Quasi-Optical Four-Port Acoustic Filters Based on NEMS Coupled Beam Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
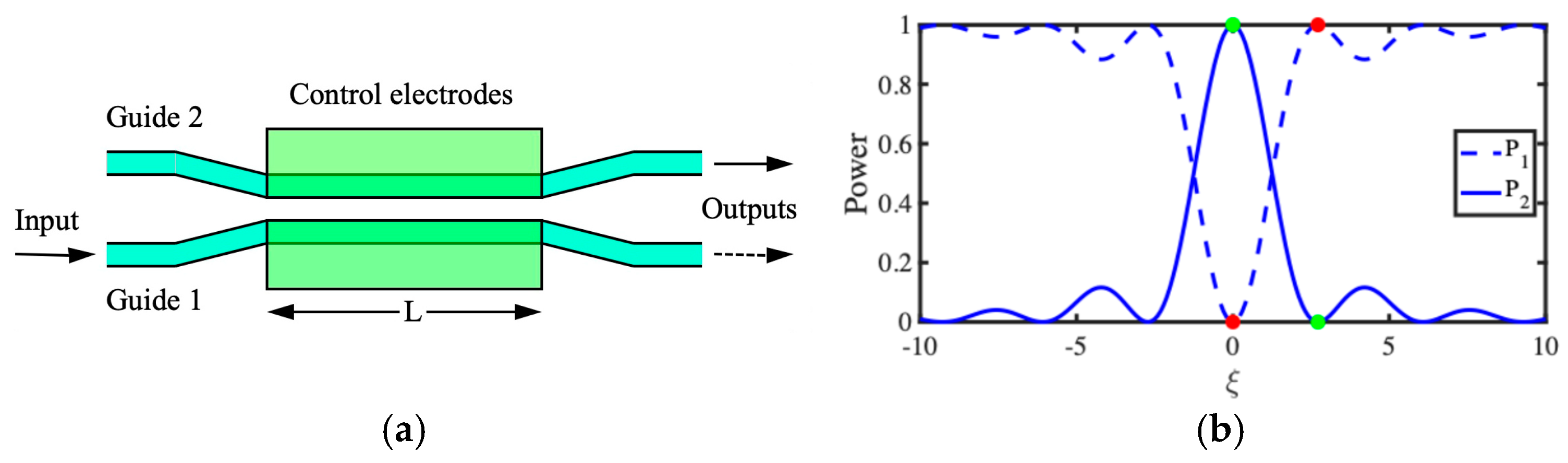
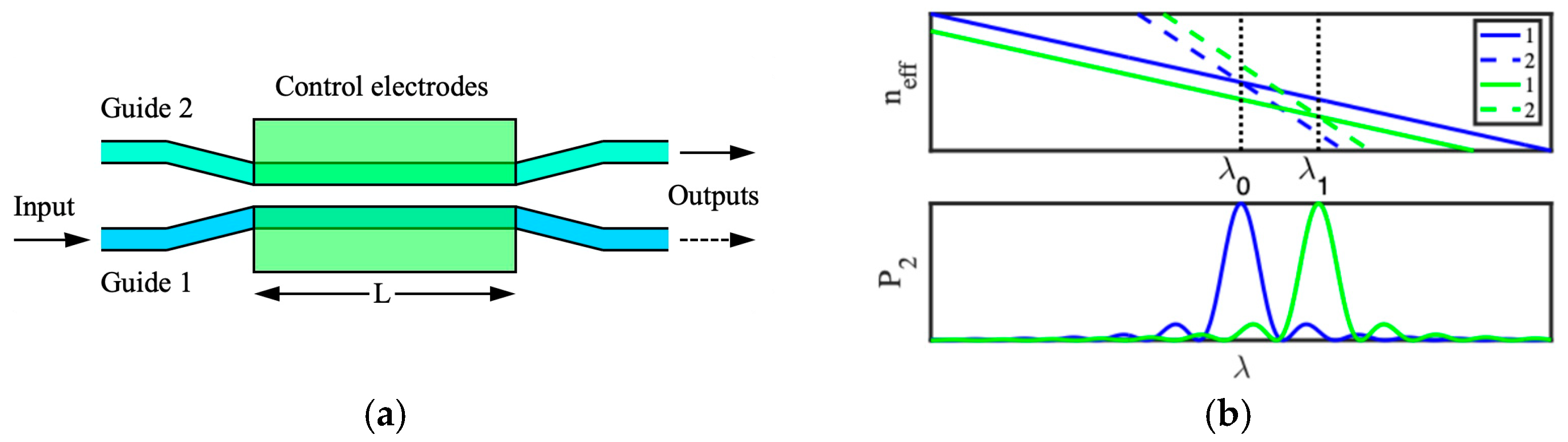
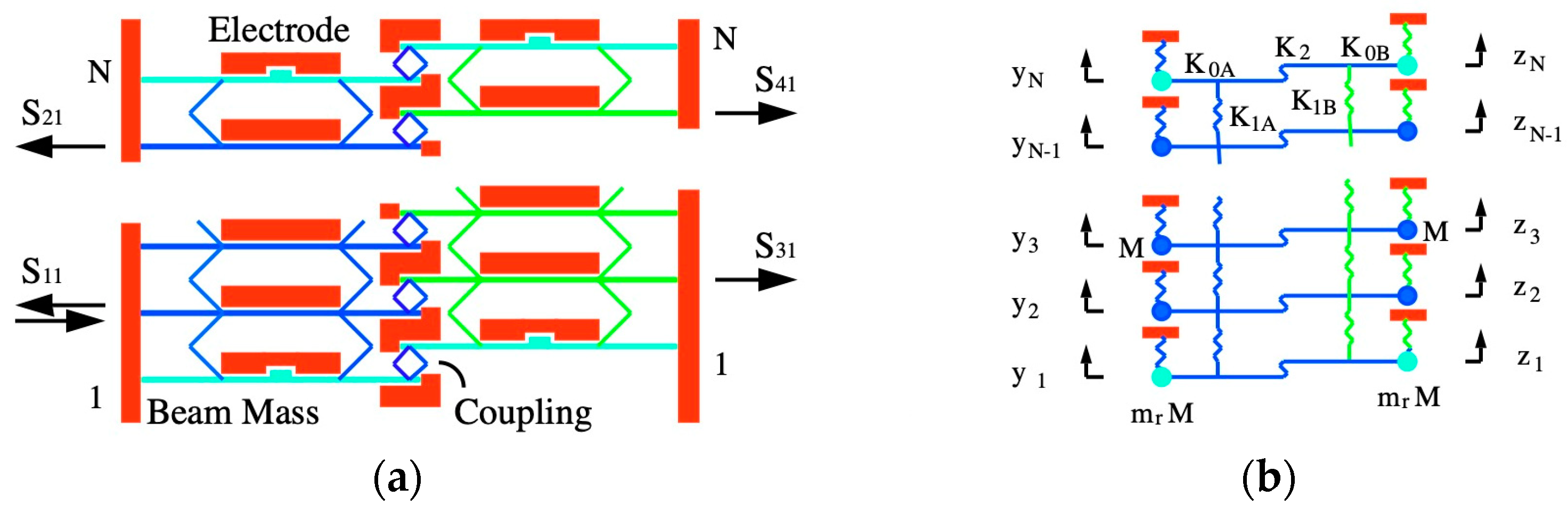
