Statics Performance and Heat Dissipation Evaluation of Lattice Structures Prepared by Laser Powder Bed Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Setup and Simulation Model
2.1. Experimental Setup
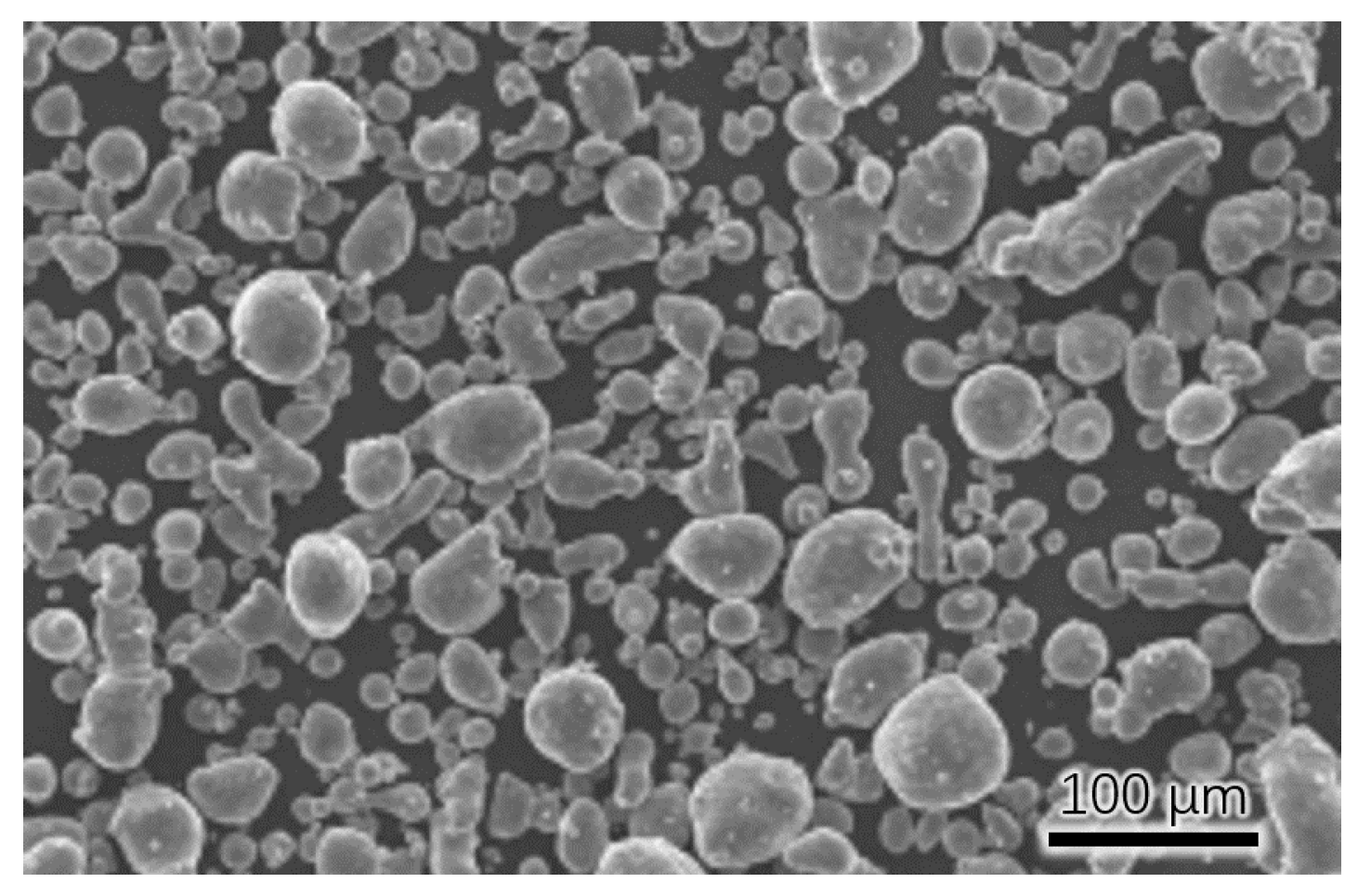
