Strong Solvent Effects on Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with [Ir(cod)(NHC)(PR3)] Catalysts in 2-Propanol-Water Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalysts Used for Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones from Basic 2-Propanol and Solid-State Structural Characterization of [IrCl(Cod)(Emim)] (1), [IrCl(Cod)(Bnmim)] (3) and [Ir(Cod)(Emim)(Mtppms)] (6)
2.2. General Features of Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with Ir(I)-NHC-PR3 Catalysts
2.3. Studies on the Kinetics of the Transfer Hydrogenation of Acetophenone
2.4. The Effect of Water on the Reduction of Acetophenone by Transfer Hydrogenation from Basic 2-Propanol with Ir(I)-NHC and Ir(I)-NHC-PR3 Complexes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of [IrCl(Cod)(Bnmim)] (3)
3.2. Synthesis of [Ir(Cod)(Emim)(PPh3)]Cl (5)
3.3. Synthesis of [Ir(Cod)(Emim)(Mtppms)] (6) with the Use of [emimH][Mtppms] Salt
3.4. Synthesis of [Ir(Cod)(Bnmim)(Mtppms)] (9)
3.5. Methods of Characterization of the Complexes
3.6. Hydrogen Transfer Experiments and Product Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danopoulos, A.A. N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes in Additions to Multiple Bonds. In N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Transition Metal Catalysis and Organocatalysis; Cazin, C.S.J., Ed.; Catalysis by Metal Complexes; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 23–61. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Astruc, D. The golden age of transfer hydrogenation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 6621–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corberán, R.; Mas-Marzá, E.; Peris, E. Mono-, Bi- and tridentate N-Heterocyclic carbene ligands for the preparation of transition-metal-based homogeneous catalysts. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 2009, 1700–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Xiao, J. Broader, greener, and more efficient: Recent advances in asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 3, 1750–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.L.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Efficient ruthenium-catalysed transfer hydrogenation of ketones by propan-2-ol. J. Chem. Soc. 1991, 16, 1063–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pámies, O.; Bäckvall, J.-E. Studies on the mechanism of metal-catalyzed hydrogen transfer from alcohols to ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 5052–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, S.; Fujii, A.; Takehara, J.; Ikariya, T.; Noyori, R. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of aromatic ketones catalyzed by chiral ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 7562–7563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyori, R.; Hashiguchi, S. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation catalyzed by chiral ruthenium complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1997, 30, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, S.J.M.; Roth, P.; Tarnai, T.; Alonso, D.A.; Brandt, P.; Andersson, P.G. Remote dipole effects as a means to accelerate [Ru(amino alcohol)]-catalyzed transfer hydrogenation of ketones. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, P.; Karlen, T.; Gossage, R.A.; Serafino, G.; van Koten, G. Hydrogen-transfer catalysis with pincer-aryl ruthenium(II) complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathó, Á.; Carmona, D.; Viguri, F.; Remacha, C.D.; Kovács, J.; Joó, F.; Oro, L.A. Enantioselective hydride transfer hydrogenation of ketones catalyzed by [(η6-p-cymene)Ru(amino acidato)Cl] and [(η6-p-cymene)Ru(amino acidato)]3(BF4)3 complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2000, 593–594, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadierno, V.; Francos, J.; Gimeno, J.; Nebra, N. Ruthenium-catalyzed reduction of allylic alcohols: An efficient isomerization/transfer hydrogenation tandem process. Chem. Commun. 2007, 24, 2536–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fekete, M.; Joó, F. Transfer Hydrogenation of Carbonyl Compounds and Alkenes Catalyzed by Ruthenium(II)-N-Heterocycle Carbene Complexes. Collect. Czechoslov. Chem. Commun. 2007, 72, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.; Crabtree, R.H.; Mata, J.; Peris, E. Chelating bis-carbene rhodium(iii) complexes in transfer hydrogenation of ketones and imines. Chem. Commun. 2002, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas-Marzá, E.; Poyatos, M.; Sanaú, M.; Peris, E. A New rhodium(III) complex with a tripodal Bis(imidazolylidene) ligand. synthesis and catalytic properties. Organometallics 2004, 23, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokić, N.B.; Zhang-Presse, M.; Goh, S.L.M.; Straubinger, C.S.; Bechlars, B.; Herrmann, W.A.; Kühn, F.E. Symmetrically bridged bis-N-heterocyclic carbene rhodium (I) complexes and their catalytic application for transfer hydrogenation reaction. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 24, 3900–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestroni, G.; Zassinovich, G.; Camus, A.; Martinelli, F. Transfer of hydrogen from alcohols to ketones catalyzed by iridium complexes with 2,2′-bipyridine, 1,10-phenanthroline, and their derivatives. J. Organomet. Chem. 1980, 198, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.V.; Fernández-Tornos, J.; Pérez-Torrente, J.J.; Modrego, F.J.; Winterle, S.; Cunchillos, C.; Lahoz, F.J.; Oro, L.A. Iridium(I) complexes with hemilabile N-heterocyclic carbenes: Efficient and versatile transfer hydrogenation catalysts. Organometallics 2011, 30, 5493–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García, N.; Jaseer, E.A.; Munarriz, J.; Miguel, P.J.S.; Polo, V.; Iglesias, M.; Oro, L.A. An insight into transfer hydrogenation reactions catalysed by iridium(III) Bis-N-heterocyclic carbenes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4388–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iglesias, M.; Oro, L.A. A leap forward in iridium–NHC catalysis: New horizons and mechanistic insights. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2772–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, G.; Dorta, R. Iridium complexes with monodentate N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 375, 13–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Iggo, J.; Xiao, J. Half-sandwich iridium complexes—Synthesis and applications in catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 782–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeer, B.; Iglesias, M.; Beeststra, D.; Dervisi, A.; Fallis, I.; Cavell, K.J. Donor-functionalised expanded ring N-Heterocyclic carbenes: Highly effective ligands in Ir-catalysed transfer hydrogenation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 5426–5431. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Serrano, L.D.; Owens, B.T.; Buriak, J.M. Catalytic olefin hydrogenation using N-heterocyclic carbene–phosphine complexes of iridium. Chem. Commun. 2002, 21, 2518–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Serrano, L.D.; Owens, B.T.; Buriak, J.M. The search for new hydrogenation catalyst motifs based on N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2006, 359, 2786–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, M.; Miecznikowski, J.R.; Samuel, A.; Faller, J.W.; Crabtree, R.H. Chelated Iridium(III) Bis-carbene complexes as air-stable catalysts for transfer hydrogenation. Organometallics 2002, 21, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülcemal, S.; Gökçe, A.G.; Çetinkaya, B. N-benzyl substituted N-heterocyclic carbene complexes of iridium(I): Assessment in transfer hydrogenation catalyst. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10601–10609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landaeta, V.R.; Rosa, A.D.S.