba, M.J. Octopus arm movements under constrained conditions: Adaptation, modification and plasticity of motor primitives. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglielmino, E.; Godage, I.; Zullo, L.; Caldwell, D.G. A pragmatic bio-inspired approach to the design of octopus-inspired arms. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 4577–4582. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, I.D.; Dawson, D.M.; Flash, T.; Grasso, F.W.; Hanlon, R.T.; Hochner, B.; Kier, W.M.; Pagano, C.C.; Rahn, C.D.; Zhang, Q.M. Continuum robot arms inspired by cephalopods. In Proceedings of the Unmanned Ground Vehicle Technology VII; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 5804, pp. 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- McMahan, W.; Walker, I.D. Octopus-inspired grasp-synergies for continuum manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Guilin, China, 19–23 December 2009; pp. 945–950. [Google Scholar]
- Grissom, M.D.; Chitrakaran, V.; Dienno, D.; Csencits, M.; Pritts, M.; Jones, B.; McMahan, W.; Dawson, D.; Rahn, C.; Walker, I. Design and experimental testing of the OctArm soft robot manipulator. In Proceedings of the Unmanned Systems Technology VIII; SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 6230. [Google Scholar]
- Calisti, M.; Giorelli, M.; Levy, G.; Mazzolai, B.; Hochner, B.; Laschi, C.; Dario, P. An octopus-bioinspired solution to movement and manipulation for soft robots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2011, 6, 036002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Cianchetti, M.; Dario, P.; Laschi, C. Soft-robotic arm inspired by the octopus: II. From artificial requirements to innovative technological solutions. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2012, 7, 025005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschi, C.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Margheri, L.; Follador, M.; Dario, P. Soft Robot Arm Inspired by the Octopus. Adv. Robot. 2012, 26, 709–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fras, J.; Macias, M.; Noh, Y.; Althoefer, K. Fluidical bending actuator designed for soft octopus robot tentacle. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; pp. 253–257. [Google Scholar]
- Pi, J.; Liu, J.; Zhou, K.; Qian, M. An Octopus-Inspired Bionic Flexible Gripper for Apple Grasping. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzolai, B.; Mondini, A.; Tramacere, F.; Riccomi, G.; Sadeghi, A.; Giordano, G.; Del Dottore, E.; Scaccia, M.; Zampato, M.; Carminati, S. Octopus-Inspired Soft Arm with Suction Cups for Enhanced Grasping Tasks in Confined Environments. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Domel, A.G.; An, N.; Green, C.; Gong, Z.; Wang, T.; Knubben, E.M.; Weaver, J.C.; Bertoldi, K.; Wen, L. Octopus Arm-Inspired Tapered Soft Actuators with Suckers for Improved Grasping. Soft Robot. 2020, 7, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.; Pang, C. A wet-tolerant adhesive patch inspired by protuberances in suction cups of octopi. Nature 2017, 546, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zheng, X.; Liu, R.; Hou, N.; Afridi, W.H.; Afridi, R.H.; Guo, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Xie, G. Glowing Sucker Octopus (Stauroteuthis syrtensis)-Inspired Soft Robotic Gripper for Underwater Self-Adaptive Grasping and Sensing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Du, Y. A Pneumatic Novel Combined Soft Robotic Gripper with High Load Capacity and Large Grasping Range. Actuators 2022, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, P.; Ananda, C.; Rafael, P.B.; Carlos, A.R. Closed structure soft robotic gripper. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; pp. 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, B.P.; Devasia, F.; Asok, A.; Jayadevu, P.; Baby, R. Implementation of an origami inspired gripper robot for picking objects of variable geometry. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 58, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sage, H.G.; Mathelin, M.F.D.; Ostertag, E. Robust control of robot manipulators: A survey. Int. J. Control 1999, 72, 1498–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lakshmanan, S. Continuum Robots for Manipulation Applications: A Survey. J. Robot. 2020, 2020, 4187048. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, M.; Sadati, S.M.H.; Dong, X.; Mohammad, A.; Walker, I.D.; Bergeles, C.; Xu, K.; Axinte, D.A. Continuum Robots: An Overview. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirikjian, G. Conformational Modeling of Continuum Structures in Robotics and Structural Biology: A Review. Adv. Robot. 2015, 29, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, J. Webster, I.; Jones, B.A. Design and Kinematic Modeling of Constant Curvature Continuum Robots: A Review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar]
