Euler Force-Driven Siphon Valve Control for Precise Sequential Release in Centrifugal Microfluidic Chips
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
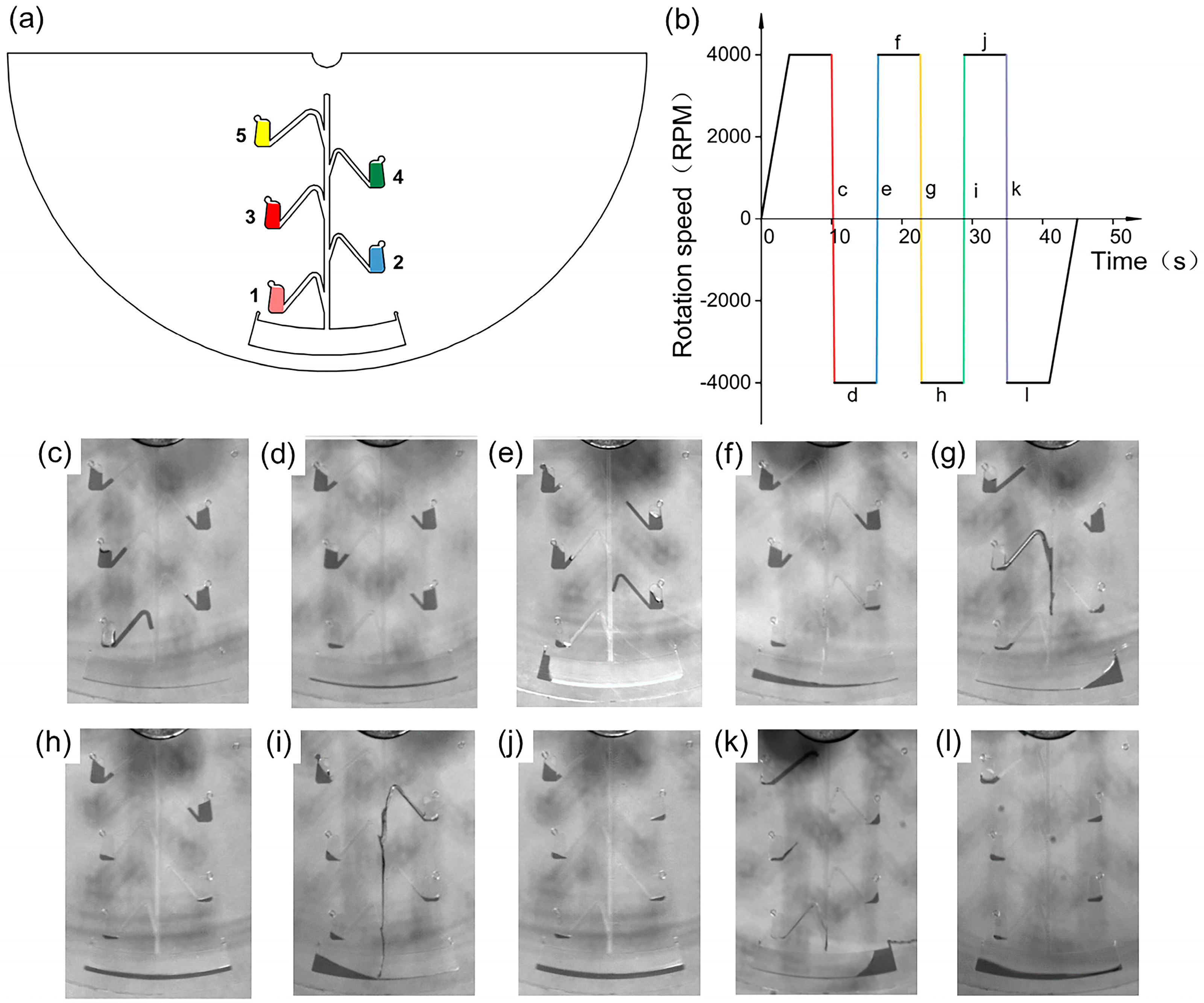
2.2. Equipment Development
3. Results and Discussion
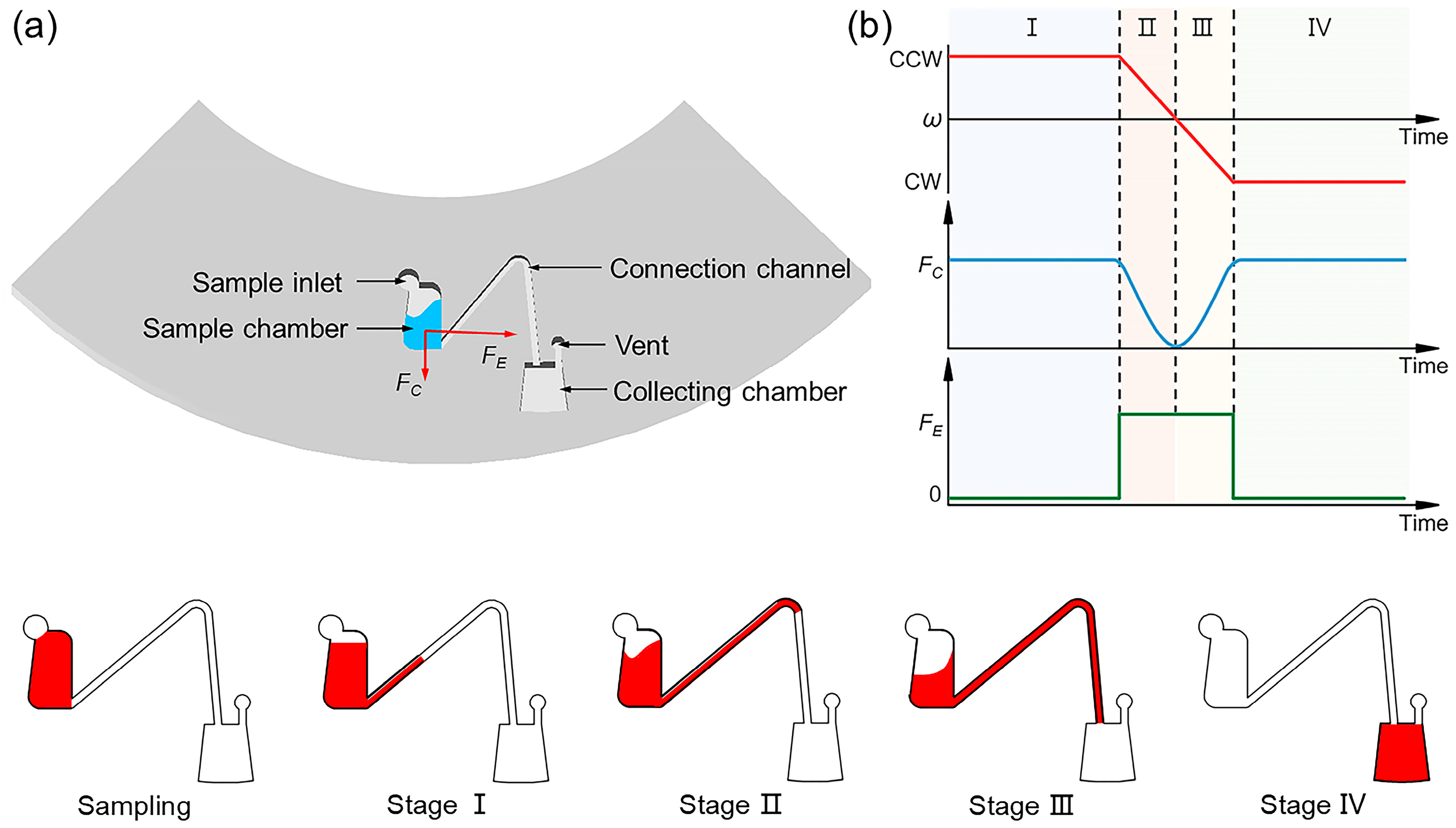
3.1. Design and Working Principle
3.2. Design of Geometric Parameters of the Connecting Channel
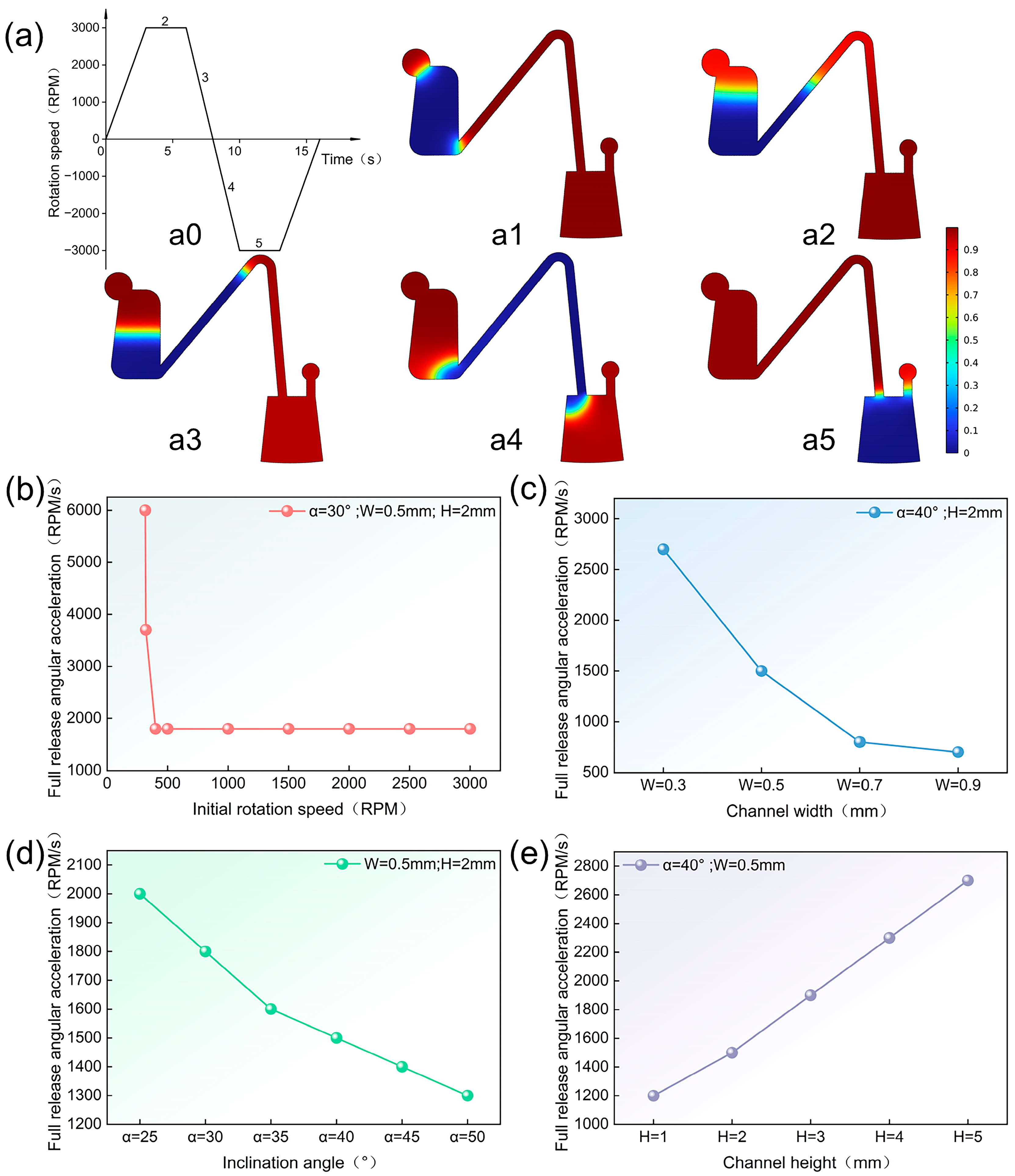
3.3. COMSOL Simulation
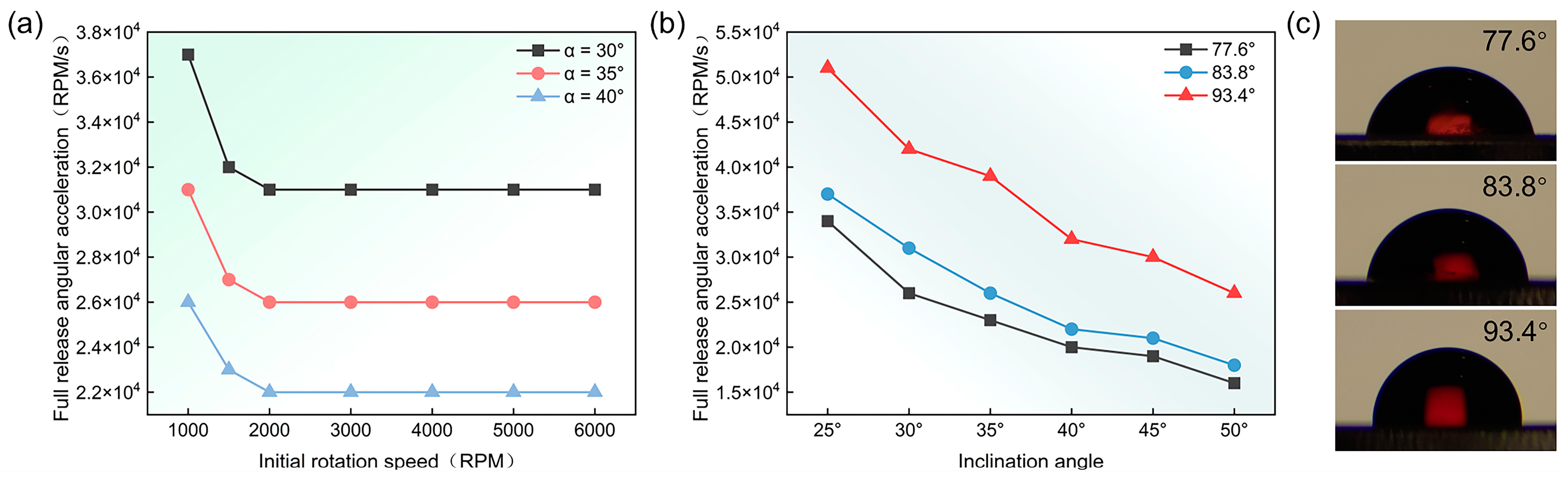
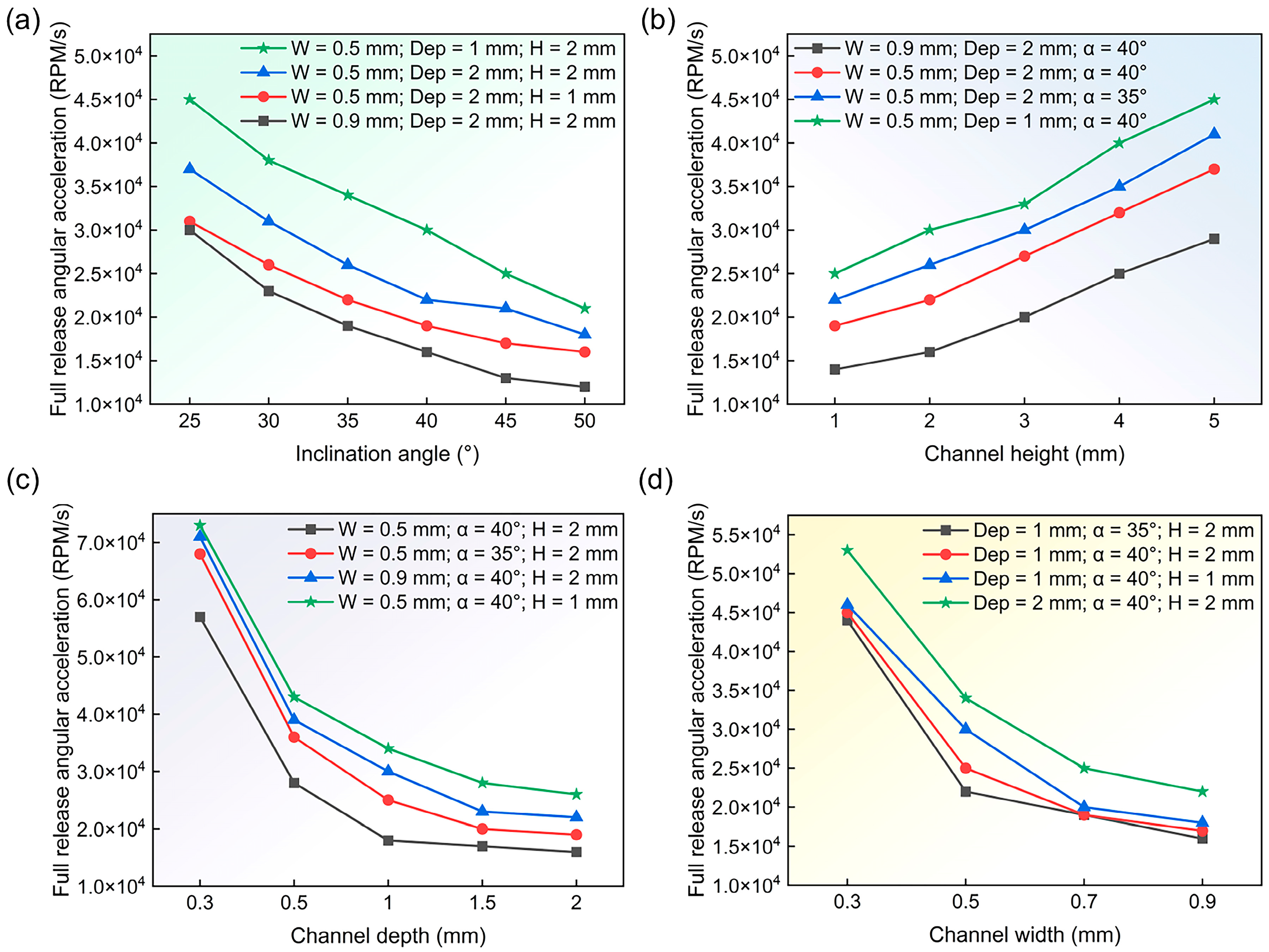
3.4. Study of Parameters Affecting Controlled Sequential Release
3.5. Design and Implementation of Sequential Release Structures
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Qian, C.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Dai, C.; Yuan, H.; Wan, C.; et al. Fully integrated and high-throughput microfluidic system for multiplexed point-of-care testing. Small 2024, 28, 2401848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, N.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Jiang, X. Automated centrifugal microfluidic chip integrating pretreatment and molecular diagnosis for hepatitis b virus genotyping from whole blood. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 5196–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Qi, W.; Wu, S.; Yuan, J.; Duan, H.; Li, Y.; Lin, J. An automatic centrifugal system for rapid detection of bacteria based on immunomagnetic separation and recombinase aided amplification. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 3780–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Lee, J.N.; Park, J.M.