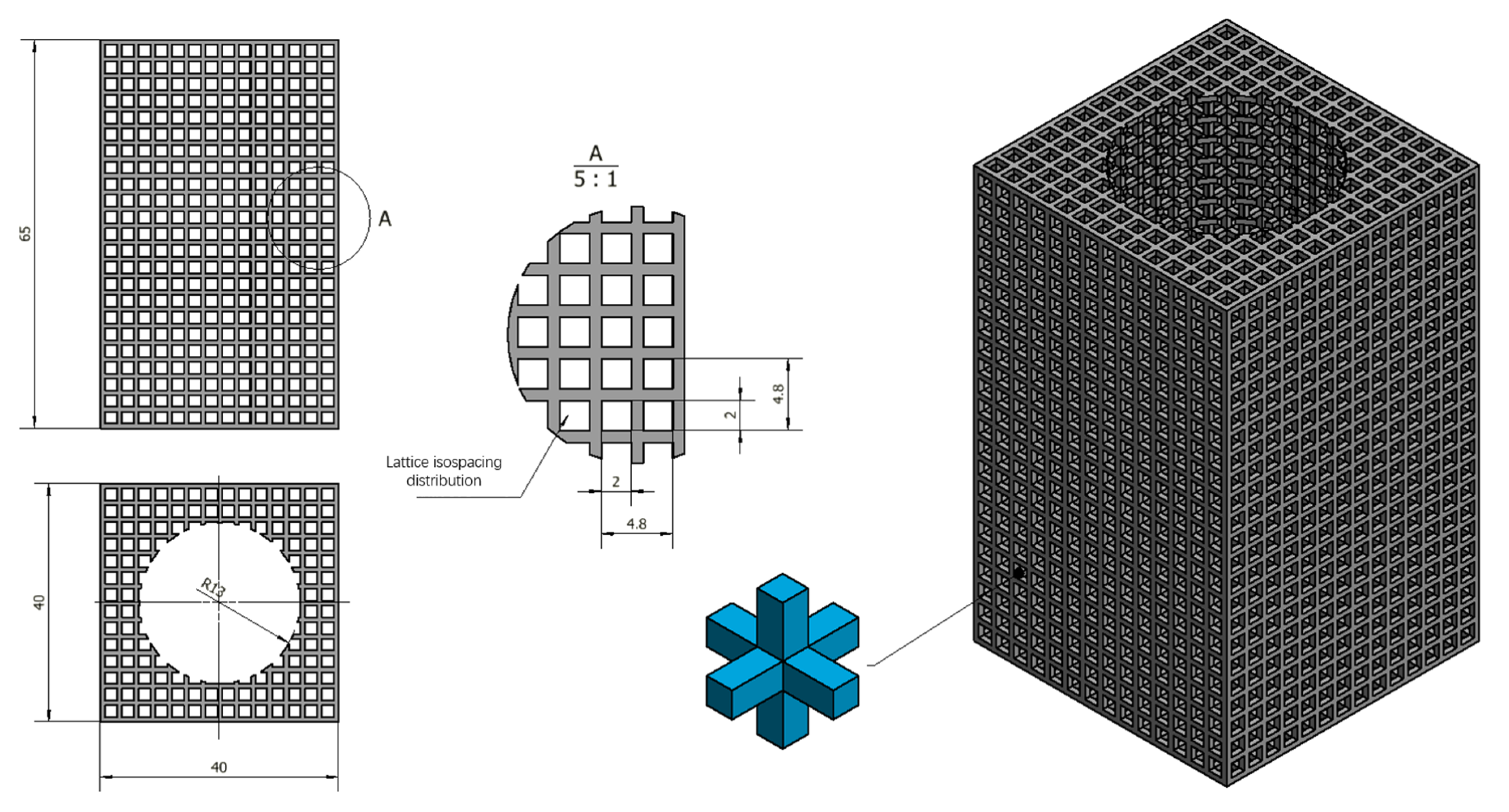
2.1.1. Test Parts
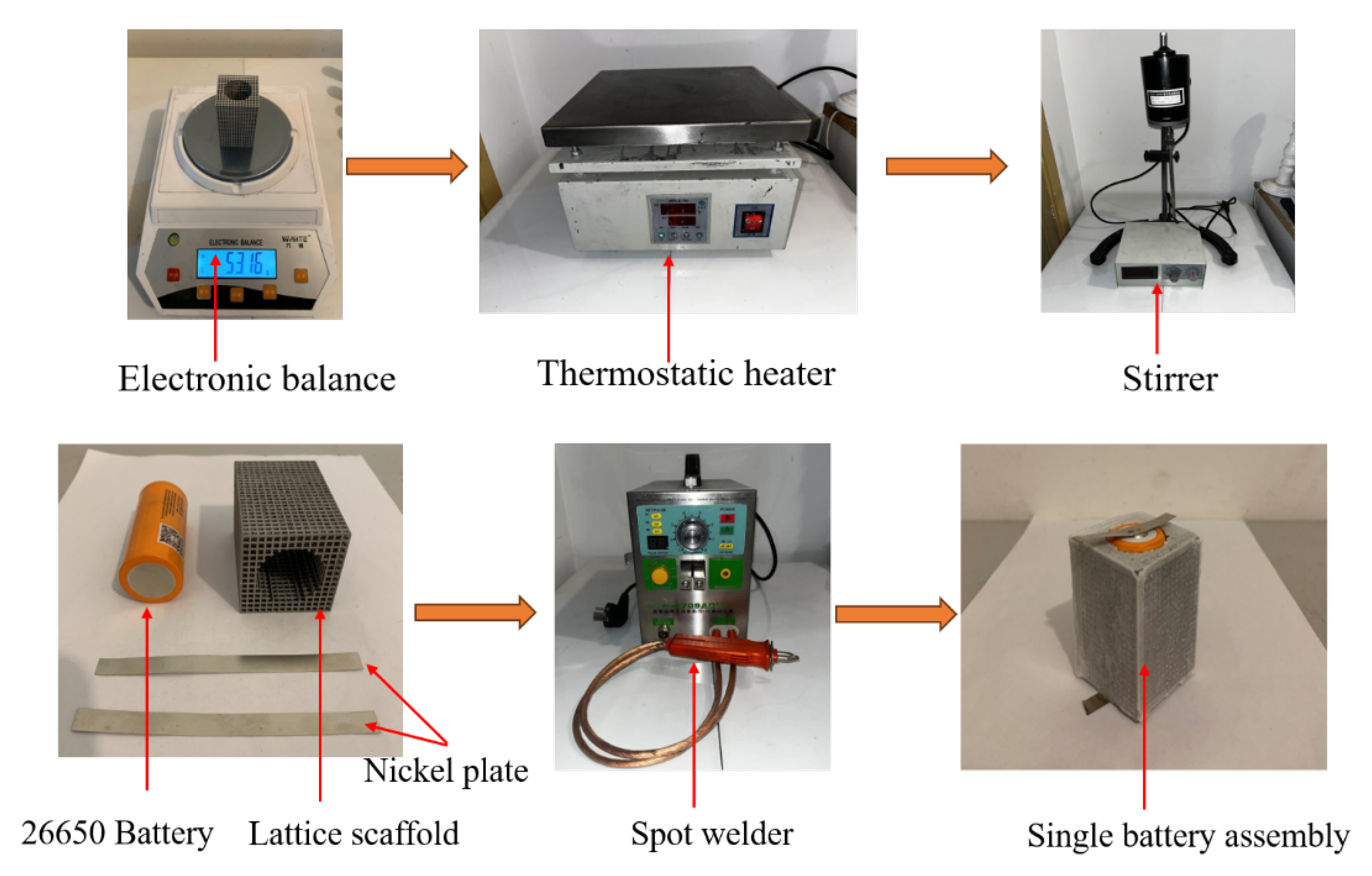
2.1.2. Prototype Preparation of the Heat Exchanger
2.1.3. Geometry Detection
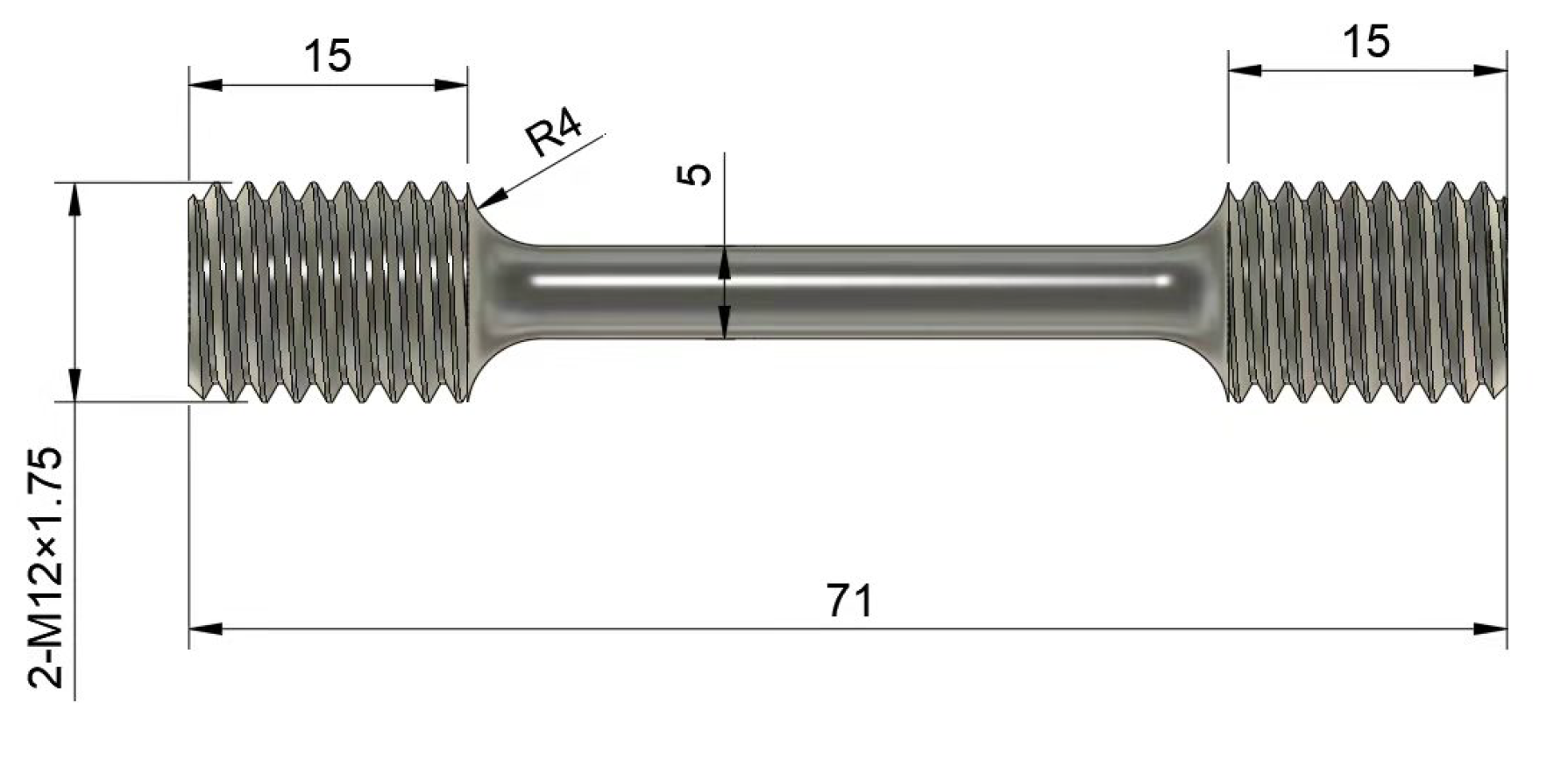
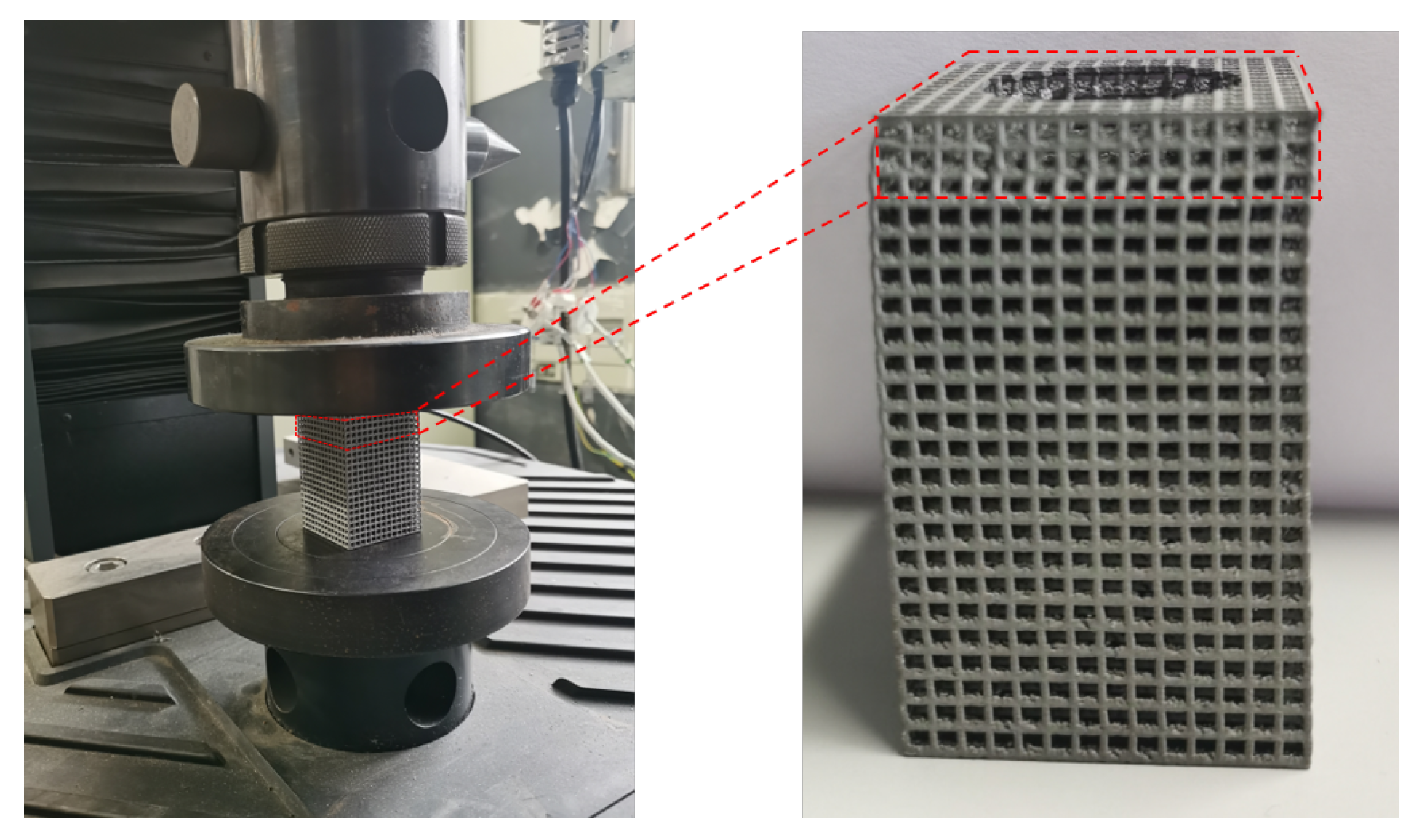