-L.; Rodríguez-Lugo, R.E. Transfer hydrogenation of ketones catalyzed by iridium-bulky phosphine complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 470, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinner, S.C.; Rentzsch, C.F.; Herdtweck, E.; Herrmann, W.A.; Kühn, F.E. N-heterocyclic carbenes of iridium(I): Ligand effects on the catalytic activity in transfer hydrogenation. Dalton Trans. 2009, 35, 7055–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillier, A.C.; Lee, H.M.; Stevens, E.D.; Nolan, S.P. Cationic iridium complexes bearing imidazol-2-ylidene ligands as transfer hydrogenation catalysts. Organometallics 2001, 20, 4246–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, H.; Kathó, Á.; Udvardy, A.; Papp, G.; Szikszai, D.; Joó, F. New water-soluble iridium(I)–N-heterocyclic carbene–Tertiary phosphine mixed-ligand complexes as catalysts of hydrogenation and redox isomerization. Organometallics 2014, 33, 6330–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, H.; Papp, G.; Szabolcsi, R.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F. Water-soluble iridium-NHC-phosphine complexes as catalysts for chemical hydrogen batteries based on formate. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 3036–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, H.; Papp, G.; Kovács, H.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F. Iridium(I)NHC-phosphine complex-catalyzed hydrogen generation and storage in aqueous formate/bicarbonate solutions using a flow reactor—Effective response to changes in hydrogen demand. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28527–28532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papp, G.; Horváth, H.; Joó, F. A simple and efficient procedure for Rh(I)- and Ir(I)-complex catalyzed para-hydrogenation of alkynes and alkenes in aqueous media resulting in strong PHIP effects. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 3000–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De, S.; Udvardy, A.; Czégéni, C.E.; Joó, F. Poly-N-heterocyclic carbene complexes with applications in aqueous media. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 400, 213038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliedel, C.; Labande, A.; Manoury, E.; Poli, R. Chiral N-heterocyclic carbene ligands with additional chelating group(s) applied to homogeneous metal-mediated asymmetric catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 394, 65–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poyatos, M.; Mata, J.A.; Peris, E. Complexes with poly(N-heterocyclic carbene) ligands: Structural features and catalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3677–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Shi, M. Chiral NHC–metal-based asymmetric catalysis. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 804–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolan, S.P. (Ed.) ; N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: Effective Tools for Organometallic Synthesis; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huynh, H.V. The Organometallic Chemistry of N-heterocyclic Carbenes; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Diez-Gonzalez, S. (Ed.) ; N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: From Laboratory Curiosities to Efficient Synthetic Tools; Catalysis Series; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ramasamy, B.; Gangwar, M.K.; Ghosh, P. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds to saturated alcohols as catalyzed by iridium complexes of tricyclic bioxazoline-fused imidazole-derived N-heterocyclic carbene ligands. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Botella, S.; Peris, E. Unveiling the importance of π-stacking in borrowing-hydrogen processes catalysed by iridium complexes with pyrene tags. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15263–15271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.L.; Gyton, M.R.; Harper, J.B. Metal complexes of an ionic liquid-derived carbene. Aust. J. Chem. 2011, 64, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, P.V.; Radacki, K.; Braunschweig, H.; Schatzschneider, U. An iridium N-heterocyclic carbene complex [IrCl(CO)2(NHC)] as a carbon monoxide-releasing molecule (CORM). J. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 782, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothe, Y.; Marzo, T.; Messori, L.; Metzler-Nolte, N. Cytotoxic activity and protein binding through an unusual oxidative mechanism by an iridium(i)–NHC complex. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3151–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dyson, P.J.; Jessop, P.G. Solvent effects in catalysis: Rational improvements of catalysts via manipulation of solvent interactions. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3302–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thorpe, T.; Blacker, J.; Brown, S.M.; Bubert, C.; Crosby, J.; Fitzjohn, S.; Muxworthy, J.P.; Williams, J.M.J. Efficient rhodium and iridium-catalysed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation using water-soluble aminosulfonamide ligands. Tetrahedron Lett. 2001, 42, 