Motor Behavior Regulation of Rat Robots Using Integrated Electrodes Stimulated by Micro-Nervous System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Ethical Statement
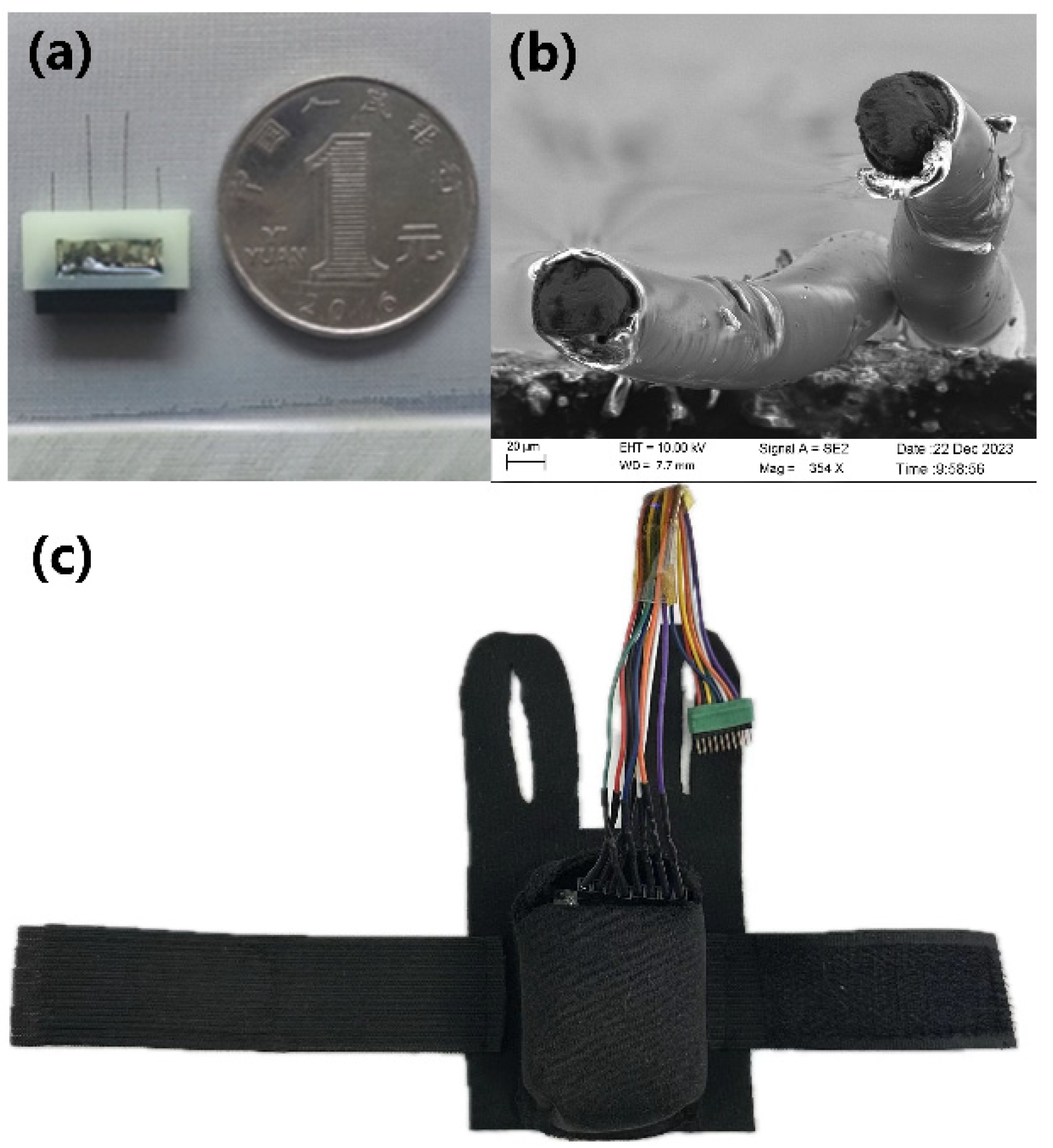
2.2. Integrated Electrode
- (1)
- Two electrode wires of appropriate length were twisted together using a twisting device to ensure sufficient strength when piercing the cerebral cortex. Four twisted-pair Ni-Ti electrodes were manufactured, with 1 cm of insulation removed from the tails, and the two electrode wires at the end of the twisted pair were wrapped around the 1.27 mm pitch row mother.
- (2)
- Holes were drilled in the electrode sockets (length of 15 mm, width of 5 mm, height of 7 mm) following the mediolateral (ML) and anteroposterior (AP) coordinates of the implantation site, and then the electrode was passed through the hole in the electrode base.