2.1.4. Tensile and Compression Test
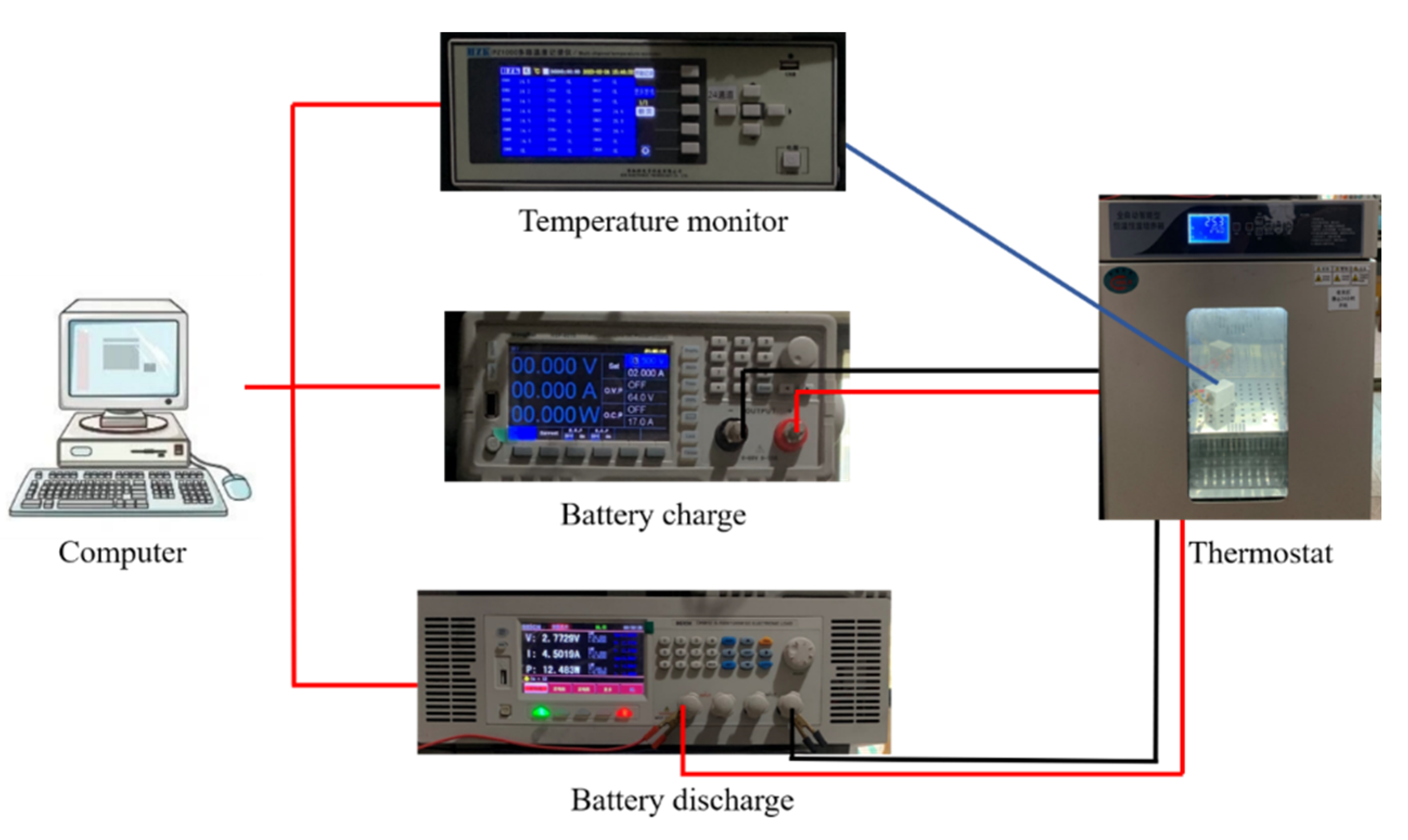
2.1.5. Heat Dissipation Evaluation
2.2. Simulation Model
3. Results and Discussion
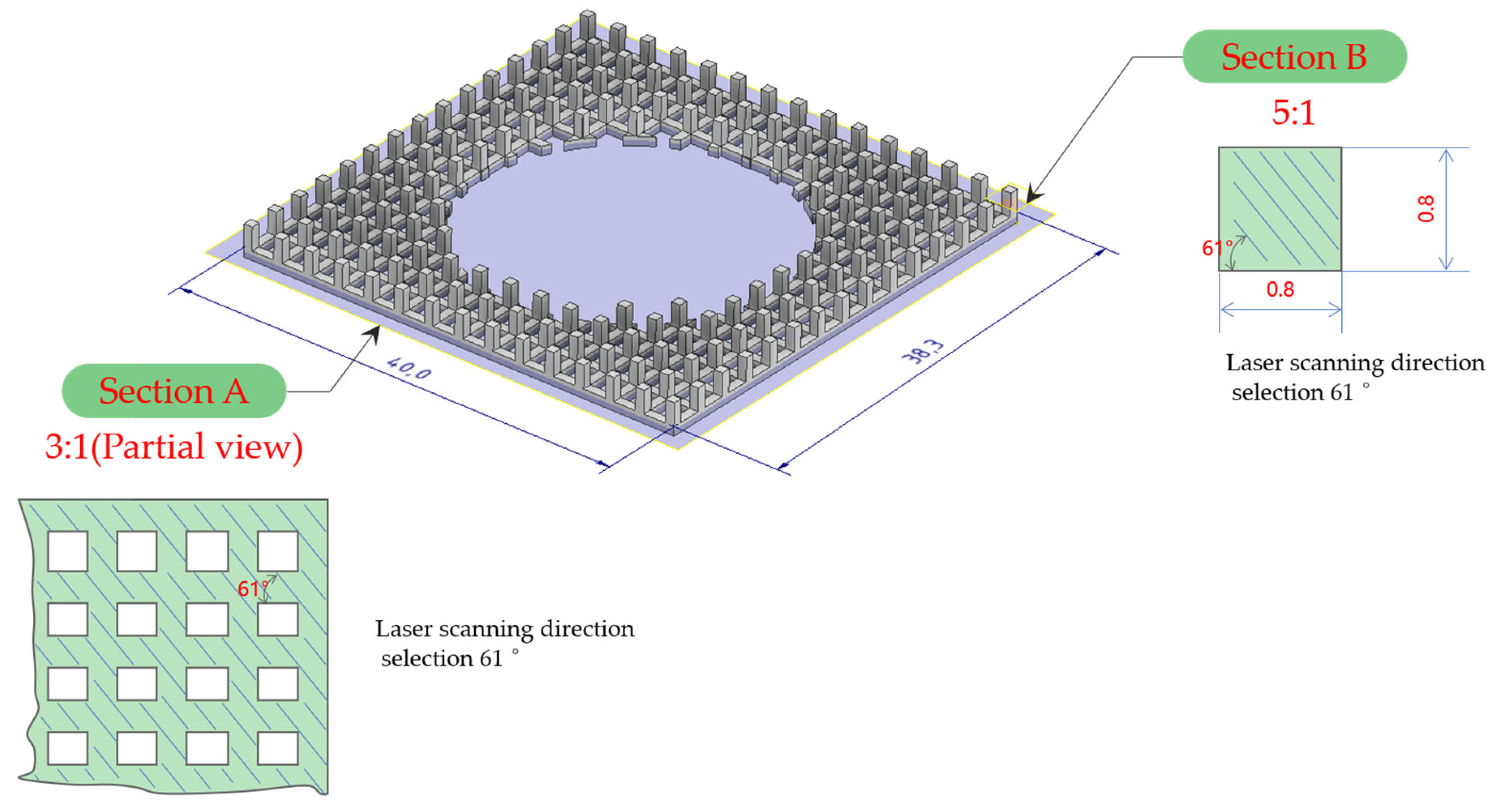
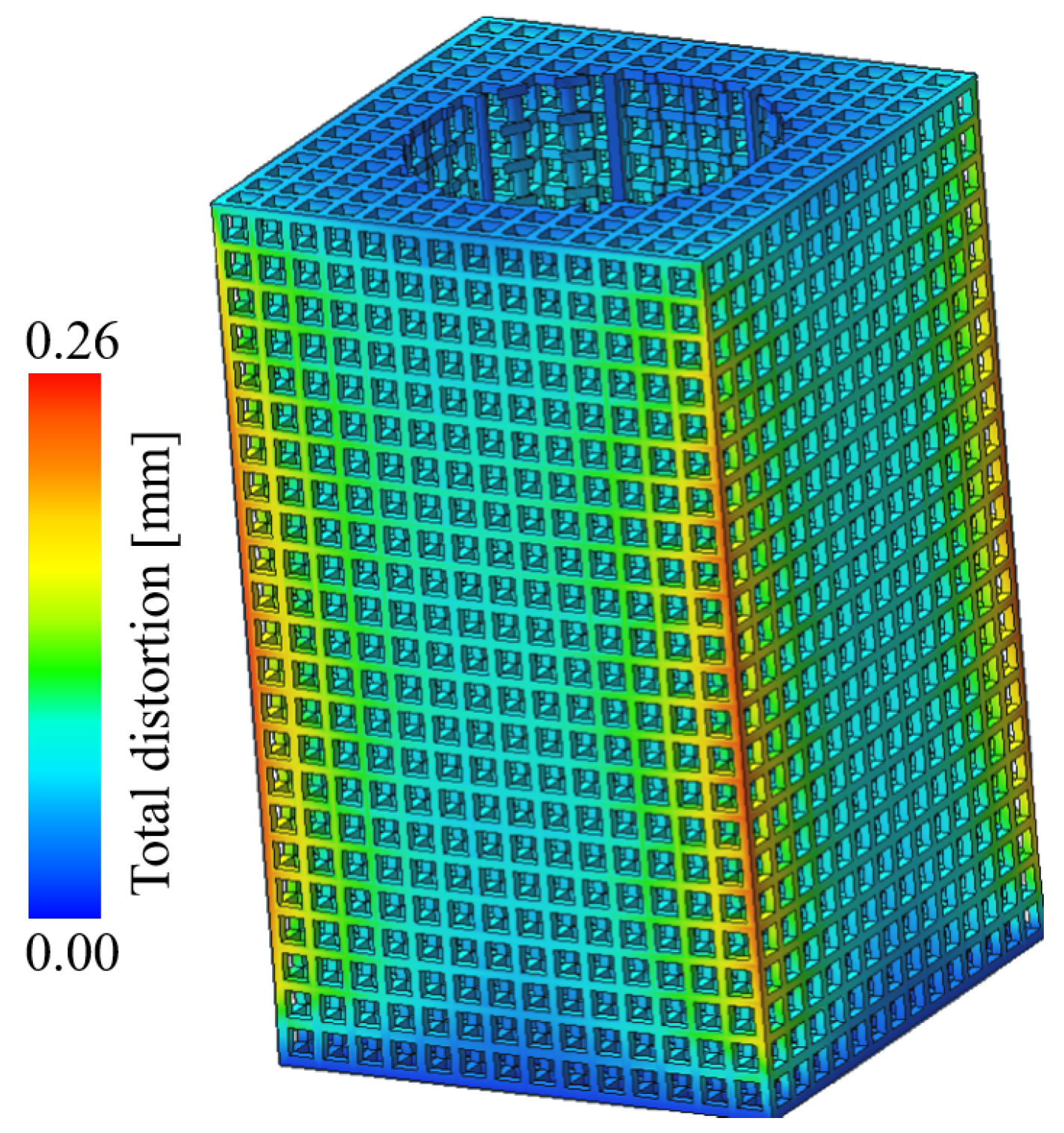
