Sensorless Impedance Control of Micro Finger Using Coprime Factorization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
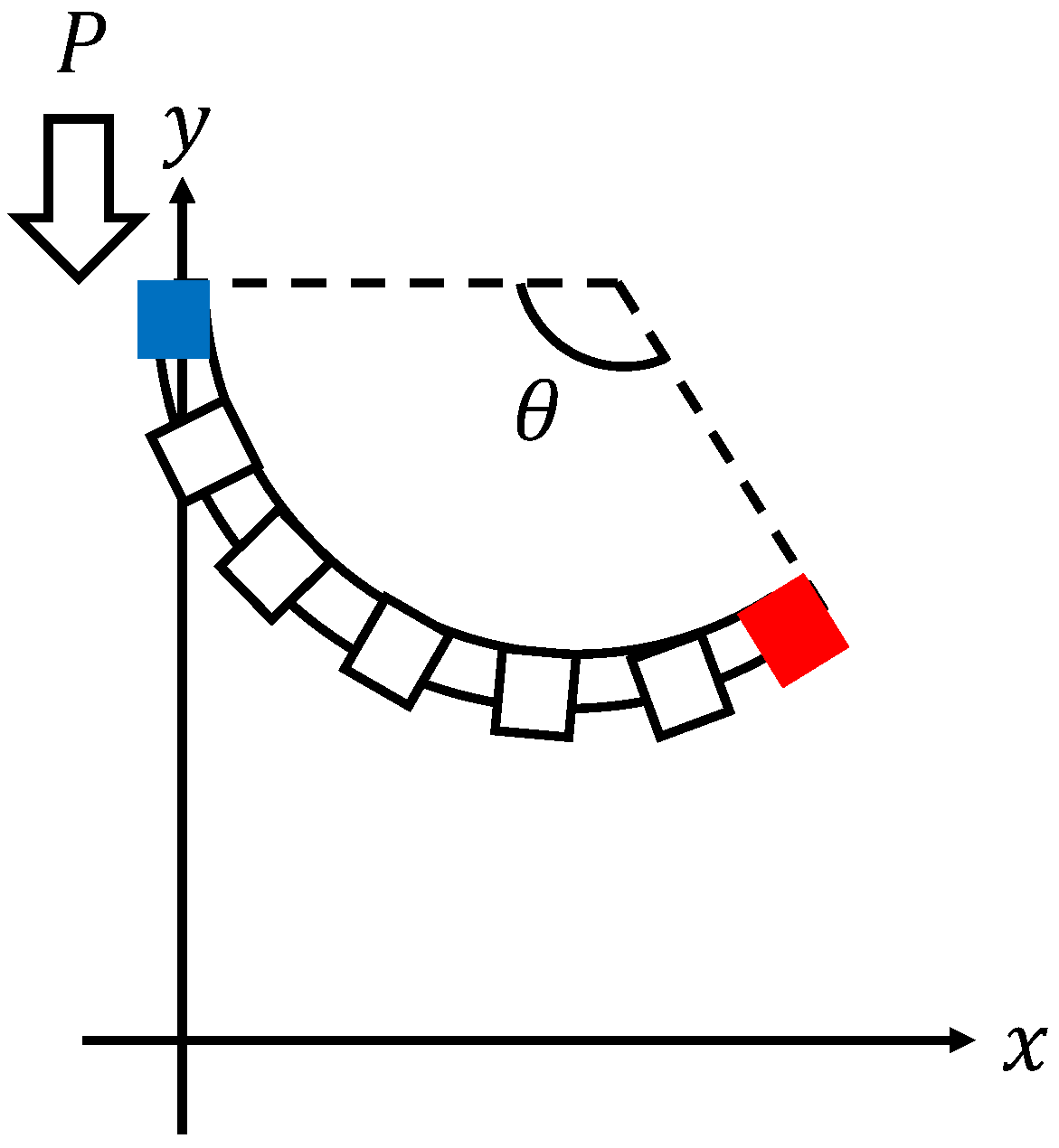
2.1. Micro Finger
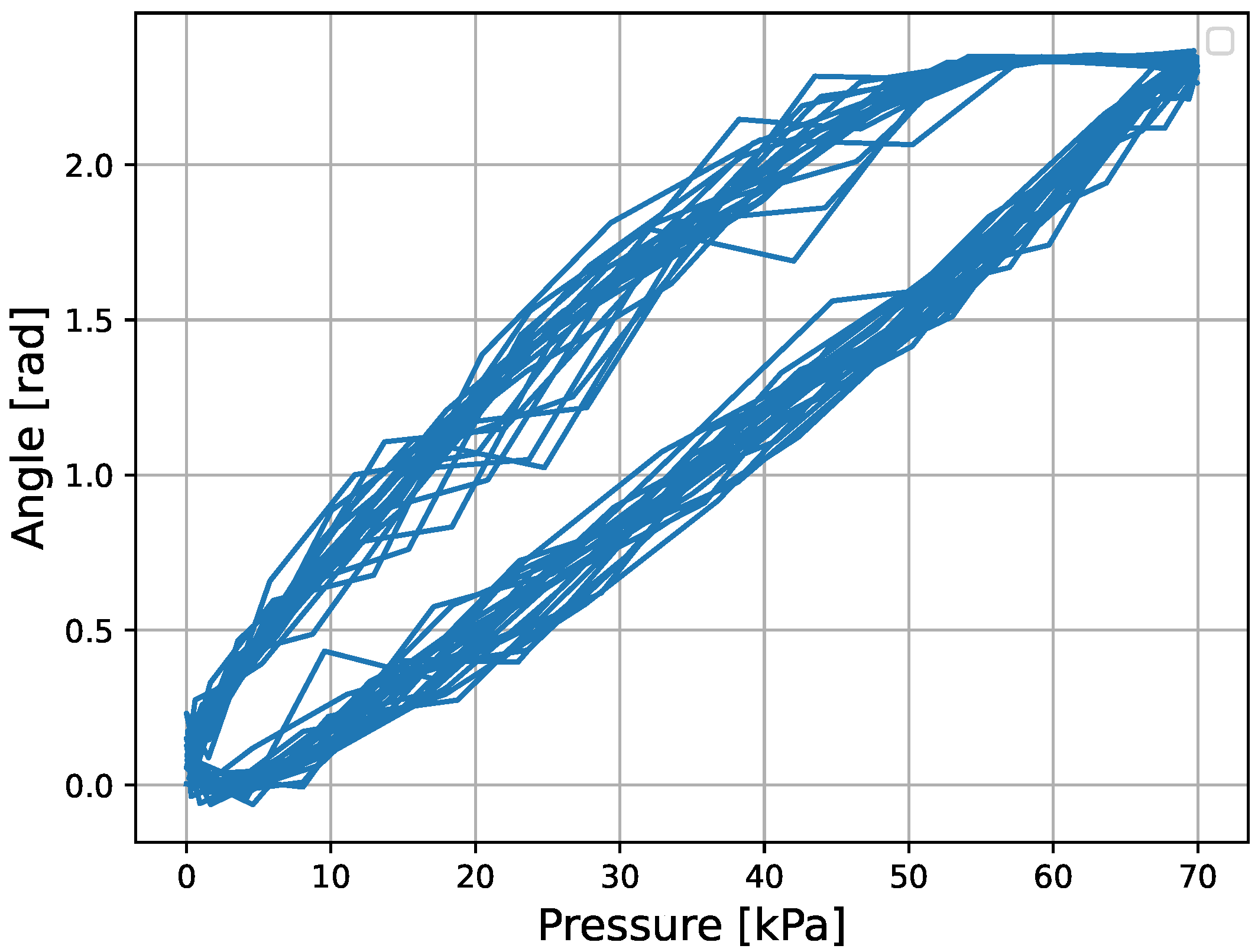
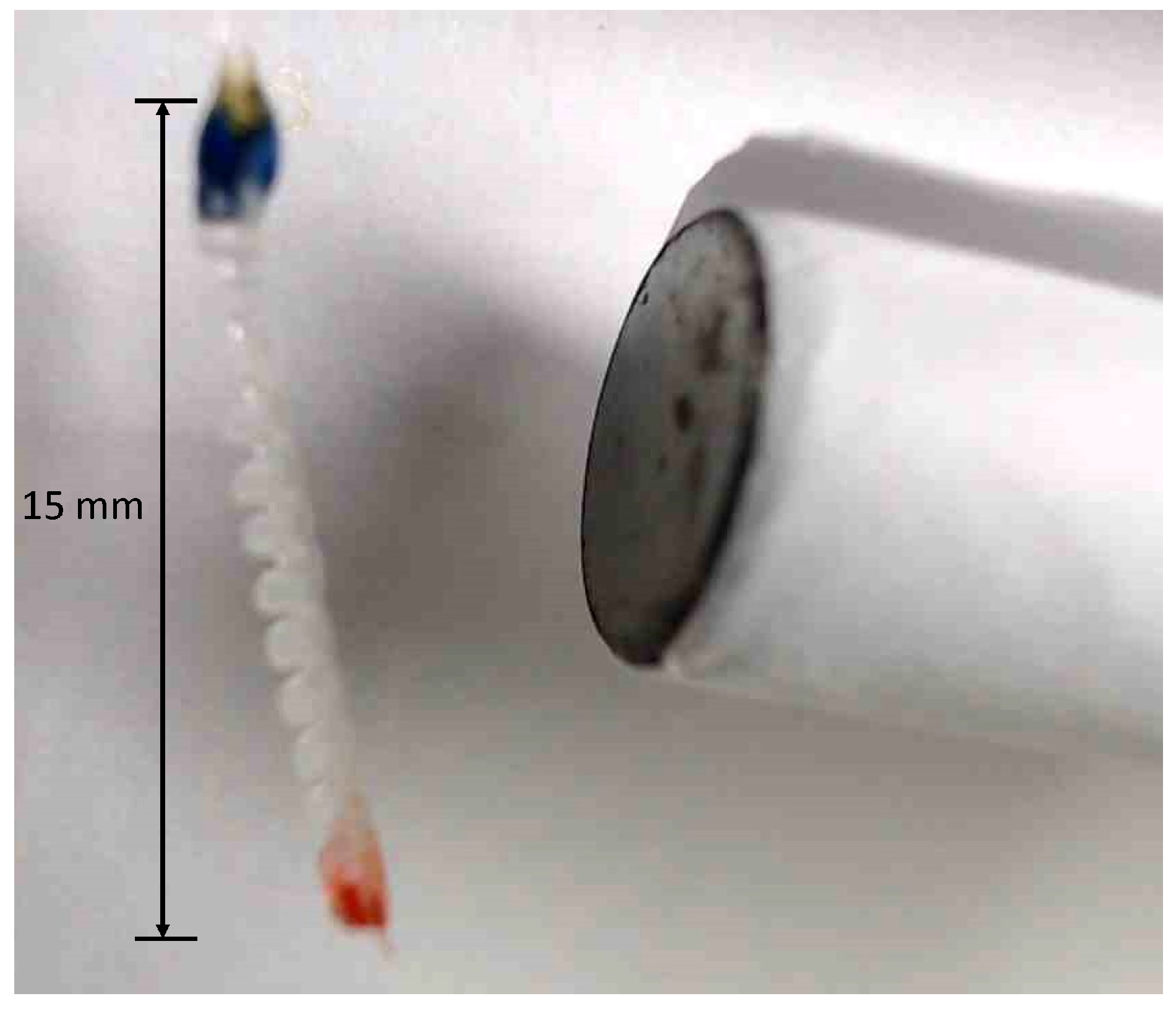
2.1.1. Overview of Micro Finger
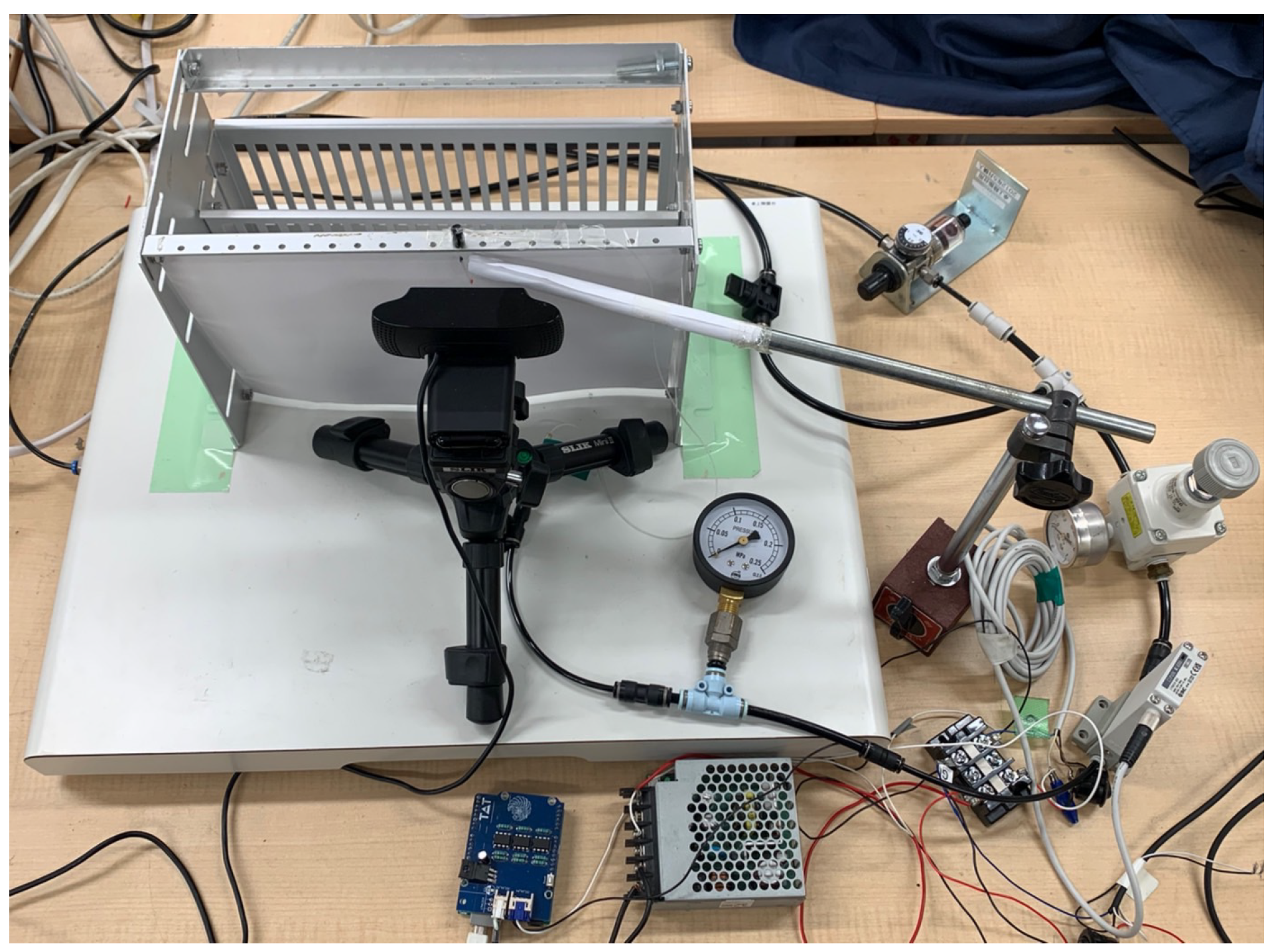
2.1.2. Experimental Equipment
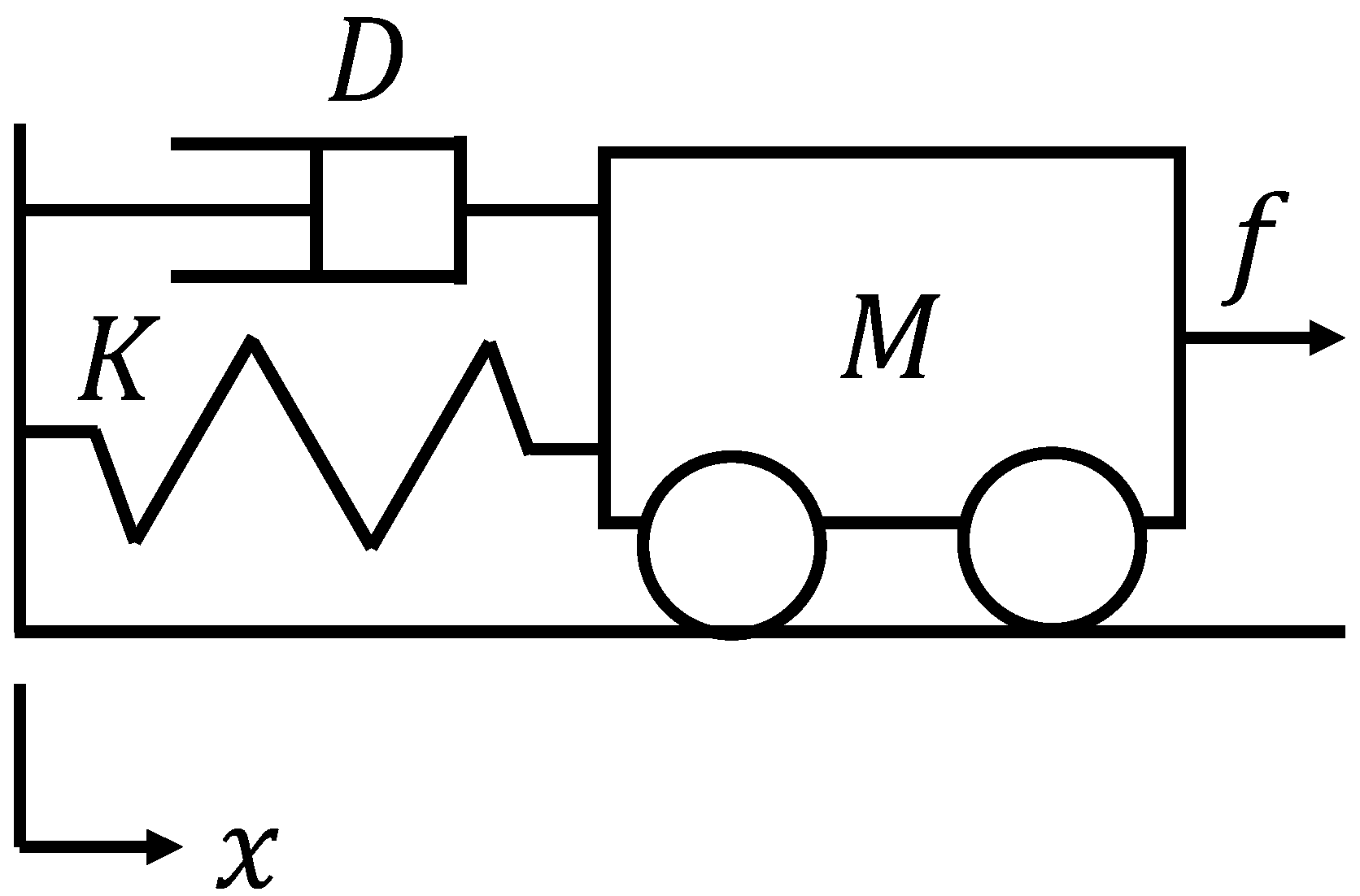
2.2. Impedance Control
3. Problem Setting
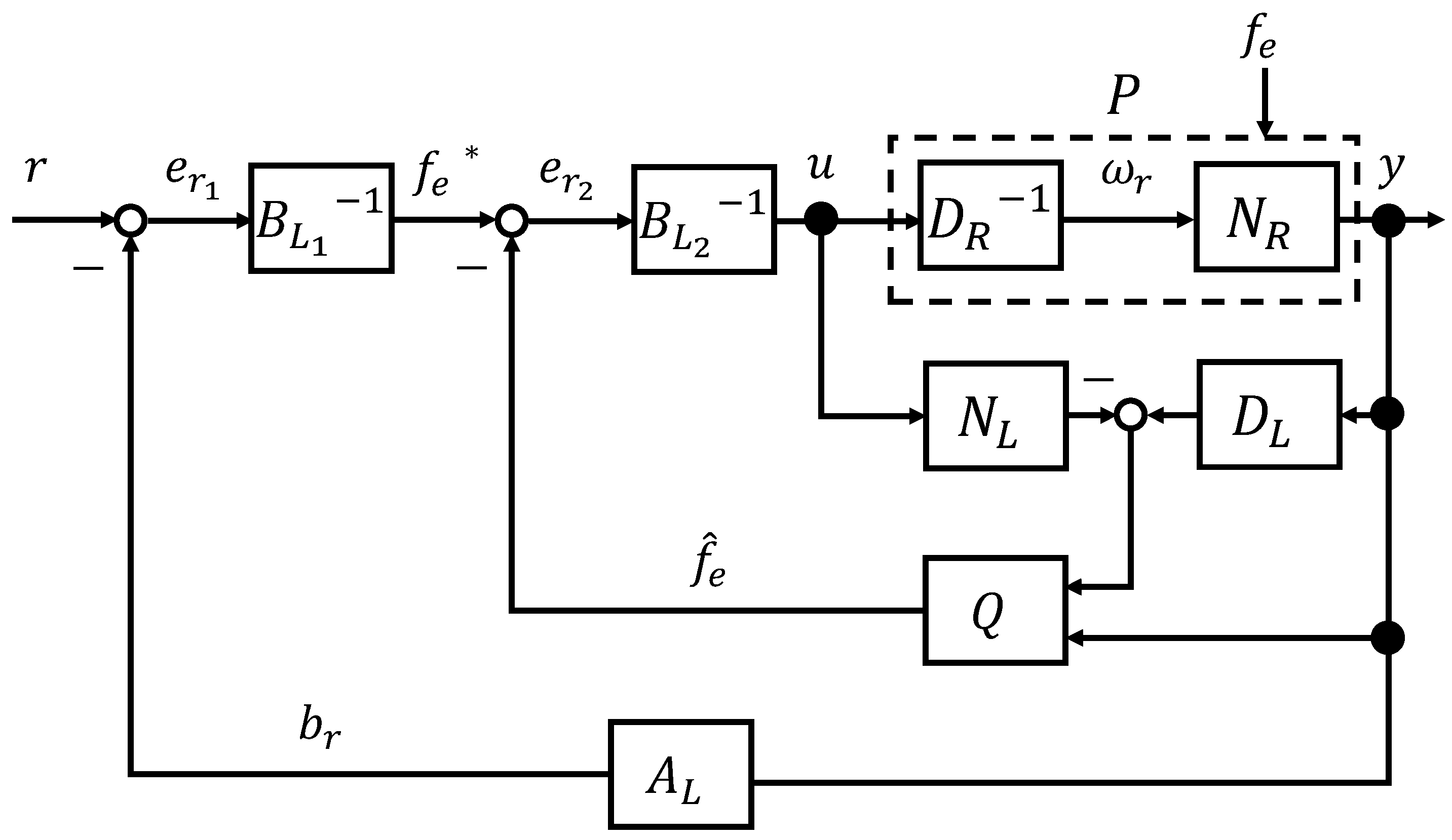
4. Control System Design
4.1. Right Coprime Factorization
4.2. External Force Estimator
4.3. System Stability with External Force Estimator
4.4. Proof of Tracking Performance
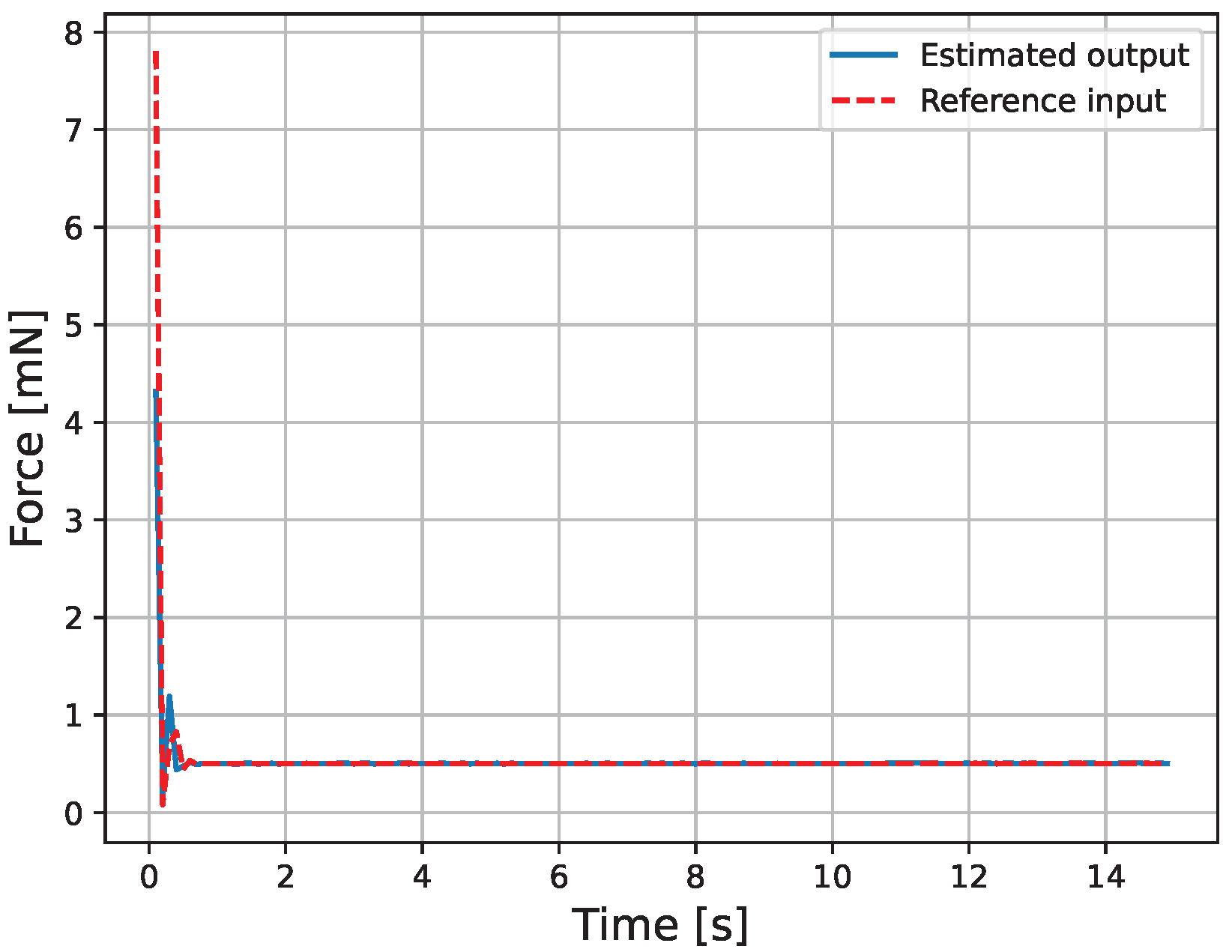
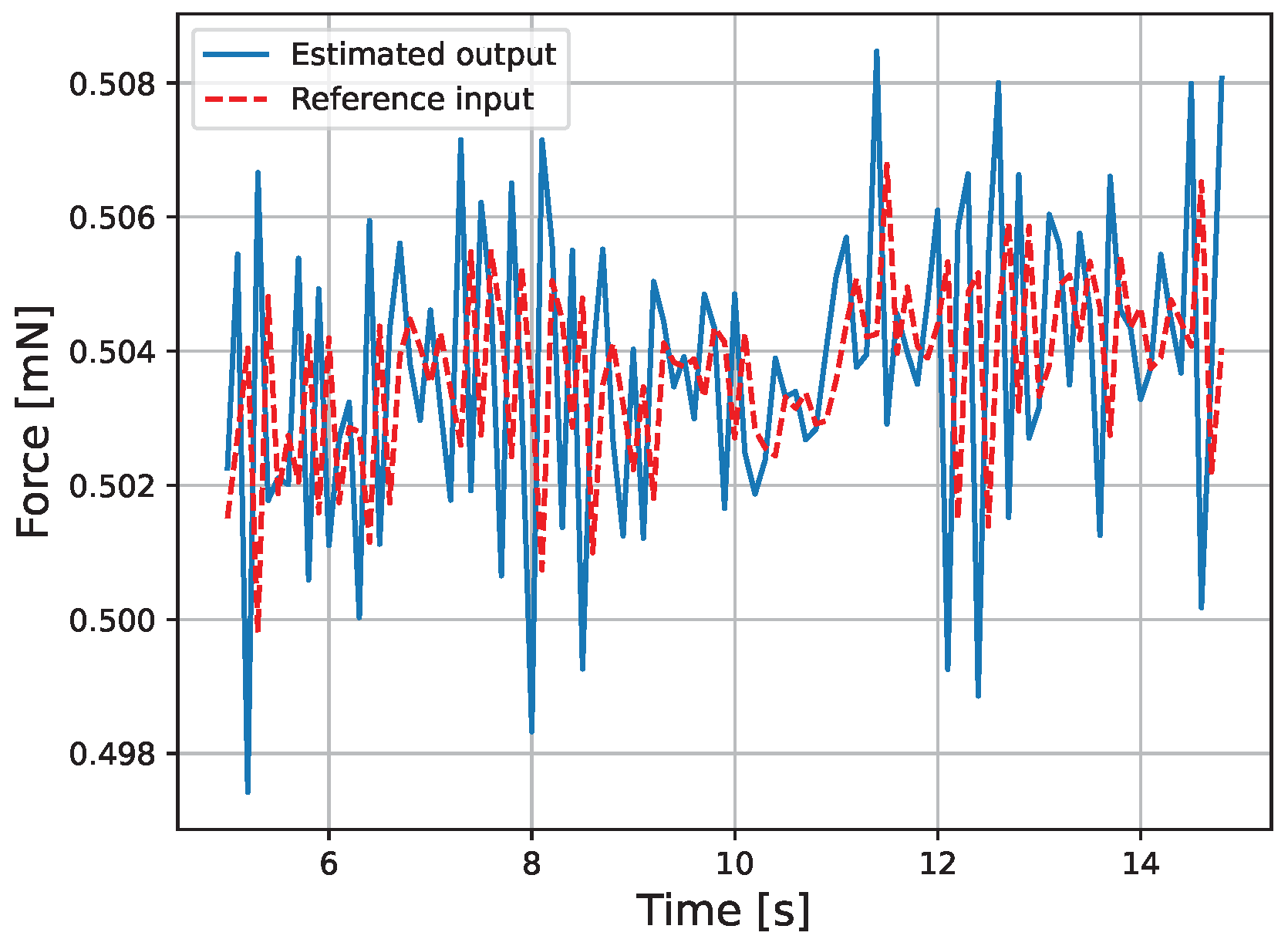
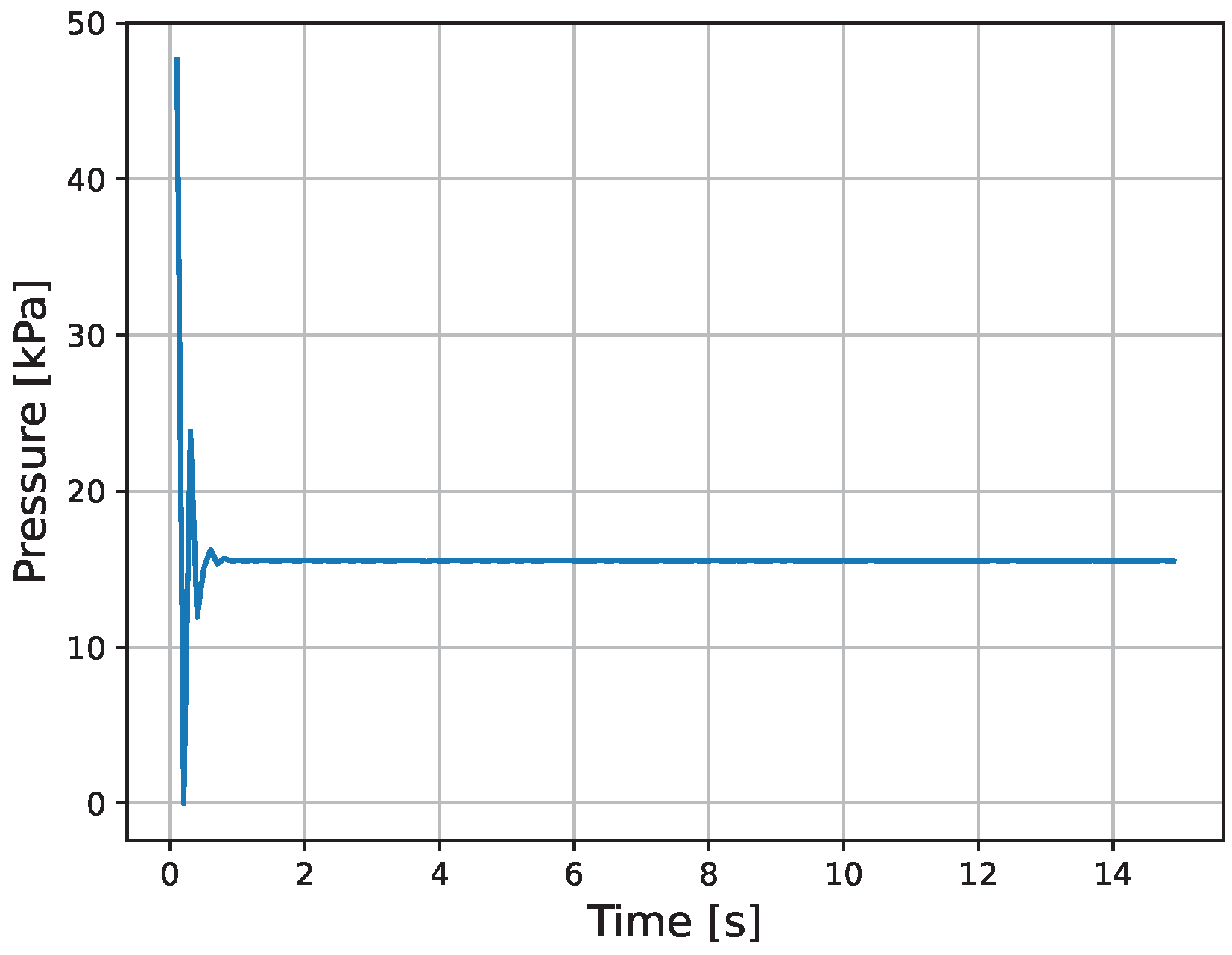
5. Experimental Results
Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morohoshi, Y.; Bu, N.; Deng, M. Experimental Study on Nonlinear Position Control of Micro-Hand Considering Hysteresis Characteristics. Power Energy Electr. Eng. 2024, 54, 635–647. [Google Scholar]
