Posture Detection of Dual-Hemisphere Capsule Robot Based on Magnetic Tracking Effects and ORB-AEKF Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
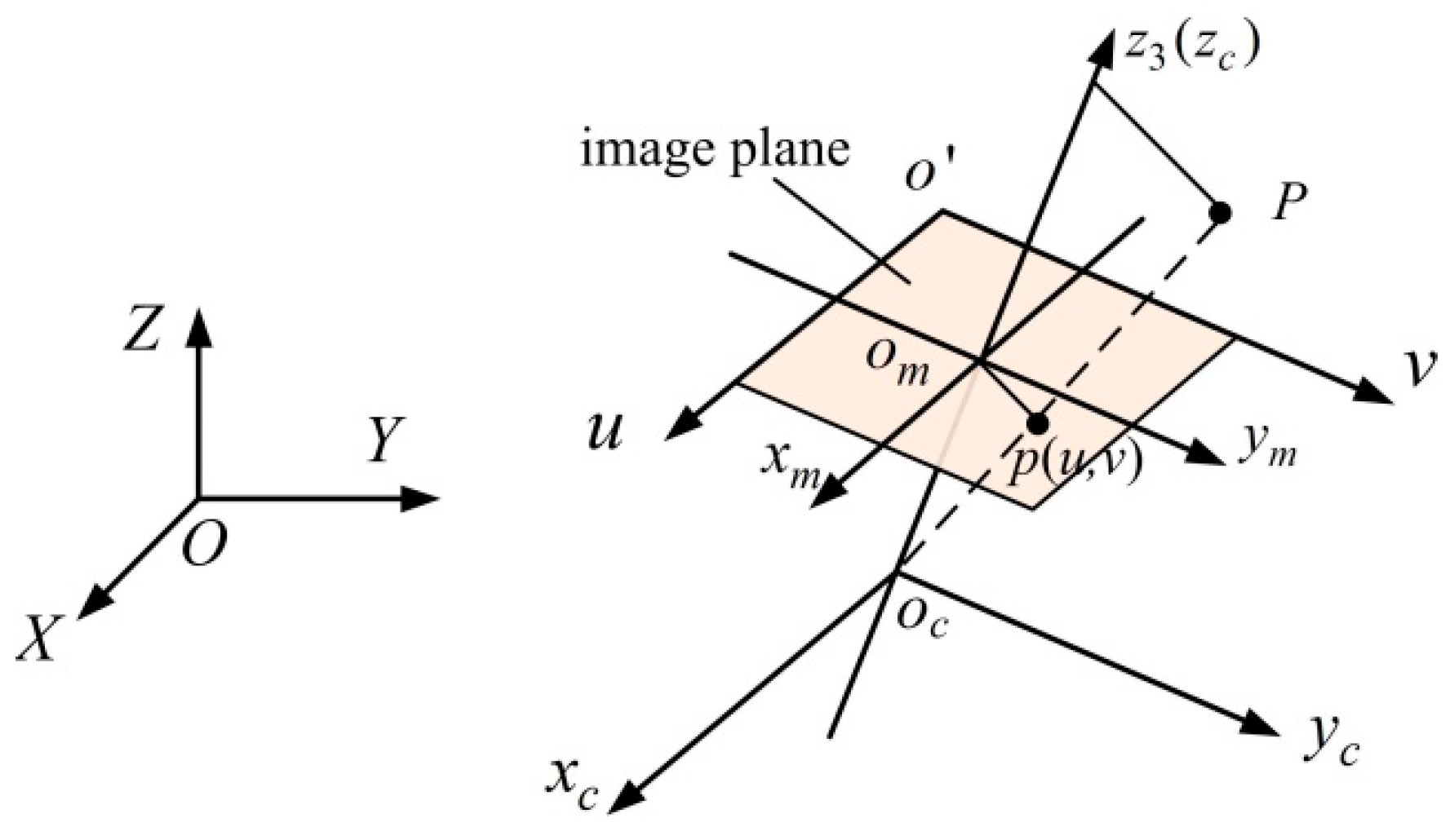
2. Posture Detection Method Overview
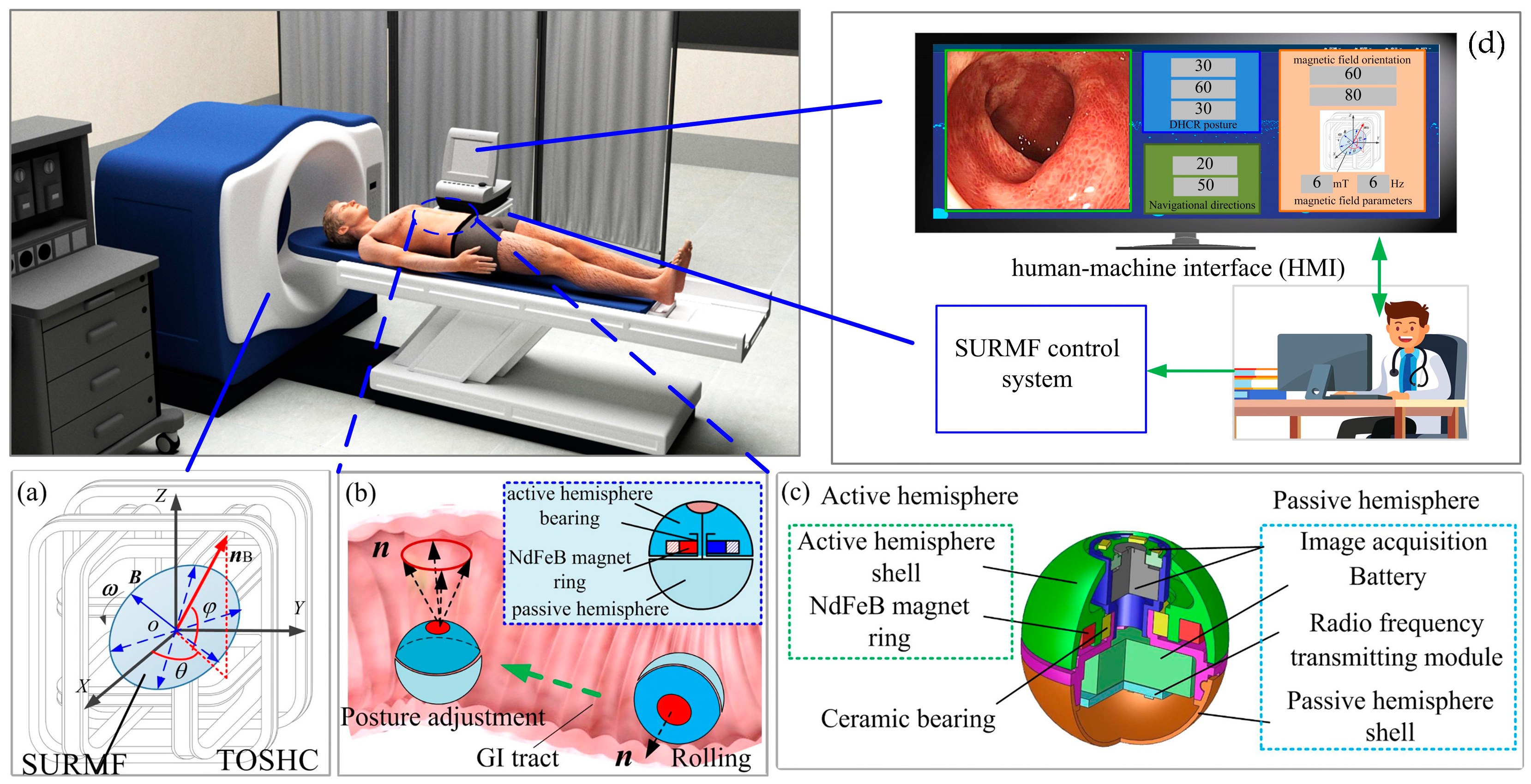
2.1. Magnetic-Actuated DHCR Diagnostic System
2.2. Posture Detection Method
3. Tracking Effects Mechanism and Motion Model Establishment
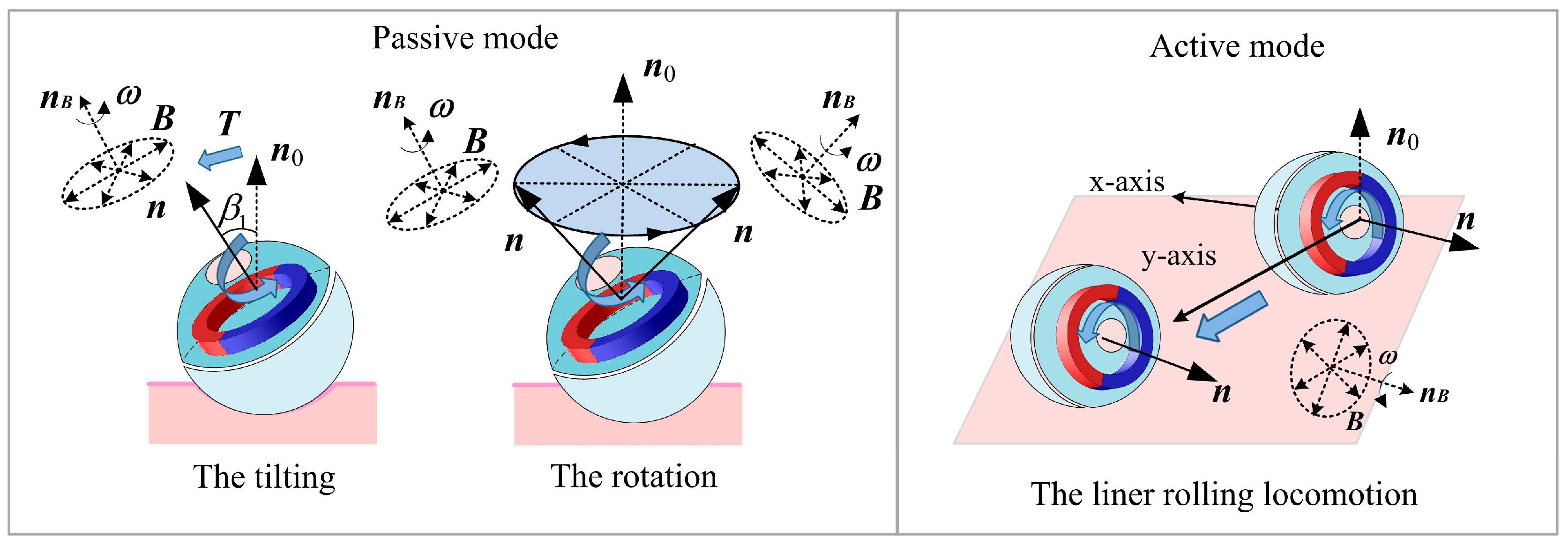
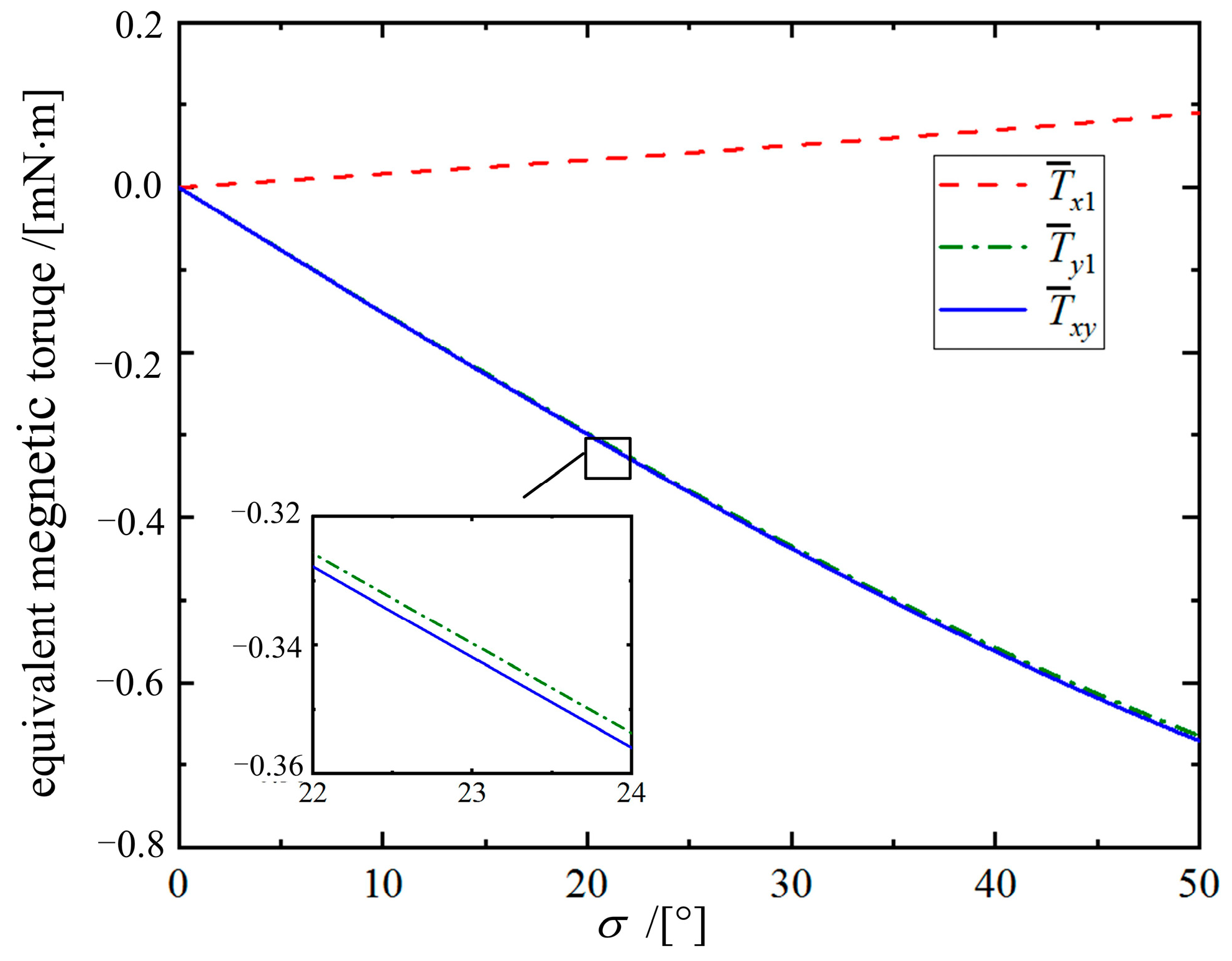
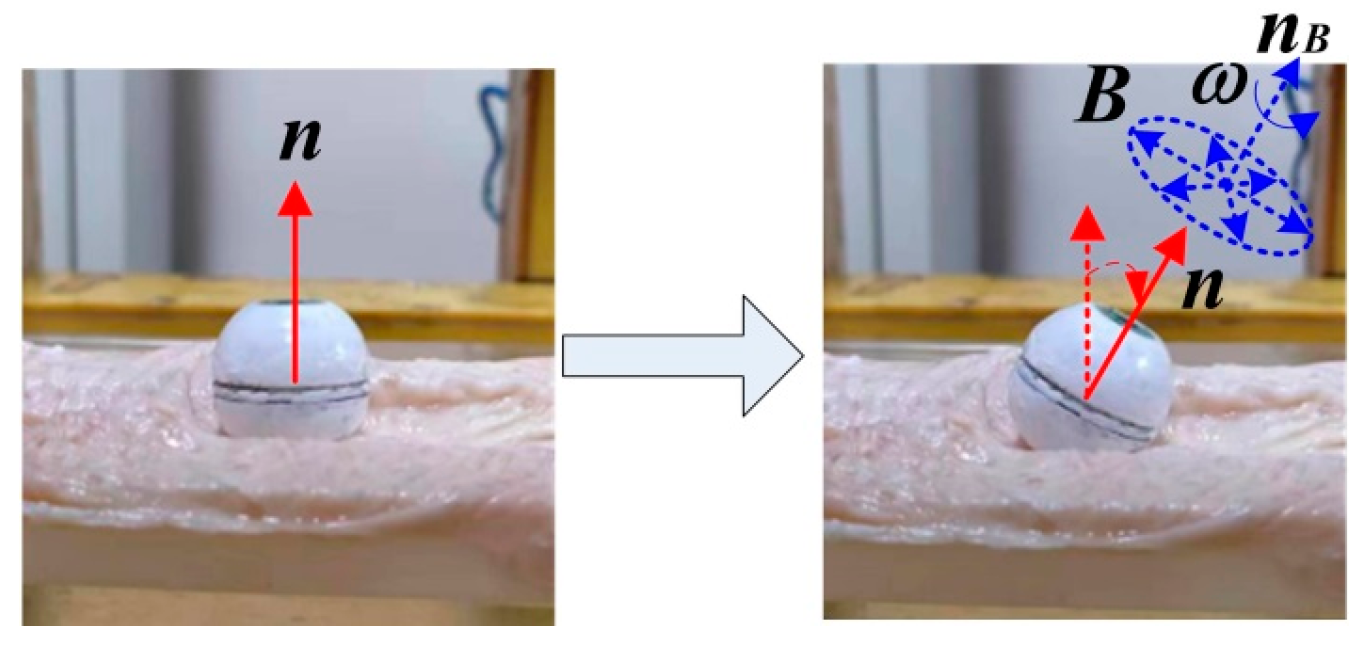
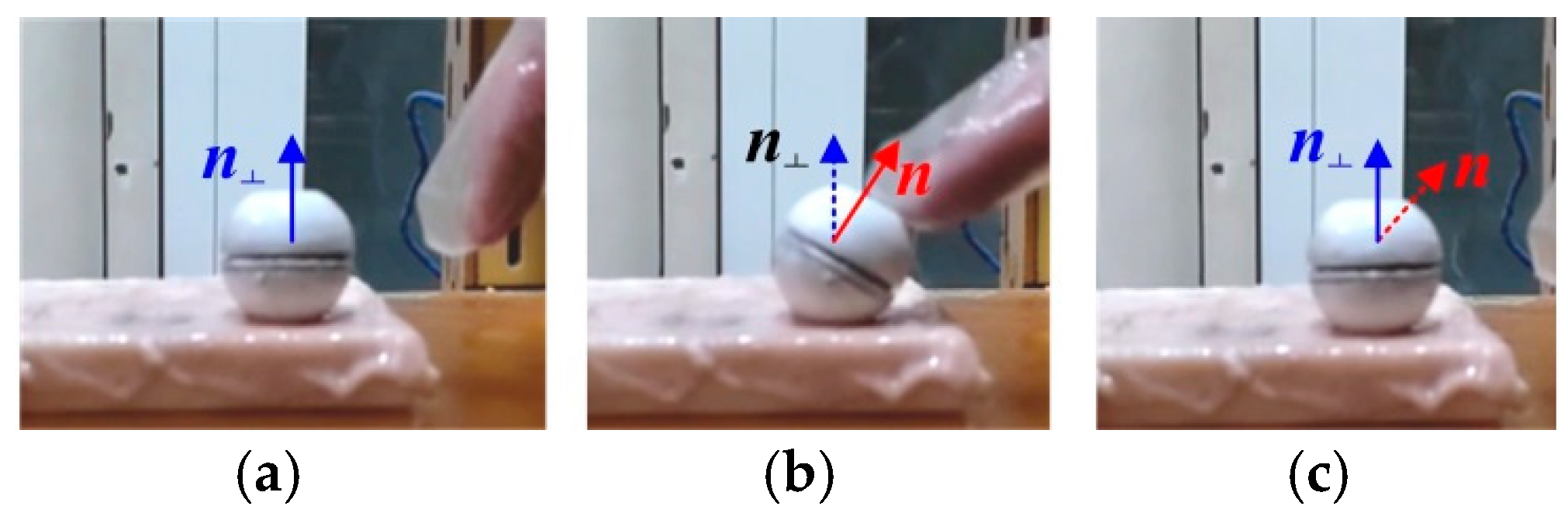
3.1. Tracking Effects Analysis
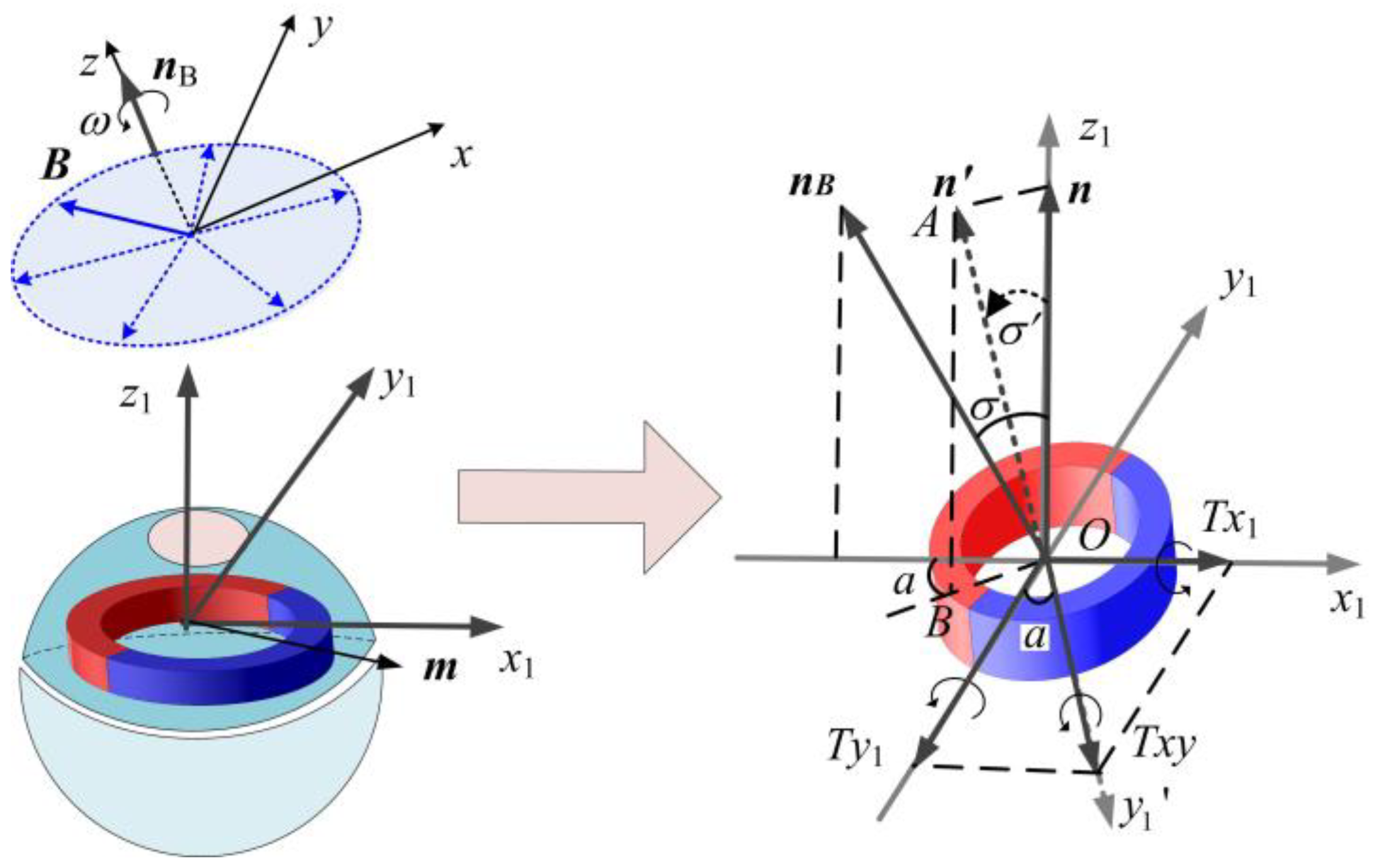
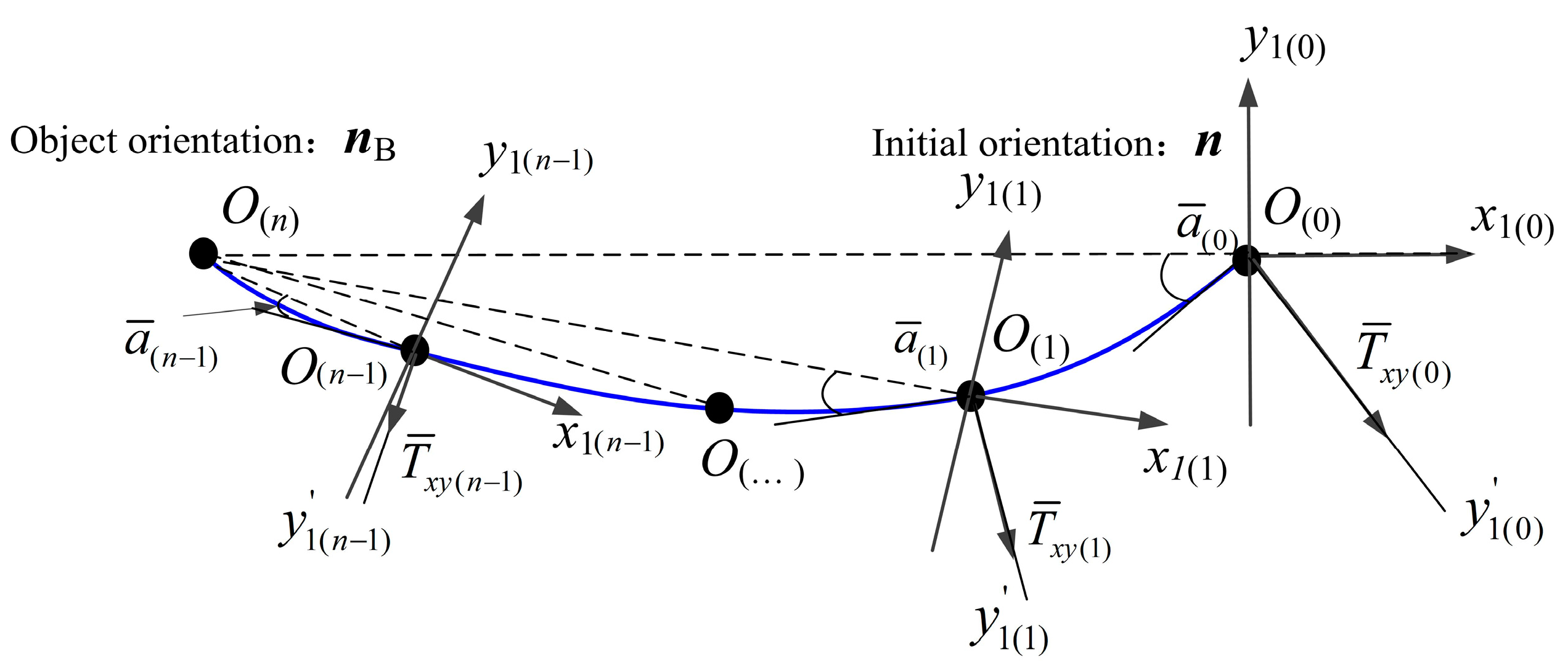
3.2. Motion Model Establishment
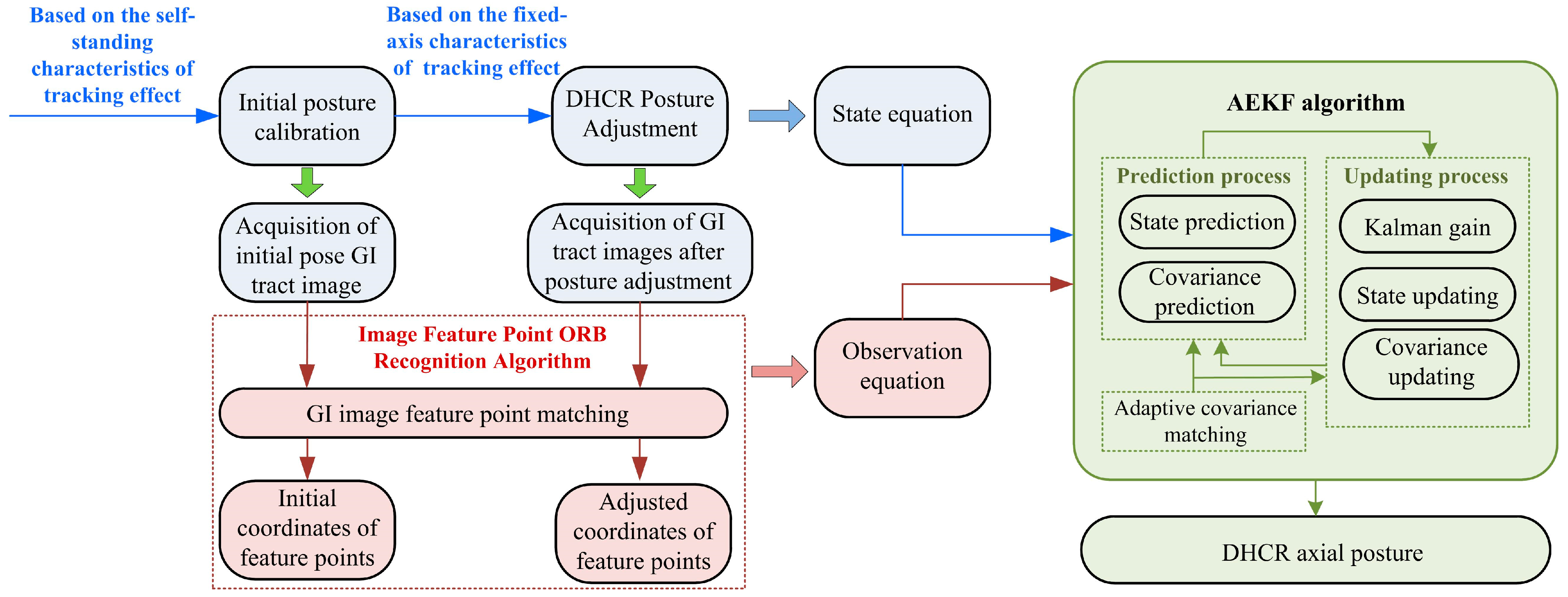
4. Posture Detector Design Based on ORB-AEKF Algorithm
4.1. State Equation
4.2. Observation Equation
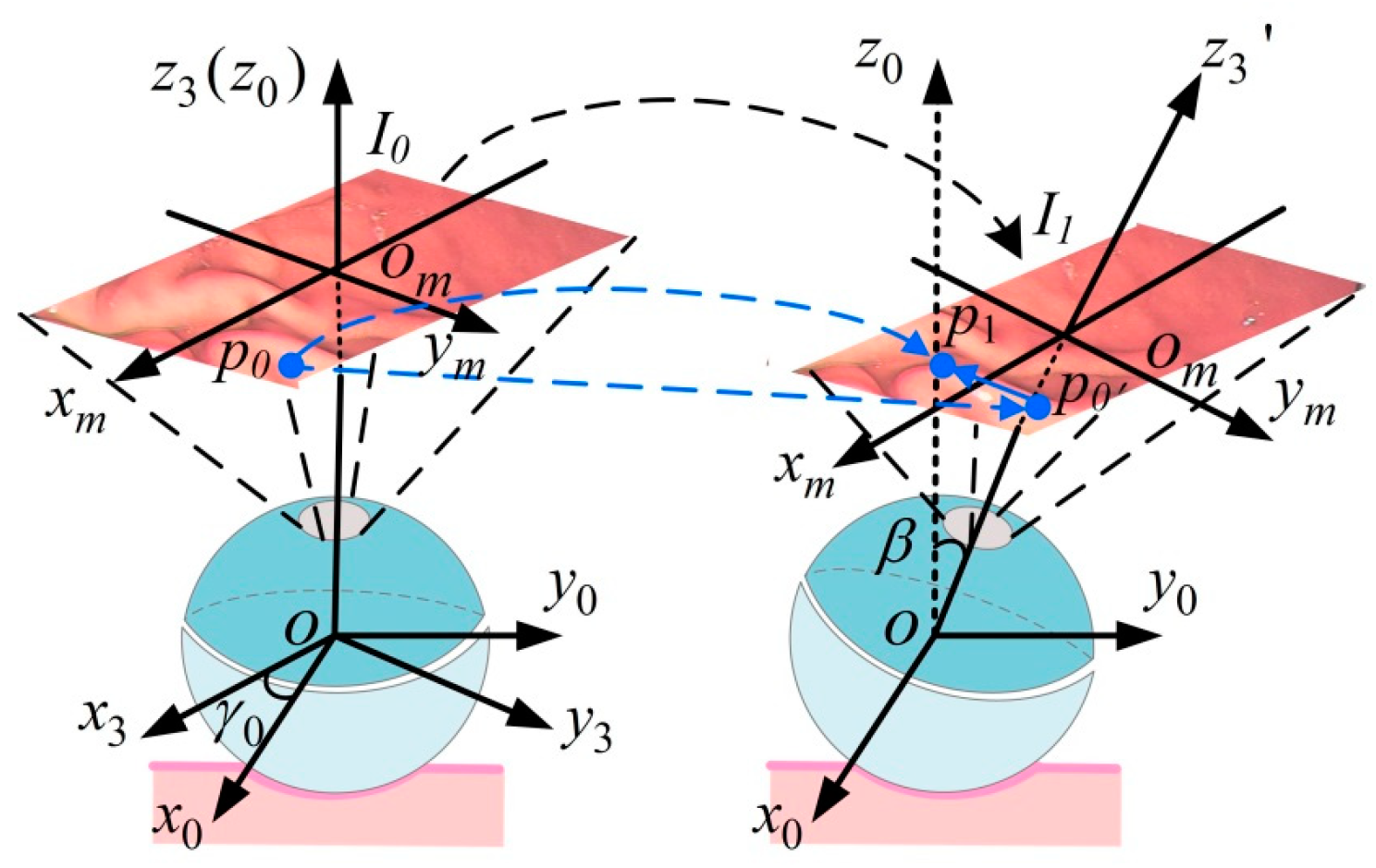
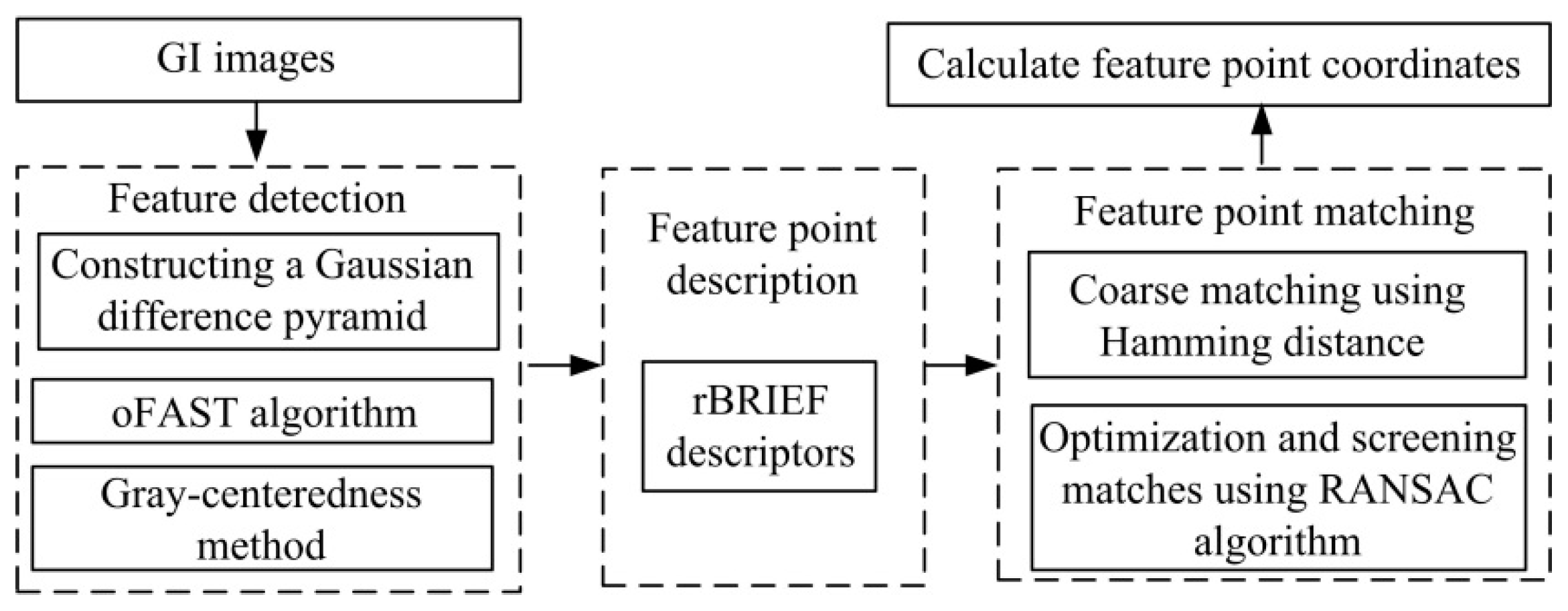
4.2.1. GI Image Feature Point Recognition and Matching Based on the ORB Algorithm
4.2.2. Observation Equation Establishment
4.3. AEKF Algorithm
5. Experiment
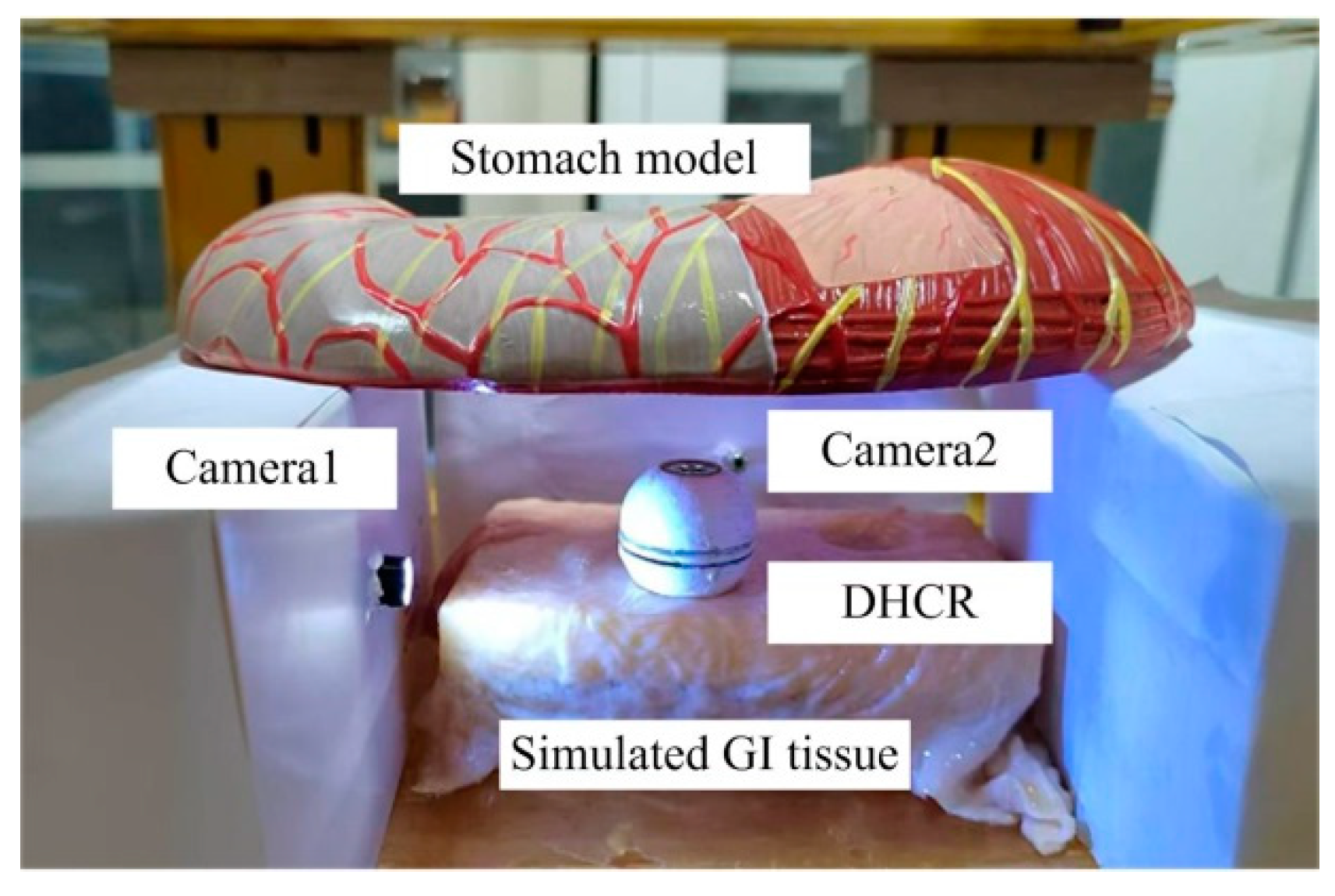
5.1. Experimental Platform
5.2. Tracking Effects Verification Experiments
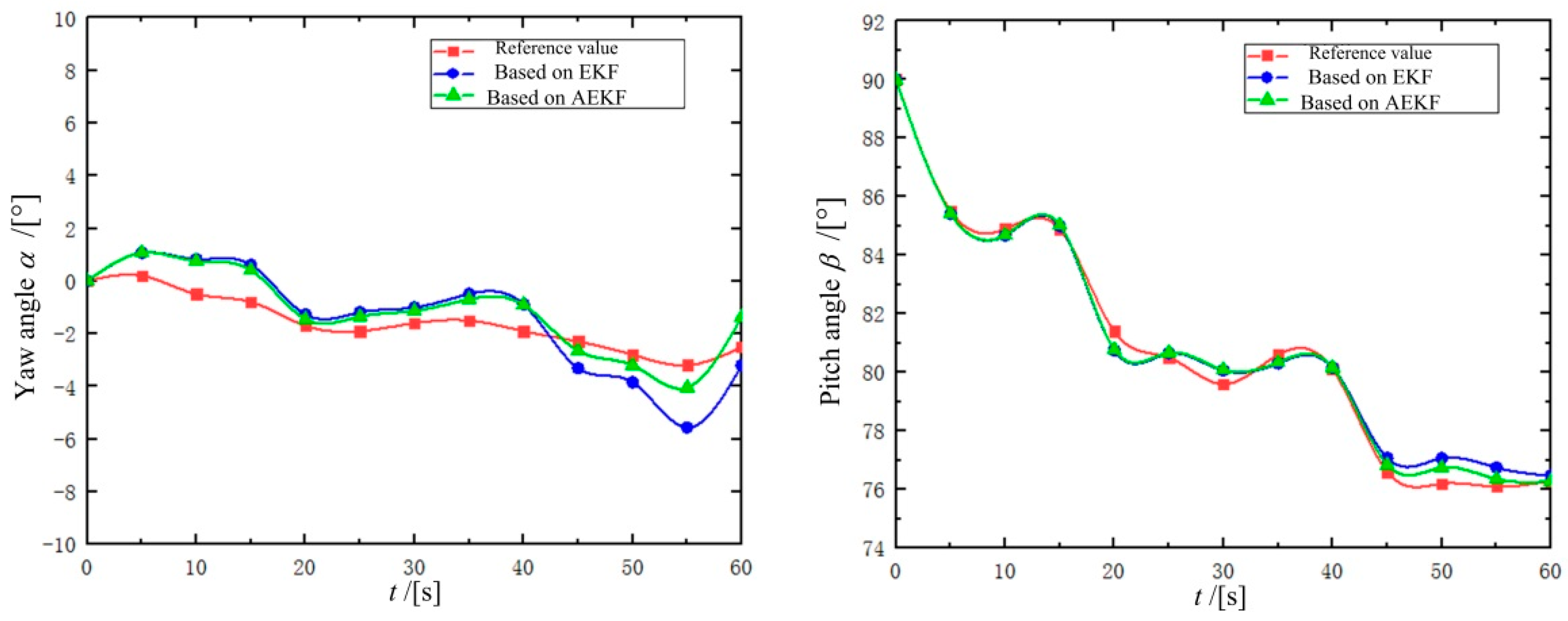
5.3. ORB-AEKF-Based Posture Detection Verification Experiments
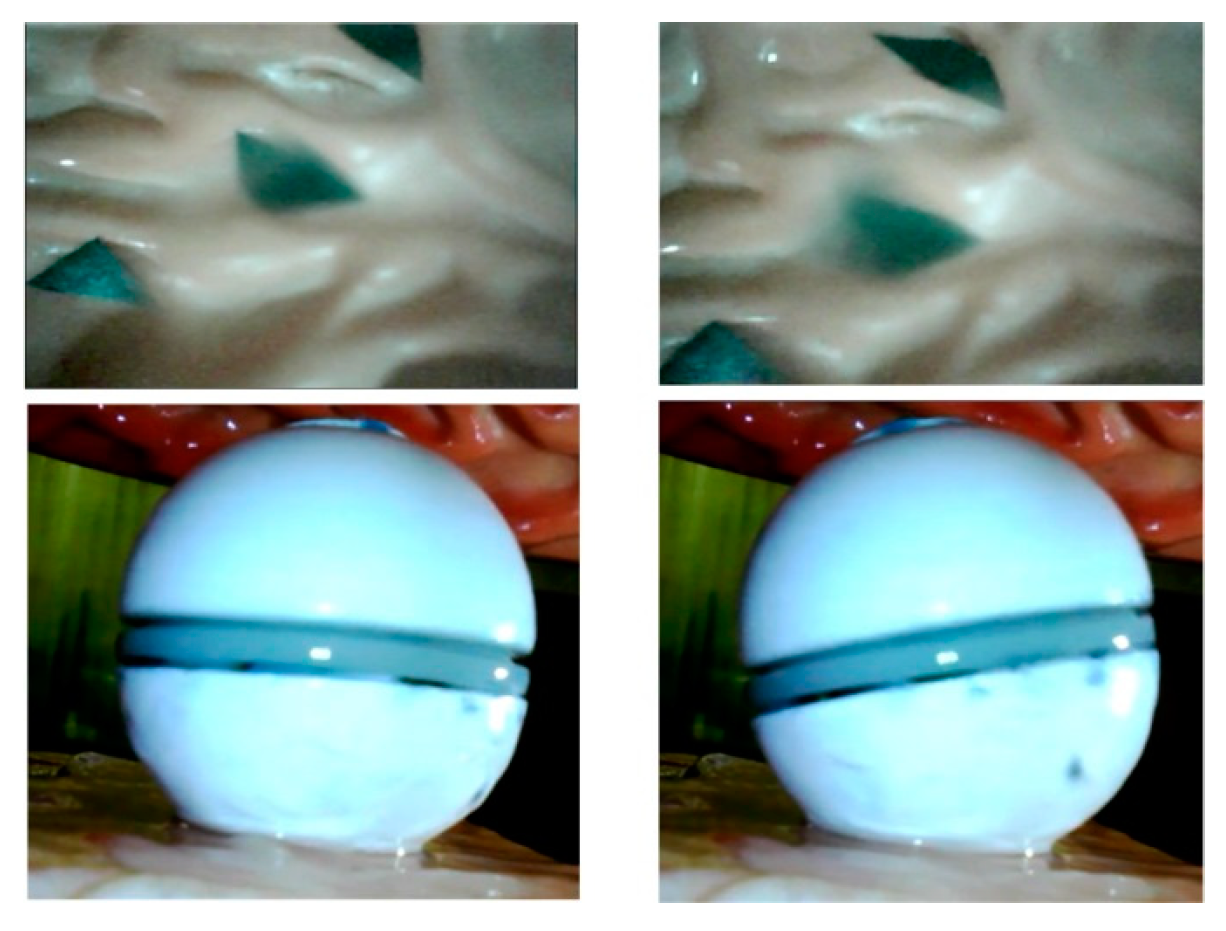
5.3.1. Simulated GI Condition Experiments
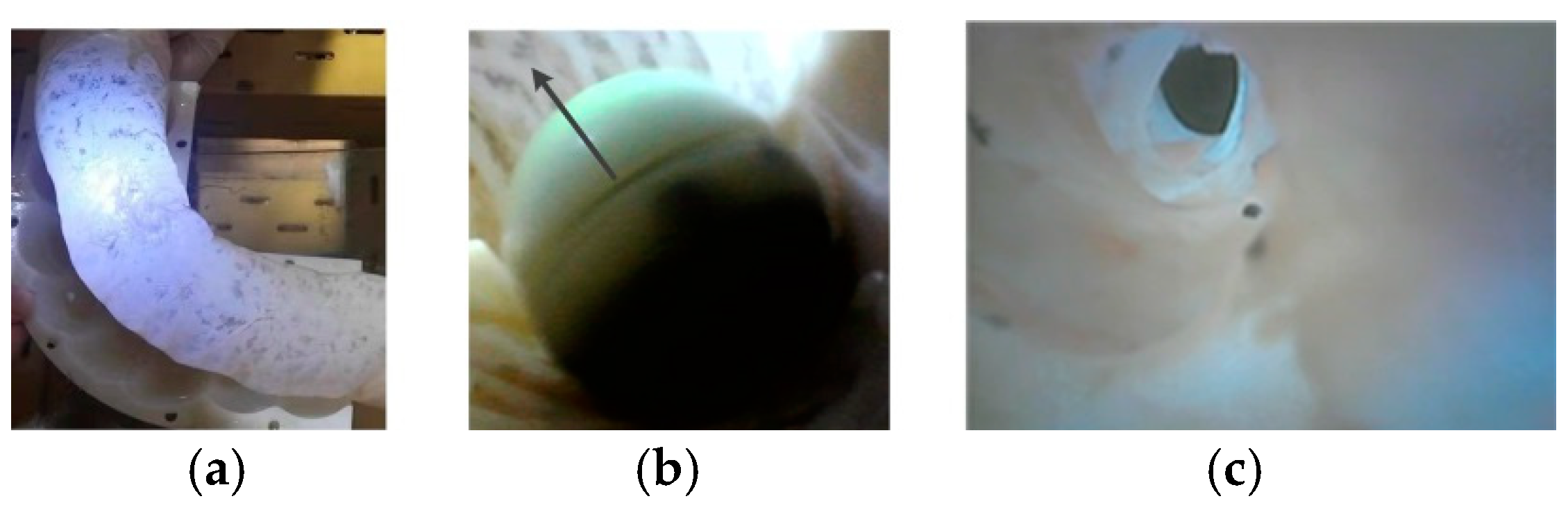
