Magnetic Bead—Magic Bullet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Classification | Authors | Year | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basics | Magnetic Bead Technology | Sinclair | 2015 | [2] |
| Gijs | 2004 | [4] | ||
| Gijs et al. | 2010 | [9] | ||
| Ruffert | 2015 | [10] | ||
| Nano- and Microparticle Fabrication | Veiseh et al. | 2010 | [16] | |
| Park et al. | 2007 | [17] | ||
| Zhao et al. | 2005 | [18] | ||
| Kim et al. | 2006 | [19] | ||
| Ito et al. | 2005 | [20] | ||
| Jing et al. | 2012 | [22] | ||
| Chen et al. | 2009 | [29] | ||
| Bigall et al. | 2011 | [31] | ||
| Zhang et al. | 2008 | [32] | ||
| Applications | Separation with Magnetic Beads | Pamme | 2007 | [6] |
| Ruffert et al. | 2014 | [13] | ||
| Zhang et al. | 2008 | [32] | ||
| Miltenyi et al. | 1990 | [47] | ||
| Zborowski et al. | 2008 | [52] | ||
| Pamme et al. | 2006 | [53] | ||
| Magnetic Bead-based Immunoassays | Tekin | 2013 | [7] | |
| Bhalla et al. | 2013 | [11] | ||
| Ruffert et al. | 2014 | [12] | ||
| Sivagnanam | 2010 | [39] | ||
| Biomedical Bead Applications | Thanh | 2012 | [21] | |
| Colombo et al. | 2012 | [23] | ||
| Llandro et al. | 2010 | [28] | ||
| Figuerola et al. | 2010 | [33] | ||
| Na et al. | 2009 | [34] | ||
| Mahmoudi et al. | 2011 | [36] | ||
| Jordan et al. | 2001 | [37] | ||
| Pankhurst et al. | 2003 | [38] | ||
