MXene-Enhanced Laser-Induced Graphene Flexible Sensor with Rapid Response for Monitoring Pilots’ Body Motion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Innovative modification of conventional LIG fabrication protocols enables the single-step fabrication of MXene-enhanced LIG. This advancement overcomes the inherent limitations of multi-step doping methodologies, offering a novel and efficient methodology for the production of high-performance flexible sensors.
- Significant performance enhancement was achieved through MXene modification, characterized by a reduced sheet resistance (14.1 Ω), an expanded strain detection limit (0.05%), and a rapid response time (65 ms). These improvements substantiate the critical role of MXene in optimizing conductive networks and enhancing interfacial charge transfer dynamics.
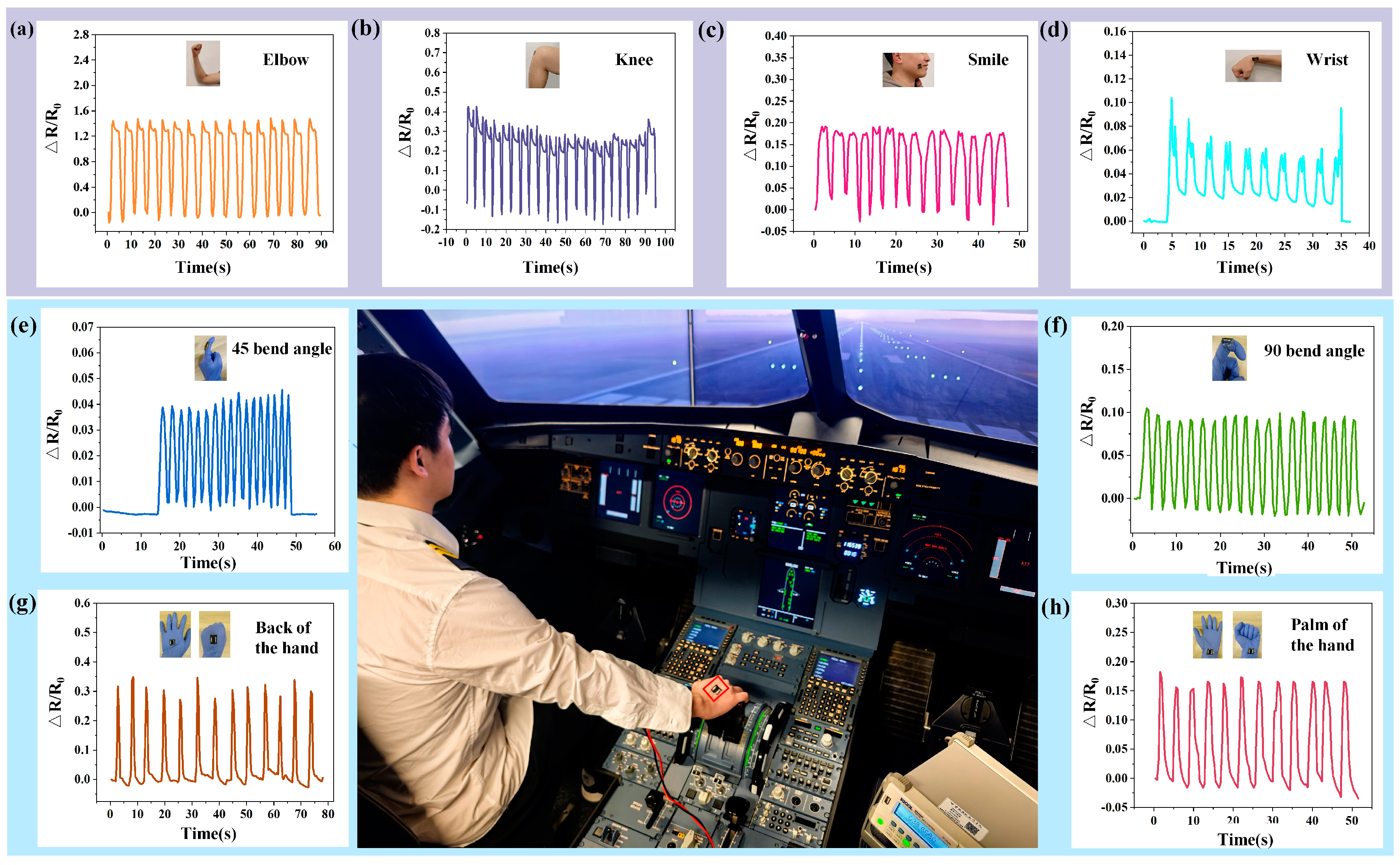
- Pioneering advancements have been made in the application of pilot health monitoring within the civil aviation sector. The MXene/LIG sensor exhibits remarkable capability in detecting subtle body movement signals. This innovation establishes an effective technological framework for real-time monitoring of pilots’ motion states during operational scenarios.
