A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 4: The Effect of Humidity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. SMO Sensors and GMOS Sensors
1.2. GMOS Sensor
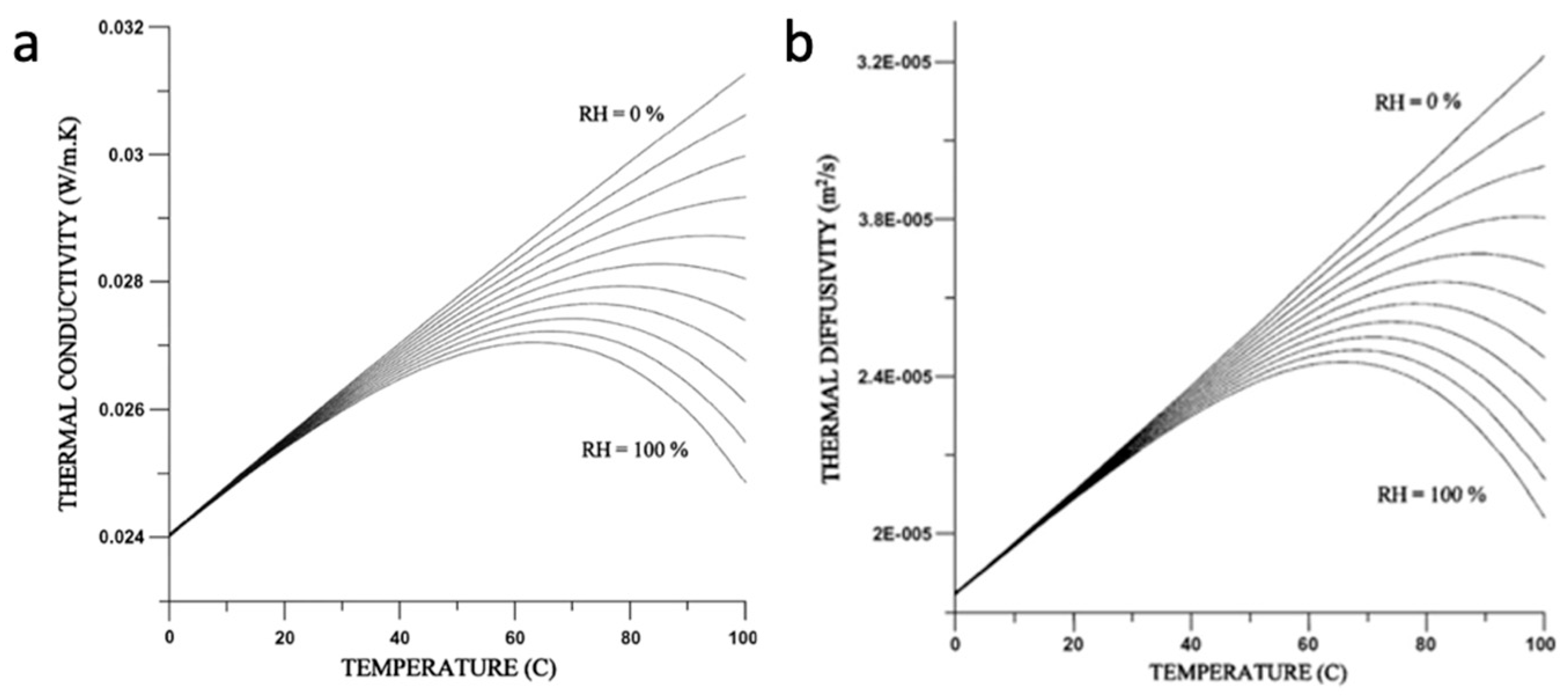
2. The Thermophysical Properties of Humid Air
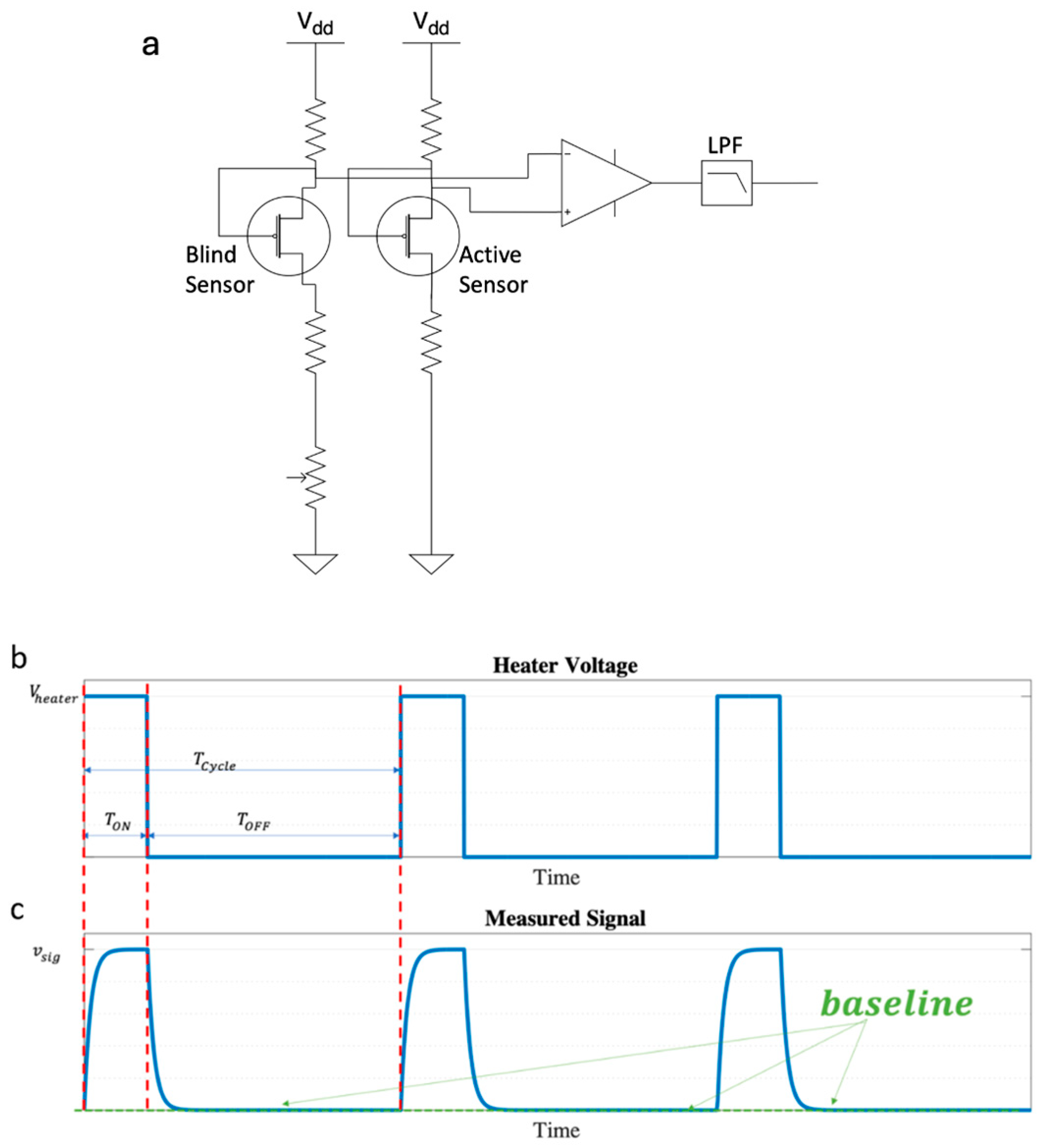
3. Revisiting the Static and Dynamic Operation of the GMOS Designed with a Bridge-like Readout in the Presence of Humidity
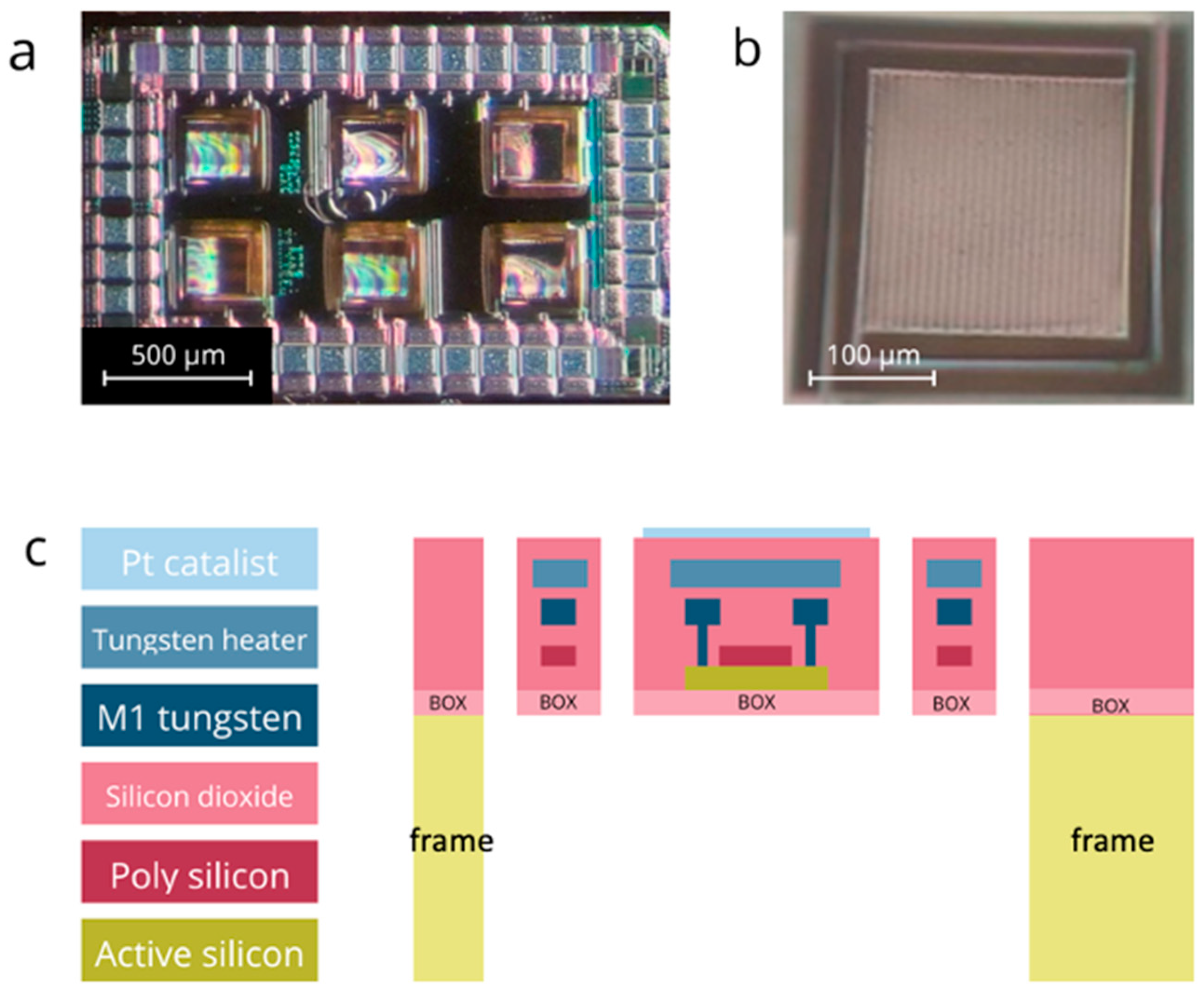
GMOS Sensor
