Design and Fabrication of an Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
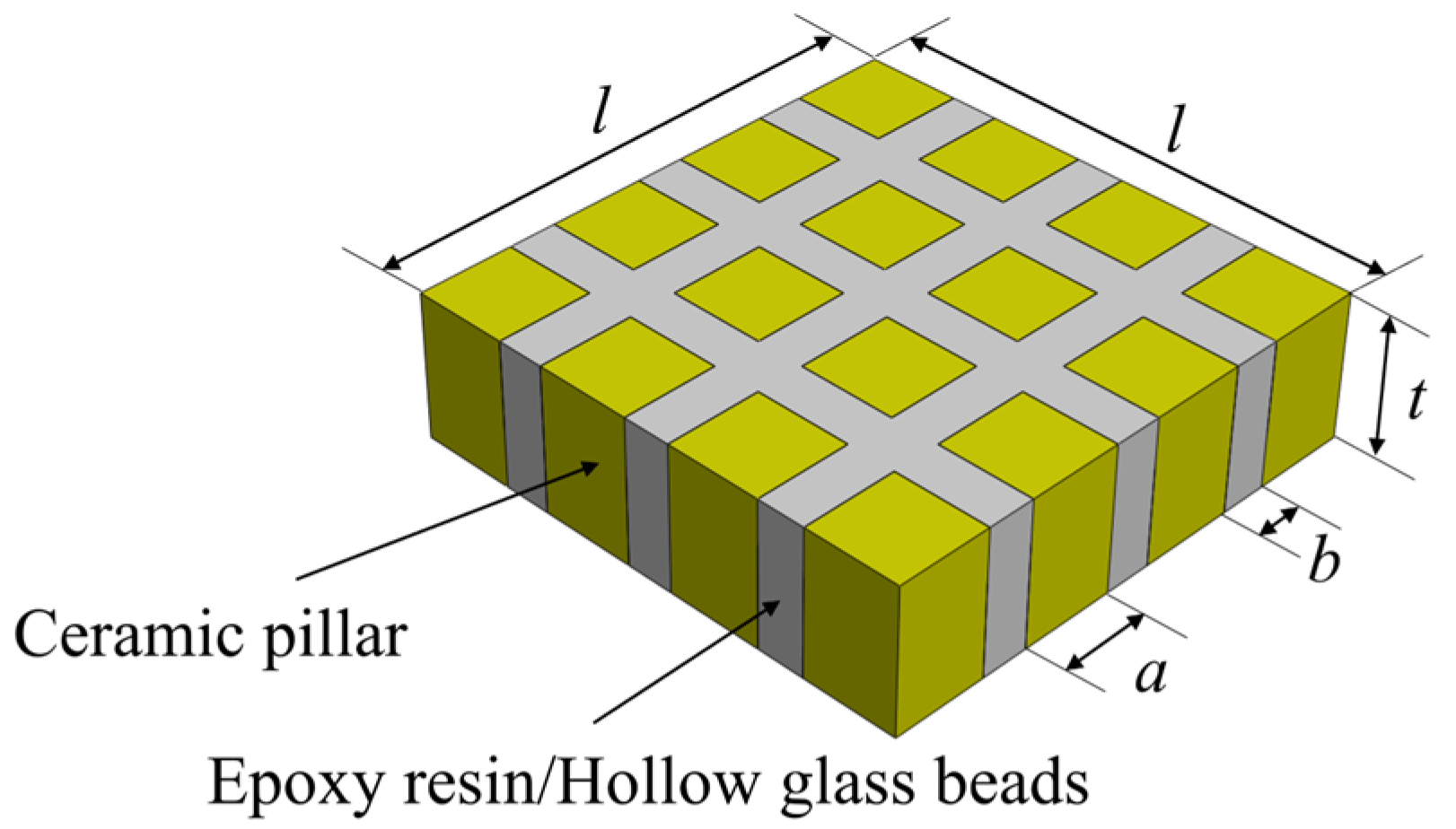
2. Models of the Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite
2.1. Theoretical Model
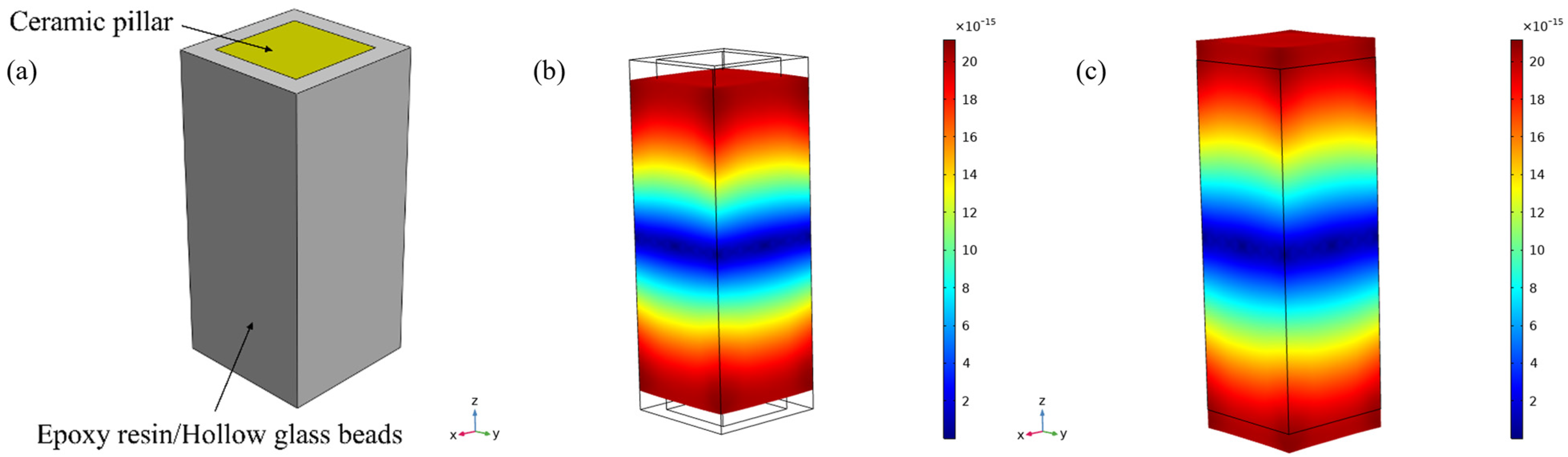
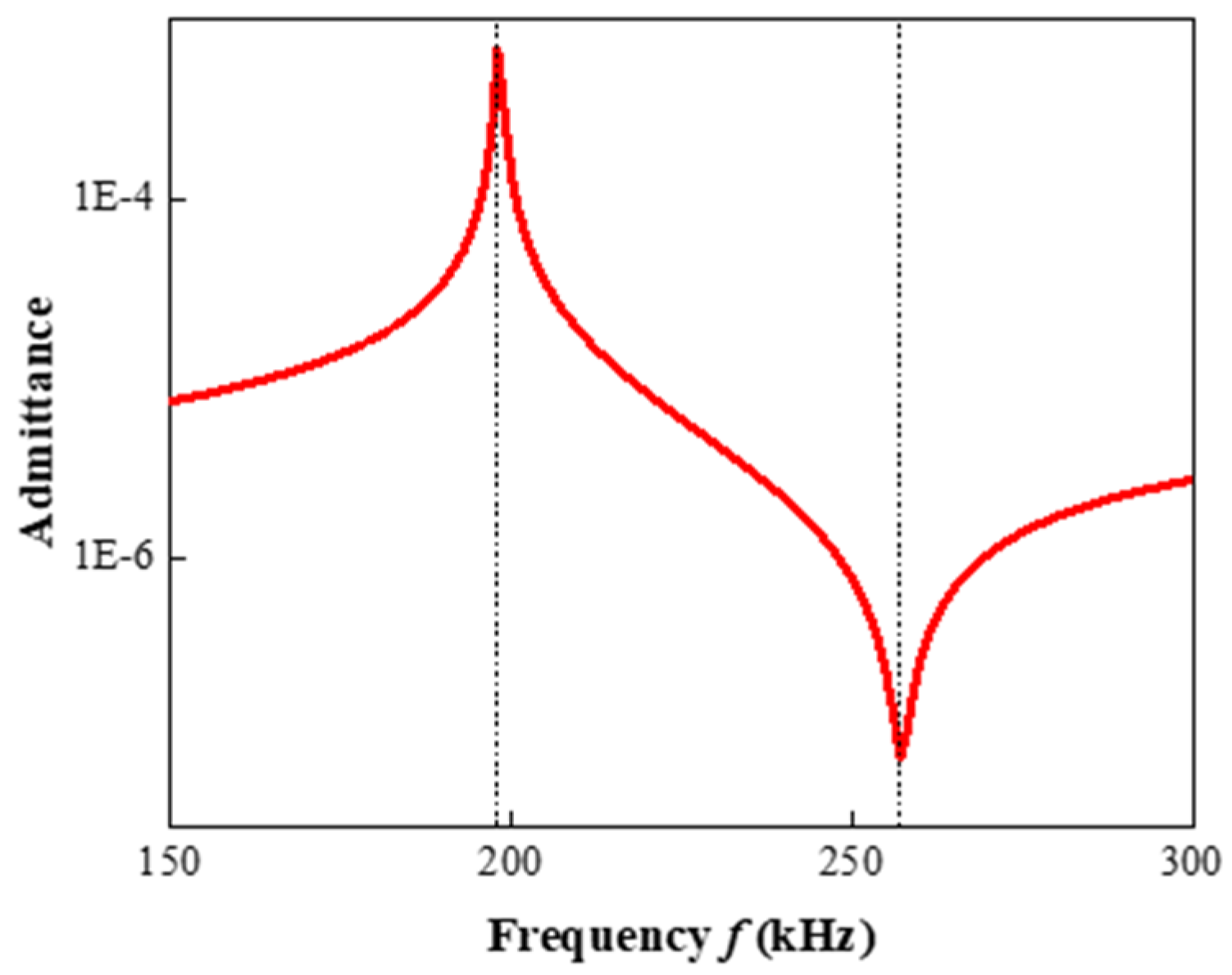
2.2. Finite Element Model
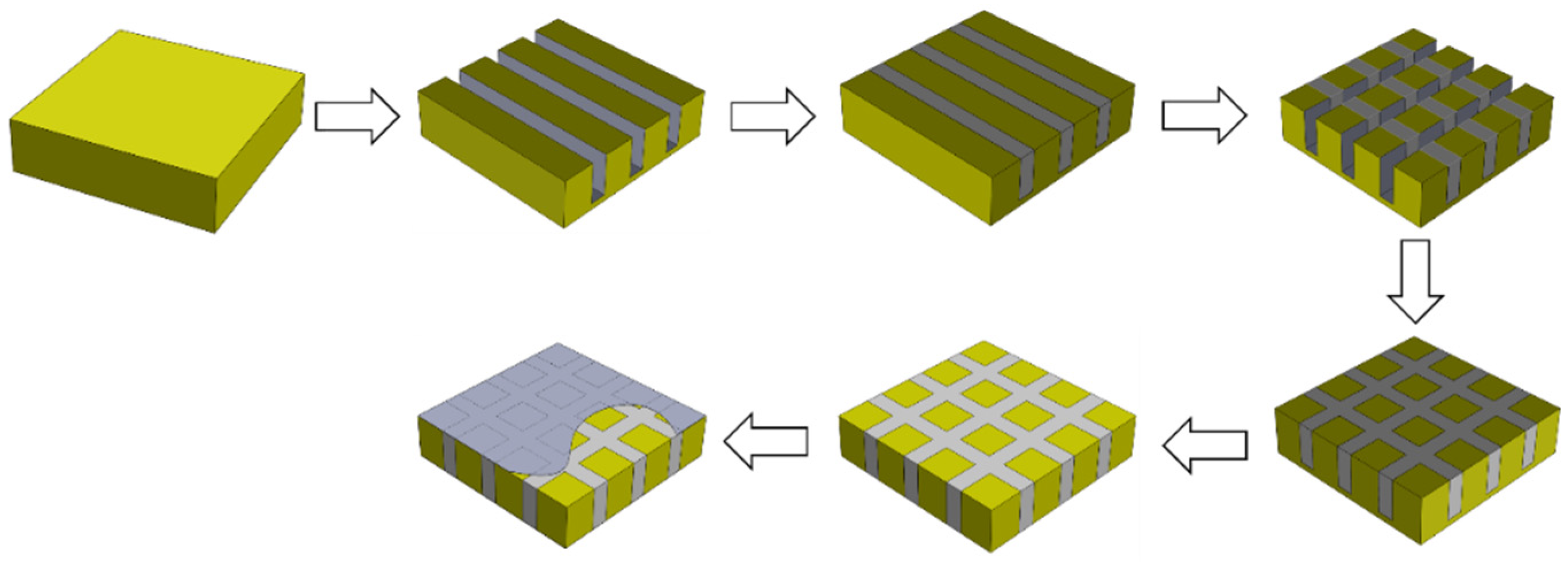
3. Preparation of the Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite
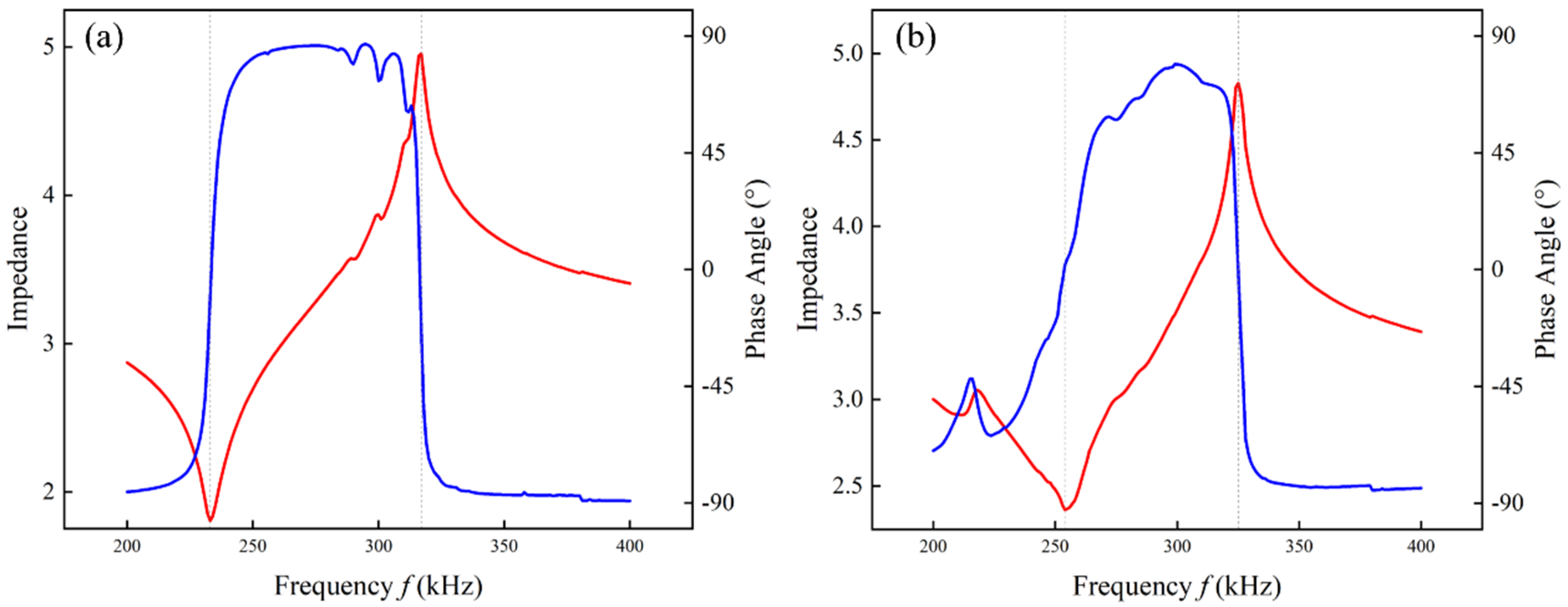
4. Effect Factors of the Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite
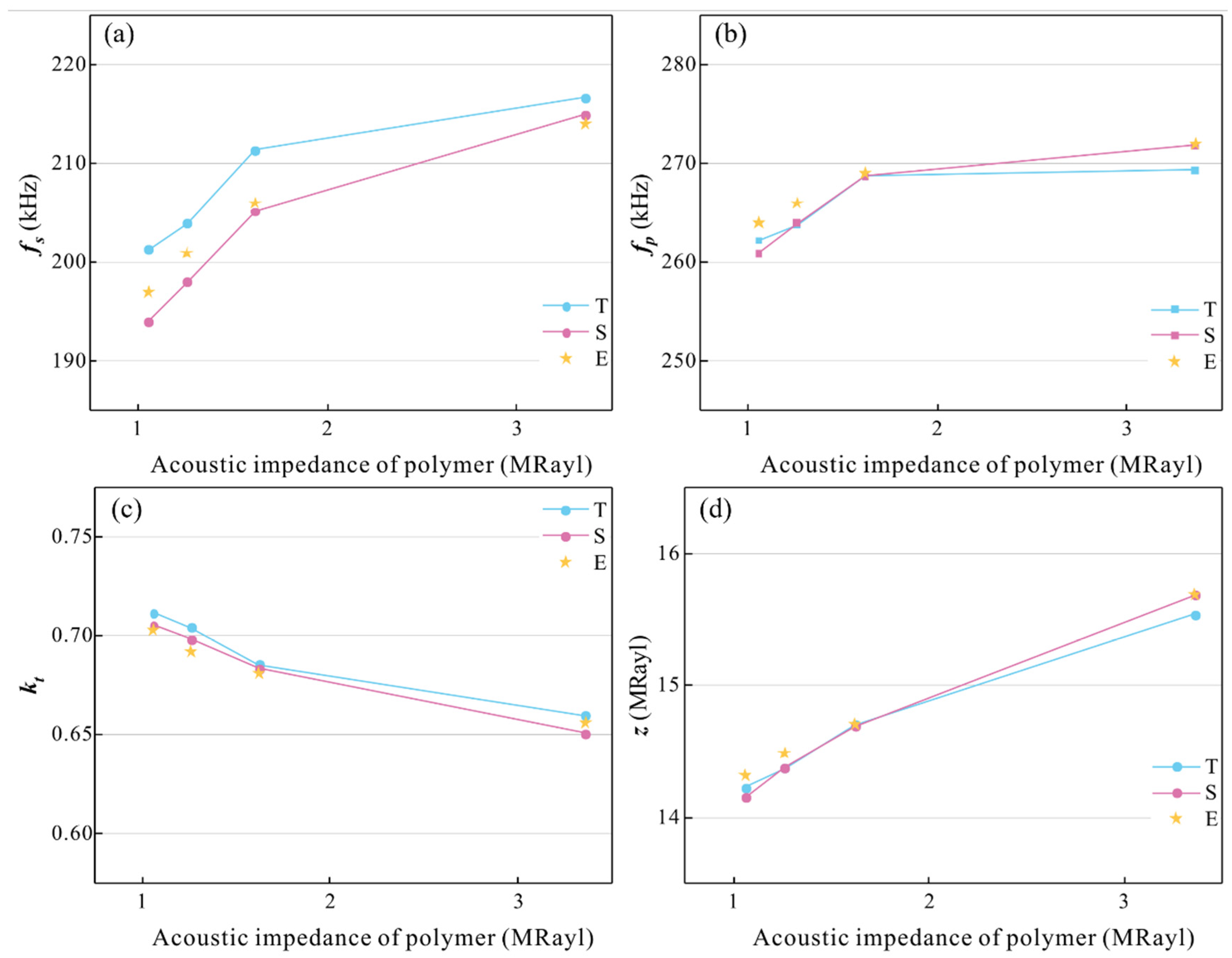
4.1. Effect of the Polymers with Different Acoustic Impedance
4.2. Effect of Different Thicknesses
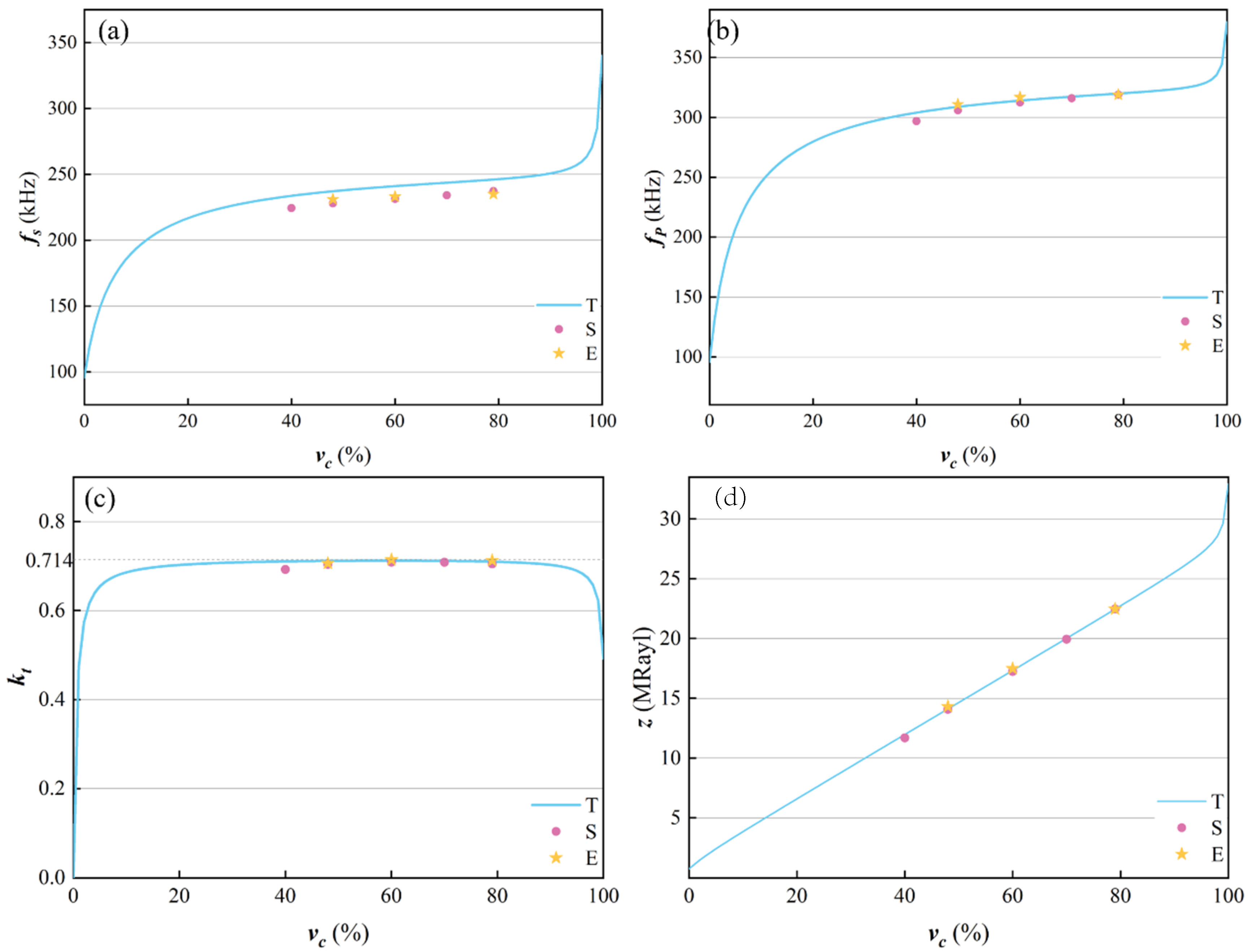
4.3. Effect of Different Ceramic Volume Fractions
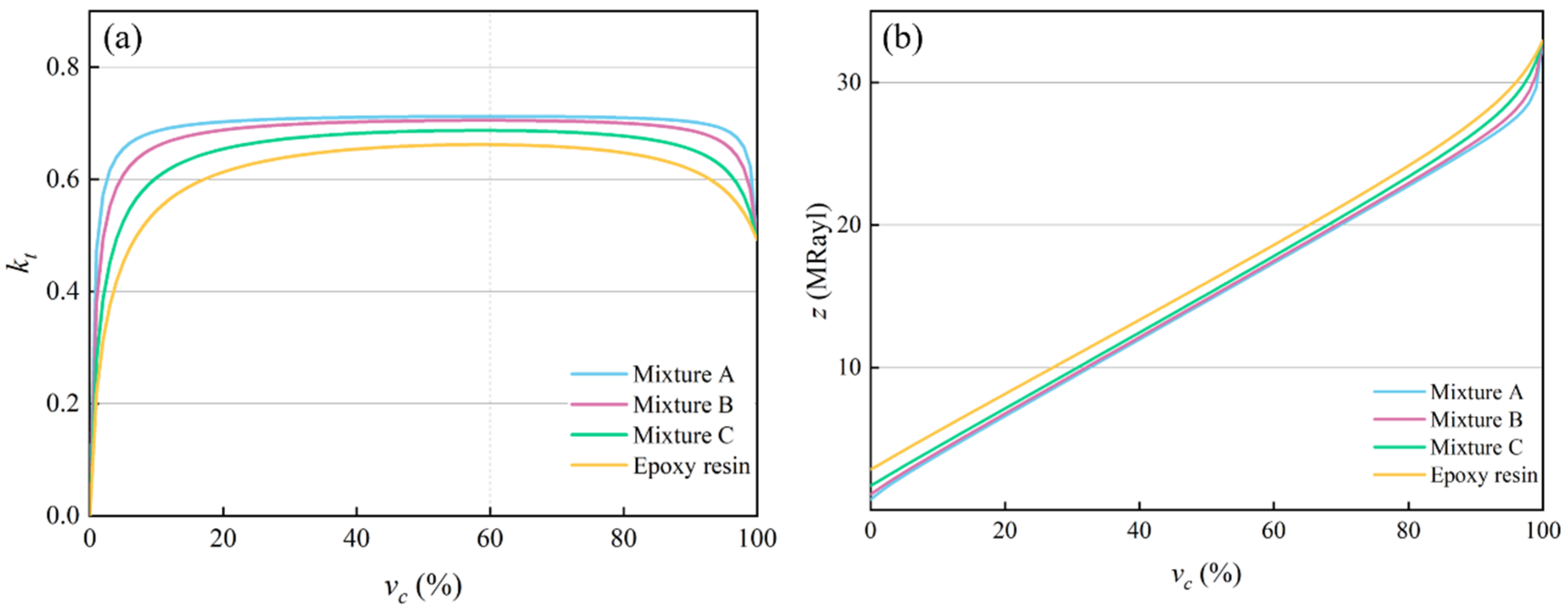
4.4. Effect of Different Polymers on Different Volume Fractions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The theoretical, simulation, and experimental results show that with the increase in the acoustic impedance of the polymer, the resonant frequency and anti-resonant frequency of the epoxy/glass microbeads-based 1-3 piezoelectric composite increase, and its acoustic impedance value also increases, but the electromechanical coupling factor decreases. When the thickness of the epoxy/glass microbeads-based 1-3 piezoelectric composites increases, the resonant frequency and anti-resonant frequency decrease and the electromechanical coupling factor and acoustic impedance are almost unchanged.
- (2)
- The resonant frequency and anti-resonant frequency of the epoxy/glass microbeads-based 1-3 piezoelectric composite increase with the increase in the ceramic volume fraction, and the electromechanical coupling factor reaches 0.714 when the ceramic volume fraction is 60.0%.
