A Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
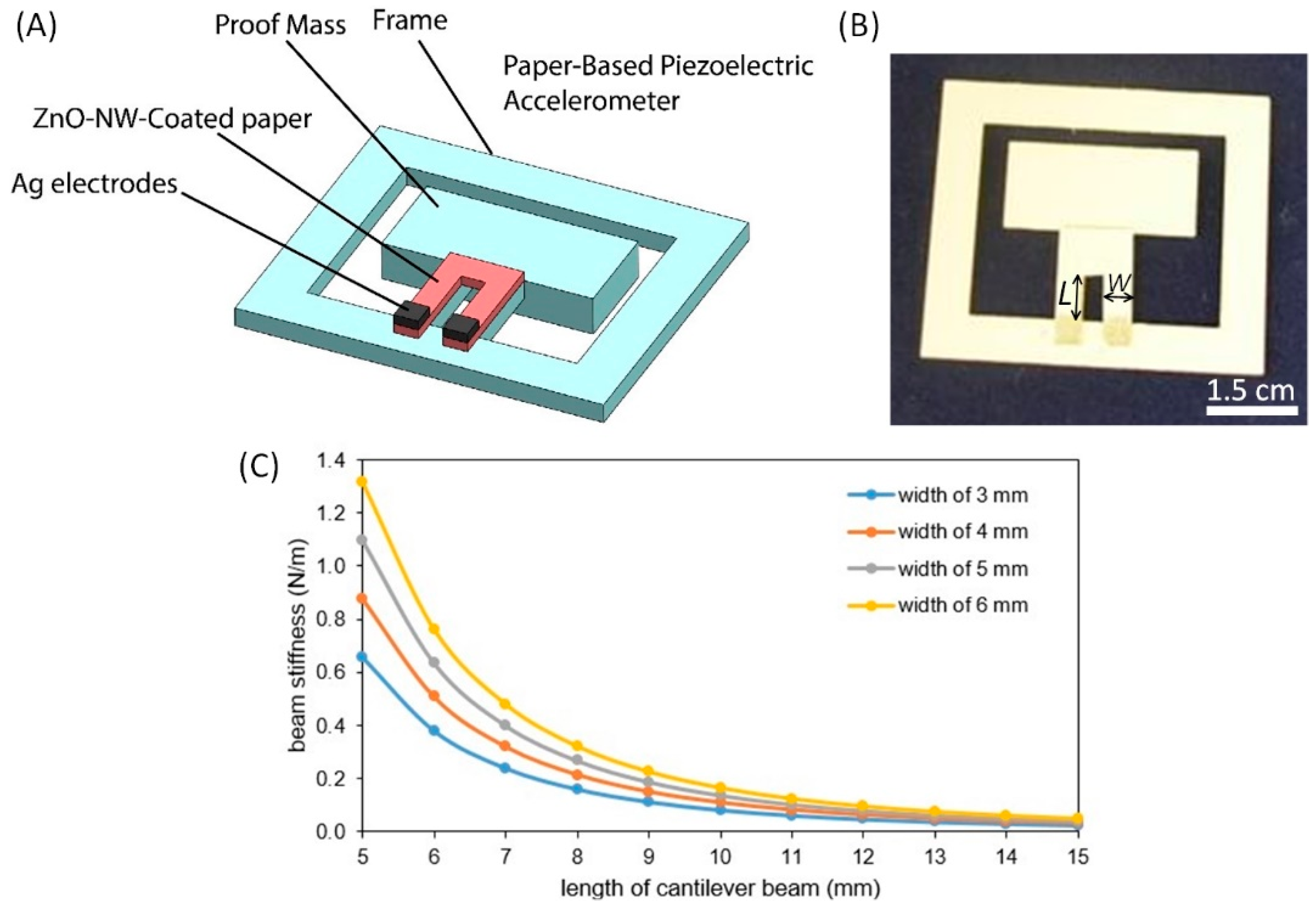
2.1. Design of the Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer
2.2. Hydrothermal Growth of ZnO NWs on Cellulose Papers
2.3. Fabrication of the Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer
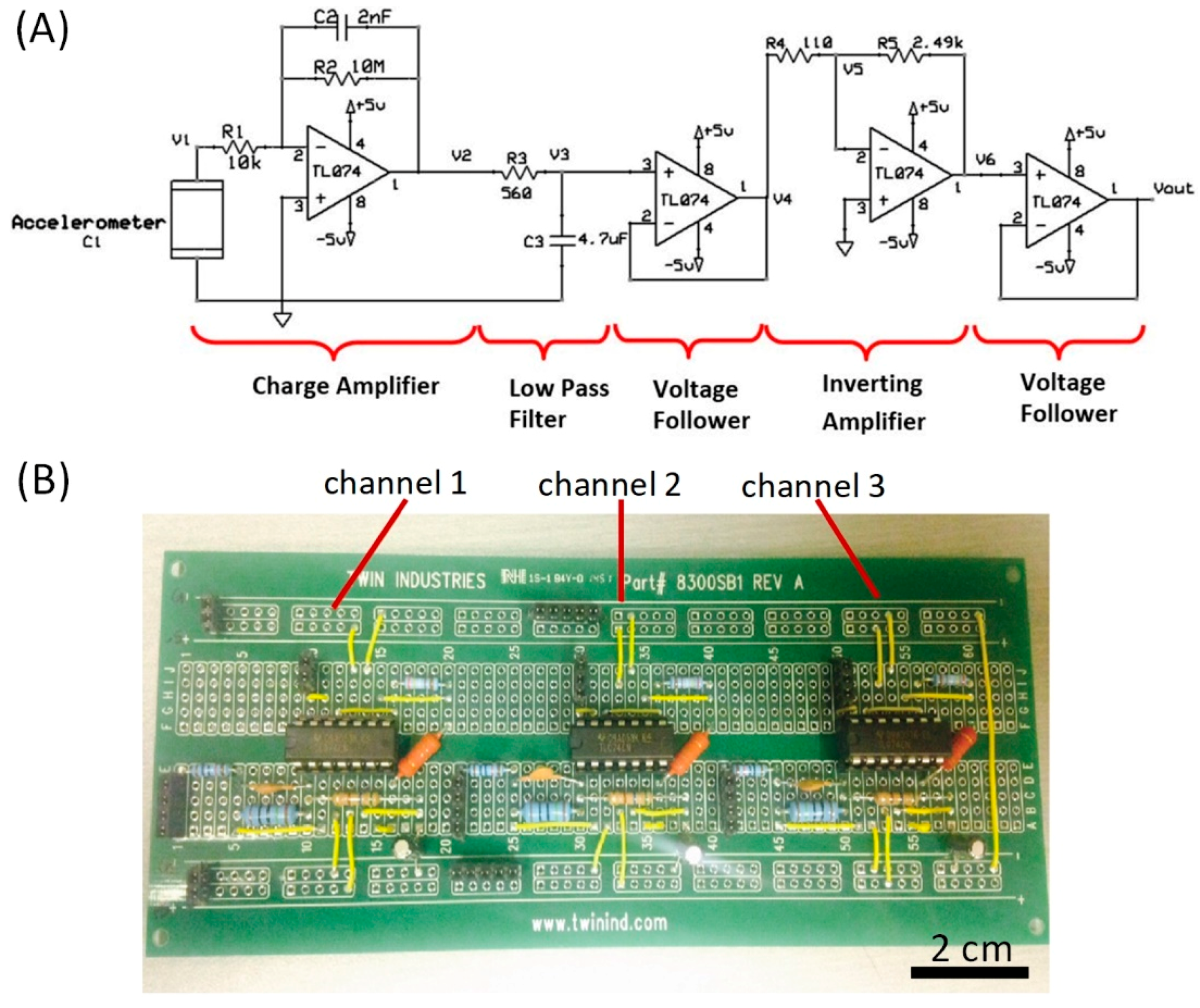
2.4. Design of the Charge Amplifier Circuit
3. Results
3.1. Quality Assessment of ZnO NWs Grown on Paper
3.2. Frequency Response Testing of the Paper-Based Accelerometer
3.3. Comparison with Commercial MEMS Accelerometer
3.4. Sensitivity Measurement of the Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lakin, K.M.; Kline, G.R.; McCarron, K.T. High-Q microwave acoustic resonators and filters. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1993, 41, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.; Park, Y.; Ha, B.; Kim, C.; Shin, J.; Yun, S.; Pak, J.; Park, G.; Song, I. Monolithic 1-chip FBAR duplexer for W-CDMA handsets. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 143, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalzik, M.; Wendler, J.; Rabe, J.; Buttgenbach, S.; Bilitewski, U.B. Development and application of a miniaturised quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) as immunosensor for bone morphogenetic protein-2. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 105, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, P.; Allara, D.; Tadigadapa, S. Characterization of viscoelastic properties of adsorbed biomolecules and biomolecular assemblies with high frequency micromachined quartz resonators. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 142, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.S.; Lee, H.M.; Kuo, C.T.; Gwo, S. Immobilization of DNA-Au nanoparticles on aminosilane-functionalized aluminum nitride epitaxial films for surface acoustic wave sensing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 163106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiculescu, I.; Nordin, A.N. Acoustic wave based MEMS devices for biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 33, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVoe, D.L.; Pisano, A.P. Surface micromachined piezoelectric accelerometers (piXLs). J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2001, 10, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; Tan, W.; Kim, E.S.; Loeb, G.E. Single- and triaxis piezoelectric-bimorph accelerometers. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi, S.; Kumagai, S.; Yoshikawa, D.; Isono, Y. Surface micromachined accelerometer using ferroelectric substrate. