Journal Description
Computers
Computers
is an international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal of computer science, including computer and network architecture and computer–human interaction as its main foci, published monthly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), dblp, Inspec, Ei Compendex, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q2 (Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications) / CiteScore - Q1 (Computer Science (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 16.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Journal Cluster of Artificial Intelligence: AI, AI in Medicine, Algorithms, BDCC, MAKE, MTI, Stats, Virtual Worlds and Computers.
Impact Factor:
4.2 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
3.5 (2024)
Latest Articles
Digital Transformation in Design Education: Exploring the Challenges and Opportunities in Jordanian Higher Education
Computers 2025, 14(12), 535; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120535 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
In recent years, design education has experienced major changes as the number of digital tools and technologies has rapidly developed. Many design programs encounter difficulties in integrating these innovations, despite their potential benefits. In this research, the adoption of digital tools in the
[...] Read more.
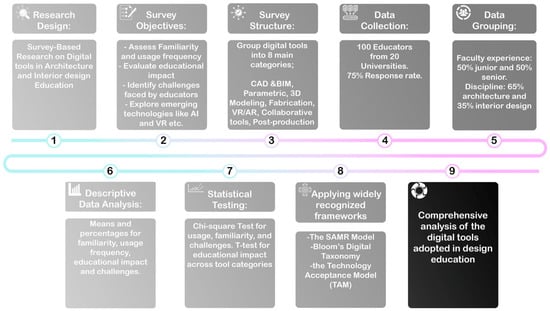
In recent years, design education has experienced major changes as the number of digital tools and technologies has rapidly developed. Many design programs encounter difficulties in integrating these innovations, despite their potential benefits. In this research, the adoption of digital tools in the teaching of design in Jordanian universities is explored, focusing on the views of educators in relation to their use, the challenges associated with it, and the resultant effects on the pedagogical process. Faculty members working in various departments of design were surveyed gauging the frequency of usage of tools, their knowledge of new technologies, their perceptions of the potential results of an educational process, and the barriers that were met during the integration process. To guide the analysis, three theoretical frameworks were applied: the SAMR model of technology integration, Bloom’s Digital Taxonomy, and the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). The findings reveal that while traditional tools like AutoCAD and Revit are predominantly used at the Substitution and Augmentation stages, emerging technologies such as VR/AR and AI show potential for higher-order integration. However, barriers related to ease of use and perceived usefulness limit their broader adoption. The study contributes to the understanding of digital transformation in design education and provides insights into the pedagogical implications for future curriculum development. The research highlights the need to invest more in the professional development of educators and to work more closely with the technological industry. The proposed implications of these insights concern the restructuring of design education to reflect the needs of the digital age and provide approaches to overcoming obstacles to the successful adoption of technology in teaching environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Transformative Approaches in Education: Harnessing AI, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality for Innovative Teaching and Learning)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Generation of Natural-Language Explanations for Static-Analysis Warnings Using Single- and Multi-Objective Optimization
by
Ivan Malashin
Computers 2025, 14(12), 534; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120534 - 5 Dec 2025
Abstract
Explanations for static-analysis warnings assist developers in understanding potential code issues. An end-to-end pipeline was implemented to generate natural-language explanations, evaluated on 5183 warning–explanation pairs from Java repositories, including a manually validated gold subset of 1176 examples for faithfulness assessment. Explanations were produced
[...] Read more.
Explanations for static-analysis warnings assist developers in understanding potential code issues. An end-to-end pipeline was implemented to generate natural-language explanations, evaluated on 5183 warning–explanation pairs from Java repositories, including a manually validated gold subset of 1176 examples for faithfulness assessment. Explanations were produced by a transformer-based encoder–decoder model (CodeT5) conditioned on warning types, contextual code snippets, and static-analysis evidence. Initial experiments employed single-objective optimization for hyperparameters (using a genetic algorithm with dynamic search-space correction, which adaptively adjusted search bounds based on the evolving distribution of candidate solutions, clustering promising regions, and pruning unproductive ones), but this approach enforced a fixed faithfulness–fluency trade-off; therefore, a multi-objective evolutionary algorithm (NSGA-II) was adopted to jointly optimize both criteria. Pareto-optimal configurations improved normalized faithfulness by up to 12% and textual quality by 5–8% compared to baseline CodeT5 settings, with batch sizes of 10–21, learning rates
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Machine Learning and Statistical Learning with Applications 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Towards a Framework for Covert Communications for Mitigating Traffic Detection Attacks
by
Abdallah Farraj
Computers 2025, 14(12), 533; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120533 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
This article addresses a critical security challenge in Internet of Things (IoT) systems, which are vulnerable to traffic detection attacks due to their reliance on shared wireless communication channels. We propose a novel cooperative covert transmission strategy to enhance the security of IoT
[...] Read more.
This article addresses a critical security challenge in Internet of Things (IoT) systems, which are vulnerable to traffic detection attacks due to their reliance on shared wireless communication channels. We propose a novel cooperative covert transmission strategy to enhance the security of IoT communications against these attacks through the implementation of physical-layer security mechanisms. Inspired by zero-forcing precoding techniques, the proposed approach enables cooperation between different IoT devices in the system to increase the likelihood of adversaries making incorrect conclusions about the communication activity of the targeted IoT device. The proposed covert communication strategy complements traditional security measures, provides a scalable solution, and is suitable for resource-constrained IoT environments. The numerical results in this article demonstrate significant improvements in protecting communications against traffic detection attacks, which contributes to the overall security and privacy of IoT systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Internet of Things—Current Trends, Applications, and Future Challenges (2nd Edition))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Directional Perception in Game-Based Dyslexia Risk Screening: A Mouse-Tracking Analysis
by
Natsinee Tangsiripaiboon, Sakgasit Ramingwong, Kenneth Cosh, Narissara Eiamkanitchat and Lachana Ramingwong
Computers 2025, 14(12), 532; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120532 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
Dyslexia is not easily observed from outward appearance alone; differences typically emerge through learning performance and certain behavioral indicators. This study introduces the Direction Game, a computer-based task that uses mouse-tracking to capture behavioral signals related to directional perception, a common challenge among
[...] Read more.