| Varadan et al. | 2008 | [40] | ||
| Mixing with Beads/Chaining | Martin et al. | 2009 | [42] | |
| Owen et al. | 2013 | [43] | ||
| Raman et al. | 2012 | [44] | ||
| Dreyfus et al. | 2009 | [45] | ||
| Sensing | Magnetic Particle Sensing | Eickenberg et al. | 2013 | [26] |
| Takamura et al. | 2015 | [27] | ||
2. Magnetic Bead Properties and Synthesis
2.1. Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles in Microfluidics

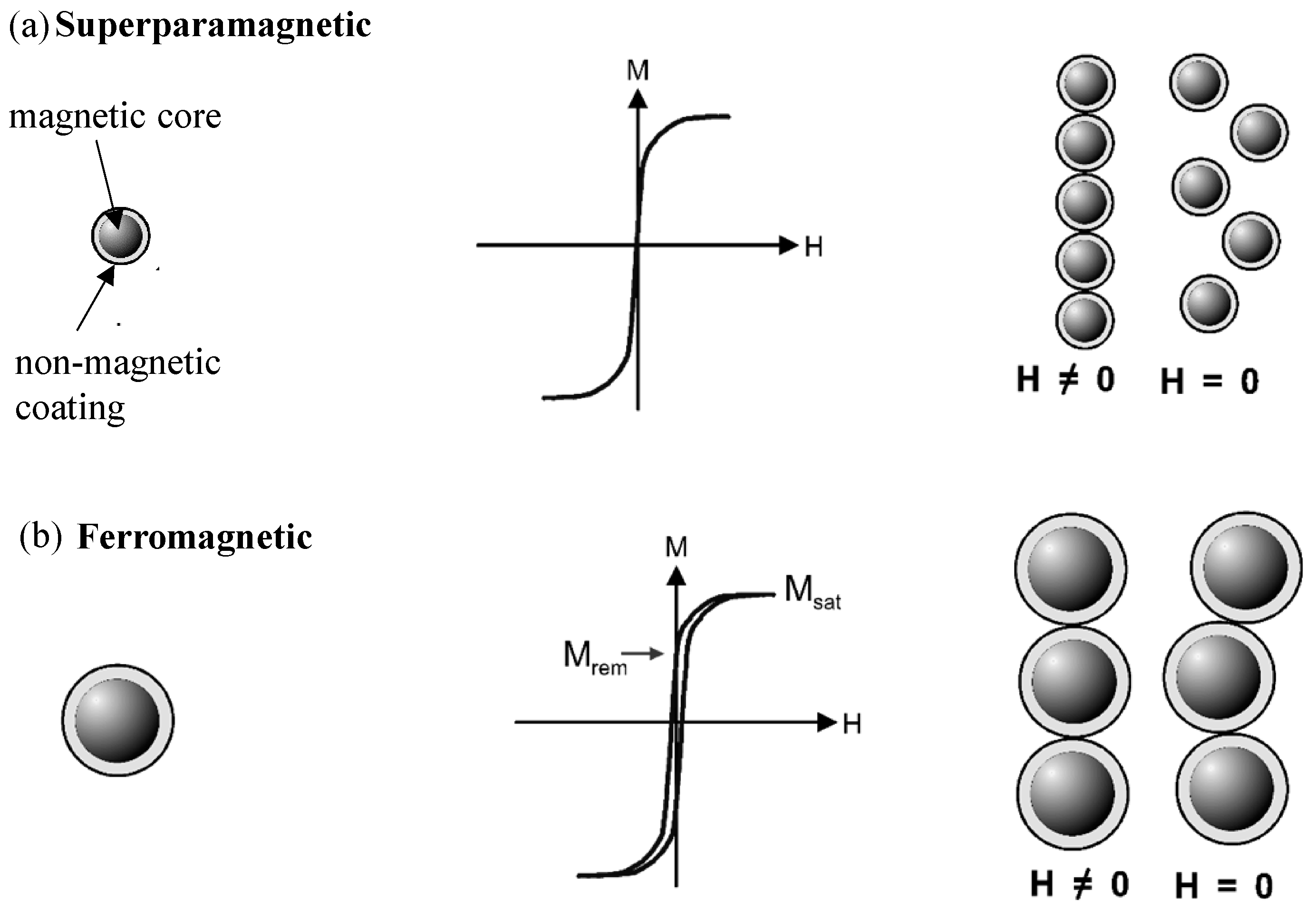
2.2. Magnetic Bead Fabrication and Detection

2.3. Multifunctional Hybrid Nanoparticles
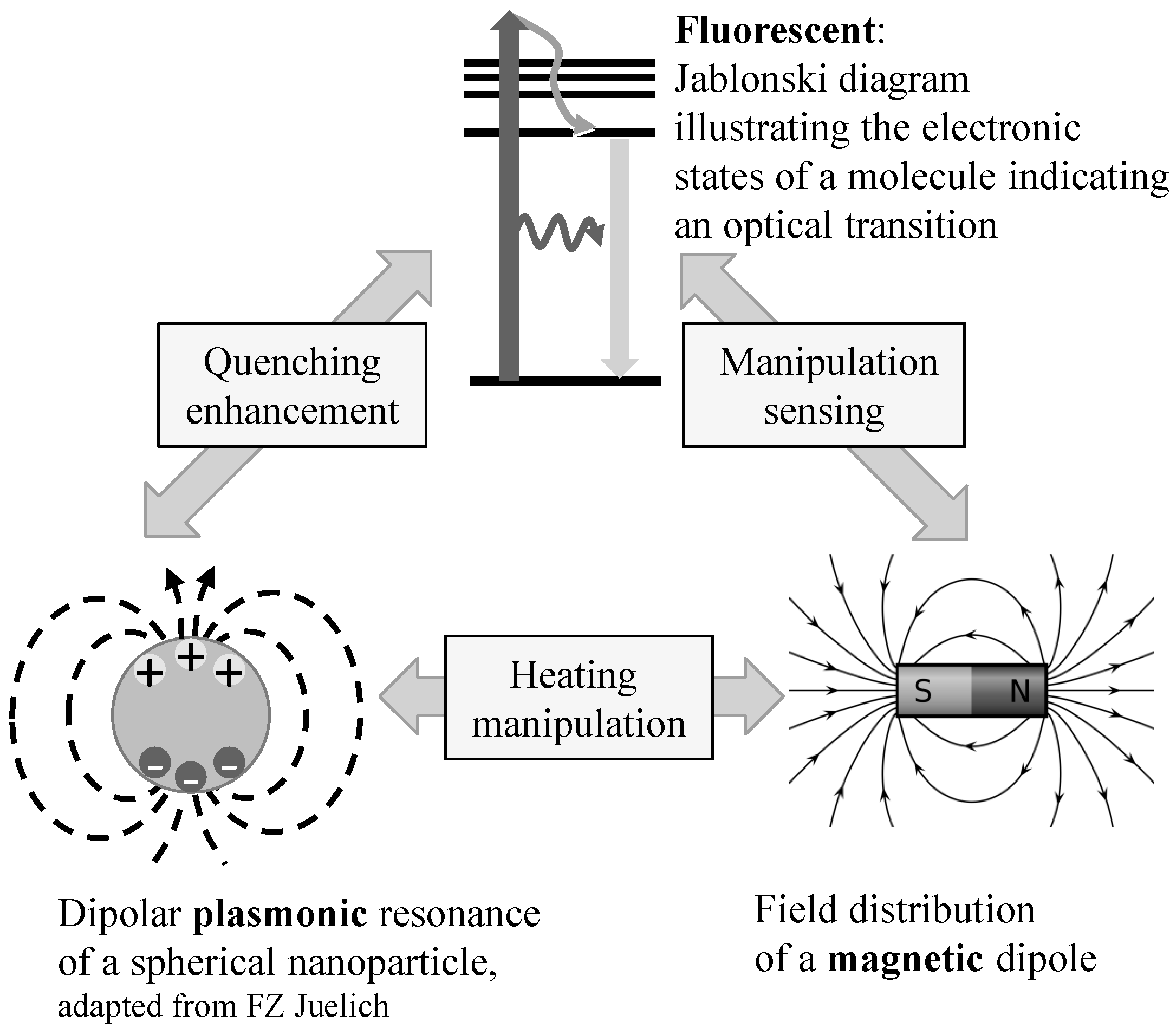
3. Magnetic Bead Applications
3.1. Introduction to the Use of Magnetic Beads
3.2. Magnetic Beads in Nanomedicine


- (i)
- Significant reduction of sample and reagents (even down to the picoliter scale);
- (ii)
- Fast reaction times (when the molecular diffusion length matches the channel dimensions);
- (iii)
- Large surface-to-volume ratio (enabling efficient binding processes of the sample).
3.3. Magnetic Chaining
3.4. Biomolecule Detection—Multiplex vs. Singleplex Approaches
4. Magnetic Manipulation—Practical Aspects

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References and Notes
- Manz, A.S.; Graber, N.; Widmer, H.M. Miniaturized total chemical analysis systems: A novel concept for chemical sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1990, 1, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, B. To Bead or Not to Bead: Applications of Magnetic Bead Technology. Available online: http://www.the-scientist.com/?articles.view/articleNo/18984/title/To-Bead-or-Not-To-Bead--Applications-of-Magnetic-Bead-Technology/ (accessed on 21 November 2015).
- Whitesides, G.M. The lab finally comes to the chip. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3125–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gijs, M.A.M. Magnetic bead handling on-chip: New opportunities for analytical applications. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2004, 1, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickstein, B.; Peuker, U.A. Characterization of protein capacity of nanocation exchanger particles as filling material for functional magnetic beads for bio-separation purposes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamme, N. Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 1644–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tekin, C.; Gijs, M.A.M. Ultrasensitive protein detection: A case for microfluidic magnetic bead-based assays. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 4711–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Search Results: Springer, http://link.springer.com/search?query=magnetic+bead; RSC Publishing, http://pubs.rsc.org/en/results?searchtext=magnetic%20bead.