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 139, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.P.; Wolf, R.A.; Wang, Y.; Deng, K.K.; Zou, L.C.; Davis, R.J.; Trolier-McKinstry, S. Design, fabrication and measurement of high-sensitivity piezoelectric microelectromechanical systems accelerometers. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2003, 12, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, B.; Calame, F.; Muralt, P. Piezoelectric micromachined ultrasonic transducers with thick PZT sol gel films. J. Electroceram. 2007, 19, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percin, G.; Atalar, A.; Degertekin, F.L.; Khuri-Yakub, B.T. Micromachined two-dimensional array piezoelectrically actuated transducers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 1397–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobjörk, D.; Österbacka, R. Paper electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1935–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liu, X. Flexible physical sensors made from paper substrates integrated with zinc oxide nanostructures. Flex. Print. Electron. 2017, 2, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berggren, M.; Nilsson, D.; Robinson, N.D. Organic materials for printed electronics. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.; Lim, N.; Lim, C.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.; Kang, H.; Jung, K.; Leonard, A.D.; et al. All-printed and roll-to-roll-printable 13.56-MHZ-operated 1-bit RF tag on plastic foils. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2010, 57, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Akram, M.S.; Lowe, C.R. Paper-based microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 2210–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, X. A microfluidic paper-based origami nanobiosensor for label-free, ultrasensitive immunoassays. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X. A paper-based microfluidic biosensor integrating zinc oxide nanowires for electrochemical glucose detection. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2015, 1, 15014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mwangi, M.; Li, X.; O’Brien, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Paper-based piezoresistive mems sensors. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.-H.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X. Paper-based piezoelectric touch pads with hydrothermally grown zinc oxide nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22004–22012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, G.; Frazier, E.J.; Subramanian, V. Printed unmanned aerial vehicles using paper-based electroactive polymer actuators and organic ion gel transistors. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2016, 2, 16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, R.; Nathan, A.; Barros, R.; Pereira, L.; Barquinha, P.; Correia, N.; Costa, R.; Ahnood, A.; Ferreira, I.; Fortunato, E. Complementary metal oxide semiconductor technology with and on paper. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4491–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiemann, S.; Sachnov, S.J.; Pettersson, F.; Bollström, R.; Österbacka, R.; Wasserscheid, P.; Zaumseil, J. Cellulose-based ionogels for paper electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.Y.; Hu, L.B.; Wu, H.; Xie, X.; Cui, Y. Paper supercapacitors by a solvent-free drawing method. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3368–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.Y.; Xiao, X.; Ding, T.P.; Zhong, J.W.; Zhang, X.H.; Shen, Y.; Hu, B.; Huang, Y.H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.L. Paper-based supercapacitors for self-powered nanosystems. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4934–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.; Steckl, A.J. Three-color electrowetting display device for electronic paper. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 023514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, E.F.; Steckl, A.J. Improved performance of OLEDs on cellulose/epoxy substrate using adenine as a hole injection layer. ACS Photonics 2015, 2, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gullapalli, H.; Balakrishnan, K.; Botello-Mendez, A.; Vajtai, R.; Terrones, M.; Ajayan, P.M. Flexible ZnO-cellulose nanocomposite for multisource energy conversion. Small 2011, 7, 2173–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.B.; Choi, J.W.; Yang, Y.; Jeong, S.; La Mantia, F.; Cui, L.F.; Cui, Y. Highly conductive paper for energy-storage devices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21490–21494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unander, T.; Nilsson, H.E. Characterization of printed moisture sensors in packaging surveillance applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Hu, L.Z.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, L.N.; Wang, B.; Ji, J.Y.; Liu, G.Q.; Liu, X.; Lin, J.F.; et al. Flexible piezoelectric nanogenerators based on ZnO nanorods grown on common paper substrates. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6568–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.Z.; Zhong, J.W.; Hu, B.; Hu, Q.Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.L. A paper-based nanogenerator as a power source and active sensor. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1779–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullapalli, H.; Vemuru, V.S.M.; Kumar, A.; Botello-Mendez, A.; Vajtai, R.; Terrones, M.