Dyslexia is not easily observed from outward appearance alone; differences typically emerge through learning performance and certain behavioral indicators. This study introduces the Direction Game, a computer-based task that uses mouse-tracking to capture behavioral signals related to directional perception, a common challenge among children at risk for dyslexia. The prototype consists of language-independent mini-games targeting three main types of directional confusion and was piloted with 102 primary school students. Analyses showed that concentration-related variables, particularly attentional control and visuo-motor planning, may provide more informative indicators of risk than simple accuracy scores. Machine learning models demonstrated promising classification performance relative to standardized school screening protocols. Additionally, an exploratory analysis of mouse trajectories revealed five tentative interaction profiles: hesitation, impulsivity, deliberate processing, fluent performance, and disengagement. Together, these findings highlight the potential of a simple, game-based mouse-tracking tool to support accessible and preliminary dyslexia risk assessment in classroom environments.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Game-Based Learning, Gamification in Education and Serious Games)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Advanced System for Remote Updates on ESP32-Based Devices Using Over-the-Air Update Technology
by
Lukas Formanek, Michal Kubascik, Ondrej Karpis and Peter Kolok
Computers 2025, 14(12), 531; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120531 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
Over-the-air (OTA) firmware updating has become a fundamental requirement in modern Internet of Things (IoT) deployments, where thousands of heterogeneous embedded devices operate in remote and distributed environments. Manual firmware maintenance in such systems is impractical, costly, and prone to security risks, making
[...] Read more.
Over-the-air (OTA) firmware updating has become a fundamental requirement in modern Internet of Things (IoT) deployments, where thousands of heterogeneous embedded devices operate in remote and distributed environments. Manual firmware maintenance in such systems is impractical, costly, and prone to security risks, making automated update mechanisms essential for long-term reliability and lifecycle management. This paper presents a unified OTA update architecture for ESP32-based IoT devices that integrates centralized version control and multi-protocol communication support (Wi-Fi, BLE, Zigbee, LoRa, and GSM), enabling consistent firmware distribution across heterogeneous networks. The system incorporates version-compatibility checks, rollback capability, and a server-driven release routing mechanism for development and production branches. An analytical model of timing, reliability, and energy consumption is provided, and experimental validation on a fleet of ESP32 devices demonstrates reduced update latency compared to native vendor OTA solutions, together with reliable operation under simultaneous device loads. Overall, the proposed solution provides a scalable and resilient foundation for secure OTA lifecycle management in smart-industry, remote sensing, and autonomous infrastructure applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue The Internet of Things—Current Trends, Applications, and Future Challenges (2nd Edition))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
EvalCouncil: A Committee-Based LLM Framework for Reliable and Unbiased Automated Grading
by
Catalin Anghel, Marian Viorel Craciun, Andreea Alexandra Anghel, Adina Cocu, Antonio Stefan Balau, Constantin Adrian Andrei, Calina Maier, Serban Dragosloveanu, Dana-Georgiana Nedelea and Cristian Scheau
Computers 2025, 14(12), 530; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120530 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used for rubric-based assessment, yet reliability is limited by instability, bias, and weak diagnostics. We present EvalCouncil, a committee-and-chief framework for rubric-guided grading with auditable traces and a human adjudication baseline. Our objectives are to (i) characterize
[...] Read more.