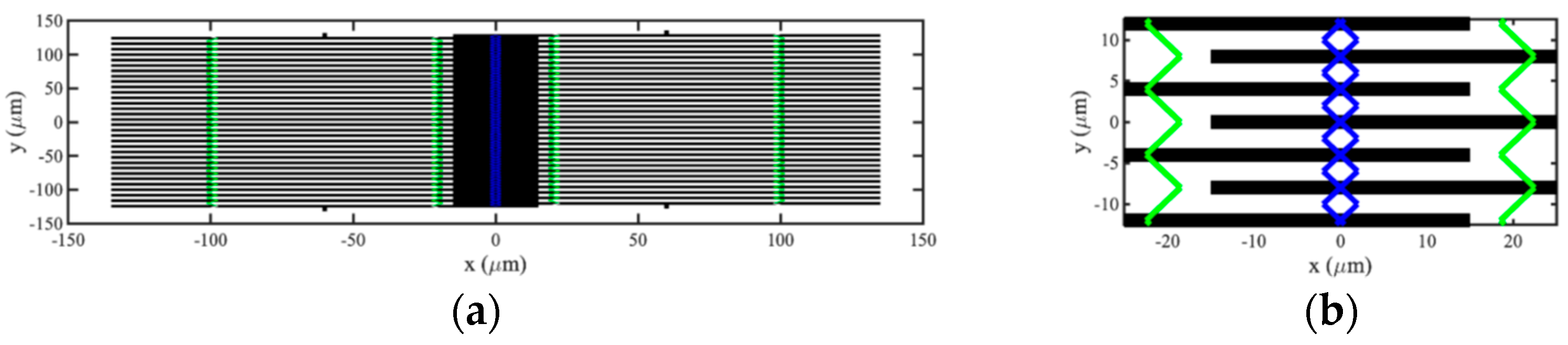
2.1. Optical Coupled Mode Devices
2.2. Mechanical Coupled Beam Arrays
2.3. Analytic Modeling
- and are the Young’s modulus of the beam and spring material;
- is the common material density;
- is a distributed damping coefficient.
