Spatial Decoupling Method for a Novel Dual-Orthogonal Induction MEMS Three-Dimensional Electric Field Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dual-Orthogonal Induction MEMS 3D Electric Field Sensor
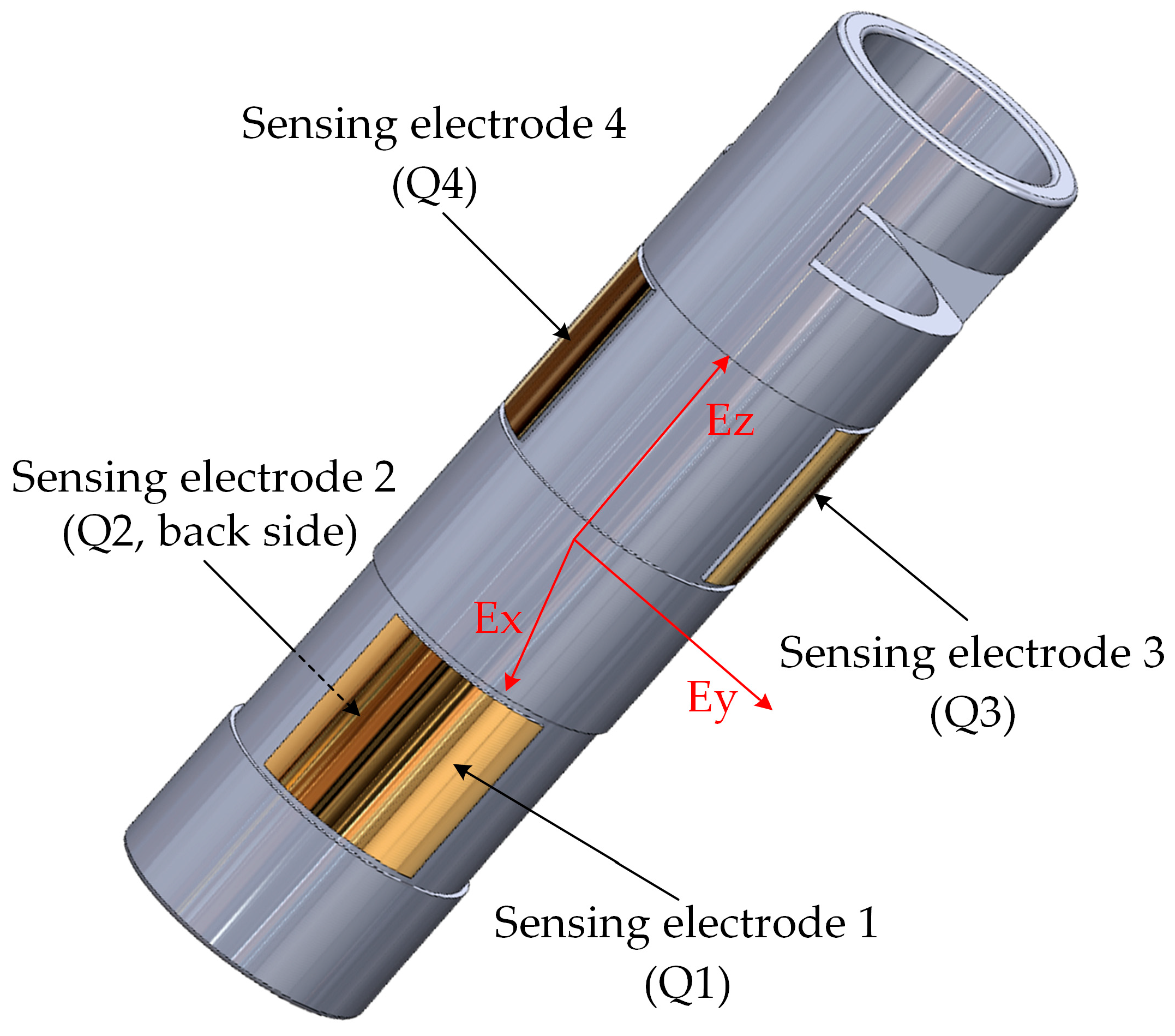
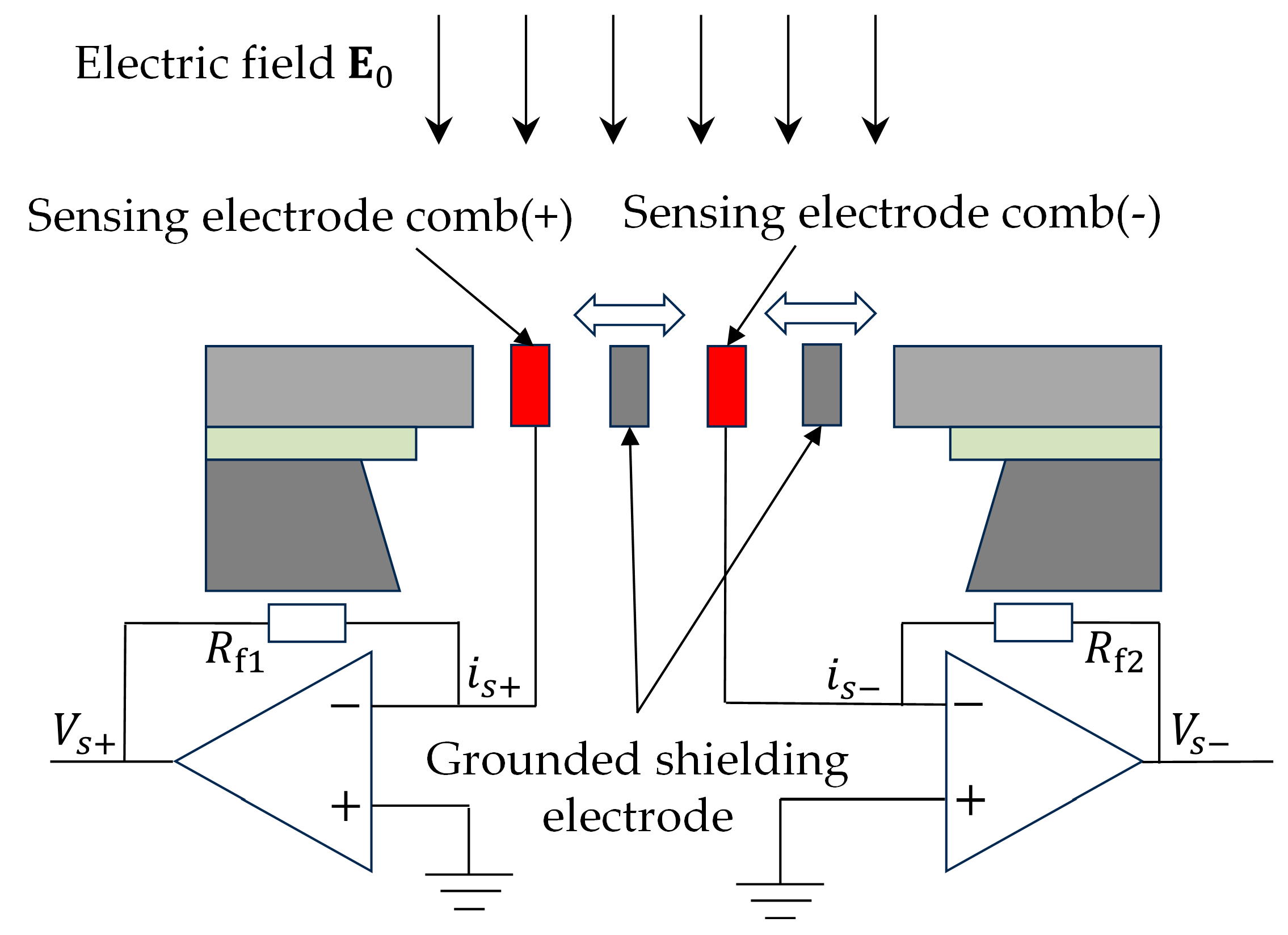
2.1. Sensor Structure Design and Operating Principle
2.2. Basic Decoupling Method of Spatial 3D Electric Field Measurements
3. Spatial Decoupling Method for 3D Electric Field Measurement Based on the CRLB
3.1. Decoupling Model for the MEMS 3D Electric Field Sensor
3.2. Decoupling Method Based on the CRLB
4. Coordinate Transformation Model and Calibration System
4.1. Calibration Coordinate Transformation Model Based on Rotation Matrix
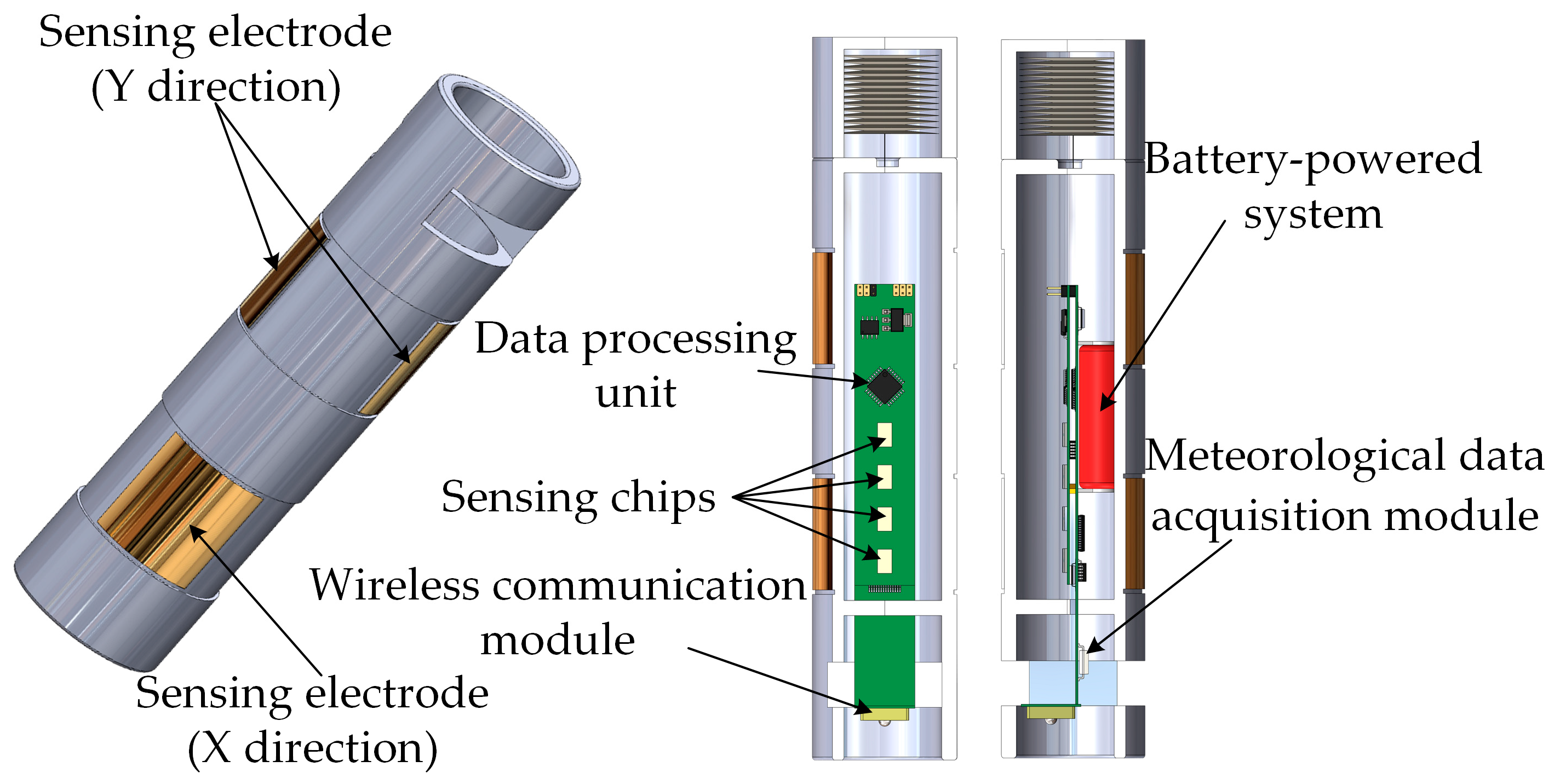
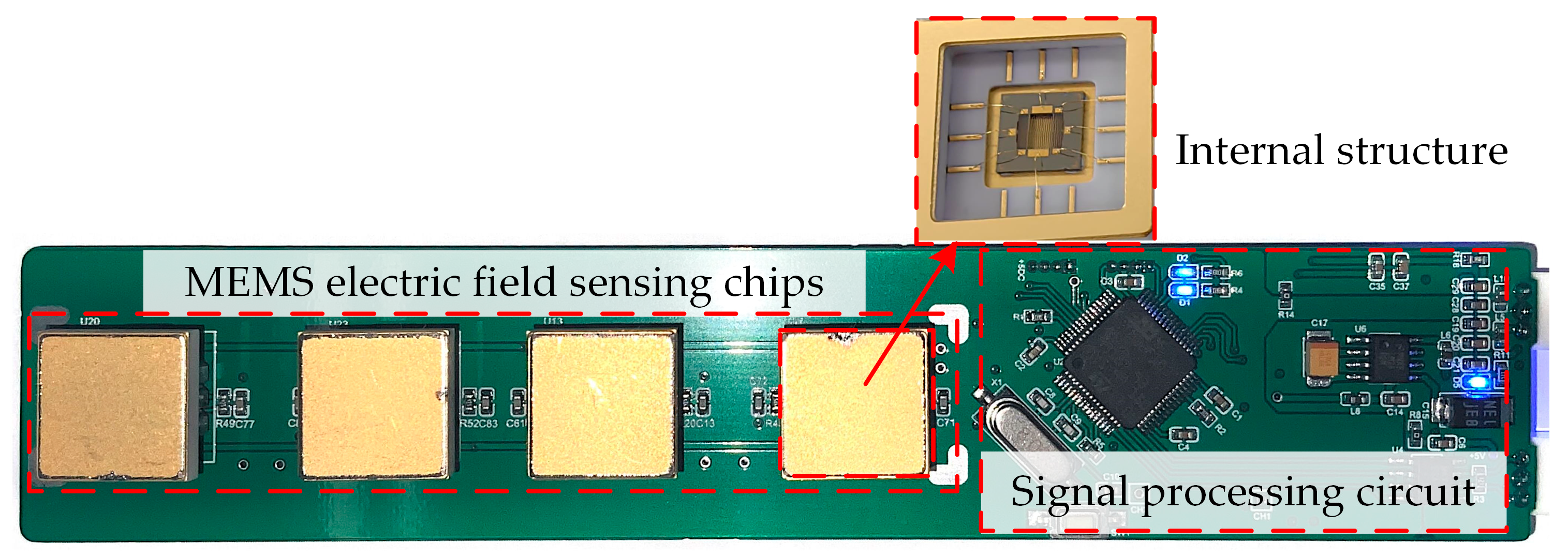
4.2. Sensor Prototype and Calibration System
4.3. Decoupling Calibration Procedure
5. Experimental Validation and Results
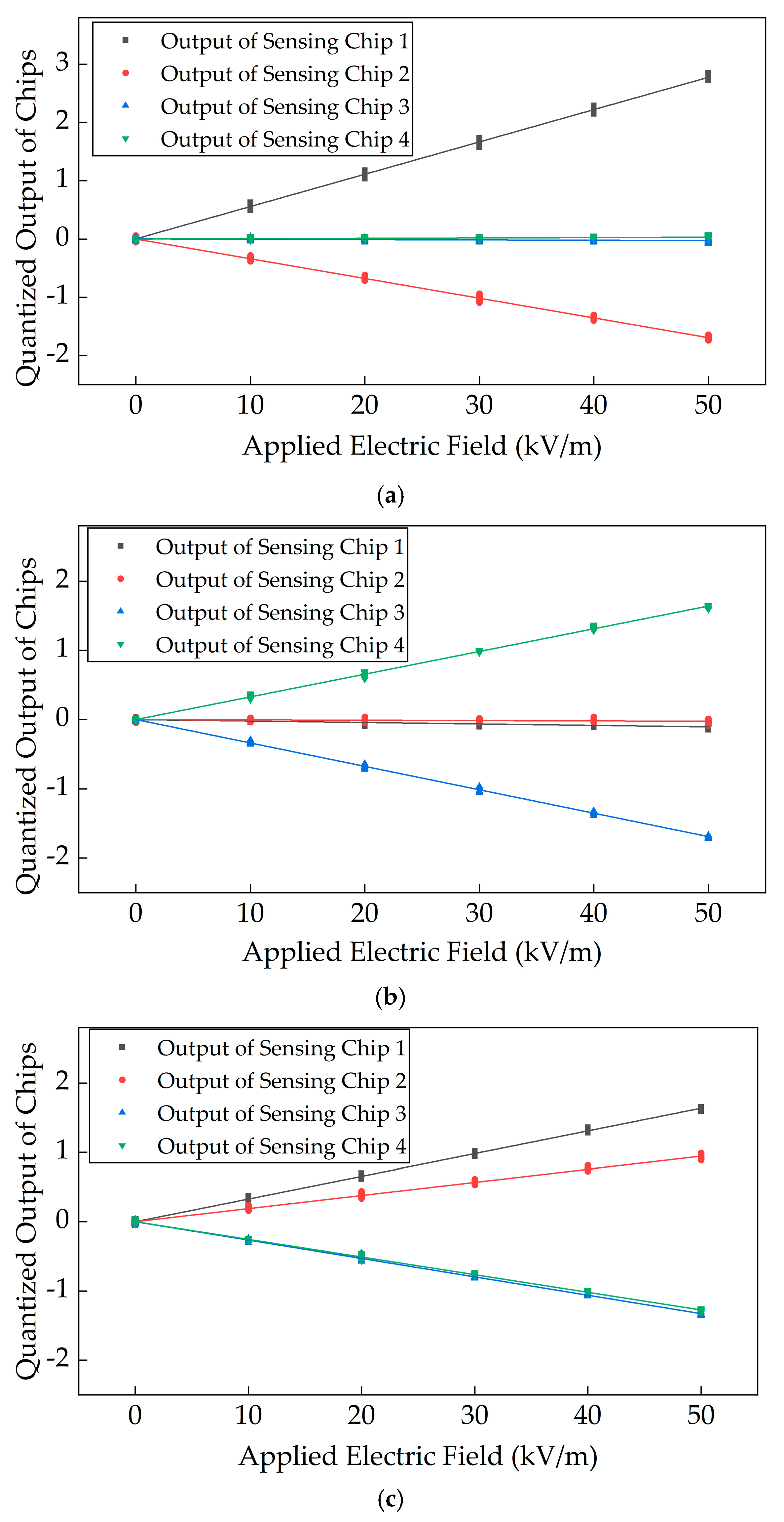
5.1. Calibration Results
5.2. Three-Dimensional Electric Field Testing
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montanya, J.; Bergas, J.; Hermoso, B. Electric field measurements at ground level as a basis for lightning hazard warning. J. Electrostat. 2004, 60, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harridon, G.; Giles, R. A balloon-carried electrometer for high-resolution atmospheric electric field measurements in clouds. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 2738–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F. Lightning Strike Incidents on Aircraft and Launch Regulations in U.S. Aerospace Activities. Aerosp. China 1993, 1, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, F. Lightning Protection System at Kennedy Space Center. World Missiles Spacecr. 1991, 3, 43–46. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.K.; Qie, X.S.; Zhang, T.L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.F.; Wang, Y.; She, Y.; Sun, B.L.; Wang, H.B. Detection of Electric Fields in a Single Thunderstorm Cloud and Its Internal Charge Structure. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2009, 54, 3532–3536. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, J.T.; Zhang, X.X.; He, F.; Huang, C. State studios of Earth’s plasmasphere. Rev. Geophys. Planet. Phys. 2023, 54, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubb, J. The measurement of atmospheric electric fields using pole-mounted electrostatic fieldmeters. J. Electrostat. 2014, 72, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranski, P.; Loboda, M.; Wiszniowski, J.; Morawski, M. Evaluation of multiple ground flash charge structure from electric field measurements using the local lightning detection network in the region of Warsaw. Atmos. Res. 2012, 117, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, M.G.; Stewart, M.F.; Podgorny, S.J.; Christian, H.J.; Mach, D.M.; Blakeslee, R.J.; Bailey, J.C.; Daskar, D. A low-noise, microprocessor-controlled, internally digitizing rotating-vane electric field mill for airborne platforms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, Q.; Xia, S.; Zheng, F.; Chen, S. Design and measurement of a miniaturized three-dimensional electric field sensor. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2007, 29, 1002–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Yang, P.; Chu, Z.; Peng, C.; Liu, Y.; Wu, S. Toward atmospheric electricity research: A low-cost, highly sensitive and robust balloon-borne electric field sounding sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13405–13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, M.D.; Koshak, J.W. General matrix inversion technique for the calibration of electric field sensor arrays on aircraft platforms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Xia, S. Spatial three-dimensional electric field measuring system based on L-band meteorological radar. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2012, 34, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yuan, H.; Song, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Lin, L. Model, design, and testing of field mill sensors for measuring electric fields under high-voltage direct-current power lines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, B.Y.; Peng, C.R.; Ren, R.; Chu, Z.Z.; Zhang, Z.W.; Lei, H.C.; Xia, S.H. MEMS-based three-dimensional electric field sensor with low cross-axis coupling interference. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2018, 40, 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xing, X.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; Xia, S. A single-chip 3-D electric field microsensor with piezoelectric excitation. IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 2023, 70, 4359–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Peng, C.; Ling, B.; Zheng, F.; Chen, B.; Xia, S. The decoupling calibration method based on genetic algorithm of three-dimensional electric field sensor. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2017, 39, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Cui, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Decoupling calibration method of 3D electric field sensor based on differential evolution algorithm. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2021, 36, 3993–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Z. A decoupled calibration method based on the multi-output support vector regression algorithm for three-dimensional electric-field sensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wu, Y.; He, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, R. Nonlinear decoupling of spatially hierarchically structured FBG 3D vibration acceleration sensor based on WOA-ELM. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2024, 45, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ding, Z.; Sun, Y. Comparison of decoupling algorithms for six-dimensional force sensors based on least squares method and RBF neural network. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Computer Applications (ICIPCA), Shenyang, China, 21–23 June 2024; pp. 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Meng, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, Z. Decoupling method for six-axis force sensors based on WOA-ELM. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Symposium on Robotics & Intelligent Manufacturing Technology (ISRIMT), Changzhou, China, 15–17 May 2024; pp. 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Peng, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Fang, D.; Xia, S. A high sensitivity SOI electric-field sensor with novel comb-shaped mi-croelectrodes. In Proceedings of the 2011 16th International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference (TRANS-DUCERS), Beijing, China, 5–9 June 2011; pp. 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Angle | Applied Electric Field (kV/m) | Chip 1 Output | Chip 2 Output | Chip 3 Output | Chip 4 Output | Sensitivity Matrix Inversion-Based Decoupling Method | Method Proposed in This Paper | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic Electric Field (kV/m) | Relative Error (%) | Synthetic Electric Field (kV/m) | Relative Error (%) | ||||||
| Angle 1 | 30 | −1.5605 | 0.8540 | 0.5017 | −0.3904 | 29.9529 | −0.1569 | 30.0340 | 0.1133 |