- (3)
- Compared with the traditional 1-3 piezoelectric composite under the same dimension parameters, the electromechanical coupling factor of the epoxy/glass microbeads-based 1-3 piezoelectric composite is raised to 0.714, which is increased by 7.8%. Therefore, it can achieve higher sensitivity and resolution of the transducers, which has potential advantages for improving the performance of transducers.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Z.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Yu, Z. Design, preparation, properties analysis and simulations of 1-3-3 piezoelectric composites. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 4222–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh Khameneh, A.; Chabok, H.; Nejat Pishkenari, H. Optimized integrated design of a high-frequency medical ultrasound transducer with genetic algorithm. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Thongchai, T.; Bai, Y.; Meggs, C.; Hughes, H. Lead-free piezoelectric materials and composites for high frequency medical ultrasound transducer applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 September 2014; pp. 903–906. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Huang, H.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Yin, L. A wearable cardiac ultrasound imager. Nature 2023, 613, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newnham, R.; Skinner, D.; Cross, L. Connectivity and Piezoelectric-Pyroelectric Composite. Mater. Res. Bull. 1978, 13, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, C.; Hao, S.; Wang, L. Design and Properties Analysis of Novel Modified 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite. Materials 2021, 14, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Lan, C. Analysis of 1-3 PZT/Polymer Piezoelectric Composite Material Performances. Piezoelectrics Acoustooptics 2001, 23, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Or, S.; Yue, Q. Ternary piezoelectric single-crystal PIMNT based 2-2 composite for ultrasonic transducer applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 196, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Du, P.; Wang, J. Design and properties of Gaussian-type 1-3 piezoelectric composites. Compos. Struct. 2016, 140, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Gong, X.; Zhang, D. Investigation of a multi-element focused air-coupled transducer. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 095010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Duan, Z. Enhanced compressive strengths and induced cell growth of 1-3-type BaTiO3/PMMA bio-piezoelectric composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Sahebi, L.; Eslami, B. Using a combination of superb microvascular imaging and other auxiliary ultrasound techniques to increase the accuracy of grayscale ultrasound for breast masses. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffarivardavagh, R.; Afzal, S.; Rodriguez, O. Underwater Transducer for Wide-Band Communication. U.S. Patent No. 11,678,112, 13 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H.; Unsworth, J. Simple model for piezoelectric ceramic/polymer 1-3 composites used in ultrasonic transducer applications. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1989, 36, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo-Castillero, J.; Guinovart-Diaz, R.; Otero, J.A.