Fiber Optic LSPR Sensing AFM1 in Milk with Enhanced Sensitivity by the Hot Spot Effect Based on Nanogap Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. LSPR Spectrum Collection System
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Simulation of the Hot Spots in the AuNP Multimers
2.3.2. Synthesis of the AuNPs
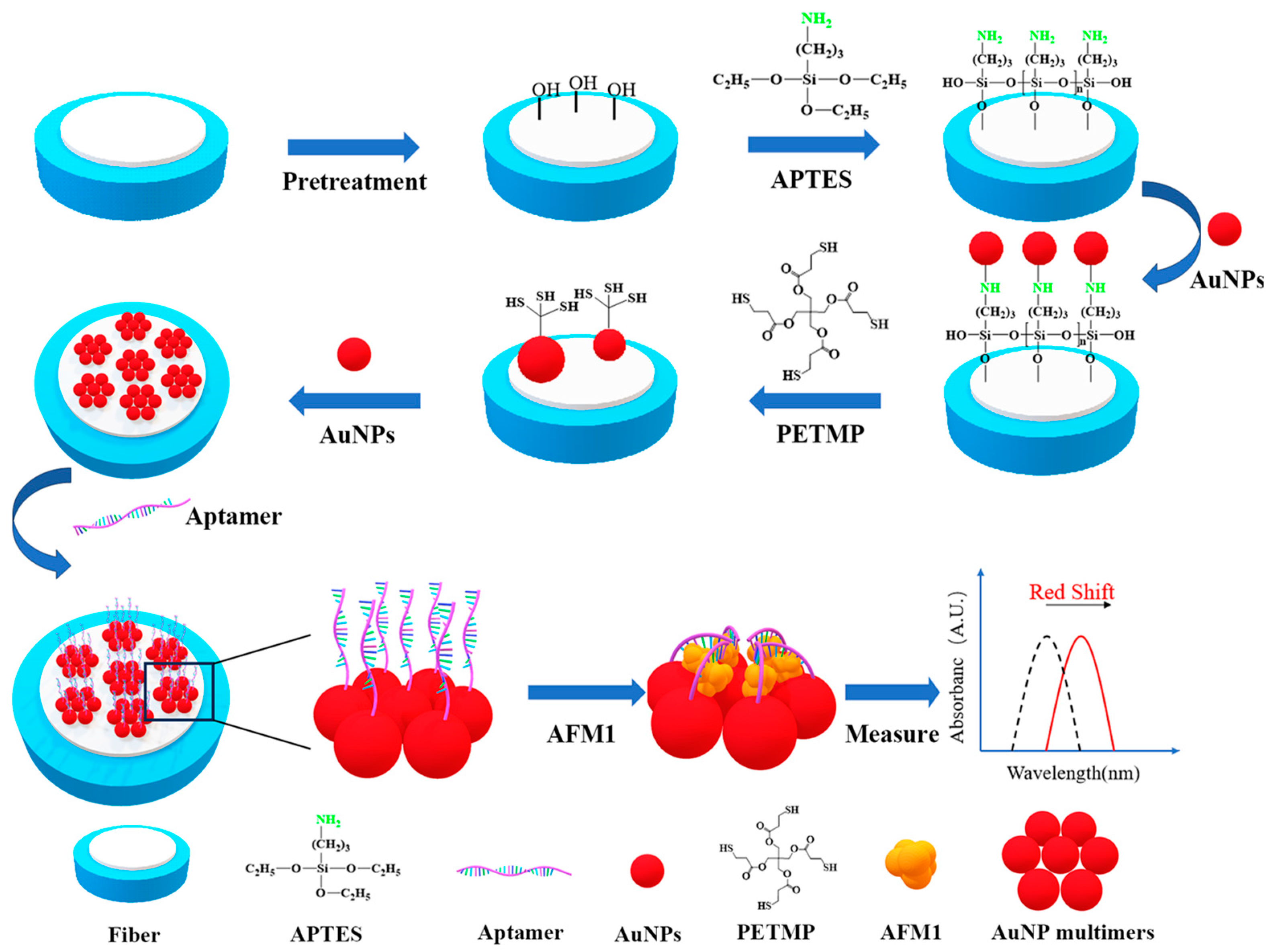
2.3.3. Pretreatment of the FO End Face
2.3.4. Amination of the FO End Face
2.3.5. Preparation of the AuNP Multimers
2.3.6. Coupling AFM1 Aptamer on the AuNP Multimers
2.3.7. Characterization of the AuNPs and the AuNP Multimers
2.3.8. Establishment of the Method for AFM1 Detection
2.3.9. Detection of the Actual Sample
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FDTD Simulation
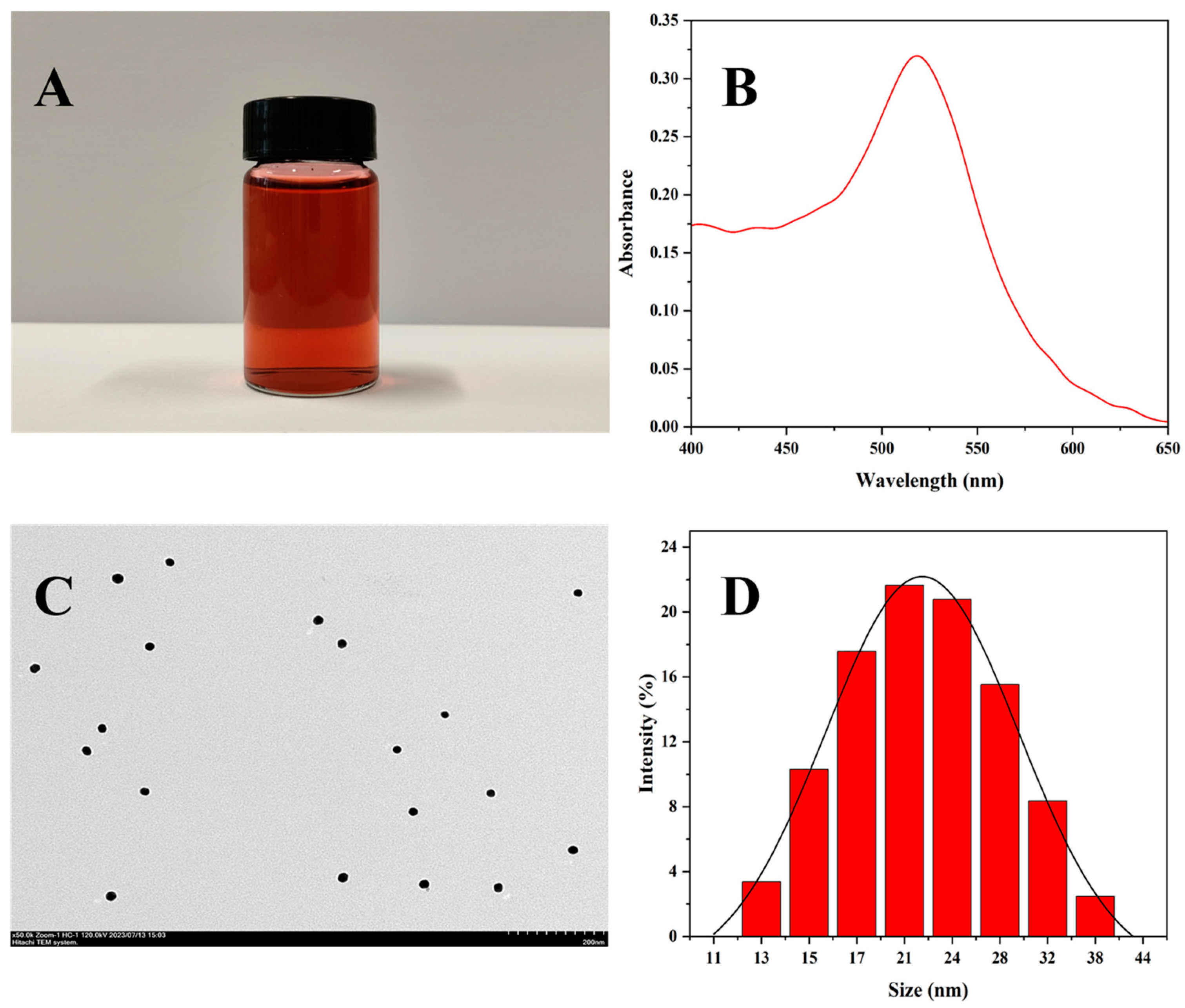
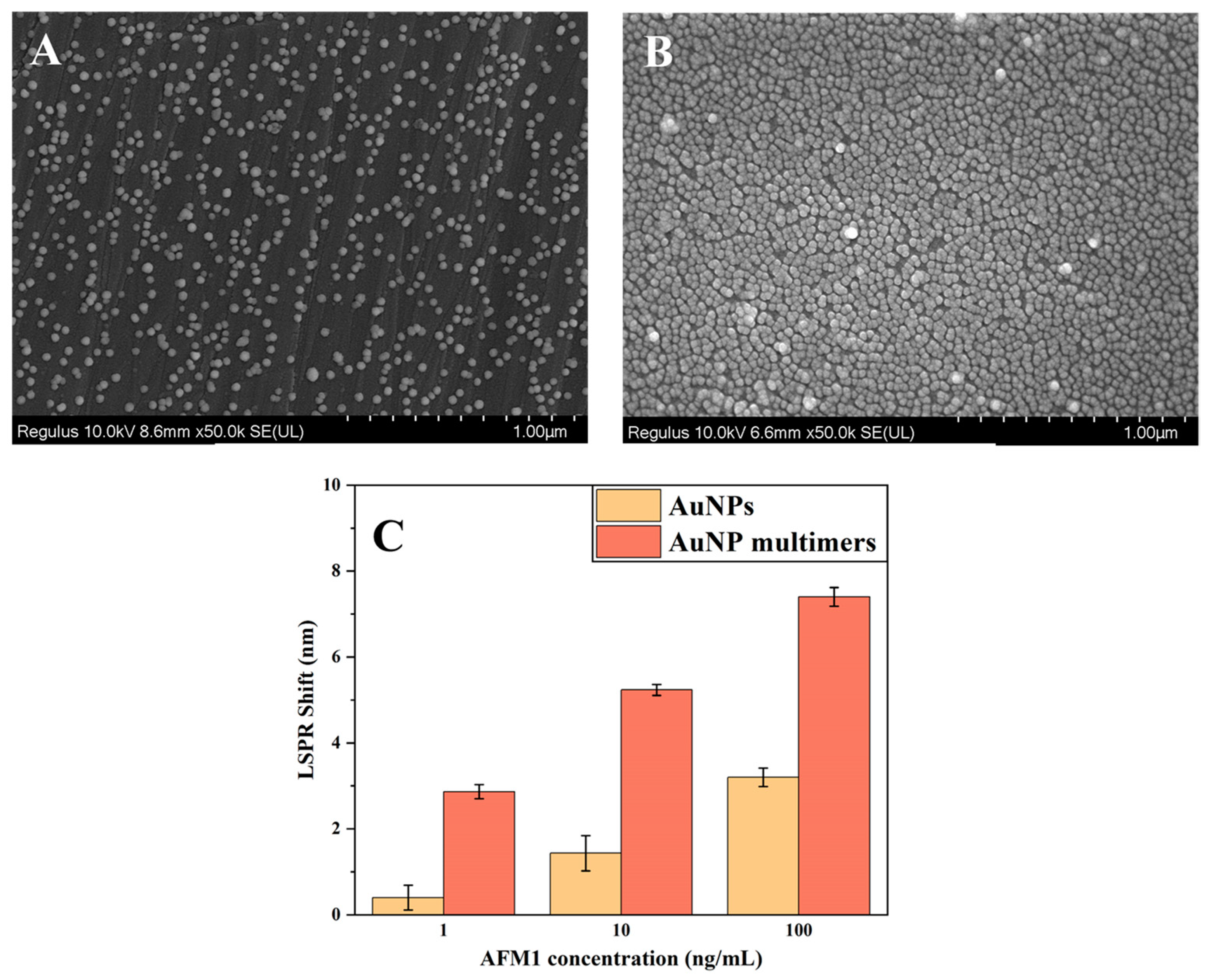
3.2. Characterization of the AuNPs
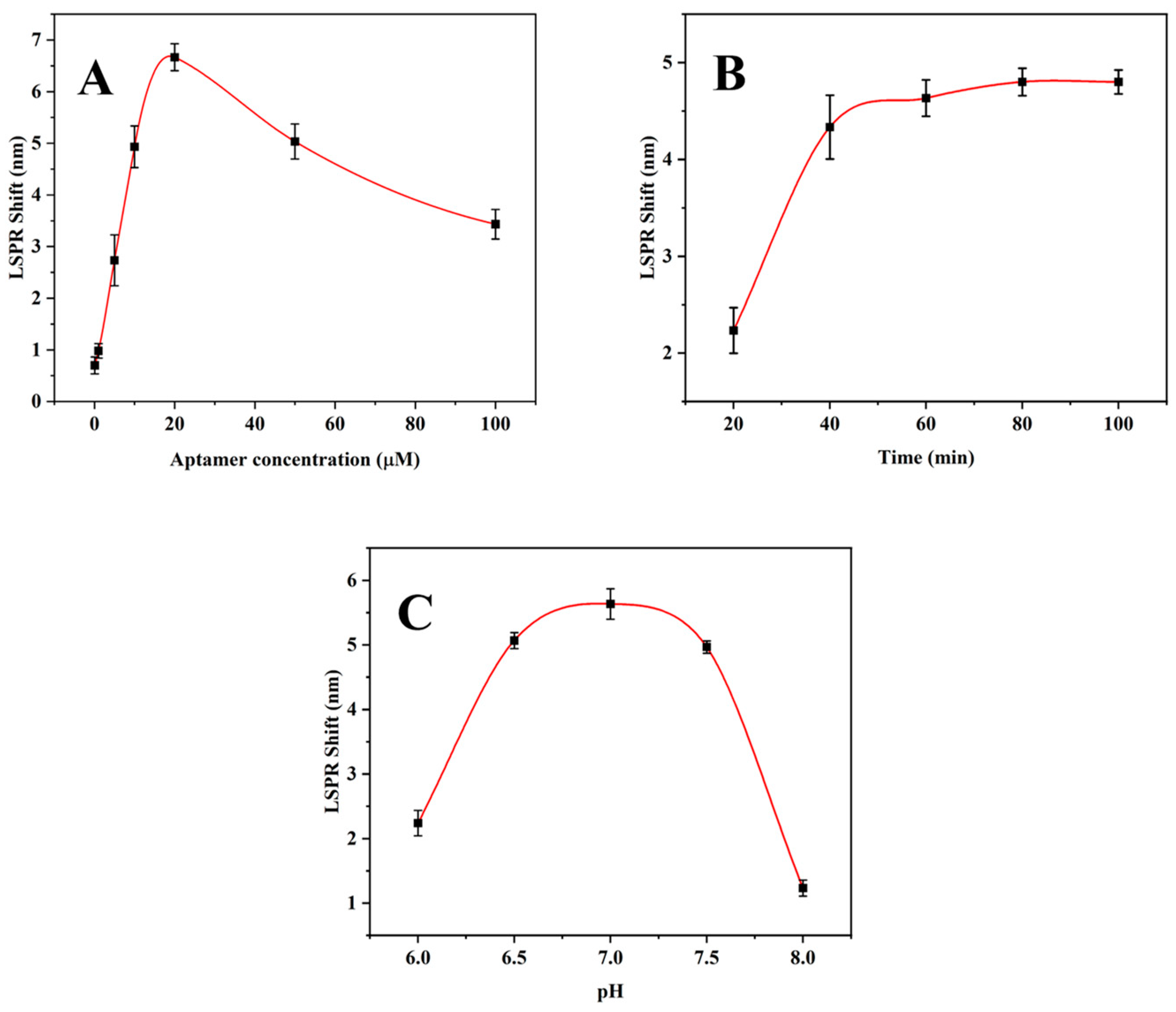
3.3. Condition Optimization
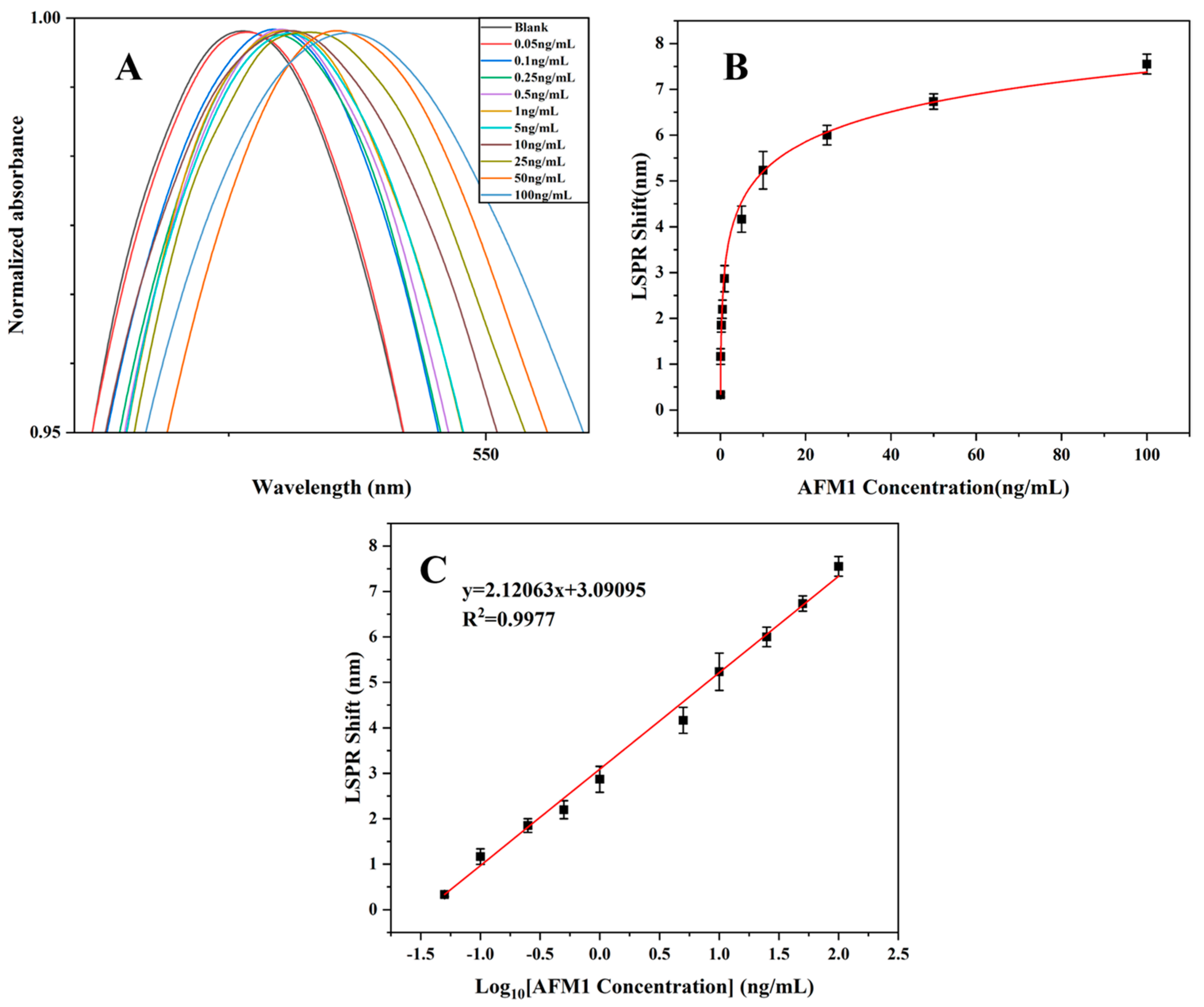
3.4. Detection of AFM1 with the FO LSPR Sensor
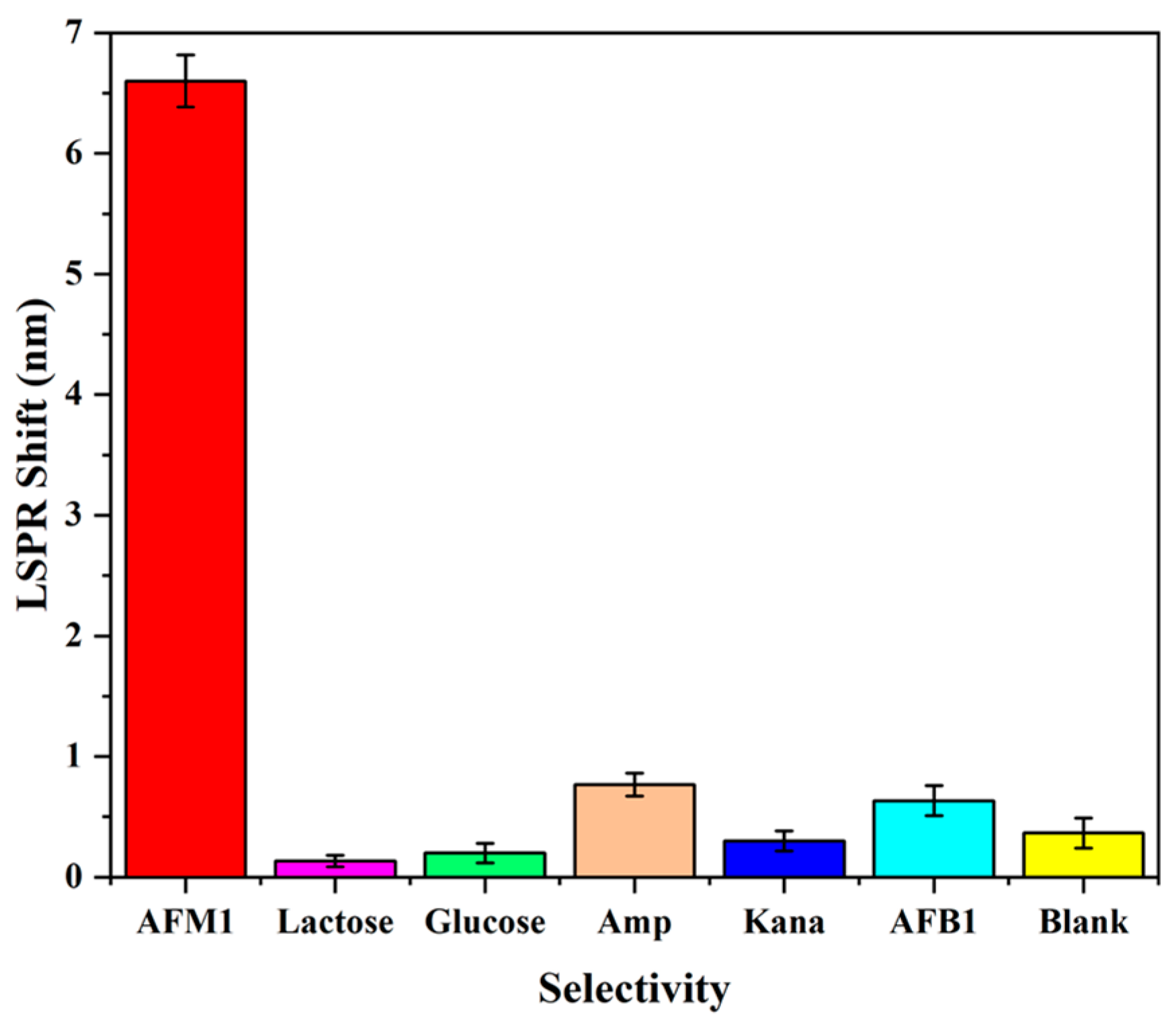
3.5. Selectivity
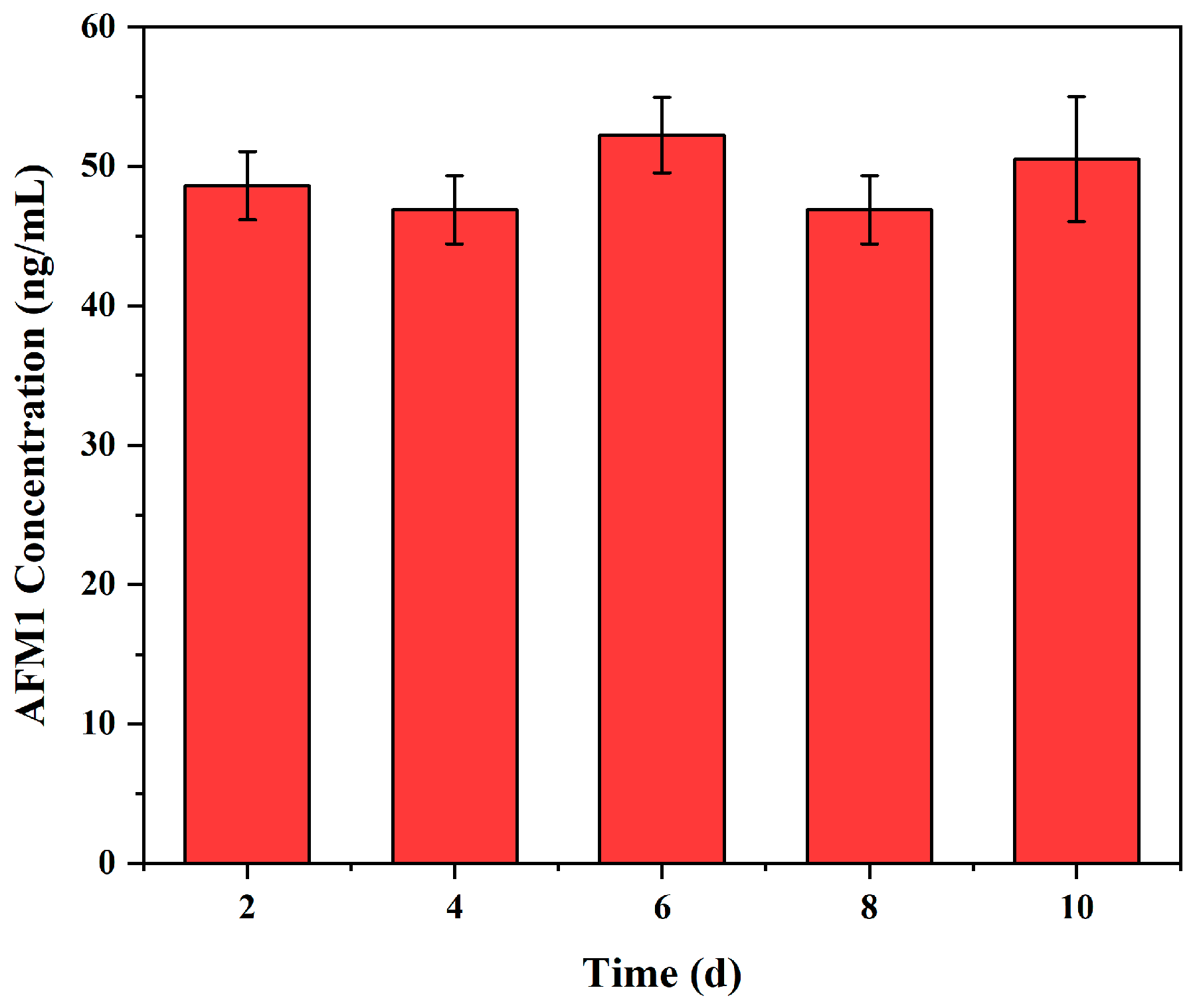
3.6. Repeatability and Reproducibility
3.7. Performance Evaluation of the AuNP Multimers
3.8. Detection of Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Nennich, T.D.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.X. Transfer of dietary aflatoxin B1 to milk aflatoxin M1 and effect of inclusion of adsorbent in the diet of dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jallow, A.; Xie, H.L.; Tang, X.Q.; Qi, Z.; Li, P.W. Worldwide aflatoxin contamination of agricultural products and foods: From occurrence to control. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2332–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahato, D.K.; Lee, K.E.; Kamle, M.; Devi, S.; Dewangan, K.N.; Kumar, P.; Kang, S.G. Aflatoxins in Food and Feed: An Overview on Prevalence, Detection and Control Strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakiris, I.N.; Tzatzarakis, M.N.; Alegakis, A.K.; Vlachou, M.I.; Renieri, E.A.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Risk assessment scenarios of children’s exposure to aflatoxin M1 residues in different milk types from the Greek market. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 56, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prandini, A.; Tansini, G.; Sigolo, S.; Filippi, L.; Laporta, M.; Piva, G. On the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Zheng, N. Metabolomics analysis underlay mechanisms in the renal impairment of mice caused by combination of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, G.E.; Eaton, D.L.; Judah, D.J.; Verma, A. Metabolism and toxicity of aflatoxins M1 and B1 in human-derived in vitro systems. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 151, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Lu, P.; Gail, M.H.; Pee, D.; Zhang, Q.; Ming, L.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Wu, Y.; et al. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in male hepatitis B surface antigen carriers with chronic hepatitis who have detectable urinary aflatoxin metabolite M1. Hepatology 1999, 30, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-N.; Wang, Z.-W.; Yang, X.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A induce a competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network of intestinal immunosuppression by whole-transcriptome analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurban, A.