| 40 | −2.0517 | 1.2246 | 0.7795 | −0.4241 | 40.1963 | 0.4906 | 39.8480 | −0.3800 | |
| 50 | −2.5862 | 1.5655 | 0.9748 | −0.5436 | 50.8974 | 1.7947 | 50.4352 | 0.8704 | |
| Angle 2 | 30 | −0.8947 | 0.5504 | −0.8389 | 0.8597 | 30.0686 | 0.2287 | 30.0240 | 0.0799 |
| 40 | −1.2016 | 0.7139 | −1.1234 | 1.1353 | 39.9884 | −0.0290 | 39.9490 | −0.1274 | |
| 50 | −1.5097 | 0.8879 | −1.4108 | 1.4097 | 50.0004 | 0.0007 | 49.9617 | −0.0766 | |
| Angle 3 | 20 | −0.7919 | −0.0565 | 0.7871 | −0.1510 | 20.1022 | 0.5108 | 20.0342 | 0.1709 |
| 30 | −1.1828 | −0.0734 | 1.1926 | −0.2354 | 30.3099 | 1.0331 | 30.2222 | 0.7405 | |
| Angle 4 | 20 | 0.7758 | −0.5570 | −0.1766 | 0.5028 | 19.3720 | −3.1398 | 19.8506 | −0.7469 |
| Angle 5 | 30 | −1.1879 | 0.6568 | 0.7300 | −0.7096 | 29.8631 | −0.4563 | 30.0415 | 0.1382 |
| 40 | −1.5951 | 0.8264 | 0.8914 | −0.9782 | 39.1579 | −2.1052 | 39.6570 | −0.8575 | |
| 50 | −1.9939 | 1.0417 | 1.1603 | −1.1997 | 49.1539 | −1.6921 | 49.6567 | −0.6866 | |
| Angle 6 | 30 | −1.3949 | 0.0148 | 1.1200 | −0.0827 | 30.1511 | 0.5035 | 30.0829 | 0.2763 |
| 40 | −1.8419 | −0.0434 | 1.4948 | −0.0956 | 40.2161 | 0.5403 | 40.0813 | 0.2034 | |
| 50 | −2.3049 | −0.0276 | 1.8528 | −0.1330 | 49.9997 | −0.0006 | 49.8436 | −0.3128 | |
| Angle 7 | 30 | 1.2808 | −0.6690 | −0.6763 | 0.6413 | 29.4107 | −1.9642 | 29.6403 | −1.1991 |
| 40 | 1.7120 | −0.9192 | −0.8863 | 0.8711 | 39.5225 | −1.1937 | 39.8358 | −0.4106 | |
| 50 | 2.1928 | −1.0571 | −1.0370 | 1.1394 | 49.0831 | −1.8337 | 49.8662 | −0.2676 | |