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used for rubric-based assessment, yet reliability is limited by instability, bias, and weak diagnostics. We present EvalCouncil, a committee-and-chief framework for rubric-guided grading with auditable traces and a human adjudication baseline. Our objectives are to (i) characterize domain structure in Human–LLM alignment, (ii) assess robustness to concordance tolerance and panel composition, and (iii) derive a domain-adaptive audit policy grounded in dispersion and chief–panel differences. Authentic student responses from two domains–Computer Networks (CNs) and Machine Learning (ML)–are graded by multiple heterogeneous LLM evaluators using identical rubric prompts. A designated chief arbitrator operates within a tolerance band and issues the final grade. We quantify within-panel dispersion via MPAD (mean pairwise absolute deviation), measure chief–panel concordance (e.g., absolute error and bias), and compute Human–LLM deviation. Robustness is examined by sweeping the tolerance and performing leave-one-out perturbations of panel composition. All outputs and reasoning traces are stored in a graph database for full provenance. Human–LLM alignment exhibits systematic domain dependence: ML shows tighter central tendency and shorter upper tails, whereas CN displays broader dispersion with heavier upper tails and larger extreme spreads. Disagreement increases with item difficulty as captured by MPAD, concentrating misalignment on a relatively small subset of items. These patterns are stable to tolerance variation and single-grader removals. The signals support a practical triage policy: accept low-dispersion, small-gap items; apply a brief check to borderline cases; and adjudicate high-dispersion or large-gap items with targeted rubric clarification. EvalCouncil instantiates a committee-and-chief, rubric-guided grading workflow with committee arbitration, a human adjudication baseline, and graph-based auditability in a real classroom deployment. By linking domain-aware dispersion (MPAD), a policy tolerance dial, and chief–panel discrepancy, the study shows how these elements can be combined into a replicable, auditable, and capacity-aware approach for organizing LLM-assisted grading and identifying instability and systematic misalignment, while maintaining pedagogical interpretability.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section AI-Driven Innovations)
►▼
Show Figures
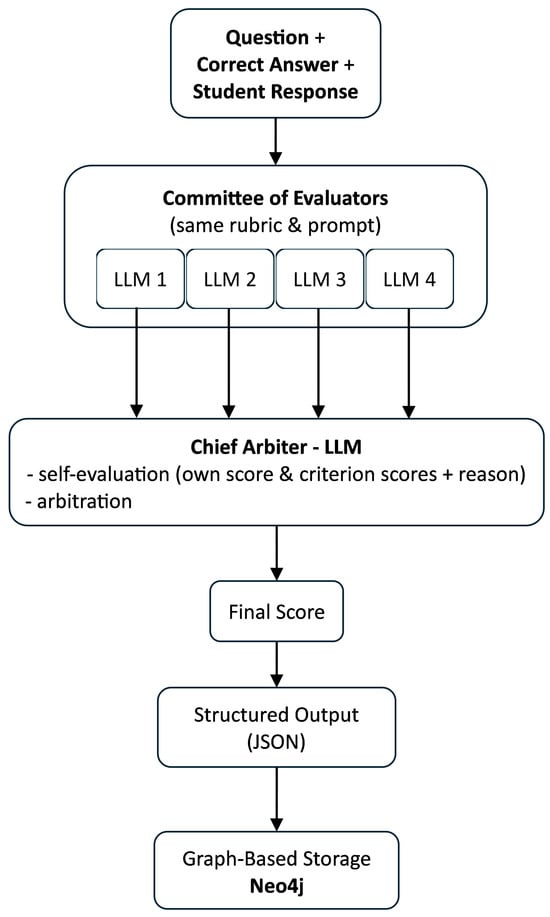
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Quantum Neural Networks in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Advancing Diagnostic Precision Through Emerging Computational Paradigms
by
Enrico Rosa, Maria Vaccaro, Elisa Placidi, Maria Luisa D’Andrea, Flavia Liporace, Gian Luigi Natali, Aurelio Secinaro and Antonio Napolitano
Computers 2025, 14(12), 529; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120529 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs) combine quantum computing and artificial intelligence to provide powerful solutions for high-dimensional data analysis. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), they address the challenges of advanced imaging sequences and data complexity, enabling faster optimization, enhanced feature extraction, and real-time
[...] Read more.
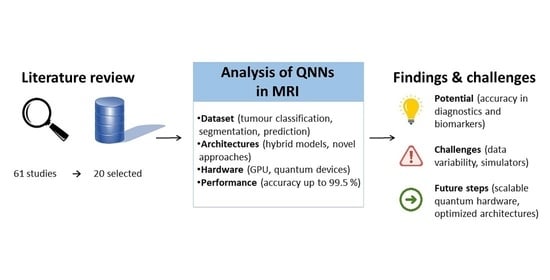
Background: Quantum Neural Networks (QNNs) combine quantum computing and artificial intelligence to provide powerful solutions for high-dimensional data analysis. In magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), they address the challenges of advanced imaging sequences and data complexity, enabling faster optimization, enhanced feature extraction, and real-time clinical applications. Methods: A literature review using Scopus, PubMed, IEEE Xplore, ACM Digital Library and arXiv identified 84 studies on QNNs in MRI. After filtering for peer-reviewed original research, 20 studies were analyzed. Key parameters such as datasets, architectures, hardware, tasks, and performance metrics were summarized to highlight trends and gaps. Results: The analysis identified datasets supporting tasks like tumor classification, segmentation, and disease prediction. Architectures included hybrid models (e.g., ResNet34 with quantum circuits) and novel approaches (e.g., Quantum Chebyshev Polynomials). Hardware ranged from high-performance GPUs to quantum-specific devices. Performance varied, with accuracy up to 99.5% in some configurations but lower results for complex or limited datasets. Conclusions: The findings provide the first glimpse into the potential of QNNs in MRI, demonstrating accuracy and specificity in diagnostic tasks and biomarker detection. However, challenges such as dataset variability, limited quantum hardware access, and reliance on simulators remain. Future research should focus on scalable quantum hardware, standardized datasets, and optimized architectures to support clinical applications and precision medicine.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Digital Literacy in Higher Education: Examining University Students’ Competence in Online Information Practices
by
Maria Sofia Georgopoulou, Christos Troussas, Akrivi Krouska and Cleo Sgouropoulou
Computers 2025, 14(12), 528; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120528 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
Accessing, processing, and sharing of information have been completely transformed by the speedy progress of digital technologies. However, as tech evolution accelerates, it presents notable challenges in the form of misinformation spreading rapidly and an increased demand for critical thinking competences. Digital literacy,
[...] Read more.
