Accurate Modelling of AFM Force-Indentation Curves with Blunted Indenters at Small Indentation Depths
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
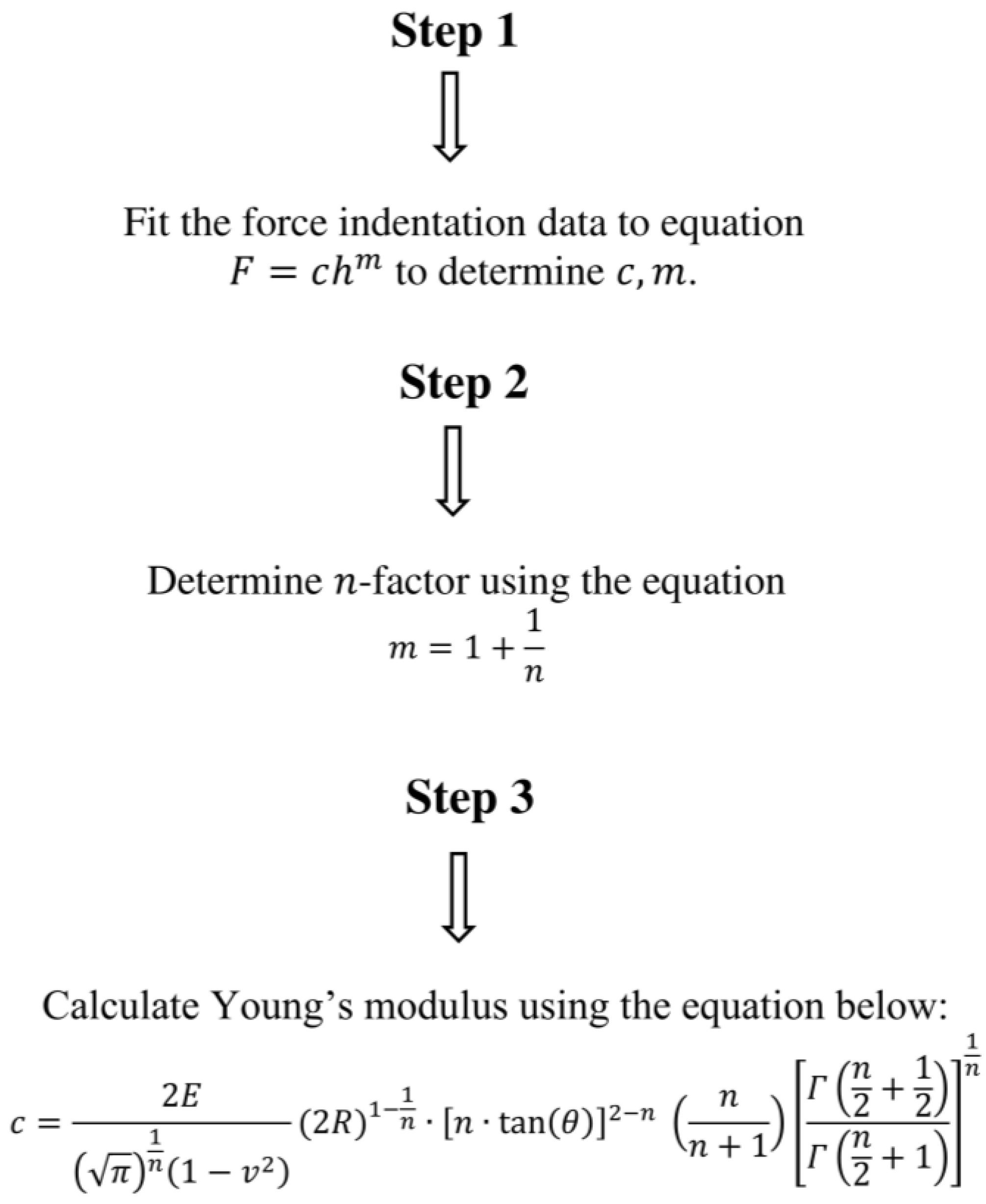
2.1. Equations for Approximating the Behavior of Real Indenters
2.2. Deriving a Simple Equation for Real Indenters
2.3. Open-Access Simulated Data (AtomicJ Repository)
2.4. Open-Access Experimental Data (AtomicJ Repository)
2.5. Collagen Hydrogels
2.6. AFM Experiment
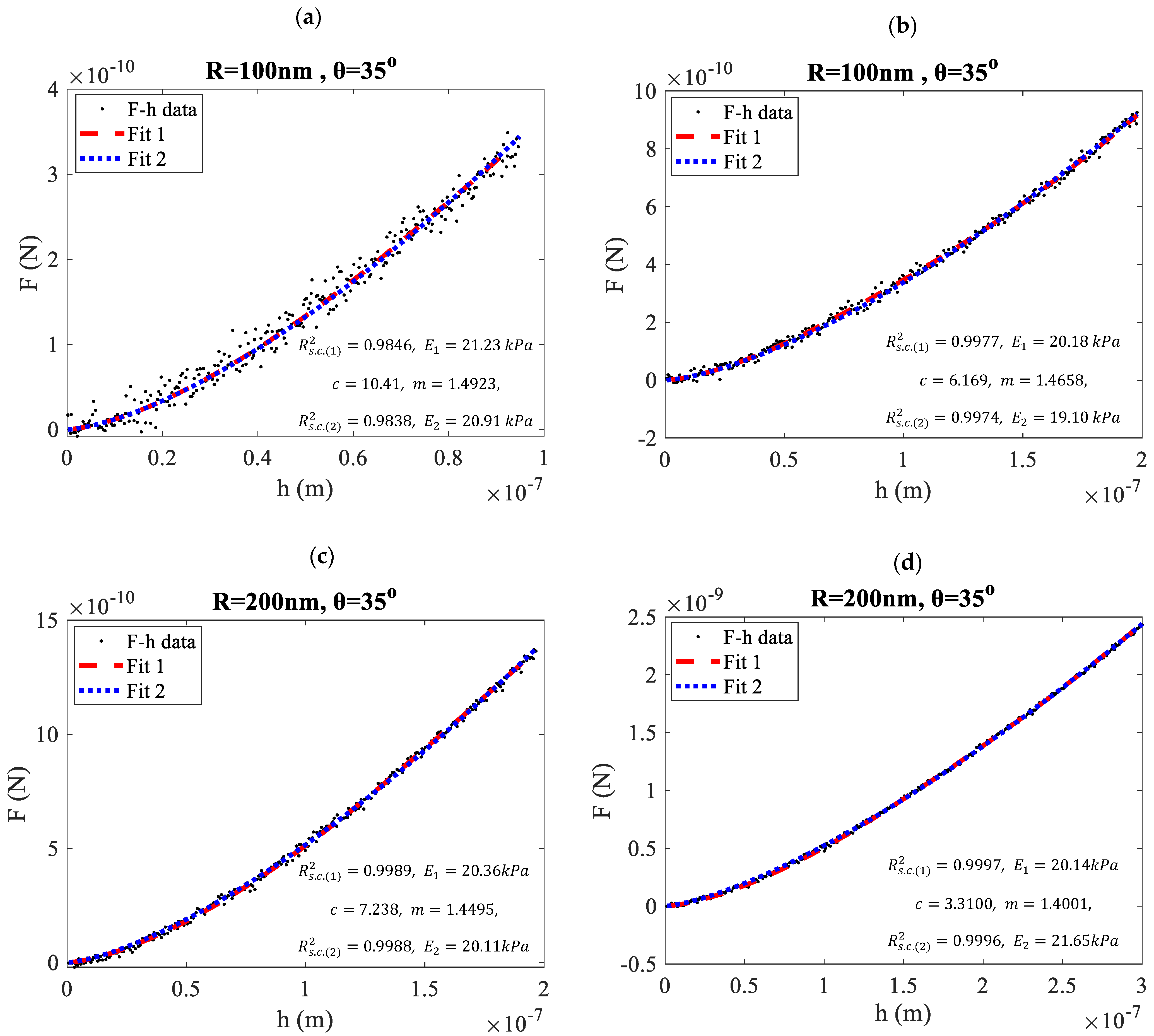
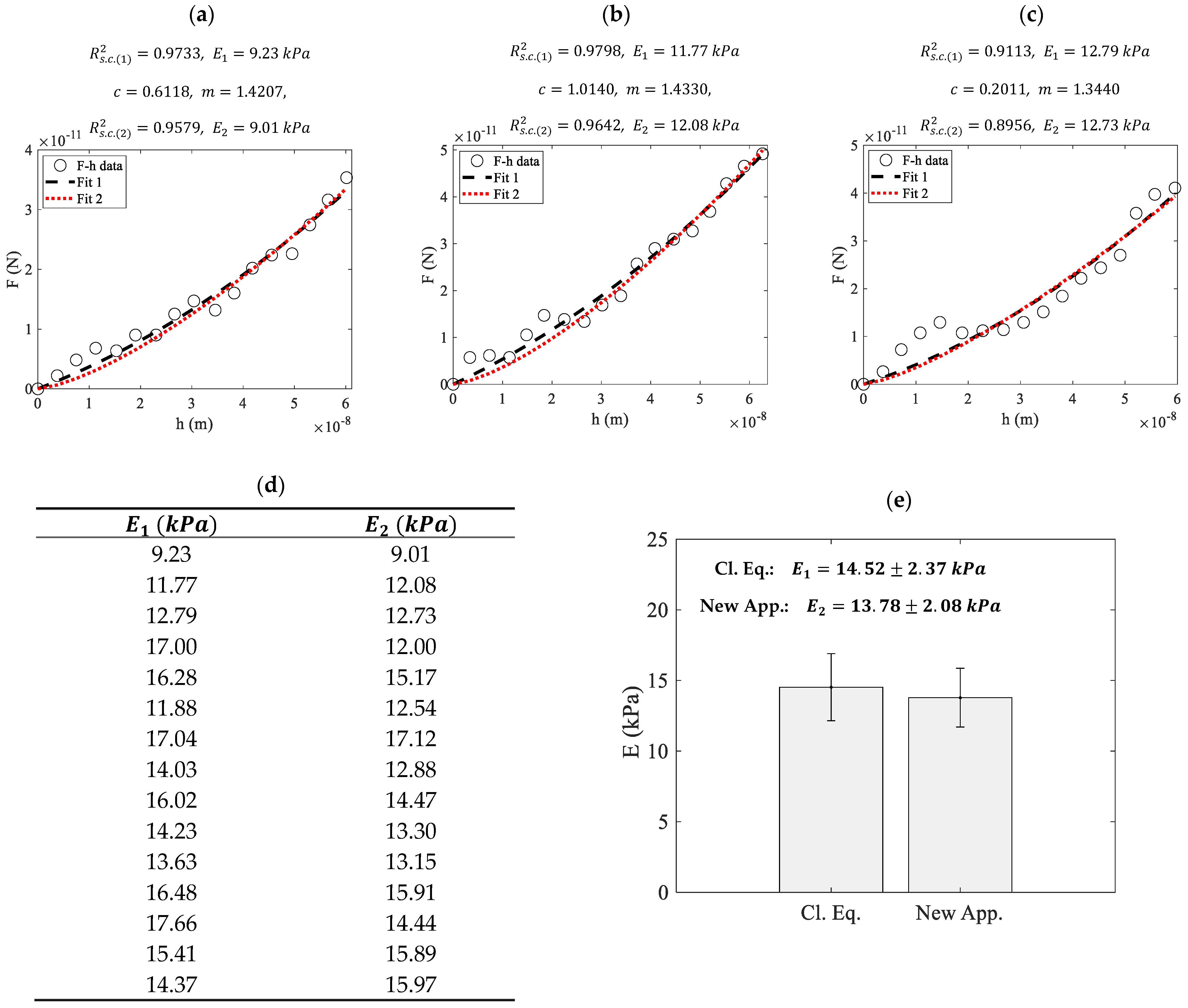
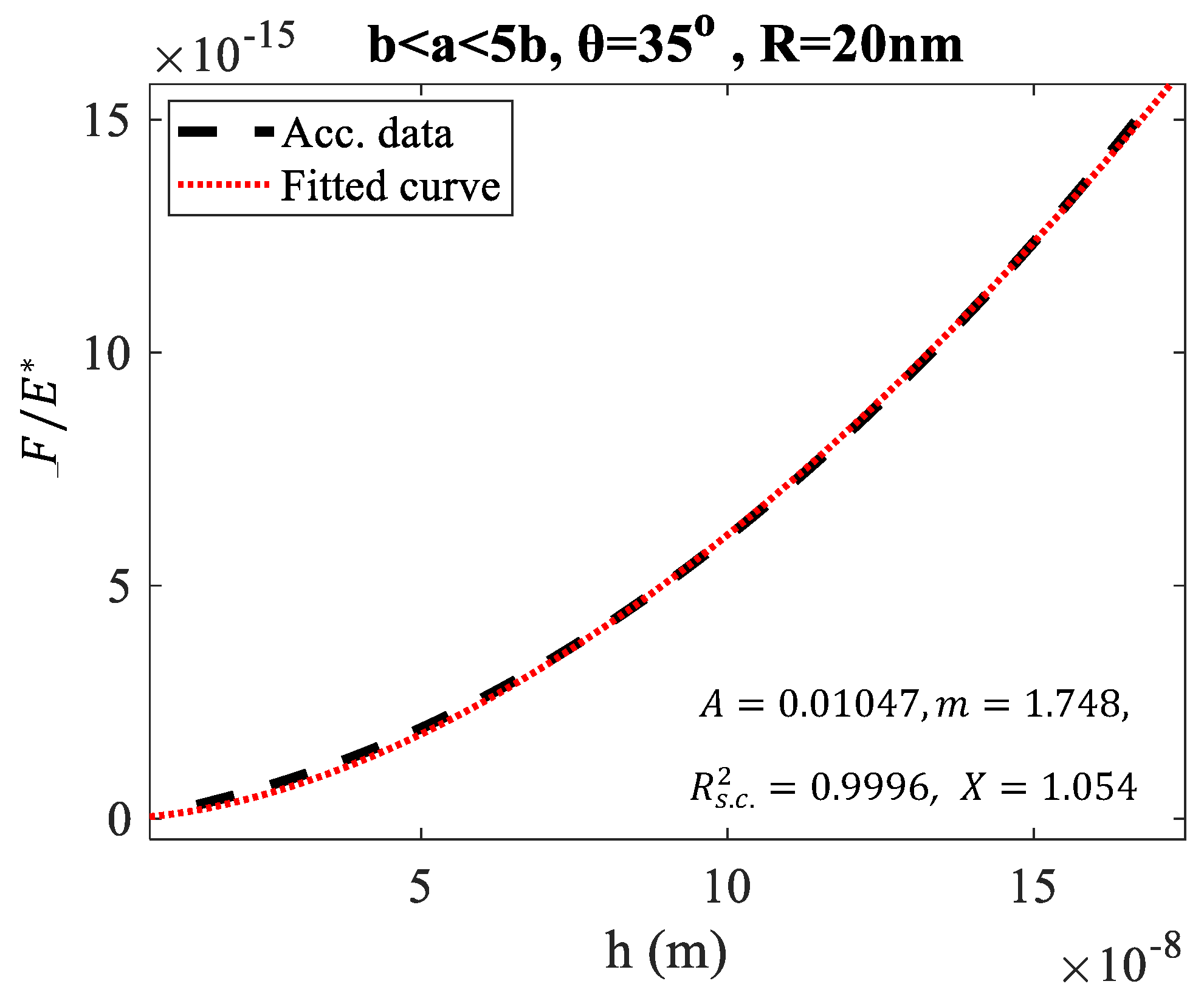
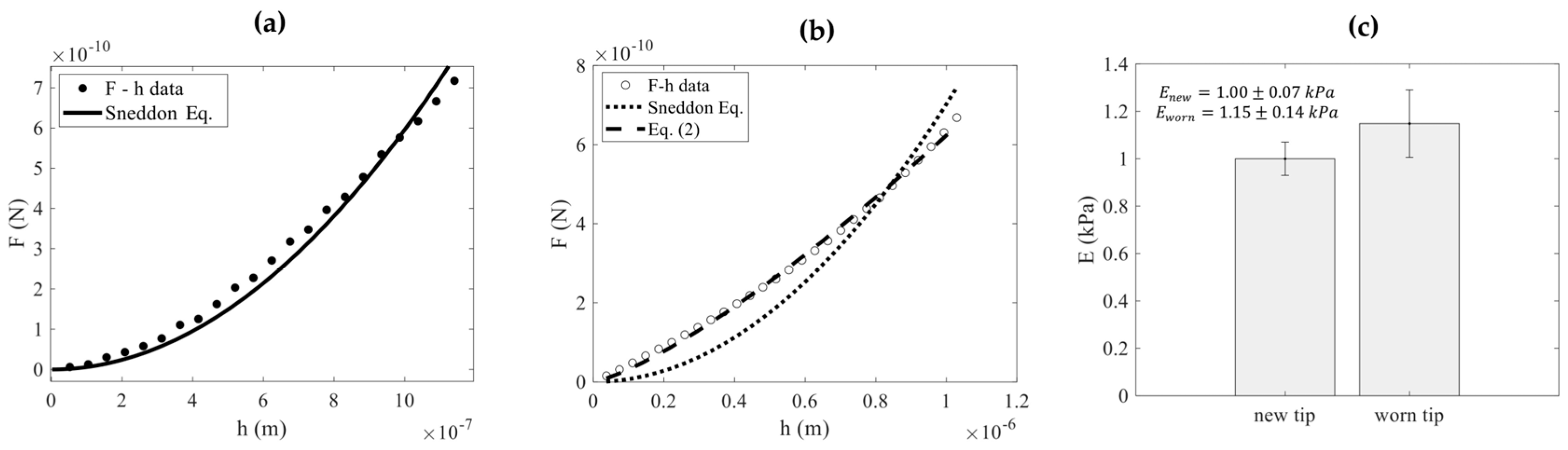
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amabili, M.; Asgari, M.; Breslavsky, I.D.; Franchini, G.; Giovanniello, F.; Holzapfel, G.A. Microstructural and Mechanical Characterization of the Layers of Human Descending Thoracic Aortas. Acta Biomater. 2021, 134, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyasnavichyus, M.; Young, S.L.; Geryak, R.; Tsukruk, V.V. Probing Elastic Properties of Soft Materials with AFM: Data Analysis for Different Tip Geometries. Polymer 2016, 102, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, A.; Lekka, M.; Stylianopoulos, T. AFM Assessing of Nanomechanical Fingerprints for Cancer Early Diagnosis and Classification: From Single Cell to Tissue Level. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 20930–20945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Yao, A.; Zheng, E.E.; Lin, J.; Zheng, Y. Shear Wave Dispersion Ultrasound Vibrometry Based on a Different Mechanical Model for Soft Tissue Characterization. Appl. Sci. 2012, 31, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magazzù, A.; Marcuello, C. Investigation of Soft Matter Nanomechanics by Atomic Force Microscopy and Optical Tweezers: A Comprehensive Review. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, C.J.; Chemla, Y.R.; Liu, S.; Wang, M.D. Optical Tweezers in Single-Molecule Biophysics. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekka, M. Discrimination Between Normal and Cancerous Cells Using AFM. BioNanoScience 2016, 6, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plodinec, M.; Loparic, M.; Monnier, C.A.; Obermann, E.C.; Zanetti-Dallenbach, R.; Oertle, P.; Hyotyla, J.T.; Aebi, U.; Bentires-Alj, M.; Lim, R.Y.; et al. The Nanomechanical Signature of Breast Cancer. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najera, J.; Rosenberger, M.R.; Datta, M. Atomic Force Microscopy Methods to Measure Tumor Mechanical Properties. Cancers 2023, 15, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolz, M.; Gottardi, R.; Raiteri, R.; Miot, S.; Martin, I.; Imer, R.; Staufer, U.; Raducanu, A.; Dueggelin, M.; Baschong, W.; et al. Early Detection of Aging Cartilage and Osteoarthritis in Mice and Patient Samples Using Atomic Force Microscopy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.; Latifi, N.; Giovanniello, F.; Espinosa, H.D.; Amabili, M. Revealing Layer-Specific Ultrastructure and Nanomechanics of Fibrillar Collagen in Human Aorta via Atomic Force Microscopy Testing: Implications on Tissue Mechanics at Macroscopic Scale. Adv. NanoBiomed Res. 2022, 2, 2100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurland, N.E.; Drira, Z.; Yadavalli, V.K. Measurement of Nanomechanical Properties of Biomolecules Using Atomic Force Microscopy. Micron 2012, 43, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalho, R.; Rankovic, S.; Zhou, J.; Aiken, C.; Rousso, I. Analysis of the Mechanical Properties of Wild Type and Hyperstable Mutants of the HIV-1 Capsid. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Xiong, F.; Li, X.; Xiang, B.