3.1. Numerical Simulation of Forming Process
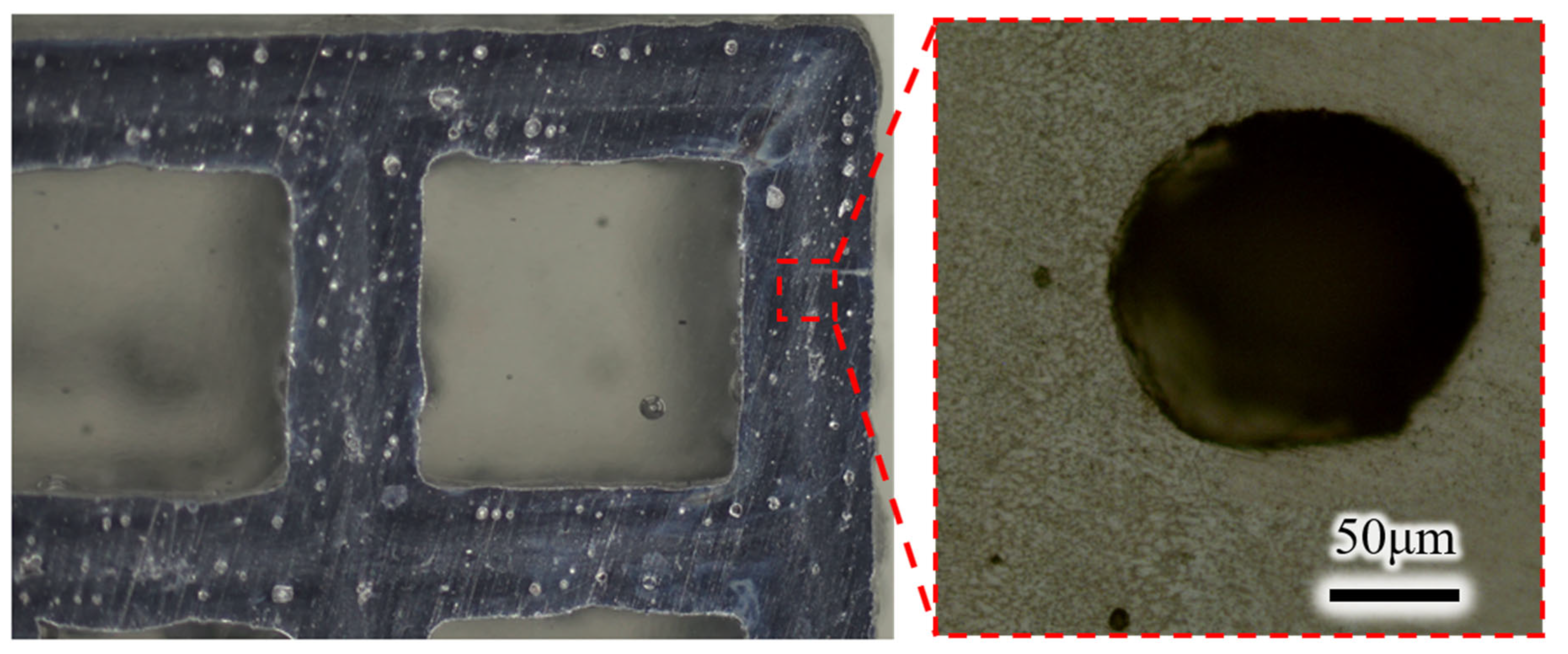
3.2. Lattice Geometry and Metallographic Inspection
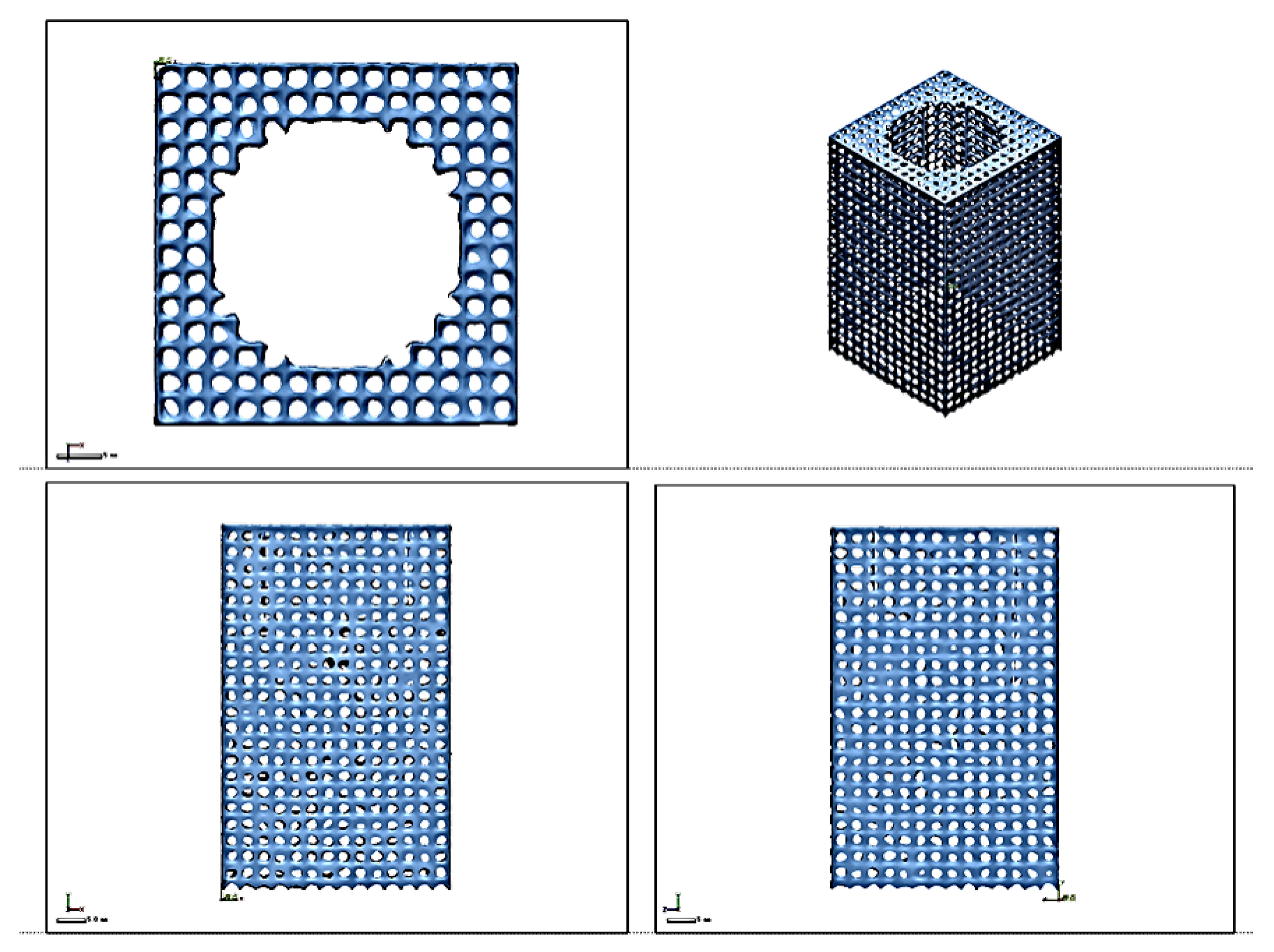
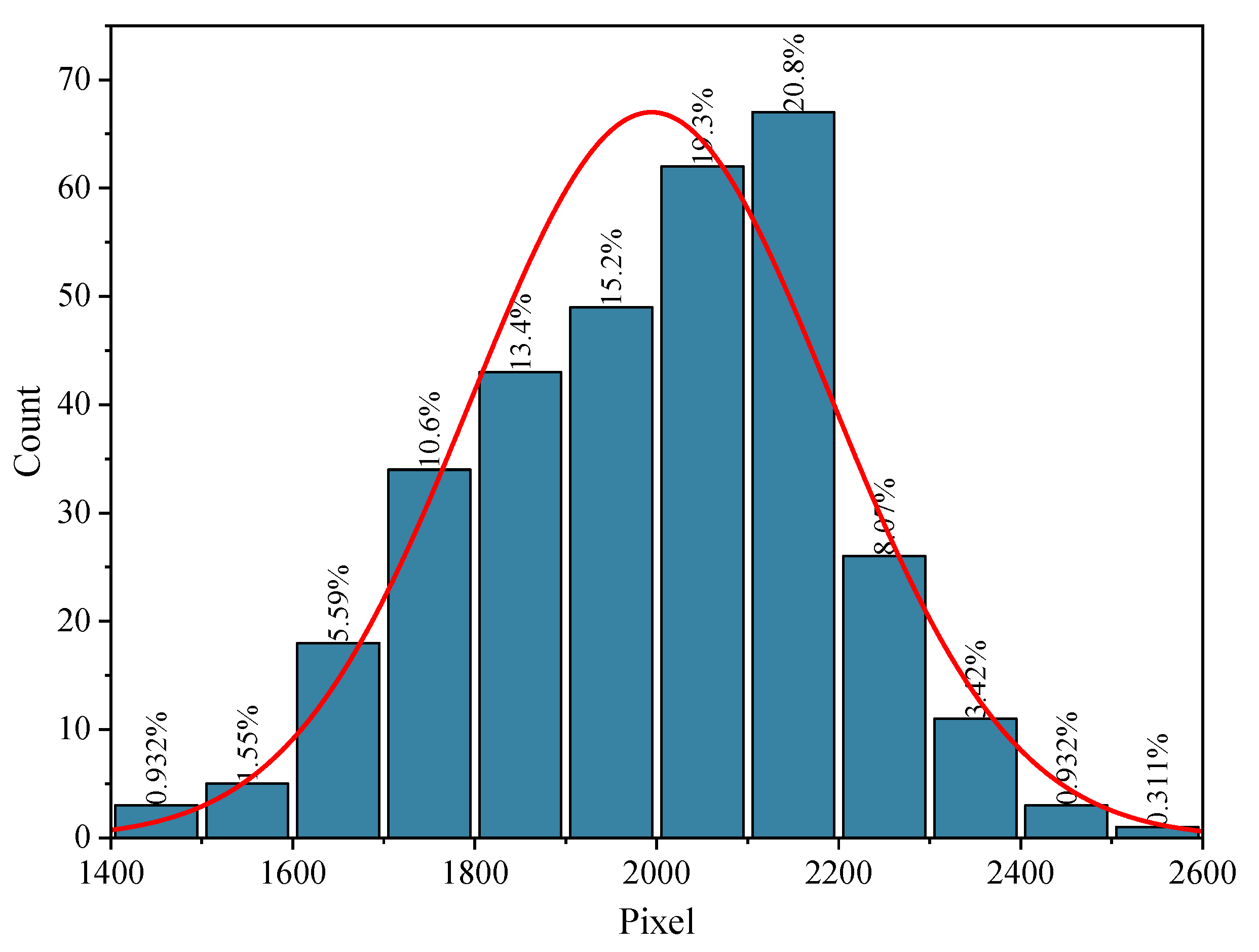
3.3. Lattice Image Recognition Detection