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.K.; Ko, C. A fully automated immunoassay from whole blood on a disc. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Lv, Y.; Sun, W.; Huang, J.; Mi, S. Full integration of nucleic acid extraction and detection into a centrifugal microfluidic chip employing chitosan-modified microspheres. Talanta 2022, 250, 123711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, G.C.; Watanabe, T.; Carlen, E.T.; Yokokawa, M.; Suzuki, H. Switchable hydrophobic valve for controlled microfluidic processing. Chemphyschem 2016, 17, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Liang, F.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z. Self-powered electrowetting valve for instantaneous and simultaneous actuation of paper-based microfluidic assays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 18089874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, W. A pinch-valve for centrifugal microfluidic platforms and its application in sequential valving operation and plasma extraction. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2015, 221, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Sunkara, V.; Park, J.; Kim, C.J.; Woo, H.K.; Cho, Y.K. A lab-on-a-disc with reversible and thermally stable diaphragm valves. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3741–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. A novel electromagnet-triggered pillar valve and its application in immunoassay on a centrifugal platform. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Lee, J.G.; Park, J.M.; Lee, B.S.; Lee, Y.; Ko, C. One-step pathogen specific DNA extraction from whole blood on a centrifugal microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasia, M.; Cozzens, M.; Madou, M.J. Centrifugal microfluidic platform for rapid PCR amplification using integrated thermoelectric heating and ice-valving. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2012, 161, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Cho, Y.K.; Lee, B.S.; Lee, J.G.; Ko, C. Multifunctional microvalves control by optical illumination on nanoheaters and its application in centrifugal microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Song, C.; Meng, Y.; Xue, P.; de Mello, A.J.; Gao, Q.; Stavrakis, S.; Ma, S.; Cao, X. An addressable electrowetting valve for centrifugal microfluidics. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2022, 369, 132276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Wan, C.; Li, S.; Xiao, Y.; Yuan, H.; Gao, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, M.; Feng, X.; Li, Y.; et al. On-line dual-active valves based centrifugal microfluidic chip for fully automated point-of-care immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 12521–12531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, V.; Kumar, S.; Del Río, J.S.; Kim, I.; Cho, Y.K. Lab-on-a-disc for point-of-care infection diagnostics. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 3643–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; McLaughlin, D.; Tanaka, Y.; Omata, T. First-come-first-store microfluidic device of droplets using hydrophobic passive microvalves. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2018, 254, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Dosso, F.; Tripodi, L.; Spasic, D.; Kokalj, T.; Lammertyn, J. Innovative hydrophobic valve allows complex liquid manipulations in a self-powered channel-based microfluidic device. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, J.; Gorkin, R.; Clime, L.; Roy, E.; Peytavi, R.; Kido, H.; Bergeron, M.; Veres, T.; Madou, M. Serial siphon valving for centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnle, S.; Schwemmer, F.; Bergmann, R.; von Stetten, F.; Zengerle, R.; Paust, N. Pneumatic siphon valving and switching in centrifugal microfluidics controlled by rotational frequency or rotational acceleration. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2015, 19, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y. Interruptible siphon valving for centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2018, 276, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kang, D.; Han, S.; Kim, S.B.; Rogers, J.A. Thin, soft, skin-mounted microfluidic networks with capillary bursting valves for chrono-sampling of sweat. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1601355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, P.; Lin, M. Analysis and experiment of capillary valves for microfluidics on a rotating disk. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2008, 4, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, T.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xuan, M.; Wu, Y. Euler force actuation mechanism for siphon valving in compact disk-like microfluidic chips. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 024101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Shen, M.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y. Euler force-assisted sequential liquid release on the centrifugal microfluidic platform. Sens. Actuator B-Chem. 2022, 359, 131642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, H.; Chang, C.; Zhao, Y. Sequential flow control by liquid decanting on a centrifugal platform. Sens. Actuator A-Phys. 2022, 347, 113957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhari, S.; Pishbin, E.; Navibakhsh, M.; Maghazeh, M.; Eghbal, M. Implementing series of dual-chamber units for sequential loading of the liquids in centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2019, 23, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, C.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y. Automated Protein Purification on a Centrifugal Platform. ECS J. Solid. State Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 115007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, X.; Ge, C.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y. Detection of VEGF165 in whole blood by differential pulse voltammetry based on a centrifugal microfluidic chip. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedev, R. Surface tension, interfacial tension and contact angles of ionic liquids. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2011, 16, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, D.; Jiang, X. Recent advancements in nucleic acid detection with microfluidic chip for molecular diagnostics. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 158, 116871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Structure | A (°) | H (mm) | W (mm) | Dep (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 2 |
| 2 | 40 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 1.5 |
| 3 | 40 | 3 | 0.9 | 2 |
| 4 | 40 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 2 |
| 5 | 50 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Shen, H.; Chen, G.; Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Xue, L.; Ou, J.; Chen, L. Euler Force-Driven Siphon Valve Control for Precise Sequential Release in Centrifugal Microfluidic Chips. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101200
Lu Y, Shen H, Chen G, Yang K, Zhang J, Xue L, Ou J, Chen L. Euler Force-Driven Siphon Valve Control for Precise Sequential Release in Centrifugal Microfluidic Chips. Micromachines. 2024; 15(10):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101200
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yu, Hao Shen, Guangyao Chen, Kaichao Yang, Jing Zhang, Liwei Xue, Jianzhen Ou, and Liguo Chen. 2024. "Euler Force-Driven Siphon Valve Control for Precise Sequential Release in Centrifugal Microfluidic Chips" Micromachines 15, no. 10: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101200
APA StyleLu, Y., Shen, H., Chen, G., Yang, K., Zhang, J., Xue, L., Ou, J., & Chen, L. (2024). Euler Force-Driven Siphon Valve Control for Precise Sequential Release in Centrifugal Microfluidic Chips. Micromachines, 15(10), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101200