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Guo, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Application of Atomic Force Microscopy in Cancer Research. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemła, J.; Bobrowska, J.; Kubiak, A.; Zieliński, T.; Pabijan, J.; Pogoda, K.; Bobrowski, P.; Lekka, M. Indenting Soft Samples (Hydrogels and Cells) with Cantilevers Possessing Various Shapes of Probing Tip. Eur. Biophys. J. 2020, 49, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirghi, L.; Ponti, J.; Broggi, F.; Rossi, F. Probing Elasticity and Adhesion of Live Cells by Atomic Force Microscopy Indentation. Eur. Biophys. J. 2008, 37, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Lacroix, D.; Tan, L.P.; Chen, J. Revealing the Nanoindentation Response of a Single Cell Using a 3D Structural Finite Element Model. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, D.S. Toward a Better Modulus at Shallow Indentations—Enhanced Tip and Sample Characterization for Quantitative Atomic Force Microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2023, 86, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offroy, M.; Razafitianamaharavo, A.; Beaussart, A.; Pagnout, C.; Duval, J.F.L. Fast Automated Processing of AFM PeakForce Curves to Evaluate Spatially Resolved Young Modulus and Stiffness of Turgescent Cells. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 19258–19275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Sebastian, K.S.; Adams, M.J. The Effect of Indenter Geometry on the Elastic Response to Indentation. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 1994, 27, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico, F.; Roca-Cusachs, P.; Gavara, N.; Farré, R.; Rotger, M.; Navajas, D. Probing Mechanical Properties of Living Cells by Atomic Force Microscopy with Blunted Pyramidal Cantilever Tips. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 021914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Malamou, A.; Stylianou, A. The Hertzian Theory in AFM Nanoindentation Experiments Regarding Biological Samples: Overcoming Limitations in Data Processing. Micron 2022, 155, 103228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. Measurement of Hardness and Elastic Modulus by Instrumented Indentation: Advances in Understanding and Refinements to Methodology. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneddon, I.N. The Relation Between Load and Penetration in the Axisymmetric Boussinesq Problem for a Punch of Arbitrary Profile. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1965, 3, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanowicz, P.; Sarna, M.; Burda, K.; Gabryś, H. An Open Source Software for Analysis of Force Curves. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2014, 85, 063703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, A.; Gkretsi, V.; Stylianopoulos, T. Atomic Force Microscopy Nano-Characterization of 3D Collagen Gels with Tunable Stiffness. MethodsX 2018, 5, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stylianou, A.; Gkretsi, V.; Patrickios, C.S.; Stylianopoulos, T. Exploring the Nano-Surface of Collagenous and Other Fibrotic Tissues with AFM. In Fibrosis: Methods and Protocols; Rittié, L., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 453–489. [Google Scholar]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Malamou, A. A Novel Approximate Method to Calculate the Force Applied on an Elastic Half Space by a Rigid Sphere. Eur. J. Phys. 2021, 42, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Malamou, A.; Stylianou, A.; Chliveros, G. Towards