- (3)
- A UV curing adhesive was injected into the electrode base, and the position of the electrode wire was adjusted before irradiation with a UV lamp for 5–10 s to secure it.
- (4)
- The electrodes were diagonally cut according to the dorsoventral (DV) coordinates to prevent short-circuiting of the electrodes. Additionally, a 1 mm margin in length was retained for the electrodes, accounting for the thickness of the skull itself. The final electrode length was 9.2 mm for the MFB site and 3.5 mm for the SIBF site.
2.3. Animal Experiment
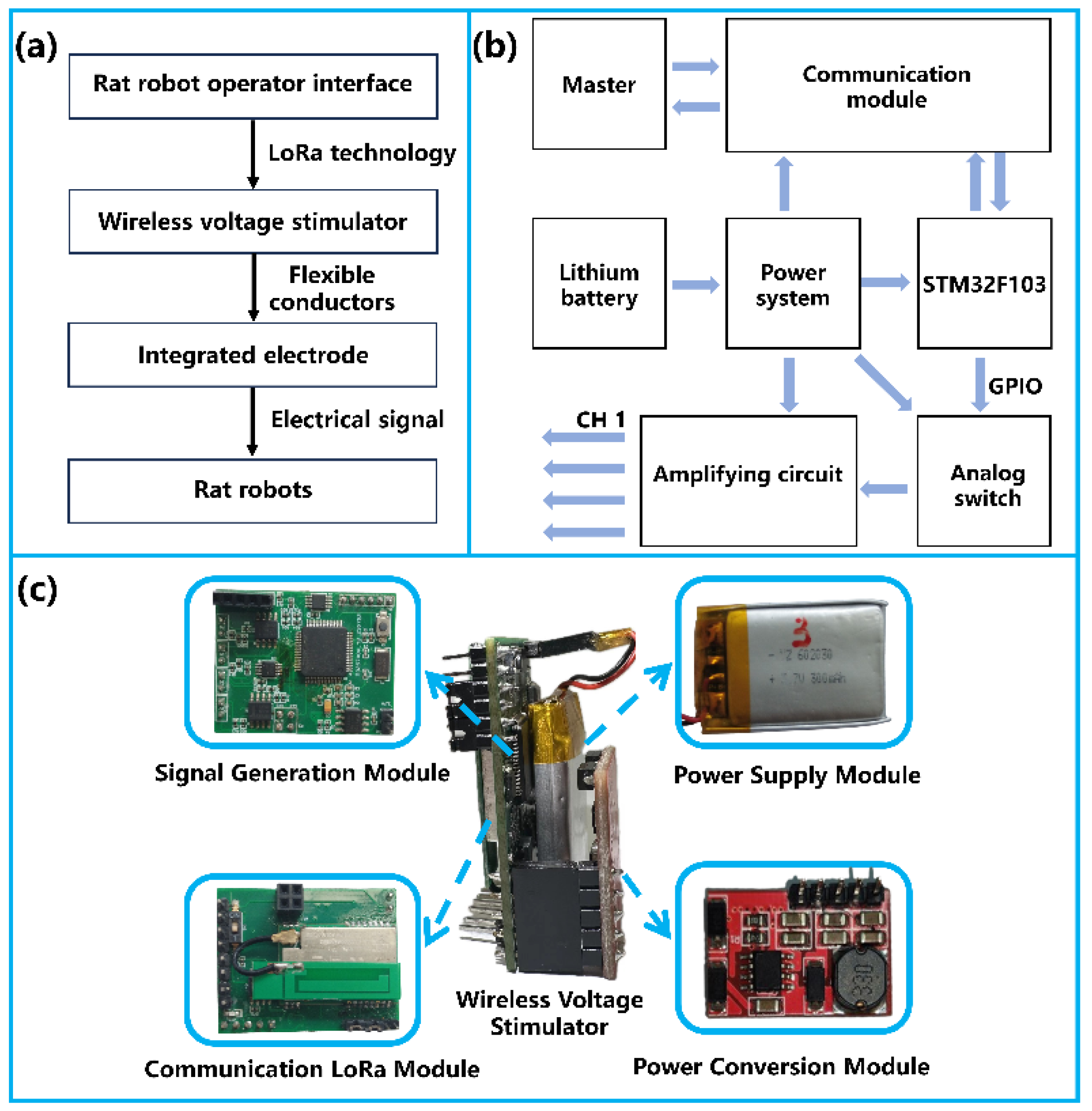
2.4. Remote Control System for Rat Robots
2.5. Electrical Stimulation Experiments
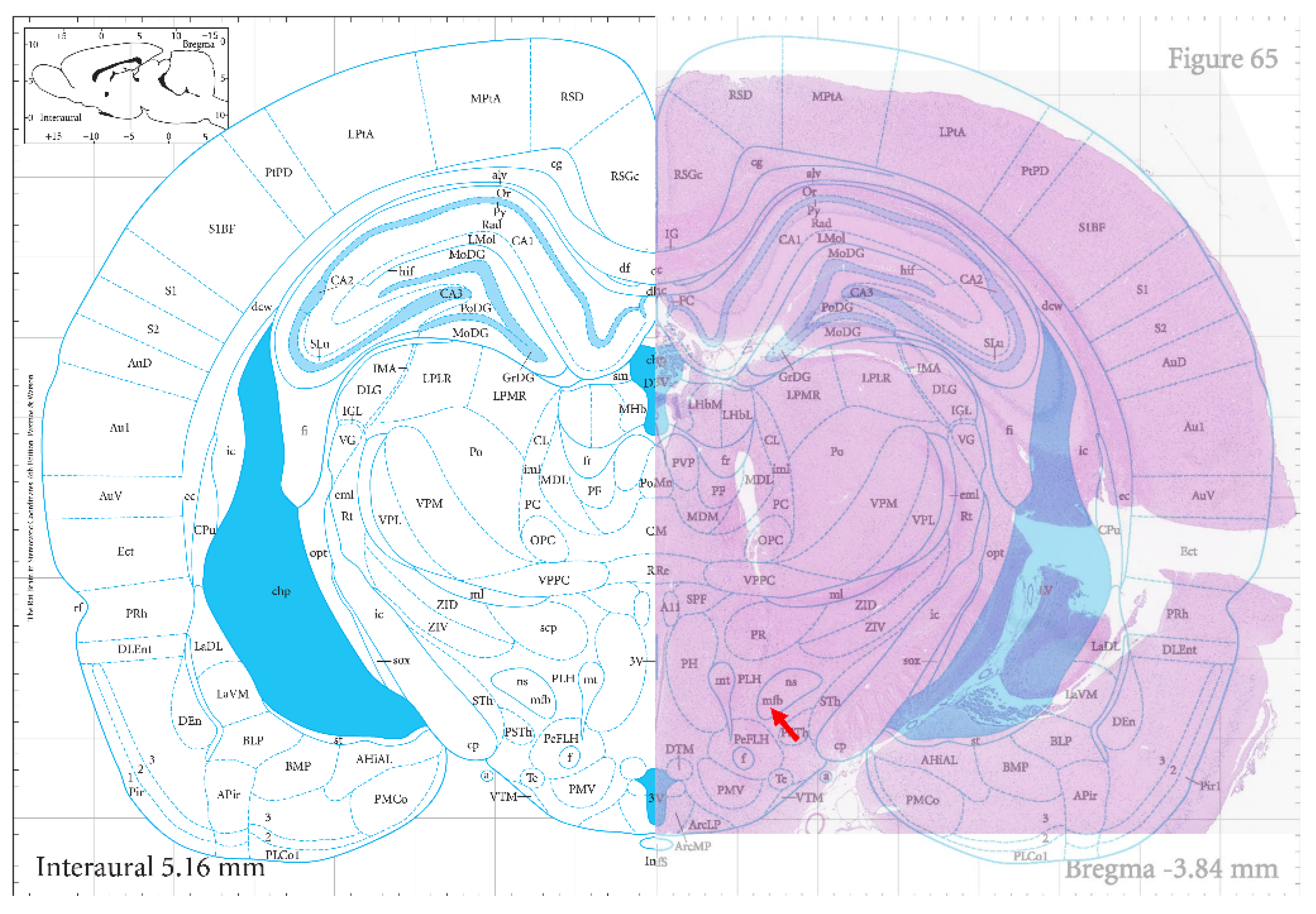
2.6. Histological Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Integrated Electrodes and Backpack
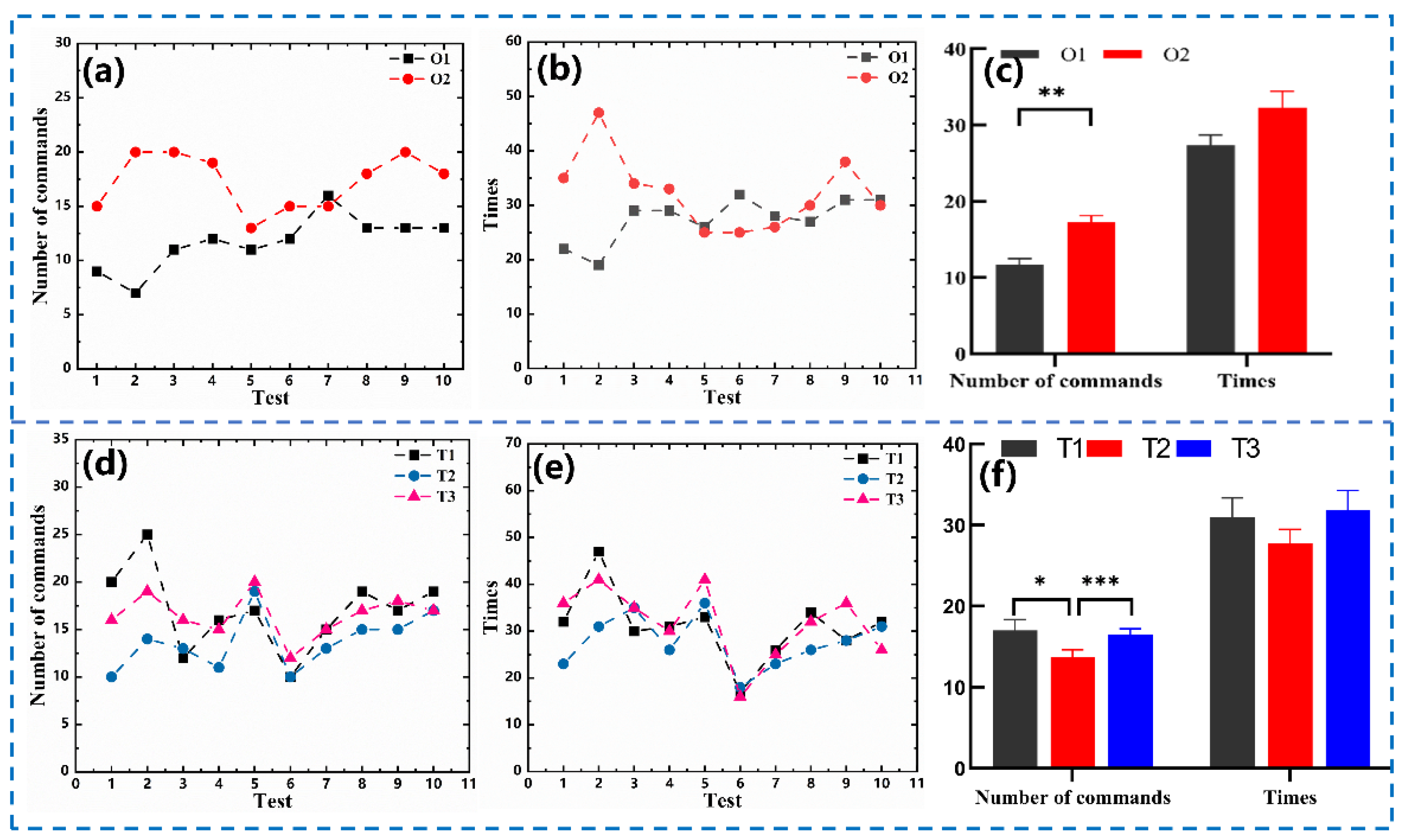
3.2. Activation Parameters of Rat Robotic Brain Regions
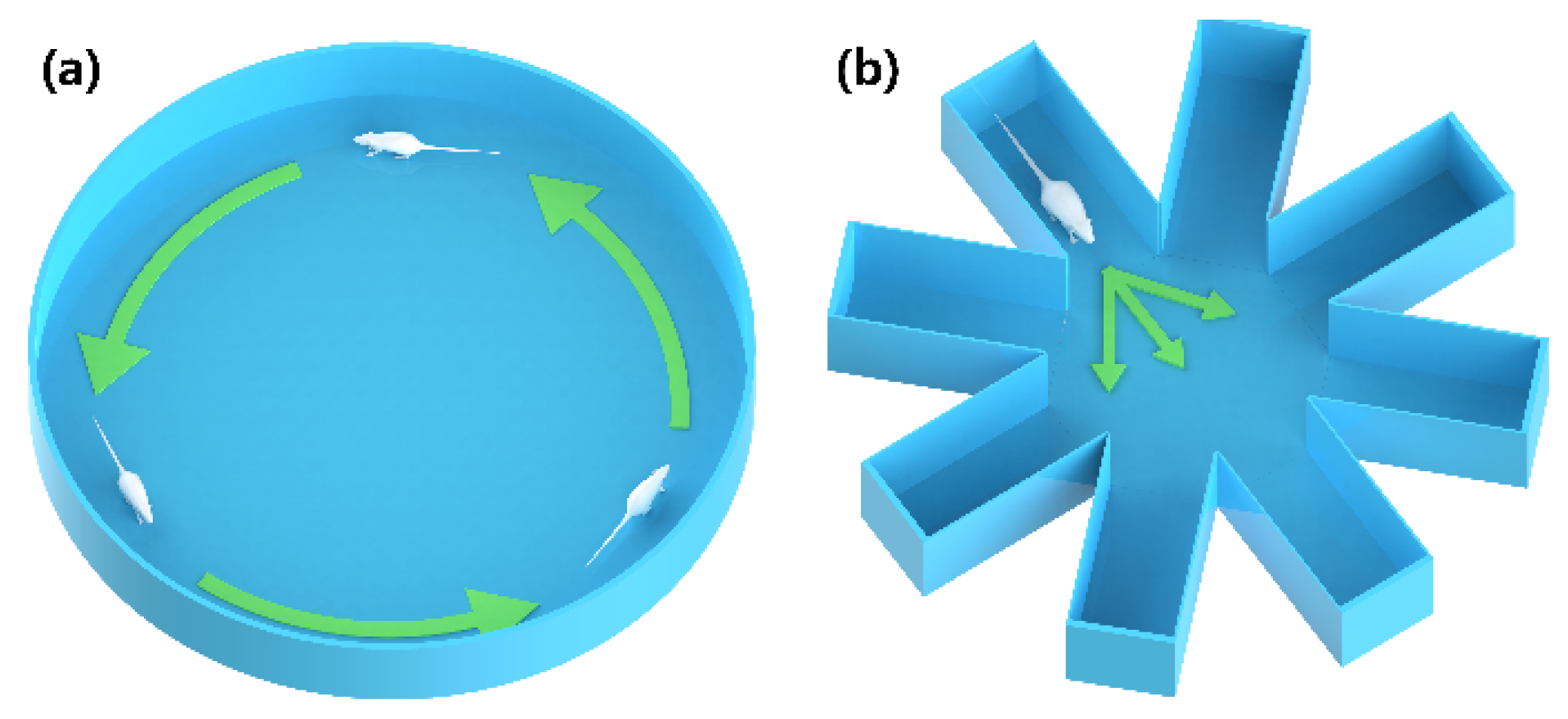
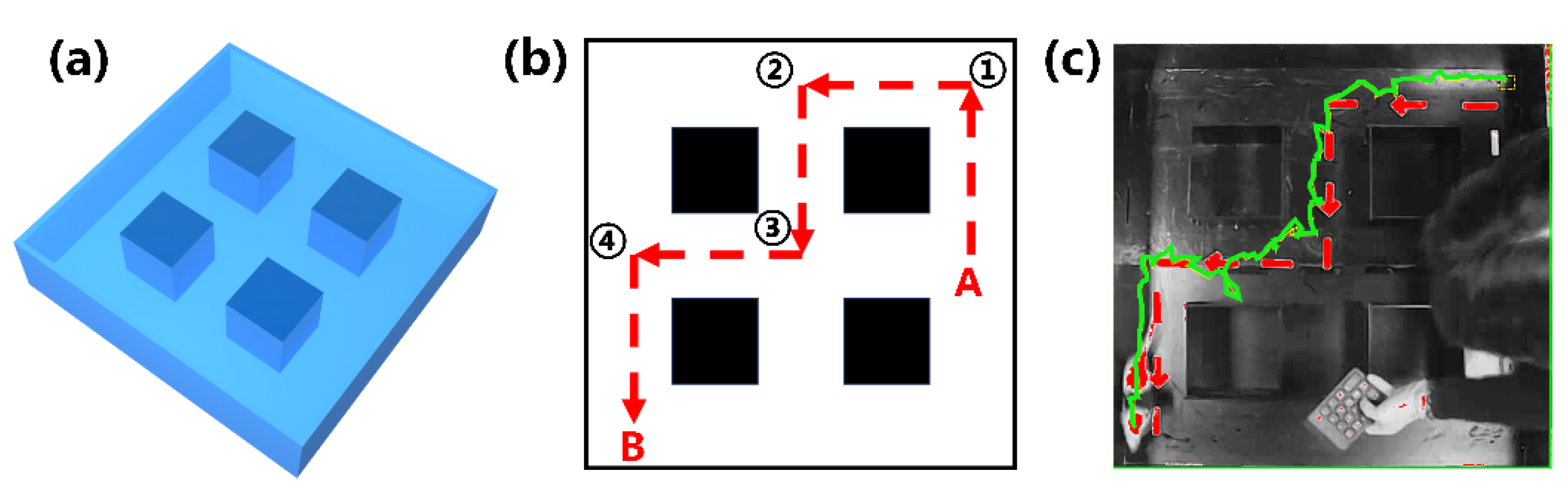
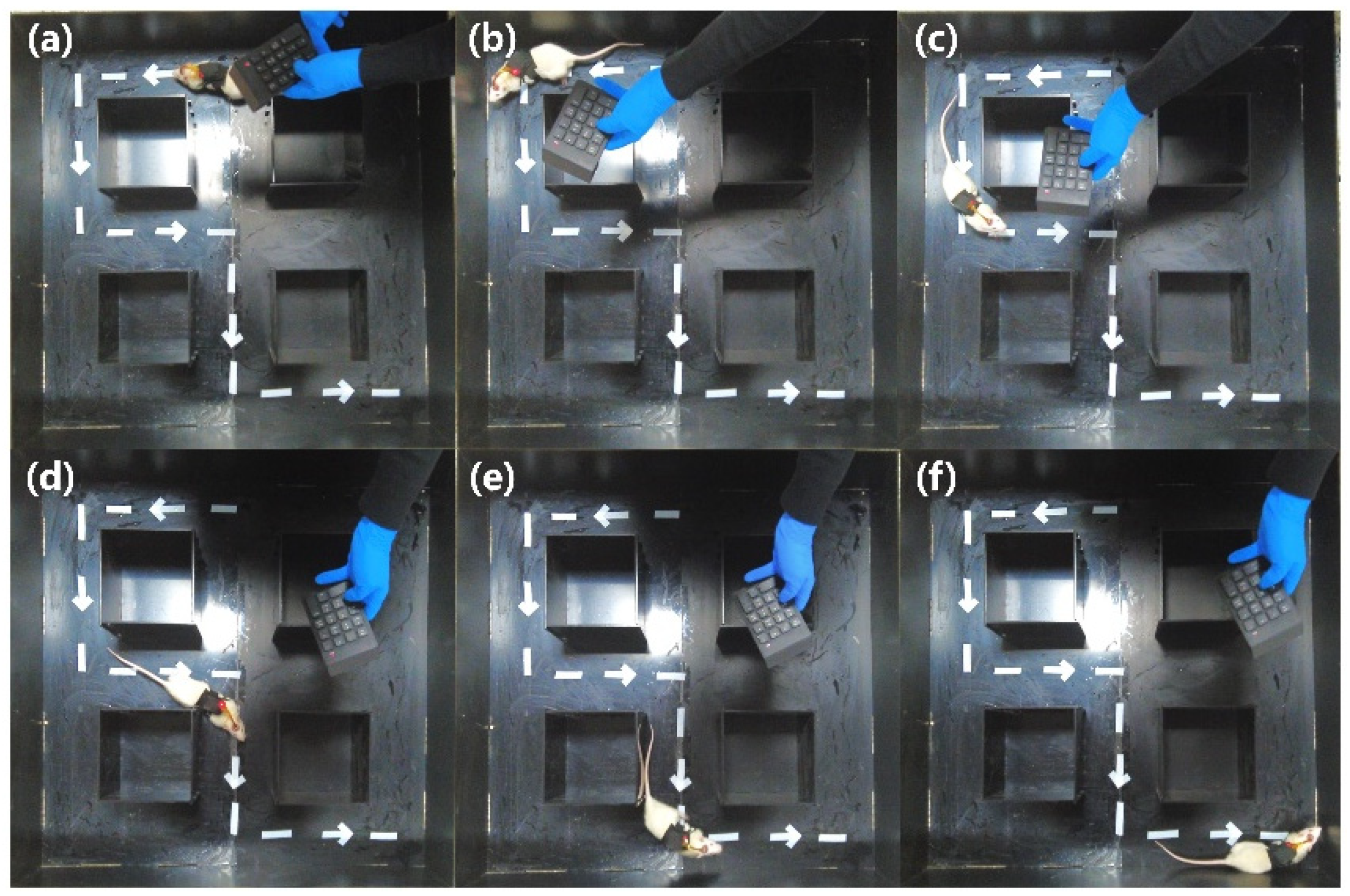
3.3. Maze Training
3.4. The Cube Maze Mission
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Exploring motor imagery EEG patterns for stroke patients with deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, AB, Canada, 15–20 April 2018; pp. 2561–2565. [Google Scholar]
- Slimen, I.B.; Boubchir, L.; Seddik, H. Epileptic seizure prediction based on EEG spikes detection of ictal-preictal states. J. Biomed. Res. 2020, 34, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, D.S.B.A.; Goyal, S.; Bedi, P. Integration of deep learning for improved diagnosis of depression using EEG and facial features. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 80, 1965–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, M.; Leonardis, D.; Loconsole, C.; Solazzi, M.; Sotgiu, E.; Procopio, C.; Chisari, C.; Bergamasco, M.; Frisoli, A. A full upper limb robotic exoskeleton for reaching and grasping rehabilitation triggered by MI-BCI. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ganzer, P.D.; Colachis, S.C.; Schwemmer, M.A.; Friedenberg, D.A.; Dunlap, C.F.; Swiftney, C.E.; Jacobowitz, A.F.; Weber, D.J.; Bockbrader, M.A.; Sharma, G. Restoring the sense of touch using a sensorimotor demultiplexing neural interface. Cell 2020, 181, 763–773.e712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, D.; Chennu, S.; Fernández-Espejo, D.; Payne, W.L.; Young, G.B.; Owen, A.M. Detecting awareness in the vegetative state: Electroencephalographic evidence for attempted movements to command. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, R.; Shimoyama, I. Locomotion control of a bio-robotic system via electric stimulation. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robot and Systems. Innovative Robotics for Real-World Applications. IROS’97, Grenoble, France, 7–11 September 1997; pp. 1514–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Koh, C.S.; Jeong, J.; Seo, J.; Ahn, S.-H.; Choi, G.J.; Shim, S.; Shin, J.; Jung, H.H.; Chang, J.W. Remote-controlled fully implantable neural stimulator for freely moving small animal. Electronics 2019, 8, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Behroozi, M.; Shalchyan, V.; Daliri, M.R. Rat navigation by