3.4. Metallographic Inspection
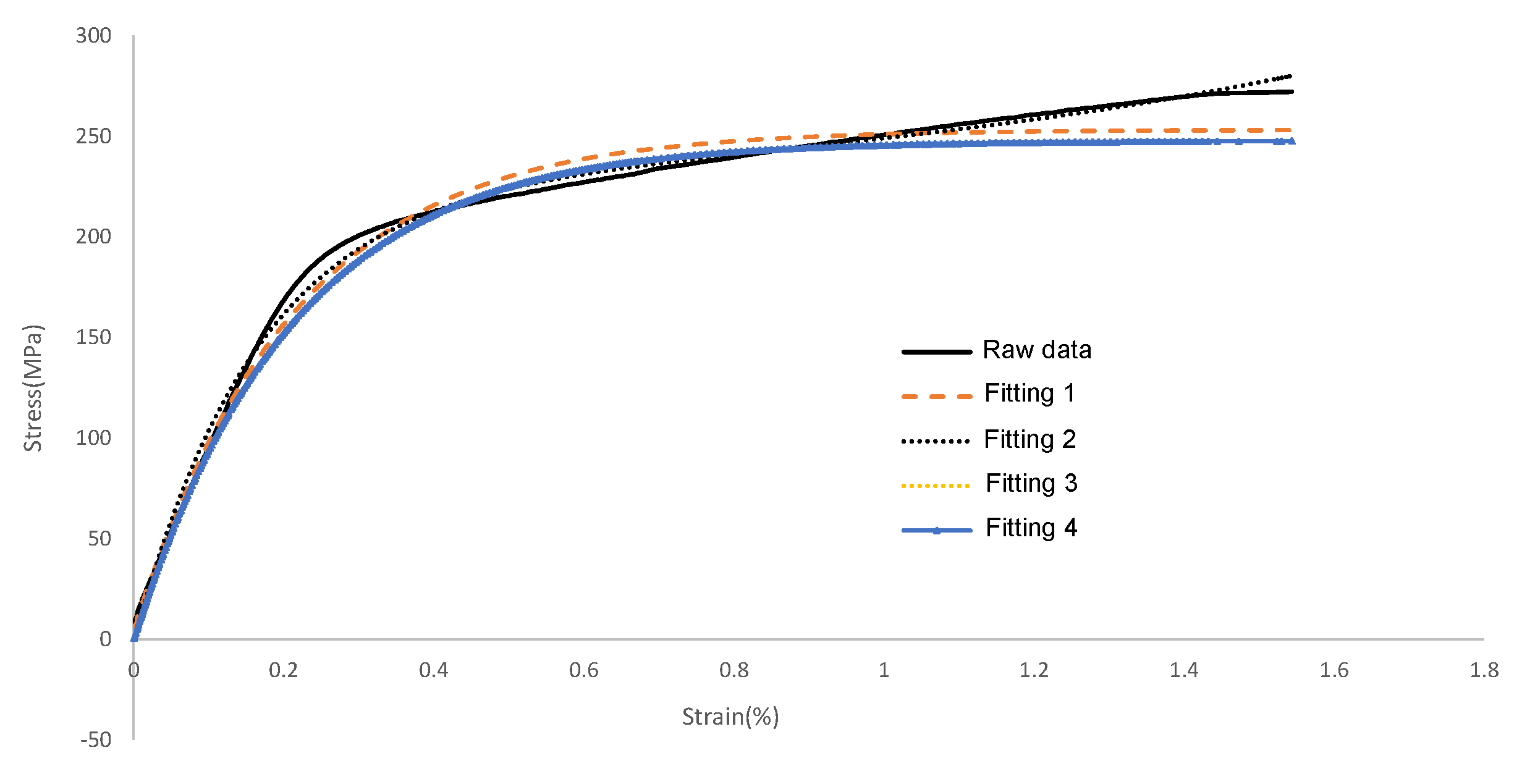
3.5. Tensile and Compression Test
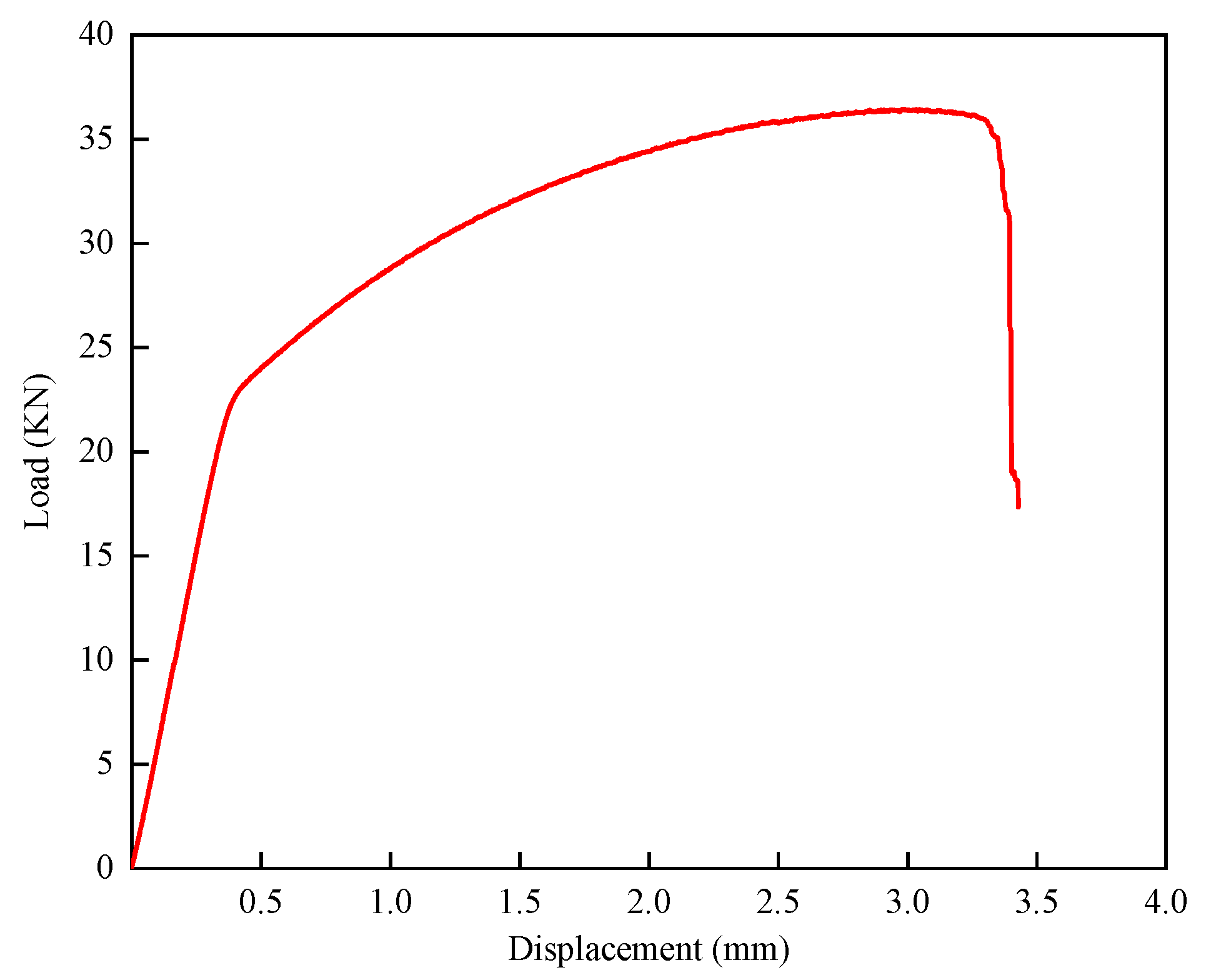
3.6. Point Structure Compression Test Analysis
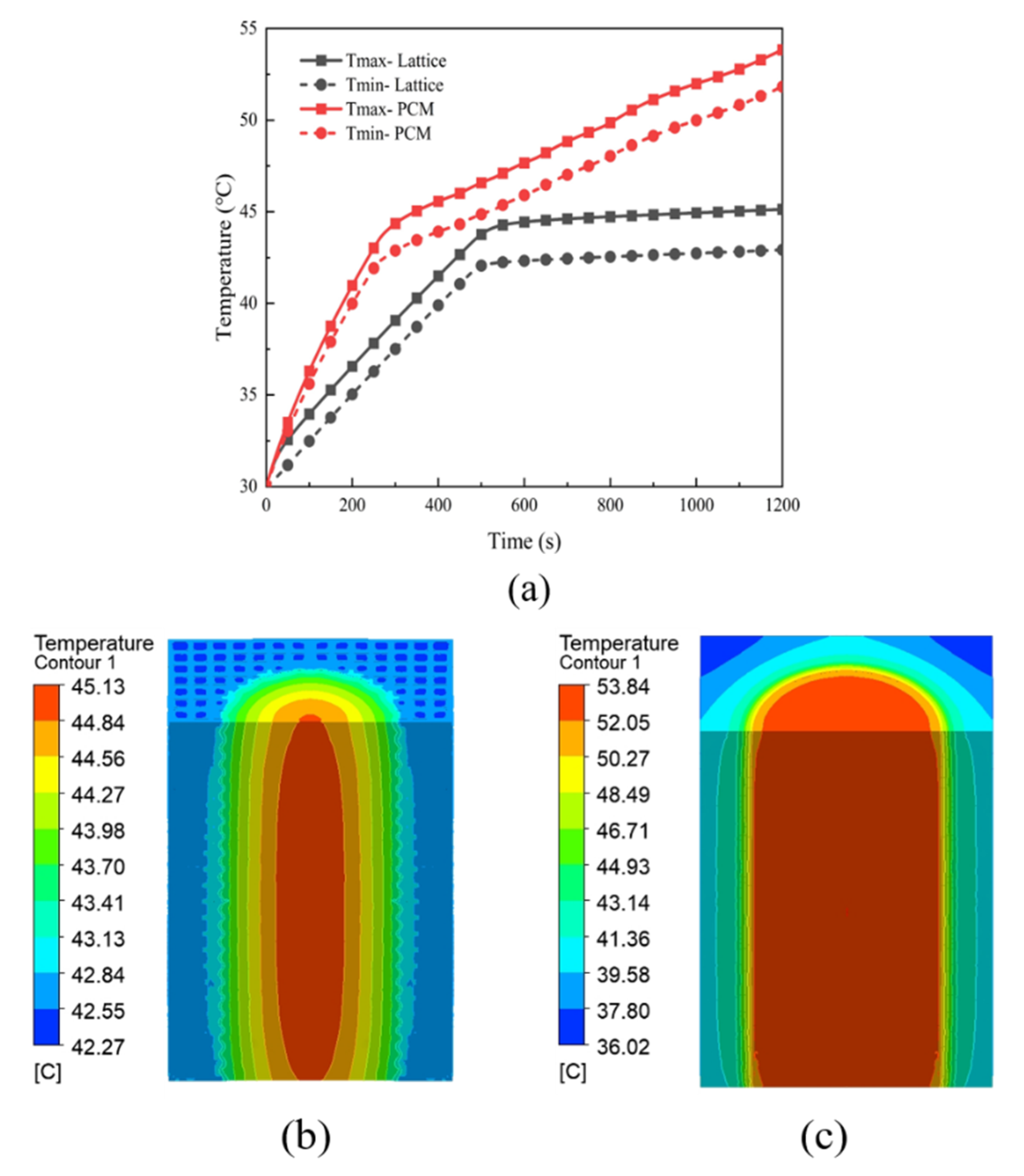