- Gijs, M.A.M.; Lacharme, F.; Lehmann, U. Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1518–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruffert, C. Magnetic beads—Basics and applications. ECS Trans. 2015, 64, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, N.; Chung, D.W.Y.; Chang, Y.-J.; Uy, K.J.S.; Ye, Y.Y.; Chin, T.-Y.; Yang, H.C.; Pijanowska, D.G. Microfluidic platform for enzyme-linked and magnetic particle-based immunoassay. Micromachines 2013, 4, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffert, C.; Ramadan, Q.; Ruegg, M.; Vergères, G.; Gijs, M.A.M. Integrated microfluidic chip for cell culture and stimulation and magnetic bead-based biomarker detection. Micro Nanosyst. 2014, 6, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffert, C.; Bigall, N.C.; Feldhoff, A.; Rissing, L. Investigations on the separation of platinum nanoparticles with magnetic beads. IEEE Trans. Mag. 2014, 50, 5200804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurti, N. Selected Works of Louis Néel; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: London, UK, 1988; pp. 405–427. [Google Scholar]
- Kittel, C. Introduction to Solid State Physics, 7th ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Veiseh, O.; Gunn, J.W.; Zhang, M. Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 284–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-Y.; Schadt, M.J.; Lingyan, I.-I.; Lim, S.; Njoki, P.N.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, M.-J.; Luo, J.; Zhong, C.-J. Fabrication of magnetic core@shell Fe oxide@Au nanoparticles for interfacial bioactivity and bio-separation. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9050–9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Gu, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. Fabrication of uniform magnetic nanocomposite spheres with a magnetic core/mesoporous silica shell structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 8916–8917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Park, S.; Lee, J.E.; Jin, S.M.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, I.S.; Yang, I.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.K.; Cho, M.-H.; et al. Designed fabrication of multifunctional magnetic gold nanoshells and their application to magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy. Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 7918–7922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Ino, K.; Hayashida, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Matsunuma, H.; Kagami, H.; Ueda, M.; Honda, H. Novel methodology for fabrication of tissue-engineered tubular constructs using magnetite nanoparticles and magnetic force. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh, N.T.K. Magnetic Nanoparticles—From Fabrication to Clinical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; Chapter 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Bryant, E.; Avendano, C.; Colvin, V.L.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Yu, W.W. One-step reverse precipitation synthesis of water-dispersible superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Romero, S.C.; Casula, M.F.; Gutiérrez, L.; Morales, M.P.; Böhm, I.B.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Prosperi, D.; Parak, W.J. Biological applications of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4306–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Business Wire. Applied BioCode Granted 2 Patents for Its Barcoded Magnetic Beads Used in Highly Multiplexed MDx Testing. Available online: http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20110125005821/en/Applied-BioCodeGranted-2-Patents-Barcoded-Magnetic-Beads (accessed on 22 September 2015).
- Ho, W.Z.; Collins, J. Apparatus and Method for Digital Magnetic Beads Analysis. U.S. Patent 8,232,092, 25 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Eickenberg, B.; Meyer, J.; Helmich, L.; Kappe, D.; Auge, A.; Weddemann, A.; Wittbracht, F.; Hütten, A. Review: Lab-on-a-chip magneto-immunoassays: How to ensure contact between superparamagnetic beads and the sensor surface. Biosensors 2013, 3, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamura, T.; Ko, P.J.; Sharma, J.; Yukino, R.; Ishizawa, Sh.; Sandhu, A. Review: Magnetic-particle-sensing based diagnostic protocols and applications. Sensors 2015, 15, 12983–12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llandro, J.; Palfreyman, J.J.; Ionescu, A.; Barnes, C.H.W. Magnetic biosensor technologies for medical applications: A review. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 977–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Lim, B.; Lee, E.P.; Xia, Y. Shape-controlled synthesis of platinum nanocrystals for catalytic and electrocatalytic applications. Nano Today 2009, 4, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Corato, R.; Bigall, N.C.; Ragusa, A.; Dorfs, D.; Genovese, A.; Marotta, R.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. Multifunctional nanobeads based on quantum dots and magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis and cancer cell targeting and sorting. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigall, N.C.; Parak, W.J.; Dorfs, D. Fluorescent, magnetic and plasmonic—Hybrid multifunctional colloidal nano objects. Nano Today 2012, 7, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, S.; Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Budihartono, S.; Stahr, F.; Yan, Z.; Wang, X.; Hao, Z.; Lu, G.Q. Fabrication and size-selective bioseparation of magnetic silica nanospheres with highly ordered periodic mesostructure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3203–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figuerola, A.; di Corato, R.