stimulating somatosensory cortex. J. Bionic Eng. 2019, 16, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wan, H.; Shang, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, L. Intracortical microstimulation parameters modulate flight behavior in pigeon. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2019, 18, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, D.; Sun, H.; Xu, W.; Tian, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Z. Pigeon robot for navigation guided by remote control: System construction and functional verification. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Ngoc, P.T.; Le, D.L.; Chong, B.S.; Nguyen, H.D.; Dung, V.T.; Cao, F.; Li, Y.; Kai, K.; Gan, J.H.; Vo-Doan, T.T. Intelligent Insect–Computer Hybrid Robot: Installing Innate Obstacle Negotiation and Onboard Human Detection onto Cyborg Insect. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Yoshida, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Uematsu, K. Artificial control of swimming in goldfish by brain stimulation: Confirmation of the midbrain nuclei as the swimming center. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 452, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Jin, M.; Hong, H.; Huang, L.; Gu, Z.; Li, H. Real--time and precise insect flight control system based on virtual reality. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 387–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubanek, J.; Brown, J.; Ye, P.; Pauly, K.B.; Moore, T.; Newsome, W. Remote, brain region–specific control of choice behavior with ultrasonic waves. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Qu, Y.; Guo, S.; Shi, Z.; Xu, K.; Zheng, X. Encode the “STOP” command by photo-stimulation for precise control of rat-robot. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 2172–2175. [Google Scholar]