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R. Electromechanical properties of continous fibre-reinforced piezoelectric composites. Mech. Compos. Mater. 1997, 33, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinovart-Díaz, R.; Bravo-Castillero, J.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R. Application of piezoelectric composite materials to sensors design. Quim. Analítica. 1999, 18, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Guinovart-Díaz, R.; Bravo-Castillero, J.; Rodríguez-Ramos, R.; Sabina, F.J.; Martínez-Rosado, R. Overall properties of piezocomposite materials 1-3. Mater. Lett. 2001, 48, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qin, L.; Wang, L. Researching on resonance characteristics influenced by the structure parameters of 1-3-2 piezocomposites plate. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2008, 55, 946–951. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Zuo, R.; Yu, J. Alkaline niobate based lead-free ceramic fiber/polymer 1-3 composites: Processing and electromechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2011, 22, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, R. Microscale 1-3-Type (Na,K)NbO3-Based Pb-Free Piezocomposites for High-Frequency Ultrasonic Transducer Applications. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite with a 3-Tier Polymer Structure. Materials 2020, 13, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Lu, H.; Zhou, J. Effect of thickness on the performance parameters of modified 1-3 piezoelectric composites. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10928–10935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Lu, H.; Shen, X. Design, preparation and electromechanical characteristics analysis of piezoelectric 1-3-type composites with sandwich polymer structures. Sens. Actuators A. Phys. 2024, 366, 115024. [Google Scholar]