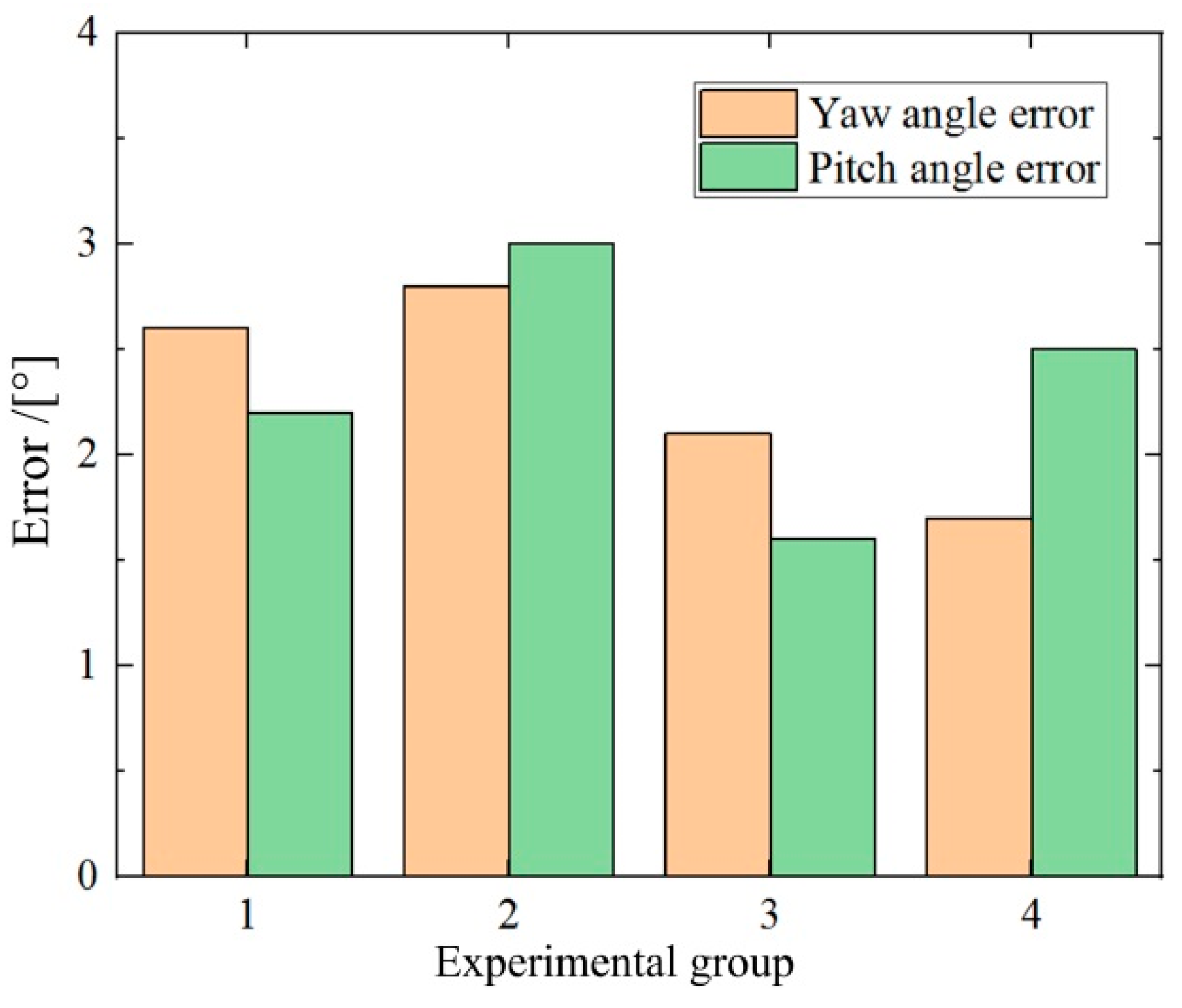
5.3.2. Posture Detection Application to the Navigation in Porcine Colon
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Clarification |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| MACR | Magnetic-actuated capsule robot |
| SURMF | Spatial universal rotating magnetic field |
| EKF | Extended Kalman filtering |
| HMI | Human–machine interaction |
| DHCR | Dual hemisphere capsule robot |
| ORB | Oriented FAST and rotated BRIEF |
| TOSHC | Three-axis orthogonal square Helmholtz coils |
| AEKF | Adaptive extended Kalman filtering |
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
Appendix C.1. Prediction Phase
Appendix C.2. Updating Phase
Appendix C.3. Adaptive Covariance Matching
References
- Hua, D.Z.; Deng, L.; Goldasz, J.; Liu, X.H.; Du, H.P.; Królczyk, G.; Li, W.H.; Li, Z.X. Functional capsule robots: A review of locomotion, pose, medical operation and wireless power transmission reported in 2018–2023. Smart Mater. Struct. 2024, 33, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.X.; Zhang, W.; Gu, J.N.; Xia, L.Y.; Cao, Y.H.; Zhu, X.H.; Wen, H.; Ouyang, S.W.; Liu, R.Q.; Li, J.L.; et al. Magnetically driven capsules with multimodal response and multifunctionality for biomedical applications. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.; Deng, R.Y.; Pan, Y.; Liu, R.J.; Chen, Y.C.; Gong, G.F.