| Error (%) | Sensitivity Matrix Inversion-Based Decoupling Method | Genetic Algorithm-Based Decoupling Method [20] | Method Proposed in This Paper |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Relative Error | 3.14 | 1.90 | 1.20 |
| Average Relative Error | 0.98 | 0.59 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Liu, W.; Luo, J.; Wu, Z.; Ren, R.; Lv, Y. Spatial Decoupling Method for a Novel Dual-Orthogonal Induction MEMS Three-Dimensional Electric Field Sensor. Micromachines 2025, 16, 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040381
Li J, Wang J, Peng C, Liu W, Luo J, Wu Z, Ren R, Lv Y. Spatial Decoupling Method for a Novel Dual-Orthogonal Induction MEMS Three-Dimensional Electric Field Sensor. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):381. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040381
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiacheng, Junpeng Wang, Chunrong Peng, Wenjie Liu, Jiahao Luo, Zhengwei Wu, Ren Ren, and Yao Lv. 2025. "Spatial Decoupling Method for a Novel Dual-Orthogonal Induction MEMS Three-Dimensional Electric Field Sensor" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040381
APA StyleLi, J., Wang, J., Peng, C., Liu, W., Luo, J., Wu, Z., Ren, R., & Lv, Y. (2025). Spatial Decoupling Method for a Novel Dual-Orthogonal Induction MEMS Three-Dimensional Electric Field Sensor. Micromachines, 16(4), 381. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040381