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. From iron oxide nanoparticles towards advanced iron-based inorganic materials designed for biomedical applications. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 62, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.B.; Song, I.C.; Hyeon, T. Inorganic nanoparticles for MRI contrast agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuillan, A.J.; Green, D.P. In situ IR spectroscopic studies of the avidin-biotin bioconjugation reaction on CdS particle films. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7416–7423. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Sant, S.; Wang, B.; Laurent, S.; Sen, T. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): Development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A.; Scholz, R.; Maier-Hauff, K.; Johannsen, M.; Wust, P.; Nadobny, J.; Schirra, H.; Schmidt, H.K.; Deger, S.; Loening, S.; et al. Presentation of a new magnetic field therapy system for the treatment of human solid tumors with magnetic fluid hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 225, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagnanam, V. Microfluidic Immunoassays Based on Self-Assembled Magnetic Bead Patterns and Time-Resolved Luminescence Detection. Ph.D. Thesis, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland, February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Varadan, V.K.; Chen, L.F.; Xie, J. Nanomedicine Design and Applications of Magnetic Nanomaterials, Nanosensors and Nanosystems, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Cui, F.-Z. Biocompatibility and toxicity of nanoparticles and nanotubes. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 548389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.E.; Shea-Rohwer, L.; Solis, K.J. Strong intrinsic mixing in vortex magnetic fields. Phys. Rev. E 2009, 80, 016312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.; Mao, W.; Alexeev, A.; Cannon, J.L.; Hesketh, P.J. Microbeads for sampling and mixing in a complex sample. Micromachines 2013, 4, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, V.; Bose, A.; Olsen, B.D.; Hatton, T.A. Long-range ordering of symmetric block copolymer domains by chaining of superparamagnetic nanoparticles in external magnetic fields. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 9373–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfus, R.; Lacoste, D.; Bibette, J.; Baudry, J. Measuring colloidal forces with the magnetic chaining technique. Eur. Phys. J. E 2009, 28, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sachdeva, N.; Asthana, D. Cytokine quantitation: Technologies and applications. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 4682–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltenyi, S.; Müller, W.; Weichel, W.; Radbruch, A. High gradient magnetic cell separation with MACS. Cytometry 1990, 11, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R&D Systems Inc. MagCellect™ Cell Selection Kits & Reagents. Available online: https://www.rndsystems.com/products/magcellect-cell-selection-kits-reagents (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- StemCell Technologies Inc. Web Page. Available online: http://www.stemcell.com/en/Search.aspx?ts=magnet (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- Jansson Diagnostics LLC. Cell Search. Available online: https://www.veridex.com/cellsearch/CSProducts/CTCKit.aspx (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- Becton Dickinson. Technical Data Sheet: Cell Separation Magnet. Available online: http://www.bdbiosciences.com/external_files/pm/doc/tds/cell_sep/live/web_enabled/552311.pdf (accessed on 20 September 2015).
- Zborowski, M.; Chalmes, J.J. Magnetic Cell Separation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pamme, N.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Manz, A. On-chip free-flow magnetophoresis: Separation and detection of mixtures of magnetic particles in continuous flow. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 307, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpatti, L.R.; Yetisen, A.K. Commercialization of microfluidic devices. Trends Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Business Innovation. 7th Microfluidics Consortium. Available online: http://www.cfbi.com/microfluidics.htm (accessed on 26 December 2015).
- LinkedIn Group: Lab on a Chip and Microfluidic Devices (a.k.a., Microfluidics). Available online: https://www.linkedin.com/grp/post/713657-6080102873197264898 (accessed on 21 January 2016).
© 2016 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruffert, C. Magnetic Bead—Magic Bullet. Micromachines 2016, 7, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020021
Ruffert C. Magnetic Bead—Magic Bullet. Micromachines. 2016; 7(2):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuffert, Christine. 2016. "Magnetic Bead—Magic Bullet" Micromachines 7, no. 2: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020021
APA StyleRuffert, C. (2016). Magnetic Bead—Magic Bullet. Micromachines, 7(2), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7020021