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.Y.; Han, D. Robotic wireless capsule endoscopy: Recent advances and upcoming technologies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zeng, D.T.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, B. Magnetic actuation for wireless capsule endoscopy in a large workspace using a mobile-coil system. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.Z.; Liu, X.H.; Królczyk, G.M.; Li, W.H.; Andriukaitis, D.; Goldasz, J.; Li, Z.X. A new industrially magnetic capsule MedRobot integrated with smart motion controller. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 4561–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.G.; Gui, X.R.; Guo, X.D.; Chen, S.M. Simulation and verification of a magnetically controlled system for a wireless capsule robot. J. Med. Devices 2023, 17, 044502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hoang, M.C.; Kim, J.; Park, S. Multiple sampling capsule robot for studying gut microbiome. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2024, 2300625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.Y.; Fan, C.L.; Cai, Z.C.; Wang, L.L. A magnetically capsule robot for biomedical application. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2022, 1, 2233417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.X.; Ji, X.; Yang, H.Y.; Liu, Z.H. Design and implementation of a highly integrated dual hemisphere capsule robot. Biomed. Microdevices 2022, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z. Multimodal conversion of a magnetic navigated dual-hemisphere capsule robot based on self-standing characteristics. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2024, 38, 5087–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhao, Z.H.; Dong, H.; Wang, D.L. Dynamic tracking effect of a magnetic navigated dual hemisphere capsule robot. Robotica 2022, 40, 4586–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, B.; Yu, Y.; Chen, R.Z. Performance evaluation and future prospects of capsule robot localization technology. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2024, 2354239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Zheng, L.; He, J.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Niu, S.; et al. Liquid-metal soft electronics coupled with multi-legged robots for targeted delivery in the gastrointestinal tract. Device 2024, 2, 100181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.K.; Li, Y.; Wei, T.Y.; Lu, D.; Shi, C.Y.; Hu, C.Z. Enhanced localization strategy for magnetic capsule robot using on-board nine-axis imu through incorporation of alternating magnetic field. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 7501512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.X.; Li, K.Y.