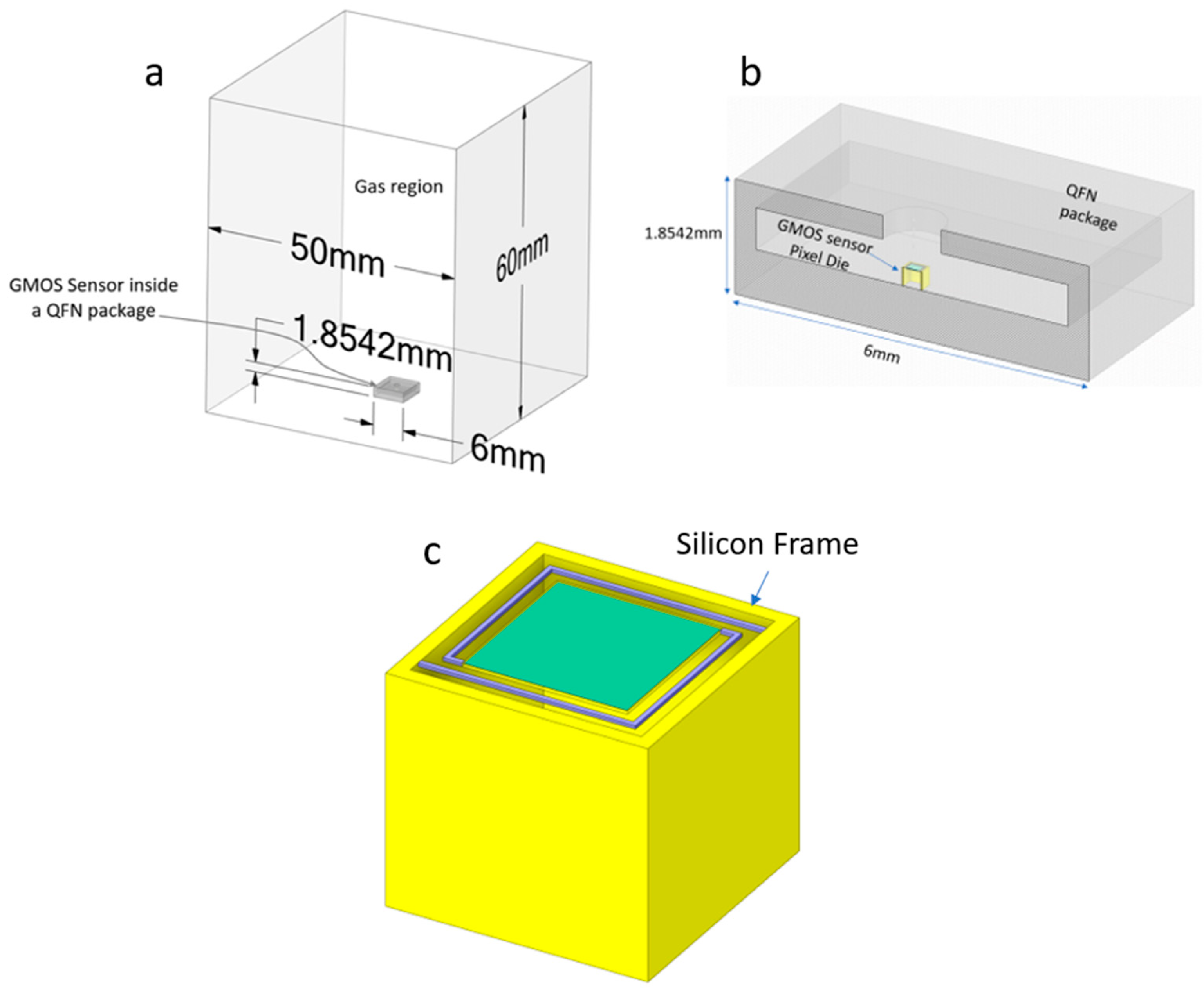
4. Simulation Results
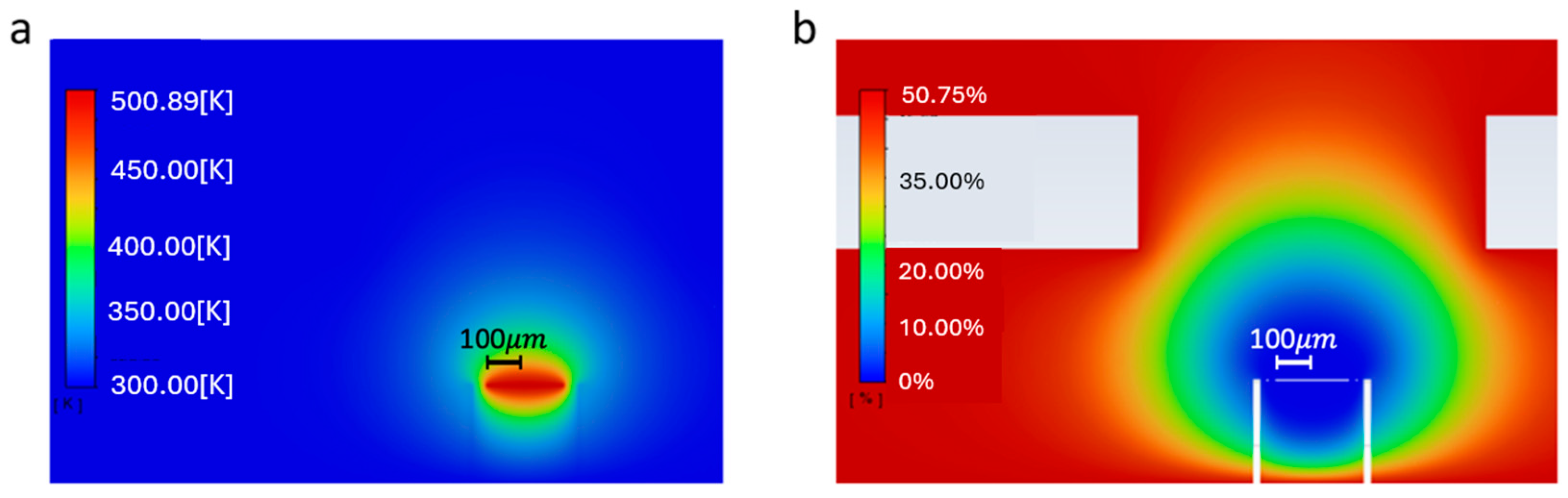
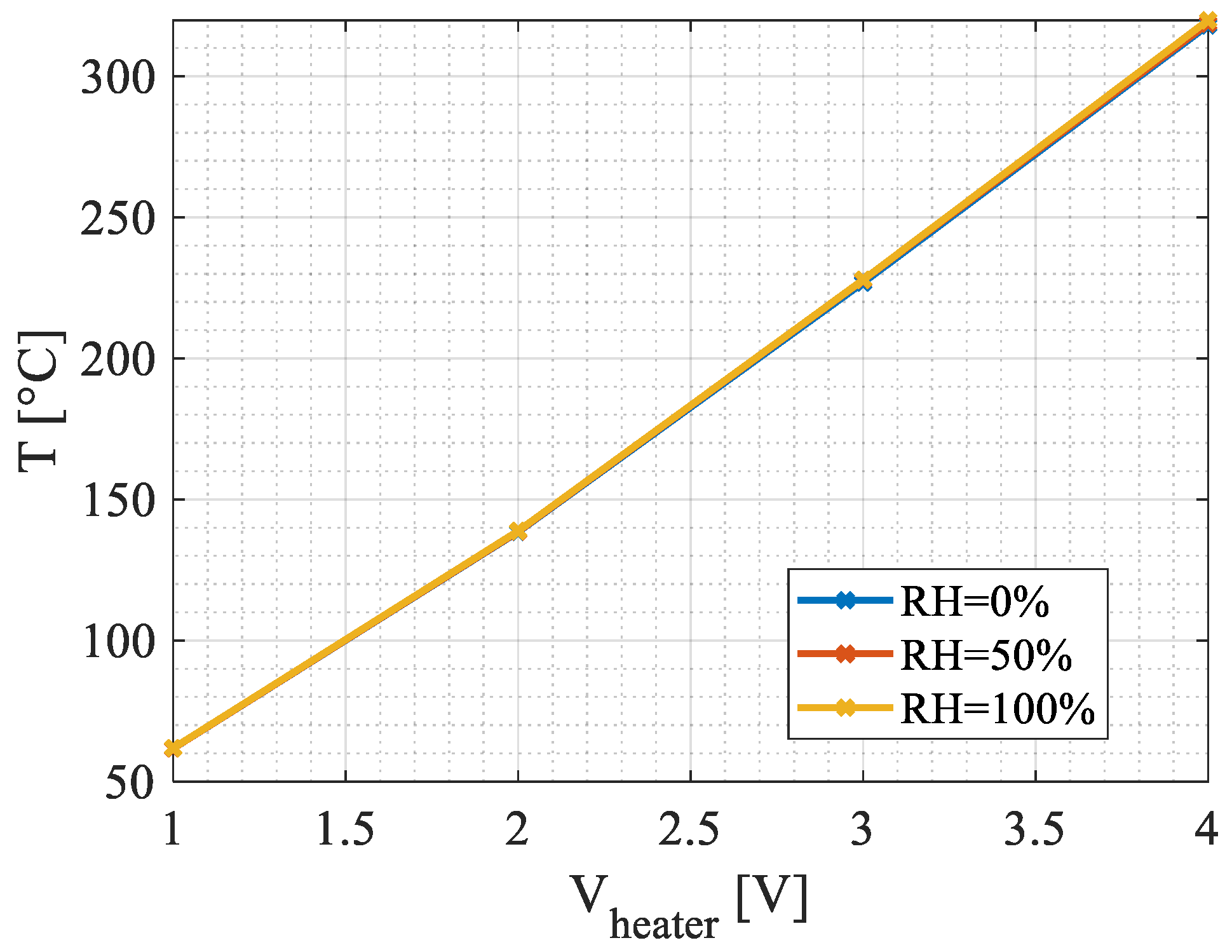
4.1. Steady-State Simulations
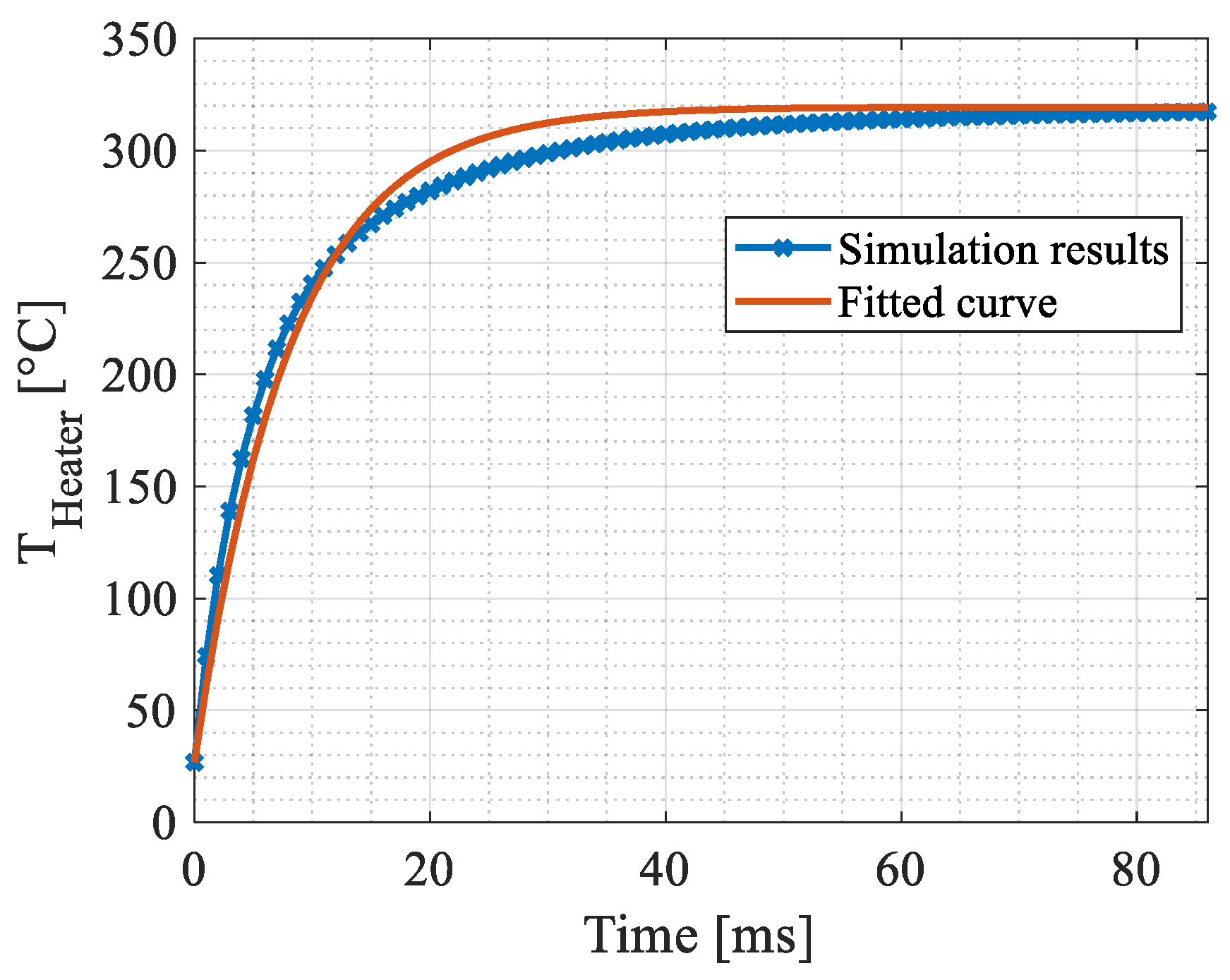
4.2. Transient Simulations
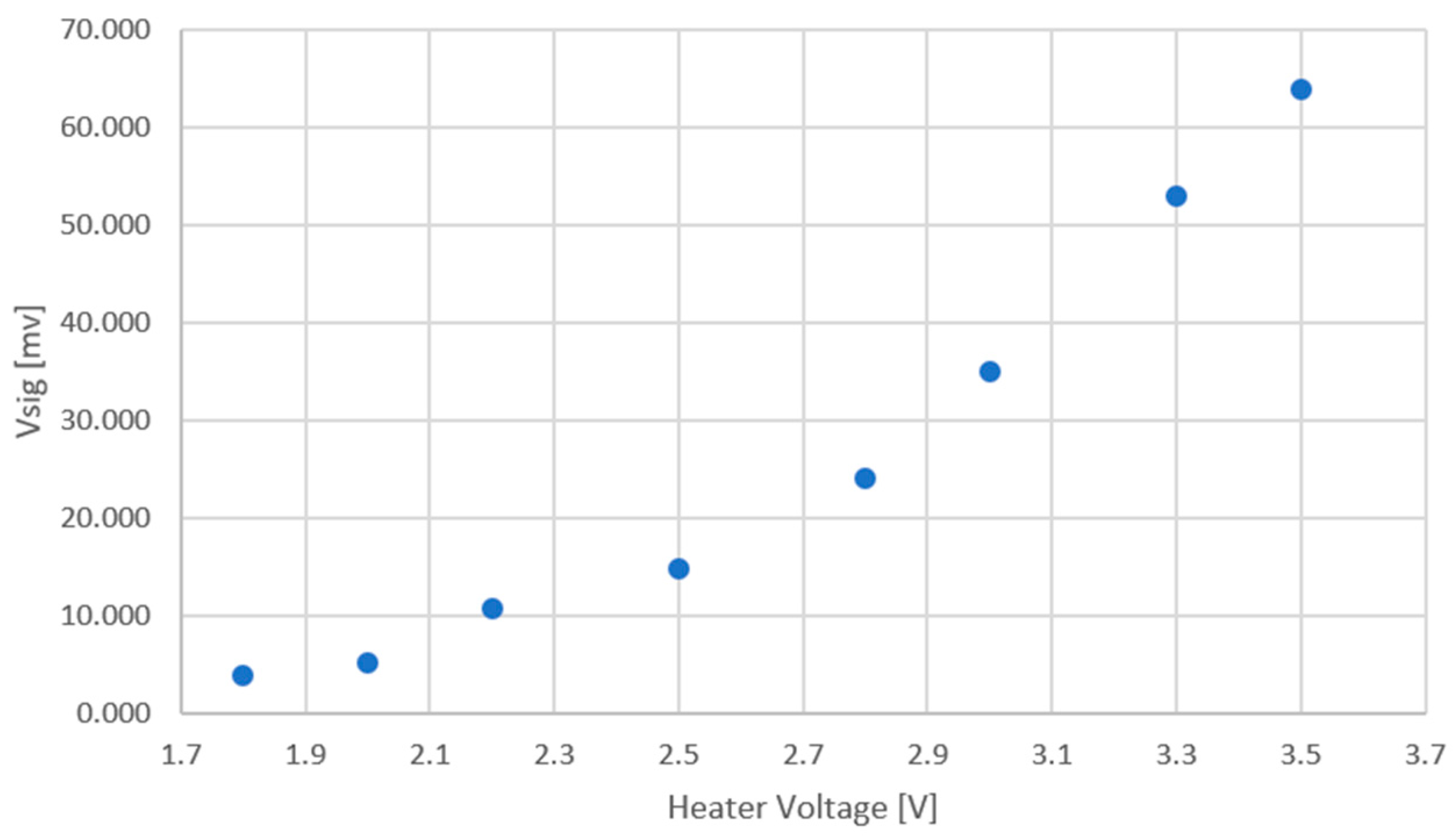
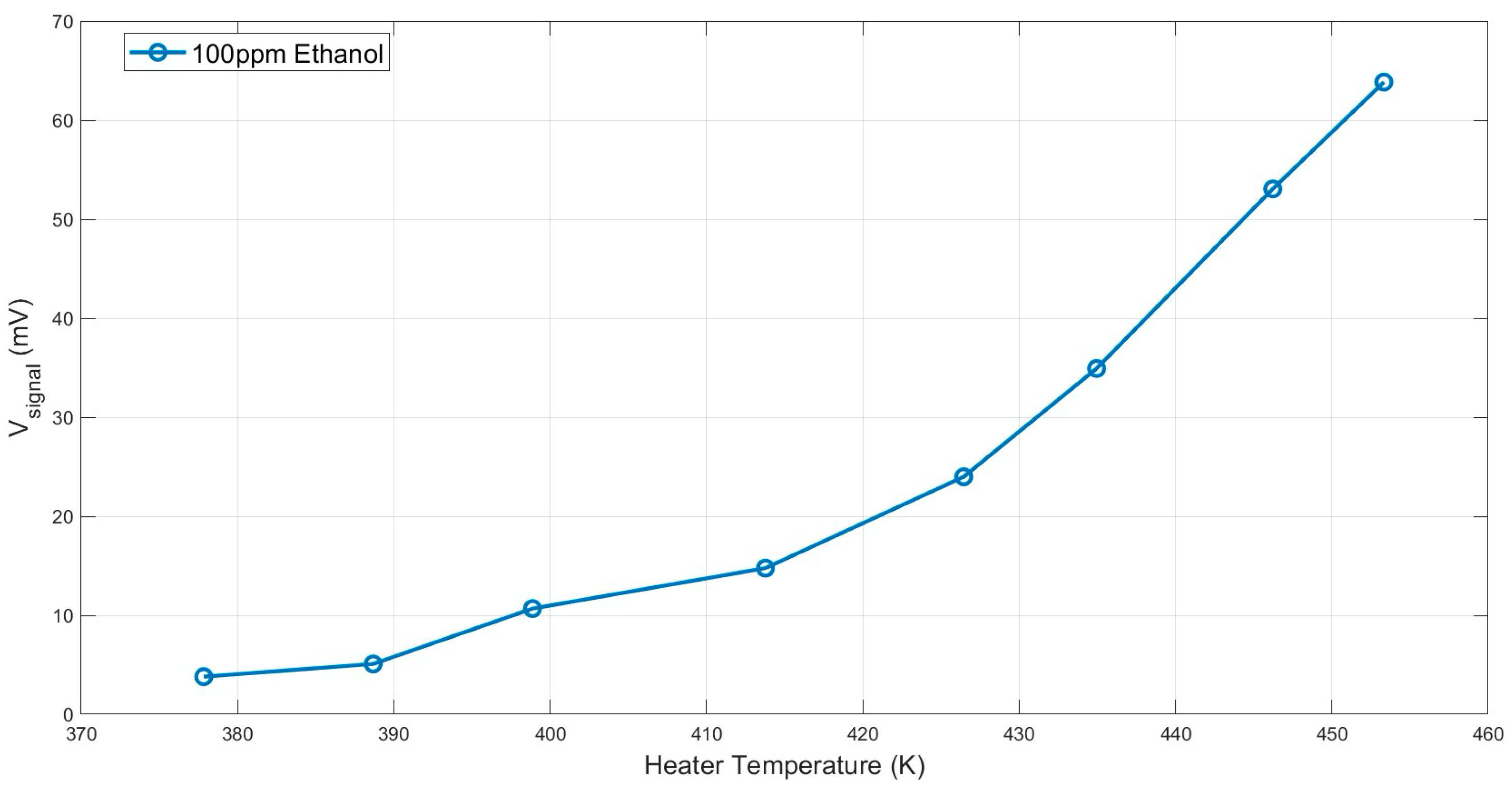
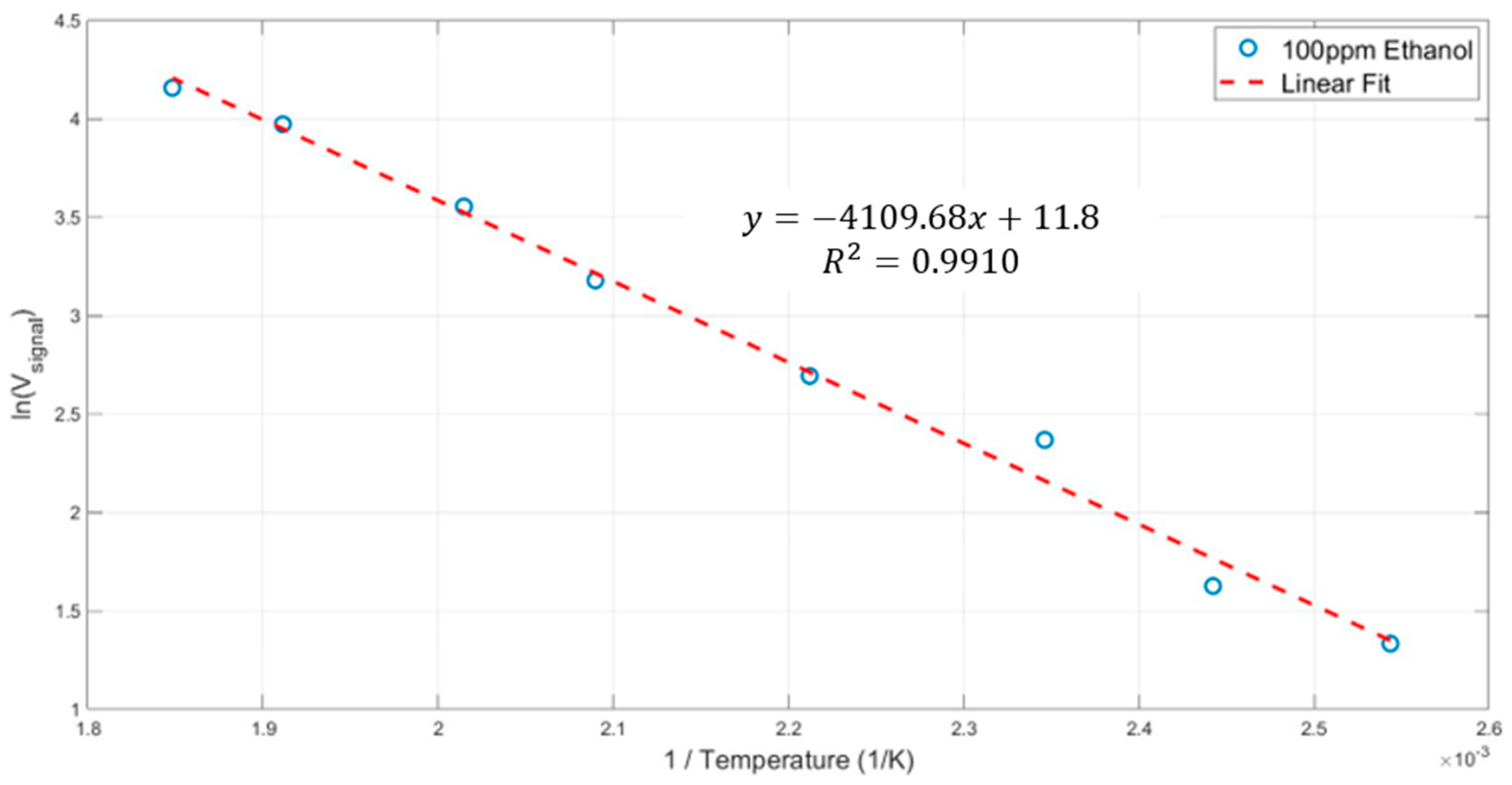
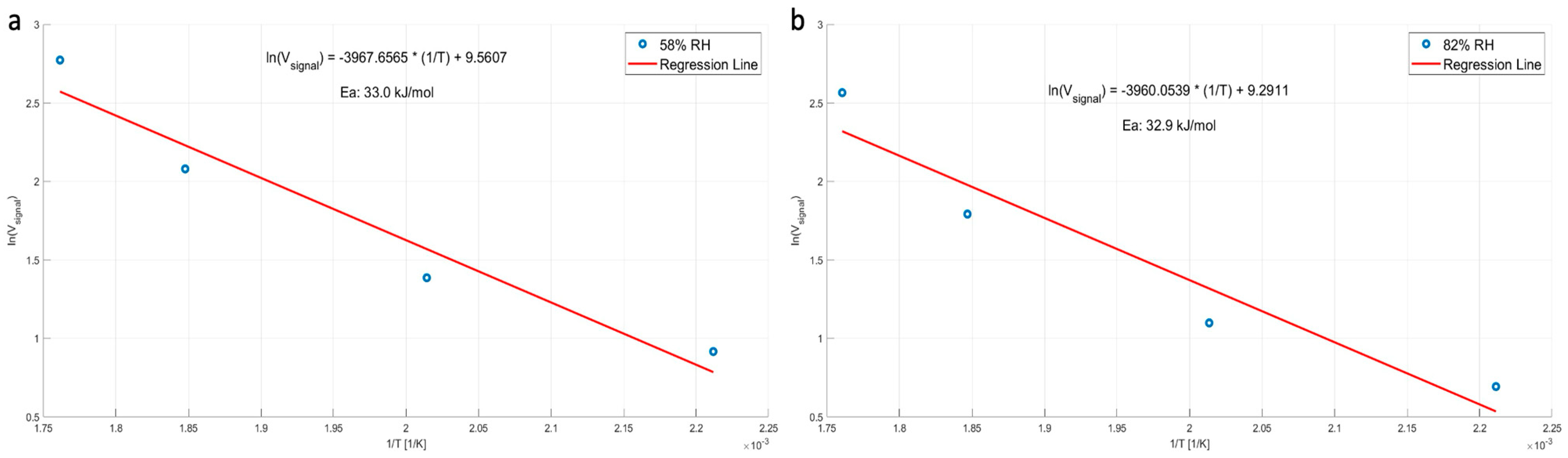
5. Measured Results
6. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