- Aravanis, A.M.; Wang, L.-P.; Zhang, F.; Meltzer, L.A.; Mogri, M.Z.; Schneider, M.B.; Deisseroth, K. An optical neural interface: In vivo control of rodent motor cortex with integrated fiberoptic and optogenetic technology. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyden, E.S.; Zhang, F.; Bamberg, E.; Nagel, G.; Deisseroth, K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-y.; Yu, C.-n.; Jia, J.; Zhang, S.-m.; Wang, Y.-w.; Chen, W.-d.; Zheng, X.-x. Using dlPAG-evoked immobile behavior in animal-robotics navigation. In Proceedings of the 2010 5th International Conference on Computer Science & Education, Valencia, Spain, 7–10 April 2010; pp. 1295–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, F.; Zhang, C.; Choo, H.Y.; Sato, H. Insect-machine hybrid robot: Insect walking control by sequential electrical stimulation of leg muscles. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; pp. 4576–4582. [Google Scholar]
- Sholomenko, G.; Funk, G.; Steeves, J. Avian locomotion activated by brainstem infusion of neurotransmitter agonists and antagonists: I. Acetylcholine, excitatory amino acids and substance P. Exp. Brain Res. 1991, 85, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capelli, P.; Pivetta, C.; Soledad Esposito, M.; Arber, S. Locomotor speed control circuits in the caudal brainstem. Nature 2017, 551, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farakhor, S.; Shalchyan, V.; Daliri, M.R. Adaptation effects of medial forebrain bundle micro-electrical stimulation. Bioengineered 2019, 10, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Lee, J.C.T.; Zheng, X. A novel turning behavior control method for rat-robot through the stimulation of ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 298, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.; Koh, C.S.; Park, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-G.; Chang, J.W.; Choi, S.; Shin, H.-C. Manipulation of rat movement via nigrostriatal stimulation controlled by human visually evoked potentials. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.S.; Park, H.-Y.; Shin, J.; Kong, C.; Park, M.; Seo, I.-S.; Koo, B.; Jung, H.H.; Chang, J.W.; Shin, H.-C. A novel rat robot controlled by electrical stimulation of the nigrostriatal pathway. Neurosurg. Focus 2020, 49, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, Z. Recent advances in silicon-based neural microelectrodes and microsystems: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 300–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, V.; Trumpis, M.; Bent, B.; Palopoli-Trojani, K.; Chiang, C.-H.; Wang, C.; Yu, C.; Insanally, M.N.; Froemke, R.C.; Viventi, J. Long-term recording reliability of liquid crystal polymer µECoG arrays. J. Neural Eng. 2018, 15, 066024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhuang, L.; Qin, Z.; Wei, X.; Yuan, Q.; Qin, C.; Wang, P. A wearable system for olfactory electrophysiological recording and animal motion control. J. Neurosci. Methods 