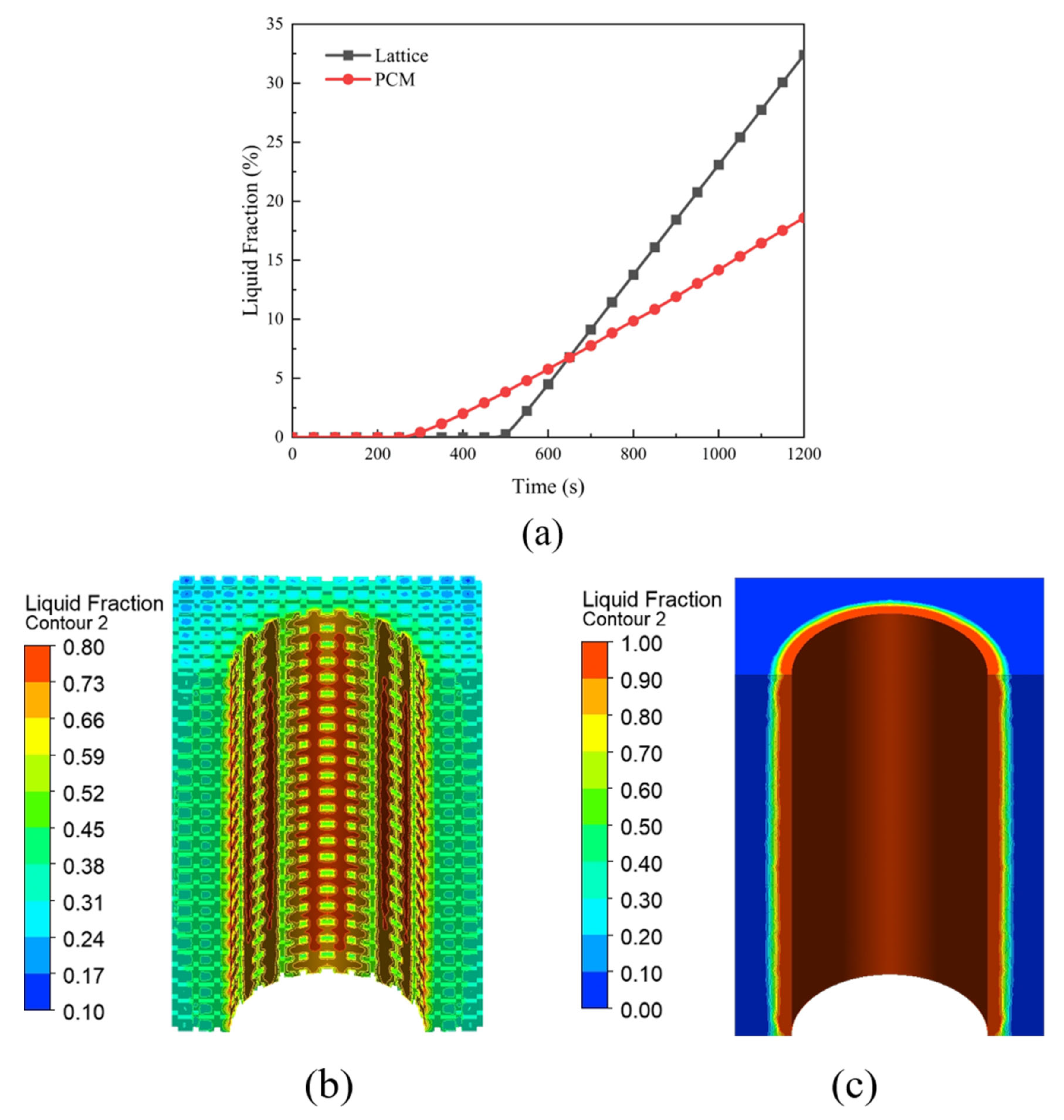
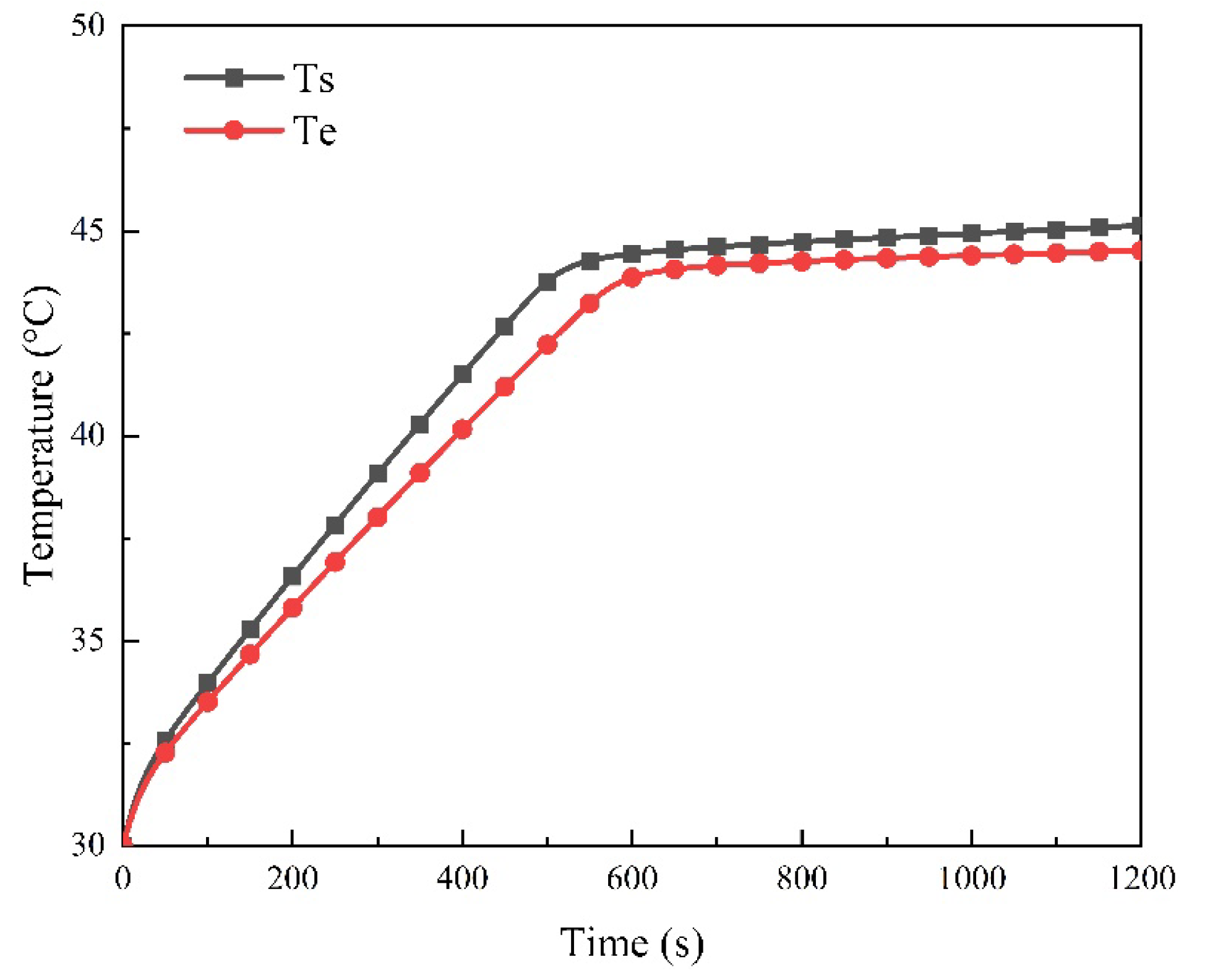
3.7. Heat Dissipation Performance
4. Conclusions
- The introduction of the lattice skeleton significantly improves the thermal conductivity of the PCM. This improvement enables the heat generated by the cell in the heat exchanger to be transferred more rapidly, and the part of the cell far away from the phase change material can also absorb the heat effectively, thus realizing the efficient distribution of heat in the system.
