Delay to Deal: Bargaining with Indivisibility and Round-Dependent Transfer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Motivation
3. Model
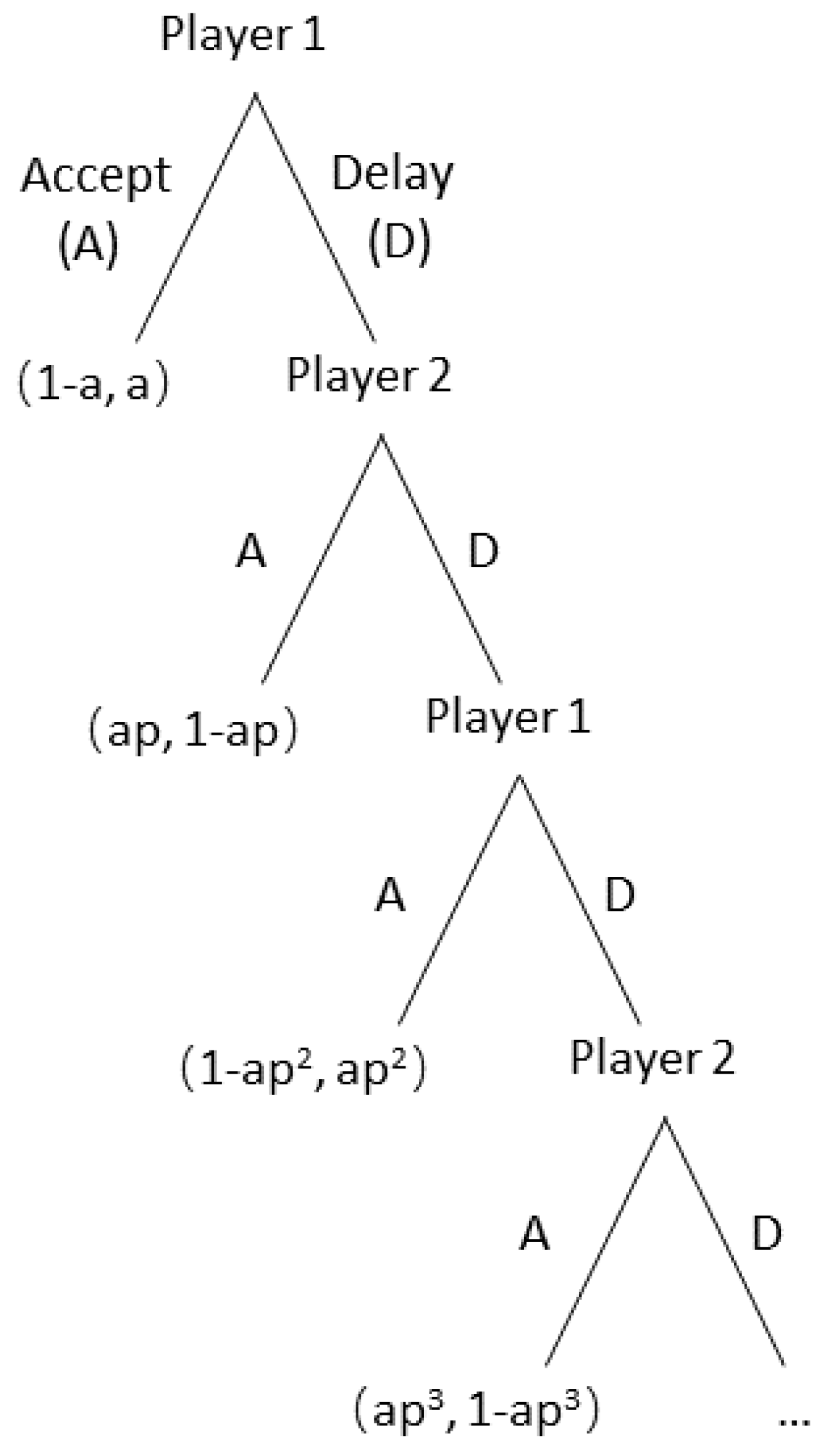
3.1. Model Setup
3.2. Strategy Analysis
3.3. Equilibrium
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Note that, for , we have , and for . For , this condition is always satisfied. |
References
- Rubinstein, A. Perfect equilibrium in a bargaining model. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1982, 50, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backus, M.; Blake, T.; Larsen, B.; Tadelis, S. Sequential bargaining in the field: Evidence from millions of online bargaining interactions. Q. J. Econ. 2020, 135, 1319–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Admati, A.R.; Perry, M. Strategic delay in bargaining. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1987, 54, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, D.; Gul, F. Bargaining and reputation. Econometrica 2000, 68, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embrey, M.; Fréchette, G.R.; Lehrer, S.F. Bargaining and reputation: An experiment on bargaining in the presence of behavioural types. Rev. Econ. Stud. 2015, 82, 608–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakovics, J. Delay in bargaining games with complete information. J. Econ. Theory 1993, 59, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H. Delay in Multilateral Bargaining under Complete Information. J. Econ. Theory 2000, 93, 260–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Huerta, I.; Volij, O. Field centipedes. Am. Econ. Rev. 2009, 99, 1619–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, M. Waiting to persuade. Q. J. Econ. 2004, 119, 223–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenthal, R.W. Games of perfect information, predatory pricing and the chain-store paradox. J. Econ. Theory 1981, 25, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, R.D.; Palfrey, T.R. An experimental study of the centipede game. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1992, 60, 803–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumann, R.J. On the centipede game. Games Econ. Behav. 1998, 23, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.F., Jr. The bargaining problem. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1950, 18, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalai, E.; Smorodinsky, M. Other solutions to Nash’s bargaining problem. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1975, 43, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, M.; Reny, P.J. A non-cooperative bargaining model with strategically timed offers. J. Econ. Theory 1993, 59, 50–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, I.N.; Varas, F. Bargaining in Securities. Working Paper. 