Accessing, processing, and sharing of information have been completely transformed by the speedy progress of digital technologies. However, as tech evolution accelerates, it presents notable challenges in the form of misinformation spreading rapidly and an increased demand for critical thinking competences. Digital literacy, encompassing the ability to navigate, evaluate, and create digital content effectively, emerges as a crucial skillset for individuals to succeed in the modern world. This study aims to assess the digital literacy levels of university students and understand their ability to critically engage with digital technologies, with a specific focus on their competences in evaluating information, utilizing technology, and engaging in online communities. A quiz-type questionnaire, informed by frameworks such as DigComp 2.2 and Eshet-Alkalai’s model, was developed to assess participants’ self-perceived and applied competences, with a focus on emerging challenges like deepfake detection not fully covered in existing tools. The findings indicate that while most students are aware of various criteria for accessing and evaluating online content, there is room for improvement in consistently applying these criteria and understanding the potential risks of misinformation and responsible use of online sources. Exploratory analyses reveal minimal differences by department and year of study, suggesting that targeted interventions are required across all study fields. The results underline the importance of cultivating critical and ethical digital literacy within higher education to enhance digital citizenship.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Computer-Assisted Learning (2nd Edition))
►▼
Show Figures
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Zero-Inflated Text Data Analysis Using Imbalanced Data Sampling and Statistical Models
by
Sunghae Jun
Computers 2025, 14(12), 527; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120527 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Text data often exhibits high sparsity and zero inflation, where a substantial proportion of entries in the document–keyword matrix are zeros. This characteristic presents challenges to traditional count-based models, which may suffer from reduced predictive accuracy and interpretability in the presence of excessive
[...] Read more.
Text data often exhibits high sparsity and zero inflation, where a substantial proportion of entries in the document–keyword matrix are zeros. This characteristic presents challenges to traditional count-based models, which may suffer from reduced predictive accuracy and interpretability in the presence of excessive zeros and overdispersion. To overcome this issue, we propose an effective analytical framework that integrates imbalanced data handling by undersampling with classical probabilistic count models. Specifically, we apply Poisson’s generalized linear models, zero-inflated Poisson, and zero-inflated negative binomial models to analyze zero-inflated text data while preserving the statistical interpretability of term-level counts. The framework is evaluated using both real-world patent documents and simulated datasets. Empirical results demonstrate that our undersampling-based approach improves the model fit without modifying the downstream models. This study contributes a practical preprocessing strategy for enhancing zero-inflated text analysis and offers insights into model selection and data balancing techniques for sparse count data.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
UTLAM: Unsupervised Two-Level Adapting Model for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
by
Rahman Farnoosh and Juman Abdulateef
Computers 2025, 14(12), 526; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120526 - 2 Dec 2025
Abstract
The design of an accurate cross-domain model for Alzheimer disease AD classification from MRI scans faces critical challenges, including domain shifts caused by acquisition protocol variations. To address this issue, we propose a novel unsupervised two-level adapting model for Alzheimer’s disease classification using
[...] Read more.
The design of an accurate cross-domain model for Alzheimer disease AD classification from MRI scans faces critical challenges, including domain shifts caused by acquisition protocol variations. To address this issue, we propose a novel unsupervised two-level adapting model for Alzheimer’s disease classification using 3D MRI scans. In the first level, we introduce an extended mean inter- and intra-class discrepancy metric, which statistically aligns both inter-class and inter-domain discrepancies, enabling pseudo-labeling of the unlabeled samples. The second level integrates labeled source and pseudo-labeled target features into an adversarial learning, encouraging the feature extractor to generate domain-invariant representations, thereby improving model generalizability. The proposed model uses standard Alzheimer’s disease benchmarks, including ADNI and AIBL databases. Experimental results demonstrate UTLAM’s superior transfer learning capability compared to the existing baselines in identifying cognitive normal CN, AD, and mild cognitive impairment in MCI subjects. Notably, UTLAM achieves classification accuracies of (92.02%, 77.72%, and 83.04%), (92.60%, 71.45%, and 62.50%), and (93.22%, 84.80%, and 72.19%) on (CN vs. AD, MCI vs. AD, and CN vs. MCI) classifications via ADNI-1 to AIBL, ADNI-1 to ADNI-2, and AIBL to ADNI-3 transfer learnings, respectively. Without relying on a labeled target, UTLAM offers a highly practical solution for Alzheimer’s disease classification.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Human–Computer Interactions)
►▼
Show Figures
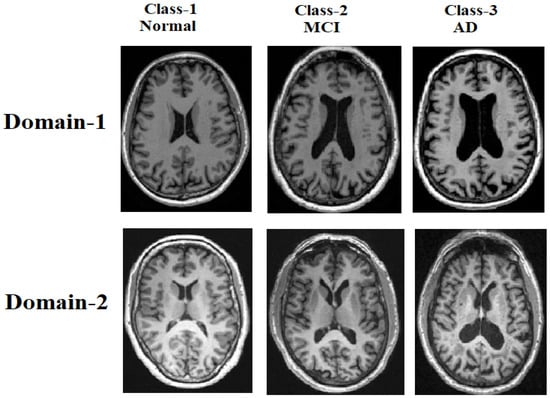
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Multi-Agent RAG Framework for Entity Resolution: Advancing Beyond Single-LLM Approaches with Specialized Agent Coordination
by
Aatif Muhammad Althaf, Muzakkiruddin Ahmed Mohammed, Mariofanna Milanova, John Talburt and Mert Can Cakmak
Computers 2025, 14(12), 525; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120525 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Entity resolution in real-world datasets remains a persistent challenge, particularly for identifying households and detecting co-residence patterns within noisy and incomplete data. While Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise, monolithic approaches often suffer from limited scalability and interpretability. This study introduces a multi-agent
[...] Read more.
