Energy-Efficient Cluster Head Selection in Wireless Sensor Networks Using an Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Contributions
Motivation
- (a)
- Rigorous literature study of algorithms and protocols are conducted that enhances the WSN lifetime with an optimal CH selection and energy-efficient techniques.
- (b)
- Study of the futuristic algorithms proposed based on the GWO algorithm for CH selection and optimal energy utilization in WSNs.
- (c)
- Proposed a novel method based on an improved GWO algorithm, distance between BS and SN for CH selection, and efficient energy utilization.
- (d)
- Defined the fitness function based on the IGWO algorithm that considers residual energy at SN to avoid randomness in CH selection for energy-efficient data deliveries.
- (e)
- Compared the performance of the proposed algorithm with existing GWO-based algorithms in terms of the number of dead nodes, number of operating rounds, energy consumption, and the average throughput.
- (f)
- Proved that the proposed EECHIGWO algorithm outperforms the existing GWO-based algorithms in WSNs.
3. Literature Survey
3.1. Energy Efficient Techniques for WSNs
3.2. Energy Aware Clustering and Performance Optimization Using Metahueristic Approach
3.3. Role of GWO Algorithm in Optimal CH Selection
3.4. Enhanced Versions of GWO Algorithms for WSNs
| Protocol | Nodes Type | Inter-Cluster Topology | Need of Energy Awareness | CH Selection | Heuristic Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSMOECHS [24] | Homogeneous | Single-hop | No | Probabilistic | No |
| GWO-C [43] | Homogeneous | Single-hop | No | Probabilistic | Yes |
| GWO-based clustering [44] | Homogeneous | Dual-hop | No | Probabilistic | Yes |
| GWO [47] | Heterogeneous | Multi-hop | Yes | Probabilistic | Yes |
| HGWCSOA [48] | Homogeneous | Single-hop | Yes | Probabilistic | Yes |
| QCGWO [54] | Homogeneous | Not applicable | No | Not applicable | Yes |
| BGWO [61] | Homogeneous | Single-hop | No | Probabilistic | Yes |
| FGWSTERP [62] | Homogeneous | Single-hop | Yes | Fuzzy based | Yes |
| LEACH-PRO [63] | Homogeneous | Single-hop | Yes | Probabilistic | No |
| HMGWO [64] | Heterogeneous | Single-hop | Yes | Probabilistic | Yes |
| FIGWO [65] | Homogeneous | Single-hop | Yes | Deterministic | Yes |
4. Methodology
- 1.
- The SNs are randomly deployed in a two-dimensional geographical space.
- 2.
- The BS is located at the center of the network terrain and there is multi-hop communication from CHs to the BS.
- 3.
- The SNs are divided into approximately equal groups, and they are randomly distributed within the group.
- 4.
- The SNs are homogeneous within the group and their mobility is limited to 0.2 m/s.
- 5.
- BS and the nodes who participate in multi-path communication only will have uninterrupted power supply.
- 6.
- BS executes the algorithm for CH selection and also it collects the aggregated data from all CHs.
- efs → energy dissipation coefficient of free-space attenuation model
- n → packet length
- emp → energy dissipation coefficient of multipath attenuation model
- d → distance between sender and receiving node
- d0 = → threshold distance
- Eelec → energy needed to transmit/receive 1-bit data.