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Meng, M.Q.H. A novel system for closed-loop simultaneous magnetic actuation and localization of wce based on external sensors and rotating actuation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2021, 18, 1640–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popek, K.M.; Schmid, T.; Abbott, J.J. Six-degree-of-freedom localization of an untethered magnetic capsule using a single rotating magnetic dipole. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 2, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marya, N.; Karellas, A.; Foley, A.; Roychowdhury, A.; Cave, D. Computerized 3-dimensional localization of a video capsule in the abdominal cavity: Validation by digital radiography. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 79, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, H. Image detection method for posture of magnetically controlled dual hemisphere capsule robot. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 48, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.X.; Liu, L.H.; Li, Z.J.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.Y. A magnetically-actuated ultrasound capsule endoscope (musce) for endoluminal imaging in tubular environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 2590–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhao, D.D.; Shao, L.; Zhang, S.Y. Magnetic localization algorithm of capsule robot based on BP neural network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 4002509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.Q. Self-supervised learning of monocular depth and ego-motion estimation for non-rigid scenes in wireless capsule endoscopy videos. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2024, 91, 105978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, A.; Ayyalasomayajula, R.; Hunter, W.; Bharadia, D. P2SLAM: Bearing based WiFi SLAM for indoor robots. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 3326–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroujeni, P.S.; Pishkenari, H.N.; Moradi, H.; Vossoughi, G. Model-aided real-time localization and parameter identification of a magnetic endoscopic capsule using extended kalman filter. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 13667–13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, L. Posture rapid correction for a double hemisphere capsule robot through self-supervised learning. Electron. Meas. Technol. 2023, 46, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wan, G.; Bai, H.Y.; Kong, X.F.; Tang, B.; Wang, F.Y. Real-time video stabilization algorithm based on SuperPoint. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, L.X.; Zheng, W.F.; Yin, L.R.; Hu, R.R.; Yang, B. Endoscope image mosaic based on pyramid ORB. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 71, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tian, Y.; Rong, L.; Cai, Y.L.; Liu, G.Y.; He, Y.; Guo, X.Y. Feasibility and safety of a cable transmission magnetically controlled capsule endoscopy system for examination of the human