- Tize Mha, P.; Maréchal, P.; Ntamack, G. Homogenized electromechanical coefficients and effective parameters of 1-3 piezocomposites for ultrasound imaging transducers. Phys. Lett. A 2021, 408, 127492. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, N.; Zhong, C.; Zhang, M. A sandwich-structured 1-3 type piezoelectric composite material for enhancing reliability. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 45165–45178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Wang, L.; Qin, L. Characterization of an improved 1-3 piezoelectric composite by simulation and experiment. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2017, 15, S38–S44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Qin, L. Equivalent parameter model of 1-3 piezocomposite with a sandwich polymer. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhong, C. 1-3-Type piezoelectric composites with three-layer cascade structure. Compos. Struct. 2023, 322, 117406. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X. Theoretical and Experimental Study on the Effective Piezoelectric Properties of 1-3 Type Cement-Based Piezoelectric Composites. Materials 2018, 11, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wang, H.; Su, J. Research, design, and analysis of a stacked piezoelectric metamaterial structured sensitive element. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 1828. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Li, M.; Sun, M. Fabrication and Properties of 1-3 Polymer Modified Cement Based Piezoelectric Composites. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 1368, 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, B. Design and Fabrication of Air-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite Transducer for Air-Coupled Ultrasonic Applications. J. Sens. 2016, 2016, 4982616. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z. Electromechanical characterization of 3–2 ceramic-air composites. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 32377–32382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Gui, B.; Tong, Z.; Yang, D. Fabrication and properties of thermal insulating material using hollow glass microspheres bonded by aluminum–chrome–phosphate and tetraethyl orthosilicate. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4886–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y. Hollow glass microsphere/polybutadiene composites with low dielectric constant and ultralow dielectric loss in high-frequency. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2024, 142, e56351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, C.; Kumar, R. Quasi-static uni-axial compression behaviour of hollow glass microspheres/epoxy based syntactic foams. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4152–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Hu, Y.; Jia, H.; Liu, P.; Xu, D. Acoustic and dielectric properties of epoxy resin/hollow glass microsphere composite acoustic materials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 135, 109105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhu, H. Short-fiber piezocomposite and its bandwidth enhancement for high-frequency medical ultrasound transducer. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, H.; Zhou, X. Design, fabrication, and characterization of 1–3 piezoelectric composite air-coupled ultrasonic transducers with micro-membrane filter matching layer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2024, 379, 115955. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y. Development of the lens-focused air-coupled ultrasonic transducer for non-destructive testing. Ultrasonics 2025, 149, 107590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Min, C. Preparation and properties of hollow glass microspheres/dicyclopentadiene phenol epoxy resin composite materials. Materials 2023, 16, 3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Baek, Y.; Jeong, J.; Sim, J.; Gwak, E.; Je, T. Acoustic and rheological characterization of hollow glass microsphere composite for development of optimized air-coupled ultrasonic matching layer. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 32036–32048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y. Fabrication and modeling of matching system for air-coupled transducer. Micromachines 2022, 13, 781. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, J. Effect of Filling Material Properties on 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite Performance. Micromachines 2024, 15, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Auld, B. Modeling 1-3 composite piezoelectrics: Thickness-Mode Oscillations. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 1991, 38, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE 176-1987; IEEE Standard on Piezoelectricity. IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1988; p. 176.