- ER(k − 1) → total remaining energy at (k − 1)th round
- CHnum(k) → number of CHs in the kth round
- SNalive (k) → total number of alive nodes in the kth round
- ECH(l) → energy consumed by lth CH
- ECH(m) → energy consumed by mth SN
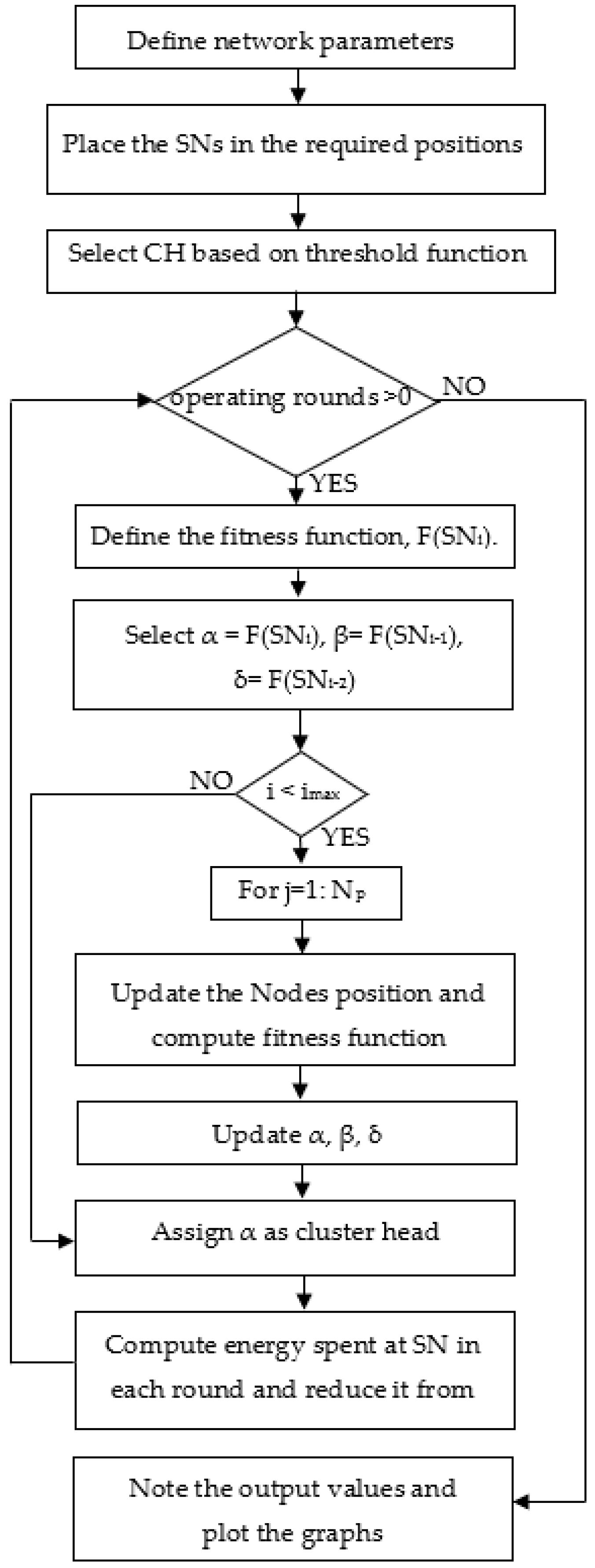
Proposed EECHIGWO Algorithm
- Einital → initial energy of SN,
- Eresidual → residual energy at SN after each round,
- d → distance between SN and BS,
- dmax → maximum distance between SN and BS,
- dmin → minimum distance between SN and BS.
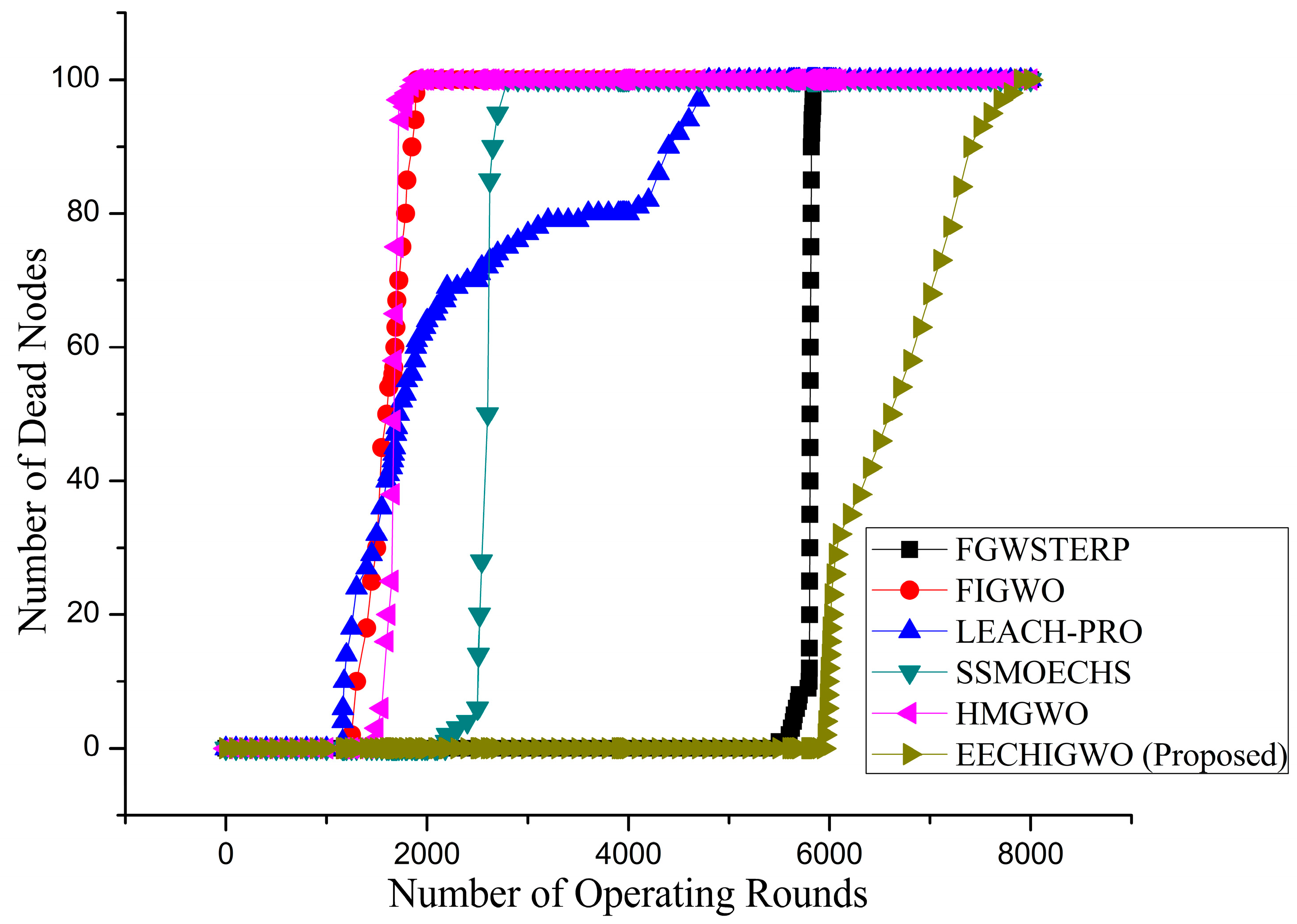
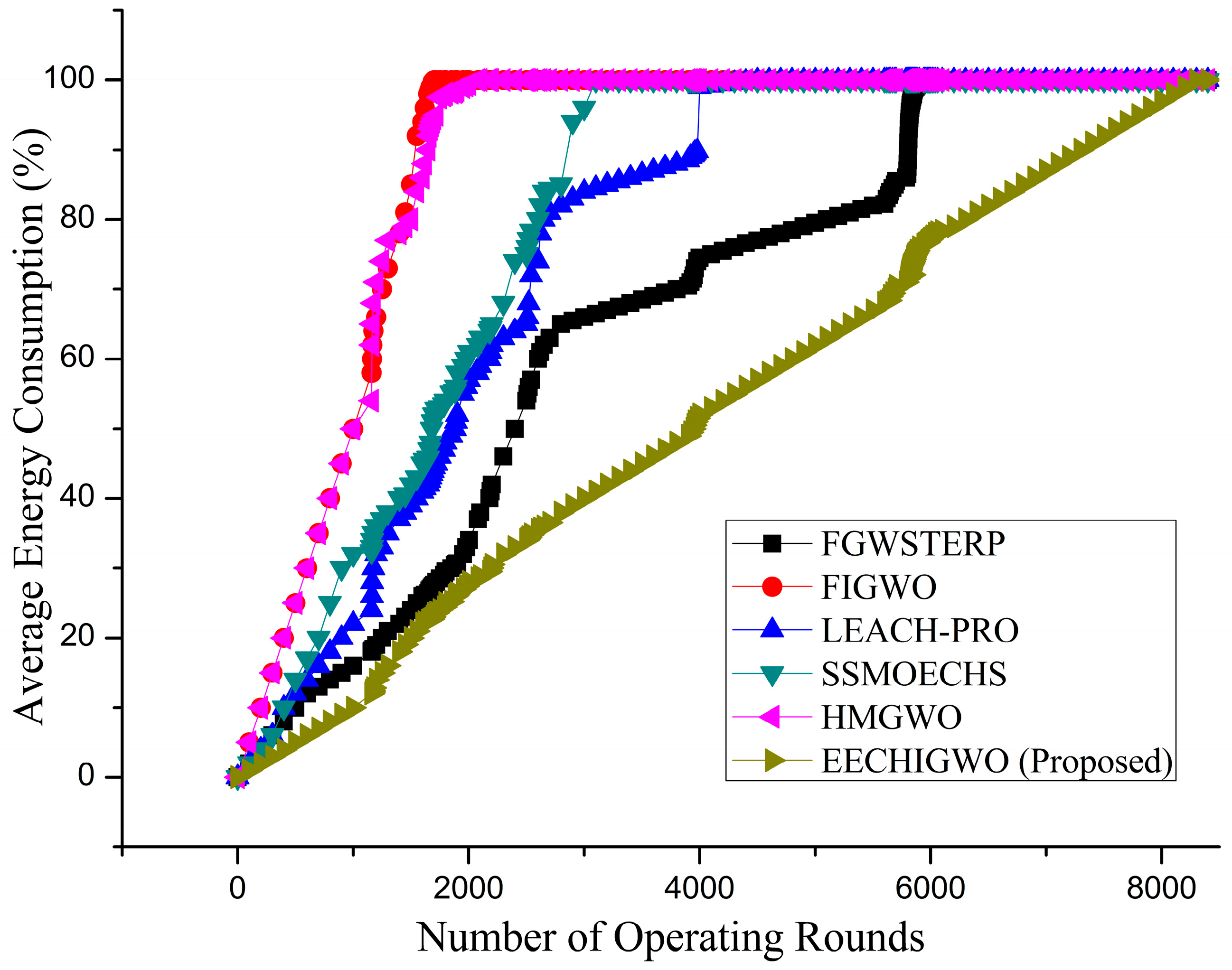
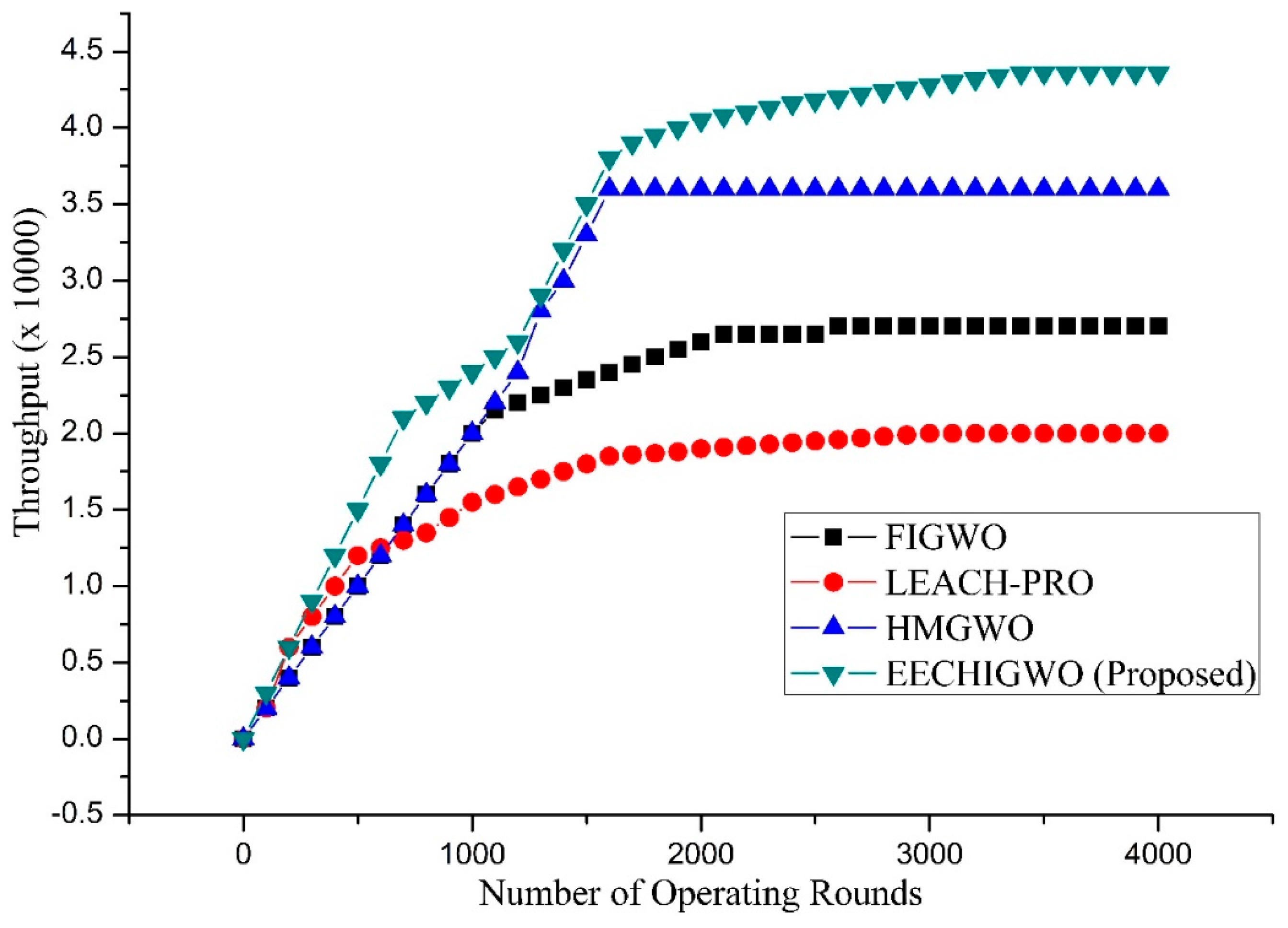
5. Results and Discussions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| ABC | artificial bee colony optimization |
| ACO | ant colony optimization |
| AFS | artificial Fish Schooling |
| BA | bat algorithm |
| BGWO | behavior-based grey wolf optimizer |
| BS | base station |
| CDMA | code division multiple access |
| CDS | connected dominating set |
| CH | cluster head |
| COA | chimp optimizer algorithm |
| CSA | cuckoo search algorithm |
| CSO | crow search optimization |
| DEEC | distributed energy efficient clustering |
| DE | differential evolution |
| DLH | dimension learning-based hunting |
| EP | evolutionary programming |
| ES | evolution strategy |
| FCGWO | firefly cyclic grey wolf optimization |
| FFO | firefly optimization |
| FGWSTERP | fuzzy GWO based stable threshold sensitive energy efficient cluster based routing protocol |
| FIGWO | fitness value based Improved GWO |
| FND | first node death |
| GA | genetic algorithm |
| GOA | grasshopper optimization algorithm |
| GSA | gravitational search algorithm |
| GWO | grey wolf optimization |
| GWO-C | GWO with clustering |
| HGWCSOA | hybrid grey wolf and crow search optimization algorithm |
| HMGWO | modified GWO for heterogeneous WSN |
| HND | half node death |
| HWGWO | hybrid whale and grey wolf optimization |
| IDS | intrusion detection system |
| IGWO | improved grey wolf optimization |
| IIoT | industrial IoT |
| IoE | internet of everything |
| IoT | internet of things |
| LEACH | low-energy adaptive clustering hierarchy |
| LND | last node death |
| MBA | modified bat algorithm |
| MFO | moth-flame optimization |
| MLHP | multilayer hierarchical routing protocol |
| MLP | multi-layer perceptron |
| PRO | probabilistic cluster head selection |
| PSO | particle Swarm Optimization |
| QCGWO | quantum clone grey wolf optimization |
| SA | simulated annealing |
| SEP | stable election protocol |
| SMO | spider Monkey Optimization |
| SN | sensor node |
| SSMOECHS | sampling based spider monkey optimization and energy efficient cluster head selection |
| WOA | whale optimization algorithm |
| WSN | wireless sensor network |
References