2021. Available online: https://isachavesv.github.io/papers/securitiesClean.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Kajanus, A.; Afshordi, N.; Warneken, F. Children’s understanding of dominance and prestige in China and the UK. Evol. Hum. Behav. 2020, 41, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Shen, S.C.; Xu, M.X.; Rao, L.L.; Li, S. Worth-based choice: Giving an offered smaller pear an even greater fictional value. J. Pac. Rim Psychol. 2019, 13, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, N.; Zeitoun, H.; Melkonyan, T. The paradox of social interaction: Shared intentionality, we-reasoning, and virtual bargaining. Psychol. Rev. 2022, 129, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunney, S.J.; van der Schalk, J.; Manstead, A.S. Emotion and intergroup cooperation: How verbal expressions of guilt, shame, and pride influence behavior in a social dilemma. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2022, 35, e2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, S.E. Uncommon ground: Indivisible territory and the politics of legitimacy. Int. Organ. 2006, 60, 35–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, P.R.; Mitchell, S.M. Issue indivisibility and territorial claims. GeoJournal 2005, 64, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaniel, W. Issue Indivisibility as a Cause of Peace. J. Politics 2023, 85, 760–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffler, A. Can international interventions secure the peace? Int. Area Stud. Rev. 2014, 17, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, M. Targeting Peace: Understanding UN and EU Targeted Sanctions; Routledge: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fey, M.; McKelvey, R.D.; Palfrey, T.R. An experimental study of constant-sum centipede games. Int. J. Game Theory 1996, 25, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selten, R. Reexamination of the perfectness concept for equilibrium points in extensive games. Int. J. Game Theory 1975, 4, 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, J. Delay to Deal: Bargaining with Indivisibility and Round-Dependent Transfer. Games 2023, 14, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/g14050060
Fan J. Delay to Deal: Bargaining with Indivisibility and Round-Dependent Transfer. Games. 2023; 14(5):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/g14050060
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Jijian. 2023. "Delay to Deal: Bargaining with Indivisibility and Round-Dependent Transfer" Games 14, no. 5: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/g14050060
APA StyleFan, J. (2023). Delay to Deal: Bargaining with Indivisibility and Round-Dependent Transfer. Games, 14(5), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/g14050060