Entity resolution in real-world datasets remains a persistent challenge, particularly for identifying households and detecting co-residence patterns within noisy and incomplete data. While Large Language Models (LLMs) show promise, monolithic approaches often suffer from limited scalability and interpretability. This study introduces a multi-agent Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework that decomposes household entity resolution into coordinated, task-specialized agents implemented using LangGraph. The system includes four agents responsible for direct matching, transitive linkage, household clustering, and residential movement detection, combining rule-based preprocessing with LLM-guided reasoning. Evaluation on synthetic S12PX dataset segments containing 200–300 records demonstrates 94.3% accuracy on name variation matching and a 61% reduction in API calls compared to single-LLM baselines, while maintaining transparent and traceable decision processes. These results indicate that coordinated multi-agent specialization improves efficiency and interpretability, providing a structured and extensible approach for entity resolution in census, healthcare, and other administrative data domains.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Multimodal Pattern Recognition of Social Signals in HCI (2nd Edition))
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Realization of a Gateway Device for Photovoltaic Application Using Open-Source Tools in a Virtualized Environment
by
Emmanuel Luwaca and Senthil Krishnamurthy
Computers 2025, 14(12), 524; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120524 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Electronic communication and industrial protocols are critical to the reliable operation of modern electrical grids and Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). Communication loss between devices in renewable power plants can lead to significant revenue losses and jeopardize operational safety. While current control and automation
[...] Read more.
Electronic communication and industrial protocols are critical to the reliable operation of modern electrical grids and Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). Communication loss between devices in renewable power plants can lead to significant revenue losses and jeopardize operational safety. While current control and automation systems for renewable plants are primarily based on the IEC 61131-3 standard, it lacks defined communication frameworks, leading most deployments to depend on Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM)-specific protocols. The IEC 61499 standard, in contrast, offers a reference model for distributed automation systems, introducing Service Interface Function Blocks (SIFBs) and high-level communication abstractions that enable hardware-independent integration. This study proposes adopting the IEC 61499 standard for DER automation systems to enhance interoperability and flexibility among plant components. A photovoltaic power plant gateway is developed on a virtualized platform using open-source tools and libraries, including Python version 3, libmodbus version 3.1.7, and open62541 version 1 The implemented gateway successfully interfaces with industry-validated software applications, including UAExpert and Matrikon OPC Unified Architecture (OPC UA) clients, demonstrating the feasibility and effectiveness of IEC 61499-based integration in DER environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Two-Stage Deep Learning Framework for AI-Driven Phishing Email Detection Based on Persuasion Principles
by
Peter Tooher and Harjinder Singh Lallie
Computers 2025, 14(12), 523; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120523 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
AI-generated phishing emails present a growing cybersecurity threat, exploiting human psychology with high-quality, context-aware language. This paper introduces a novel two-stage detection framework that combines deep learning with psychological analysis to address this challenge. A new dataset containing 2995 GPT-o1-generated phishing emails, each
[...] Read more.
AI-generated phishing emails present a growing cybersecurity threat, exploiting human psychology with high-quality, context-aware language. This paper introduces a novel two-stage detection framework that combines deep learning with psychological analysis to address this challenge. A new dataset containing 2995 GPT-o1-generated phishing emails, each labelled with Cialdini’s six persuasion principles, is created across five organisational sectors—forming one of the largest and most behaviourally annotated corpora in the field. The first stage employs a fine-tuned DistilBERT model to predict the presence of persuasion principles in each email. These confidence scores then feed into a lightweight dense neural network at the second stage for final binary classification. This interpretable design balances performance with insight into attacker strategies. The full system achieves 94% accuracy and 98% AUC, outperforming comparable methods while offering a clearer explanation of model decisions. Analysis shows that principles like authority, scarcity, and social proof are highly indicative of phishing, while reciprocation and likeability occur more often in legitimate emails. This research contributes an interpretable, psychology-informed framework for phishing detection, alongside a unique dataset for future study. Results demonstrate the value of behavioural cues in identifying sophisticated phishing attacks and suggest broader applications in detecting malicious AI-generated content.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section AI-Driven Innovations)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Accurate Seamless Vertical Handover Prediction Using Peephole LSTM Based on Light-GBM Algorithm in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks
by
Ali M. Mahmood and Omar Younis Alani
Computers 2025, 14(12), 522; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120522 - 1 Dec 2025
Abstract
Present and future mobile networks combine wireless radio access technologies from multiple cellular network generations, all of which coexist. Seamless Vertical Handover (VH) decision-making is still a challenging issue in heterogeneous cellular networks due to the dynamic conditions of networks, different demands on
[...] Read more.
