Temperature Effects in Packaged RF MEMS Switches with Optimized Gold Electroplating Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Switch Design
3. Fabrication
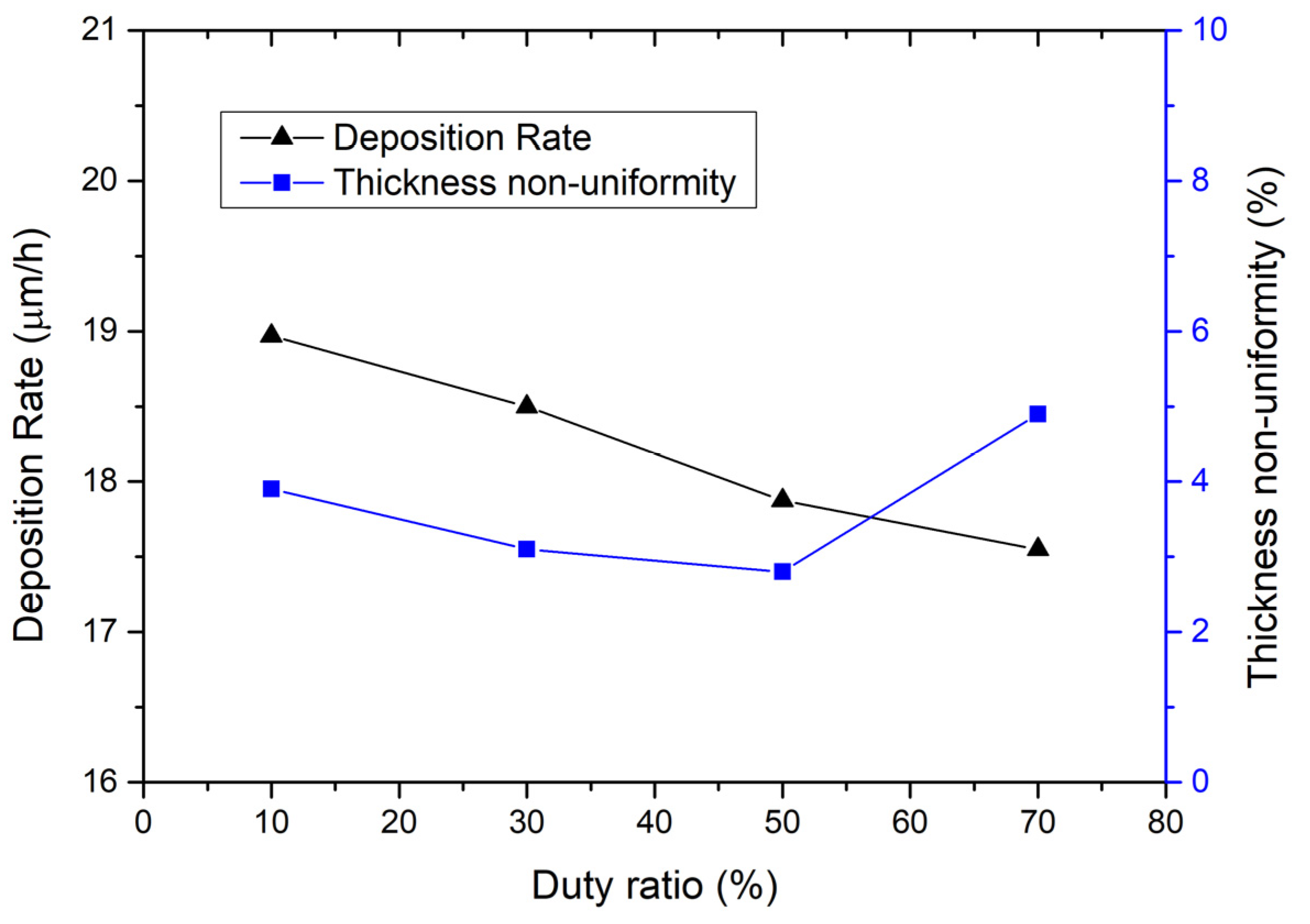
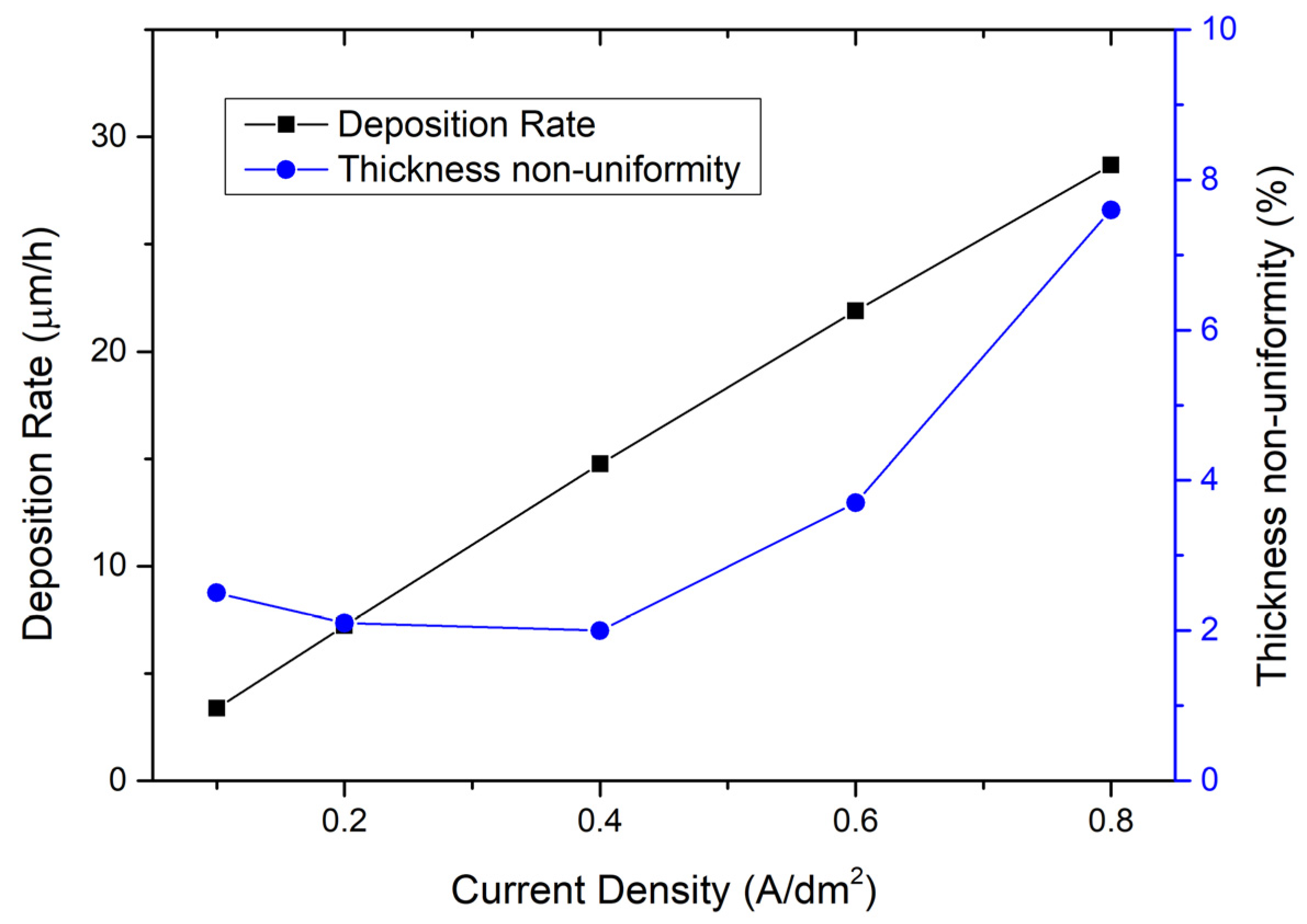
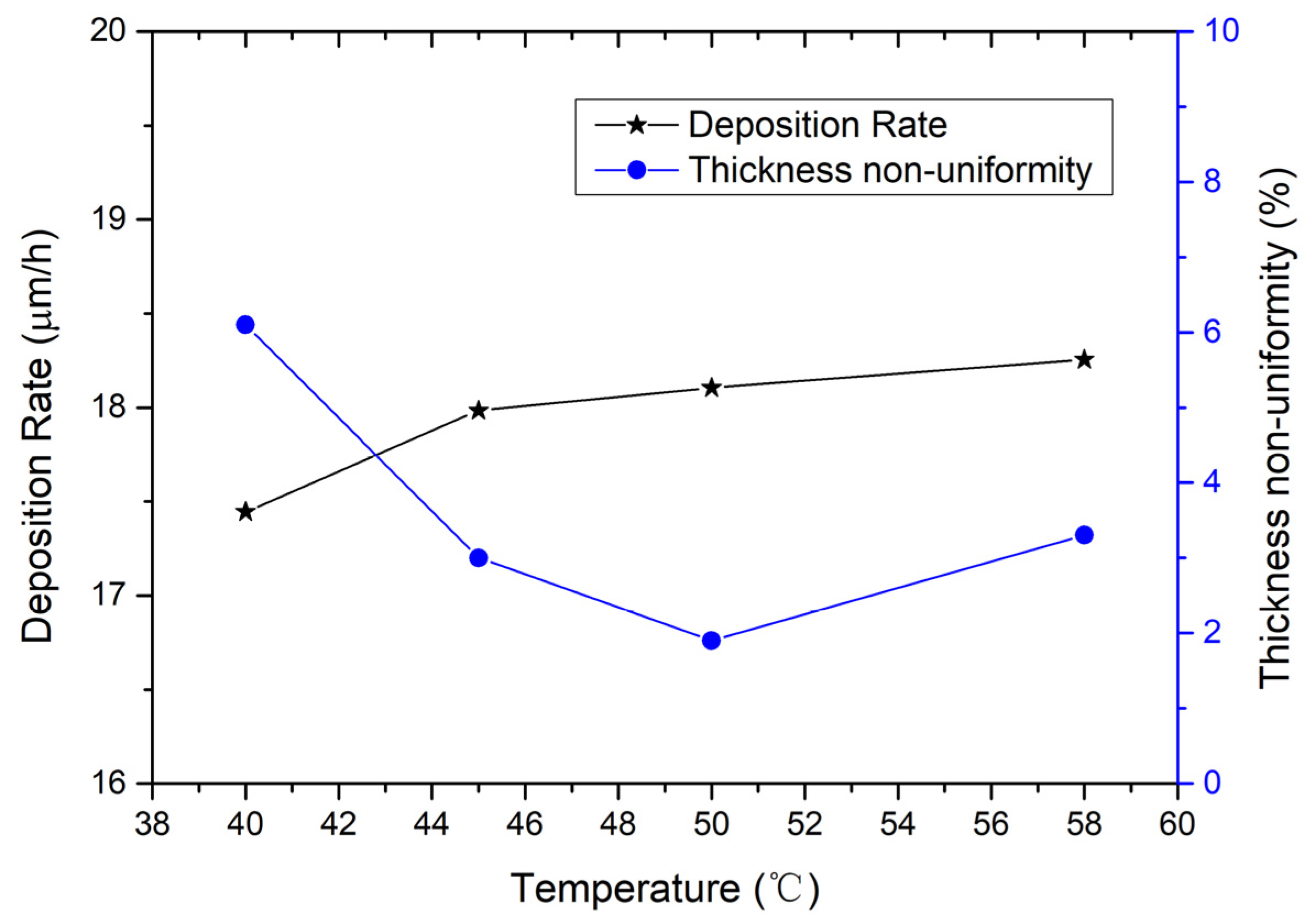
3.1. Optimization of Gold Electroplating Process
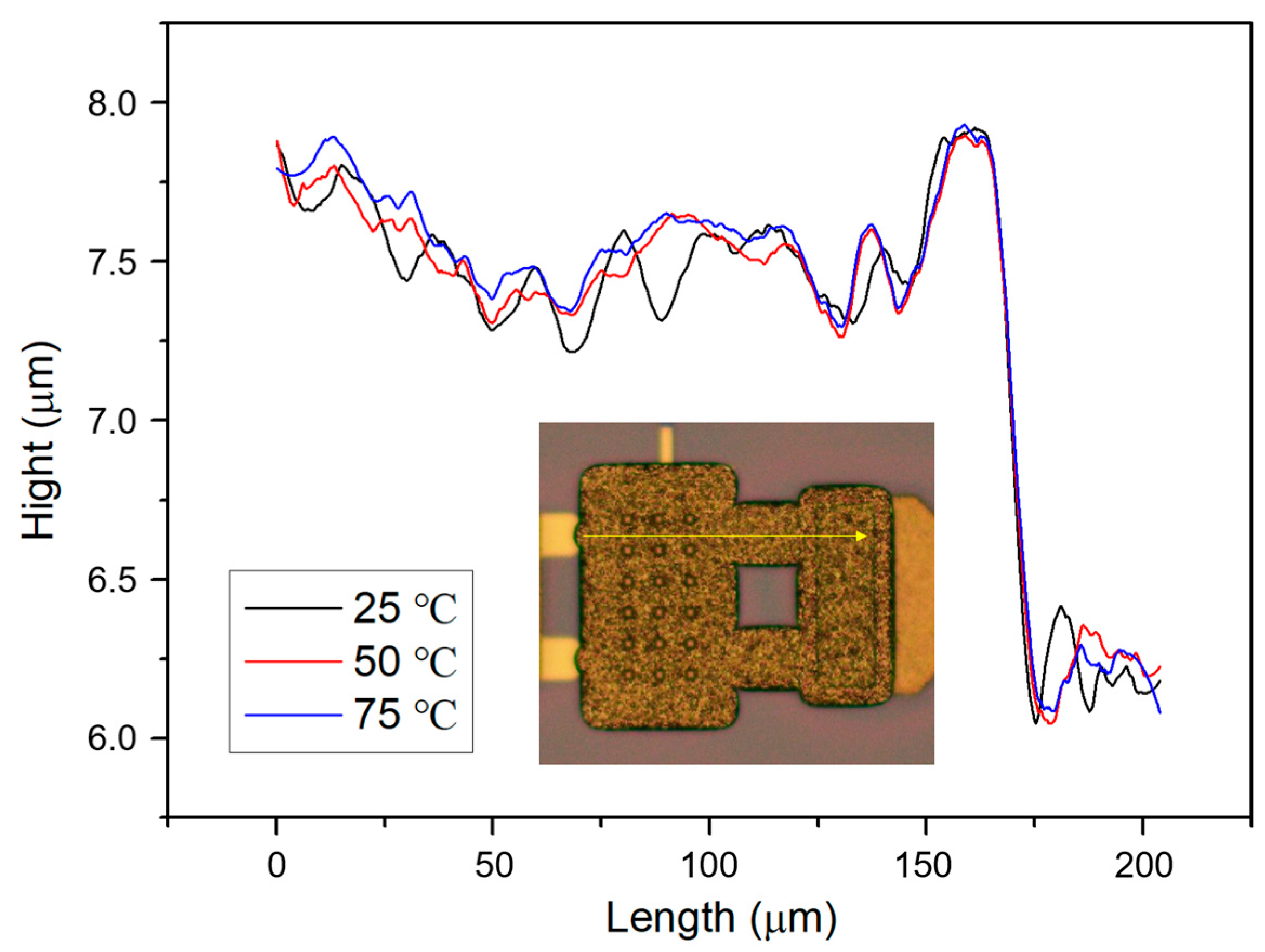
3.2. Characterization of the Optimized Electroplated Gold
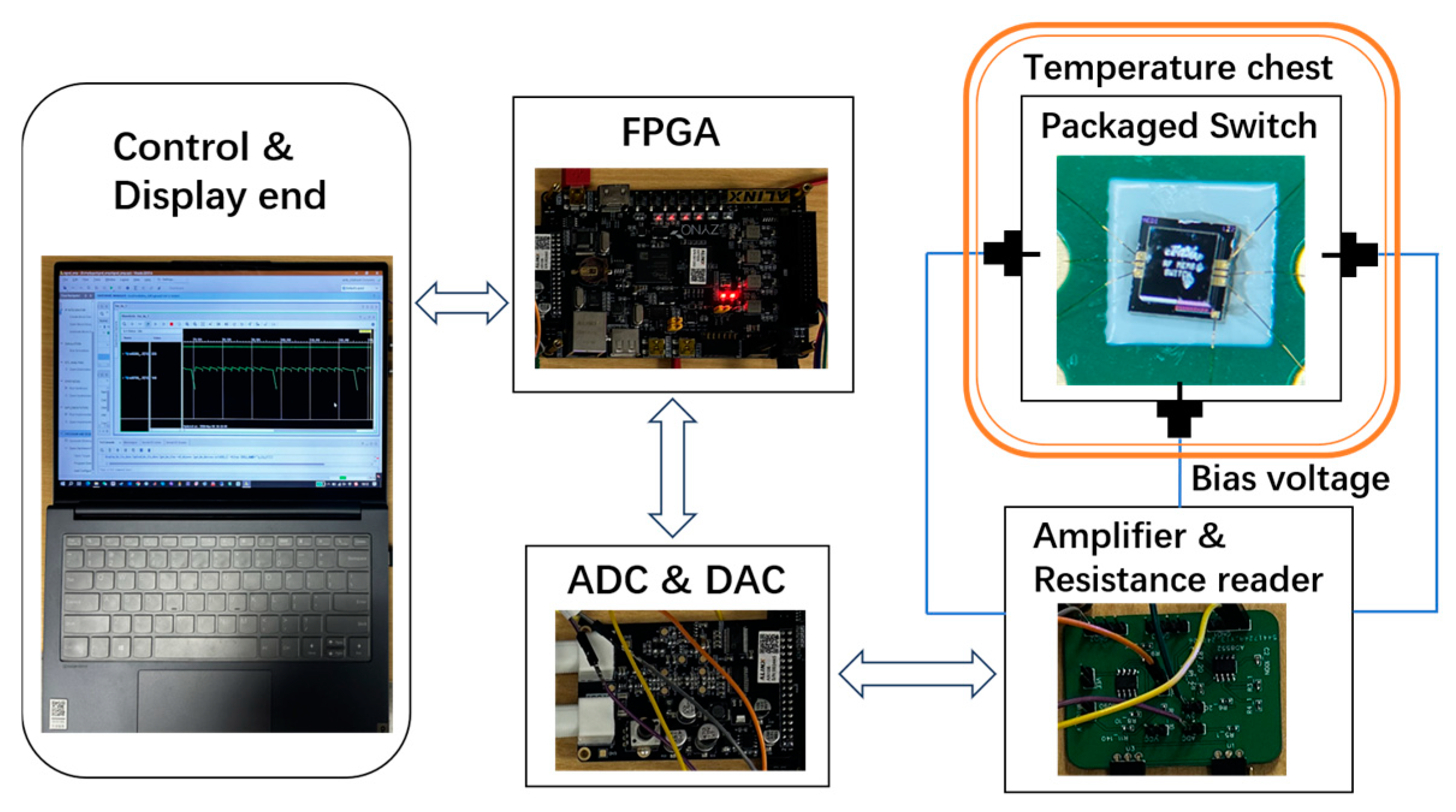
4. Measurements and Discussion
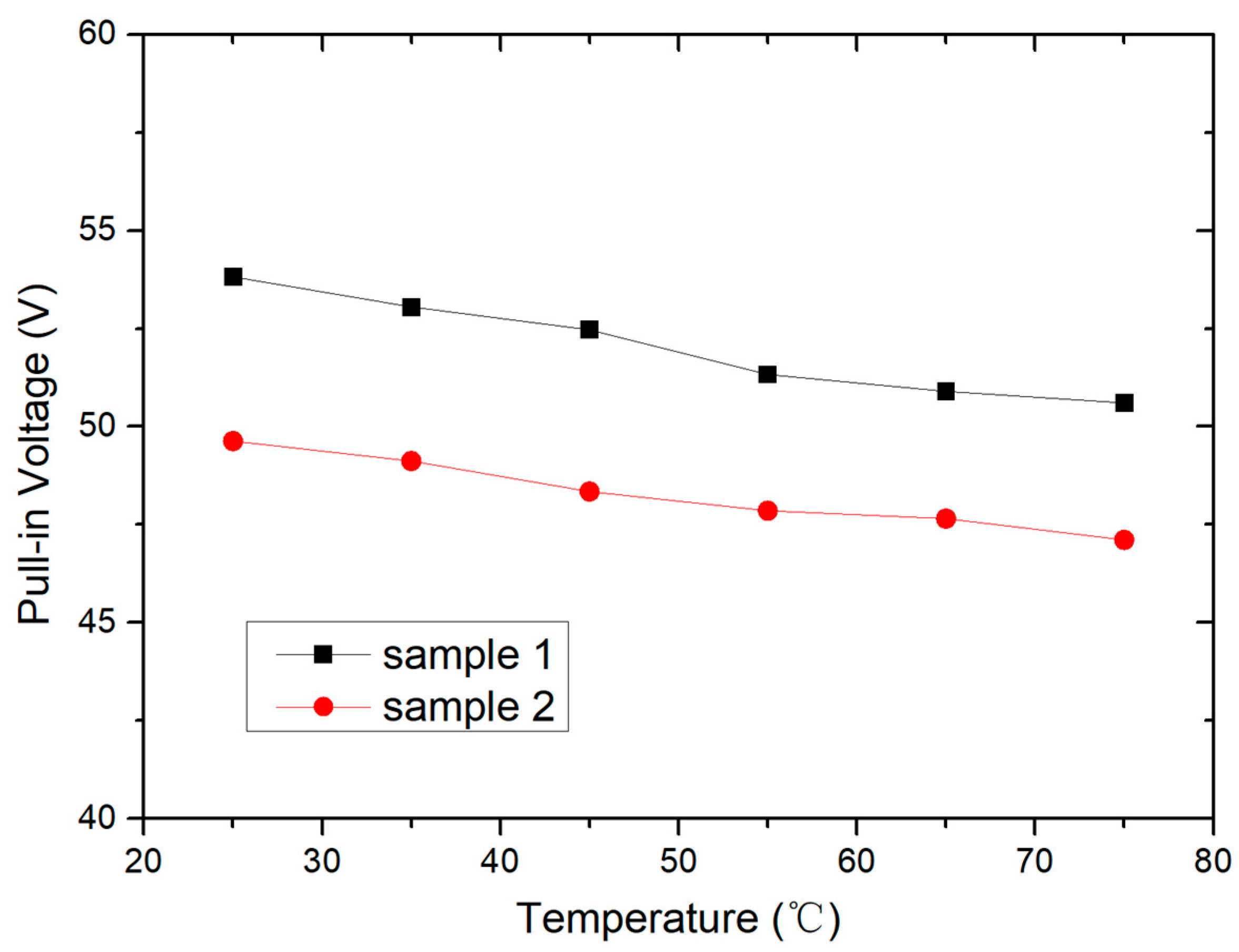
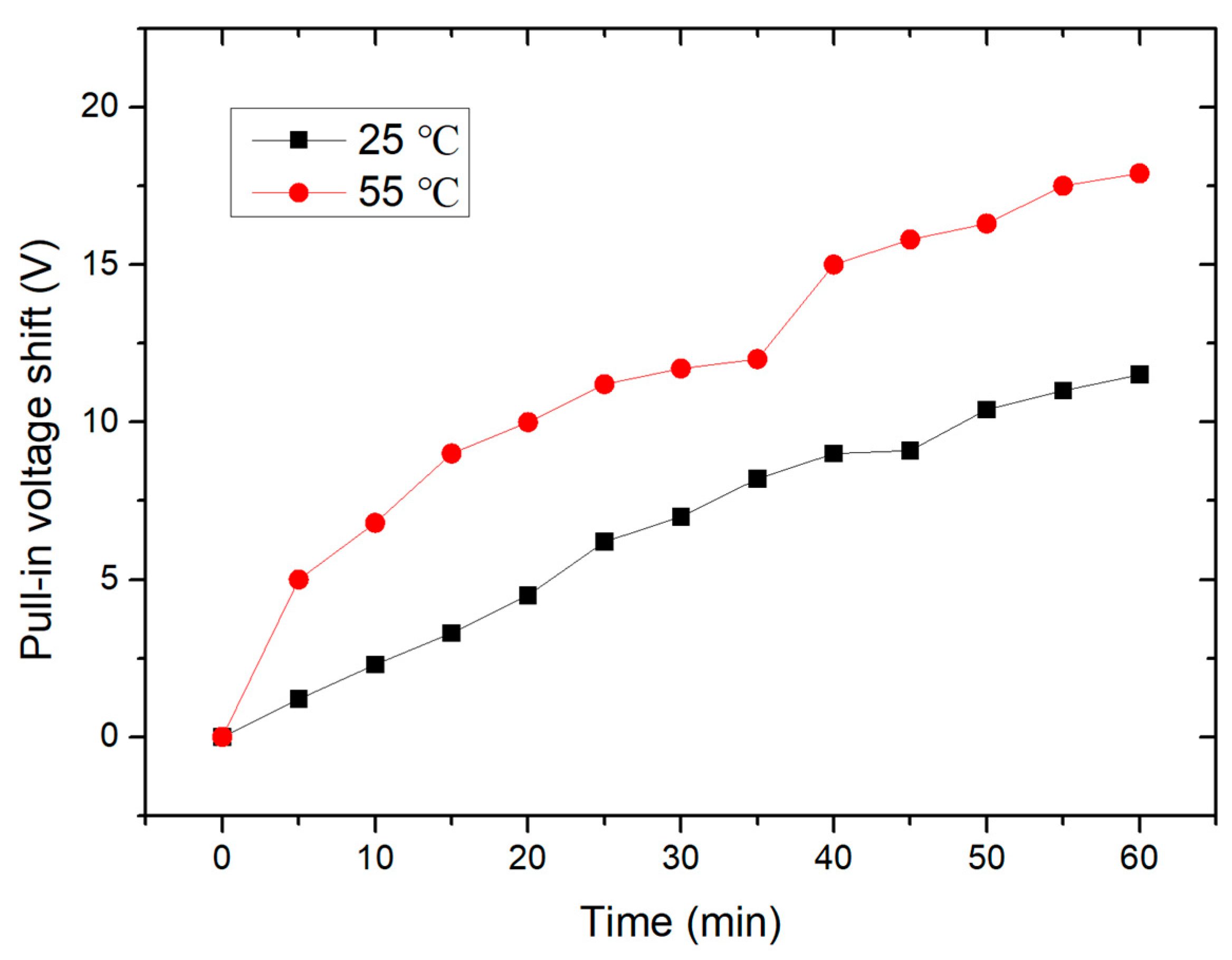
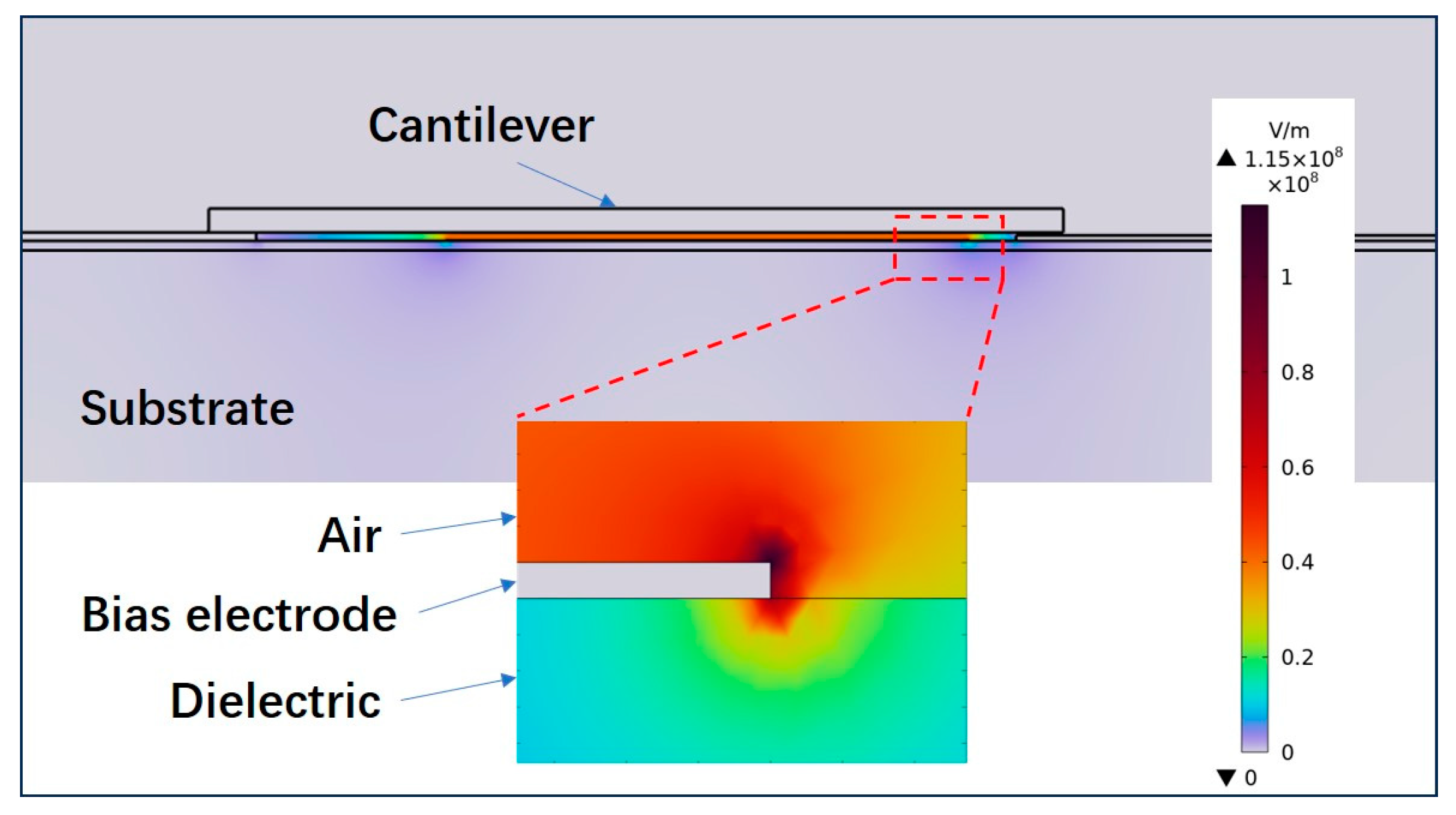
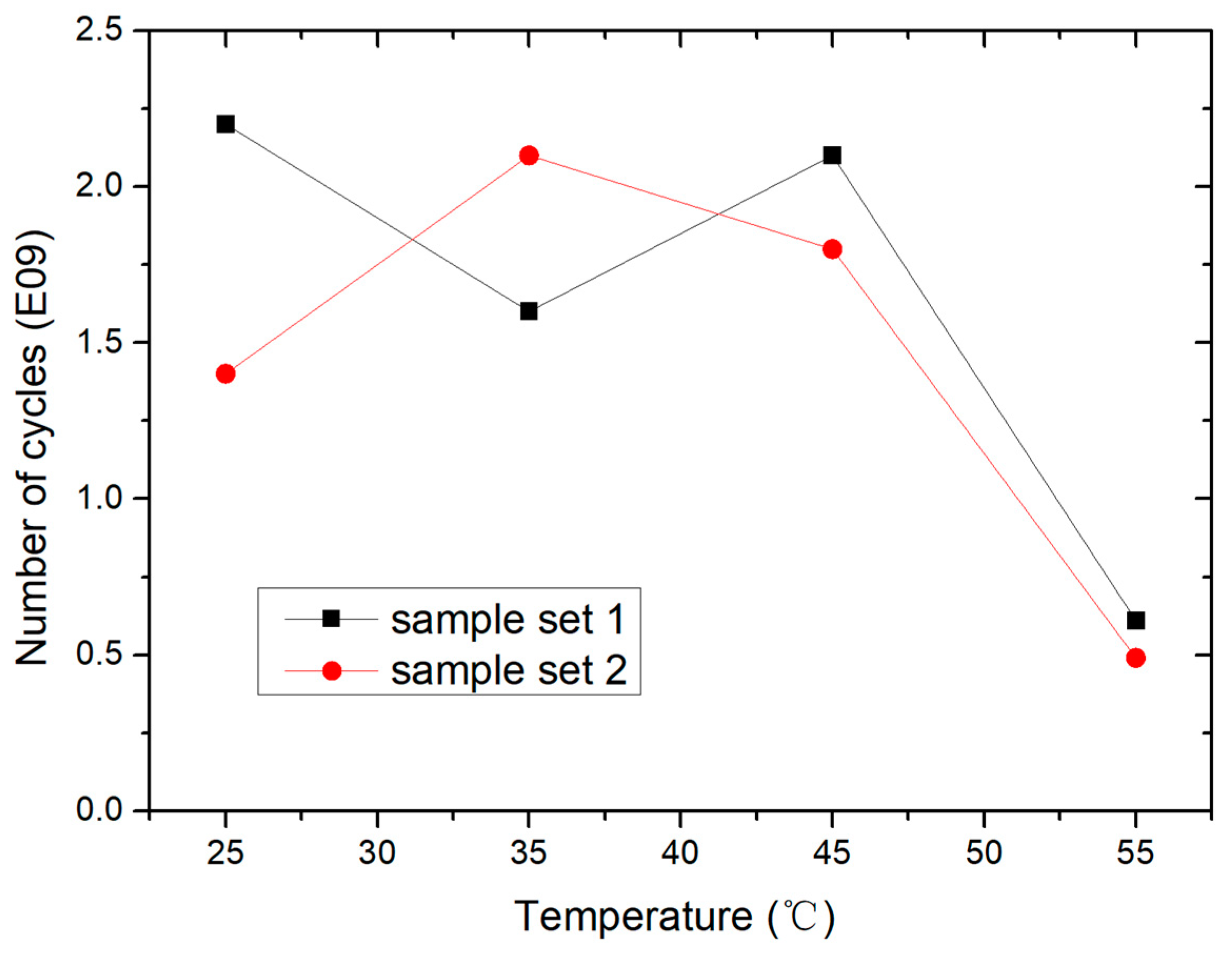
4.1. Temperature Effect on Mechanical Performance
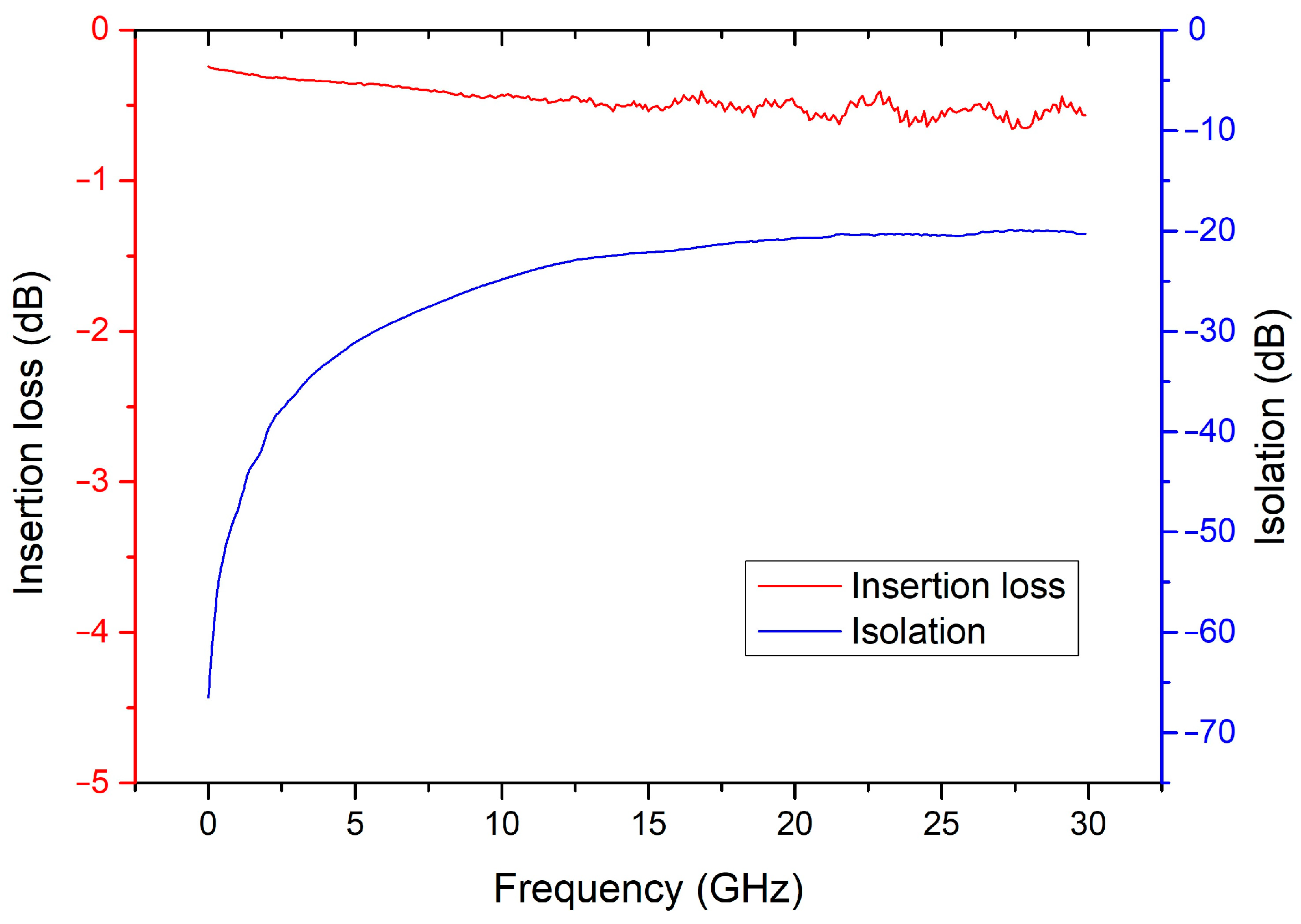
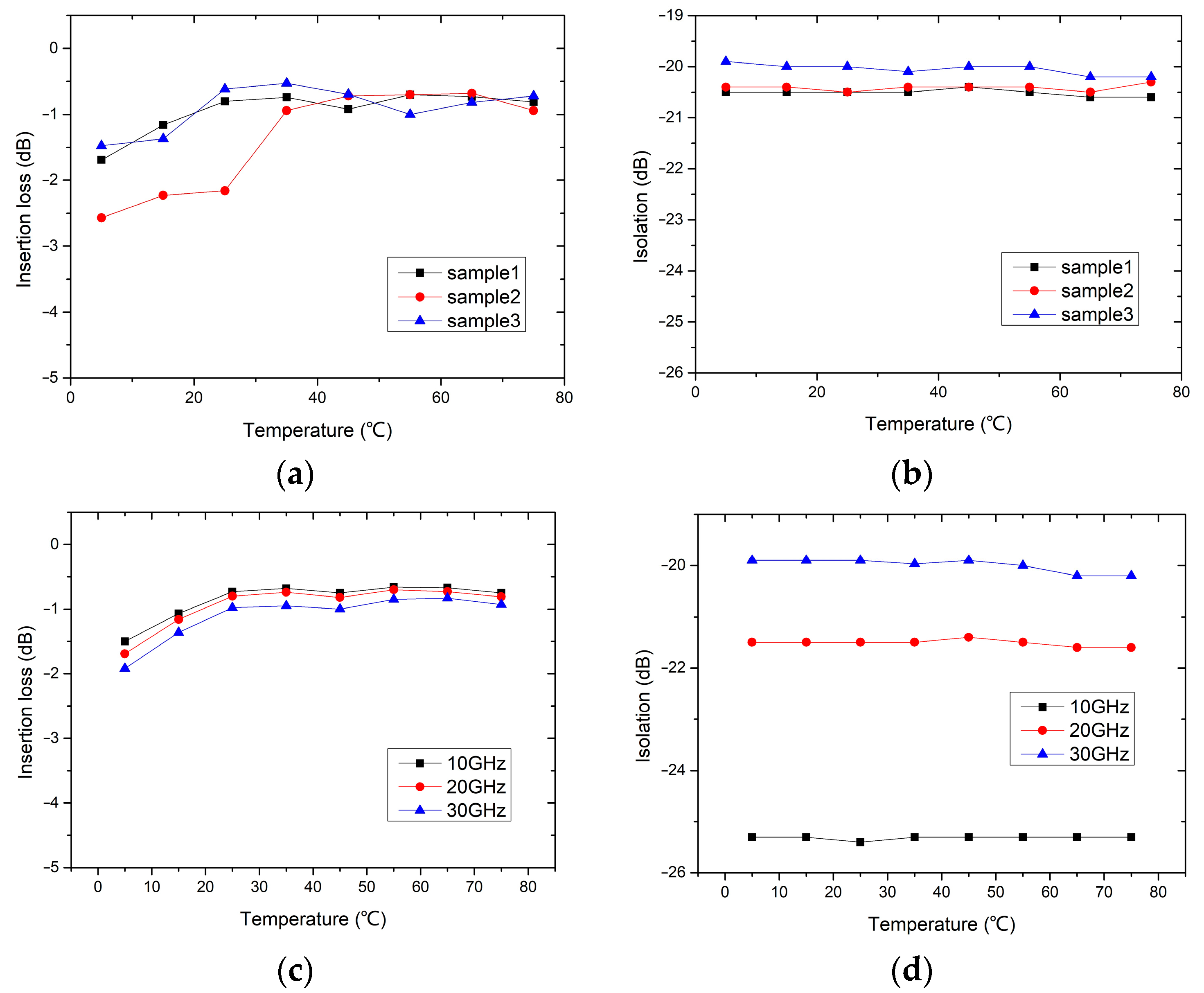
4.2. Temperature Effect on RF Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rebeiz, G.M. RF MEMS Theory, Design, and Technology; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rebeiz, G.M.; Muldavin, J.B. RF MEMS switches and switch circuits. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2001, 2, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadan, V.K.; Vinoy, K.J.; Jose, K.A. RF MEMS and Their Applications; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Si, C. A High-Reliability RF MEMS Metal-Contact Switch Based on Al-Sc Alloy. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, R.; Lesnick, R.; Becher, D.; Feng, M. Low-Actuation Voltage RF MEMS Shunt Switch with Cold Switching Lifetime of Seven Billion Cycles. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, K. Novel High Isolation and High Capacitance Ratio RF MEMS Switch: Design, Analysis and Performance Verification. Micromachines 2022, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hu, G. Design and Fabrication of a Capacitive Series RF MEMS Switch. Chin. J. Sens. Actuators 2008, 21, 660–663. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Bansal, D.; Kumar, A.; Bajpai, A.; Mehta, K.; Ashudeep; Rangra, K.; Boolchandani, D. Sacrificial layer optimization for RF MEMS switches. Microsyst. Technol. 2021, 27, 2147–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, A.; Quaranta, F.; Capoccia, G.; Proietti, E.; Lucibello, A.; Marcelli, R.; Bagolini, A.; Iannacci, J.; Taurino, A.; Siciliano, P. Influence of design and fabrication on RF performance of capacitive RF MEMS switches. Microsyst. Technol. 2016, 22, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.; Rangra, K.; Bansal, D. Fabrication process improvement of high isolation of RF MEMS switch for 5 G applications. Sensor. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 376, 115582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jung, C.; Bachman, M.; De Flaviis, F.; Li, G.P. A Novel Membrane Process for RF MEMS Switches. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2010, 19, 715–717. [Google Scholar]