Simpler Modelling Expressions for the Mechanical Characterization of Soft Materials. Micro Nano Syst. 2024, 16, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Malamou, A.; Zachariades, A.; Stylianou, A. A Linear Fit for Atomic Force Microscopy Nanoindentation Experiments on Soft Samples. Processes 2024, 12, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, M.; Flaschner, G.; Alsteens, D.; Gaub, B.M.; Roos, W.H.; Wuite, G.J.L.; Gaub, H.E.; Gerber, C.; Dufrêne, Y.F.; Müller, D.J. Atomic Force Microscopy-Based Mechanobiology. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2019, 1, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopycinska-Müller, M.; Geiss, R.H.; Hurley, D.C. Contact Mechanics and Tip Shape in AFM-Based Nanomechanical Measurements. Ultramicroscopy 2006, 106, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, C.A.; Brockwell, D.J.; Radford, S.E.; Thomson, N.H. Effects of hydration on the mechanical response of individual collagen fibrils. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 233902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, M.P.E.; Bozec, L.; Horton, M.A.; Mesquidaz, P. Mechanical properties of collagen fibrils. Biophys. J. 2007, 93, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, A.J.; Matthews, W.G.; Koob, T.J. Determination of the elastic modulus of native collagen fibrils via radial indentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 181902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minary-Jolandan, M.; Yu, M.F. Nanomechanical heterogeneity in the gap and overlap regions of type I collagen fibrils with implications for bone heterogeneity. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2565–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadavalli, V.K.; Svintradze, D.V.; Pidaparti, R.M. Nanoscale measurements of the assembly of collagen to fibrils. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 46, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriotis, O.G.; Manuyakorn, W.; Zekonyte, J.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Fabri, S.; Howarth, P.H.; Davies, D.E.; Thurner, P.J. Nanomechanical assessment of human and murine collagen fibrils via atomic force microscopy cantilever-based nanoindentation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 39, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Stylianou, A.; Malamou, A. Atomic Force Microscopy Nanoindentation Method on Collagen Fibrils. Materials 2022, 15, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Stylianou, A.; Yova, D.; Politopoulos, K. Mechanical Properties of Collagen Fibrils on Thin Films by Atomic Force Microscopy Nanoindentation. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on Bioinformatics & Bioengineering (BIBE), Larnaca, Cyprus, 11–13 November 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriadis, E.K.; Horkay, F.; Maresca, J.; Kachar, B.; Chadwick, R.S. Determination of Elastic Moduli of Thin Layers of Soft Material Using the Atomic Force Microscope. Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 2798–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.A.C.; Rebêlo, L.M.; Araujo, A.C.; Barros, E.B.; de Sousa, J.S. Thickness-Corrected Model for Nanoindentation of Thin Films with Conical Indenters. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavara, N.; Chadwick, R.S. Determination of the Elastic Moduli of Thin Samples and Adherent Cells Using Conical Atomic Force Microscope Tips. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pogoda, K.; Jaczewska, J.; Wiltowska-Zuber, J.; Klymenko, O.; Zuber, K.; Fornal, M.; Lekka, M. Depth-Sensing Analysis of Cytoskeleton Organization Based on AFM Data. Eur. Biophys. J. 2012, 41, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, G.K.; Wang, G.F. Are Elastic Moduli of Biological Cells Depth Dependent or Not? Another Explanation Using a Contact Mechanics Model with Surface Tension. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 7534–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Malamou, A.; Stylianou, A. The Average Young’s Modulus as a Physical Quantity for Describing the Depth-Dependent Mechanical Properties of Cells. Mech. Mater. 2021, 158, 103846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, T.; Pabijan, J.; Zapotoczny, B.; Zemła, J.; Wesołowska, J.; Pera, J.; Lekka, M. Changes in Nanomechanical Properties of Single Neuroblastoma Cells as a Model for Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation (OGD). Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontomaris, S.-V.; Malamou, A. The Truncated Cone Effect in AFM Nanoindentation on Soft Materials. Micro Nanosyst. 2023, 15, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontomaris, S.V.; Stylianou, A.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Malamou, A. Is it Mathematically Correct to Fit AFM Data (Obtained on Biological Materials) to Equations Arising from Hertzian Mechanics? Micron 2023, 164, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharr, G.M.; Oliver, W.C.; Brotzen, F.R. On the Generality of the Relationship Among Contact Stiffness, Contact Area, and Elastic Modulus During Indentation. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An Improved Technique for Determining Hardness and Elastic Modulus Using Load and Displacement Sensing Indentation Experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polezzi, M. On the Weighted Mean Value Theorem for Integrals. Int. J. Math. Educ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 37, 868–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schillers, H.; Rianna, C.; Schäpe, J.; Luque, T.; Doschke, H.; Wälte, M.; Uriarte, J.J.; Campillo, N.; Michanetzis, G.P.; Bobrowska, J.; et al. Standardized Nanomechanical Atomic Force Microscopy Procedure (SNAP) for Measuring Soft and Biological Samples. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matei, G.A.; Thoreson, E.J.; Pratt, J.R.; Newell, D.B.; Burnham, N.A. Precision and Accuracy of Thermal Calibration of Atomic Force Microscopy Cantilevers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 083703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
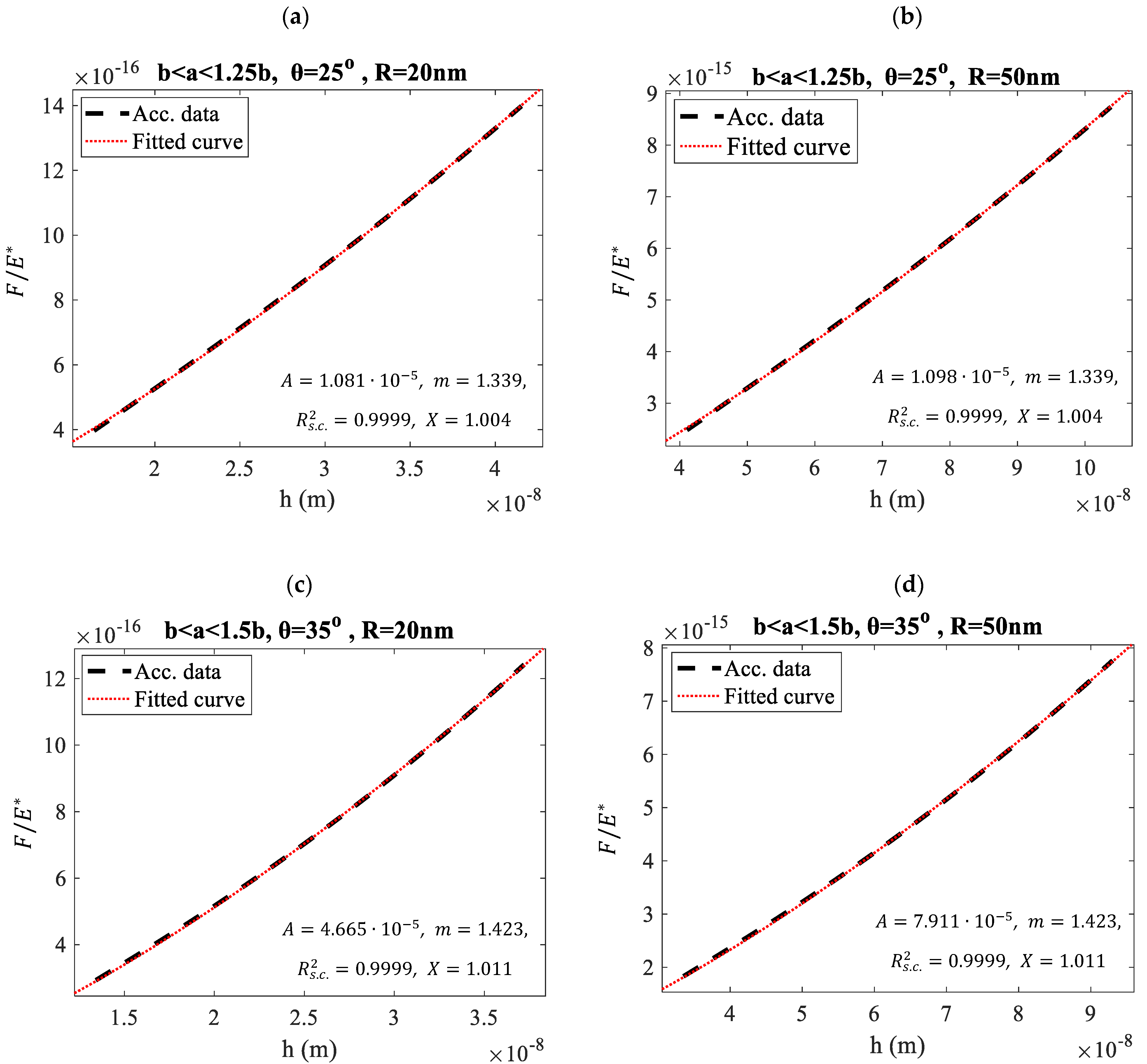

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kontomaris, S.V.; Malamou, A.; Stylianou, A. Accurate Modelling of AFM Force-Indentation Curves with Blunted Indenters at Small Indentation Depths. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101209
Kontomaris SV, Malamou A, Stylianou A. Accurate Modelling of AFM Force-Indentation Curves with Blunted Indenters at Small Indentation Depths. Micromachines. 2024; 15(10):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101209
Chicago/Turabian StyleKontomaris, Stylianos Vasileios, Anna Malamou, and Andreas Stylianou. 2024. "Accurate Modelling of AFM Force-Indentation Curves with Blunted Indenters at Small Indentation Depths" Micromachines 15, no. 10: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101209
APA StyleKontomaris, S. V., Malamou, A., & Stylianou, A. (2024). Accurate Modelling of AFM Force-Indentation Curves with Blunted Indenters at Small Indentation Depths. Micromachines, 15(10), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101209