Present and future mobile networks combine wireless radio access technologies from multiple cellular network generations, all of which coexist. Seamless Vertical Handover (VH) decision-making is still a challenging issue in heterogeneous cellular networks due to the dynamic conditions of networks, different demands on QoS, and the latency of the handover process. Maintaining a very high-accuracy VH decision requires considering several network parameters. There is a trade-off between the gain of the VH accuracy and the corresponding latency in the computational complexity of the decision-making methods. This paper proposes a lightweight VH prediction DL strategy for 3G, 4G, and 5G networks based on the Light-Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM) feature selection and Peephole Long Short-Term Memory (PLSTM) prediction model. For dense networks with large datasets and high-dimensional data, the combination of PLSTM and the fast feature selection LGBM, can reduce the computing complexity while preserving prediction accuracy and excellent performance levels. The proposed methods are evaluated using three case study scenarios using different feature selection thresholds. The performance evaluation is achieved by training and testing the proposed model, which shows an improvement using the proposed LGBM and PLSTM in terms of reducing the number of features by 64.28% and enhancing the VH accuracy prediction by 43.81% in Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE), and reducing the VH decision time of up to 51%. Furthermore, a network simulation using the proposed VH prediction algorithm shows an enhancement in overall network performance, with the number of successful VHs being 87%. Consequently, the data throughput is significantly enhanced.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Shaping the Future of Green Networking: Integrated Approaches of Joint Intelligence, Communication, Sensing, and Resilience for 6G)
►▼
Show Figures
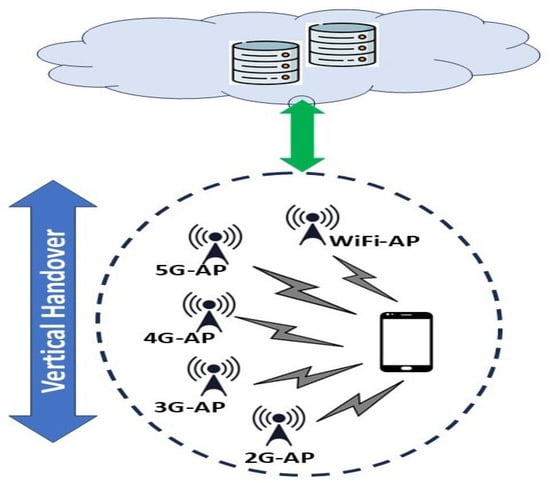
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
AI-Assisted Documentation: An Implosion Animation Method for CAD Designs
by
Jorge Cesar Mariscal-Melgar
Computers 2025, 14(12), 521; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120521 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Free/Libre and Open-Source Hardware requires documentation that ensures replicability and accessibility for both experts and non-experts. Existing tools for generating assembly animations are often difficult to use, require specialized knowledge, and are poorly suited for instructional or workshop contexts. This paper addresses this
[...] Read more.
Free/Libre and Open-Source Hardware requires documentation that ensures replicability and accessibility for both experts and non-experts. Existing tools for generating assembly animations are often difficult to use, require specialized knowledge, and are poorly suited for instructional or workshop contexts. This paper addresses this gap by proposing a method for generating implosion-style CAD animations that separates transformation logic from geometry. The method enables fast, low-effort creation of animations through either manual grouping or large language model (LLM) automation. The approach is validated through a web-based implementation that can produce complete animations within minutes using mesh or boundary-representation input. The system supports step-wise playback, interactive part grouping, and export of vector-based views for technical documentation. Evaluation includes nine models ranging from simple parts to assemblies with over 1400 components. The system successfully generated animations for all models, with the LLM-based schema generation achieving high sequence coherence and coverage in most cases. The proposed method enables scalable, reusable, and version-controlled animation workflows that are particularly suited for open-source documentation, manufacturing education, and distributed design environments.
Full article
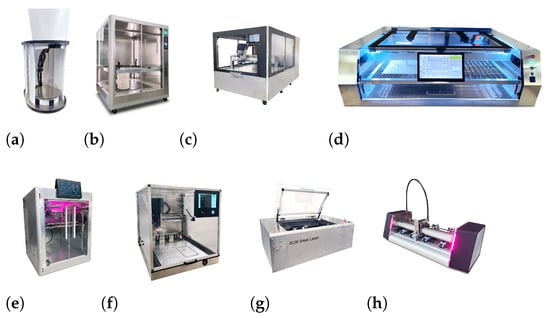
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Evolution and Perspectives in IT Governance: A Systematic Literature Review
by
Álvaro Vaya-Arboledas, Mikel Ferrer-Oliva and José Amelio Medina-Merodio
Computers 2025, 14(12), 520; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120520 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The study presents a systematic review of the state of the art on Information Technology (IT) governance research. Following the PRISMA 2020 protocol and drawing on Scopus and Web of Science, covering publications from 1999 to May 2025, 380 relevant articles were identified,
[...] Read more.
The study presents a systematic review of the state of the art on Information Technology (IT) governance research. Following the PRISMA 2020 protocol and drawing on Scopus and Web of Science, covering publications from 1999 to May 2025, 380 relevant articles were identified, analysed and categorised. A bibliometric analysis supported by tools such as VOSviewer and SciMaT mapped the principal thematic strands, influential authors and institutions, and revealed research gaps. The results indicate a consolidated field in which resource allocation, industrial management, strategic alignment and board-level IT governance operate as driving themes, while information management, the configuration of the IT function and the regulatory nexus between laws and information security remain emerging areas. The conclusions emphasise the theoretical implications of clarifying how IT governance shapes IT investment and initiative prioritisation, sectoral configurations and strategic alignment, and the practical implications of using these mechanisms to design and refine governance structures, processes and metrics in regulated organisations so that value creation risk control and accountability are more explicitly aligned.