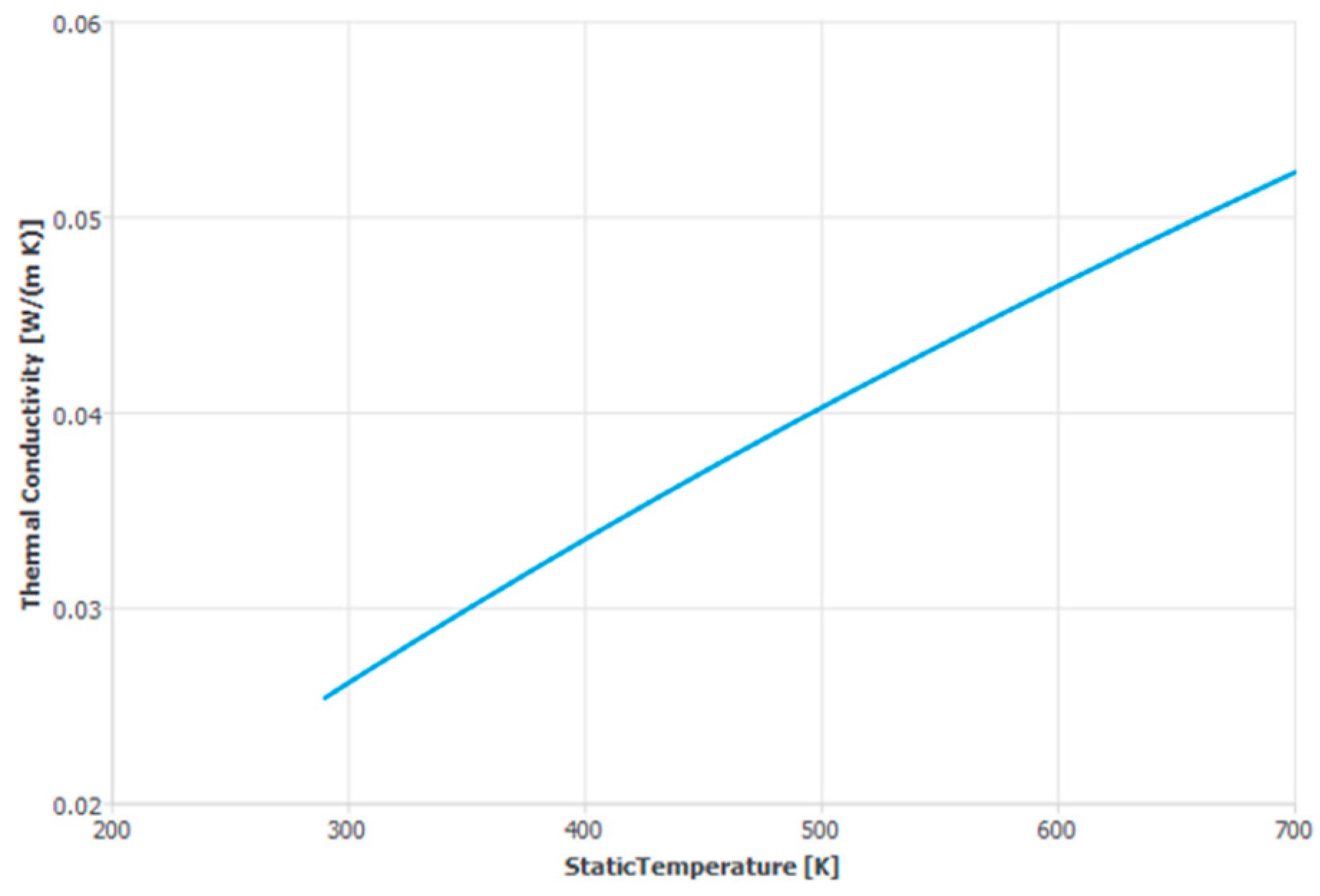
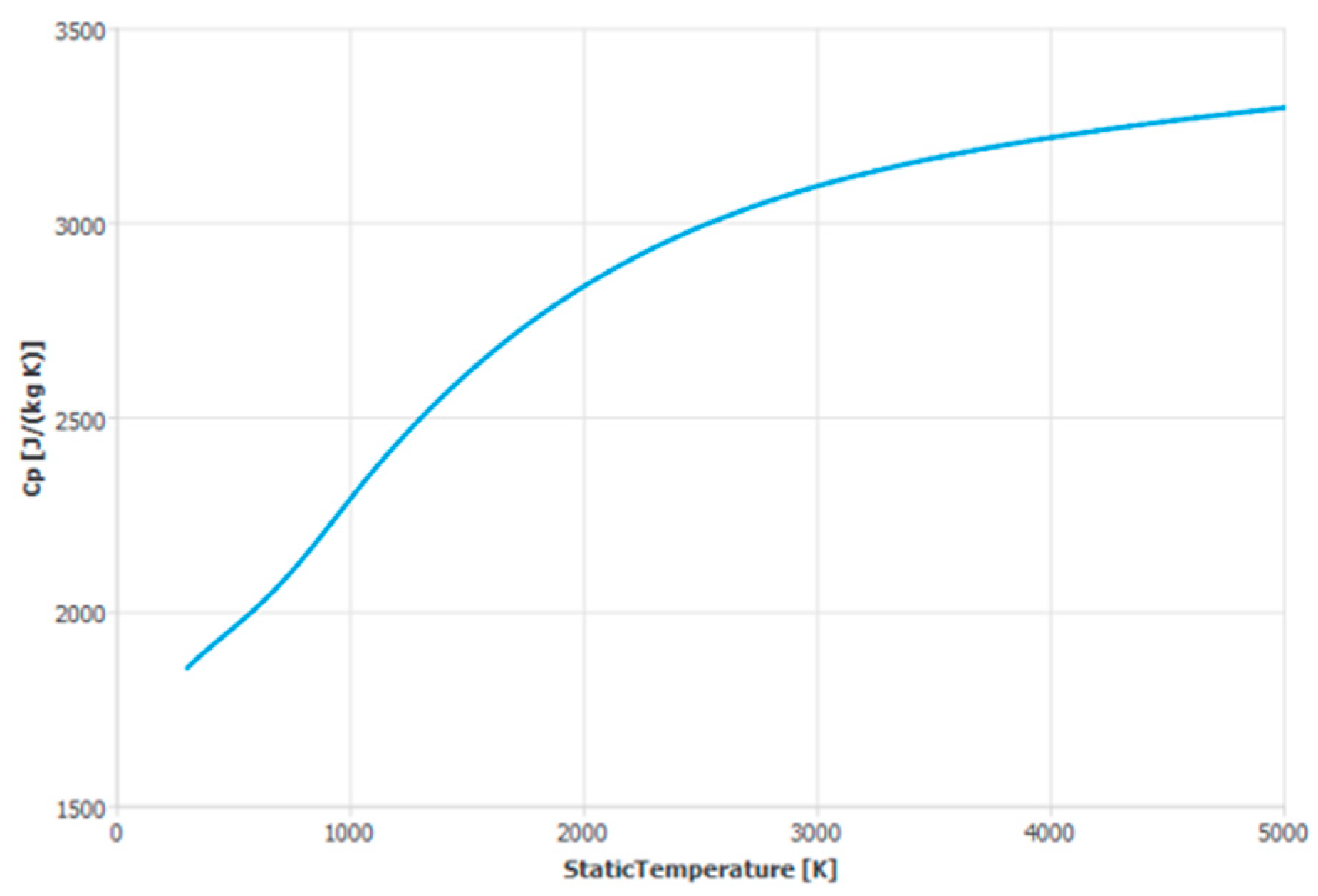
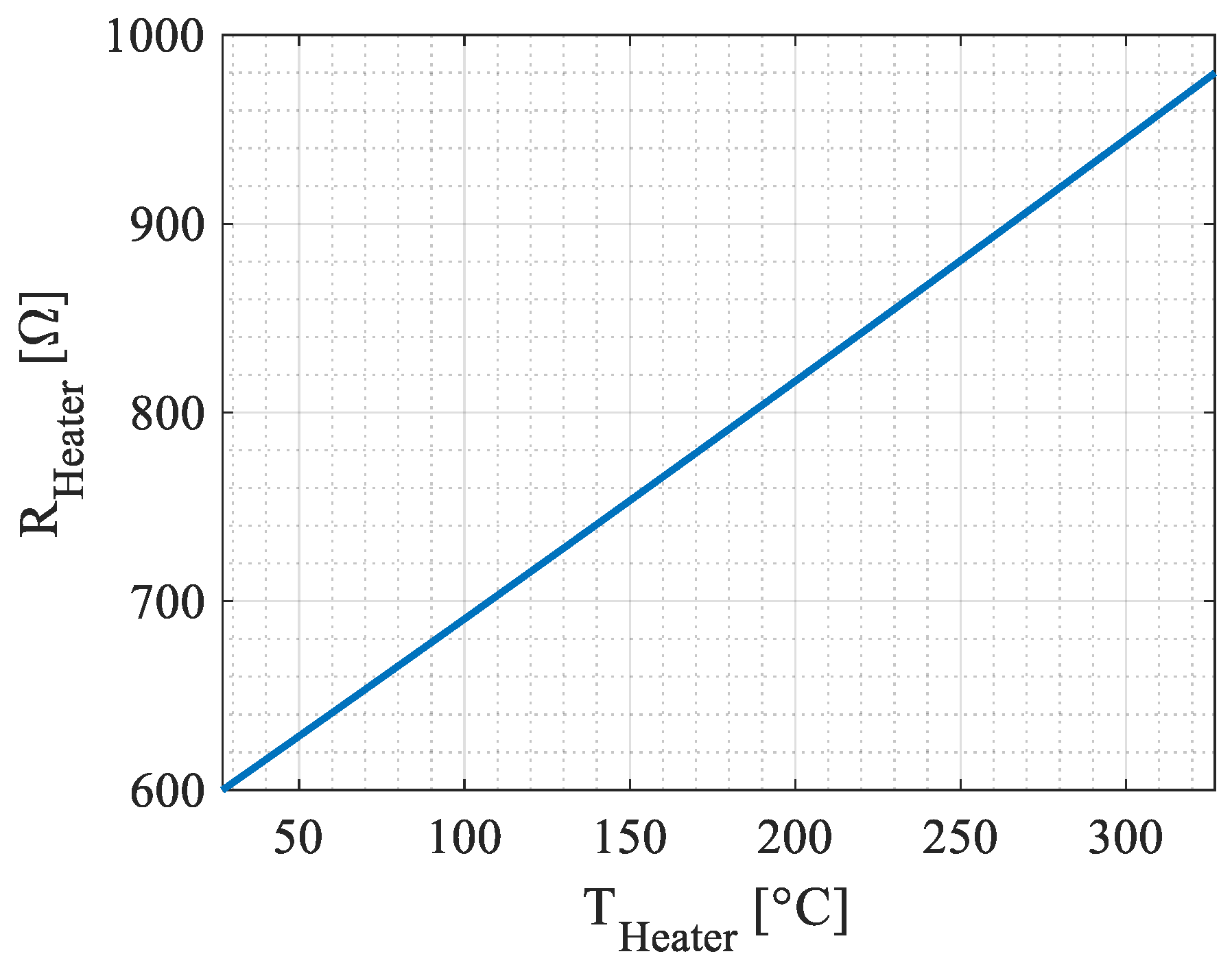
Appendix A. Parameters for Simulation
References
- Nicolic, M.V.; Milovanovic, V.; Vasiljevic, Z.Z.; Stamenkovic, V. Semiconductor Gas Sensors: Materials, Technology, Design, and Application. Sensors 2020, 20, 6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, N.; Kunal, K.; Kushwaha, A.; Kumar, M. Metal Oxide nanostructures-based Gas