- and are the cross-sectional area of the beam and spring;
- /12 and are the second moment of area of the beam and spring;
- is the stiffness of one of the meander springs.
- is the angular resonant frequency of the lowest-order mode
- is a constant arising from the eigenvalue equation, defined by
- is the normalized displacement pattern of the lowest-order mode
- is the ratio of the average to the maximum of
- is the ratio of the average to the maximum of
- is the capacitance where is a static displacement
- The normalized static displacement is the solution to the snap-down equation where
2.4. Equations of Motion
2.5. Example Responses
3. Results
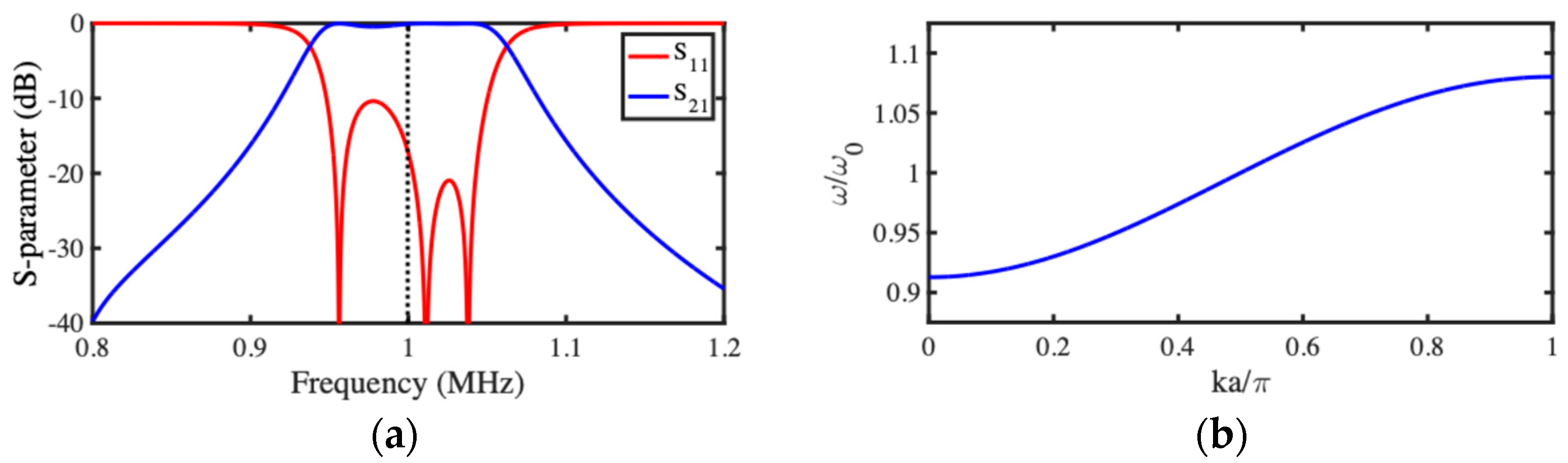
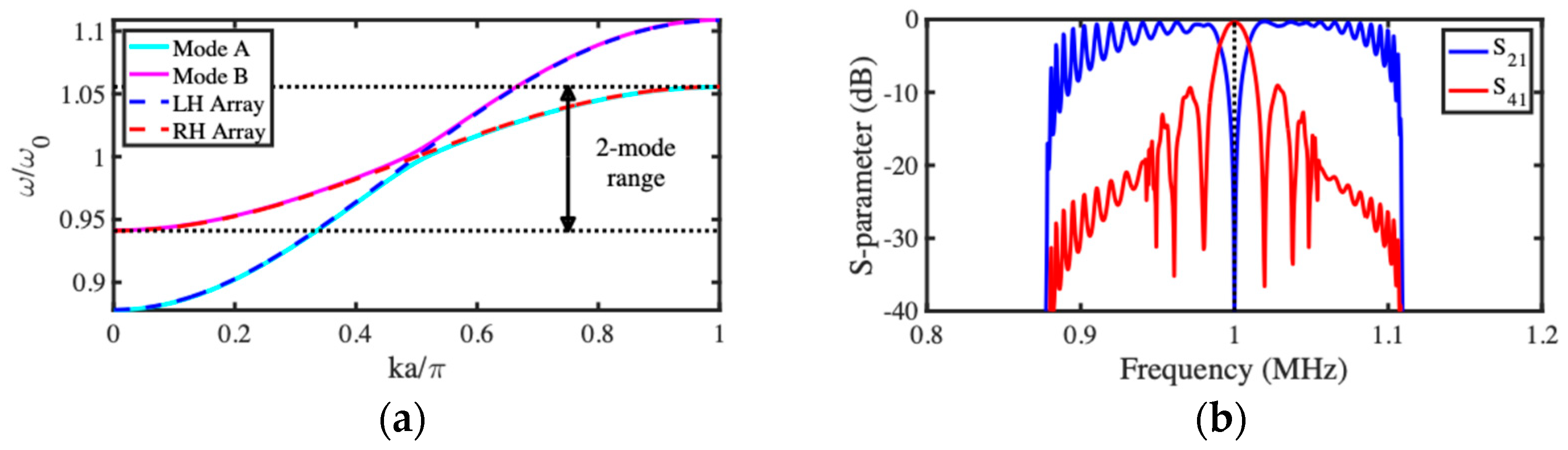
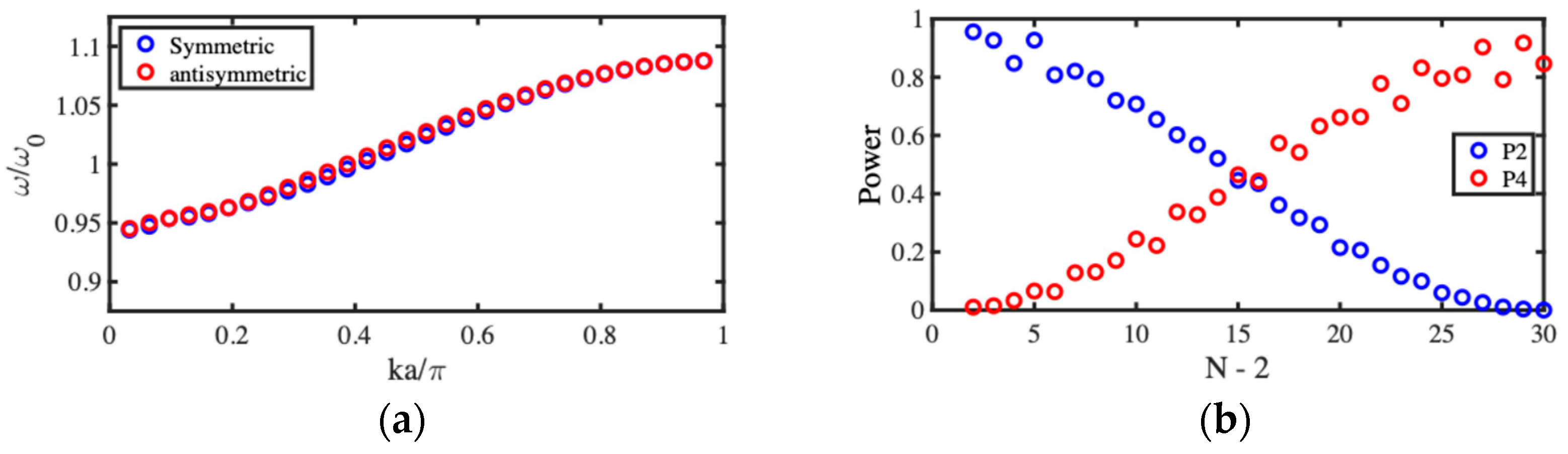
3.1. Acoustic Wave Dispersion
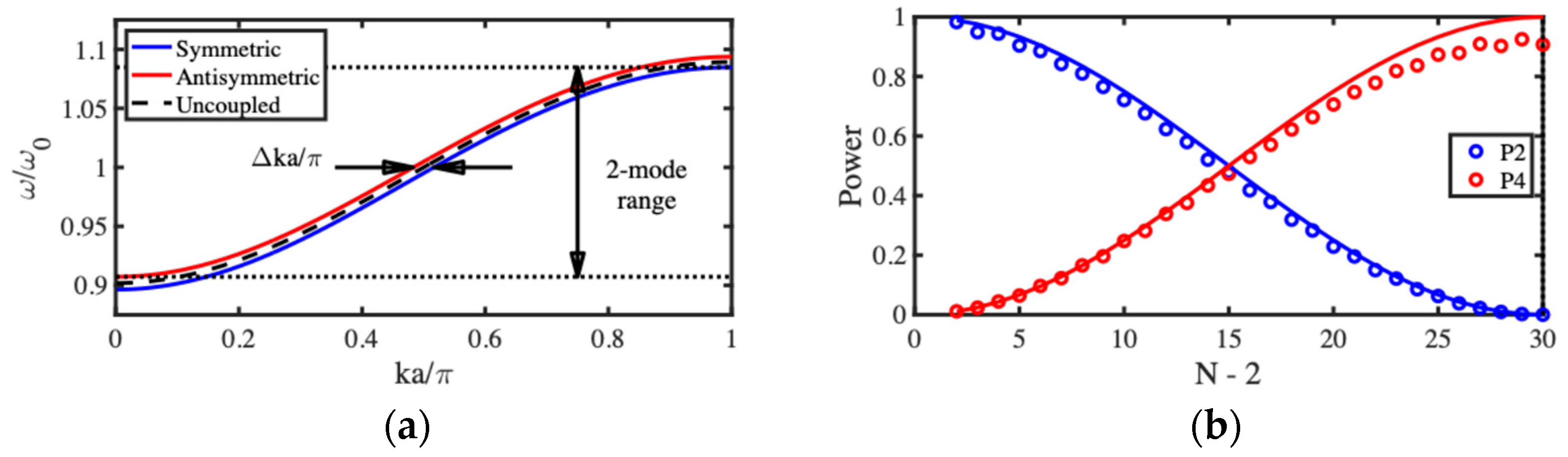
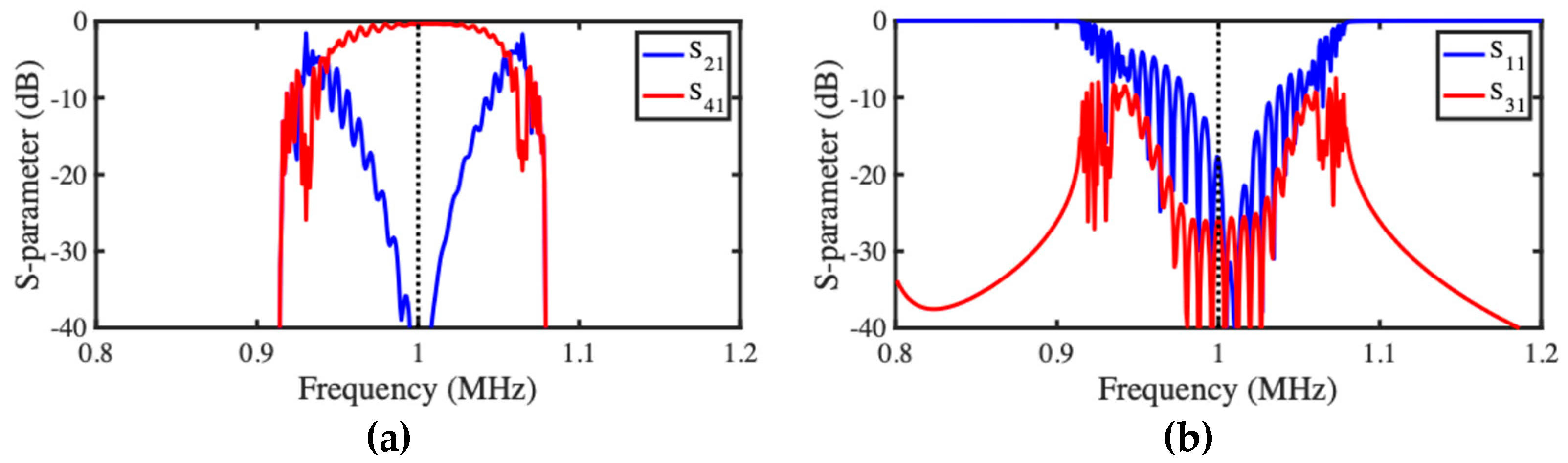
3.2. NEMS Acoustic Directional Coupler
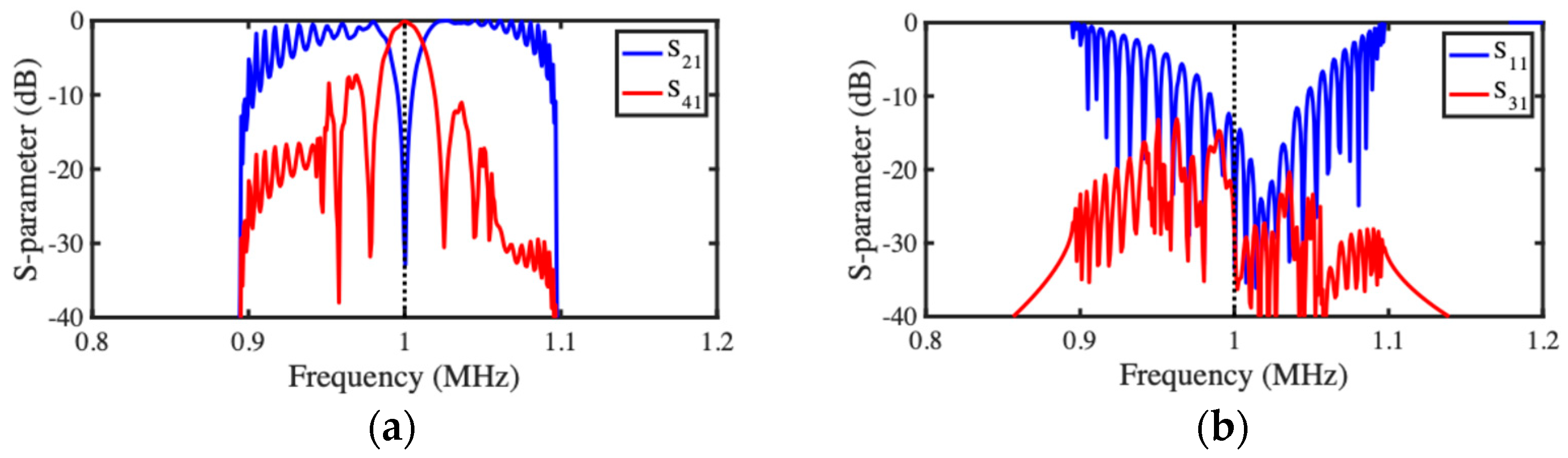
3.3. NEMS Acoustic Coupler Filter
4. Discussion
4.1. Stiffness Matrix Model
4.2. NEMS Acoustic Directional Coupler
4.3. NEMS Acoustic Coupler Filter
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mason, W.P. Electromechanical Transducers and Wave Filters; D. Van Nostrand Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway, J.C.; Babcock, D.F. Survey of mechanical filters and their applications. Proc. IRE 1957, 45, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A.; Börner, M.; Konno, M. Mechanical filters—A review of progress. IEEE Trans. Sonics Ultrasonics 1971, SU-18, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.A. Mechanical Filters in Electronics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.C.; Nguyen, T.-C.H.; Howe, R.T. Laterally driven polysilicon resonant microstructures. Sens. Actuators 1989, 20, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.-C.; Nguyen, T.-C.H.; Judy, M.W.; Howe, R.T. Electrostatic comb-drive of lateral polysilicon resonators. Sens. Actuators 1990, A21–A23, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Howe, R.T.; Pisano, A.P. Micromechanical filters for signal processing. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1998, 7, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Nguyen, C.T.-C. High-order medium frequency micromechanical electronic filters. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 1999, 8, 534–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannon, F.D.; Clark, J.R.; Nguyen, C.T.-C. High-Q HF microelectromechanical filters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wong, A.-C.; Nguyen, C.T.-C. VHF free-free beam high-Q micromechanical resonators. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghsh Nilchi, J.; Liu, R.; Nguyen, C.T.-C. 7th order sharp-roll-off bridged micromechanical filter. In Proceedings of the 2015 Transducers-2015 18th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Anchorage, AK, USA, 21–25 June 2015; pp. 137–140. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.-C. Frequency-selective MEMS for miniaturized low-power communication devices. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1999, 47, 1486–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-S.; Lin, Y.-W.; Ren, Z.; Nguyen, C.T.-C. Self-switching vibrating micromechanical filter bank. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and Exposition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 29–31 August 2005; pp. 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Pourkamali, S.; Ayazi, F. Electrically-coupled MEMS bandpass filters: Part I. With coupling element. Sens. Actuators A 2005, 122, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourkamali, S.; Ayazi, F. Electrically-coupled MEMS bandpass filters: Part II. Without coupling element. Sens. Actuators A 2005, 122, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galayko, D.; Kaiser, A.; Legrand, B.; Buchaillot, L.; Combi, C.; Collard, D. Coupled resonator micromechanical filters with voltage tunable bandpass characteristic in thick-film polysilicon technology. Sens. Actuators A 2006, 126, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajhashemi, M.S.; Amini, A.; Bahreyni, B. A micromechanical bandpass filter with adjustable bandwidth and bidirectional control of centre frequency. Sens. Actuators A 2012, 187, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolvand, R.; Ho, G.K.; Ayazi, F. Poly-wire-coupled single crystal HARPSS micromechanical filters using oxide islands. In Proceedings of the Solid State Sensor, Actuator and Microsystems Workshop, Hilton Head, SC, USA, 6–10 June 2004; pp. 242–245. [Google Scholar]
- Arellano, N.; Quévy, E.P.; Provine, J.; Maboudian, R.; Howe, R.T. Silicon nanowire coupled micro-resonators. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE 21st International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Tuczon, AZ, USA, 13–17 January 2008; pp. 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Tasdemir, Z.; Wollschläger, N.; Österle, W.; Leblebici, Y.; Alaca, B.E. A deep etching mechanism for trench-bridging silicon nanowires. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 095303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourkamali, S.; Hashimura, A.; Abdolvand, R.; Ho, G.K.; Erbil, A.; Ayazi, F. High-Q single crystal silicon HARPSS capacitive beam resonators with self- aligned sub-100-nm transduction gaps. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Chun, K. Photo-assisted electrochemical etching of nano-gap trench with high aspect ratio for MEMS applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Konno, M.; Ikehara, T.; Maeda, R.; Mihara, T. Fabrication of 150-nm-wide transducer gaps for disc-type resonators by single dry etching process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 49, 06GN04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greywall, D.S.; Busch, P.A. Coupled mechanical drumhead resonators with practical application as electromechanical bandpass filters. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2002, 12, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivukula, V.B.; Rhoads, J.F. Microelectromechanical bandpass filters based on cyclic coupling architectures. J. Sound Vibr. 2010, 329, 4313–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachkawade, V.; Junghare, R.; Patrikar, R.; Kraft, M. Mechanically coupled ring-resonator filter and array (analytical and finite element model). IET Comput. Digit. Tech. 2016, 10, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchaala, A.; Syms, R.R.A. New architectures for micromechanical coupled beam array filters. Microsyst. Technol. 2020, 27, 3377–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.R.; Pai, M.; Wissman, B.; He, G.; Hsu, W.T. Parallel-coupled square-resonator micromechanical filter arrays. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium and Exposition, Miami, FL, USA, 4–7 June 2006; pp. 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, M.U.; Nguyen, C.T.C. Mechanically corner-coupled square microresonator array for reduced series motional resistance. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 1419–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-Y.; Li, M.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, C.-Y.; Li, S.-S. An innovative 3-D mechanically-coupled array design for MEMS resonator and oscillators. In Proceedings of the 2017 19th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (TRANSDUCERS), Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Mumford, W.W. Directional couplers. Proc. IRE 1947, 35, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riblet, H.J. A mathematical theory of directional couplers. Proc. IRE 1947, 35, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.E.; Mumford, W.W. Multi-element directional couplers. Proc. IRE 1952, 40, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.E. Coupled wave theory and waveguide applications. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1954, 33, 661–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, S.B.; Levy, R. History of microwave passive components with particular attention to directional couplers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1984, MTT-32, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheleg, B.; Spielman, B.E. Broad-band directional couplers using microstrip with dielectric overlays. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1974, MTT-22, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, S.-M.; Gopinath, A.; Vaughan, J.T. A compact, high power capable, and tunable high directivity microstrip coupler. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 3217–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-B.; Wei, X.; Fang, H.-P.; Zhang, H.-M.; Zhang, Y.-R. A compact and broadband directional coupler for high-power radio frequency applications. IEEE Microw. Wireless Comp. Letts. 2020, 30, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, F.G.; Newton, C.O.; Paige, E.G.S. Surface acoustic wave multistrip components and their applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1973, 21, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, F.G.; Newton, C.O.; Paige, E.G.S. Theory and design of the surface acoustic wave multistrip coupler. IEEE Trans Microw. Theory Tech. 1974, MTT-21, 206–215. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, H.; Rupp, C.; Schikfus, M.v.; Hunklinger, S. Multistrip couplers for surface acoustic wave sensor applications. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1996, 43, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.-J.; Gong, S. GHz low-loss acoustic RF couplers in lithium niobate thin film. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2020, 67, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, M.; Cao, N.; John, D.D.; Hashemi, H. Surface-acoustic-wave waveguides for radio frequency signal processing. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2023, 71, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcatili, E.A.J. Dielectric rectangular waveguide and directional coupler for integrated optics. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1969, 48, 2071–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F. Optical switching and modulation in parallel dielectric waveguides. J. Appl. Phys. 1973, 44, 3257–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yariv, A. Coupled mode theory for guided wave optics. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 1973, QE-9, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuchon, M.; Combemale, Y.; Matthieu, X.; Ostrowsky, D.B.; Reiber, L.; Roy, A.M.; Sejourne, B.; Werner, M. Electrically switched optical directional coupler: COBRA. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1975, 27, 289–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogelnik, H.; Schmidt, R.V. Switched directional couplers with alternating Δβ. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 1976, QE-12, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Ohta, Y.; Fujiwara, M.; Sakaguchi, M. Integrated optical switch matrix for single-mode fiber networks. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1982, MTT-30, 1747–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, H.F. Frequency-selective coupling in parallel dielectric waveguides. Opt. Commun. 1973, 7, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elachi, C.; Yeh, C. Frequency selective coupler for integrated optics systems. Opt. Commun. 1973, 7, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferness, R.C.; Cross, P.S. Filter characteristic of codirectionally coupled waveguides with weighted coupling. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 1978, QE-14, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alferness, R.C. Guided-wave devices for optical communication. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 1981, QE-17, 946–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digonnet, M.J.F.; Shaw, H.J. Analysis of a tunable single mode optical fibre coupler. IEEE J. Quant. Electron. 1982, QE-18, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozens, J.R.; Boucouvalas, A.C.; Al-Assam, A.; Lee, M.J.; Morris, D.G. Optical coupling in coaxial fibres. Electron. Lett. 1982, 18, 679–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, M.S.; Walker, K.L. In-line optical fibre filter for wavelength multiplexing. Electron. Lett. 1985, 21, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digonnet, M.; Shaw, H.J. Wavelength multiplexing in single-mode fiber coupler. Appl. Opt. 1983, 22, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.K. Review of optical fiber couplers. Fiber Int. Opt. 1987, 6, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culshaw, B. Fiber optics in sensing and measurement. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2000, 6, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Alamo, J.A.; Eugster, C.C. Quantum field-effect directional coupler. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1990, 56, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, N.; Wieck, A.D.; Ploog, K. Proposal of novel electron wave coupled devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1990, 56, 2527–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagli, N.; Snider, G.; Waldman, J.; Hu, E. An electron wave directional coupler and its analysis. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 69, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugster, C.C.; del Alamo, J.A.; Rooks, M.J.; Melloch, M.R. One-dimensional to one dimensional tunnelling between electron waveguides. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 64, 3157–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, M.; Peskin, U. A theoretical investigation of field induced switching in a disordered electron wave coupler. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 85, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikopoulos, G.M. Directional coupling for quantum computing and communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 200502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syms, R.R.A.; Bouchaala, A. Mechanical synchronization of MEMS electrostatically driven coupled beam filters. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syms, R.R.A.; Bouchaala, A. MEMS electrostatically driven coupled beam filter banks. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopcroft, M.A.; Nix, W.D.; Kenny, T.W. What is the Young’s modulus of silicon? J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2010, 19, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, W.; Gallagher, R.H.; Ziemian, R.D. Matrix Structural Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, J.V.; Zhou, N.; Pister, K.S.J. MEMS Simulation Using SUGAR v0.5. In Proceedings of the Solid-State Sensor and Actuator Workshop, Hilton Head, SC, USA, 8–11 June 1998; pp. 191–196. [Google Scholar]



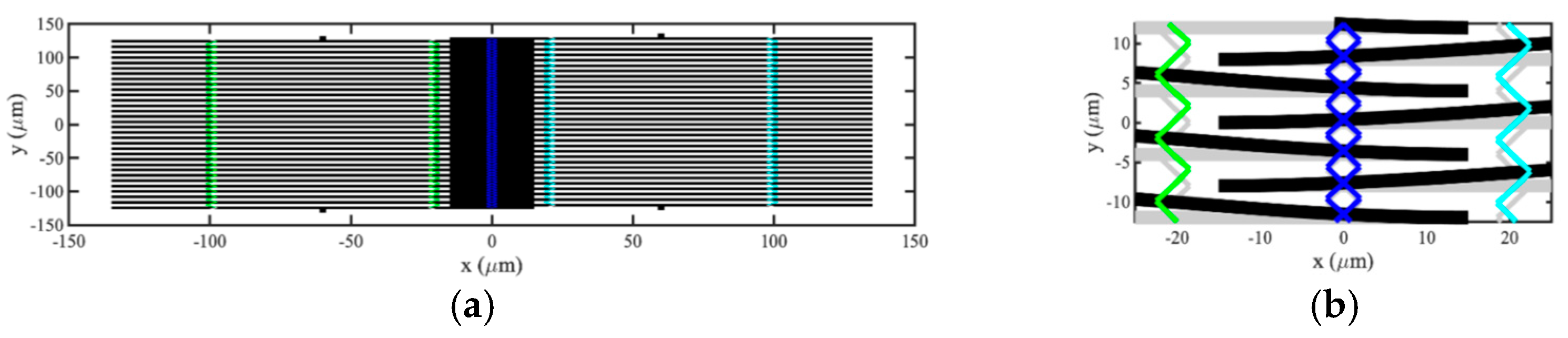
| (μm) | (μm) | (μm) | (μm) | (μm) | (μm) | |
| 150 | 3 | 4 | 0.25 | 8 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
| (kg/m3) | (N/m2) | (N/m2) | ||
| 1.5 | 5000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Syms, R. Quasi-Optical Four-Port Acoustic Filters Based on NEMS Coupled Beam Arrays. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101257
Syms R. Quasi-Optical Four-Port Acoustic Filters Based on NEMS Coupled Beam Arrays. Micromachines. 2024; 15(10):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101257
Chicago/Turabian StyleSyms, Richard. 2024. "Quasi-Optical Four-Port Acoustic Filters Based on NEMS Coupled Beam Arrays" Micromachines 15, no. 10: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101257
APA StyleSyms, R. (2024). Quasi-Optical Four-Port Acoustic Filters Based on NEMS Coupled Beam Arrays. Micromachines, 15(10), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15101257