-M.; Epure, P.; Oancea, F.; Doni, M. Achievements and Prospects in Electrochemical-Based Biosensing Platforms for Aflatoxin M1 Detection in Milk and Dairy Products. Sensors 2017, 17, 2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.K.; Shon, D.H.; Ryu, D.; Park, J.W.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, Y.B. Occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in Korean dairy products determined by ELISA and HPLC. Food Addit. Contam. 2000, 17, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Huang, L.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Chao, D.; Li, M.; Wu, S.; Dong, S. Reversible inhibition of the oxidase-like activity of Fe single-atom nanozymes for drug detection. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 4566–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, S.; Dwivedi, P.D.; Khanna, S.K.; Das, M. Detection of Aflatoxin M1 contamination in milk and infant milk products from Indian markets by ELISA. Food Control 2004, 15, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shundo, L.; Sabino, M. Aflatoxin M1 in milk by immunoaffinity column cleanup with TLC/HPLC determination. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2006, 37, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinçkaya, E.; Kınık, Ö.; Sezgintürk, M.K.; Altuğ, Ç.; Akkoca, A. Development of an impedimetric aflatoxin M1 biosensor based on a DNA probe and gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3806–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, D.B.; Li, P.W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Ding, X.X.; Mao, J.; Wu, J. Palladium Nanoparticles-Based Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Aptasensor for Highly Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Toxins 2017, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.P.; Geng, Z.X. Strategies to improve performances of LSPR biosensing: Structure, materials, and interface modification. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 174, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willets, K.A.; Van Duyne, R.P. Localized surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy and sensing. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2007, 58, 267–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhu, S.H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C.; Yan, H. Constructing the Au nanoparticle multimer on optical fiber end face to enhance the signal of localized surface plasmon resonance biosensors: A case study for deoxynivalenol detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 380, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.Y.; Heo, N.S.; Shukla, S.; Cho, H.J.; Vilian, A.T.E.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Han, Y.K.; Yoo, S.M.; Huh, Y.S. Development of gold nanoparticle-aptamer-based LSPR sensing chips for the rapid detection of Salmonella typhimurium in pork meat. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Byun, J.Y.; Yim, S.Y.; Kim, M.G. A Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance (LSPR)-based, simple, receptor-free and regeneratable Hg2+ detection system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 307, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.M.; Wang, Y.Y.; Fu, Q.Y.; Tan, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.J.; Zhou, J.H. Plasmonic Al nanopyramid array sensor for monitoring the attaching and spreading of cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 279, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakao, M.; Watanabe, S.; Kurahashi, Y.; Matsuo, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Ogawa, T.; Suzuki, K.; Yumino, T.; Myogadani, T.; Saito, A.; et al. Optical Fiber-Type Sugar Chip Using Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.K.; Punjabi, N.; Sharma, D.K.; Mukherji, S. A silicon nitride coated LSPR based fiber-optic probe for possible continuous monitoring of sucrose content in fruit juices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 222, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.H.; Erdene, N.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, D.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.K. Realtime label-free immunoassay of interferon-gamma and prostate-specific antigen using a Fiber-Optic Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barroso, J.; Ortega-Gomez, A.; Calatayud-Sanchez, A.; Zubia, J.; Benito-Lopez, F.; Villatoro, J.; Basabe-Desmonts, L. Selective Ultrasensitive Optical Fiber Nanosensors Based on Plasmon Resonance Energy Transfer. Acs Sens. 2020, 5, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y. Ultrasensitive U-shaped fiber optic LSPR cytosensing for label-free and in situ evaluation of cell surface N-glycan expression. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, Z.W.; Chen, J.M.; Huang, Z.J.; Wang, X.; An, H.F.; Duan, Y.X. Ω-Shaped Fiber-Optic Probe-Based Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensor for Real-Time Detection of Salmonella Typhimurium. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13640–13646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yockell-Lelièvre, H.; Lussier, F.; Masson, J.F. Influence of the Particle Shape and Density of Self-Assembled Gold Nanoparticle Sensors on LSPR and SERS. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 28577–28585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.Y.; Yi, J.; Li, J.F.; Ren, B.; Wu, D.Y.; Panneerselvam, R.; Tian, Z.Q. Nanostructure-based plasmon-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for surface analysis of materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, S.-K. Fabrication and measurement of fiber optic localized surface plasmon resonance sensor based on gold nanoparticle dimer. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 261, 120034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, B.H.; Tran, L.D.; Do, Q.P.; Nguyen, H.L.; Tran, N.H.; Nguyen, P.X. Label-free detection of aflatoxin M1 with electrochemical Fe3O4/polyaniline-based aptasensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 2229–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frens, G. Controlled Nucleation for the Regulation of the Particle Size in Monodisperse Gold Suspensions. Nat. Phys. Sci. 1973, 241, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB5009.24-2016; National Food Safety Standard—Determination of M Aflatoxins in Foods. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV-Vis spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.J.; Zhang, W.T.; Chen, K.; Zhu, W.X.; Liu, X.N.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Hu, N.; Suo, Y.R.; Wang, J.L. Facet-selective response of trigger molecule to CeO {110} for up-regulating oxidase-like activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Q.Q.; Guo, X.D.; Wen, F.; Chen, L.; Xu, Q.B.; Zheng, N.; Cheng, J.B.; Xue, X.H.; Wang, J.Q. Aptamer-Based Fluorescence Quenching Approach for Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Singh, S.; Bhardwaj, S.K.; Kaur, G.; Khatri, M.; Deep, A.; Bhardwaj, N. Development of carbon quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for sensitive detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczmarczyk, A.; Baeumner, A.J.; Feller, K.H. Rapid and sensitive inhibition-based assay for the electrochemical detection of Ochratoxin A and Aflatoxin M1 in red wine and milk. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 243, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.J.; Ma, P.F.; Mahmood, K.I.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.P. Screening of a High-Affinity Aptamer for Aflatoxin M1 and Development of Its Colorimetric Aptasensor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 7546–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, B.L.; Xu, S.L.; Huang, Y.J.; Su, F.M.; Huang, Z.; Fang, H.; Peng, J.; Xiong, Y.H.; Lai, W.H. Gold nanorods etching-based plasmonic immunoassay for qualitative and quantitative detection of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Food Chem. 2020, 329, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Zhang, Q.; Nidiaye, S.; Yan, H.L.; Zhang, W.; Tang, X.Q.; Li, P.W. Development of a specific anti-idiotypic nanobody for monitoring aflatoxin M1 in milk and dairy products. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Yang, R.; Fang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Long, F. A FRET-based dual-color evanescent wave optical fiberaptasensor for simultaneous fluorometric determination of aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin A. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Methods | Detection Range (ng/mL) | LOD (ng/mL) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) | 0.005–0.15 | 0.0015 | [38] |
| Aptamer-based fluorescence | 1–100 | 0.5 | [39] |
| Immunofluorescence | 0.2–0.8 | 0.07 | [40] |
| Electrochemical | 0.01–1000 | 0.037 | [41] |
| Colorimetric | 0.5–500.0 | 0.5 | [42] |
| Plasmonic immunoassay | 0.25–10 | 0.11 | [43] |