4041–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathó, Á.; Szatmári, I.; Papp, G.; Joó, F. Effect of 2-propanol on the transfer hydrogenation of aldehydes by aqueous sodium formate using a rhodium(I)-sulfonated triphenylphosphine catalyst. Chimia 2015, 69, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szatmári, I.; Papp, G.; Joó, F.; Kathó, Á. Unexpectedly fast catalytic transfer hydrogenation of aldehydes by formate in 2-propanol–water mixtures under mild conditions. Catal. Today 2015, 247, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franks, F.; Ives, D.J.G. The structural properties of alcohol–water mixtures. Q. Rev. Chem. Soc. 1966, 20, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, G.I.; Afanas’ev, V.N.; Kolker, A.M. VTx properties of the system water-2-propanol in the range 275.15-338.15 K. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2004, 74, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamuku, T.; Saisho, K.; Aoki, S.; Yamaguchi, T. Large-angle X-ray scattering investigation of the structure of 2-propanol–water mixtures. Z. Für Naturforschung A 2014, 57, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaizumi, K. Liquid–solid phase diagrams of PrOH–water and BuOH–water systems from differential scanning calorimetry. J. Solut. Chem. 2000, 29, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. Solvent Mixtures. Properties and Selective Solvation; Marcel Dekker: New York, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Franks, F. Water, a Comprehensive Treaties; Plenum Press: New York, NJ, USA, 1973; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Joó, F.; Kovács, J.; Kathó, Á.; Bényei, A.C.; Decuir, T.; Darensbourg, D.J.; Miedaner, A.; Dubois, D.L. (Meta- Sulfonatophenyl) Diphenylphosphine, sodium salt and its complexes with Rhodium(I), Ruthenium(II), Iridium(I). In Inorganic Syntheses; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: New York, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, P.B.; Sellin, M.F.; Kunene, T.E.; Williamson, S.; Slawin, A.M.Z.; Cole-Hamilton, D.J. Continuous flow hydroformylation of alkenes in supercritical fluid−ionic liquid biphasic systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15577–15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, L.J. WinGX suite for small-molecule single-crystal crystallography. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1999, 32, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burla, M.C.; Caliandro, R.; Camalli, M.; Carrozzini, B.; Cascarano, G.L.; De Caro, L.; Giacovazzo, C.; Polidori, G.; Siliqi, D.; Spagna, R. IL MILIONE: A suite of computer programs for crystal structure solution of proteins. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westrip, S.P. publCIF: Software for editing, validating and formatting crystallographic information files. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2010, 43, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macrae, C.F.; Bruno, I.J.; Chisholm, J.A.; Edgington, P.R.; McCabe, P.; Pidcock, E.; Rodriguez-Monge, L.; Taylor, R.; van de Streek, J.; Wood, P.A. Mercury CSD 2.0–new features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APEX3 v2017.3-0; Bruker AXS Inc.: Billerica, MA, USA, 2017.

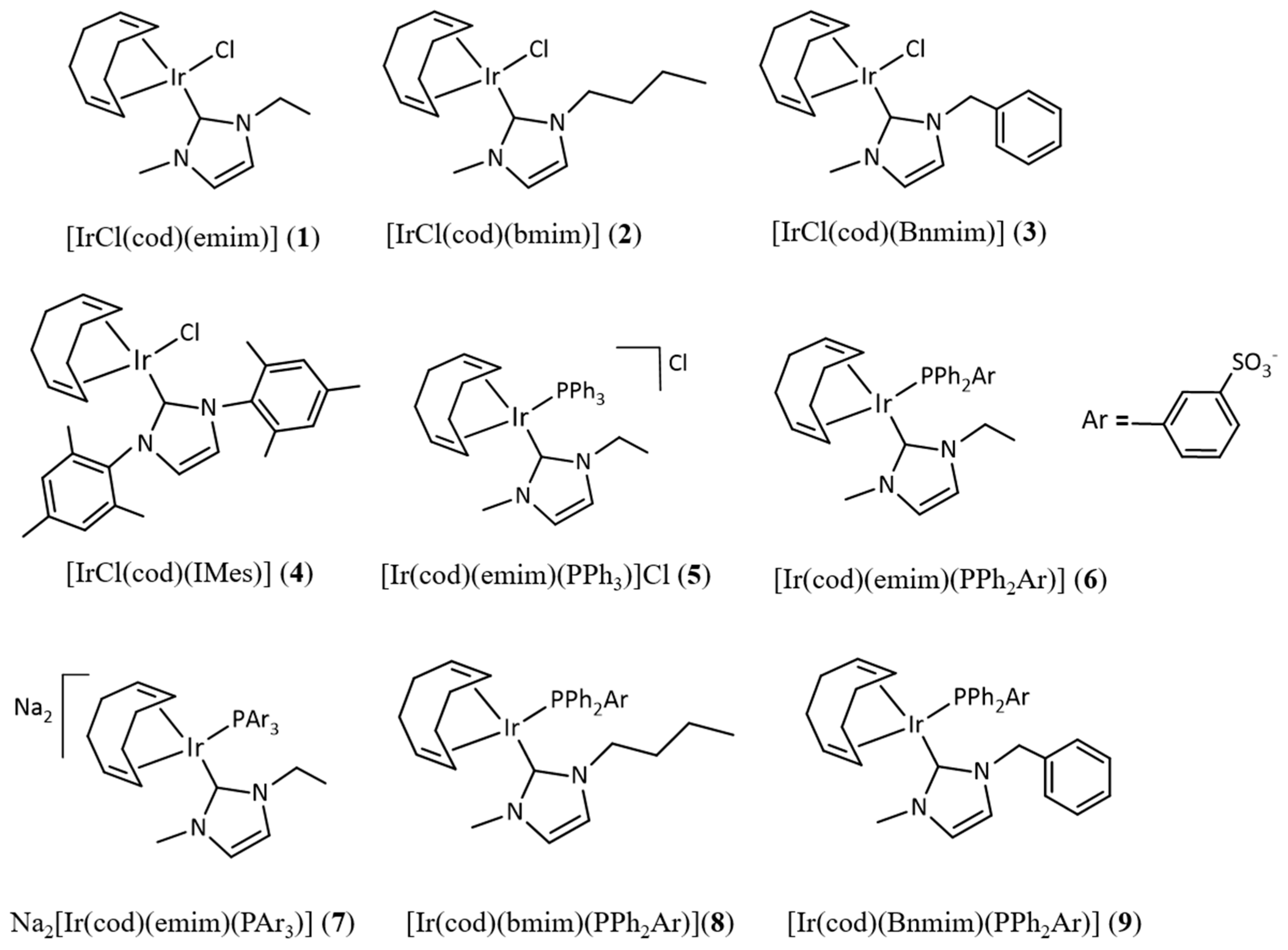






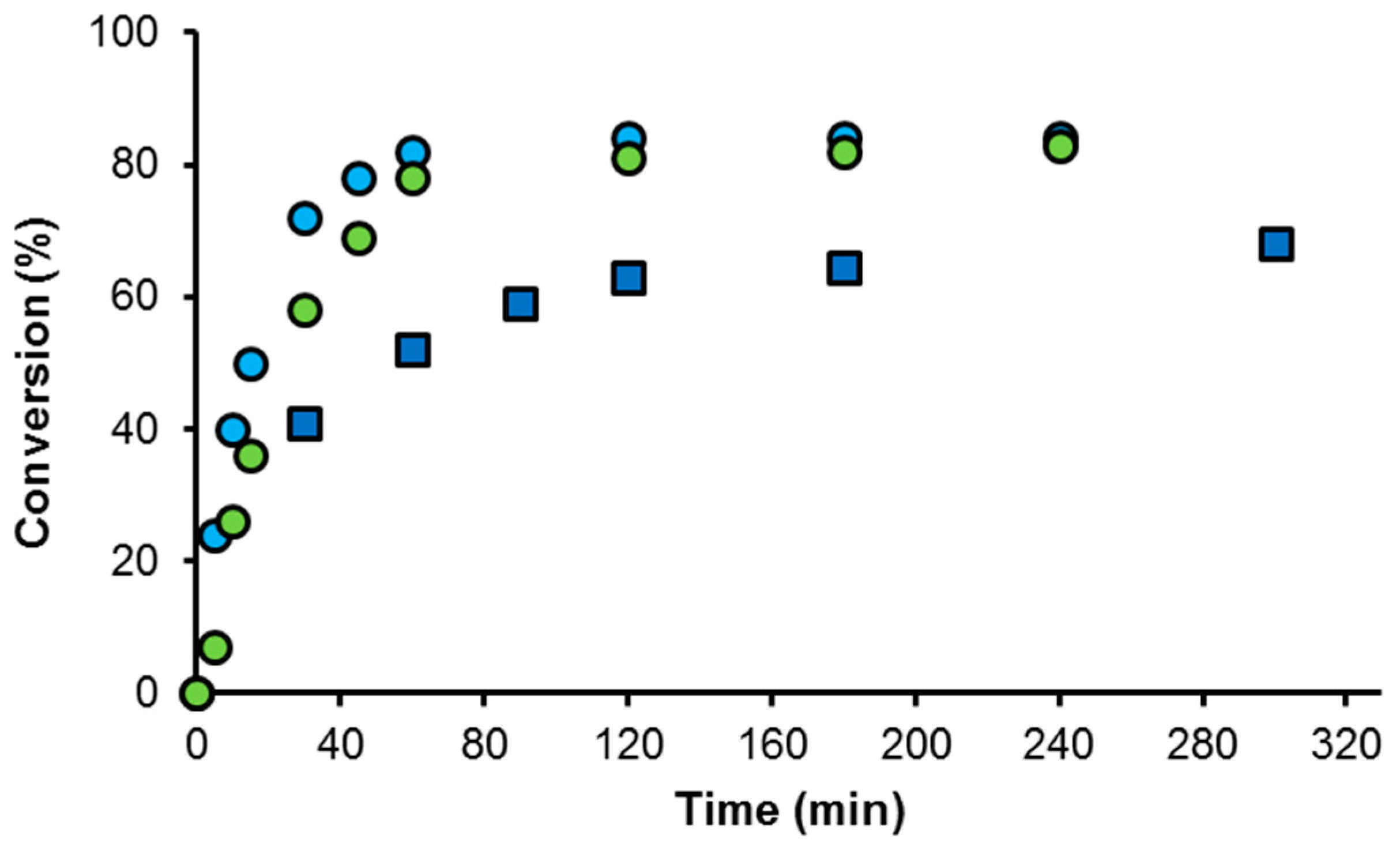

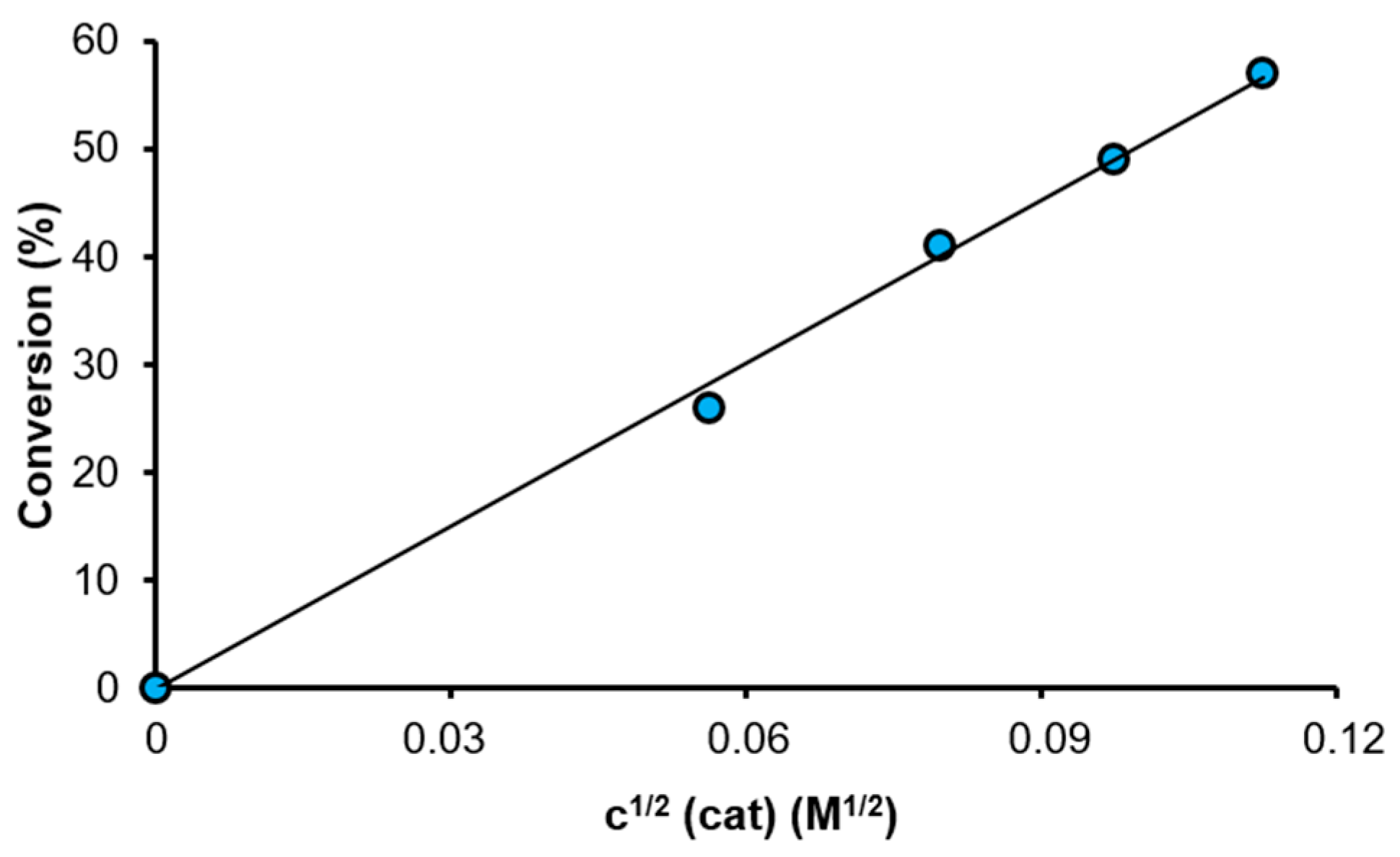





| Catalyst | Conversion a (%) | TOF (h−1) |
|---|---|---|
| [IrCl(cod)(emim)] (1) | 43 | 430 |
| [IrCl(cod)(bmim)] (2) | 49 | 490 |
| [IrCl(cod)(Bnmim)] (3) | 67 | 670 |
| [IrCl(cod)(IMes)] (4) | 11 | 110 |
| [Ir(cod)(emim)(PPh3)]Cl (5) | 54 | 540 |
| [Ir(cod)(emim)(mtppms)] (6) | 49 | 490 |
| Na2[Ir(cod)(emim)(mtppts)] (7) | 36 | 360 |
| [Ir(cod)(bmim)(mtppms)] (8) | 47 | 470 |
| [Ir(cod)(Bnmim)(mtppms)] (9) | 51 | 510 |
| Entry | Substrate | Product(s) | Yield a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  | 91 |
| 2 |  |  | 100 |
| 3 |  |  | 94 |
| 4 |  |  | 100 |
| 5 |  |  | 0 |
| 6 |  |  | 0 |
| 7 |  |  | 100 |
| 8 |  |  | 92 |
| 9 |  |  | 78 |
| 10 |  |  | 94 |
| 11 |  |  | 38 |
 | 4 | ||
 | 50 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orosz, K.; Papp, G.; Kathó, Á.; Joó, F.; Horváth, H. Strong Solvent Effects on Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with [Ir(cod)(NHC)(PR3)] Catalysts in 2-Propanol-Water Mixtures. Catalysts 2020, 10, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010017
Orosz K, Papp G, Kathó Á, Joó F, Horváth H. Strong Solvent Effects on Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with [Ir(cod)(NHC)(PR3)] Catalysts in 2-Propanol-Water Mixtures. Catalysts. 2020; 10(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrosz, Krisztina, Gábor Papp, Ágnes Kathó, Ferenc Joó, and Henrietta Horváth. 2020. "Strong Solvent Effects on Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with [Ir(cod)(NHC)(PR3)] Catalysts in 2-Propanol-Water Mixtures" Catalysts 10, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010017
APA StyleOrosz, K., Papp, G., Kathó, Á., Joó, F., & Horváth, H. (2020). Strong Solvent Effects on Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Ketones with [Ir(cod)(NHC)(PR3)] Catalysts in 2-Propanol-Water Mixtures. Catalysts, 10(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10010017