- The lattice skeleton not only accelerates the heat transfer rate, but also makes the heat distribution in the heat exchanger more uniform. This uniformity not only improves the utilization rate of the PCM and reduces the waste of energy, but also helps to maintain the stability of the cell temperature, which in turn prolongs the service life of the cell.
- The melting process of PCM is more uniform in the lattice heat exchanger. This feature maximizes the latent heat capacity of PCM and makes it more useful in the battery heat dissipation process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Careri, F.; Khan, R.H.; Todd, C.; Attallah, M.M. Additive manufacturing of heat exchangers in aerospace applications: A review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 235, 121387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, D.; Wits, W.W. The utilization of selective laser melting technology on heat transfer devices for thermal energy conversion applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 420–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romei, F.; Grubišić, A.; Gibbon, D. Manufacturing of a high-temperature resistojet heat exchanger by selective laser melting. Acta Astronaut. 2017, 138, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, T.; Al-Hajri, E.; Paul, M.C.; Nithiarasu, P.; Kumar, S. High performance, microarchitected, compact heat exchanger enabled by 3D printing. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 210, 118339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltzman, D.; Bichnevicius, M.; Lynch, S.; Simpson, T.W.; Reutzel, E.W.; Dickman, C.; Martukanitz, R. Design and evaluation of an additively manufactured aircraft heat exchanger. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 138, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.J.; Hu, Z.H.; Wang, D.; Wu, H.W. Visualized-experimental investigation on the melting performance of PCM in 3D printed metal foam. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2022, 31, 101298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, C.A.; Kaiser, A.; Andreassen, K.A. Methane storage in metal-organic framework HKUST-1 with enhanced heat management using 3D printed metal lattices. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 192, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.; Murr, L.; Li, S.; Tian, Y.; Martinez, E.; Martinez, J.; Machado, B.; Gaytan, S.; Medina, F.; Wicker, R. Open-cellular copper structures fabricated by additive manufacturing using electron beam melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5379–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratalocchi, L.; Groppi, G.; Visconti, C.G.; Lietti, L.; Tronconi, E. Adoption of 3D printed highly conductive periodic open cellular structures as an effective solution to enhance the heat transfer performances of compact Fischer-Tropsch fixed-bed reactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 386, 123988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Rankouhi, B.; Thoma, D.J.; Cheadle, M.J.; Maples, G.D.; Anderson, M.H.; Nellis, G.; Qian, X. Topology optimization, additive manufacturing and thermohydraulic testing of heat sinks. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 224, 125281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Wang, J.; Zhong, H.; Qiu, X.; Yu, B.; Shi, J.; Chen, J. Experimental investigation on heat transfer characteristics of copper heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS). Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 152, 107292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, B.W.; Fee, C.J.; Morison, K.R.; Holland, D.J. Characterisation of heat transfer within 3D printed TPMS heat exchangers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 212, 124264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, S.; Tran, P.; Marzocca, P. Design and modelling of porous gyroid heatsinks: Influences of cell size, porosity and material variation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 235, 121296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, M.; Yu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, R. 3D printing of a SiO2@BN TPMS structure: Efficient heat transfer strategy for BN/epoxy composites. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 3820–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.H.; Liu, H.L.; Yang, K.; Wang, Q.; Xu, H.; Zhang, L. Enhancing heat transfer performance in 3D-printed integrated vapor chamber using composite structures. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 234, 121292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Rasouli, E.; Ziev, T.; Lamprinakos, N.; Seo, J.; Rollett, A.; Vaishnav, P.; Narayanan, V. Design and techno economic optimization of an additively manufactured compact heat exchanger for high temperature and high pressure applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 245, 122778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, B.; Bigham, S. Performance Evaluation of hi-k Lung-inspired 3D-printed Polymer Heat Exchangers. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 204, 117993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, B.; Cesarano, J.; Nawaz, K.; Ninos, N.; Bigham, S. A high-performance lung-inspired ceramic 3D-printed heat exchanger for high-temperature energy-efficient systems. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 219, 119378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracht, S.; Will, J.; Klöppel, S.; Funke, T.; Quack, H.; Haberstroh, C. Experimental and numerical study of a 3D-printed aluminium cryogenic heat exchanger for compact Brayton refrigerators. Cryogenics 2022, 123, 103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, K.; Cheng, M.; Lu, Z. Additive manufacturing of liquid-cooled ceramic heat sinks: An experimental and numerical study. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. Addit. Manuf. Front. 2023, 2, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Si | Mg | Zn | Cu | Fe | Ni | Mn | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.24 | 0.21 | 0.01 | 0.056 | 0.09 | 0.015 | 0.036 | Bal. |
| Battery Parameters | Values | Paraffin Parameters | Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Height/mm | 65 | Density/kg·m−3 | 810 |
| Diameter/mm | 26 | Specific heat capacity/J·(kg·K)−1 | 2000 |
| Capacity/Ah | 4.5 | Thermal conductivity/W·(m·K)−1 | 0.2 |
| Specific heat capacity/J·(kg·K)−1 | 1108 | Latent heat/kg·(m·s)−1 | 275 |
| Thermal conductivity/W·(m·K)−1 | 3.91 | Viscosity/kg·(m·s)−1 | 0.0035 |
| NO. | Fitting Model | a | b | c | d | f | SSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a(1 − ) + c | 247.8 | −4.764 | 5.415 | / | / | 22,780 | 0.9891 |
| 2 | a() + c() + f | 9.504 | 1.223 | −228.2 | −6.065 | 217.3 | 7495 | 0.9964 |
| 3 | a/(1 + ) + c | 468.9 | −7.25 | −221.5 | / | / | 34,960 | 0.9833 |
| 4 | a + b(1 − ) + d(1 − ) | 13,140 | 247.8 | −4.764 | −13,140 | −43,980 | 22,783 | 0.9891 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Liao, R.; Men, Z.; Wang, L.; Ji, C.; Li, K. Statics Performance and Heat Dissipation Evaluation of Lattice Structures Prepared by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Micromachines 2024, 15, 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070888
Bai J, Zhang C, Li Z, Liao R, Men Z, Wang L, Ji C, Li K. Statics Performance and Heat Dissipation Evaluation of Lattice Structures Prepared by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Micromachines. 2024; 15(7):888. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070888
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Jingfei, Can Zhang, Ziche Li, Ruobing Liao, Zhengxing Men, Liang Wang, Chen Ji, and Kun Li. 2024. "Statics Performance and Heat Dissipation Evaluation of Lattice Structures Prepared by Laser Powder Bed Fusion" Micromachines 15, no. 7: 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070888
APA StyleBai, J., Zhang, C., Li, Z., Liao, R., Men, Z., Wang, L., Ji, C., & Li, K. (2024). Statics Performance and Heat Dissipation Evaluation of Lattice Structures Prepared by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Micromachines, 15(7), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15070888