- Al-Baz, A.; El-Sayed, A. A new Algorithm for Cluster Head Selection in LEACH protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2018, 31, e3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, S.E.; Javidan, R. A new energy aware cluster head selection for LEACH in wireless sensor networks. IET Wirel. Sens. Syst. 2021, 11, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, A.; Halder, S.; Das, S.K. Distributed on-demand clustering algorithm for lifetime optimization in wireless sensor networks. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 141, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arghavani, M.; Esmaeili, M.; Maryam, E.; Mohseni, F.; Arghavani, A. Optimal energy aware clustering in circular wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2017, 65, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhongdong, H.; Hualin, W.; Zhendong, W. Energy balanced adaptive clustering routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Comput. 2019, 16, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedr, A.M.; Pravija, R.P.V.; Ali, A.A. An Energy-Efficient Data Acquisition Technique for Hierarchical Cluster-Based Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Wirel. Mob. Netw. Ubiquitous Comput. Dependable Appl. 2020, 11, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhilesh, P.; Rajat, K.S. EEHCHR: Energy Efficient Hybrid Clustering and Hierarchical Routing for Wireless Sensor Networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2021, 123, 102692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, J.S.; Basar, A. QoS optimization of energy efficient routing in IoT wireless sensor networks. J. ISMAC 2019, 1, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolidakis, S.A.; Kandris, D.; Vergados, D.D.; Douligeris, C. Energy Efficient Routing in Wireless Sensor Networks Through Balanced Clustering. Algorithms 2013, 6, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, Y.H.; Julie, E.G.; Balaji, S.; Ayyasamy, A. Energy Aware Clustering Scheme in Wireless Sensor Network Using Neuro-Fuzzy Approach. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 95, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet, M.; Naji, H. An energy efficient multi-level route-aware clustering algorithm for wireless sensor networks: A self-organized approach. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2016, 56, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Yang, S.; Li, L.; Gao, J. Research on routing optimization of WSNs based on improved LEACH protocol. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2019, 194, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manshahia, M.S. Grey Wolf Algorithm based Energy-Efficient Data Transmission in Internet of Things. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2019, 160, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Al-Betar, M.A. Grey wolf optimizer: A review of recent variants and applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.M.; Amgoth, T.; Pandey, H.M. Enhancing the Network Performance of Wireless Sensor Networks on Meta-heuristic Approach: Grey Wolf Optimization. In Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Choudhary, A., Agrawal, A.P., Logeswaran, R., Unhelkar, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 778, pp. 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.; Baliyan, N. Grey wolf optimization with fuzzy logic for energy-efficient communication in wireless sensor network-based Internet of Things scenario. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, 34, e4981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Sharma, S. Glowworm Swarm Optimization (GSO) based energy efficient clustered target coverage routing in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs). Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabinian, Z.; Ayatollahitafti, V.; Safdarkhani, H. Energy Optimization in Wireless Sensor Networks Using Grey Wolf Optimizer. J. Soft Comput. Decis. Support Syst. 2018, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal, K.; Anand, V. A QoS aware optimal node deployment in wireless sensor network using Grey wolf optimization approach for IoT applications. Telecommun. Syst. 2021, 78, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.; Fekher, K.; Abbas, B.; Abderrezak, R.; Kaddachi, M.L.; Atri, M. A new fuzzy logic based node localization mechanism for Wireless Sensor Networks. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 93, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, A.; Indu, S.; Gupta, D. A Grey Wolf Optimization Approach for Improving the Performance of Wireless Sensor Networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2019, 106, 1429–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, M.; Senturk, A. A New Energy-Aware Cluster Head Selection Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022, 122, 2235–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaya Pratha, S.; Asanambigai, V.; Mugunthan, S.R. Grey Wolf Optimization Based Energy Efficiency Management System for Wireless Sensor Networks. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-G.; Chim, S.; Park, H.-H. Energy-Efficient Cluster-Head Selection for Wireless Sensor Networks Using Sampling-Based Spider Monkey Optimization. Sensors 2019, 19, 5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraimurugan, S.; Avudaiammal, R. Energy Efficient Nodes Clustering and Routing Using Multi-Objective Spider Monkey Optimization Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Network. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, R.S.; Sangwan, S.; Prakash, S. Hybrid WGWO: Whale grey wolf optimization-based novel energy-efficient clustering for EH-WSNs. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2020, 101, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; You, H.; Wang, S.; Cao, L. Improved whale optimization algorithm and its application in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2021, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, D.; Qureshi, M.H.W.; Pincha, P.; Srivastava, P.; Agarwal, S.; Tiwari; Pandey, S.V. GWO-C: Grey wolf optimizer-based clustering scheme for WSNs. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2020, 33, e4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorpade, S.N.; Zennaro, M.; Chaudhari, B.S. Binary grey wolf optimisation-based topology control for WSNs. IET Wirel. Sens. Syst. 2019, 9, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preeti, K.R.; Singh, D. Dimension learning based chimp optimizer for energy efficient wireless sensor networks. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, U.E.; Kuppusamy, L. A hybrid approach to energy efficient clustering and routing in wireless sensor networks. Evol. Intell. 2021, 15, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackey, S.H.; Ansere, J.A.; Anajemba, J.H.; Kamal, M.; Iwendi, C. Energy Efficient Clustering Based Routing Technique in WSN using Brain Storm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), Peshawar, Pakistan, 2–3 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Tariq, U.U.; Hussain, M.; Lu, L.; Panneerselvam, J.; Zhai, X. ARSH-FATI a Novel Metaheuristic for Cluster Head Selection in Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Syst. J. 2021, 15, 2386–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.A. Lewis, Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albina, K.; Lee, S.G. Hybrid Stochastic Exploration Using Grey Wolf Optimizer and Coordinated Multi-Robot Exploration Algorithms. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 14246–14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alok, K.; Lekhraj; Safalata, S.; Anoj, K. Grey wolf optimizer and other metaheuristic optimization techniques with image processing as their applications: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1136, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, P.; Kaarthick, B. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Oppositional based Laplacian grey wolf optimization algorithm with SVM for data mining in intrusion detection system. J. Ambient. Intel. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 3589–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaimaa, K.; Yahlal, M.; Boudıa, M.A.; Amıne, A.; Hamou, R.M.; Siham, K. Intrusion Detection System with Grey Wolf Optimizer (GWO). Int. J. Inf. Appl. Math. 2019, 2, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Alzaqebah, A.; Aljarah, I.; Al-Kadi, O.; Damaševičius, R. A Modified Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm for an Intrusion Detection System. Mathematics 2022, 10, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, N.; Karthikeyan, T.; Praghash, K. An Improved Task Allocation Scheme in Serverless Computing Using Gray Wolf Optimization (GWO) Based Reinforcement Learning (RIL) Approach. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 117, 2403–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeniffer, J.T.; Chandrasekar, A. Optimal hybrid heat transfer search and grey wolf optimization-based homomorphic encryption model to assure security in cloud-based IoT environment. Peer to Peer Netw. Appl. 2022, 15, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, R.; Rajagopalan, S.P.; Dhandapani, G. Hybridizing Gray Wolf Optimization (GWO) with Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm (GOA) for text feature selection and clustering. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 96, 106651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharawi, M.; Emary, E. Impact of grey wolf optimization on WSN cluster formation and lifetime expansion. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence, Doha, Qatar, 4–6 February 2017; pp. 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, S.M.M.H.; Mohajer, P.A.A.; Mazinani, S.M. Energy-Efficient Routing in WSN: A Centralized Cluster-Based Approach via Grey Wolf Optimizer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 170019–170031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, K.; Rajakumar, R.; Dinesh, K.; Rajkumar, Y.; Latchoumi, T.P.; Kadry, S.; Lim, S. An energy-efficient cluster head selection in wireless sensor network using grey wolf optimization algorithm. TELKOMNIKA Telecommun. Comput. Electron. Control 2020, 18, 2822–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Liang, W. Node coverage optimization algorithm for wireless sensor networks based on improved grey wolf optimizer. J. Algorithms Comput. Technol. 2019, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amruta, L.; Damodar, R.E.; Venkatanareshbabu, K. Energy efficient load balancing approach for avoiding energy hole problem in WSN using Grey Wolf Optimizer with novel fitness function. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 84, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.; Sahayaraj, J.M.; Senthilkumar, S.; Alex, D.S. A Hybrid Grey Wolf and Crow Search Optimization Algorithm-Based Optimal Cluster Head Selection Scheme for Wireless Sensor Networks. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 113, 905–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aboody, N.A.; Al-Raweshidy, H.S. Grey wolf optimization-based energy-efficient routing protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Symposium on Computational and Business Intelligence, Olten, Switzerland, 5–7 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cao, L.; Yue, Y.; Cai, Y.; Hang, B. A Novel Coverage Optimization Strategy Based on Grey Wolf Algorithm Optimized by Simulated Annealing for Wireless Sensor Networks. Comput. Intel. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipeng, W.; Xiaoping, Y.; Xingqiao, Y.; Zhihong, Q. A Virtual Force Algorithm-Lévy-Embedded Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Network Coverage Optimization. Sensors 2019, 19, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, I.A.; Alsaif, O.I.; Yahya, M.A. Optimal distributed decision in wireless sensor network using gray wolf optimization. IAES Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2020, 9, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajakumar, R.; Amudhavel, J.; Dhavachelvan, P.; Vengattaraman, T. GWO-LPWSN: Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm for Node Localization Problem in Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2017, 2017, 7348141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jing, X.; Li, C.; Qin, H.; Jie, Z. Sensor Duty Cycle for Prolonging Network Lifetime Using Quantum Clone Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm in Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Sens. 2021, 2021, 5511745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Gao, H.; Wang, Z.; Du, C. Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm and Application. Sensors 2022, 22, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J. An Improved Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm to Solve Engineering Problems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. Weighted Grey Wolf Optimizer with Improved Convergence rate in Training multi-layer Perception to solve Classification Problems. Jordanian J. Computers Inf. Technol. 2021, 7, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Shokooh, T.; Seyedali, M. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaldin, M.; Otair, M.; Abualigah, L. Improved binary gray wolf optimizer and SVM for intrusion detection system in wireless sensor networks. J. Ambient. Int. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 1559–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Li, S.X. An Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer Based on Differential Evolution and Elimination Mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Hsu, H.Y.; Pan, J.S. Behavior-based grey wolf optimizer for a wireless sensor network deployment problem. Intl. J. Ad Hoc Ubiquitous Comput. 2022, 39, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, N.; Singh, U.; Salgotra, R.; Sohi, B.S. An energy efficient stable clustering approach using fuzzy extended grey wolf optimization algorithm for WSNs. Wirel. Netw. 2019, 25, 5151–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousif, Z.; Hussain, I.; Djahel, S.; Hadjadj-Aoul, Y. A Novel Energy-Efficient Clustering Algorithm for More Sustainable Wireless Sensor Networks Enabled Smart Cities Applications. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2021, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ren, S.; Quan, H.; Gao, Q. Routing Protocol for Heterogeneous Wireless Sensor Networks Based on a Modified Grey Wolf Optimizer. Sensors 2020, 20, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, H.; Aleksic, S.; Gao, Q. Energy-Efficient Routing Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks Based on Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2018, 12, 2644–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Network Terrain | 100 m2 |
| Network size | 100 |
| Initial Energy (E0) | 1 J |
| Probability to become CH (P) | 0.1 |
| Number of CHs | P × 100 |
| Efs, Eelec, Eamp | 10 pJ/bit/m2, 50 nJ/bit, 0.0013 pJ/bit/m4 |
| Dcritical, Dmax | 20 m, 100 m |
| Data Packet size | 500-Bytes |
| BS Position | (50, 50) |
| Algorithm | FND | FND Improvement (%) | HND | HND Improvement (%) | LND | LND Improvement (%) | Overall Improvement (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSMOECHS [24] | 2190 | 171.23 | 2600 | 154 | 2798 | 182.63 | 169.29 |
| FGWSTERP [62] | 5500 | 8 | 5807 | 13.72 | 5841 | 35.38 | 19.03 |
| LEACH-PRO [63] | 1159 | 412.5 | 1720 | 283.95 | 4800 | 64.75 | 253.73 |
| HMGWO [64] | 1450 | 309.65 | 1675 | 294.27 | 1884 | 319.75 | 307.89 |
| FIGWO [65] | 1248 | 375.96 | 1612 | 309.68 | 1906 | 314.9 | 333.51 |
| EECHIGWO [Proposed] | 5940 | ---- | 6604 | ---- | 7908 | ---- | ---- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rami Reddy, M.; Ravi Chandra, M.L.; Venkatramana, P.; Dilli, R. Energy-Efficient Cluster Head Selection in Wireless Sensor Networks Using an Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm. Computers 2023, 12, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers12020035
Rami Reddy M, Ravi Chandra ML, Venkatramana P, Dilli R. Energy-Efficient Cluster Head Selection in Wireless Sensor Networks Using an Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm. Computers. 2023; 12(2):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers12020035
Chicago/Turabian StyleRami Reddy, Mandli, M. L. Ravi Chandra, P. Venkatramana, and Ravilla Dilli. 2023. "Energy-Efficient Cluster Head Selection in Wireless Sensor Networks Using an Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm" Computers 12, no. 2: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers12020035
APA StyleRami Reddy, M., Ravi Chandra, M. L., Venkatramana, P., & Dilli, R. (2023). Energy-Efficient Cluster Head Selection in Wireless Sensor Networks Using an Improved Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm. Computers, 12(2), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers12020035