- Uppalapati, N.K.; Krishnan, G. Towards Pneumatic Spiral Grippers: Modeling and Design Considerations. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Hu, L.; Xu, Y. Recent Advances in Design and Actuation of Continuum Robots for Medical Applications. Actuators 2020, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgner-Kahrs, J.; Rucker, D.C.; Choset, H. Continuum Robots for Medical Applications: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, P.; Hensman, S.; Haechler, V.; Milinkovitch, M.C. Elephants evolved strategies reducing the biomechanical complexity of their trunk. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 4727–4737.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, A.K.; Reidenberg, J.S.; Wu, J.N.; Tang, C.Y.; Seleb, B.; Mancebo, J.; Elgart, N.; Hu, D.L. Elephant trunks use an adaptable prehensile grip. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2023, 18, 026008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier-Skolnikoff, S.; Liska, J. Tool use by wild and captive elephants. Anim. Behav. 1993, 46, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnik, J.M.; Brubaker, D.L.; Dale, R.; Tiller, L.N.; Mumby, H.S.; Clayton, N.S. Elephants have a nose for quantity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 12566–12571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshani, J.; Kupsky, W.J.; Marchant, G.H. Elephant brain: Part I: Gross morphology, functions, comparative anatomy, and evolution. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 70, 124–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.F.; Li, D.; Chen, Z.; George, R.T. Flexible Robot Manipulators and Grippers: Relatives of Elephant Trunks and Squid Tentacles. In Robots and Biological Systems: Towards a New Bionics? Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 475–494. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Han, Y.J.; Han, M.W. A Shape Memory Alloy-Based Soft Actuator Mimicking an Elephant—Trunk. Polymers 2023, 15, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.G.; Lobovsky, M.B.; Keating, S.J.; Setapen, A.M.; Gero, K.I.; Hosoi, A.E.; Iagnemma, K.D. Design and Analysis of a Robust, Low-cost, Highly Articulated manipulator enabled by jamming of granular media. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, St Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 4328–4333. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, V.C.; Horn, R.C. Tensor Arm Manipulator. U.S. Patent US3497083A, 24 February 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, M.W.; Walker, I.D. Kinematics and the Implementation of an Elephant’s Trunk Manipulator and Other Continuum Style Robots. J. Robot. Syst. 2003, 20, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Li, S. Kinematic Analysis of Bionic Elephant Trunk Robot Based on Flexible Series-Parallel Structure. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Kan, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Rajabi, H.; Wu, Z.; Peng, H.; Wu, J. A Preprogrammable Continuum Robot Inspired by Elephant Trunk for Dexterous Manipulation. Soft Robot. 2023, 10, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Teeple, C.; Charles, N.; Jung, Y.; Baum, D.; Weaver, J.C.; Mahadevan, L.; Wood, R. Active entanglement enables stochastic, topological grasping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2209819119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, R.V.; Branch, J.L.; Fish, C.R.; Jin, L.; Shepherd, R.F.; Nunes, R.M.D.; Suo, Z.; Whitesides, G.M. Robotic Tentacles with Three-Dimensional Mobility Based on Flexible Elastomers. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Lee, K. Three-Dimensional Printable Origami Twisted Tower: Design, Fabrication, and Robot Embodiment. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.B.; Godage, I.S. Validation of an Extensible Rod Model for Soft continuum Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–18 April 2019; pp. 711–716. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.M. Cephalopod Sucker Design and the Physical Limits to Negative Pressure. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Wright, E.; Bonser, R.H.; Jeronimidis, G. Development of Biomimetic Squid-Inspired Suckers. J. Bionic Eng. 2012, 9, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, A.; Almubarak, Y.; Rupawat, Y.M.; Warren, J.; Tadesse, Y. Poly-Saora robotic jellyfish: Swimming underwater by twisted and coiled polymer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 045039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessler, M.; Wood, R.J. Ultra-gentle soft robotic fingers induce minimal transcriptomic response in a fragile marine animal. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R157–R158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nate, I.; Wang, Z.; Kameoka, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Nahin Islam, S.M.; Kawakami, M.; Furukawa, H.; Hirai, S. Jellyfish Grasping and Transportation with a Wire-Driven Gripper and Deep Learning Based Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Sapporo, Japan, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 1018–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, A.; Kulkarni, A.; Tadesse, Y. FludoJelly: Experimental Study on Jellyfish-Like Soft Robot Enabled by Soft Pneumatic Composite (SPC). Robotics 2019, 8, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Joo, H.J.; Song, S.; Hu, W.; Keplinger, C.; Sitti, M. A versatile jellyfish-like robotic platform for effective underwater propulsion and manipulation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg0292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devereux, D.; Nutter, P.; Richardson, R. Determining an object’s shape with a blind tactile manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 11–15 October 2009; pp. 4745–4750. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Fan, S.; Ni, F.; Liu, H. Biologically inspired guidelines for the design of the Hyper-Dexterous Manipulator. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Harbin, China, 7–10 August 2016; pp. 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Shi, G.; Shi, Y. Modeling and analysis of a parallel continuum robot using artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics (ICM), Churchill, Australia, 13–15 February 2017; pp. 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Maghooa, F.; Stilli, A.; Noh, Y.; Althoefer, K.; Wurdemann, H.A. Tendon and pressure actuation for a bio-inspired manipulator based on an antagonistic principle. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 2556–2561. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao, K.; Mochiyama, H. A wire-driven continuum manipulator model without assuming shape curvature constancy. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Jin, Y. New cable-driven continuun robot with only one actuator. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Intelligent Systems (CIS) and IEEE Conference on Robotics, Automation and Mechatronics (RAM), Ningbo, China, 19–21 November 2017; pp. 693–698. [Google Scholar]
- Sadati, S.M.H.; Naghibi, S.E.; Walker, I.D.; Althoefer, K.; Nanayakkara, T. Control Space Reduction and Real-Time Accurate Modeling of Continuum Manipulators Using Ritz and Ritz–Galerkin Methods. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Li, K.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Bao, G. Bending model of a novel long-arm biomimetic robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Okinawa, Japan, 14–18 July 2017; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Santoso, J.; Skorina, E.H.; Luo, M.; Yan, R.; Onal, C.D. Design and analysis of an origami continuum manipulation module with torsional strength. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–28 September 2017; pp. 2098–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Ossiboff, R.J. Chapter 37—Serpentes. In Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals; Terio, K.A., McAloose, D., Leger, J.S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 897–919. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang, A.Y.; Gauthier, J.A. he origin of snakes: Revealing the ecology, behavior, and evolutionary history of early snakes using genomics, phenomics, and the fossil record. BMC Evol. Biol. 1996, 15, 949–958. [Google Scholar]
- Reeder, T.W.; Townsend, T.M.; Mulcahy, D.G.; Noonan, B.P.; Wood, P.L., Jr.; Sites, J.W., Jr.; Wiens, J.J. Integrated Analyses Resolve Conflicts over Squamate Reptile Phylogeny and Reveal Unexpected Placements for Fossil Taxa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ren, L. The snake-inspired robots: A review. Assem. Autom. 2021, 42, 567–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetohul, J.; Shafiee, M. Snake Robots for Surgical Applications: A Review. Robotics 2022, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, S.; Mori, M. Biologically Inspired Snake-like Robots. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April–1 May 2004; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, W.; Iñigo, R. Design of a snake-like manipulator. Robot. Auton. Syst. 1990, 6, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, Y.; Shan, H.; Ma, S. A Snake-Like Robot with Envelope Wheels and Obstacle-Aided Gaits. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehling, J.; Diftler, M.; Chu, M.; Valvo, M. A Minimally Invasive Tendril Robot for In-Space Inspection. In Proceedings of the 2006 First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob 2006), Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; pp. 690–695. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, C.; Hiott, B.; Kapadia, A.D.; Walker, I.D. Robot tongues in space: Continuum surfaces for robotic grasping and manipulation. In Proceedings of the Micro- and Nanotechnology Sensors, Systems, and Applications VIII; George, T., Dutta, A.K., Islam, M.S., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics. SPIE: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2016; Volume 9836, p. 98362B. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Chon, S.; Kim, J.; Seo, J.; Shin, D.G.; Park, S.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, J.; Jin, M.; Cho, J. Snake Robot Gripper Module for Search and Rescue in Narrow Spaces. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, M.; Thompson, A.J.; Anastasova, S.; Yang, G.Z. A Monolithic Force-Sensitive 3D Microgripper Fabricated on the Tip of an Optical Fiber Using 2-Photon Polymerization. Small 2018, 14, 1703964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, C.; Xiao, X. Design, Control and Experiment of a Snake-like Robot with Gripper. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), Kyoto, Japan, 22–26 June 2020; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.A.; Adithya, B.; Antony, P.T.B. Snake Robots for Rescue Operation. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1055. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, T.T.; Phan, P.T.; Thai, M.T.; Lovell, N.H.; Do, T.N. Bio-Inspired Conformable and Helical Soft Fabric Gripper with Variable Stiffness and Touch Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, G.; Zellmer, S.; Preller, T.; Garnweitner, G.; Raatz, A. Actuation principles for the bioinspired soft robotic manipulator spineman. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Zhuhai, China, 6–9 December 2015; pp. 1329–1336. [Google Scholar]