upper digestive tract. Saudi Med. J. 2024, 45, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y. Kalman Filter for robot vision: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 4409–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.; Chen, Z.W.; Niu, M.; He, Z.J.; Wang, Y.R.; Cui, J. State-of-charge estimation for the lithium-ion battery based on adaptive extended Kalman filter using improved parameter identification. J. Energy Storage 2022, 45, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Brink, J.S. Thermal effects associated with RF exposures in diagnostic MRI: Overview of existing and emerging concepts of protection. Concepts Magn. Reson. Part B 2019, 2019, 9618680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, J.P. Human exposure standards in the frequency range 1 Hz to 100 kHz: The case for adoption of the IEEE standard. Health Phys. 2014, 107, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Liu, Z.H.; Liu, X.; Liu, G.X. Posture dynamic modeling and stability analysis of a magnetic driven dual-spin spherical capsule robot. Micromachines 2021, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Magnetic flux density B0 | 6 mT |
| Angular velocity ω | 16π rad/s |
| Scale factor ϑ | 0.8 |
| Process noise covariance matrix Q | diag(0.001, 0.001, 0.001, 0.001) |
| Observation noise covariance matrix R | [5;5] |
| Detection Method | Statistical Information | Yaw Angle | Pitch Angle |
|---|---|---|---|