2018, 307, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakei, Y.; Katayama, S.; Lee, S.; Takakuwa, M.; Furusawa, K.; Umezu, S.; Sato, H.; Fukuda, K.; Someya, T. Integration of body-mounted ultrasoft organic solar cell on cyborg insects with intact mobility. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2022, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.; Won, S.M.; Sohrabi, A.K.; Stuart, T.; Amirhossein, A.; Kim, J.U.; Park, Y.; Gabros, A.; Rogers, J.A.; Vitale, F. Wireless, battery-free, and fully implantable electrical neurostimulation in freely moving rodents. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.S.; Ryu, O.; Cho, K.; Kim, D.; Lim, J.; Hong, S.H.; Cho, Y.-S. The effect of charge-balanced transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on rodent facial nerve regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| S-1 | S-2 | S-3 | S-4 | S-5 | S-6 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left SIBF | Amplitude (V) | 2.7 | 4.2 | 1.5 | 2.7 | 3 | 4.2 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 180 | 250 | 150 | 170 | 250 | 230 | |
| Duration time (s) | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.7 | |
| Left MFB | Amplitude (V) | 2.1 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 2.1 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 130 | 150 | 150 | 130 | 150 | 180 | |
| Duration time (s) | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Right MFB | Amplitude (V) | 1.8 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 1.8 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 130 | 170 | 170 | 120 | 150 | 150 | |