2. Materials and Methods
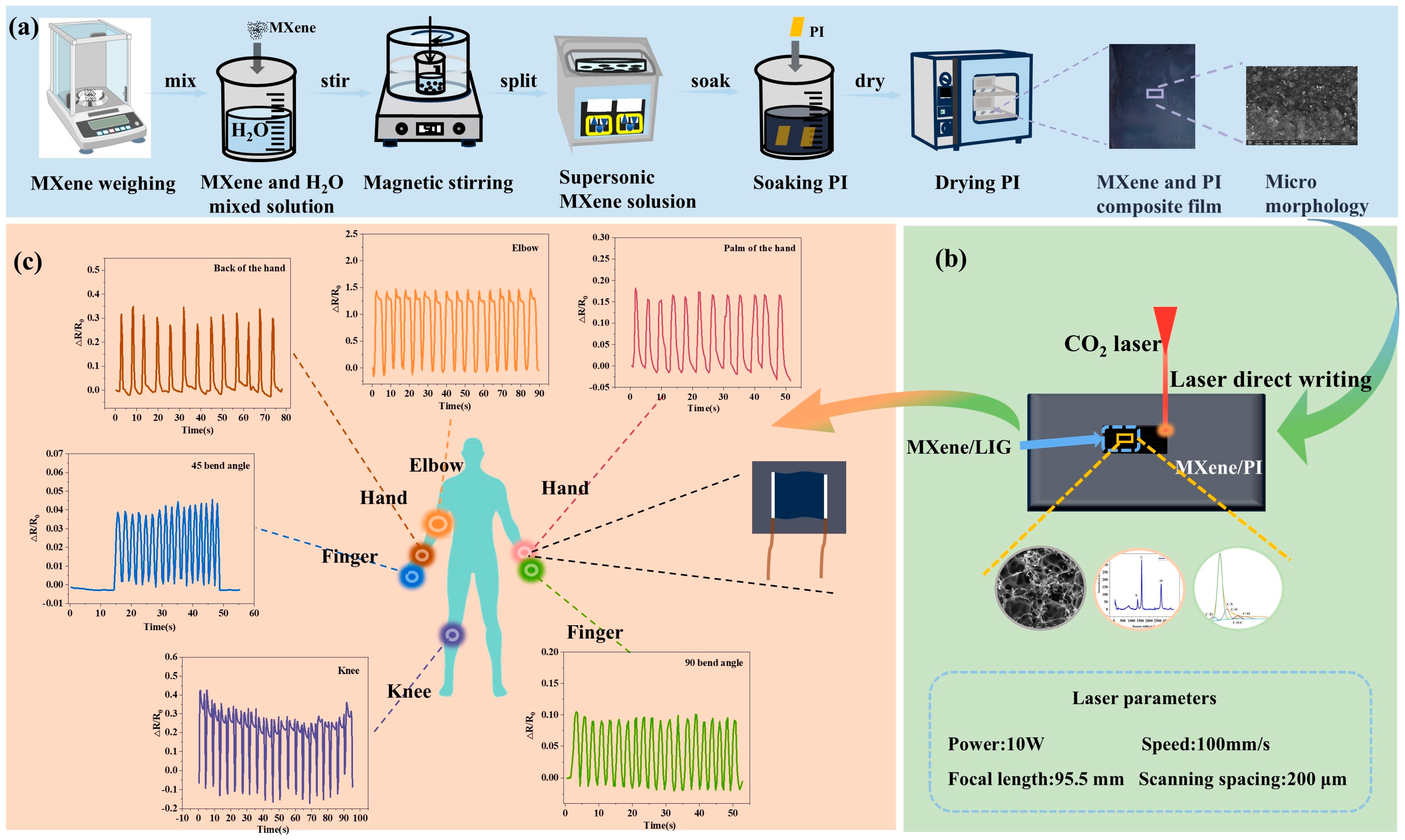
2.1. Preparation of LIG
2.2. Material Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
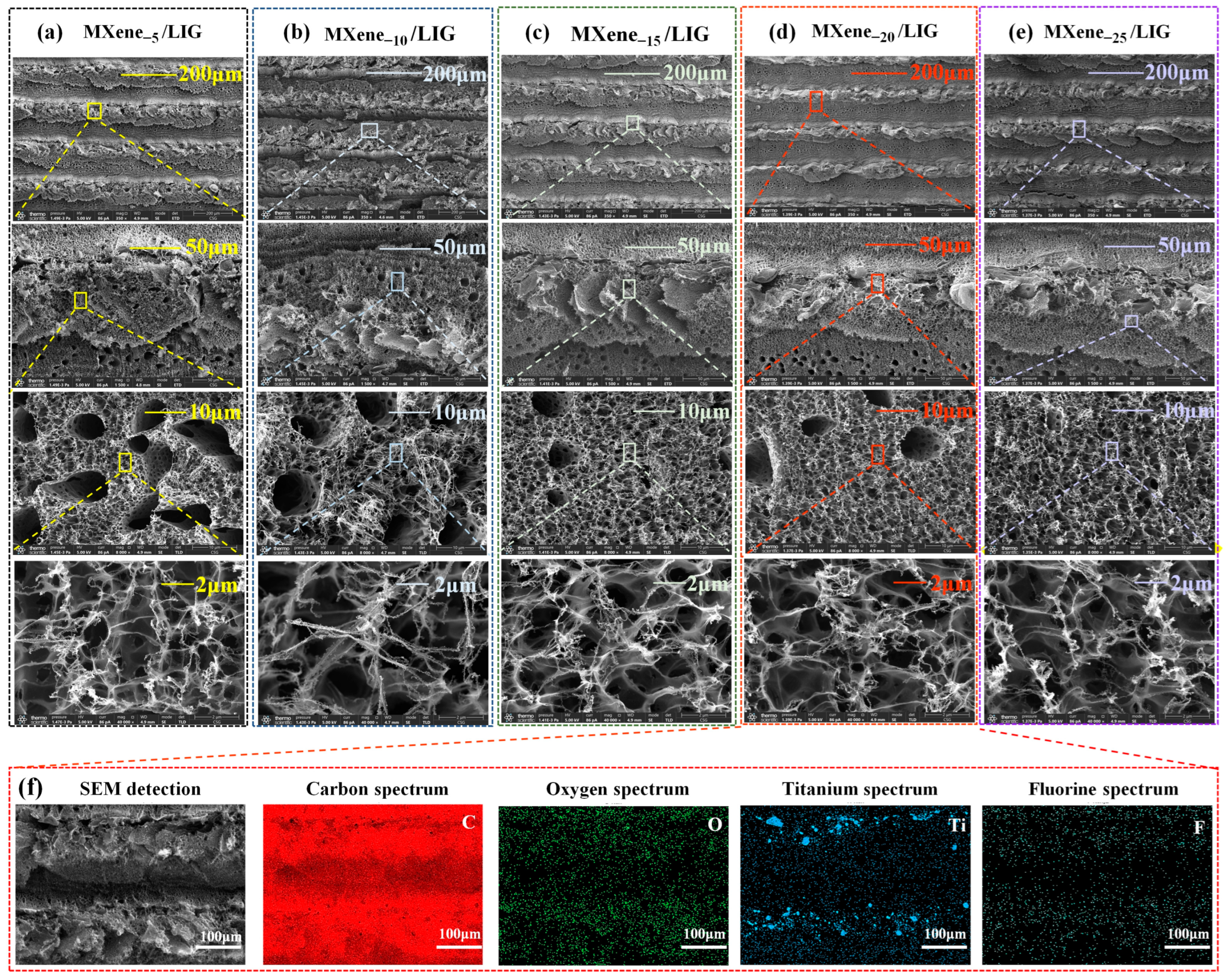
3.1. Surface Morphology Analysis of MXene/LIG
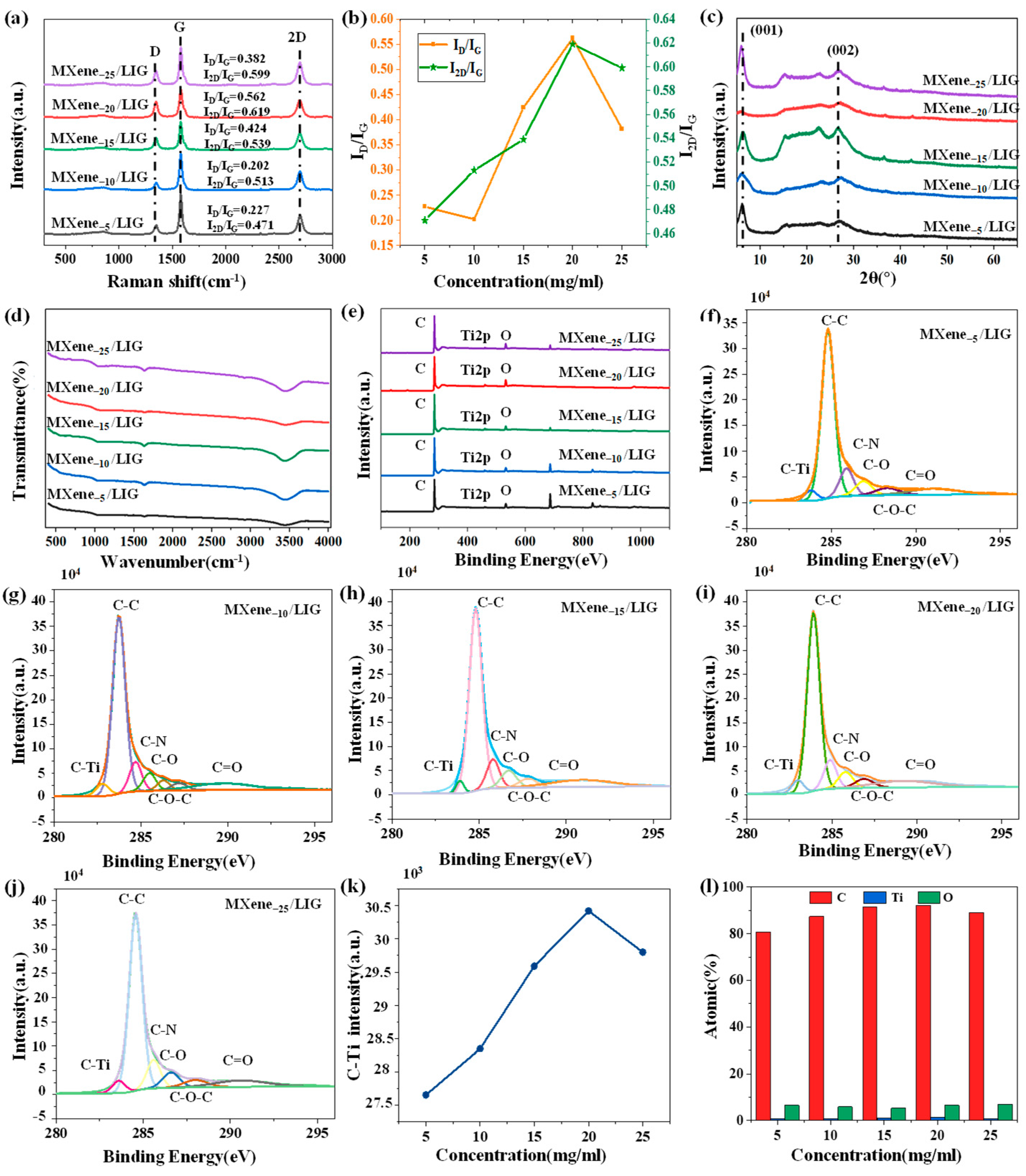
3.2. Optical Spectrum Analysis of MXene/LIG
3.3. Performance Evaluation of MXene/LIG-Based Sensor
3.4. Applications of MXene/LIG-Based Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malode, S.J.; Alshehri, M.A.; Shetti, N.P. Revolutionizing human healthcare with wearable sensors for monitoring human strain. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 246, 114384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.L.; Alfarros, Z.; Herianto, H.; Muhammad, A.M. High sensitivity flexible strain sensor for motion monitoring based on MWCNT@MXene and silicone rubber. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, G.; Honda, S.; Kikuchi, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Hara, H.; Kondo, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Watanabe, S.; Hayakawa, K.; Nakajima, K.; et al. Real-time personal healthcare data analysis using edge computing for multimodal wearable sensors. Device 2025, 3, 100597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonina, S.N.; Kazanskiy, N.L. Trends and advances in wearable plasmonic sensors utilizing surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): A Comprehensive Review. Sensors 2025, 25, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Du, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, K.; Chen, D.; Shen, G. Biomimetic honeycomb-like Ti3C2Tx MXene/Bacterial cellulose aerogel-based flexible pressure sensor for the human–computer interface. ACS Sens. 2024, 10, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zhong, M.; Li, S.; Qing, Z.; Xing, X.; Gong, G.; Yan, R.; Qin, W.; Shen, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Flexible wearable strain sensors based on laser-induced graphene for monitoring human physiological signals. Polymers 2023, 15, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirin, M.; Pilgyu, K. Laser-induced graphene: Synthesis advances, structural tailoring, enhanced properties, and sensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Qiang, H.