Full article
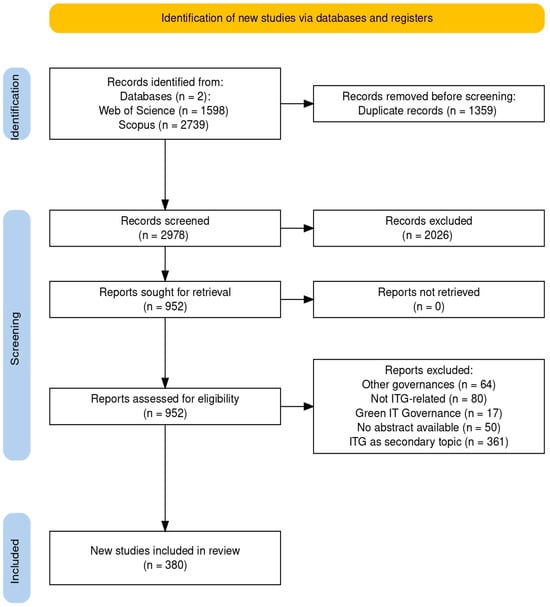
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Architecture for Managing Autonomous Virtual Organizations in the Industry 4.0 Context
by
Cindy Pamela López, Marco Santórum and Jose Aguilar
Computers 2025, 14(12), 519; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120519 - 28 Nov 2025
Abstract
A Virtual Organization (VO) unites companies or independent individuals to achieve a shared, short-term objective by leveraging information technologies for communication and coordination in personalized product creation. Despite extensive research, existing VO management architectures lack alignment with Industry 4.0 standards, do not incorporate
[...] Read more.
A Virtual Organization (VO) unites companies or independent individuals to achieve a shared, short-term objective by leveraging information technologies for communication and coordination in personalized product creation. Despite extensive research, existing VO management architectures lack alignment with Industry 4.0 standards, do not incorporate intelligent requirement-gathering mechanisms, and are not based on the RAMI 4.0 framework. These limitations hinder support for Autonomous Virtual Organizations (AVOs) in evaluation, risk management, and continuity, often excluding small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) during the partner selection process. This study proposes a comprehensive architecture for AVO management, grounded in ACODAT (Autonomous Cycle of Data Analysis Tasks) and RAMI 4.0 principles. The methodology includes a literature review, an architectural design, and a detailed specification of the ACODAT for the digital supply chain design. A prototype was developed and applied in a case study involving a virtual organization within an editorial consortium. Evaluation addressed core service performance, scalability of the batch selection algorithm, resource-use efficiency, and accessibility/SEO compliance. Benchmarking demonstrated that the prototype met or exceeded thresholds for scalability, efficiency, and accessibility, with minor performance deviations attributed to the testing environment. The results highlight significant time savings and improved automation in requirement identification, partner selection, and supply chain configuration, underscoring the architecture’s effectiveness and inclusivity.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Emerging Trends in Intelligent Connectivity and Digital Transformation)
►▼
Show Figures
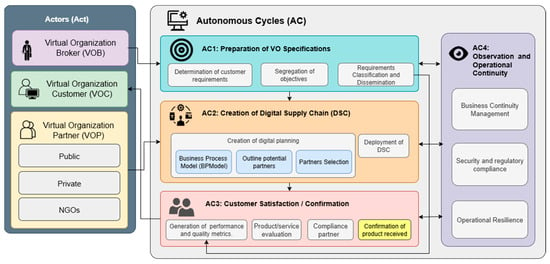
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Advancing Small Defect Recognition in PV Modules with YOLO-FAD and Dynamic Convolution
by
Lijuan Li, Gang Xie, Yin Wang, Wang Yun, Jianan Wang and Zhicheng Zhao
Computers 2025, 14(12), 518; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120518 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
To improve the detection performance of small defects in photovoltaic modules, we propose an enhanced YOLOv11n model—YOLO-FAD. Its core innovations include the following: (1) integrating RFAConv into the backbone network and neck network to better capture small defect features in complex backgrounds; (2)
[...] Read more.
To improve the detection performance of small defects in photovoltaic modules, we propose an enhanced YOLOv11n model—YOLO-FAD. Its core innovations include the following: (1) integrating RFAConv into the backbone network and neck network to better capture small defect features in complex backgrounds; (2) adding DyC3K2 for adaptive convolution optimization to improve accuracy and robustness; (3) employing ASF for multi-layer feature fusion, and combining it with DyHead-detect in the fourth detection layer to refine the classification and localization of small targets. Testing on our dataset shows that YOLO-FAD achieves an overall accuracy of 94.6% (85.3% for small defects), outperforming YOLOv11n by 3.0% and 10.1% in mAP, respectively, and surpassing YOLOv12, RT-DETR, Improved Faster-RCNN, and state-of-the-art (SOTA) improved models.
Full article
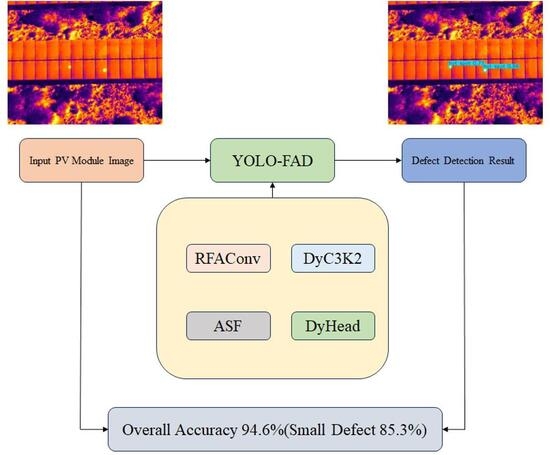
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
MSDSI-FND: Multi-Stage Detection Model of Influential Users’ Fake News in Online Social Networks
by
Hala Al-Mutair and Jawad Berri
Computers 2025, 14(12), 517; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120517 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
The rapid spread of fake news across social media poses significant threats to politics, economics, and public health. During the COVID-19 pandemic, social media influencers played a decisive role in amplifying misinformation due to their large follower bases and perceived authority. This study
[...] Read more.