- Fruehling, A.; Pimpinella, R.; Nordin, R.; Peroulis, D. A Single-crystal Silicon DC−40 GHz RF MEMS Switch. In Proceedings of the IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest 2009, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2009; pp. 1633–1636. [Google Scholar]
- Fouladi, S.; Mansour, R.R. Capacitive RF MEMS Switches Fabricated in Standard 0.35-mm CMOS Technology. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2010, 58, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurmendra; Kumar, R. Materials Selection Approaches and Fabrication Methods in RF MEMS Switches. J. Electron. Mater. 2021, 50, 3149–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lueke, J.; Quddus, N.A.; Moussa, W.; Chahal, A. A Parametric Study of Thermal Effects on the Reliability of RF MEMS Switches. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on MEMS 2005, Miami Beach, FL, USA, 30 January–3 February 2005; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Mulloni, V.; Solazzi, F.; Ficorella, F.; Collini, A.; Margesin, B. Influence of temperature on the actuation voltage of RF-MEMS switches. Microelecton. Reliab. 2013, 53, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulloni, V.; Lorenzelli, L.; Margesina, B.; Barbato, M.; Meneghesso, G. Temperature as an accelerating factor for lifetime estimation of RF-MEMS switches. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 160, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Peng, Z.; Hwang, J.C.M.; Forehand, D.; Goldsmith, C.L. Temperature Acceleration of Dielectric Charging in RF MEMS Capacitive Switches. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest 2006, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–16 June 2006; pp. 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Shen, H.; Barker, N.S. Study of Broadband Cryogenic DC-Contact RF MEMS Switches. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 57, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Ma, N.; Wang, L.; Huang, X. High-reliability circular-contact RF MEMS switches in silicon hermetic package. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2023, 33, 065004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Huang, Z.; Huang, M. Implementation of Highly Reliable Contacts for RF MEMS Switches. Micromachines 2024, 15, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogozi, A. Elastic Constant of Silver and Gold. Ph.D. Thesis, Florida International University, Miami, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoureli, M.; Birbiliotis, D.; Michalas, L.; Papaioannou, G. Dielectric charging in MEMS capacitive switches a persisting reliability issue, available models and assessment methods. In Proceedings of the 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 14–16 November 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Tang, J.; Huang, Q. Effect of Environmental Humidity on Dielectric Charging Effect in RF MEMS Capacitive Switches Based on C–V Properties. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2013, 22, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, G.J.; Wang, G.; Bessas, D.; Papapolymerou, J. Dielectric charging mechanisms in RF-MEMS capacitive switches. In Proceedings of the 2006 European Microwave Integrated Circuits, Manchester, UK, 10–15 September 2006; pp. 1157–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Exarchos, M.; Theonas, V.; Pons, P.; Papaioannou, G.J.; Melle, S.; Dubuc, D.; Cocetti, F.; Plana, R. Investigation of charging mechanisms in metal–insulator–metal structures. Microelectron. Reliab. 2005, 45, 1782–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| GSG | 40/80/40 μm |
| Beam thickness | 5 μm |
| Beam spring size | 40 × 40 μm |
| Beam electrode size | 100 × 160 μm |
| Electrostatic gap | 1.8 μm |
| Contact thickness | 0.5 μm |
| Cavity depth of silicon cap | 100 μm |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Current density | 0.4~0.6 A/dm2 |
| Temperature | 50 ± 5 °C |
| Frequency | 1 kHz |
| Duty ratio | 50% |
| Flow rate | 10~30 L/min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Ma, N.; Huang, X. Temperature Effects in Packaged RF MEMS Switches with Optimized Gold Electroplating Process. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15091085
Wang L, Jiang L, Ma N, Huang X. Temperature Effects in Packaged RF MEMS Switches with Optimized Gold Electroplating Process. Micromachines. 2024; 15(9):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15091085
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lifeng, Lili Jiang, Ning Ma, and Xiaodong Huang. 2024. "Temperature Effects in Packaged RF MEMS Switches with Optimized Gold Electroplating Process" Micromachines 15, no. 9: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15091085
APA StyleWang, L., Jiang, L., Ma, N., & Huang, X. (2024). Temperature Effects in Packaged RF MEMS Switches with Optimized Gold Electroplating Process. Micromachines, 15(9), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi15091085