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Ajayan, P.M. Flexible piezoelectric ZnO-paper nanocomposite strain sensor. Small 2010, 6, 1641–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadeva, S.K.; Walus, K.; Stoeber, B. Flexible and robust hybrid paper with a large piezoelectric coefficient. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 1448–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, A.D.; Chan, L.; Kalb, W.B.; Liu, X.; Mazzeo, B.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Capacitive, Paper-Based Accelerometers and Touch Sensors. U.S. Patent Application 14/258,166, 22 April 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Lu, A.; Liu, X. Controllable hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanowires on cellulose paper for flexible sensors and electronics. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 6100–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.K.; Shin, P.; Cao, L.L.; Gao, D. Preferential growth of long zno nanowire array and its application in dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.J.; Li, X.M.; Zhuge, F.W.; Gan, X.Y.; Gao, X.D.; He, W.Z.; Park, S.J.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, Y.H. Solution-derived 40 mu m vertically aligned ZnO nanowire arrays as photoelectrodes in dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 195602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inman, D.J. Engineering Vibration, 3rd ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008; p. xiv. 669p. [Google Scholar]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.-H.; Song, P.; Li, X.; Ru, C.; Ferrari, G.; Balasubramanian, P.; Amabili, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X. A Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer. Micromachines 2018, 9, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9010019
Wang Y-H, Song P, Li X, Ru C, Ferrari G, Balasubramanian P, Amabili M, Sun Y, Liu X. A Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer. Micromachines. 2018; 9(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu-Hsuan, Pengfei Song, Xiao Li, Changhai Ru, Giovanni Ferrari, Prabakaran Balasubramanian, Marco Amabili, Yu Sun, and Xinyu Liu. 2018. "A Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer" Micromachines 9, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9010019
APA StyleWang, Y.-H., Song, P., Li, X., Ru, C., Ferrari, G., Balasubramanian, P., Amabili, M., Sun, Y., & Liu, X. (2018). A Paper-Based Piezoelectric Accelerometer. Micromachines, 9(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9010019