The rapid spread of fake news across social media poses significant threats to politics, economics, and public health. During the COVID-19 pandemic, social media influencers played a decisive role in amplifying misinformation due to their large follower bases and perceived authority. This study proposes a Multi-Stage Detection System for Influencer Fake News (MSDSI-FND) to detect misinformation propagated by influential users on the X platform (formerly Twitter). A manually labeled dataset was constructed, comprising 68 root tweets (42 fake and 26 real) and over 40,000 engagements (26,700 replies and 14,000 retweets) collected between December 2019 and December 2022. The MSDSI-FND model employs a two-stage analytical framework integrating: (1) content-based linguistic and psycholinguistic analysis, (2) user profiles analysis, structural and propagation-based modeling of information cascades analysis. Several machine-learning classifiers were tested under single-stage, two-stage, and full multi-stage configurations. An ablation study demonstrated that performance improved progressively with each added analytical stage. The full MSDSI-FND model achieved the highest accuracy, F1-score, and AUC, confirming the effectiveness of hierarchical, stage-wise integration. The results highlight the superiority of the proposed multi-stage, influential user-aware framework over conventional hybrid or text-only models. By sequentially combining linguistic, behavioral, and structural cues, MSDSI-FND provides an interpretable and robust approach to identifying large-scale misinformation dissemination within influential user-driven social networks.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Recent Advances in Data Mining: Methods, Trends, and Emerging Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
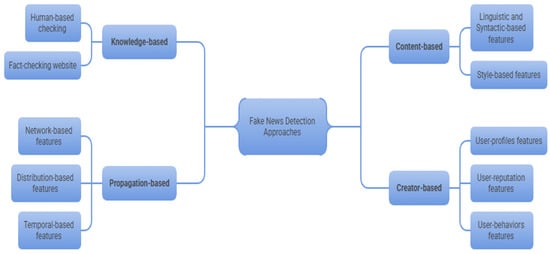
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Relevance and Evolution of Benchmarking in Computer Systems: A Comprehensive Historical and Conceptual Review
by
Isaac Zablah, Lilian Sosa-Díaz and Antonio Garcia-Loureiro
Computers 2025, 14(12), 516; https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120516 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Benchmarking has been central to performance evaluation for more than four decades. Reinhold P. Weicker’s 1990 survey in IEEE Computer offered an early, rigorous critique of standard benchmarks, warning about pitfalls that continue to surface in contemporary practice. This review synthesizes the evolution
[...] Read more.
Benchmarking has been central to performance evaluation for more than four decades. Reinhold P. Weicker’s 1990 survey in IEEE Computer offered an early, rigorous critique of standard benchmarks, warning about pitfalls that continue to surface in contemporary practice. This review synthesizes the evolution from classical synthetic benchmarks (Whetstone, Dhrystone) and application kernels (LINPACK) to modern suites (SPEC CPU2017), domain-specific metrics (TPC), data-intensive and graph workloads (Graph500), and Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML) benchmarks (MLPerf, TPCx-AI). We emphasize energy and sustainability (Green500, SPECpower, MLPerf Power), reproducibility (artifacts, environments, rules), and domain-specific representativeness, especially in biomedical and bioinformatics contexts. Building upon Weicker’s methodological cautions, we formulate a concise checklist for fair, multidimensional, reproducible benchmarking and identify open challenges and future directions.
Full article
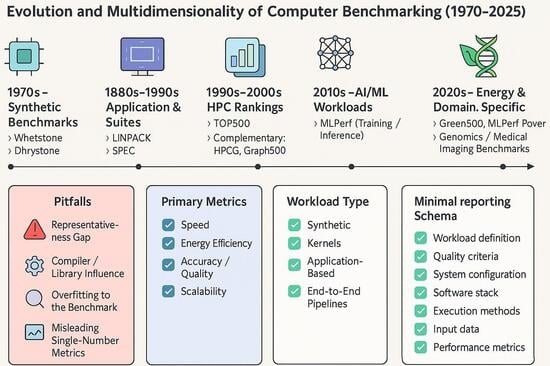
Graphical abstract
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Computers, Electronics, JSAN, Technologies
Emerging AI+X Technologies and Applications
Topic Editors: Byung-Seo Kim, Hyunsik Ahn, Kyu-Tae LeeDeadline: 31 December 2025
Topic in
AI, Computers, Electronics, Information, MAKE, Signals
Recent Advances in Label Distribution Learning
Topic Editors: Xin Geng, Ning Xu, Liangxiao JiangDeadline: 31 January 2026
Topic in
AI, Computers, Education Sciences, Societies, Future Internet, Technologies
AI Trends in Teacher and Student Training
Topic Editors: José Fernández-Cerero, Marta Montenegro-RuedaDeadline: 11 March 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Computers, JSAN, Technologies, BDCC, Sensors, Telecom, Electronics
Electronic Communications, IOT and Big Data, 2nd Volume
Topic Editors: Teen-Hang Meen, Charles Tijus, Cheng-Chien Kuo, Kuei-Shu Hsu, Jih-Fu TuDeadline: 31 March 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Computers
Generative AI in Medicine: Emerging Applications, Challenges, and Future Directions
Guest Editor: Atsushi TeramotoDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Computers
Wireless Sensor Networks in IoT
Guest Editors: Shaolin Liao, Jinxin Li, Tiaojie XiaoDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Computers
Transformative Approaches in Education: Harnessing AI, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality for Innovative Teaching and Learning
Guest Editor: Stamatios PapadakisDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Computers
Advances in Failure Detection and Diagnostic Strategies: Enhancing Reliability and Safety
Guest Editor: Rafael PalaciosDeadline: 31 December 2025