| Duration time (s) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| Right SIBF | Amplitude (V) | 3.6 | 3 | 1.5 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 3.6 |
| Frequency (Hz) | 220 | 200 | 110 | 200 | 200 | 250 | |
| Duration time(s) | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, J.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X.; Rao, Y.; Cao, P.; Hou, X.; He, J.; Mu, J.; Geng, W.; Cui, H.; et al. Motor Behavior Regulation of Rat Robots Using Integrated Electrodes Stimulated by Micro-Nervous System. Micromachines 2024, 15, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050587
Huo J, Zhang L, Luo X, Rao Y, Cao P, Hou X, He J, Mu J, Geng W, Cui H, et al. Motor Behavior Regulation of Rat Robots Using Integrated Electrodes Stimulated by Micro-Nervous System. Micromachines. 2024; 15(5):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050587
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Jiabing, Le Zhang, Xiangyu Luo, Yongkang Rao, Peili Cao, Xiaojuan Hou, Jian He, Jiliang Mu, Wenping Geng, Haoran Cui, and et al. 2024. "Motor Behavior Regulation of Rat Robots Using Integrated Electrodes Stimulated by Micro-Nervous System" Micromachines 15, no. 5: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050587
APA StyleHuo, J., Zhang, L., Luo, X., Rao, Y., Cao, P., Hou, X., He, J., Mu, J., Geng, W., Cui, H., Cheng, R., & Chou, X. (2024). Motor Behavior Regulation of Rat Robots Using Integrated Electrodes Stimulated by Micro-Nervous System. Micromachines, 15(5), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15050587