- Higueras-Ruiz, D.R.; Nishikawa, K.; Feigenbaum, H.; Shafer, M. What is an artificial muscle? A comparison of soft actuators to biological muscles. Bioinspiration Biomimetics 2021, 17, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tondu, B.; Lopez, P. Modeling and control of McKibben artificial muscle robot actuators. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2000, 20, 15–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wakimoto, S.; Suzumori, K.; Ogura, K. Miniature pneumatic curling rubber actuator generating bidirectional motion with one air-supply tube. Adv. Robot. 2011, 25, 1311–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majima, S.; Kodama, K.; Hasegawa, T. Modeling of shape memory alloy actuator and tracking control system with the model. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2001, 9, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzki, P.; Rizzello, G. Smart Shape Memory Alloy Actuator Systems and Applications. In Shape Memory Alloys-New Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, P.; Huang, Z.; Liu, H.; Huang, T. Earthworm-Inspired Multimodal Pneumatic Continuous Soft Robot Enhanced by Winding Transmission. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2025, 6, 0204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Fonseca, D.; Neto, D.; Babcinschi, M.; Neto, P. Integrated Design and Fabrication of Pneumatic Soft Robot Actuators in a Single Casting Step. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024, 5, 0137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Dohta, S.; Akagi, T. Development and Analysis of Bending Actuator Using McKibben Artificial Muscle. J. Syst. Des. Dyn. 2012, 6, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polygerinos, P.; Wang, Z.; Overvelde, J.T.B.; Galloway, K.C.; Wood, R.J.; Bertoldi, K.; Walsh, C.J. Modeling of Soft Fiber-Reinforced Bending Actuators. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariya, N.; Kumar, P.; Singh, T. Experimental study on a bending type soft pneumatic actuator for minimizing the ballooning using chamber-reinforcement. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skarpetis, M.G.; Koumboulis, F.N.; Panagiotakis, G.; Kouvakas, N.D. Robust PID Controller for a Pneumatic Actuator. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Cape Town, South Africa, 1–3 February 2016; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2016; Volume 41, p. 02001. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.H.; Shao, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Guan, N. Which is the best PID variant for pneumatic soft robots an experimental study. IEEE CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2020, 7, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Wu, J.; Su, C.Y.; Wang, Y. Tracking control of soft dielectric elastomer actuator based on nonlinear PID controller. Int. J. Control 2024, 97, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Kawashima, T. Adaptive Nonlinear Sensorless Control for an Uncertain Miniature Pneumatic Curling Rubber Actuator Using Passivity and Robust Right Coprime Factorization. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2016, 24, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Morohoshi, Y.; Deng, M. Robust Control for Hysteretic Microhand Actuator Using Robust Right Coprime Factorization. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2024, 69, 3982–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Figueiredo, R.J.P.; Chen, G. Nonlinear Feedback Control Systems: An Operator Theory Approach; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Paice, A.D.; Moore, J.B.; Horowitz, R. Nonlinear Feedback System Stability via Coprime Factorization Analysis. In Proceedings of the 1992 American Control Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 24–26 June 1992; pp. 3066–3070. [Google Scholar]
- Baños, A. Parametrization of nonlinear stabilizing controllers: The observer-controller configuration. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1998, 43, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudani, M.; Deng, M.; Wakimoto, S. Modelling and Operator-Based Nonlinear Control for a Miniature Pneumatic Bending Rubber Actuator Considering Bellows. Actuators 2018, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Rakheja, S. Adaptive variable structure control of a class of nonlinear systems with unknown Prandtl–Ishlinskii hysteresis. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2005, 50, 2069–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Miyagawa, T.; Toya, K.; Kubota, Y. Static characteristics of Pneumatic soft actuator using fiber reinforced rubber. In Proceedings of the JSME annual Conference on Robotics and Mechatronics (Robomec), Akita, Japan, 10–12 May 2007; Volume 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Ma, Z.; Zou, S.; Li, J.; Ding, H. Impedance Sliding-Mode Control Based on Stiffness Scheduling for Rehabilitation Robot Systems. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2024, 5, 0099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| E | Young’s modulus | [Pa] |
| Natural length | [m] | |
| l | Initial length of the one bellows | [m] |
| n | Number of the bellows | [–] |
| Representative radius of the small chambers | [m] | |
| Representative radius of the large chambers | [m] | |
| Initial radius of the small chambers | [m] | |
| Initial radius of the large chambers | [m] | |
| Thickness of the rubber | [m] | |
| Parameter of the control valve | [-] | |
| Parameter of the control valve | [-] | |
| Parameter of the control valve | [Pa] | |
| Correction factor | [-] |
| Symbol | Description | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angle when input is 0 kPa | rad | ||
| E | Young’s modulus | Pa | |
| Natural length | m | ||
| l | Natural length of the one bellows | m | |
| n | Number of bellows | 12 | – |
| Representative radius of the small chambers | m | ||
| Initial radius of the small chambers | m | ||
| Representative radius of the large chambers | m | ||
| Initial radius of the large chambers | m | ||
| Thickness of the rubber | m | ||
| Parameter of the control valve | 6 | 1/s | |
| Parameter of the control valve | 0.3 | – | |
| Parameter of the control valve | Pa | ||
| Correction factor | 5.61 | – | |
| Gain of hysteresis characteristics | 0.96 | – | |
| Sampling time | s | ||
| Maximum control input | Pa | ||
| Minimum control input | 0 | Pa | |
| D | Virtual damping coefficient | N·s/m | |
| K | Virtual stiffness | N/m | |
| M | Virtual mass | g | |
| Design parameter of | 2 | 1/s | |
| Design parameter of | 1 | 1/s2 | |
| Design parameter of | 1 | 1/s2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morohoshi, Y.; Deng, M. Sensorless Impedance Control of Micro Finger Using Coprime Factorization. Micromachines 2025, 16, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050510
Morohoshi Y, Deng M. Sensorless Impedance Control of Micro Finger Using Coprime Factorization. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050510
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorohoshi, Yuuki, and Mingcong Deng. 2025. "Sensorless Impedance Control of Micro Finger Using Coprime Factorization" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050510
APA StyleMorohoshi, Y., & Deng, M. (2025). Sensorless Impedance Control of Micro Finger Using Coprime Factorization. Micromachines, 16(5), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050510