Sensors. Eng. Rep. 2023, 5, 12604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Gao, S.; Huo, L. Recent Development of Hierarchical Metal Oxides Based Gas Sensors: From Gas Sensing Performance to Applications. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2022, 6, 2100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Pan, S.; He, J.; Liu, A.; Wang, J.; Sun, P.; Liu, F.; Lu, G. Room Temperature Wearable Gas Sensors for Fabrication and Applications. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2300035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, C.; Nazemi, H.; El-Masri, E.; Ambrose, K.; Freund, M.; Emadi, A. A Review on Advanced Sensing Materials for Agricultural Gas Sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesler, P.; Hornoiu, C. MOX-Based Resistive Gas Sensors with Different Types of Sensitive Materials (Powders, Pellets, Films), Used in Environmental Chemistry. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, L.; Selberherr, S. Integration of Gas Sensors with CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th IEEE Electron Devices Technology & Manufacturing Conference (EDTM), Penang, Malaysia, 6–21 April 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovic, L.; Selberherr, S. Thermo-Electro-Mechanical Simulation of Semiconductor Metal Oxide Gas Sensors. Materials 2019, 12, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zviagintsev, A.; Blank, T.; Brouk, I.; Bloom, I.; Nemirovsky, Y. Modeling the Performance of Nano Machined CMOS Transistors for Uncooled IR Sensing. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 4657–4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low-Power, High-Sensitivity Infrared Sensor for Presence and Motion Detection, STMicroelectronics. Available online: https://www.st.com/content/st_com/en/products/mems-and-sensors/infrared-ir-sensors/sths34pf80.html#overview (accessed on 6 March 2022).