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Luo, N. A review on the laser-induced synthesis of graphene and its applications in sensors. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 11644–11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Chen, X.; Song, B.; Cui, Y. Bionic spider web flexible strain sensor based on CF-L and machine learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 23761–23770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Pandey, R.; Joanni, E.; Savu, R. Laser-induced and catalyst-free formation of graphene materials for energy storage and sensing applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Ruan, L.; Chen, H.; Du, Y.; Deng, H.; Dai, N.; Tang, Y. Laser-induced graphene: Carbon precursors, fabrication mechanisms, material characteristics, and applications in energy storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, J.; Wang, W. Recent advances in flexible/stretchable sensors using laser-induced three-dimensional porous graphene: From precursor to manufacturing. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 55, 105359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chen, X.; Dutta, A.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xin, W.; Du, S.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H. Thermoelectric porous laser-induced graphene-based strain-temperature decoupling and self-powered sensing. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetlova, A.; Law, H.T.J.; Kim, D.; Enriquez, N.; Soleimani, A.; Al-Shami, A.; Kohan, S.; Peck, R.; Eremina, O.E.; Zavaleta, C.; et al. Benchtop fabrication and integration of laser-induced graphene strain gauges and stimulation electrodes in muscle on a chip devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, N.; Singh, S.P. Laser-induced graphene (LIG) as a smart and sustainable material to restrain pandemics and endemics: A perspective. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 5112–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.A.; Zhao, J.Y.; Li, R.; Zhou, Z.; Gui, Y.; Sun, R.; Wu, D.; Wang, X. Construction of laser-induced graphene/silver nanowire composite structures for low-strain, high-sensitivity flexible wearable strain sensors. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 3524–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustoloni, C.J.M.; Soltan Khamsi, P.; Kammarchedu, V.; Ebrahimi, A. Systematic study of various functionalization steps for ultrasensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 with direct laser-functionalized Au-LIG electrochemical sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 49041–49052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, P.; Guo, X. Laser-induced graphene based flexible electronic devices. Biosensors 2022, 12, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, L.; Cheng, L.; Guo, W.; Ye, R. Laser-Induced Graphene-Based Sensors in Health Monitoring: Progress, Sensing Mechanisms, and Applications. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2400118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Tu, J.; Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xu, C.; Ye, C.; IsHak, W.W.; et al. Investigation of cortisol dynamics in human sweat using a graphene-based wireless mHealth system. Matter 2020, 2, 921–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, J.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Saetang, V. A review of laser-induced graphene: From experimental and theoretical fabrication processes to emerging applications. Carbon 2023, 214, 118356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Zou, Y.; Zhong, M.; Li, S.; Fan, H.; Lei, X.; Yin, J.; Shen, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, M.; et