| Posture detection based on ORB | error maximum value | 4.87° | 6.62° |
| error mean value | 1.67° | 2.44° | |
| error variance | 1.95 | 3.56 | |
| Posture detection based on ORB-EKF | error maximum value | 4.79° | 1.14° |
| error mean value | 1.53° | 0.40° | |
| error variance | 1.57 | 0.13 | |
| Posture detection based on ORB-AEKF | error maximum value | 1.55° | 0.76° |
| error mean value | 0.76° | 0.31° | |
| error variance | 0.16 | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q. Posture Detection of Dual-Hemisphere Capsule Robot Based on Magnetic Tracking Effects and ORB-AEKF Algorithm. Micromachines 2025, 16, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040485
Liu X, Zhang Y, Wang Q. Posture Detection of Dual-Hemisphere Capsule Robot Based on Magnetic Tracking Effects and ORB-AEKF Algorithm. Micromachines. 2025; 16(4):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040485
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xu, Yongshun Zhang, and Qiancheng Wang. 2025. "Posture Detection of Dual-Hemisphere Capsule Robot Based on Magnetic Tracking Effects and ORB-AEKF Algorithm" Micromachines 16, no. 4: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040485
APA StyleLiu, X., Zhang, Y., & Wang, Q. (2025). Posture Detection of Dual-Hemisphere Capsule Robot Based on Magnetic Tracking Effects and ORB-AEKF Algorithm. Micromachines, 16(4), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16040485