- Nemirovsky, Y.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Bar-Lev, S.; Svelitza, A.; Zviaginstev, A.; Brouk, I. A New Pellistor-Like Gas Sensor Based on Micromachined CMOS Transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2018, 65, 5494–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayden, A.; Shlenkevitch, D.; Blank, T.; Stolyarova, S.; Nemirovsky, Y. Selective Sensing of Mixtures of Gases with CMOS-SOI-MEMS Sensor Dubbed GMOS. Micromachines 2023, 14, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shlenkevitch, D.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Brouk, I.; Nemirovsky, Y. A Novel Miniature and Selective Combustion Type CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 1: Emphasis on Chemical Aspects. Micromachines 2020, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avraham, M.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Bar-Lev, S.; Golan, G.; Nemirovsky, Y. A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 2: Emphasis on Physical Aspects. Micromachines 2020, 11, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goikhman, B.; Avraham, M.; Bar-Lev, S.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Nemirovsky, Y. A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 3: Extending the Chemical Modeling. Micromachines 2023, 14, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilingiris, P.T. Thermophysical and transport properties of humid air at temperature range between 0 and 100 C. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, E.L.W.; Gardner, J.W.; Udrea, F. Micromachined Thermal Gas Sensors—A Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, X. Metal Oxide Semiconductor Gas Sensors for Lung Cancer Diagnosis. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, G.; Sberveglieri, G. Origin of Baseline Drift in Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Effects of Bulk Equilibration. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansys Fluent. 2020. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/fluids/ansys-fluent (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- XFAB. Available online: https://www.xfabulous.com/our-locations/erfurt-germany (accessed on 18 January 2024).
- Melling, A.; Noppenberger, S.; Still, M.; Venzke, H. Interpolation Correlations for Fluid Properties of Humid Air in the Temperature Range 100 °C to 200 °C. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 1997, 26, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
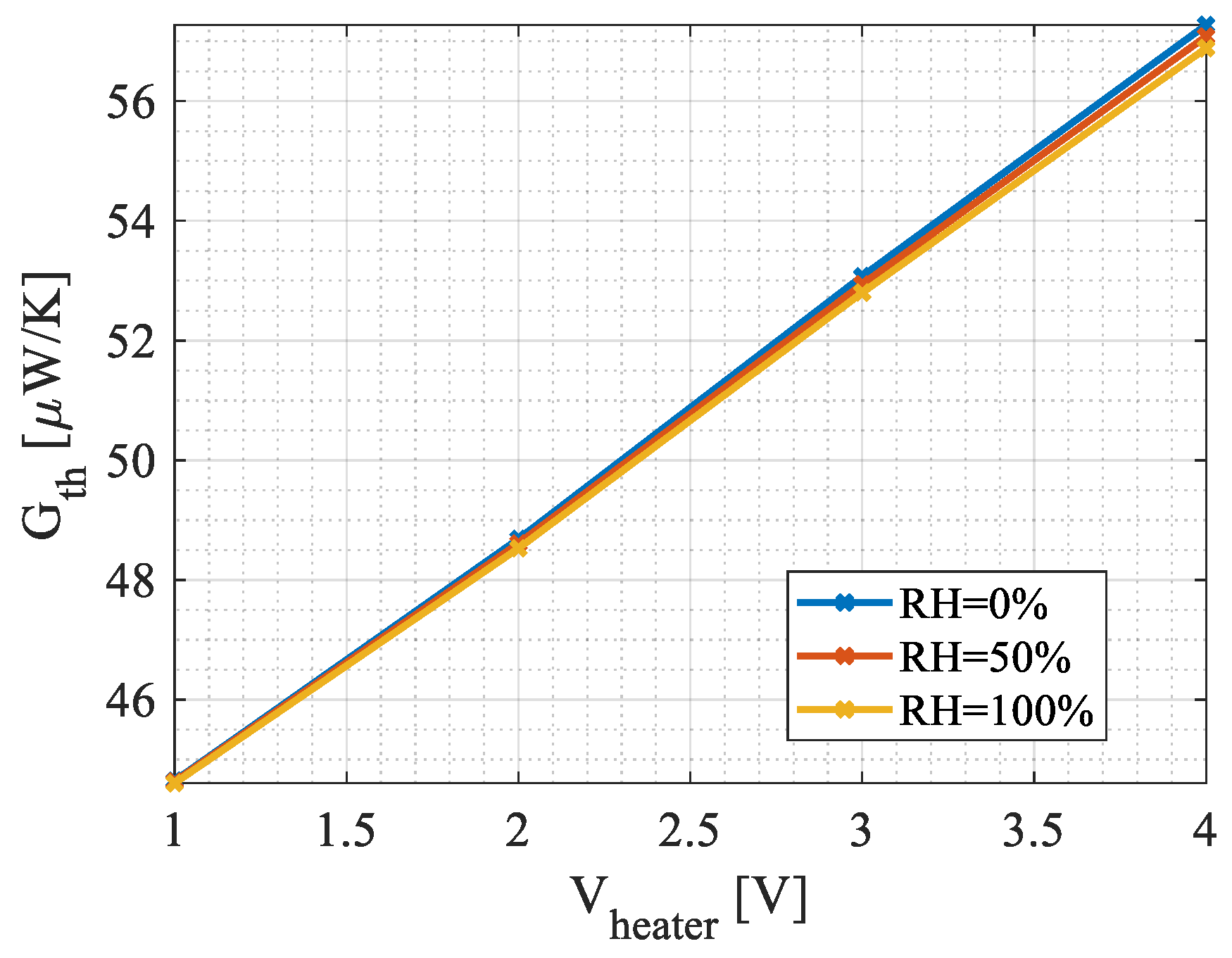
| Parameter | Description | Dry Air at 300 K | Water Vapor at 300 K | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | Thermal conductivity | 0.026 | 0.023 | Lower for water vapor |
| α | Specific thermal diffusivity | Lower for water vapor | ||
| Specific heat capacity | 1006.43 | 1857.72 | Higher for water vapor | |
| [Kg/m3] | Density | 1.225 | 0.5542 | As temp. increases, the density decreases |
| k [W/m·K] | C [J/Kg·K] | Viscosity [Kg/m·s] | Molecular Weight [Kg/kmol] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry air | See Appendix A | 1006.43 | 1.7894 × 10−5 | 28.966 |
| Water vapor | 0.0261 | See Appendix A | 1.34 × 10−5 | 18.01534 |
| k [W/m·K] | c [J/Kg·K] | Density [Kg/m3] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tungsten | 174 | 132 | 19,300 |
| Silicon | 40 | 700 | 2329 |
| Silicon Dioxide | 1.4 | 745 | 2200 |
| Lead | 35 | 0.13 | 11,342 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avraham, M.; Krayden, A.; Ashkar, H.; Aronin, D.; Stolyarova, S.; Blank, T.; Shlenkevitch, D.; Nemirovsky, Y. A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 4: The Effect of Humidity. Micromachines 2024, 15, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020264
Avraham M, Krayden A, Ashkar H, Aronin D, Stolyarova S, Blank T, Shlenkevitch D, Nemirovsky Y. A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 4: The Effect of Humidity. Micromachines. 2024; 15(2):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020264
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvraham, Moshe, Adir Krayden, Hanin Ashkar, Dan Aronin, Sara Stolyarova, Tanya Blank, Dima Shlenkevitch, and Yael Nemirovsky. 2024. "A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 4: The Effect of Humidity" Micromachines 15, no. 2: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020264
APA StyleAvraham, M., Krayden, A., Ashkar, H., Aronin, D., Stolyarova, S., Blank, T., Shlenkevitch, D., & Nemirovsky, Y. (2024). A Novel Miniature and Selective CMOS Gas Sensor for Gas Mixture Analysis—Part 4: The Effect of Humidity. Micromachines, 15(2), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15020264