al. A Flexible wearable sensor based on laser-induced graphene for high-precision fine motion capture for pilots. Sensors 2024, 24, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedheydari, F.; Sadeghzadeh, S.; Saadatbakhsh, M.; Heydariyan, A.; Khakpour, E. Silver-decorated laser-induced graphene for a linear, sensitive, and almost hysteresis-free piezoresistive strain sensor. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Zhong, M.; Fan, H.; Li, Z.; Lyu, S.; Xing, X.; Qin, W. Highly sensitive, wearable piezoresistive methylcellulose/chitosan@MXene aerogel sensor array for real-time monitoring of physiological signals of pilots. Sci. China Mater. 2025, 68, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Liang, M.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, C.; Xing, W.; Bian, X.; Lian, Y.; Wang, B.; You, Z.; You, R. High-performance sensing platform based on morphology/lattice collaborative control of femtosecond-laser-induced MXene-composited graphene. Adv. Mater. 2024, 11, 2404889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jian, M.; Jiang, Q.; Li, X. MXene key composites: A new arena for gas sensors. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Duan, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Sun, P.; Tai, H. Facilely constructed randomly distributed surface microstructure for flexible strain sensor with high sensitivity and low detection limit. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 284003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, M.; Zhai, W.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Flexible strain sensor based on CNTs/CB/TPU conductive fibrous film with wide sensing range and high sensitivity for human biological signal acquisition. Polymer 2024, 302, 127049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, F.; Zhao, X.; Chen, K.; Qin, Y. Ultrastretchable, ultralow hysteresis, high-toughness hydrogels strain sensor for pressure recognition with deep learning. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 49834–49844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liang, B.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Gao, X.; Yao, D.; Chen, J.; Lu, C.; Pang, X. Hydrogel-based bimodal sensors for high-sensitivity independent detection of temperature and strain. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 680, 832–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Ding, H.; Gu, Y.; Wu, H.; Tao, K.; Yang, B.; Pan, S.; et al. Ultrasensitive and breathable hydrogel fiber-based strain sensors enabled by customized crack design for wireless sign language recognition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2416482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Shen, T.; Yang, W.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultrasensitive strain sensor based on superhydrophobic microcracked conductive Ti3C3Tx MXene/paper for human-motion monitoring and E-skin. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhai, W.; Yue, X.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Design of flexible micro-porous fiber with double conductive network synergy for high-performance strain sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Zou, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Li, B.; Jiang, Y.; Xing, X.; Shen, J.; et al. A flexible wearable strain sensor based on nano-Silver-modified laser-induced graphene for monitoring hand movements. Micromachines 2024, 15, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xie, X.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, Y. Development of highly sensitive and stable patterned PDMS flexible strain sensors for motion monitoring via laser direct writing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 182, 112212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
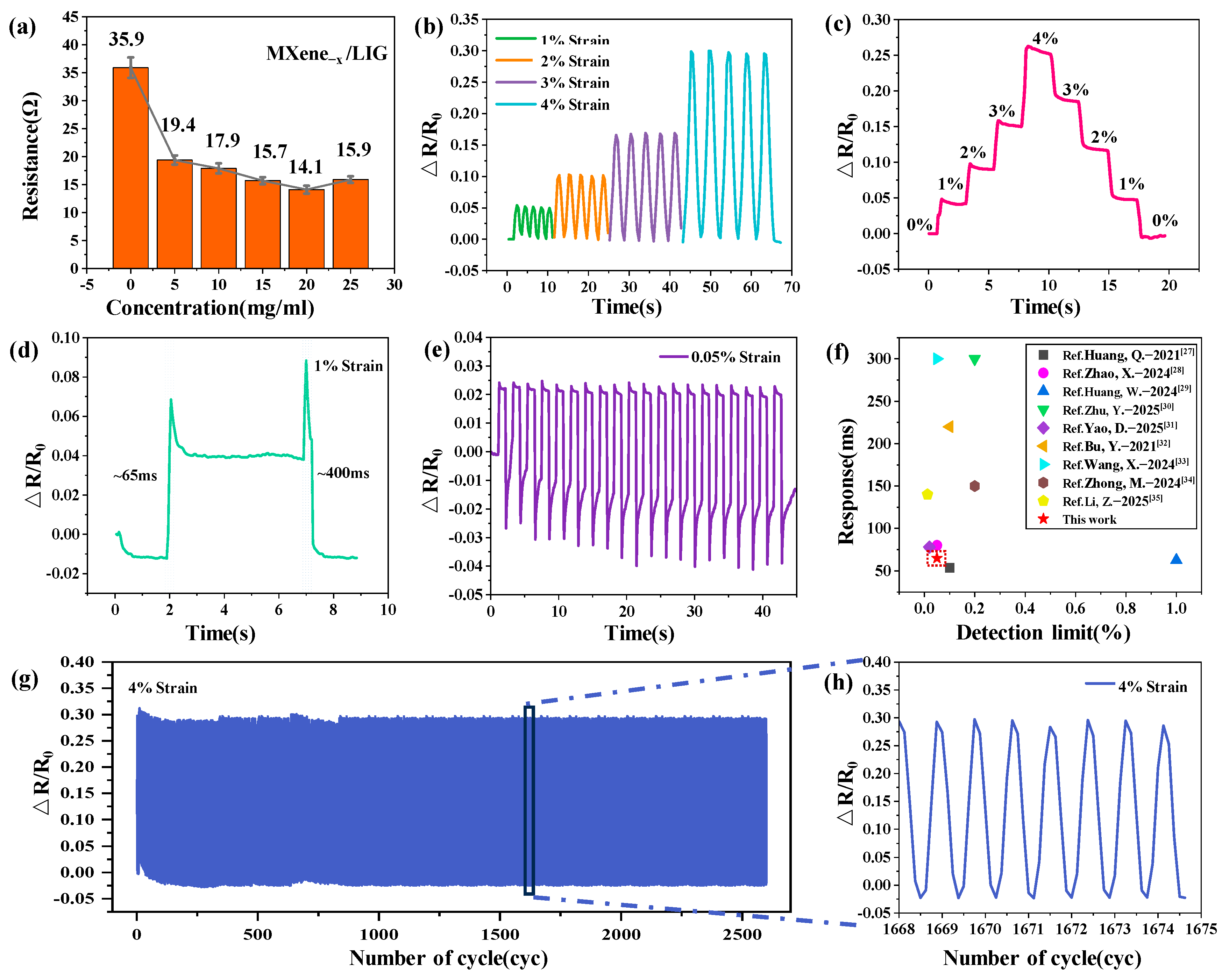