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J. Study of dicing mechanism influence on pzt-4h composite performance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 5089–5100. [Google Scholar]
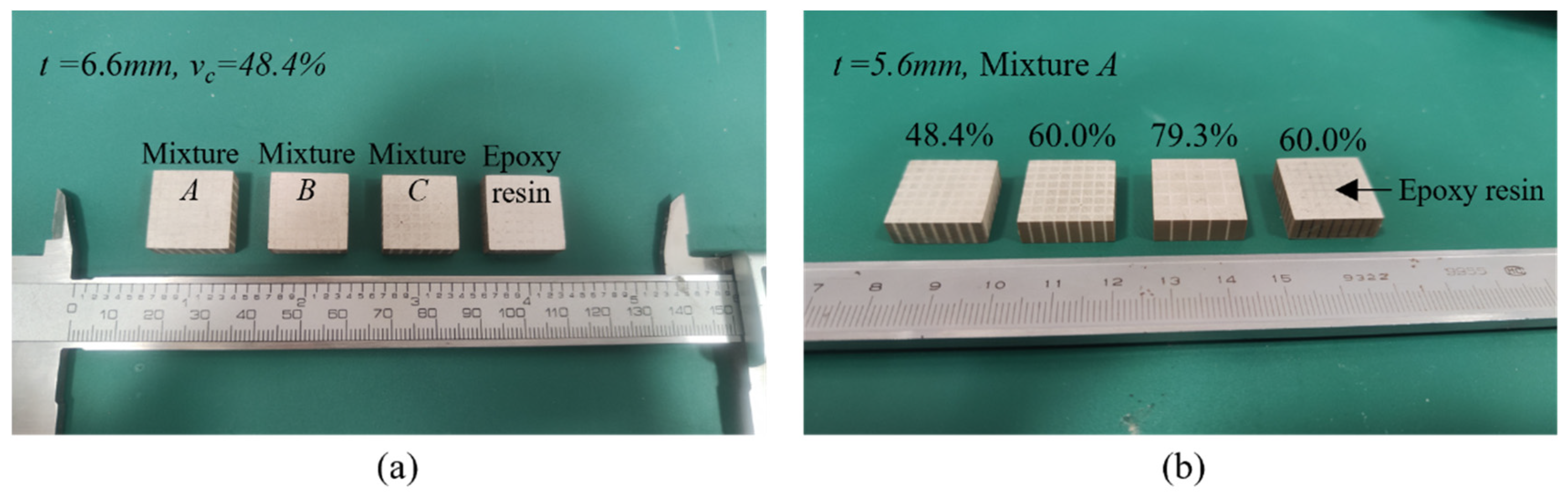

| Hollow Glass Microbeads | Real Density ρ (kg/m3) | Wall Thickness (μm) | Acoustic Impedance Z(MRayl) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BR20 | 200 | 0.5–1 | 0.456 |
| Epoxy/Glass Microbeads Mixture | Volume Fraction (%) |
|---|---|
| A | 27.5% |
| B | 22.0% |
| C | 18.8% |
| Parameters | PZT-5A | Mixture A | Mixture B | Mixture C | Epoxy Resin 618 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7750 | 694 | 727 | 756 | 1200 | |
| 32.93 | 1.06 | 1.26 | 1.62 | 3.36 | |
| 12.1 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.68 | |
| 7.54 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.2 | 0.42 | |
| 7.52 | - | - | - | - | |
| 10.6 | - | - | - | - | |
| −5.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Polymer | Mixture A | Mixture B | Mixture C | Epoxy Resin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kHz) | Theory | 201.33 | 204.02 | 204.02 | 216.71 |
| Simulation | 194.06 | 198.04 | 198.04 | 214.98 | |
| Experiment | 197.00 | 201.00 | 206.00 | 214.00 | |
| (kHz) | Theory | 262.24 | 263.85 | 263.85 | 269.35 |
| Simulation | 260.92 | 264.00 | 264.00 | 271.88 | |
| Experiment | 264.00 | 266.00 | 269.00 | 272.00 | |
| (mm) | 5.0 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.6 | 7.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kHz) | Simulation | 254.48 | 227.96 | 213.1 | 194.06 | 183.15 |
| Experiment | - | 231.00 | 215.00 | 197.00 | - | |
| (kHz) | Simulation | 340.88 | 306.01 | 286.29 | 260.92 | 246.33 |
| Experiment | - | 311.00 | 289.00 | 264.00 | - | |
| (%) | 40.0 | 48.4 | 60.0 | 70.0 | 79.3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kHz) | Simulation | 224.34 | 227.96 | 231.41 | 234.08 | 237.3 |
| Experiment | - | 231.00 | 233.00 | - | 235.00 | |
| (kHz) | Simulation | 296.94 | 306.01 | 312.6 | 316.1 | 318.97 |
| Experiment | - | 311.00 | 317.00 | - | 319.00 | |
| Polymer | (MRayl) | |
|---|---|---|
| Mixture A | 0.712 | 17.33 |
| Mixture B | 0.705 | 17.48 |
| Mixture C | 0.687 | 17.81 |
| Epoxy resin | 0.662 | 18.60 |
| t (mm) | vc (%) | fs (kHz) | fp (kHz) | kt | z (MRayl) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy/glass microbeads-based | 5.6 | 60.0 | 233.00 | 317.00 | 0.714 | 17.49 |
| Traditional epoxy resin-based | 5.6 | 60.0 | 254.00 | 325.00 | 0.662 | 18.67 |
| Common Structure Types | |
|---|---|
| Epoxy/glass microbeads-based 1-3 piezoelectric composite | 0.714 |
| Air-based 1-3 piezoelectric composite [32] | 0.70 |
| 3-2 Ceramic–Air Composite [33] | 0.71 |
| 1-3 piezoelectric composites with three-layer cascade [28] | 0.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, P. Design and Fabrication of an Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite. Micromachines 2025, 16, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040361
Liu Q, Zhou J, Jia Z, Zhou P. Design and Fabrication of an Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040361
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qiyun, Jinjie Zhou, Ziliang Jia, and Pengfei Zhou. 2025. "Design and Fabrication of an Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040361
APA StyleLiu, Q., Zhou, J., Jia, Z., & Zhou, P. (2025). Design and Fabrication of an Epoxy/Glass Microbeads-Based 1-3 Piezoelectric Composite. Micromachines, 16(4), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040361