| ELISA | 0.1–0.6 | 0.05 | [44] |
| Optical fiber aptasensor | 1–1000 | 21 | [45] |
| This method | 0.05–100 | 0.04 | This work |
| Spiked (ng/mL) | ELISA Method (ng/mL) | This Method (ng/mL) | RSD (%) ** | Recovery (%) | p *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | N.D. * | N.D. | - | - | - |
| 5 | 5.61 ± 0.12 | 4.46 ± 0.22 | 5.03 | 89.2 | 0.756 |
| 10 | 11.81 ± 0.06 | 11.84 ± 0.66 | 5.02 | 118.4 | 0.932 |
| 50 | 51.52 ± 0.14 | 44.45 ± 2.97 | 6.67 | 88.9 | 0.081 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Ni, Y.; Zhang, W.; Nteppe Nteppe, E.L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, H. Fiber Optic LSPR Sensing AFM1 in Milk with Enhanced Sensitivity by the Hot Spot Effect Based on Nanogap Construction. Micromachines 2024, 15, 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060779
Li J, Ni Y, Zhang W, Nteppe Nteppe EL, Li Y, Zhang Y, Yan H. Fiber Optic LSPR Sensing AFM1 in Milk with Enhanced Sensitivity by the Hot Spot Effect Based on Nanogap Construction. Micromachines. 2024; 15(6):779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060779
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiacong, Yuxin Ni, Wei Zhang, Elvige Laure Nteppe Nteppe, Yurong Li, Yeshun Zhang, and Hui Yan. 2024. "Fiber Optic LSPR Sensing AFM1 in Milk with Enhanced Sensitivity by the Hot Spot Effect Based on Nanogap Construction" Micromachines 15, no. 6: 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060779
APA StyleLi, J., Ni, Y., Zhang, W., Nteppe Nteppe, E. L., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., & Yan, H. (2024). Fiber Optic LSPR Sensing AFM1 in Milk with Enhanced Sensitivity by the Hot Spot Effect Based on Nanogap Construction. Micromachines, 15(6), 779. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15060779