| Materials | Processing | Response Time (ms) | Detection Limit (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIG | Laser direct writing | 150 | 0.05 | [22] |
| PDMS/PEI/CNT Sandpaper | Spray-coating | 53.6 | 0.1 | [27] |
| CNT/CB/TPU | Spraying carbon black | 80 | 0.05 | [28] |
| PAM/HA/MMT hydrogel | Dual physically cross-linked | 62.5 | 1 | [29] |
| PAAM/CS hydrogels | Surface coating | 300 | 0.2 | [30] |
| Hydrogel fiber | Introduction crack | 78 | 0.02 | [31] |
| MXene/paper | Dip coating | 220 | 0.1 | [32] |
| rGO/CNTs/TPU-TPU composite fibers | Dip coating | 300 | 0.05 | [33] |
| Nano-Silver-modified LIG | Laser direct writing | 150 | 0.2 | [34] |
| P-PDMS | Laser direct writing | 140 | 0.0125 | [35] |
| MXene/LIG | Laser direct writing | 65 | 0.05 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, X.; Fan, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, M.; Wu, Z.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Xing, X.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. MXene-Enhanced Laser-Induced Graphene Flexible Sensor with Rapid Response for Monitoring Pilots’ Body Motion. Micromachines 2025, 16, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050513
Lei X, Fan H, Zhao Y, Zhong M, Wu Z, Li L, Li S, Xing X, Liu J, Sun Y, et al. MXene-Enhanced Laser-Induced Graphene Flexible Sensor with Rapid Response for Monitoring Pilots’ Body Motion. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Xia, Hongyun Fan, Yilin Zhao, Mian Zhong, Zhanghui Wu, Lin Li, Shouqing Li, Xiaoqing Xing, Jianhua Liu, Yibo Sun, and et al. 2025. "MXene-Enhanced Laser-Induced Graphene Flexible Sensor with Rapid Response for Monitoring Pilots’ Body Motion" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050513
APA StyleLei, X., Fan, H., Zhao, Y., Zhong, M., Wu, Z., Li, L., Li, S., Xing, X., Liu, J., Sun, Y., Jiang, Y., & Ren, G. (2025). MXene-Enhanced Laser-Induced Graphene Flexible Sensor with Rapid Response for Monitoring Pilots’ Body Motion. Micromachines, 16(5), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050513