- Niikura, A.; Nabae, H.; Endo, G.; Gunji, M.; Mori, K.; Niiyama, R.; Suzumori, K. Giraffe Neck Robot: First Step Toward a Powerful and Flexible Robot Prototyping Based on Giraffe Anatomy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 3539–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchige, D.D.K.; Godage, I.S. Hybrid Soft Robots Incorporating Soft and Stiff Elements. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), San Diego, CA, USA, 14–17 April 2022; pp. 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Freris, N.M. Bioinspired Soft Spiral Robots for Versatile Grasping and Manipulation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.09861. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, A.; Bels, V. Biomechanics and kinematics of limb-based locomotion in lizards: Review, synthesis and prospectus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 131, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autumn, K.; Full, R.J. Adhesive force of a single gecko foot-hair. Nature 2000, 405, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesika, N.S.; Zeng, H.; Kristiansen, K.; Zhao, B.; Tian, Y.; Autumn, K.; Israelachvili, J. Gecko adhesion pad: A smart surface? J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 464132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, D.; Chen, C.; Zhang, J.; Duan, W. Theoretical modelling of soft robotic gripper with bioinspired fibrillar adhesives. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 2250–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chary, S.; Das, S.; Tamelier, J.; Pesika, N.S.; Turner, K.L.; Israelachvili, J.N. Gecko-Inspired Dry Adhesive for Robotic Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3010–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikdar, S.; Rahman, M.H.; Siddaiah, A.; Menezes, P.L. Gecko-Inspired Adhesive Mechanisms and Adhesives for Robots—A Review. Robotics 2022, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, W.; Brouwer, D.; Cutkosky, M.R. From grasping to manipulation with gecko-inspired adhesives on a multifinger gripper. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabi9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, P.; Suresh, S.A.; Ruffatto, D.; Cutkosky, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Parness, A. A Soft Robotic Gripper with Gecko-Inspired Adhesive. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadehyazdi, V.; Bonthron, M.; Spenko, M. An Electrostatic/Gecko-Inspired Adhesives Soft Robotic Gripper. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4679–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.K.; Hajj-Ahmad, A.; Cutkosky, M.R. Hybrid electrostatic and gecko-inspired gripping pads for manipulating bulky, non-smooth items. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 30, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, H.; Shao, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Chen, X. An electrically active gecko-effect soft gripper under a low voltage by mimicking gecko’s adhesive structures and toe muscles. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 5599–5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, T.T.; Quek, J.J.S.; Thai, M.T.; Phan, P.T.; Lovell, N.H.; Do, T.N. Soft robotic fabric gripper with gecko adhesion and variable stiffness. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2021, 323, 112673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modabberifar, M.; Spenko, M. A shape memory alloy-actuated gecko-inspired robotic gripper. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2018, 276, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwon, M.; Koh, J.s. Soft Directional Adhesion Gripper Fabricated by 3D Printing Process for Gripping Flexible Printed Circuit Boards. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2009, 9, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Sun, F. A gecko-inspired adhesive robotic end effector for critical-contact manipulation. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 182203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, H.; Shao, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Switchable Adhesion for Nonflat Surfaces Mimicking Geckos’ Adhesive Structures and Toe Muscles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39745–39755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhao, Z. Magnetic-field-driven switchable adhesion of NdFeB/PDMS composite with gecko-like surface. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, X.; Shao, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, H. Gecko-Effect Inspired Soft Gripper with High and Switchable Adhesion for Rough Surfaces. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1900875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, E.W. Grasping Without Squeezing: Design and Modeling of Shear-Activated Grippers. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2018, 34, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federle, W.; Barnes, W.; Baumgartner, W.; Drechsler, P.; Smith, J. Wet but not slippery: Boundary friction in tree frog adhesive toe pads. J. R. Soc. Interface 2006, 3, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. Wet adhesion with application to tree frog adhesive toe pads and tires. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 376110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Meng, F.; Tan, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, B.; Xiao, K.; Xue, L. Gradient Micropillar Array Inspired by Tree Frog for Robust Adhesion on Dry and Wet Surfaces. Biomimetics 2022, 7, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, M.; Tresztenyak, A.; Fülöp, G.; Jahr, W.; Prinz, A.; Prinz, I.; Danzl, J.G.; Schütz, G.J.; Sevcsik, E. A Fast and Simple Contact Printing Approach to Generate 2D Protein Nanopatterns. Front. Chem. 2019, 6, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Kovalev, A.; Eichler-Volf, A.; Steinhart, M.; Gorb, S.N. Humidity-enhanced wet adhesion on insect-inspired fibrillar adhesive pads. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrs, C.; Azimi, A.; He, P. Wetting on Micropatterned Surfaces: Partial Penetration in the Cassie State and Wenzel Deviation Theoretically Explained. Langmuir 2019, 35, 15421–15430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Sanz, B.; Luo, A.; Turner, K.T.; Wang, X.; Tan, D.; Zhang, R.; Du, H.; Steinhart, M.; Mijangos, C.; et al. Hybrid Surface Patterns Mimicking the Design of the Adhesive Toe Pad of Tree Frog. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9711–9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Li, M.; Dai, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Key parameters of biomimetic patterned surface for wet adhesion. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2018, 82, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Meng, F.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Tan, D.; Li, Q.; Shi, Z.; Shi, K.; Chen, W.; Liu, S.; et al. Tree Frog-Inspired Micropillar Arrays with Nanopits on the Surface for Enhanced Adhesion under Wet Conditions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19116–19122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Tan, D.; Meng, F.; Yang, B.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Nie, C.; Liu, S.; Xue, L. Adhesion Enhancement of Micropillar Array by Combining the Adhesive Design from Gecko and Tree Frog. Small 2021, 17, 2005493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langowski, J.K.A.; Dodou, D.; Kamperman, M.; van Leeuwen, J.L. Tree frog attachment: Mechanisms, challenges, and perspectives. Front. Zool. 2018, 15, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, X.; Xu, X.; Teng, P.; Wang, S. Recent progress of tree frog toe pads inspired wet adhesive materials. Biosurf. Biotribol. 2022, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langowski, J.K.A.; Dodou, D.; van Assenbergh, P.; van Leeuwen, J.L. Design of Tree-Frog-Inspired Adhesives. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2020, 64, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Long, G.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Chang, Z. An Optimal Wet Friction Plate Inspired by Biological Surface Patterns. J. Bionic Eng. 2018, 15, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, K. Surface Texture of Deformable Robotic Fingertips for a Stable Grasp Under Both Dry and Wet Conditions. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 2048–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.S. Milliscale Features Increase Friction of Soft Skin in Lubricated Contact. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4781–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.V.; Huynh, N.V.; Phan, T.T.; Ho, V.A. Soft grasping with wet adhesion: Preliminary evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018; pp. 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.V.; Ho, V. Mechanics of wet adhesion in soft interaction with patterned morphology. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2018, 14, 016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nguyen, P.; Ho, V.A. Wet Adhesion of Soft Curved Interfaces with Micro Pattern. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 4273–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.V.; Ho, V.A. Grasping Interface with Wet Adhesion and Patterned Morphology: Case of Thin Shell. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.N.; Dang, L.M.; Lee, J.; Nguyen, P.V. Load-Carrying Capacity of Ultra-Thin Shells with and without CNTs Reinforcement. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Pham, V.C.; Tan, Y.; Ho, V.A. Toward a Tactile Ontology for Semantic Interoperability of the Tactile Internet. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Semantic Computing (ICSC), Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 26–28 January 2022; pp. 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, P.V.; Luu, Q.; Takamura, Y.; Ho, V. Wet Adhesion of Micro-patterned Interfaces for Stable Grasping of Deformable Objects. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 9213–9219. [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher, B.A.; Motta, P.J. Suction disk performance of echeneid fishes. Can. J. Zool. 2006, 84, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wainwright, D.K.; Kenaley, C.P.; Gong, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Guan, J.; Wang, T.; et al. A biorobotic adhesive disc for underwater hitchhiking inspired by the remora suckerfish. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaan8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zi, P.; Xu, K.; Tian, Y.; Ding, X. A mechanical adhesive gripper inspired by beetle claw for a rock climbing robot. Mech. Mach. Theory 2023, 181, 105168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, Y.; Tian, Y. An Underactuated Adaptive Microspines Gripper for Rough Wall. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Z. A Mathematical Modeling Method Elucidating the Integrated Gripping Performance of Ant Mandibles and Bio-inspired Grippers. J. Bionic Eng. 2020, 17, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhakypov, Z.; Paik, J. Designing minimal and scalable insect-inspired multi-locomotion millirobots. Nature 2019, 571, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiao, N.; Tung, S.; Liu, L. Target clamping and cooperative motion control of ant robots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2019, 14, 066015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Han, X.; Jing, Y.; Guo, N.; Wan, F.; Song, C. Rigid–Soft Interactive Design of a Lobster-Inspired Finger Surface for Enhanced Grasping Underwater. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 787187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, T.; Agrawal, S.K.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, J. A Bioinspired Soft Swallowing Gripper for Universal Adaptable Grasping. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 36–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Liao, B.; Lang, X.; Zhao, Z.L.; Yuan, W.; Feng, X.Q. Bionic torus as a self-adaptive soft grasper in robots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 023701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, X. Grasping Performance Analysis and Comparison of Multi-Chamber Ring-Shaped Soft Grippers. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washio, S.; Gilday, K.; Iida, F. Design and Control of a Multi-Modal Soft Gripper Inspired by Elephant Fingers. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 4228–4235. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.; Chen, J.Q.; Sun, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.L. A Chameleon Tongue Inspired Shooting Manipulator with Vision-Based Localization and Preying. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 4923–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Jung, G.P. Snatcher: A Highly Mobile Chameleon-Inspired Shooting and Rapidly Retracting Manipulator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 6097–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Ahn, J.; Ha, J.H.; Ko, J.; Hwang, S.H.; Jeon, S.; Bok, M.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, I. Biomimetic, Programmable, and Part-by-Part Maneuverable Single-Body Shape-Morphing Film. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhong, Y.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Y.; Yang, H.; et al. A Bioinspired Stress-Response Strategy for High-Speed Soft Grippers. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cooper, L.P.; Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Fok, M.P. Twining plant inspired pneumatic soft robotic spiral gripper with a fiber optic twisting sensor. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 35158–35167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, M.; Frazelle, C.; Walker, I.D.; Kapadia, A.; Lee, J.H. Exploration and Inspection with Vine-Inspired Continuum Robots. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May2018; pp. 5526–5533. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, I.D. Biologically inspired vine-like and tendril-like robots. In Proceedings of the 2015 Science and Information Conference (SAI), London, UK, 28–30 July 2015; pp. 714–720. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, F.; Lyu, L.; He, Y. A 3D Printed Paper-Based Thermally Driven Soft Robotic Gripper Inspired by Cabbage. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 023701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruhn, B.R.; Schroeder, T.B.H.; Li, S.; Billeh, Y.N.; Wang, K.W.; Mayer, M. Osmosis-Based Pressure Generation: Dynamics and Application. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; D’Ambrosio, N.; Liu, P.; Pasini, D.; Ma, L. Shape memory mechanical metamaterials. Mater. Today 2023, 66, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Dhyan, S.B.; Hoang, C.C.; Han, B.S.; Tan, J.Y.; Chow, W.T. Mitigate Inertia for Wrist and Forearm Towards Safe Interaction in 5-DOF Cable-Driven Robot Arm. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Seattle, WA, USA, 27 June–3 July 2023; pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.P.; Dhyan, S.B.; Mai, V.; Han, B.S.; Chow, W.T. Bioinspiration and Biomimetic Art in Robotic Grippers. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14091772
Nguyen VP, Dhyan SB, Mai V, Han BS, Chow WT. Bioinspiration and Biomimetic Art in Robotic Grippers. Micromachines. 2023; 14(9):1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14091772
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Van Pho, Sunil Bohra Dhyan, Vu Mai, Boon Siew Han, and Wai Tuck Chow. 2023. "Bioinspiration and Biomimetic Art in Robotic Grippers" Micromachines 14, no. 9: 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14091772
APA StyleNguyen, V. P., Dhyan, S. B., Mai, V., Han, B. S., & Chow, W. T. (2023). Bioinspiration and Biomimetic Art in Robotic Grippers. Micromachines, 14(9), 1772. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14091772








